



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (01): 167-179.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.104
孟文1,2( ), 郭长宝1,2, 毛邦燕3, 卢海峰1,2, 陈群策1,2, 徐学渊3
), 郭长宝1,2, 毛邦燕3, 卢海峰1,2, 陈群策1,2, 徐学渊3
收稿日期:2020-06-20
修回日期:2020-11-02
出版日期:2021-02-12
发布日期:2021-03-12
作者简介:孟文,女,助理研究员,1987年出生,地质工程专业,主要从事地应力测量、数值分析及构造应力场综合研究。Email: mwen19@sina.com。
基金资助:
MENG Wen1,2( ), GUO Changbao1,2, MAO Bangyan3, LU Haifeng1,2, CHEN Qunce1,2, XU Xueyuan3
), GUO Changbao1,2, MAO Bangyan3, LU Haifeng1,2, CHEN Qunce1,2, XU Xueyuan3
Received:2020-06-20
Revised:2020-11-02
Online:2021-02-12
Published:2021-03-12
摘要:
拟建中尼铁路位于印欧板块碰撞推挤的前缘地带,区域深大断裂发育,地震频发,新构造活动强烈,应力状态复杂。基于中尼铁路交通廊道震源机制解及原地应力测量资料,分析中尼铁路沿线区域构造应力场分布特征,进一步讨论现今构造应力场对铁路方案和重要工程设置的潜在影响。研究结果表明,研究区震源深度主压应力优势方向在板块碰撞边界为NEE向,高原内部则表现出明显的非均匀性特征。中国境内日喀则至吉隆段主要处于拉张-剪切应力环境,尼泊尔境内区段处于印欧板块推挤控制的挤压应力环境。在缺少中尼铁路沿线原地应力实测资料的现状下,结合邻区实测数据分析认为,该区地壳浅表层应力结构以逆断型为主,水平最大主压应力优势方向为NE向。基于研究区内主应力方向分布特征将中尼铁路沿线划分为日喀则―萨迦、萨迦―定结、定结―吉隆、聂拉木、吉隆―讷瓦果德和加德满都共6段。根据构造应力场分析结果并基于σθmax/Rc理论对铁路隧道工程围岩岩爆可能性进行了讨论,结果表明最大水平主应力方向与隧道轴向夹角较大时对隧道围岩稳定性不利,且隧道埋深越大则围岩岩爆的可能性越大。中尼铁路大多区段轴向与最大水平主应力方向呈大角度相交甚至近垂直,当隧道埋深较大时具有发生岩爆的可能,需重点防护。研究结果可为中尼铁路交通廊道工程勘察选线提供参考。
中图分类号:
孟文, 郭长宝, 毛邦燕, 卢海峰, 陈群策, 徐学渊. 中尼铁路交通廊道现今构造应力场及其工程影响[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 167-179.
MENG Wen, GUO Changbao, MAO Bangyan, LU Haifeng, CHEN Qunce, XU Xueyuan. Tectonic Stress Field and Engineering Influence of China-Nepal Railway Corridor[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(01): 167-179.

图1 中尼铁路交通廊道构造背景图((a), 断裂构造据文献[28]及遥感影像解译综合汇编; 历史地震数据引自http://data.earthquake.cn)和喜马拉雅造山带中段剖面结构示意图((b), 据文献[18, 21]修编) (a)图中:F1.藏南滑脱拆离系断裂;F2.雅鲁藏布江断裂带;F3.申扎—定结断裂;F4.达吉岭—昂仁—仁布断裂;F5.札达—拉孜—邛多江断裂;F6.参达隐伏断裂;F7.打加错—佩枯错南北向断裂;F8. 喜马拉雅主中央逆冲断裂;F9. 喜马拉雅主边界逆冲断裂;F10. 喜马拉雅主前缘逆冲断裂。(b)图中:STDS. 藏南滑脱拆离系断裂;MCT. 喜马拉雅主中央逆冲断裂;MBT. 喜马拉雅主边界逆冲断裂;MFT. 喜马拉雅主前缘逆冲断裂;MHT. 喜马拉雅主逆冲断裂
Fig.1 Geological sketch of China-Nepal Railway Corridor ((a), modified after ref.[28] and http://data.earthquake.cn) and structure profile of the middle section of the Himalayan orogenic belt ((b), modified from refs.[18, 21])
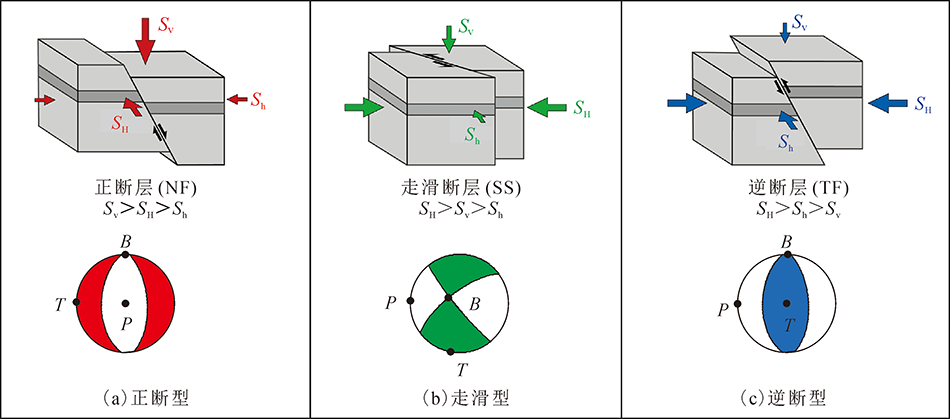
图2 断层活动类型及对应的应力结构和震源机制解示意图(据文献[30, 34]修改) SH. 最大水平主应力;Sh. 最小水平主应力;Sv. 垂向应力;P、T、B. 震源机制解中的P、T和B轴
Fig.2 Schematic diagrams of fault types and corresponding stress regimes and focal mechanism solutions (modified from refs. [30,34])
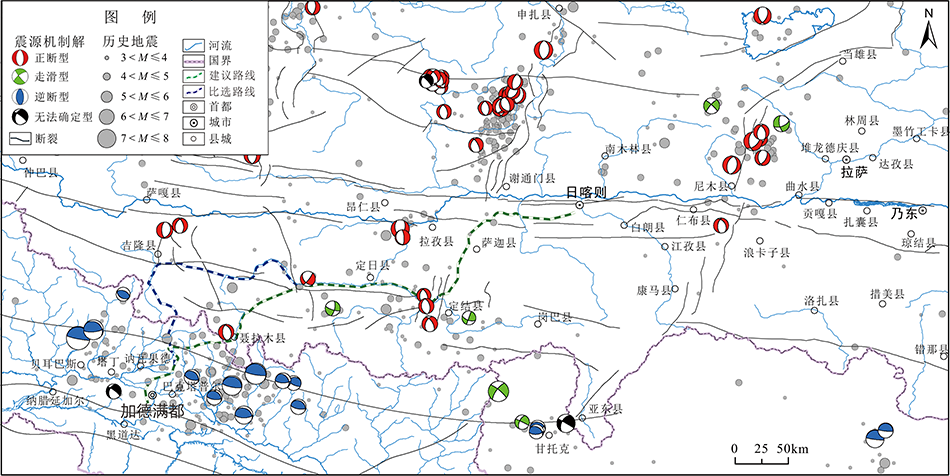
