



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (01): 117-127.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.053
朱拓1,2,3( ), 何登洋1,2,3, 黄雅琪1,2,3, 邱昆峰1,2,3(
), 何登洋1,2,3, 黄雅琪1,2,3, 邱昆峰1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-13
修回日期:2023-11-27
出版日期:2024-02-10
发布日期:2024-03-20
通讯作者:
邱昆峰,男,博士生导师,教授,1986年出生,矿床学专业,主要从事矿床学研究工作。Email:作者简介:朱 拓,男,本科生,2002年出生,地质学专业,主要从事岩石学与地球化学相关工作。Email:tuo.zhu@qq.com。
基金资助:
ZHU Tuo1,2,3( ), HE Dengyang1,2,3, HUANG Yaqi1,2,3, QIU Kunfeng1,2,3(
), HE Dengyang1,2,3, HUANG Yaqi1,2,3, QIU Kunfeng1,2,3( )
)
Received:2022-12-13
Revised:2023-11-27
Online:2024-02-10
Published:2024-03-20
摘要:
五莲—青岛—烟台断裂是胶莱盆地重要的控盆断裂之一,控制了盆地的形成与演化,主要由牟平—即墨断裂和桃村断裂等多条NNE向断裂组成。前人研究表明,五莲—青岛—烟台断裂运动学转换历史先后可划分为晚侏罗世左旋走滑、早白垩世伸展断陷和晚白垩世—古新世右旋走滑三个阶段,但其新生代右旋走滑事件的持续时间仍存在争议。已有研究表明,区域上同尺度断裂走滑运动温度为550~650 ℃,显著高于磷灰石U-Pb体系封闭温度(350~550 ℃),因此磷灰石可能是记录五莲—青岛—烟台断裂右旋走滑的理想对象。本文选取胶莱盆地马山粗面英安岩中的磷灰石进行U-Pb年代学研究,拟约束五莲—青岛—烟台断裂的右旋走滑持续时间。磷灰石U-Pb年龄为(64.1±3.7) Ma,明显晚于早白垩世寄主粗面英安岩锆石U-Pb年龄(119.3±1.6) Ma,表明自早白垩世以来磷灰石至少经历了一次热事件导致其U-Pb同位素体系重置。早白垩世以来,由于印度板块和欧亚板块的碰撞,以及古太平洋板块由NWW向俯冲转变为NW向俯冲,导致了古新世胶莱盆地N—S向拉分和牟平—即墨断裂右旋走滑。因此,本文认为马山粗面英安岩磷灰石U-Pb年龄记录了五莲—青岛—烟台断裂右旋走滑热事件,表明其右旋走滑可能持续到古新世。
中图分类号:
朱拓, 何登洋, 黄雅琪, 邱昆峰. 华北克拉通胶莱盆地马山地区粗面英安岩磷灰石U-Pb年代学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 117-127.
ZHU Tuo, HE Dengyang, HUANG Yaqi, QIU Kunfeng. Apatite U-Pb Geochronology of the Trachy Dacite in Mashan Area, Jiaolai Basin, North China Craton, and Its Geological Significance[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(01): 117-127.

图2 马山粗面英安岩野外岩相特征 (a)粗面英安岩柱状节理;(b)气孔及晶洞构造;(c)流纹构造;(d)砂岩捕虏体
Fig.2 Photographs showing characteristics of texture and lithology of the trachy-dacite in Mashan
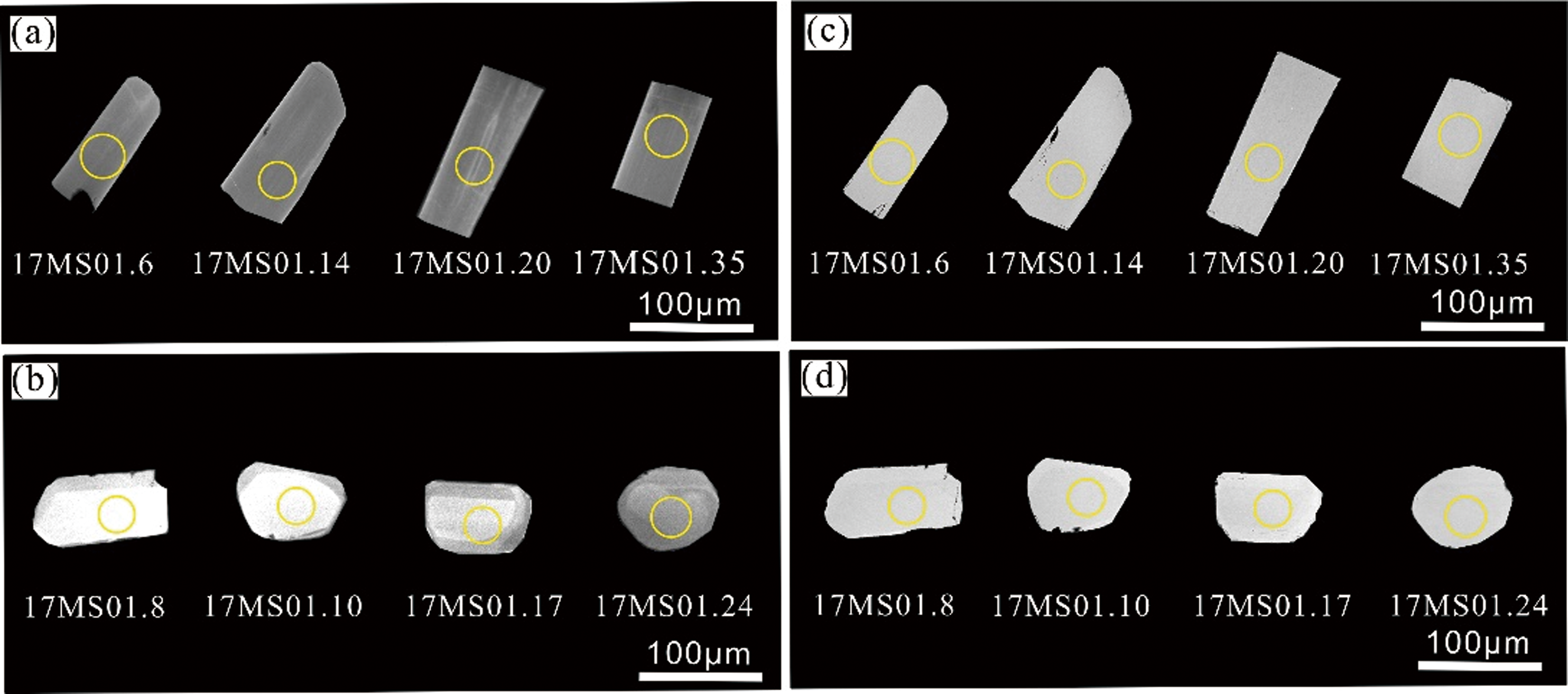
图4 马山粗面英安岩代表性磷灰石的阴极发光图像及背散射图像 (a)均质纹理磷灰石阴极发光图像;(b)重结晶磷灰石阴极发光图像;(c)均质纹理磷灰石背散射图像;(d)重结晶磷灰石阴极发光图像
Fig.4 Cathodoluminescence and backscatter electron (BSE) images of representative apatite of the trachy-dacite in Mashan
| 测点号 | Th | U | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | 206Pb/238U | 测点号 | Th | U | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | 206Pb/238U | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (10-6) | 比值 | 1σ | 比值 | 1σ | (10-6) | 比值 | 1σ | 比值 | 1σ | |||||||||
