



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (04): 883-913.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.04.01
陈静1( ), 李大鹏1(
), 李大鹏1( ), 康欢2, 耿建珍3, 张菁菁1
), 康欢2, 耿建珍3, 张菁菁1
收稿日期:2020-12-25
修回日期:2021-04-20
出版日期:2021-08-10
发布日期:2021-09-08
通讯作者:
李大鹏
作者简介:李大鹏,男,教授,博士生导师,1983年出生,地球化学专业,主要从事岩石地球化学研究。Email: dpli@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
CHEN Jing1( ), LI Dapeng1(
), LI Dapeng1( ), KANG Huan2, GENG Jianzhen3, ZHANG Jingjing1
), KANG Huan2, GENG Jianzhen3, ZHANG Jingjing1
Received:2020-12-25
Revised:2021-04-20
Online:2021-08-10
Published:2021-09-08
Contact:
LI Dapeng
摘要:
前人通过滇西三江带内岩浆记录精细刻画了古特提斯洋分支洋——哀牢山洋的形成及演化历史,然而区域沉积记录是如何响应哀牢山洋俯冲及闭合过程的,目前仍未得到深入研究。我们通过对哀牢山构造带北段点苍山变质杂岩内三叠纪至侏罗纪3件沉积岩样品中255颗碎屑锆石进行U-Pb定年、微量元素及Hf同位素分析,结合区域已有研究,恢复哀牢山洋末期演化的区域沉积响应。结果表明,变质砂岩DC1801、片岩DC1703和碳酸盐岩DC1702中最年轻岩浆锆石群加权平均年龄分别为~180 Ma、~247 Ma和~254 Ma,结合其接触关系以及区域地层对比,约束其最大沉积年龄分别为侏罗纪早期(DC1801)和三叠纪早期(DC1702和DC1703)。不同时期碎屑沉积岩物源分析表明三叠纪碎屑沉积岩(DC1703)主要源自哀牢山构造带内部近源的多期岩浆物质(~0.8 Ga、~0.45 Ga和~0.25 Ga)、冈瓦纳裂解前印度大陆内部多期再循环的格林威尔晚期(~0.95 Ga)和泛非期(~0.6 Ga)岩浆物质贡献。侏罗纪碎屑沉积岩(DC1801)物质主要源自思茅地块内部印支期岩浆活动,而~0.45 Ga、~0.8 Ga和~0.95 Ga等时期的碎屑物质贡献比例明显降低。同一沉积盆地同时代碳酸盐岩与陆源碎屑岩中碎屑锆石结构大体相似,但碳酸盐岩中代表多期循环的远源物质的年龄所占比例却降低。点苍山碎屑沉积岩锆石Hf同位素组成随时间变化证实了哀牢山洋闭合时间为~247 Ma,而在点苍山变质地体南段发育的海相碳酸盐岩与陆源碎屑岩(片岩)的沉积组合记录了哀牢山洋末期演化至闭合过程。碎屑锆石Eu/Eu*异常揭示了区域地壳自~247 Ma哀牢山洋闭合至~235 Ma的加厚过程,三叠纪至侏罗纪碎屑沉积物源的转化可能与哀牢山洋闭合引发的沉积区抬升有关。
中图分类号:
陈静, 李大鹏, 康欢, 耿建珍, 张菁菁. 滇西点苍山变质地体三叠纪至侏罗纪沉积岩碎屑锆石源区信息及构造指示[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 883-913.
CHEN Jing, LI Dapeng, KANG Huan, GENG Jianzhen, ZHANG Jingjing. Provenances and Tectonic Significance of Detrital Zircons from the Triassic to Jurassic Sedimentary Rocks in the Diancangshan Metamorphic Massif, Western Yunnan Province[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(04): 883-913.
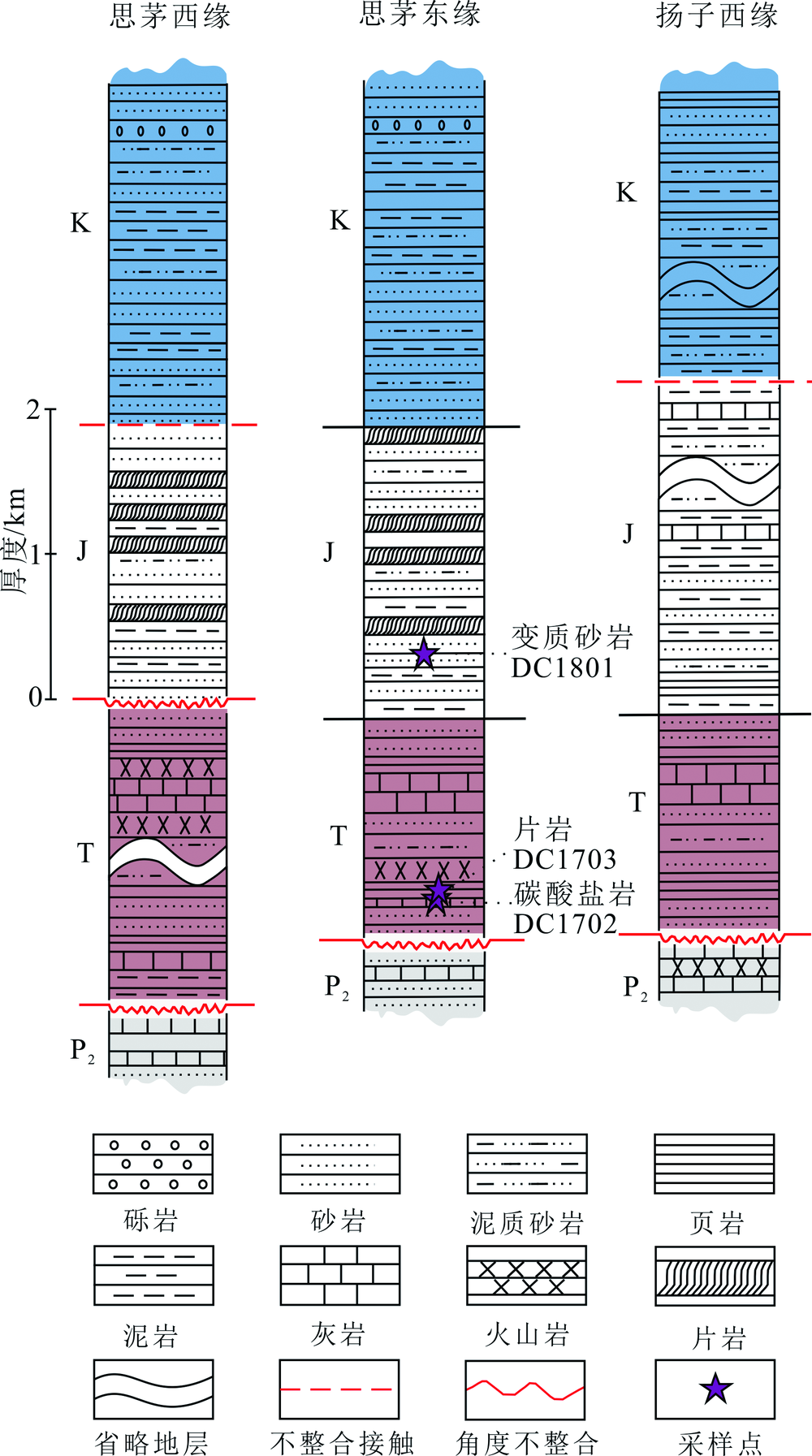
图2 思茅地块东缘、西缘与扬子地块西缘岩性地层对比图
Fig.2 Stratigraphic comparison between the eastern and wes-tern margins of the Simao block and the western margin of the Yangtze block
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 碳酸盐岩DC1702 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-01 | 133 | 125 | 188 | 0.67 | 0.068 85 | 0.001 50 | 1.48 | 0.155 70 | 0.001 71 | 894 | 44 | 920 | 13 | 933 | 10 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-02 | 31 | 95 | 187 | 0.51 | 0.056 30 | 0.001 98 | 0.31 | 0.040 19 | 0.000 44 | 465 | 78 | 274 | 8 | 254 | 3 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-03 | 20 | 326 | 396 | 0.82 | 0.049 98 | 0.002 75 | 0.06 | 0.008 59 | 0.000 10 | 195 | 128 | 58 | 3 | 55 | 1 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-04 | 72 | 65 | 93 | 0.70 | 0.077 01 | 0.002 03 | 1.68 | 0.158 00 | 0.001 76 | 1 121 | 20 | 1 000 | 17 | 946 | 10 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-05 | 436 | 993 | 1 871 | 0.53 | 0.097 28 | 0.006 87 | 0.58 | 0.041 37 | 0.000 50 | 1 573 | 132 | 462 | 31 | 261 | 3 | 177 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-06 | 724 | 2 916 | 1 386 | 2.10 | 0.060 49 | 0.001 30 | 0.34 | 0.040 67 | 0.000 44 | 620 | 47 | 296 | 6 | 257 | 3 | 115 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-07 | 288 | 274 | 598 | 0.46 | 0.068 89 | 0.000 96 | 1.17 | 0.122 01 | 0.002 27 | 894 | 29 | 784 | 14 | 742 | 13 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-08 | 1 030 | 4 307 | 1 455 | 2.96 | 0.083 57 | 0.001 80 | 0.37 | 0.032 42 | 0.000 32 | 1 283 | 42 | 322 | 6 | 206 | 2 | 157 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-09 | 157 | 621 | 297 | 2.09 | 0.053 61 | 0.001 56 | 0.31 | 0.042 43 | 0.000 45 | 354 | 67 | 277 | 7 | 268 | 3 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-10 | 92 | 287 | 554 | 0.52 | 0.056 29 | 0.001 36 | 0.32 | 0.041 54 | 0.000 42 | 465 | 54 | 284 | 6 | 262 | 3 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-11 | 39 | 147 | 176 | 0.84 | 0.053 06 | 0.002 12 | 0.29 | 0.040 39 | 0.000 48 | 332 | 91 | 261 | 9 | 255 | 3 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-12 | 440 | 399 | 763 | 0.52 | 0.069 36 | 0.000 91 | 1.51 | 0.157 66 | 0.001 86 | 909 | 58 | 935 | 11 | 944 | 10 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-13 | 159 | 76 | 149 | 0.51 | 0.108 65 | 0.001 47 | 4.35 | 0.290 16 | 0.002 79 | 1 777 | 29 | 1 702 | 12 | 1 642 | 14 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-14 | 325 | 1 254 | 1 051 | 1.19 | 0.060 03 | 0.005 07 | 0.31 | 0.039 44 | 0.000 52 | 606 | 184 | 270 | 6 | 249 | 3 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-15 | 272 | 143 | 283 | 0.51 | 0.105 96 | 0.001 43 | 3.53 | 0.241 56 | 0.004 35 | 1 731 | 30 | 1 534 | 17 | 1 395 | 23 | 124 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-16 | 53 | 10 | 290 | 0.03 | 0.068 57 | 0.001 19 | 1.21 | 0.127 62 | 0.001 62 | 887 | 35 | 807 | 10 | 774 | 9 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-17 | 238 | 80 | 101 | 0.79 | 0.161 75 | 0.002 00 | 10.82 | 0.485 53 | 0.005 18 | 2 474 | 21 | 2 508 | 14 | 2 551 | 22 | 97 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-18 | 224 | 649 | 1 437 | 0.45 | 0.053 47 | 0.000 90 | 0.30 | 0.040 83 | 0.000 41 | 350 | 39 | 267 | 4 | 258 | 3 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-19 | 397 | 341 | 951 | 0.36 | 0.067 63 | 0.000 82 | 1.35 | 0.144 48 | 0.001 70 | 857 | 26 | 867 | 10 | 870 | 10 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-20 | 177 | 255 | 2 048 | 0.12 | 0.057 53 | 0.000 88 | 0.33 | 0.041 43 | 0.000 76 | 522 | 35 | 289 | 6 | 262 | 5 | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-21 | 172 | 701 | 819 | 0.86 | 0.054 04 | 0.001 13 | 0.28 | 0.038 21 | 0.000 51 | 372 | 48 | 253 | 5 | 242 | 3 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-22 | 237 | 867 | 1 022 | 0.85 | 0.051 51 | 0.000 92 | 0.29 | 0.041 54 | 0.000 43 | 265 | 43 | 262 | 4 | 262 | 3 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-23 | 11 | 33 | 66 | 0.49 | 0.060 85 | 0.003 31 | 0.35 | 0.042 19 | 0.000 67 | 635 | 112 | 303 | 13 | 266 | 4 | 114 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-24 | 80 | 299 | 286 | 1.04 | 0.052 79 | 0.001 92 | 0.30 | 0.041 37 | 0.000 43 | 320 | 116 | 267 | 9 | 261 | 3 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-25 | 86 | 33 | 288 | 0.12 | 0.106 37 | 0.001 43 | 2.10 | 0.143 02 | 0.001 92 | 1 739 | 25 | 1 149 | 13 | 862 | 11 | 133 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-26 | 184 | 590 | 952 | 0.62 | 0.056 99 | 0.000 96 | 0.32 | 0.041 20 | 0.000 54 | 500 | 37 | 284 | 5 | 260 | 3 | 109 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-27 | 47 | 188 | 147 | 1.28 | 0.055 92 | 0.002 23 | 0.30 | 0.039 39 | 0.000 48 | 450 | 117 | 270 | 10 | 249 | 3 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-28 | 344 | 283 | 1 026 | 0.28 | 0.067 37 | 0.000 84 | 1.19 | 0.127 86 | 0.001 66 | 850 | 21 | 798 | 10 | 776 | 9 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-29 | 274 | 210 | 962 | 0.22 | 0.066 38 | 0.000 87 | 1.19 | 0.128 75 | 0.002 87 | 818 | 32 | 794 | 15 | 781 | 16 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-31 | 300 | 166 | 2 267 | 0.07 | 0.059 98 | 0.000 96 | 0.70 | 0.084 56 | 0.000 85 | 611 | 34 | 540 | 6 | 523 | 5 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-32 | 452 | 1 688 | 2 665 | 0.63 | 0.065 40 | 0.001 29 | 0.31 | 0.034 28 | 0.000 34 | 787 | 41 | 277 | 5 | 217 | 2 | 127 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-33 | 60 | 174 | 450 | 0.39 | 0.051 46 | 0.001 41 | 0.30 | 0.041 56 | 0.000 42 | 261 | 63 | 265 | 6 | 262 | 3 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-34 | 34 | 197 | 195 | 1.01 | 0.075 81 | 0.003 54 | 0.26 | 0.024 52 | 0.000 32 | 1 100 | 93 | 234 | 9 | 156 | 2 | 150 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-35 | 433 | 401 | 451 | 0.89 | 0.078 64 | 0.001 87 | 1.64 | 0.148 38 | 0.001 63 | 1 165 | 46 | 986 | 11 | 892 | 9 | 111 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-36 | 268 | 345 | 352 | 0.98 | 0.065 66 | 0.001 95 | 1.18 | 0.127 42 | 0.001 15 | 794 | 63 | 790 | 10 | 773 | 7 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-37 | 121 | 416 | 688 | 0.61 | 0.050 38 | 0.001 63 | 0.30 | 0.042 00 | 0.000 43 | 213 | 44 | 265 | 5 | 265 | 3 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-38 | 383 | 111 | 498 | 0.22 | 0.151 18 | 0.004 79 | 7.31 | 0.340 40 | 0.004 65 | 2 361 | 54 | 2 150 | 17 | 1 889 | 22 | 125 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-41 | 694 | 2 777 | 1 379 | 2.01 | 0.053 18 | 0.001 83 | 0.31 | 0.041 58 | 0.000 42 | 345 | 78 | 277 | 4 | 263 | 3 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-42 | 259 | 310 | 441 | 0.70 | 0.063 66 | 0.002 09 | 1.15 | 0.128 36 | 0.001 30 | 731 | 70 | 779 | 10 | 778 | 7 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-43 | 268 | 998 | 1 249 | 0.80 | 0.049 20 | 0.001 42 | 0.29 | 0.041 48 | 0.000 36 | 167 | 73 | 257 | 4 | 262 | 2 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-44 | 323 | 358 | 350 | 1.02 | 0.073 34 | 0.001 95 | 1.39 | 0.135 50 | 0.002 47 | 1 033 | 54 | 885 | 11 | 819 | 14 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-45 | 19 | 516 | 2 245 | 0.23 | 0.047 