图3 研究区内Mw≥4.7级地震(1976―2019)震源机制解空间分布示意图(震源机制解数据取自GCMT; 断裂构造据文献[28]及遥感影像解译综合汇编)
Fig.3 Focal mechanism solutions from the GCMT catalogue (Mw≥4.7, 1976-2019) in the study area (modified after ref.[28])

图4 研究区最大水平主应力方向分布(断裂构造据文献[28]及遥感影像解译综合汇编)
Fig.4 Distribution of the maximum horizontal principal stress derived from the focal mechanism solutions and in-situ stress measurements(modified after ref.[28])
| 编号 | 测试 深度/m | SH / MPa | Sh/ MPa | SH 方位 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YBJ-p-1 | 13 | 10.4 | 8.4 | N70°E | [50] |
| YBJ-p-2 | 12 | 5.7 | 2.8 | N81°E | |
| YBJ-p-3 | 12 | 6.6 | 4.6 | N45°E | |
| YBJ-p-4 | 11 | 3.3 | 2.5 | N45°E | |
| PYL | 21.93 | 27.4 | 15.4 | N35°E | [51] |
| 25.18 | 24.9 | 14.7 | |||
| 27.13 | 24.7 | 14.6 | |||
| YBJ-h | 60 | 4.62 | 3.82 | [52] | |
| 85 | 4.30 | 3.82 | N55°E | ||
| 113 | 6.02 | 4.82 | |||
| 139 | 7.92 | 6.14 | |||
| 165 | 6.75 | 6.16 | N46°E | ||
| 209 | 10.67 | 8.39 | |||
| 222 | 9.77 | 8.10 | |||
| 243 | 11.06 | 9.20 | |||
| 261 | 12.88 | 10.80 | N65°E | ||
| 286 | 11.34 | 10.20 | N53°E | ||
| QS | 73.8 | 11.73 | 8.54 | [52] | |
| 115.8 | 14.36 | 9.03 | N47°W | ||
| 122.3 | 14.15 | 8.63 | N40°W | ||
| 134.8 | 12.07 | 7.65 | |||
| LS | 133 | 9.51 | 5.75 | [53] | |
| 170 | 13.01 | 6.80 | |||
| 241 | 18.12 | 10.90 | |||
| 283 | 17.53 | 10.31 | |||
| 296 | 13.59 | 9.08 | |||
| ND | 117.0 | 5.45 | 3.42 | [39] | |
| 131.2 | 6.37 | 4.20 | |||
| 146.5 | 9.25 | 6.00 | |||
| 178.3 | 5.22 | 3.76 | |||
| 190.8 | 6.83 | 4.48 | |||
| 216.8 | 11.85 | 6.94 | N12°E | ||
| 226.3 | 14.90 | 8.67 | |||
| 247.2 | 14.02 | 8.50 | N28°E | ||
| 273.3 | 12.97 | 7.83 | N14°W | ||
| 295.8 | 9.53 | 6.15 | N28°E | ||
| 370.0 | 23.40 | 14.52 | |||
| 396.3 | 30.30 | 16.69 | |||
| 463.7 | 28.84 | 16.25 |
表1 中尼铁路交通廊道邻区实测地应力结果
Table 1 Results of in-situ stress measurements along/around the China-Nepal Railway Corridor
| 编号 | 测试 深度/m | SH / MPa | Sh/ MPa | SH 方位 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YBJ-p-1 | 13 | 10.4 | 8.4 | N70°E | [50] |
| YBJ-p-2 | 12 | 5.7 | 2.8 | N81°E | |
| YBJ-p-3 | 12 | 6.6 | 4.6 | N45°E | |
| YBJ-p-4 | 11 | 3.3 | 2.5 | N45°E | |
| PYL | 21.93 | 27.4 | 15.4 | N35°E | [51] |
| 25.18 | 24.9 | 14.7 | |||
| 27.13 | 24.7 | 14.6 | |||
| YBJ-h | 60 | 4.62 | 3.82 | [52] | |
| 85 | 4.30 | 3.82 | N55°E | ||
| 113 | 6.02 | 4.82 | |||
| 139 | 7.92 | 6.14 | |||