| 17MS01.2 | 1270 | 1181 | 1.08 | 0.5207 | 3.0654 | 49.087 | 1.8747 | 17MS01.35 | 464 | 472 | 0.98 | 0.8951 | 1.4044 | 1.3221 | 1.8974 | |||
| 17MS01.3 | 6878 | 249 | 27.66 | 0.891 | 1.2942 | 3.0512 | 4.23195 | 17MS01.37 | 123 | 25 | 4.93 | 0.5263 | 4.0704 | 39.6814 | 2.5101 | |||
| 17MS01.5 | 61 | 7 | 8.57 | 0.8688 | 1.2268 | 2.5613 | 1.1505 | 17MS01.38 | 1362 | 136 | 10.01 | 0.8535 | 1.3220 | 2.5465 | 4.5574 | |||
| 17MS01.6 | 1644 | 187 | 8.81 | 0.8868 | 1.3172 | 2.5214 | 1.7101 | 17MS01.39 | 56 | 16 | 3.37 | 0.8497 | 1.0897 | 2.7783 | 1.1734 | |||
| 17MS01.7 | 106 | 22 | 4.88 | 0.8586 | 1.2233 | 4.5204 | 1.2678 | 17MS01.40 | 5 | 17 | 0.28 | 0.8740 | 1.2181 | 1.0480 | 1.9597 | |||
| 17MS01.8 | 86 | 13 | 6.91 | 0.8760 | 1.1689 | 2.4897 | 1.3219 | 17MS01.42 | 196 | 30 | 6.50 | 0.8243 | 2.5830 | 0.6932 | 4.8606 | |||
| 17MS01.9 | 79 | 16 | 5.09 | 0.9095 | 1.1094 | 1.2497 | 2.1105 | 17MS01.43 | 59 | 7 | 8.42 | 0.9094 | 0.8948 | 0.1111 | 11.2151 | |||
| 17MS01.10 | 76 | 14 | 5.30 | 0.8834 | 1.5750 | 2.9378 | 1.5872 | 17MS01.44 | 192 | 52 | 3.69 | 0.5016 | 2.0304 | 44.7253 | 1.9601 | |||
| 17MS01.12 | 94 | 14 | 6.60 | 0.8743 | 1.4404 | 1.9390 | 1.5487 | 17MS01.45 | 1391 | 1995 | 0.70 | 0.6291 | 3.7503 | 30.8625 | 2.4905 | |||
| 17MS01.13 | 463 | 462 | 1.00 | 0.8804 | 1.3690 | 1.6412 | 1.3879 | 17MS01.46 | 1274 | 1874 | 0.68 | 0.5888 | 3.5811 | 35.6714 | 2.1179 | |||
| 17MS01.14 | 453 | 461 | 0.98 | 0.4845 | 3.3717 | 45.5478 | 2.3638 | 17MS01.47 | 6466 | 381 | 16.96 | 0.9039 | 1.4358 | 2.2080 | 3.0184 | |||
| 17MS01.16 | 155 | 16 | 9.97 | 0.8527 | 2.0586 | 0.5450 | 8.0893 | 17MS01.49 | 15 | 2 | 8.38 | 0.8546 | 1.0487 | 1.7677 | 1.4732 | |||
| 17MS01.17 | 70 | 7 | 9.93 | 0.8753 | 1.0525 | 2.1948 | 2.5031 | 17MS01.50 | 95 | 33 | 2.89 | 0.8817 | 1.0195 | 1.6856 | 1.9057 | |||
| 17MS01.18 | 46 | 12 | 3.89 | 0.9082 | 1.0402 | 2.0720 | 1.9266 | 17MS01.52 | 1 | 2 | 0.60 | 0.8931 | 1.1777 | 2.4336 | 1.4093 | |||
| 17MS01.20 | 1277 | 170 | 7.51 | 0.8974 | 0.9356 | 1.8199 | 2.3891 | 17MS01.53 | 663 | 253 | 2.62 | 0.8999 | 1.3397 | 2.9198 | 1.4218 | |||
| 17MS01.22 | 4 | 5 | 0.86 | 0.8559 | 1.0636 | 2.0625 | 1.1626 | 17MS01.56 | 45 | 15 | 3.13 | 0.8644 | 1.6027 | 2.6286 | 1.5413 | |||
| 17MS01.23 | 1316 | 1104 | 1.19 | 0.5093 | 2.3223 | 55.2046 | 1.8992 | 17MS01.57 | 462 | 467 | 0.99 | 0.8634 | 1.3099 | 4.1745 | 1.4078 | |||
