



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (01): 1-17.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.023
郭长宝1,2( ), 吴瑞安1,2, 蒋良文3, 钟宁1,2, 王炀1,2, 王栋3, 张永双4, 杨志华1,2, 孟文1,2, 李雪1,2, 刘贵1,2
), 吴瑞安1,2, 蒋良文3, 钟宁1,2, 王炀1,2, 王栋3, 张永双4, 杨志华1,2, 孟文1,2, 李雪1,2, 刘贵1,2
收稿日期:2020-12-13
修回日期:2021-01-10
出版日期:2021-02-12
发布日期:2021-03-12
作者简介:郭长宝,男,博士,研究员,1980年出生,地质工程专业,主要从事工程地质与地质灾害调查研究。Email: guochangbao@163.com。
基金资助:
GUO Changbao1,2( ), WU Rui’an1,2, JIANG Liangwen3, ZHONG Ning1,2, WANG Yang1,2, WANG Dong3, ZHANG Yongshuang4, YANG Zhihua1,2, MENG Wen1,2, LI Xue1,2, LIU Gui1,2
), WU Rui’an1,2, JIANG Liangwen3, ZHONG Ning1,2, WANG Yang1,2, WANG Dong3, ZHANG Yongshuang4, YANG Zhihua1,2, MENG Wen1,2, LI Xue1,2, LIU Gui1,2
Received:2020-12-13
Revised:2021-01-10
Online:2021-02-12
Published:2021-03-12
摘要:
川藏铁路是中国正在规划建设的重点工程,穿越地形地貌和地质构造都极为复杂的青藏高原东部。铁路沿线活动断裂发育、地震频发,新建铁路雅安—林芝段直接穿越或近距离展布于龙门山断裂带、鲜水河断裂带等10条大型区域性活动断裂带,部分断裂活动速率值达10 mm/a,潜在强震危险性高。在内外动力耦合作用下,铁路沿线地质灾害极为发育,密集分布于大渡河、雅砻江、金沙江、澜沧江、怒江和雅鲁藏布江及其一级支流、活动断裂带和公路沿线,其中高位远程滑坡及链式灾害、深层蠕变-剧滑型滑坡、地震滑坡等灾害危害严重,成为了铁路建设的“拦路虎”。铁路沿线处于以水平构造应力为主导的高地应力环境,穿越华南主体应力区、龙门山—松潘应力区、川滇应力区、墨脱—昌都应力区和喜马拉雅应力区等5个大的一级构造应力区;雅安—康定段最大主应力方向为NWW—NW向,并向林芝方向呈现NNE向偏转,地应力在平面和垂向空间上表现为强烈局部差异性,如折多山某隧道地应力测试结果揭示了在垂向上存在应力释放区。在高地应力条件下,铁路沿线深埋隧道潜在围岩岩爆和大变形危害风险大。铁路建设应加强活动断裂安全避让、重大地质灾害早期识别和监测预警、深埋隧道地应力和岩爆大变形超前预测预报等工作,科学指导铁路选线与防灾减灾。
中图分类号:
郭长宝, 吴瑞安, 蒋良文, 钟宁, 王炀, 王栋, 张永双, 杨志华, 孟文, 李雪, 刘贵. 川藏铁路雅安—林芝段典型地质灾害与工程地质问题[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 1-17.
GUO Changbao, WU Rui’an, JIANG Liangwen, ZHONG Ning, WANG Yang, WANG Dong, ZHANG Yongshuang, YANG Zhihua, MENG Wen, LI Xue, LIU Gui. Typical Geohazards and Engineering Geological Problems Along the Ya’an-Linzhi Section of the Sichuan-Tibet Railway,China[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(01): 1-17.