| 165 | 6.75 | 6.16 | N46°E | ||
| 209 | 10.67 | 8.39 | |||
| 222 | 9.77 | 8.10 | |||
| 243 | 11.06 | 9.20 | |||
| 261 | 12.88 | 10.80 | N65°E | ||
| 286 | 11.34 | 10.20 | N53°E | ||
| QS | 73.8 | 11.73 | 8.54 | [52] | |
| 115.8 | 14.36 | 9.03 | N47°W | ||
| 122.3 | 14.15 | 8.63 | N40°W | ||
| 134.8 | 12.07 | 7.65 | |||
| LS | 133 | 9.51 | 5.75 | [53] | |
| 170 | 13.01 | 6.80 | |||
| 241 | 18.12 | 10.90 | |||
| 283 | 17.53 | 10.31 | |||
| 296 | 13.59 | 9.08 | |||
| ND | 117.0 | 5.45 | 3.42 | [39] | |
| 131.2 | 6.37 | 4.20 | |||
| 146.5 | 9.25 | 6.00 | |||
| 178.3 | 5.22 | 3.76 | |||
| 190.8 | 6.83 | 4.48 | |||
| 216.8 | 11.85 | 6.94 | N12°E | ||
| 226.3 | 14.90 | 8.67 | |||
| 247.2 | 14.02 | 8.50 | N28°E | ||
| 273.3 | 12.97 | 7.83 | N14°W | ||
| 295.8 | 9.53 | 6.15 | N28°E | ||
| 370.0 | 23.40 | 14.52 | |||
| 396.3 | 30.30 | 16.69 | |||
| 463.7 | 28.84 | 16.25 |
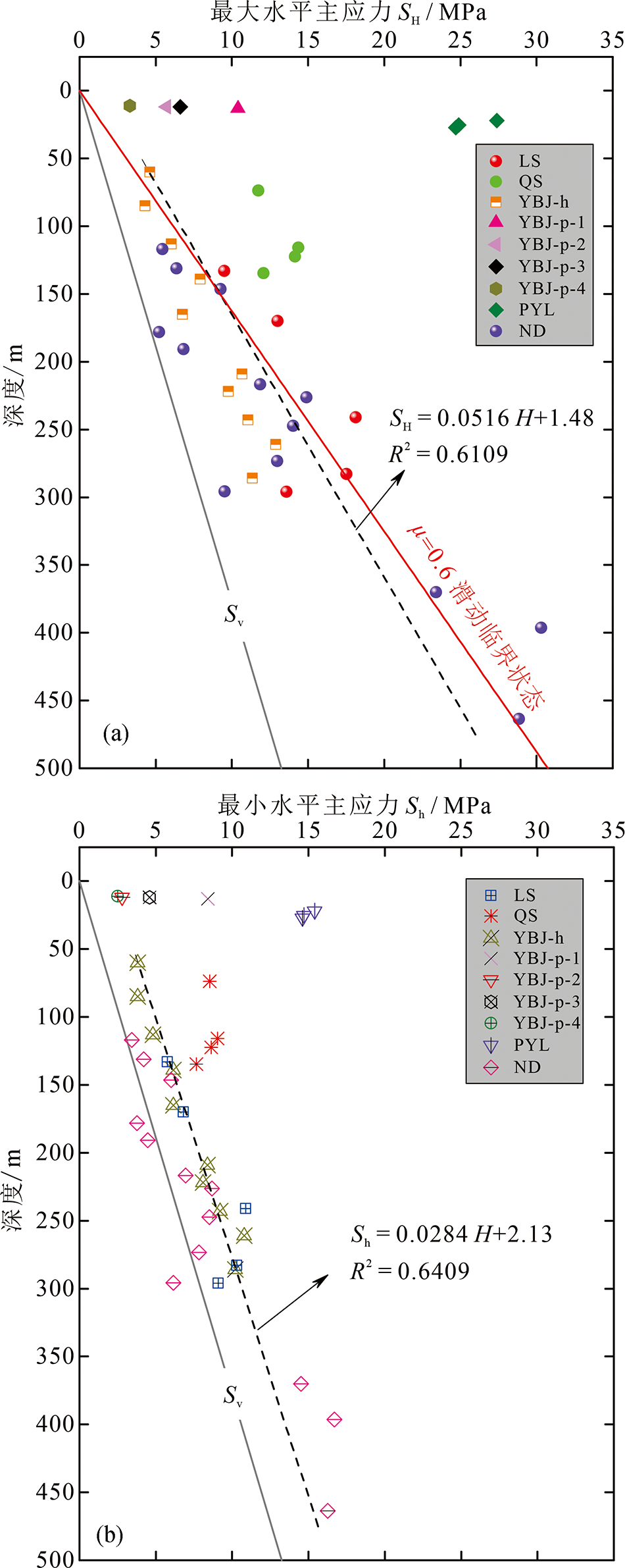
图5 中尼铁路交通廊道邻区实测水平主应力值随深度变化 (a)最大水平主应力; (b)最小水平主应力;应力测量点位置见图4;上覆岩层密度取2.65 g/cm3;应力数据据文献[39,50-53]
Fig.5 Stress magnitude plots along/around the China-Nepal Railway Corridor
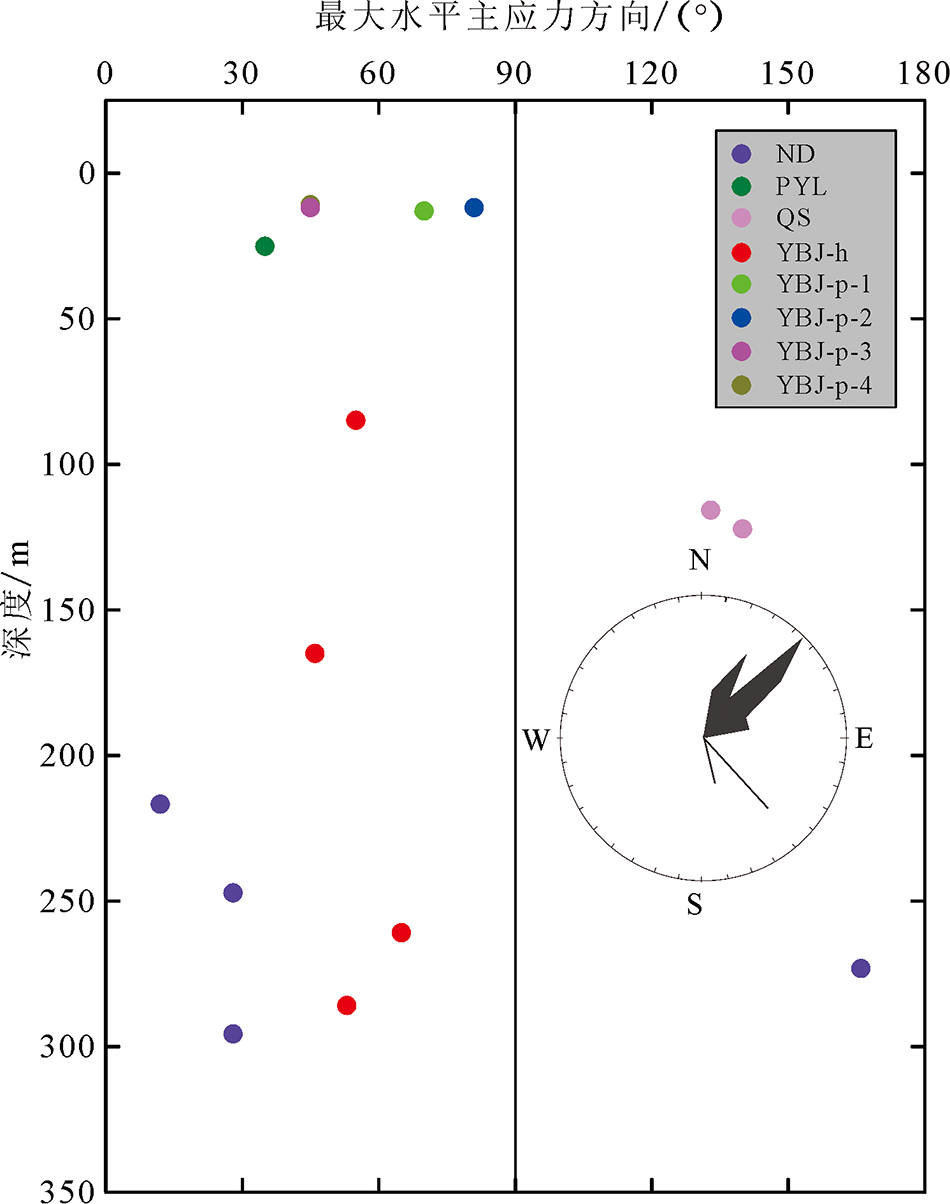
图6 中尼铁路交通廊道邻区实测最大水平主应力方向随深度变化
Fig.6 Variation in the orientations of the maximum horizontal stresses with depth along/around the China-Nepa Railway Corridor
| Russenes判别法[ | Hoek判别法[ | 综合判别法[ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 结果 | 结果 | 结果 | ||||||
| <0.20 | 无岩爆 | 0.34 | 少量片帮 | <0.30 | 无岩爆 | |||
| 0.20(含)~0.30 | 弱岩爆 | 0.42 | 严重片帮 | 0.30(含)~0.50 | 弱岩爆 | |||
| 0.30(含)~0.55 | 中岩爆 | 0.56 | 需重型支护 | 0.50(含)~0.70(含) | 中等岩爆 | |||
| ≥0.55 | 强岩爆 | 0.70 | 有严重岩爆 | >0.70 | 强烈岩爆 | |||
表2 主要岩爆判别法
Table 2 Major discriminating methods of rockbrust
| Russenes判别法[ | Hoek判别法[ | 综合判别法[ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 结果 | 结果 | 结果 | ||||||
| <0.20 | 无岩爆 | 0.34 | 少量片帮 | <0.30 | 无岩爆 | |||
| 0.20(含)~0.30 | 弱岩爆 | 0.42 | 严重片帮 | 0.30(含)~0.50 | 弱岩爆 | |||
| 0.30(含)~0.55 | 中岩爆 | 0.56 | 需重型支护 | 0.50(含)~0.70(含) | 中等岩爆 | |||
| ≥0.55 | 强岩爆 | 0.70 | 有严重岩爆 | >0.70 | 强烈岩爆 | |||
| 分段编号 | 分段 | 最大主应力方向 |
|---|---|---|
| A | 日喀则―萨迦 | NS |
| B | 萨迦―定结 | N4°W |
| C | 定结―吉隆 | N1°W |
| D | 聂拉木县段 | N5°W |
| E | 吉隆―讷瓦果德段 | N8°E |
| F | 加德满都段 | N12°E |
表3 中尼铁路交通廊道分段及主应力方向
Table 3 Sections and corresponding orientations of the maximum principal stress of the China-Nepal Railway Corridor
| 分段编号 | 分段 | 最大主应力方向 |
|---|---|---|