| 17MS01.25 | 1583 | 70 | 22.75 | 0.8505 | 1.1378 | 2.6453 | 1.5710 | 17MS01.59 | 556 | 197 | 2.82 | 0.7957 | 3.2110 | 6.1032 | 2.3855 | |||
| 17MS01.27 | 122 | 19 | 6.25 | 0.8714 | 1.2965 | 1.7653 | 1.6522 | 17MS01.60 | 0 | 7 | 0.06 | 0.4696 | 3.8509 | 41.6457 | 2.0471 | |||
| 17MS01.28 | 118 | 19 | 6.24 | 0.8385 | 1.1699 | 1.6493 | 1.4157 | 17MS01.61 | 17 | 7 | 2.62 | 0.9328 | 1.2852 | 0.8348 | 2.5080 | |||
| 17MS01.31 | 2 | 1 | 1.86 | 0.9170 | 1.5418 | 0.7938 | 2.6302 | 17MS01.62 | 1801 | 509 | 3.54 | 0.9005 | 1.7886 | 2.2449 | 5.1810 | |||
| 17MS01.32 | 107 | 19 | 5.57 | 0.8156 | 1.2677 | 4.6167 | 1.3848 | 17MS01.63 | 851 | 210 | 4.05 | 0.4586 | 2.7958 | 56.5846 | 1.8309 | |||
| 17MS01.34 | 207 | 12 | 17.27 | 0.8531 | 1.3984 | 2.5556 | 1.3361 | |||||||||||
表1 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂马山粗面英安岩磷灰石 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating results of the Mashan trachy-dacite apatite in the Wulian-Qingdao-Yantai fault
| 测点号 | Th | U | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | 206Pb/238U | 测点号 | Th | U | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | 206Pb/238U | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (10-6) | 比值 | 1σ | 比值 | 1σ | (10-6) | 比值 | 1σ | 比值 | 1σ | |||||||||
| 17MS01.2 | 1270 | 1181 | 1.08 | 0.5207 | 3.0654 | 49.087 | 1.8747 | 17MS01.35 | 464 | 472 | 0.98 | 0.8951 | 1.4044 | 1.3221 | 1.8974 | |||
| 17MS01.3 | 6878 | 249 | 27.66 | 0.891 | 1.2942 | 3.0512 | 4.23195 | 17MS01.37 | 123 | 25 | 4.93 | 0.5263 | 4.0704 | 39.6814 | 2.5101 | |||
| 17MS01.5 | 61 | 7 | 8.57 | 0.8688 | 1.2268 | 2.5613 | 1.1505 | 17MS01.38 | 1362 | 136 | 10.01 | 0.8535 | 1.3220 | 2.5465 | 4.5574 | |||
| 17MS01.6 | 1644 | 187 | 8.81 | 0.8868 | 1.3172 | 2.5214 | 1.7101 | 17MS01.39 | 56 | 16 | 3.37 | 0.8497 | 1.0897 | 2.7783 | 1.1734 | |||
| 17MS01.7 | 106 | 22 | 4.88 | 0.8586 | 1.2233 | 4.5204 | 1.2678 | 17MS01.40 | 5 | 17 | 0.28 | 0.8740 | 1.2181 | 1.0480 | 1.9597 | |||
| 17MS01.8 | 86 | 13 | 6.91 | 0.8760 | 1.1689 | 2.4897 | 1.3219 | 17MS01.42 | 196 | 30 | 6.50 | 0.8243 | 2.5830 | 0.6932 | 4.8606 | |||
| 17MS01.9 | 79 | 16 | 5.09 | 0.9095 | 1.1094 | 1.2497 | 2.1105 | 17MS01.43 | 59 | 7 | 8.42 | 0.9094 | 0.8948 | 0.1111 | 11.2151 | |||