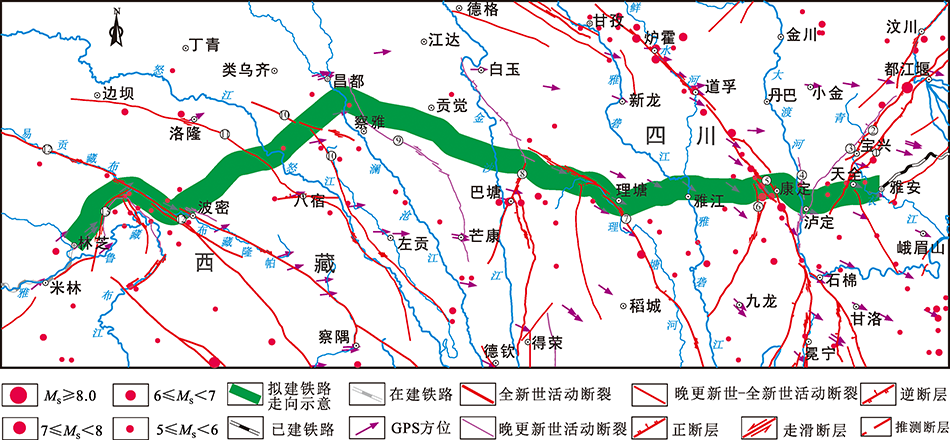
图2 川藏铁路雅安—林芝段活动断裂与地震分布图(据郭长宝等[18];铁路线为走向示意图,非正式线路) F1.双石—大川断裂;F2.盐井—五龙断裂;F3.耿达—陇东断裂;F4.大渡河断裂带;F5.鲜水河断裂带;F6.玉农希断裂带;F7.理塘—徳巫断裂带;F8.巴塘断裂带;F9.香堆—洛尼断裂;F10.怒江断裂带;F11.边坝—洛隆断裂;F12.嘉黎—察隅断裂;F13.鲁朗—易贡断裂
Fig.2 Distribution map of active faults and earthquakes in the Ya’an-Linzhi section of the Sichuan-Tibet Railway
| 序号 | 活动断裂带名称 | 分段特征 | 活动性质 | 活动时代 | 与铁路关系 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 龙门山断裂带 | 耿达—陇东断裂 | 右旋逆冲 | 晚更新世—全新世 | 正交穿越 |
| 盐井—五龙断裂 | 右旋逆冲 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | ||
| 双石—大川断裂 | 右旋逆冲 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | ||
| 2 | 鲜水河断裂带 | 雅拉河断裂 | 左旋 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 |
| 色拉哈断裂 | 左旋 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | ||
| 木格措南断裂 | 左旋兼正断 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | ||
| 折多塘断裂 | 左旋 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | ||
| 3 | 玉农希断裂带 | 左旋 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | |
| 4 | 理塘—德巫断裂带 | 毛垭坝盆地北缘断裂 | 左旋 | 全新世 | 小角度斜交 |
| 理塘断裂 | 左旋 | 全新世 | 小角度斜交 | ||
| 5 | 巴塘断裂带 | 右旋 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | |
| 6 | 澜沧江断裂带 | 巴青—类乌齐断裂 | 左旋 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 |
| 7 | 怒江断裂带 | 羊达—亚许断裂 | 左旋逆冲 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 |
| 邦达断裂 | 左旋逆冲 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | ||
| 8 | 边坝—洛隆断裂带 | 左旋 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | |
| 9 | 嘉黎—察隅断裂带 | 右旋逆冲 | 全新世 | 近平行或小角度斜交 | |
| 10 | 鲁朗—易贡断裂带 | 左旋正断 | 全新世 | 近平行 |
表1 川藏铁路雅安—林芝段主要活动断裂发育特征
Table 1 Characteristics of main active faults in the Ya’an-Linzhi section of the Sichuan-Tibet Railway
| 序号 | 活动断裂带名称 | 分段特征 | 活动性质 | 活动时代 | 与铁路关系 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 龙门山断裂带 | 耿达—陇东断裂 | 右旋逆冲 | 晚更新世—全新世 | 正交穿越 |
| 盐井—五龙断裂 | 右旋逆冲 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | ||
| 双石—大川断裂 | 右旋逆冲 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | ||
| 2 | 鲜水河断裂带 | 雅拉河断裂 | 左旋 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 |
| 色拉哈断裂 | 左旋 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | ||
| 木格措南断裂 | 左旋兼正断 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | ||
| 折多塘断裂 | 左旋 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | ||
| 3 | 玉农希断裂带 | 左旋 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | |
| 4 | 理塘—德巫断裂带 | 毛垭坝盆地北缘断裂 | 左旋 | 全新世 | 小角度斜交 |
| 理塘断裂 | 左旋 | 全新世 | 小角度斜交 | ||
| 5 | 巴塘断裂带 | 右旋 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | |
| 6 | 澜沧江断裂带 | 巴青—类乌齐断裂 | 左旋 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 |
| 7 | 怒江断裂带 | 羊达—亚许断裂 | 左旋逆冲 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 |