72 | 0.002 21 | 0.02 | 0.003 72 | 0.000 06 | 87 | 104 | 25 | 1 | 24 | 1 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-46 | 589 | 2 390 | 1 429 | 1.67 | 0.049 32 | 0.001 12 | 0.29 | 0.042 37 | 0.000 45 | 161 | 54 | 260 | 4 | 268 | 3 | 97 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-47 | 108 | 414 | 546 | 0.76 | 0.057 19 | 0.003 62 | 0.28 | 0.036 25 | 0.000 44 | 498 | 139 | 251 | 8 | 230 | 3 | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-48 | 40 | 126 | 222 | 0.56 | 0.058 18 | 0.001 92 | 0.34 | 0.041 84 | 0.000 43 | 600 | 72 | 295 | 8 | 264 | 3 | 111 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-49 | 609 | 2 396 | 1 837 | 1.30 | 0.070 75 | 0.002 01 | 0.34 | 0.034 68 | 0.000 35 | 950 | 54 | 295 | 6 | 220 | 2 | 134 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-50 | 355 | 333 | 367 | 0.91 | 0.158 84 | 0.002 36 | 3.72 | 0.168 51 | 0.005 65 | 2 444 | 25 | 1 575 | 29 | 1 004 | 31 | 243 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-51 | 31 | 107 | 135 | 0.79 | 0.055 10 | 0.001 97 | 0.31 | 0.040 60 | 0.000 51 | 417 | 75 | 271 | 8 | 257 | 3 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-52 | 74 | 54 | 278 | 0.19 | 0.074 23 | 0.001 46 | 1.27 | 0.124 58 | 0.002 39 | 1 048 | 39 | 835 | 14 | 757 | 14 | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-53 | 109 | 404 | 228 | 1.77 | 0.094 44 | 0.003 88 | 0.51 | 0.038 90 | 0.000 43 | 1 517 | 77 | 416 | 14 | 246 | 3 | 169 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-54 | 79 | 293 | 337 | 0.87 | 0.051 77 | 0.001 44 | 0.30 | 0.042 06 | 0.000 44 | 276 | 65 | 266 | 6 | 266 | 3 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-55 | 96 | 310 | 454 | 0.68 | 0.072 84 | 0.002 11 | 0.36 | 0.035 97 | 0.000 38 | 1 009 | 92 | 313 | 8 | 228 | 2 | 138 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-56 | 213 | 355 | 2 081 | 0.17 | 0.057 28 | 0.001 53 | 0.33 | 0.042 08 | 0.000 74 | 502 | 59 | 287 | 6 | 266 | 5 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-57 | 78 | 229 | 204 | 1.12 | 0.072 89 | 0.004 11 | 0.50 | 0.047 97 | 0.000 60 | 1 011 | 115 | 409 | 27 | 302 | 4 | 135 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-58 | 215 | 715 | 1 282 | 0.56 | 0.052 94 | 0.001 17 | 0.28 | 0.038 63 | 0.000 28 | 328 | 50 | 252 | 5 | 244 | 2 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-59 | 227 | 396 | 697 | 0.57 | 0.132 98 | 0.008 75 | 0.89 | 0.044 50 | 0.000 87 | 2 139 | 116 | 645 | 38 | 281 | 5 | 230 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-60 | 508 | 828 | 2 262 | 0.37 | 0.068 73 | 0.000 81 | 1.13 | 0.118 62 | 0.001 31 | 900 | 25 | 767 | 9 | 723 | 8 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-61 | 34 | 140 | 129 | 1.09 | 0.056 40 | 0.003 09 | 0.28 | 0.036 48 | 0.000 50 | 478 | 120 | 253 | 12 | 231 | 3 | 109 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-62 | 219 | 189 | 542 | 0.35 | 0.072 36 | 0.001 33 | 1.23 | 0.123 05 | 0.000 98 | 996 | 33 | 814 | 10 | 748 | 6 | 109 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-63 | 725 | 737 | 1 841 | 0.40 | 0.071 15 | 0.000 77 | 1.48 | 0.150 41 | 0.001 56 | 961 | 22 | 921 | 8 | 903 | 9 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-64 | 299 | 1 160 | 748 | 1.55 | 0.054 12 | 0.001 11 | 0.32 | 0.042 60 | 0.000 49 | 376 | 46 | 280 | 5 | 269 | 3 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-65 | 229 | 189 | 373 | 0.51 | 0.078 98 | 0.001 29 | 1.67 | 0.152 23 | 0.001 28 | 1 172 | 32 | 996 | 13 | 913 | 7 | 109 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-66 | 158 | 733 | 867 | 0.85 | 0.051 96 | 0.001 07 | 0.24 | 0.033 43 | 0.000 25 | 283 | 48 | 218 | 4 | 212 | 2 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-67 | 388 | 1 616 | 744 | 2.17 | 0.068 21 | 0.002 25 | 0.38 | 0.040 19 | 0.000 40 | 876 | 69 | 326 | 9 | 254 | 2 | 128 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-68 | 63 | 242 | 286 | 0.84 | 0.052 52 | 0.001 68 | 0.29 | 0.040 55 | 0.000 45 | 309 | 77 | 262 | 8 | 256 | 3 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-69 | 386 | 1 032 | 1 007 | 1.02 | 0.062 17 | 0.001 04 | 0.67 | 0.077 50 | 0.003 04 | 680 | 37 | 522 | 19 | 481 | 18 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-71 | 287 | 307 | 662 | 0.46 | 0.069 19 | 0.001 02 | 1.24 | 0.129 66 | 0.002 22 | 906 | 63 | 819 | 13 | 786 | 13 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-72 | 333 | 459 | 381 | 1.21 | 0.068 05 | 0.001 23 | 1.16 | 0.123 22 | 0.001 04 | 870 | 38 | 780 | 11 | 749 | 6 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-73 | 76 | 