| 17MS01.10 | 76 | 14 | 5.30 | 0.8834 | 1.5750 | 2.9378 | 1.5872 | 17MS01.44 | 192 | 52 | 3.69 | 0.5016 | 2.0304 | 44.7253 | 1.9601 | |||
| 17MS01.12 | 94 | 14 | 6.60 | 0.8743 | 1.4404 | 1.9390 | 1.5487 | 17MS01.45 | 1391 | 1995 | 0.70 | 0.6291 | 3.7503 | 30.8625 | 2.4905 | |||
| 17MS01.13 | 463 | 462 | 1.00 | 0.8804 | 1.3690 | 1.6412 | 1.3879 | 17MS01.46 | 1274 | 1874 | 0.68 | 0.5888 | 3.5811 | 35.6714 | 2.1179 | |||
| 17MS01.14 | 453 | 461 | 0.98 | 0.4845 | 3.3717 | 45.5478 | 2.3638 | 17MS01.47 | 6466 | 381 | 16.96 | 0.9039 | 1.4358 | 2.2080 | 3.0184 | |||
| 17MS01.16 | 155 | 16 | 9.97 | 0.8527 | 2.0586 | 0.5450 | 8.0893 | 17MS01.49 | 15 | 2 | 8.38 | 0.8546 | 1.0487 | 1.7677 | 1.4732 | |||
| 17MS01.17 | 70 | 7 | 9.93 | 0.8753 | 1.0525 | 2.1948 | 2.5031 | 17MS01.50 | 95 | 33 | 2.89 | 0.8817 | 1.0195 | 1.6856 | 1.9057 | |||
| 17MS01.18 | 46 | 12 | 3.89 | 0.9082 | 1.0402 | 2.0720 | 1.9266 | 17MS01.52 | 1 | 2 | 0.60 | 0.8931 | 1.1777 | 2.4336 | 1.4093 | |||
| 17MS01.20 | 1277 | 170 | 7.51 | 0.8974 | 0.9356 | 1.8199 | 2.3891 | 17MS01.53 | 663 | 253 | 2.62 | 0.8999 | 1.3397 | 2.9198 | 1.4218 | |||
| 17MS01.22 | 4 | 5 | 0.86 | 0.8559 | 1.0636 | 2.0625 | 1.1626 | 17MS01.56 | 45 | 15 | 3.13 | 0.8644 | 1.6027 | 2.6286 | 1.5413 | |||
| 17MS01.23 | 1316 | 1104 | 1.19 | 0.5093 | 2.3223 | 55.2046 | 1.8992 | 17MS01.57 | 462 | 467 | 0.99 | 0.8634 | 1.3099 | 4.1745 | 1.4078 | |||
| 17MS01.25 | 1583 | 70 | 22.75 | 0.8505 | 1.1378 | 2.6453 | 1.5710 | 17MS01.59 | 556 | 197 | 2.82 | 0.7957 | 3.2110 | 6.1032 | 2.3855 | |||
| 17MS01.27 | 122 | 19 | 6.25 | 0.8714 | 1.2965 | 1.7653 | 1.6522 | 17MS01.60 | 0 | 7 | 0.06 | 0.4696 | 3.8509 | 41.6457 | 2.0471 | |||
| 17MS01.28 | 118 | 19 | 6.24 | 0.8385 | 1.1699 | 1.6493 | 1.4157 | 17MS01.61 | 17 | 7 | 2.62 | 0.9328 | 1.2852 | 0.8348 | 2.5080 | |||
| 17MS01.31 | 2 | 1 | 1.86 | 0.9170 | 1.5418 | 0.7938 | 2.6302 | 17MS01.62 | 1801 | 509 | 3.54 | 0.9005 | 1.7886 | 2.2449 | 5.1810 | |||
| 17MS01.32 | 107 | 19 | 5.57 | 0.8156 | 1.2677 | 4.6167 | 1.3848 | 17MS01.63 | 851 | 210 | 4.05 | 0.4586 | 2.7958 | 56.5846 | 1.8309 | |||
| 17MS01.34 | 207 | 12 | 17.27 | 0.8531 | 1.3984 | 2.5556 | 1.3361 | |||||||||||
| 年代 | 区内构造活动 | 区内岩浆活动 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 古新世 | 晚期 | 胶莱盆地萎缩 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂右旋挤压走滑 | |