| 邦达断裂 | 左旋逆冲 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | ||
| 8 | 边坝—洛隆断裂带 | 左旋 | 全新世 | 大角度斜交 | |
| 9 | 嘉黎—察隅断裂带 | 右旋逆冲 | 全新世 | 近平行或小角度斜交 | |
| 10 | 鲁朗—易贡断裂带 | 左旋正断 | 全新世 | 近平行 |

图13 川藏铁路部分地应力实测点及应力方向分布(数据截至2018年10月)
Fig.13 Measured geostress distribution map and stress directions along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway (data collected by October 2018)
| 序 号 | 深度 /m | 主应力值/MPa | KHv | Khv | Kav | KHh | SH 方向 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH | Sh | Sv | |||||||
| 1 | 196.5 | 9.32 | 5.92 | 5.34 | 1.74 | 1.11 | 1.43 | 1.58 | |
| 2 | 270.5 | 14.95 | 10.23 | 7.36 | 2.03 | 1.39 | 1.71 | 1.46 | |
| 3 | 330.0 | 20.85 | 12.45 | 8.98 | 2.32 | 1.39 | 1.85 | 1.68 | |
| 4 | 389.5 | 16.28 | 9.93 | 10.59 | 1.54 | 0.94 | 1.24 | 1.64 | |
| 5 | 458.5 | 12.92 | 9.74 | 12.47 | 1.04 | 0.78 | 0.91 | 1.33 | |
| 6 | 540.0 | 17.79 | 12.32 | 14.69 | 1.21 | 0.84 | 1.02 | 1.44 | |
| 7 | 560.5 | 11.88 | 9.08 | 15.25 | 0.78 | 0.60 | 0.69 | 1.31 | |
| 8 | 642.0 | 35.68 | 19.59 | 17.46 | 2.04 | 1.12 | 1.58 | 1.82 | N84°W |
表2 折多山某隧道水压致裂地应力测量结果[66]
Table 2 Results of hydraulic fracturing measurement of one tunnel in Zheduo Mountain[66]
| 序 号 | 深度 /m | 主应力值/MPa | KHv | Khv | Kav | KHh | SH 方向 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH | Sh | Sv | |||||||
| 1 | 196.5 | 9.32 | 5.92 | 5.34 | 1.74 | 1.11 | 1.43 | 1.58 | |
| 2 | 270.5 | 14.95 | 10.23 | 7.36 | 2.03 | 1.39 | 1.71 | 1.46 | |
| 3 | 330.0 | 20.85 | 12.45 | 8.98 | 2.32 | 1.39 | 1.85 | 1.68 | |
| 4 | 389.5 | 16.28 | 9.93 | 10.59 | 1.54 | 0.94 | 1.24 | 1.64 | |
| 5 | 458.5 | 12.92 | 9.74 | 12.47 | 1.04 | 0.78 | 0.91 | 1.33 | |
| 6 | 540.0 | 17.79 | 12.32 | 14.69 | 1.21 | 0.84 | 1.02 | 1.44 | |
| 7 | 560.5 | 11.88 | 9.08 | 15.25 | 0.78 | 0.60 | 0.69 | 1.31 | |
| 8 | 642.0 | 35.68 | 19.59 | 17.46 | 2.04 | 1.12 | 1.58 | 1.82 | N84°W |

图14 川藏铁路拉萨—林芝段典型深埋隧道围岩岩爆现象 (a)桑珠岭隧道岩爆(据田四明等[68]);(b)巴玉隧道岩爆(据严健等[12])
Fig.14 Typical rockburst damage in deep-buried tunnel surrounding rock along the Lhasa-Linzhi section of Sichuan-Tibet Railway

图15 川藏铁路已修建拉萨至林芝段深埋隧道围岩大变形现象 (a)藏噶隧道钢架被剪断(据方星桦等[69]);(b)米拉山隧道混凝土开裂(据吴树元[70])
Fig.15 Typically large deformation damage in deep-buried tunnel surrounding rocks along the Lhasa-Linzhi section of Sichuan-Tibet Railway
| [1] | 朱颖. 川藏铁路建设的挑战与对策(2016学术交流会论文集)[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社股份有限公司, 2016. |
| [2] | 郭长宝, 张永双, 蒋良文, 等. 川藏铁路沿线及邻区环境工程地质问题概论[J]. 现代地质, 2017,31(5):877-899. |
| [3] | LU Chunfang, CAI Chaoxun. Challenges and countermeasures for construction safety during the Sichuan-Tibet Railway Project[J]. Engineering, 2019,5(5):833-838. |
| [4] | 彭建兵, 崔鹏, 庄建琦. 川藏铁路对工程地质提出的挑战[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020,39(12):2377-2389. |