309 | 380 | 0.81 | 0.054 75 | 0.001 52 | 0.29 | 0.038 96 | 0.000 35 | 467 | 61 | 262 | 7 | 246 | 2 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-74 | 803 | 582 | 1 652 | 0.35 | 0.081 38 | 0.001 09 | 1.71 | 0.154 03 | 0.003 23 | 1 231 | 26 | 1 012 | 12 | 923 | 18 | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-75 | 122 | 152 | 131 | 1.16 | 0.074 77 | 0.002 63 | 1.28 | 0.126 12 | 0.001 36 | 1 063 | 70 | 838 | 15 | 766 | 8 | 109 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-76 | 208 | 841 | 706 | 1.19 | 0.055 58 | 0.001 28 | 0.33 | 0.043 33 | 0.000 45 | 435 | 52 | 291 | 6 | 273 | 3 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-77 | 58 | 221 | 245 | 0.90 | 0.049 29 | 0.001 74 | 0.28 | 0.040 74 | 0.000 41 | 161 | 83 | 247 | 8 | 257 | 3 | 96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-78 | 13 | 37 | 53 | 0.69 | 0.065 78 | 0.003 81 | 0.46 | 0.051 07 | 0.000 89 | 798 | 122 | 386 | 20 | 321 | 5 | 120 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-81 | 963 | 758 | 3 370 | 0.22 | 0.066 95 | 0.000 81 | 1.08 | 0.116 29 | 0.001 85 | 835 | 25 | 742 | 11 | 709 | 11 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-82 | 339 | 1 150 | 1 490 | 0.77 | 0.060 83 | 0.001 57 | 0.33 | 0.039 87 | 0.000 42 | 633 | 56 | 293 | 7 | 252 | 3 | 116 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-84 | 593 | 1 866 | 2 774 | 0.67 | 0.065 26 | 0.001 79 | 0.40 | 0.044 59 | 0.000 43 | 783 | 57 | 341 | 7 | 281 | 3 | 121 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-85 | 1 042 | 2 592 | 3 974 | 0.65 | 0.093 63 | 0.010 10 | 0.66 | 0.043 28 | 0.001 05 | 1 502 | 205 | 513 | 66 | 273 | 7 | 188 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-86 | 2 079 | 6 034 | 4 774 | 1.26 | 0.074 86 | 0.001 41 | 0.00 | 0.000 00 | 0.000 00 | 1 065 | 37 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-87 | 698 | 5 241 | 4 007 | 1.31 | 0.070 53 | 0.001 39 | 0.26 | 0.026 52 | 0.000 30 | 944 | 41 | 232 | 4 | 169 | 2 | 138 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 片岩DC1703 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-01 | 46 | 154 | 1 100 | 0.14 | 0.050 54 | 0.000 89 | 0.27 | 0.038 78 | 0.000 36 | 220 | 36 | 243 | 4 | 245 | 2 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-02 | 571 | 668 | 2 455 | 0.27 | 0.091 05 | 0.001 04 | 2.47 | 0.195 80 | 0.002 10 | 1 448 | 22 | 1 262 | 11 | 1 153 | 11 | 126 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-03 | 281 | 1 374 | 1 277 | 1.08 | 0.069 94 | 0.000 71 | 1.55 | 0.160 27 | 0.001 49 | 928 | 20 | 949 | 7 | 958 | 8 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-04 | 107 | 796 | 423 | 1.88 | 0.072 60 | 0.000 92 | 1.55 | 0.154 45 | 0.001 34 | 1 003 | 25 | 949 | 8 | 926 | 7 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-05 | 233 | 78 | 732 | 0.11 | 0.132 80 | 0.001 56 | 5.06 | 0.275 46 | 0.003 70 | 2 135 | 26 | 1 830 | 15 | 1 568 | 19 | 136 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-06 | 260 | 535 | 1 416 | 0.38 | 0.069 57 | 0.000 70 | 1.53 | 0.159 49 | 0.001 53 | 917 | 21 | 943 | 7 | 954 | 8 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-07 | 31 | 417 | 679 | 0.61 | 0.051 34 | 0.001 07 | 0.26 | 0.037 39 | 0.000 45 | 257 | 46 | 238 | 4 | 237 | 3 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-08 | 768 | 129 | 1 433 | 0.09 | 0.170 36 | 0.001 79 | 10.76 | 0.458 32 | 0.004 06 | 2 561 | 23 | 2 503 | 10 | 2 432 | 18 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-09 | 181 | 274 | 932 | 0.29 | 0.075 26 | 0.000 97 | 1.77 | 0.170 75 | 0.001 79 | 1 076 | 26 | 1 034 | 9 | 1 016 | 10 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-10 | 469 | 534 | 1 238 | 0.43 | 0.113 77 | 0.001 37 | 4.89 | 0.312 55 | 0.003 39 | 1 861 | 22 | 1 800 | 9 | 1 753 | 17 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-11 | 544 | 1 337 | 3 252 | 0.41 | 0.072 14 | 0.000 95 | 1.44 | 0.144 63 | 0.002 08 | 991 | 27 | 904 | 9 | 871 | 12 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-12 | 555 | 582 | 832 | 0.70 | 0.184 93 | 0.002 15 | 12.61 | 0.494 91 | 0.005 32 | 2 698 | 19 | 2 651 | 13 | 2 592 | 23 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-13 | 70 | 538 | 273 | 1.97 | 0.072 56 | 0.000 97 | 1.52 | 0.152 39 | 0.001 66 | 1 011 | 26 | 939 | 9 | 914 | 9 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-14 | 237 | 332 | 1 989 | 0.17 | 0.062 59 | 0.000 83 | 0.94 | 0.108 92 | 0.001 10 | 694 | 30 | 672 | 6 | 666 | 6 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-15 | 186 | 287 | 1 769 | 0.16 | 0.060 02 | 0.000 77 | 0.80 | 0.096 