| 早期 | 胶莱盆地N—S向拉分 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂右旋伸展走滑 | ||
| 晚白垩世 | 晚期 | 胶莱盆地NW—SE向伸展 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂右旋伸展走滑 | 莒南火山角砾岩((66.8±1.5) Ma)[ 胶州玄武岩(72 Ma)[ 诸城玄武岩(76 Ma)[ 青岛基性脉岩((86.0±1.6) Ma)[ |
| 早期 | 胶莱盆地NW—SE向伸展 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂右旋伸展走滑 | ||
| 早白垩世 | 中晚期 | 胶莱盆地早白垩世E—W向拉分 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂E—W向伸展 | 分岭山安粗岩((110.4±1.7) Ma)[ 海阳安山质熔岩((118.06±3.22) Ma)[ 马山粗面英安岩((119.3±1.6) Ma)[ 七宝山次火山岩((126±3) Ma)[ |
| 早期 | 胶莱盆地早白垩世E—W向拉分 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂NW—SE向伸展 | ||
| 晚侏罗世 | 早期 | 胶莱盆地拉分 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂左旋走滑 | 昆嵛山花岗闪长岩(147 Ma)[ 昆嵛山二长闪长岩((152.2±1.2) Ma)[ 鹊山二长花岗岩((154.0±1.2) Ma)[ 玲珑花岗闪长岩((153±4) Ma)[ |
| 晚期 | 胶莱盆地拉分 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂左旋走滑 | 鹊山石英二长岩((156.3±1.8) Ma)[ 文登二长花岗岩((157±5) Ma)[ 玲珑二长花岗岩((160±3) Ma)[ 玲珑金矿二长花岗岩((164±2) Ma)[ | |
表2 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂地区构造-岩浆演化简表
Table 2 Brief table of tectono-magmatic evolution in the Wulian-Qingdao-Yantai fault
| 年代 | 区内构造活动 | 区内岩浆活动 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 古新世 | 晚期 | 胶莱盆地萎缩 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂右旋挤压走滑 | |
| 早期 | 胶莱盆地N—S向拉分 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂右旋伸展走滑 | ||
| 晚白垩世 | 晚期 | 胶莱盆地NW—SE向伸展 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂右旋伸展走滑 | 莒南火山角砾岩((66.8±1.5) Ma)[ 胶州玄武岩(72 Ma)[ 诸城玄武岩(76 Ma)[ 青岛基性脉岩((86.0±1.6) Ma)[ |
| 早期 | 胶莱盆地NW—SE向伸展 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂右旋伸展走滑 | ||
| 早白垩世 | 中晚期 | 胶莱盆地早白垩世E—W向拉分 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂E—W向伸展 | 分岭山安粗岩((110.4±1.7) Ma)[ 海阳安山质熔岩((118.06±3.22) Ma)[ 马山粗面英安岩((119.3±1.6) Ma)[ 七宝山次火山岩((126±3) Ma)[ |
| 早期 | 胶莱盆地早白垩世E—W向拉分 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂NW—SE向伸展 | ||
| 晚侏罗世 | 早期 | 胶莱盆地拉分 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂左旋走滑 | 昆嵛山花岗闪长岩(147 Ma)[ 昆嵛山二长闪长岩((152.2±1.2) Ma)[ 鹊山二长花岗岩((154.0±1.2) Ma)[ 玲珑花岗闪长岩((153±4) Ma)[ |
| 晚期 | 胶莱盆地拉分 五莲—青岛—烟台断裂左旋走滑 | 鹊山石英二长岩((156.3±1.8) Ma)[ 文登二长花岗岩((157±5) Ma)[ 玲珑二长花岗岩((160±3) Ma)[ 玲珑金矿二长花岗岩((164±2) Ma)[ | |
| [1] |
索艳慧, 李三忠, 曹现志, 等. 中国东部中新生代反转构造及其记录的大洋板块俯冲过程[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(4): 249-267.