| [5] | 国家发展和改革委员会. 关于新建川藏铁路雅安至林芝段可行性研究报告批复的主要内容[EB/OL].[2020-09-29].https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xxgk/zcfb/ghwb/202009/t20200930_1239951.html. |
| [6] | 中国国家铁路集团有限公司. 习近平对川藏铁路开工建设作出重要指示强调发扬“两路”精神和青藏铁路精神高质量推进工程建设[EB/OL]. [2020- 11- 08]. http://www.china-railway.com.cn/xwzx/ywsl/202011/t20201108_110244.html. |
| [7] | 殷跃平. 西藏波密易贡高速巨型滑坡概况[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2000,11(2):103. |
| [8] | XU Qiang, SHANG Yanjun, VAN ASCH Theo, et al. Observations from the large, rapid Yigong rock slide-debris avalanche, southeast Tibet[J]. Revue Canadienne De Géotechnique, 2012,49(5):589-606. |
| [9] | 王立朝, 温铭生, 冯振, 等. 中国西藏金沙江白格滑坡灾害研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2019,30(1):1-9. |
| [10] | 张永双, 巴仁基, 任三绍, 等. 中国西藏金沙江白格滑坡的地质成因分析[J]. 中国地质, 2020,47(6):1637-1645. |
| [11] | 严健, 何川, 汪波, 等. 高地温对隧道岩爆发生的影响性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2019,40(4):1543-1550. |
| [12] | 严健, 何川, 汪波, 等. 雅鲁藏布江缝合带深埋长大隧道群岩爆孕育及特征[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2019,38(4):769-781. |
| [13] | 邓起东, 高翔, 杨虎. 断块构造、活动断块构造与地震活动[J]. 地质科学, 2009,44(4):1083-1093. |
| [14] | 潘桂棠, 王立全, 张万平, 等. 青藏高原及邻区大地构造图及说明书(1:1500000)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2013: 1-208. |
| [15] | 邓起东. 中国活动构造研究[J]. 地质论评, 1996,42(4):295-299. |
| [16] | 王栋, 张广泽, 蒋良文, 等. 川藏铁路成康段活动断裂工程效应及地质选线[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2015,32(10):6-11. |
| [17] | 潘家伟, 李海兵, CHEVALIER Marie-Luce, 等. 鲜水河断裂带色拉哈—康定段新发现的活动断层: 木格措南断裂[J]. 地质学报, 2020,94(11):3178-3188. |
| [18] | 郭长宝, 王保弟, 刘建康, 等. 川藏铁路交通廊道地质调查工程主要进展与成果[J]. 中国地质调查, 2020,7(6):1-12. |
| [19] | 熊探宇, 姚鑫, 张永双, 等. 鲜水河断裂带全新世活动性研究进展综述[J]. 地质力学学报, 2010,16(2):176-188. |
| [20] | BAI M, CHEVALIER M L, PAN J, et al. Southeastward increase of the Late Quaternary slip-rate of the Xianshuihe fault, eastern Tibet:Geodynamic and seismic hazard implications[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2018,485:19-31. |
| [21] | 梁明剑. 鲜水河断裂晚第四纪活动习性[D]. 北京:中国地震局地质研究所, 2019. |
| [22] | 郭长宝, 杜宇本, 佟元清, 等. 青藏高原东缘理塘乱石包高速远程滑坡发育特征与形成机理[J]. 地质通报, 2016,35(8):1332-1345. |
| [23] | 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 于贵华, 等. 川西理塘断裂带平均滑动速率、地震破裂分段与复发特征[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2005,35(6):540-551. |
| [24] | 周荣军, 陈国星, 李勇, 等. 四川西部理塘—巴塘地区的活动断裂与1989年巴塘6.7级震群发震构造研究[J]. 地震地质, 2005,27(1):31-43. |
| [25] | 张克旗, 吴中海, 周春景, 等. 川西理塘断裂带奔戈—村戈段古地震事件及其非均匀性活动特征[J]. 地质学报, 2020,94(4):1295-1303. |
| [26] | LIN T H, CHUNG S L, HSU F J, et al. 40Ar/ 39Ar dating of the Jiali and Gaoligong shear zones: implications for crustal deformation around the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009,34:674-685. |