39 | 0.000 87 | 606 | 28 | 595 | 5 | 593 | 5 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-16 | 37 | 218 | 831 | 0.26 | 0.054 59 | 0.001 55 | 0.30 | 0.039 27 | 0.000 57 | 394 | 63 | 263 | 8 | 248 | 4 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-17 | 709 | 1 264 | 2 557 | 0.49 | 0.159 30 | 0.001 63 | 4.91 | 0.222 74 | 0.004 01 | 2 450 | 17 | 1 804 | 18 | 1 296 | 21 | 189 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-18 | 128 | 131 | 950 | 0.14 | 0.073 34 | 0.000 94 | 1.24 | 0.123 12 | 0.001 40 | 1 033 | 26 | 821 | 8 | 749 | 8 | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-19 | 361 | 246 | 1 381 | 0.18 | 0.089 39 | 0.001 10 | 2.86 | 0.231 86 | 0.002 36 | 1 413 | 24 | 1 370 | 9 | 1 344 | 12 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-20 | 185 | 297 | 562 | 0.53 | 0.101 98 | 0.001 31 | 3.65 | 0.260 29 | 0.002 97 | 1 661 | 24 | 1 561 | 10 | 1 491 | 15 | 111 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-21 | 39 | 731 | 749 | 0.98 | 0.053 53 | 0.001 17 | 0.28 | 0.038 32 | 0.000 47 | 350 | 48 | 253 | 5 | 242 | 3 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-22 | 53 | 174 | 494 | 0.35 | 0.062 58 | 0.001 11 | 0.80 | 0.093 32 | 0.001 13 | 694 | 38 | 598 | 7 | 575 | 7 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-23 | 141 | 472 | 623 | 0.76 | 0.076 53 | 0.001 10 | 1.84 | 0.174 72 | 0.002 58 | 1 109 | 30 | 1 061 | 11 | 1 038 | 14 | 107 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-24 | 264 | 242 | 418 | 0.58 | 0.171 74 | 0.002 24 | 11.47 | 0.485 03 | 0.004 94 | 2 576 | 22 | 2 562 | 11 | 2 549 | 21 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-25 | 35 | 181 | 808 | 0.22 | 0.051 77 | 0.001 02 | 0.28 | 0.039 62 | 0.000 42 | 276 | 46 | 253 | 4 | 250 | 3 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-26 | 88 | 339 | 282 | 1.20 | 0.087 17 | 0.001 25 | 2.62 | 0.217 58 | 0.002 29 | 1 365 | 27 | 1 305 | 11 | 1 269 | 12 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-27 | 13 | 145 | 203 | 0.71 | 0.133 44 | 0.012 07 | 0.99 | 0.047 27 | 0.001 30 | 2 144 | 159 | 698 | 56 | 298 | 8 | 234 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-28 | 367 | 161 | 1 919 | 0.08 | 0.075 40 | 0.001 11 | 1.86 | 0.179 22 | 0.002 10 | 1 080 | 30 | 1 067 | 10 | 1 063 | 11 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-29 | 217 | 316 | 680 | 0.47 | 0.093 41 | 0.001 13 | 3.41 | 0.264 77 | 0.002 60 | 1 496 | 24 | 1 506 | 9 | 1 514 | 13 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-30 | 574 | 1 000 | 936 | 1.07 | 0.161 44 | 0.002 07 | 9.41 | 0.423 41 | 0.005 27 | 2 472 | 21 | 2 379 | 12 | 2 276 | 24 | 109 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-31 | 324 | 329 | 1 808 | 0.18 | 0.071 45 | 0.000 86 | 1.60 | 0.162 85 | 0.001 80 | 970 | 24 | 972 | 8 | 973 | 10 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-32 | 174 | 178 | 823 | 0.22 | 0.075 72 | 0.000 93 | 1.97 | 0.189 15 | 0.001 91 | 1 087 | 30 | 1 107 | 8 | 1 117 | 10 | 97 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-33 | 219 | 501 | 1 141 | 0.44 | 0.071 64 | 0.000 81 | 1.61 | 0.162 55 | 0.001 63 | 976 | 22 | 972 | 7 | 971 | 9 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-34 | 46 | 66 | 259 | 0.25 | 0.073 06 | 0.001 28 | 1.59 | 0.157 29 | 0.001 72 | 1 017 | 31 | 965 | 12 | 942 | 10 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-35 | 266 | 650 | 1 361 | 0.48 | 0.071 40 | 0.000 82 | 1.61 | 0.163 18 | 0.001 55 | 969 | 23 | 974 | 8 | 974 | 9 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-36 | 73 | 564 | 1 306 | 0.43 | 0.057 34 | 0.001 13 | 0.38 | 0.047 54 | 0.000 55 | 506 | 43 | 324 | 5 | 299 | 3 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-37 | 77 | 271 | 1 678 | 0.16 | 0.052 25 | 0.000 78 | 0.31 | 0.042 47 | 0.000 41 | 298 | 35 | 271 | 3 | 268 | 3 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-38 | 31 | 355 | 488 | 0.73 | 0.053 95 | 0.001 20 | 0.38 | 0.051 01 | 0.000 66 | 369 | 50 | 326 | 6 | 321 | 4 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-39 | 28 | 90 | 663 | 0.14 | 0.053 58 | 0.001 97 | 0.28 | 0.038 69 | 0.000 97 | 354 | 51 | 254 | 7 | 245 | 6 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-40 | 328 | 513 | 1 403 | 0.37 | 0.078 93 | 0.001 05 | 2.17 | 0.199 36 | 0.002 40 | 1 170 | 27 | 1 171 | 10 | 1 172 | 13 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-41 | 185 | 316 | 956 | 0.33 | 0.073 05 | 0.001 05 | 1.67 | 0.165 81 | 0.001 93 | 1 017 | 29 | 997 | 10 | 989 | 11 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-42 | 65 | 114 | 