DOI |
| [2] | ZHAI M G, ZHU R X, LIU J M, et al. Time range of Mesozoic tectonic regime inversion in eastern North China Block[J]. Science in China (Series D: Earth Sciences), 2004, 47(2): 151-159. |
| [3] |
ZHANG Y Q, DONG S W, SHI W. Cretaceous deformation history of the middle Tan-Lu fault zone in Shandong Province, Eastern China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2003, 363(3/4): 243-258.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
TANG J, ZHENG Y F, WU Y B, et al. Zircon U-Pb age and geochemical constraints on the tectonic affinity of the Jiaodong terrane in the Sulu orogen, China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2008, 161(3/4): 389-418.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 张岳桥, 李金良, 张田, 等. 胶东半岛牟平—即墨断裂带晚中生代运动学转换历史[J]. 地质论评, 2007, 53(3): 289-300. |
| [6] | 刘凤, 栾锡武. 桃村断裂在北黄海盆地的延伸问题探讨[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2009. |
| [7] | 周本刚, 冉勇康, 环文林, 等. 山东海阳断裂东石兰沟段晚更新世以来地表断错特征与最大潜在地震估计[J]. 地震地质, 2002, 24(2): 159-166. |
| [8] | 戴俊生, 陆克政, 宋全友, 等. 胶莱盆地的运动学特征[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版), 1995, 19(2): 1-6. |
| [9] | WATSON E B, HARRISON T M, RYERSON F J. Diffusion of Sm,Sr, and Pb in fluorapatite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochi-mica Acta, 1985, 49(8): 1813-1823. |
| [10] |
CHERNIAK D J, LANFORD W A, RYERSON F J. Lead diffusion in apatite and zircon using ion implantation and Rutherford Backscattering techniques[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1991, 55(6): 1663-1673.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
SMYE A J, MARSH J H, VERMEESCH P, et al. Applications and limitations of U-Pb thermochronology to middle and lower crustal thermal histories[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 494: 1-18.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
RIBEIRO B V, LAGOEIRO L, FALEIROS F M, et al. Strain localization and fluid-assisted deformation in apatite and its influence on trace elements and U-Pb systematics[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2020, 545: 116421.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
NAKANO T, AWAZU T, UMAKOSHI Y. Plastic deformation and operative slip system in mineral fluorapatite single crystal[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2001, 44(5): 811-815.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
SAKA H, GOTO D, MOON W. Dislocations in plastically deformed apatite[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2008, 43(9): 3234-3239.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
HARLOV D E. Apatite: A fingerprint for metasomatic processes[J]. Elements, 2015, 11(3): 171-176.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 王微, 宋传中, 李加好, 等. 郯庐断裂带肥东桃源韧性剪切带构造分析及时限探究[J]. 地质科学, 2016, 51(4): 1040-1058. |
| [17] | 孙晓猛, 刘永江, 孙庆春, 等. 敦密断裂带走滑运动的40Ar/39Ar年代学证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2008, 38(6): 965-972. |
| [18] |
TANG J, ZHENG Y F, WU Y B, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of metamorphic rocks in the Jiaobei terrane: Constraints on its tectonic affinity in the Sulu orogen[J]. Precambrian Research, 2007, 152(1/2): 48-82.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
XIE S W, WU Y B, ZHANG Z M, et al. U-Pb ages and trace elements of detrital zircons from Early Cretaceous sedimentary rocks in the Jiaolai Basin, north margin of the Sulu UHP terrane: Provenances and tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 2012, 154: 346-360.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
DENG J, YANG L Q, LI R H, et al. Regional structural control on the distribution of world-class gold deposits: An overview from the Giant Jiaodong Gold Province, China[J]. Geological Journal, 2019, 54(1): 378-391.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
LI S Z, ZHAO G C, DAI L M, et al. Mesozoic Basins in Eastern China and their bearing on the deconstruction of the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 47: 64-79.