| A | 日喀则―萨迦 | NS |
| B | 萨迦―定结 | N4°W |
| C | 定结―吉隆 | N1°W |
| D | 聂拉木县段 | N5°W |
| E | 吉隆―讷瓦果德段 | N8°E |
| F | 加德满都段 | N12°E |

图8 中尼铁路沿线最大水平主应力分布及铁路分段情况
Fig.8 Maximum horizontal principal stress along the China-Nepal Railway Corridor and railway segmentations based on the stress characteristics
| 铁路 区段 | SH方位 | 铁路 轴向 | SH与铁路轴向 法线夹角/(°) | σn/MPa | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rc=60 MPa | 岩爆预判 | Rc=100 MPa | 岩爆预判 | ||||||
| A | NS | EW | 0 | 27.28 | 68.59 | 1.14 | 强烈 | 0.69 | 中等 |
| B | N4°W | N30°E | 56 | 19.75 | 46.01 | 0.77 | 强烈 | 0.46 | 轻微 |
| C | N1°W | N85°W | 6 | 27.16 | 68.23 | 1.14 | 强烈 | 0.68 | 中等 |
| D | N5°W | N40°W | 25 | 25.32 | 62.72 | 1.05 | 强烈 | 0.63 | 中等 |
| E | N8°E | N10°W | 72 | 17.38 | 38.88 | 0.65 | 中等 | 0.39 | 轻微 |
| F | N12°E | N30°E | 72 | 17.38 | 38.88 | 0.65 | 中等 | 0.39 | 轻微 |
表4 埋深500 m围岩岩爆分析结果
Table 4 Results of wallrock burst at 500 m burial depth
| 铁路 区段 | SH方位 | 铁路 轴向 | SH与铁路轴向 法线夹角/(°) | σn/MPa | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rc=60 MPa | 岩爆预判 | Rc=100 MPa | 岩爆预判 | ||||||
| A | NS | EW | 0 | 27.28 | 68.59 | 1.14 | 强烈 | 0.69 | 中等 |
| B | N4°W | N30°E | 56 | 19.75 | 46.01 | 0.77 | 强烈 | 0.46 | 轻微 |
| C | N1°W | N85°W | 6 | 27.16 | 68.23 | 1.14 | 强烈 | 0.68 | 中等 |
| D | N5°W | N40°W | 25 | 25.32 | 62.72 | 1.05 | 强烈 | 0.63 | 中等 |
| E | N8°E | N10°W | 72 | 17.38 | 38.88 | 0.65 | 中等 | 0.39 | 轻微 |
| F | N12°E | N30°E | 72 | 17.38 | 38.88 | 0.65 | 中等 | 0.39 | 轻微 |
| 铁路 区段 | SH方位 | 铁路轴向 | SH与铁路轴向 法线夹角/(°) | σn/MPa | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rc=60 MPa | 岩爆预判 | Rc=100 MPa | 岩爆预判 | ||||||
| A | NS | EW | 0 | 53.08 | 132.74 | 2.21 | 强烈 | 1.33 | 强烈 |
| B | N4°W | N30°E | 56 | 37.58 | 86.24 | 1.44 | 强烈 | 0.86 | 强烈 |
| C | N1°W | N85°W | 6 | 52.83 | 132.00 | 2.20 | 强烈 | 1.32 | 强烈 |
| D | N5°W | N40°W | 25 | 49.05 | 120.66 | 2.01 | 强烈 | 1.21 | 强烈 |
| E | N8°E | N10°W | 72 | 32.68 | 71.55 | 1.19 | 强烈 | 0.72 | 强烈 |
| F | N12°E | N30°E | 72 | 32.68 | 71.55 | 1.19 | 强烈 | 0.72 | 强烈 |
表5 埋深1 000 m围岩岩爆分析结果
Table 5 Results of wallrock burst at 1,000 m burial depth
| 铁路 区段 | SH方位 | 铁路轴向 | SH与铁路轴向 法线夹角/(°) | σn/MPa | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rc=60 MPa | 岩爆预判 | Rc=100 MPa | 岩爆预判 | ||||||
| A | NS | EW | 0 | 53.08 | 132.74 | 2.21 | 强烈 | 1.33 | 强烈 |
| B | N4°W | N30°E | 56 | 37.58 | 86.24 | 1.44 | 强烈 | 0.86 | 强烈 |