| [27] | 钟宁, 郭长宝, 黄小龙, 等. 嘉黎—察隅断裂带中南段晚第四纪活动性及其古地震记录[J]. 地质学报, 2021,待刊. |
| [28] | 宋键, 唐方头, 邓志辉, 等. 青藏高原嘉黎断裂晚第四纪运动特征[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2013,49(6):973-980. |
| [29] | WANG Hu, LI Kaijin, CHEN Lichun, et al. Evidence for Holocene activity on the Jiali Fault, an active block boundary in the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Seismological Research Letters, 2020,91:1776-1780. |
| [30] | 唐方头, 宋键, 曹忠权, 等. 最新GPS数据揭示的东构造结周边主要断裂带的运动特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2010,53(9):2119-2128. |
| [31] | 王晓楠. 南迦巴瓦构造结周边地区主要断裂带现今运动特征[D]. 北京:中国地震局地球物理研究所, 2018: 1-79. |
| [32] | 殷跃平, 王文沛, 张楠, 等. 强震区高位滑坡远程灾害特征研究——以四川茂县新磨滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质, 2017,44(5):827-841. |
| [33] | 许强, 董秀军, 李为乐. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2019,44(7):957-966. |
| [34] | 高杨, 李滨, 高浩源, 等. 高位远程滑坡冲击铲刮效应研究进展及问题[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020,26(4):510-519. |
| [35] | 刘伟. 西藏易贡巨型超高速远程滑坡地质灾害链特征研析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2002,13(3):11-20. |
| [36] | ZHOU J W, CUI P, HAO M H. Comprehensive analyses of the initiation and entrainment processes of the 2000 Yigong catastrophic landslide in Tibet, China[J]. Landslides, 2016,13(1):39-54. |
| [37] |
GUO Changbao, MONTGOMERY DAVID R, ZHANG Yongshuang, et al. Evidence for repeated failure of the giant Yigong Landslide on the Edge of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020,10(1):14371. Doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71335-w.
DOI URL PMID |
| [38] | FAN Xuanmei, XU Qiang, SCARINGI Gianvito, et al. Failure mechanism and kinematics of the deadly June 24th 2017 Xinmo landslide, Maoxian, Sichuan, China[J]. Landslides, 2017,14(3):2129-2146. |
| [39] | 何思明, 白秀强, 欧阳朝军, 等. 四川省茂县叠溪镇新磨村特大滑坡应急科学调查[J]. 山地学报, 2017,35(4):598-603. |
| [40] | GUO Changbao, ZHANG Yongshuang, MONTGOMERY DAVID R, et al. How unusual is the long-runout of the earthquake-triggered giant Luanshibao landslide, Tibetan Plateau, China?[J] Geomorphology, 2016,259:145-154. |
| [41] | WANG Yufeng, CHENG Qiangong, LIN Qiwen, et al. Insights into the kinematics and dynamics of the Luanshibao rock avalanche (Tibetan Plateau, China) based on its complex surface landforms[J]. Geomorphology, 2018,317:170-183. |
| [42] | ZENG Qingli, ZHANG Luqing, DAVIES Timothy, et al. Morphology and inner structure of Luanshibao rock avalanche in Litang, China and its implications for long-runout mechanisms[J]. Engineering Geology, 2019,260:105216. |
| [43] | 刘铮, 李滨, 贺凯, 等. 地震作用下西藏易贡滑坡动力响应特征分析[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020,26(4):471-480. |
| [44] | 夏式伟. 易贡滑坡-碎屑流-堰塞坝溃决三维数值模拟研究[D]. 上海:上海交通大学, 2018. |