DOI URL |
| [22] | 李金良, 张岳桥, 柳宗泉, 等. 胶莱盆地沉积-沉降史分析与构造演化[J]. 中国地质, 2007, 34(2): 240-250. |
| [23] |
DENG J, WANG C M, BAGAS L, et al. Cretaceous-Cenozoic tectonic history of the Jiaojia Fault and gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from zircon U-Pb, illite K-Ar, and apatite fission track thermochronometry[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2015, 50(8): 987-1006.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
YANG Q Y, SANTOSH M, SHEN J F, et al. Juvenile vs.recycled crust in NE China: Zircon U-Pb geochronology, Hf isotope and an integrated model for Mesozoic gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25(4): 1445-1468.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 郭云成, 段留安, 韩小梦, 等. 胶东前垂柳金矿区花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(3): 876-897. |
| [26] | 高建伟, 赵国春, 毛小红, 等. 山东乳山金青顶金矿成矿构造和应力场研究[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(6): 1099-1107. |
| [27] | 李秀章, 王立功, 李衣鑫, 等. 胶东艾山岩体二长花岗岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Lu-Hf同位素特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(1): 333-346. |
| [28] | 张华全, 张维昕, 李洪杰. 山东胶莱盆地金矿成矿条件及找矿方向[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2008, 16(2): 12-17, 23. |
| [29] | 付文钊. 胶莱盆地白垩纪层序地层与盆地演化过程研究[D]. 青岛: 山东科技大学, 2014. |
| [30] | 佟彦明. 胶莱盆地构造演化研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2007. |
| [31] | 曹光跃, 薛怀民, 刘哲, 等. 鲁西临朐地区早白垩世青山群火山岩的年代学、地球化学及岩石成因[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(3): 503-519. |
| [32] | 张岳桥, 李金良, 张田, 等. 胶莱盆地及其邻区白垩纪—古新世沉积构造演化历史及其区域动力学意义[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(9): 1229-1257. |
| [33] |
NI J L, LIU J L, TANG X L, et al. The Wulian metamorphic core complex: A newly discovered metamorphic core complex along the Sulu orogenic belt, Eastern China[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2013, 24(3): 297-313.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
LI S Z, ZHAO G C, DAI L M, et al. Cenozoic faulting of the Bohai Bay Basin and its bearing on the destruction of the eastern North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 47: 80-93.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
LAN H Y, LI S Z, LI X Y, et al. Early Mesozoic intracontinental deformation in the eastern North China Block: Implication for an indentation model of North China to South China blocks[J]. Geological Journal, 2017, 52(Suppl): 8-21.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 李三忠, 索艳慧, 李玺瑶, 等. 西太平洋中生代板块俯冲过程与东亚洋陆过渡带构造-岩浆响应[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(16): 1550-1593. |
| [37] |
BARFOD G H, KROGSTAD E J, FREI R, et al. Lu-Hf and PbSL geochronology of apatites from Proterozoic terranes: A first look at Lu-Hf isotopic closure in metamorphic apatite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(7): 1847-1859.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
LIU Y S, GAO S, HU Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the trans-north China orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2): 537-571.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
ANDERSEN T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1/2): 59-79.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
YU H C, QIU K F, NASSIF M T, et al. Early orogenic gold mineralization event in the West Qinling related to closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean-Constraints from the Ludousou gold deposit, central China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 117: 103217.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
STRECK M J. Mineral textures and zoning as evidence for open system processes[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2008, 69(1): 595-622.
DOI URL |
| [42] | LADENBURGER S, MARKS M A W, UPTON B, et al. Compositional variation of apatite from rift-related alkaline igneous rocks of the Gardar Province, South Greenland[J]. American Minera-logist, 2016, 101(3): 612-626. |
| [43] |
KRNETA S, CIOBANU C L, COOK N J, et al. Apatite at Olympic Dam, South Australia: A petrogenetic tool[J]. Lithos, 2016, 262: 470-485.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
DENG J, WANG Q F, LIU X F, et al. The formation of the Jiaodong gold Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(6): 1801-1820.
DOI URL |
| [45] | QIU K F, DENG J, SAI S X, et al. Low-temperature thermochronology for defining the tectonic controls on heterogeneous gold endowment across the Jiaodong peninsula, eastern China[J]. Tectonics, 2023, 42(1): e2022TC007669. |
| [46] |
DENG J, YANG L Q, GROVES D I, et al. An integrated mineral system model for the gold deposits of the giant Jiaodong Province, Eastern China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 208: 103274.
DOI URL |