| C | N1°W | N85°W | 6 | 52.83 | 132.00 | 2.20 | 强烈 | 1.32 | 强烈 |
| D | N5°W | N40°W | 25 | 49.05 | 120.66 | 2.01 | 强烈 | 1.21 | 强烈 |
| E | N8°E | N10°W | 72 | 32.68 | 71.55 | 1.19 | 强烈 | 0.72 | 强烈 |
| F | N12°E | N30°E | 72 | 32.68 | 71.55 | 1.19 | 强烈 | 0.72 | 强烈 |
| [1] | 孙先锋. 中尼铁路沿线活动断裂对地质选线的影响浅析[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2019,63(3):44-48. |
| [2] | 姚志勇. 中尼铁路夏木德至加德满都段主要工程地质问题及地质比选[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2017,61(9):21-25. |
| [3] | 李四光. 地壳构造与地壳运动[J]. 中国科学, 1973,3(4):400-429. |
| [4] | 黄相宁, 康仲远, 张超, 等. 地应力变化与地震预报[J]. 中国地质科学院地质力学研究所所刊, 1982(3):154-169. |
| [5] | 孙叶, 谭成轩, 杨贵生, 等. 中国区域地壳稳定性定量化评价与分区[J]. 地质力学学报, 1997,3(3):42-52. |
| [6] | 陈群策, 丰成君, 孟文, 等. 5·12汶川地震后龙门山断裂带东北段现今地应力测量结果分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012,55(12):3923-3932. |
| [7] | 张鹏, 曲亚明, 郭长宝, 等. 西藏林芝地应力测量监测与尼泊尔Ms8.1级强震远场响应分析[J]. 现代地质, 2017,31(5):900-910. |
| [8] | KLEE G, RUMMEL F, WILLIAMS A. Hydraulic fracturing stress measurements in Hong Kong[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 1999,36 : 731-741. |
| [9] | 白世伟, 李光煜. 二滩水电站坝区岩体应力场研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 1982,1(1):45-56. |
| [10] | 孟文, 陈群策, 杜建军, 等. 新加坡地应力测量[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012,55(8):2611-2619. |
| [11] | 吉锋, 郑罗斌, 周春宏. 四川锦屏二级电站高水头超深埋隧洞围岩质量分级快速评价方法[J]. 现代地质, 2015,29(2):428-433. |
| [12] | 丰成君, 张鹏, 戚帮申, 等. 郯庐断裂带附近地壳浅层现今构造应力场[J]. 现代地质, 2017,31(1):46-70. |
| [13] | 刘卓岩, 王成虎, 徐鑫, 等. 基于地应力实测数据分析郯庐断裂带中段滑动趋势[J]. 现代地质, 2017,31(4):869-876. |
| [14] | 张倬元, 王士天, 王兰生. 工程地质分析原理[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016: 45-46. |
| [15] | 杨树新, 姚瑞, 崔效锋, 等. 中国大陆与各活动地块、南北地震带实测应力特征分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012,55(12):4207-4217. |
| [16] | 姚瑞, 杨树新, 谢富仁, 等. 青藏高原及周缘地壳浅层构造应力场量值特征分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017,60(6):2147-2158. |
| [17] | 郭长宝, 张永双, 蒋良文, 等. 川藏铁路沿线及邻区环境工程地质问题概论[J]. 现代地质, 2017,31(5):877-889. |
| [18] | 潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 等. 中国大地构造单元划分[J]. 中国地质, 2009,36(1):1-28. |
| [19] | CATTIN R, AVOUAC J P. Modeling mountain building and the seismic cycle in the Himalaya of Nepal[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2000,105:13389-13407. |
| [20] | BETTINELLI P, AVOUAC J P, FLOUZAT M, et al. Plate motion of India and interseismic strain in the Nepal Himalaya from GPS and DORIS measurements[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2006,80:567-589. |