272 | 0.42 | 0.077 22 | 0.001 32 | 2.14 | 0.201 14 | 0.002 07 | 1 128 | 34 | 1 161 | 12 | 1 181 | 11 | 95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-43 | 181 | 1 213 | 1 917 | 0.63 | 0.056 38 | 0.000 83 | 0.59 | 0.076 61 | 0.000 84 | 478 | 31 | 474 | 6 | 476 | 5 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-44 | 331 | 378 | 812 | 0.47 | 0.110 04 | 0.001 21 | 5.07 | 0.334 43 | 0.004 08 | 1 811 | 20 | 1 832 | 11 | 1 860 | 20 | 97 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-45 | 638 | 256 | 1 225 | 0.21 | 0.159 76 | 0.001 95 | 9.42 | 0.427 59 | 0.003 69 | 2 453 | 21 | 2 380 | 12 | 2 295 | 17 | 107 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-46 | 356 | 1 039 | 2 126 | 0.49 | 0.074 33 | 0.001 15 | 1.46 | 0.143 00 | 0.003 06 | 1 050 | 30 | 912 | 13 | 862 | 17 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-47 | 419 | 368 | 1 177 | 0.31 | 0.105 15 | 0.001 23 | 4.46 | 0.307 52 | 0.004 80 | 1 717 | 22 | 1 723 | 14 | 1 729 | 24 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-48 | 79 | 202 | 503 | 0.40 | 0.066 62 | 0.001 07 | 1.23 | 0.133 53 | 0.001 74 | 828 | 34 | 812 | 10 | 808 | 10 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-49 | 95 | 597 | 552 | 1.08 | 0.065 03 | 0.001 02 | 1.09 | 0.121 88 | 0.001 64 | 776 | 33 | 749 | 9 | 741 | 9 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-50 | 139 | 226 | 234 | 0.97 | 0.140 18 | 0.001 81 | 8.11 | 0.420 30 | 0.004 85 | 2 229 | 22 | 2 243 | 12 | 2 262 | 22 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-51 | 76 | 951 | 1 361 | 0.70 | 0.061 08 | 0.001 40 | 0.37 | 0.044 24 | 0.000 48 | 643 | 55 | 320 | 5 | 279 | 3 | 115 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-52 | 181 | 471 | 1 172 | 0.40 | 0.080 39 | 0.001 51 | 1.51 | 0.131 93 | 0.004 58 | 1 206 | 37 | 935 | 27 | 799 | 26 | 117 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-53 | 26 | 204 | 293 | 0.70 | 0.056 87 | 0.001 37 | 0.55 | 0.070 12 | 0.000 84 | 487 | 54 | 444 | 9 | 437 | 5 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-54 | 539 | 611 | 1 339 | 0.46 | 0.115 46 | 0.001 07 | 5.15 | 0.323 97 | 0.003 65 | 1 887 | 18 | 1 845 | 9 | 1 809 | 18 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-55 | 125 | 414 | 1 521 | 0.27 | 0.054 66 | 0.000 78 | 0.55 | 0.073 12 | 0.000 70 | 398 | 33 | 445 | 5 | 455 | 4 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-56 | 50 | 307 | 574 | 0.53 | 0.056 50 | 0.001 23 | 0.56 | 0.072 52 | 0.000 85 | 472 | 44 | 454 | 8 | 451 | 5 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-57 | 54 | 421 | 769 | 0.55 | 0.054 56 | 0.001 10 | 0.42 | 0.056 67 | 0.001 07 | 394 | 44 | 359 | 7 | 355 | 7 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-58 | 363 | 786 | 1 718 | 0.46 | 0.071 93 | 0.000 98 | 1.75 | 0.177 28 | 0.002 12 | 983 | 23 | 1 028 | 8 | 1 052 | 12 | 93 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-59 | 25 | 221 | 527 | 0.42 | 0.051 26 | 0.001 29 | 0.28 | 0.040 20 | 0.000 49 | 254 | 57 | 252 | 5 | 254 | 3 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-60 | 282 | 1 210 | 5 342 | 0.23 | 0.051 86 | 0.000 87 | 0.34 | 0.047 91 | 0.000 71 | 280 | 39 | 299 | 4 | 302 | 4 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-61 | 130 | 1 096 | 1 022 | 1.07 | 0.058 33 | 0.000 84 | 0.74 | 0.092 63 | 0.001 17 | 543 | 31 | 564 | 6 | 571 | 7 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-62 | 43 | 298 | 855 | 0.35 | 0.051 51 | 0.001 04 | 0.31 | 0.044 16 | 0.000 56 | 265 | 46 | 278 | 6 | 279 | 3 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-63 | 69 | 5 871 | 13 304 | 0.44 | 0.045 51 | 0.000 84 | 0.03 | 0.004 52 | 0.000 05 | — | — | 28 | 1 | 29 | 0 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-64 | 380 | 141 | 2 183 | 0.06 | 0.071 14 | 0.000 78 | 1.60 | 0.163 37 | 0.001 87 | 961 | 22 | 971 | 8 | 975 | 10 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-65 | 109 | 186 | 257 | 0.72 | 0.102 52 | 0.001 30 | 4.61 | 0.326 22 | 0.003 59 | 1 670 | 24 | 1 751 | 11 | 1 820 | 17 | 92 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-66 | 16 | 171 | 125 | 1.36 | 0.058 48 | 0.001 68 | 0.67 | 0.083 74 | 0.001 10 | 546 | 63 | 521 | 11 | 518 | 7 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-67 | 55 | 526 | 438 | 1.20 | 0.058 82 | 0.000 96 | 0.73 | 0.089 99 | 0.001 18 | 561 | 35 | 555 | 7 | 555 | 7 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-68 | 204 | 772 | 2 418 | 0.32 | 0.054 78 | 0.000 72 | 0.56 | 0.074 88 | 0.000 86 | 467 | 30 | 454 | 4 | 466 | 5 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-69 | 171 | 430 | 801 | 0.54 | 0.073 42 | 0.000 94 | 1.78 | 0.175 71 | 0.002 31 | 1 026 | 26 | 1 038 | 10 | 1 044 | 13 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-70 | 173 | 215 | 871 | 0.25 | 0.072 90 | 0.001 42 | 1.75 | 0.174 75 | 0.002 27 | 1 013 | 39 | 1 028 | 10 | 1 038 | 12 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-71 | 74 | 157 | 908 | 0.17 | 0.055 56 | 0.000 76 | 0.57 | 0.074 78 | 0.000 73 | 435 | 1 | 460 | 5 | 465 | 4 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-72 | 55 | 511 | 578 | 0.89 | 0.055 95 | 0.000 97 | 0.56 | 0.072 08 | 0.000 81 | 450 | 37 | 449 | 6 | 449 | 5 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-73 | 68 | 294 | 792 | 0.37 | 0.055 07 | 0.000 88 | 0.56 | 0.073 59 | 0.000 73 | 417 | 31 | 451 | 6 | 458 | 4 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-74 | 176 | 330 | 750 | 0.44 | 0.076 17 | 0.000 87 | 2.05 | 0.194 86 | 0.002 02 | 1 100 | 24 | 1 132 | 9 | 1 148 | 11 | 96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-75 | — | — | — | — | 0.059 92 | 0.005 68 | 0.46 | 0.057 91 | 0.003 01 | 611 | 203 | 387 | 31 | 363 | 18 | 107 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-76 | 68 | 209 | 831 | 0.25 | 0.055 05 | 0.000 86 | 0.55 | 0.072 12 | 0.000 78 | 413 | 31 | 443 | 5 | 449 | 5 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-77 | 31 | 363 | 608 | 0.60 | 0.052 31 | 0.000 98 | 0.29 | 0.040 71 | 0.000 37 | 298 | 43 | 261 | 4 | 257 | 2 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-78 | 22 | 204 | 422 | 0.48 | 0.050 03 | 0.001 43 | 0.30 | 0.043 90 | 0.000 70 | 198 | 67 | 268 | 7 | 277 | 4 | 97 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-79 | 98 | 250 | 371 | 0.67 | 0.077 85 | 0.001 05 | 2.21 | 0.206 19 | 0.002 64 | 1 143 | 27 | 1 184 | 9 | 1 208 | 14 | 95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-80 | 178 | 889 | 691 | 1.29 | 0.071 50 | 0.000 86 | 1.78 | 0.180 03 | 0.002 88 | 972 | 25 | 1 037 | 11 | 1 067 | 16 | 91 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-81 | 42 | 430 | 432 | 1.00 | 0.059 64 | 0.001 29 | 0.57 | 0.069 35 | 0.000 89 | 591 | 46 | 457 | 8 | 432 | 5 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-82 | 263 | 485 | 1 316 | 0.37 | 0.071 21 | 0.000 80 | 1.67 | 0.169 42 | 0.001 89 | 965 | 23 | 996 | 8 | 1 009 | 10 | 96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-83 | 91 | 411 | 433 | 0.95 | 0.069 96 | 0.000 99 | 1.50 | 0.155 80 | 0.001 61 | 928 | 34 | 932 | 9 | 933 | 9 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-84 | 153 | 624 | 1 860 | 0.34 | 0.055 88 | 0.000 86 | 0.57 | 0.073 49 | 0.000 86 | 456 | 33 | 455 | 5 | 457 | 5 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-85 | 322 | 2 219 | 3 587 | 0.62 | 0.058 26 | 0.000 72 | 0.58 | 0.072 68 | 0.000 75 | 539 | 21 | 467 | 5 | 452 | 4 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-86 | 58 | 398 | 1 334 | 0.30 | 0.058 29 | 0.001 17 | 0.31 | 0.038 15 | 0.000 40 | 539 | 44 | 273 | 5 | 241 | 2 | 113 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-87 | 276 | 515 | 1 397 | 0.37 | 0.073 15 | 0.000 99 | 1.72 | 0.170 68 | 0.001 97 | 1 018 | 32 | 1 017 | 9 | 1 016 | 11 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-88 | 628 | 502 | 1 563 | 0.32 | 0.116 07 | 0.001 29 | 5.45 | 0.339 83 | 0.003 80 | 1 898 | 20 | 1 892 | 11 | 1 886 | 18 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-89 | 340 | 328 | 872 | 0.38 | 0.113 17 | 0.001 42 | 5.09 | 0.326 23 | 0.003 56 | 1 851 | 23 | 1 834 | 10 | 1 820 | 17 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-90 | 119 | 164 | 394 | 0.42 | 0.091 46 | 0.001 34 | 3.21 | 0.254 06 | 0.002 73 | 1 457 | 28 | 1 459 | 11 | 1 459 | 14 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-91 | 152 | 511 | 1 360 | 0.38 | 0.060 58 | 0.000 81 | 0.81 | 0.097 29 | 0.000 97 | 633 | 30 | 604 | 6 | 599 | 6 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-92 | 435 | 251 | 2 496 | 0.10 | 0.070 75 | 0.000 92 | 1.58 | 0.162 08 | 0.001 67 | 950 | 26 | 963 | 8 | 968 | 9 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-93 | 193 | 191 | 404 | 0.47 | 0.128 58 | 0.001 79 | 6.79 | 0.383 34 | 0.004 80 | 2 080 | 24 | 2 085 | 14 | 2 092 | 22 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-94 | 82 | 337 | 983 | 0.34 | 0.056 27 | 0.000 87 | 0.57 | 0.073 67 | 0.000 85 | 461 | 35 | 459 | 6 | 458 | 5 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-95 | 1 260 | 183 | 2 217 | 0.08 | 0.161 84 | 0.001 82 | 10.94 | 0.490 23 | 0.005 52 | 2 476 | 18 | 2 518 | 12 | 2 572 | 24 | 