| [45] | 李俊, 陈宁生, 欧阳朝军, 等. 扎木弄沟滑坡型泥石流物源及堵河溃坝可能性分析[J]. 灾害学, 2017,32(1):80-84. |
| [46] | 彭国喜. 西南山区“关键块体”控制型滑坡的形成条件与失稳机理研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2011. |
| [47] | MÜLLER S L. The Vajont catastrophe-A personal review[J]. Müller-Salzburg Leopold, 1987,24(1/4):423-444. |
| [48] | 骆培云. 新滩滑坡的变形发育和临阵预报[J]. 水土保持通报, 1986(4):40-45. |
| [49] | 许强, 郑光, 李为乐, 等. 2018年10月和11月金沙江白格两次滑坡-堰塞堵江事件分析研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2018,26(6):1534-1551. |
| [50] | 邓建辉, 高云建, 余志球, 等. 堰塞金沙江上游的白格滑坡形成机制与过程分析[J]. 工程科学与技术, 2019,51(1):9-16. |
| [51] | 曹鹏, 黎应书, 李宗亮, 等. 西藏昌都白格滑坡斜坡地质结构特征及成因机制[J/OL]. 地球科学, 2021: 1-18. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20201214.1358.002.html. |
| [52] | 周礼, 范宣梅, 许强, 等. 金沙江白格滑坡运动过程特征数值模拟与危险性预测研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2019,27(6):1395-1404. |
| [53] | 朱德明, 李鹏岳, 胡孝洪, 吴新明. 金沙江白格滑坡残留体稳定性分析与防治对策[J]. 现代地质, 2021,35(1):56-63.DOI. org/10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.012. |
| [54] | 郭长宝, 吴瑞安, 李雪, 等. 川西日扎潜在巨型岩质滑坡发育特征与形成机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020,28(4):772-783. |
| [55] | 殷跃平. 汶川八级地震滑坡高速远程特征分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2009,17(2):153-166. |
| [56] | 白永健, 倪化勇, 葛华, 等. 青藏高原东南缘活动断裂地质灾害效应研究现状[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019,25(6):1116-1128. |
| [57] | 周洪福, 韦玉婷, 王运生, 等. 1786年磨西地震触发的摩岗岭滑坡演化过程与成因机理[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2017,44(6):649-658. |
| [58] | 张御阳. 强震触发摩岗岭滑坡成因机制及运动特性研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2013. |
| [59] | 朱焕春, 陶振宇. 不同岩石中地应力分布[J]. 地震学报, 1994,16(1):49-63. |
| [60] | 张辉, 高原, 石玉涛, 等. 基于地壳介质各向异性分析青藏高原东北缘构造应力特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012,55(1):95-104. |
| [61] | 王成虎, 高桂云, 杨树新, 等. 基于中国西部构造应力分区的川藏铁路沿线地应力的状态分析与预估[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2019,38(11):2242-2253. |
| [62] | 谢富仁, 崔效锋, 赵建涛, 等. 中国大陆及邻区现代构造应力场分区[J]. 地球物理学报, 2004,47(4):654-662. |
| [63] | MENG Wen, GUO Changbao, ZHANG Yongshuang, et al. In situ stress measurements in the Lhasa terrane, Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016,90(6):2022-2035. |
| [64] | 任洋, 王栋, 李天斌, 等. 川藏铁路雅安至新都桥段地应力特征及工程效应分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021,40(1):65-76. |
| [65] | 杨树新, 陆远忠, 米琦, 等. 在地应力测量中准确求解最大、最小水平应力问题的探讨[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2012,34(2):317-325. |
| [66] | 徐正宣, 孟文, 郭长宝, 等. 川西折多山某深埋隧道地应力测量及其应用研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021,35(1):114-125.DOI. org/10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.018. |
| [67] | 隧道网. 川藏铁路首座超长隧道桑珠岭隧道贯通[EB/OL]. [2018-1-18].https://www.tunnelling.cn/PNews/NewsDetail.aspx?newsId=26747. |