| [21] | 吴中海, 赵根模, 刘杰. 2015年尼泊尔Ms8.1地震构造成因及对青藏高原及对邻区未来强震趋势的影响[J]. 地质学报, 2016,90(6):1062-1085. |
| [22] | 李水平. 喜马拉雅造山带现今地壳变形: GPS观测与模拟解释[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉), 2019. |
| [23] | 尹安. 喜马拉雅造山带新生代构造演化:沿走向变化的构造几何形态、剥露历史和前陆沉积的约束[J]. 地学前缘, 2006,13(5):416-515. |
| [24] | 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 等. 印度-亚洲碰撞大地构造[J]. 地质学报, 2011,85(1):1-33. |
| [25] | BILLA R, LARSON K, FREYMUELLER J, et al. GPS measurements of present-day convergence across the Nepal Himalaya[J]. Nature, 1997,386:61-64 |
| [26] | ADER T, AVOUAC J P, LIU-ZENG J, et al. Convergence rate across the Nepal Himalaya and interseismic coupling on the Main Himalayan Thrust: Implications for seismic hazard[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2012,117:B04403. doi: 10.1029/2011JB009071. |
| [27] | KUMAR S, WESNOUSKY S G, JAYANGONDAPERUMAL R, et al. Paleoseismological evidence of surface faulting along the northeastern Himalayan front, India: Timing, size, and spatial extent of great earthquakes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: (Solid Earth), 2010,115:B12422. |
| [28] | 邓起东, 张培震, 冉勇康, 等. 中国活动构造基本特征[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2002,32(12):1020-1030. |
| [29] | ZANG A, STEPHANSSON O. Stress Field of the Earth’s Crust[M]. London: Springer, 2010. |
| [30] | ZOBACK M D. Reservoir Geomechanics[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007. |
| [31] | 王成虎. 地应力主要测试和估算方法回顾与展望[J]. 地质论评, 2014,60(5):971-995. |
| [32] | ZOBACK M L, ZOBACK M D. State of stress in the conterminous United States[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1980,85:6113-6156. |
| [33] | ZOBACK M L, ZOBACK M D, ADAMS J, et al. Global patterns of tectonic stress, review article[J]. Nature, 1989,341:291-298. doi: 10.1038/341291a0. |
| [34] | ANDERSON E M. The Dynamics of Faulting and Dyke Formation, with Application to Britain[M]. Edinburgh: Oliver and Boyd, 1951. |
| [35] | HAIMSON B C, CORNET F H. ISRM Suggested Methods for rock stress estimation-Part 3:Hydraulic fracturing (HF) and/or hydraulic testing of pre-existing fractures (HTPF)[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2003,40:1011-1020. |