| [47] | 何登洋, 邱昆峰, 于皓丞, 等. 华北克拉通胶莱盆地马山地区早白垩世粗面英安岩岩石成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(12): 3705-3720. |
| [48] | 丁正江, 孙丰月, 刘福来, 等. 胶东中生代动力学演化及主要金属矿床成矿系列[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(10): 3045-3080. |
| [49] | 邱连贵, 任凤楼, 曹忠祥, 等. 胶东地区晚中生代岩浆活动及对大地构造的制约[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2008, 32(1): 117-123. |
| [50] | 苗来成, 罗镇宽, 关康, 等. 玲珑花岗岩中锆石的离子质谱U-Pb年龄及其岩石学意义[J]. 岩石学报, 1998, 14(2): 198-206. |
| [51] | 徐洪林, 张德全, 孙桂英. 胶东昆嵛山花岗岩的特征、成因及其与金矿的关系[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 1997, 16(2): 131-143. |
| [52] | 郭敬辉, 陈福坤, 张晓曼, 等. 苏鲁超高压带北部中生代岩浆侵入活动与同碰撞—碰撞后构造过程: 锆石 U-Pb 年代学[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(4): 1281-1301. |
| [53] | 张田, 张岳桥. 胶北隆起晚中生代构造-岩浆演化历史[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(9): 1210-1228. |
| [54] | 胡世玲, 王松山, 桑海清, 等. 山东玲珑和郭家岭岩体的同位素年龄及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 1987, 3(3):83-89. |
| [55] | 周建波, 郑永飞, 赵子福. 山东五莲中生代岩浆岩的锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 高校地质学报, 2003, 9(2): 185-194. |
| [56] | 谭俊, 魏俊浩, 杨春福, 等. 胶东郭城地区脉岩类岩石地球化学特征及成岩构造背景[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(8): 1177-1188. |
| [57] | 张宏福, 英基丰, 汤艳杰, 等. 华北东部中、新生代岩石圈地幔的不均一性: 来自橄榄石的组成填图结果[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(9): 2279-2288. |
| [58] | 孟繁聪, 李天福, 薛怀民, 等. 胶莱盆地晚白垩世不同地幔源区的两种基性岩浆: 诸城玄武岩和胶州玄武岩的对比[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(6): 1644-1656. |
| [59] | 邱检生, 王德滋, 罗清华, 等. 鲁东胶莱盆地青山组火山岩的40Ar-39Ar定年: 以五莲分岭山火山机构为例[J]. 高校地质学报, 2001, 7(3): 351-355. |
| [60] |
FAN W M, ZHANG H F, BAKER J, et al. On and off the North China Craton: Where is the Archaean keel?[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2000, 41(7): 933-950.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
RUDNICK R L, GAO S, LING W L, et al. Petrology and geochemistry of spinel peridotite xenoliths from Hannuoba and Qixia, North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2004, 77(1/2/3/4): 609-637.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
QIU K F, DENG J, LAFLAMME C, et al. Giant Mesozoic gold ores derived from subducted oceanic slab and overlying sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2023, 343: 133-141.
DOI URL |
| [63] | 唐华风, 程日辉, 白云风, 等. 胶莱盆地构造演化规律[J]. 世界地质, 2003, 22(3): 246-251. |
| [64] | 施炜, 张岳桥, 董树文, 等. 山东胶莱盆地构造变形及形成演化: 以王氏群和大盛群变形分析为例[J]. 地质通报, 2003, 22(5): 325-334. |
| [65] | 任凤楼, 张岳桥, 邱连贵, 等. 胶莱盆地白垩纪构造应力场与转换机制[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2007, 31(2): 157-167. |
| [66] |
MARUYAMA S, ISOZAKI Y, KIMURA G, et al. Paleogeographic maps of the Japanese Islands: Plate tectonic synthesis from 750Ma to the present[J]. Island Arc, 1997, 6(1): 121-142.
DOI URL |
| [67] | 翟慎德. 胶莱盆地莱阳凹陷构造特征及演化[J]. 石油实验地质, 2003, 25(2): 137-142. |
| [68] |
CHARLES N, AUGIER R, GUMIAUX C, et al. Timing, duration and role of magmatism in wide rift systems: Insights from theJiaodong Peninsula (China, East Asia)[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 24(1): 412-428.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
DENG J, QIU K F, WANG Q F, et al. In situ dating of hydrothermal monazite and implications for the geodynamic controls on ore formation in the Jiaodong gold Province, eastern China[J]. Economic Geology, 2020, 115(3): 671-685.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [2] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [3] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [4] | 张靓, 陈奇, 高添, 李雯, 钱金龙, 刘俐君, 王长明. 三江特提斯马厂箐斑岩铜钼矿床成矿时间尺度探讨:来自石英中Ti-Al扩散年代学的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1509-1523. |
| [5] | 苏惠, 曾认宇, 甘德斌, 严杰. 阿拉善北大山地区花岗斑岩岩石成因及构造启示:元素地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1580-1596. |
| [6] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [7] | 席振, 马德成, 李欢, 高光明, 向夏楠. 新疆东昆仑土窑洞地区新元古代早期侵入岩年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1609-1623. |
| [8] | 梁乾坤, 陈岳龙, 王善辉, 于洋, 杨帆. 嫩江河漫滩沉积物碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 529-546. |
| [9] | 韩飞, 宋元宝, 张伟, 李道凌, 黄永高, 李应栩, 贾小川, 杨学俊, 杨青松, 宋旭波, 卢柳. 西藏冈底斯南木林地区晚三叠世中酸性岩浆作用及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 547-561. |
| [10] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [11] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [12] | 王向伟, 张保涛, 杨浩强, 韩进国. 青海省海晏县团宝山一带变质岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 586-598. |
| [13] | 马德成, 席振, 高光明, 李欢. 新疆祁漫塔格花土沟地区中酸性侵入岩的年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 599-612. |
| [14] | 徐立明, 刘涛, 郑吉林. 大兴安岭北段阿里河镇早白垩世高分异花岗岩的确定及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 613-626. |
| [15] | 薛仲凯, 范堡程, 黄豪擎, 唐卫东, 葛战林, 李朋伟, 胡建辉, 杨晓奇, 郭永超, 李空. 内蒙古北山地区中基性岩脉年代学和地球化学特征:对塔里木板块北缘构造演化的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 627-644. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||