| [68] | 田四明, 赵勇, 石少帅, 等. 中国铁路隧道建设期典型灾害防控方法现状、问题与对策[J]. 隧道与地下工程灾害防治, 2019,1(2):24-48. |
| [69] | 方星桦, 杨曾, 阳军生, 等. 高地应力隧道蚀变花岗岩地层围岩大变形特征及控制措施[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2020,41(5):92-101. |
| [70] | 吴树元, 程勇, 谢全敏, 等. 西藏米拉山隧道围岩大变形成因分析[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2019,56(4):69-73. |
| [71] | 徐锡伟, 于贵华, 马文涛, 等. 活断层地震地表破裂“避让带”宽度确定的依据与方法[J]. 地震地质, 2002,24(4):470-483. |
| [72] | 中国地震局地壳应力研究所. 《活动断层避让》(立项编号20174031-Q-419,征求意见稿)[R]. 北京:中国地震局地壳应力研究所, 2019. |
| [73] | 张永双, 孙萍, 石菊松, 等. 汶川地震地表破裂影响带调查与建筑场地避让宽度探讨[J]. 工程地质学报, 2010,18(3):312-319. |
| [74] | 张永双, 任三绍, 郭长宝, 等. 活动断裂带工程地质研究[J]. 地质学报, 2019,93(4):763-775. |
| [75] | 廖椿庭. 根据地应力测量结果设计采场和巷道[J]. 中国地质科学院地质力学研究所所刊, 1981(1):37-47. |
| [1] | 王瑞丰, 翟延亮, 张宝君, 申国强, 曾一凡. 基于GIS与AHP耦合技术的承德地区地质灾害危害性评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 1023-1032. |
| [2] | 李信, 薛桂澄, 夏南, 柳长柱, 杨永鹏, 马波. 基于CF、CF-LR和CF-AHP模型的国家热带雨林公园地质灾害易发性研究:以海南保亭为例[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 1033-1043. |
| [3] | 李成路, 张绪教, 武法东, 叶培盛, 卢晶. 河套盆地西南缘巴音恩格尔活动断裂的发现及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 340-352. |
| [4] | 魏永恒, 葛燕燕, 王刚, 王文峰, 田继军, 李鑫, 吴斌, 张晓. 新疆库拜煤田铁列克矿区地应力分布及其对煤层气开发的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1324-1332. |
| [5] | 冯鹏, 李松, 汤达祯, 陈博, 钟广浩. 支持向量机在煤层地应力预测中的应用[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1333-1340. |
| [6] | 王家柱, 高延超, 冉涛, 铁永波, 张凡. 川藏铁路交通廊道某大型古滑坡成因及失稳模式分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 18-25. |
| [7] | 权雪瑞, 黄靥欢, 刘春, 郭长宝. 川藏铁路线V形深切河谷地形地震放大效应数值模拟[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 38-46. |
| [8] | 张佳佳, 高波, 刘建康, 陈龙, 黄海, 李杰. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的川藏铁路澜沧江段滑坡隐患早期识别[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 64-73. |
| [9] | 周杰, 丁明涛, 黄涛, 陈宁生. 基于虚拟现实技术的川藏铁路地质灾害易发区减灾选线优化:以洛隆车站为例[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 92-102. |
| [10] | 徐正宣, 孟文, 郭长宝, 张鹏, 张广泽, 孙明乾, 陈群策, 陈宇. 川西折多山某深埋隧道地应力测量及其应用研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 114-125. |
| [11] | 孙炜锋, 郭长宝, 张广泽, 张永双, 徐正宣, 谭成轩, 李丹, 王献礼. 川西郭达山隧道水平孔地应力测量与工程意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 126-136. |
| [12] | 王磊, 郭长宝, 郭朋瑜, 吉锋. 川藏铁路孜拉山区片麻岩蠕变特性及本构模型研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 153-160. |
| [13] | 孟文, 郭长宝, 毛邦燕, 卢海峰, 陈群策, 徐学渊. 中尼铁路交通廊道现今构造应力场及其工程影响[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 167-179. |
| [14] | 赵志宏, 徐浩然, 刘峰, 魏帅超, 张薇, 王贵玲. 川藏铁路折多山段隧道温度场与热害初步预测[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 180-187. |
| [15] | 王思源, 赵敏敏, 闫晶, 马鑫, 刁玉杰, 付雷, 罗倩. 川藏铁路西藏昌都段生态保护重要性评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 234-243. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||