| [36] | SJÖBERG J, CHRISTIANSSON R, HUDSON J A. ISRM Suggested Methods for rock stress estimation-Part 2: Overcoring methods[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2003,40(7/8) : 999-1010. |
| [37] | CHANG C, LEE J B, KANG T S. Interaction between regional stress state and faults: Complementary analysis of borehole in situ stress and earthquake focal mechanism in southeastern Korea[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010,485:164-177. |
| [38] | 郭啟良, 赵仕广, 丁立丰, 等. 地下硐室围岩应力状态及相关参数测量结果的分析与评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007,26(增):3361-3366. |
| [39] | 孟文, 郭长宝, 张重远, 等. 青藏高原拉萨块体地应力测量及其意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017,60(6):2159-2171. |
| [40] | HAIMSON B C. Crustal stress in the Michigan basin[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1978,83(12):5857-5863. |
| [41] | 陈群策, 孙东生, 崔建军, 等. 雪峰山深孔水压致裂地应力测量及其意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019,25(5):853-865. |
| [42] | 吴满路, 张重远. 新型压磁应力解除测量系统及其测试分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016,35(增):3119-3126. |
| [43] | 张重远, 吴满路, 陈群策, 等. 地应力测量方法综述[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2012,31(3):305-310. |
| [44] | 刘静, 纪晨, 张金玉, 等. 2015年4月25日尼泊尔Mw7.8级地震的孕震构造背景和特征[J]. 科学通报, 2015,60(27):2640-2655. |
| [45] | 王卫民, 郝金来, 何建坤, 等. 2015年4月25日尼泊尔Mw7.9级地震震源过程[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2015,45(9):1421-1426. |
| [46] | 谢富仁, 崔效锋, 赵建涛, 等. 中国大陆及邻区现代构造应力场分区[J]. 地球物理学报, 2004,47(4):654-662. |
| [47] | 吴中海, 叶培盛, 吴珍汉. 2008年10月6日西藏当雄Ms6.6级强震的地震烈度控震构造和发震机理[J]. 地质通报, 2009,28(6):713-725. |
| [48] | 景锋, 盛谦, 张勇慧, 等. 中国大陆浅层地壳实测地应力分布规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007,26(10):2056-2062. |
| [49] | 李方全, 祁英男. 地壳应力随深度的变化规律[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 1988,7(4):301-309. |
| [50] | 廖椿庭, 吴满路, 张春山, 等. 青藏高原昆仑山和羊八井现今地应力测量及其工程意义[J]. 地球学报, 2002,23(4):353-357. |
| [51] | 王喜华, 赵志明, 尹建勋, 等. 雅鲁藏布江峡谷段盆因拉隧道岩爆预测[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2013,35(2):115-119. |
| [52] | WU Z H, CHEN Q C, BAROSH P J, et al. Stress rise precursor to earthquakes in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Natural Science, 2013,5(8):46-55. |
| [53] | 曹忠权, 谢平, 金花, 等. 雅鲁藏布江断裂带附近地应力场的变化特征[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2003,18(1):167-172. |
| [54] |
MOLNAR P, TAPPONNIER P. Cenozoic tectonics of Asia: effects of a continental collision[J]. Science, 1975,189:419-426.
DOI URL PMID |
| [55] | MOLNAR P, CAENT L. Fault plane solutions of earthquakes and active tectonics of the Tibetan Plateau and its margins[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1989,99(1):123-154. |
| [56] | 张培震, 沈正康, 王敏. 青藏高原及周边现今构造变形的运动学[J]. 地震地质, 2004,26(3):367-377. |
| [57] | GAN W J, ZHANG P Z, SHEN Z K, et al. Present-day crustal motion within the Tibetan Plateau inferred from GPS measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2007,112:B08416.doi: 10.1029/2005JB004120. |
| [58] | 张健, 石耀霖. 中国西部地区重力位能与板内变形动力[J]. 中国科学院研究生院学报, 2001,18(1):43-50. |
| [59] | 张东宁, 许忠淮. 青藏高原南部上地壳正断层地震活动的一种可能解释[J]. 地震学报, 1995,17(2):188-195. |
| [60] | MENG W, CHEN Q C, ZHAO Z, et al. Characteristics and implications of the stress state in the Longmen Shan fault zone, eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonophysics, 2015,656:1-19. |
| [61] | RATSCHBACHER L, FRISCH W, LIU G, et al. Distributed deformation in southern and western Tibet during and after the India-Asia Collision[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth), 1994,99(10):19917-19945. |
| [62] | TAPPONNIER P, MERCIER J L, ARMIJO R, et al. Field evidence for active normal faulting in Tibet[J]. Nature, 1981,294:410-414. |
| [63] | TAPPONNIER P, ZHIQIN X, ROGER F, et al. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet plateau[J]. Science, 2001,294:1671-1677. |
| [64] | 张永双, 胡道功, 吴中海, 等. 滇藏铁路沿线地壳稳定性及重大工程地质问题[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009: 196-198. |
| [65] | CHEN Q, FREYMUELLER J T, YANG Z, et al. Spatially variable extension in southern Tibet based on GPS measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth), 2004,109:1-20. |
| [66] | 徐则民, 黄润秋, 范柱国, 等. 长大隧道岩爆灾害研究进展[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2004,13(2):16-24. |
| [67] | 谭以安. 岩爆形成机理研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1989(1):34-38. |
| [68] | 张咸恭, 王思敬, 张倬元, 等. 中国工程地质学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000. |
| [69] | 刘元坤, 罗超文, 尹健民. 西部地应力测量与岩爆分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2003,24(增):94-95. |
| [70] | 王元汉, 李卧东, 李启光, 等. 岩爆预测的模糊数学综合评判方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 1998,17(5):493-501. |
| [71] | HOEK E, BROWN E T. Underground Excavation in Rock[M]. London: Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 1980. |
| [72] | 侯发亮, 刘小明, 王敏强. 岩爆成因再分析及烈度划分探讨[M] //中国岩石力学与工程学会岩石动力学专业委员会.第三届全国岩石动力学学术会议论文集. 武汉: 武汉测绘科技大学出版社, 1992: 463-472. |
| [73] | 谢富仁, 崔效锋. 中国及邻区现代构造应力场图 [M]. 北京: 中国地图出版社, 2015. |
| [1] | 李俊磊, 张绪教, 王一凡, 张向格, 王重歌, 袁晓宁, 刘心兰, 王凯雅, 饶昊舒, 刘江, 秦渊. 青海省化隆县地学研学旅行的路线规划与思考[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1411-1422. |
| [2] | 田社权. 遥感综合地质解译方法在中尼铁路勘察中的应用研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 1054-1064. |
| [3] | 刘心兰, 张绪教, 李俊磊, 王一凡, 张向格, 袁晓宁, 王凯雅, 王重歌, 刘江, 侯恩刚. 青海化隆县独特的峡谷丹山地貌景观及其科学价值[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(01): 233-244. |
| [4] | 胡梦珺, 吉天琪, 郑登友, 庄静, 孙文丽, 许澳康. 9.4 ka以来青藏高原东北部风成沉积物色度参数变化特征及其环境演变[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 439-448. |
| [5] | 方念乔. 关于“海陆对比”研究的若干实践和思考[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 1-13. |
| [6] | 陈静, 李大鹏, 康欢, 耿建珍, 张菁菁. 滇西点苍山变质地体三叠纪至侏罗纪沉积岩碎屑锆石源区信息及构造指示[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 883-913. |
| [7] | 闫怡秋, 杨志华, 张绪教, 孟少伟, 郭长宝, 吴瑞安, 张怡颖. 基于加权证据权模型的青藏高原东部巴塘断裂带滑坡易发性评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 26-37. |
| [8] | 李雪, 郭长宝, 杨志华, 廖维, 吴瑞安, 金继军, 何元宵. 金沙江断裂带雄巴巨型古滑坡发育特征与形成机理[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 47-55. |
| [9] | 徐正宣, 孟文, 郭长宝, 张鹏, 张广泽, 孙明乾, 陈群策, 陈宇. 川西折多山某深埋隧道地应力测量及其应用研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 114-125. |
| [10] | 赵远方, 公王斌, 江万, 陈龙耀, 仇度伟. 藏南嘉黎断裂古乡—通麦段多期活动特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 220-233. |
| [11] | 夏蒙蒙, 高万里, 胡道功, 张耀玲, 徐久晟, 贾丽云, 王超群. 青藏高原北部巴颜喀拉山群火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(05): 957-969. |
| [12] | 张舜尧, 杨帆, 张富贵, 施泽明, 杨志斌, 周亚龙, 王惠艳. 青藏高原冻土区湿地甲烷排放及同位素特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 1089-1096. |
| [13] | 李郎平, 兰恒星, 郭长宝, 张永双, 李全文, 伍宇明. 基于改进频率比法的川藏铁路沿线及邻区地质灾害易发性分区评价[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(05): 911-929. |
| [14] | 宿方睿, 郭长宝, 张学科, 申维, 刘筱怡, 任三绍. 基于面向对象分类法的川藏铁路沿线大型滑坡遥感解译[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(05): 930-942. |
| [15] | 郭长宝, 周家作, 刘筱怡, 任三绍, 吴瑞安. 青藏高原东部冻融作用下花岗岩力学性质弱化机理研究[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(05): 943-955. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||