96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-96 | 88 | 226 | 743 | 0.30 | 0.061 37 | 0.000 89 | 0.88 | 0.103 92 | 0.001 08 | 654 | 31 | 641 | 7 | 637 | 6 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-97 | 1 919 | 2 484 | 2 395 | 1.04 | 0.199 56 | 0.002 55 | 15.02 | 0.546 42 | 0.005 37 | 2 833 | 21 | 2 817 | 11 | 2 810 | 22 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-98 | 67 | 333 | 825 | 0.40 | 0.055 05 | 0.001 07 | 0.52 | 0.069 24 | 0.000 78 | 413 | 44 | 428 | 7 | 432 | 5 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-99 | 44 | 229 | 1 010 | 0.23 | 0.051 24 | 0.001 09 | 0.28 | 0.039 11 | 0.000 43 | 250 | 44 | 247 | 4 | 247 | 3 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-100 | 174 | 442 | 586 | 0.75 | 0.082 82 | 0.001 18 | 2.61 | 0.229 30 | 0.002 68 | 1 265 | 28 | 1 304 | 11 | 1 331 | 14 | 95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 变质砂岩DC1801 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-01 | 2 | 0.090 5 | 1 | 0.10 | 0.764 47 | 0.161 08 | 0.16 | 0.818 10 | 0.197 02 | — | — | 4 840 | 354 | 3 854 | 699 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-02 | 27 | 68 | 161 | 0.43 | 0.067 29 | 0.010 37 | 0.01 | 0.138 15 | 0.009 53 | 856 | 326 | 864 | 93 | 834 | 54 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-03 | 112 | 51 | 669 | 0.08 | 0.070 73 | 0.003 24 | 0.00 | 0.154 69 | 0.004 34 | 950 | 93 | 955 | 28 | 927 | 24 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-04 | 9 | 92 | 137 | 0.67 | 0.053 93 | 0.016 99 | 0.02 | 0.054 34 | 0.002 00 | 369 | 587 | 359 | 104 | 341 | 12 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-05 | 28 | 16 | 144 | 0.11 | 0.135 31 | 0.013 03 | 0.01 | 0.188 03 | 0.010 52 | 2 168 | 169 | 1 554 | 75 | 1 111 | 57 | 195 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-06 | 11 | 0.281 | 2 | 0.18 | 1.647 83 | 0.514 46 | 0.51 | 1.375 95 | 0.415 09 | — | — | 5 596 | 451 | 5 579 | 1 126 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-07 | 17 | 244 | 313 | 0.78 | 0.055 26 | 0.010 85 | 0.01 | 0.044 37 | 0.002 40 | 433 | 376 | 290 | 31 | 280 | 15 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-08 | 13 | 82 | 229 | 0.36 | 0.050 69 | 0.007 54 | 0.01 | 0.048 83 | 0.002 25 | 233 | 306 | 314 | 37 | 307 | 14 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-09 | 24 | 205 | 389 | 0.53 | 0.056 52 | 0.011 07 | 0.01 | 0.054 70 | 0.001 44 | 472 | 385 | 372 | 66 | 343 | 9 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-10 | 9 | 196 | 449 | 0.44 | 0.046 94 | 0.006 63 | 0.01 | 0.017 38 | 0.000 59 | 56 | 298 | 112 | 15 | 111 | 4 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-11 | 41 | 695 | 2 702 | 0.26 | 0.053 64 | 0.008 94 | 0.01 | 0.014 60 | 0.000 85 | 367 | 328 | 107 | 11 | 93 | 5 | 114 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-12 | 89 | 88 | 123 | 0.71 | 0.194 39 | 0.010 32 | 0.01 | 0.538 47 | 0.027 15 | 2 780 | 87 | 2 801 | 57 | 2 777 | 114 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-13 | 42 | 36 | 143 | 0.25 | 0.100 51 | 0.004 96 | 0.00 | 0.259 51 | 0.007 23 | 1 635 | 93 | 1 575 | 38 | 1 487 | 37 | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-14 | 20 | 120 | 336 | 0.36 | 0.052 84 | 0.004 62 | 0.00 | 0.051 16 | 0.001 97 | 320 | 200 | 323 | 20 | 322 | 12 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-15 | 22 | 150 | 403 | 0.37 | 0.051 88 | 0.004 85 | 0.00 | 0.042 02 | 0.001 99 | 280 | 215 | 270 | 20 | 265 | 12 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-16 | 92 | 120 | 290 | 0.42 | 0.152 43 | 0.016 73 | 0.02 | 0.257 29 | 0.024 15 | 2 373 | 188 | 1 935 | 163 | 1 476 | 124 | 161 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-17 | 7 | 71 | 105 | 0.68 | 0.052 59 | 0.007 35 | 0.01 | 0.051 15 | 0.002 76 | 322 | 289 | 316 | 30 | 322 | 17 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-18 | 42 | 104 | 209 | 0.50 | 0.069 35 | 0.004 83 | 0.00 | 0.151 00 | 0.006 79 | 909 | 144 | 935 | 42 | 907 | 38 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-19 | 13 | 68 | 127 | 0.54 | 0.053 22 | 0.006 08 | 0.01 | 0.083 69 | 0.002 90 | 339 | 266 | 507 | 40 | 518 | 17 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-20 | 4 | 22 | 78 | 0.29 | 0.052 26 | 0.009 30 | 0.01 | 0.035 20 | 0.002 01 | 298 | 361 | 229 | 29 | 223 | 13 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-21 | 84 | 230 | 380 | 0.61 | 0.069 86 | 0.005 76 | 0.01 | 0.157 39 | 0.006 26 | 924 | 169 | 960 | 36 | 942 | 35 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-22 | 50 | 402 | 1 712 | 0.23 | 0.046 52 | 0.004 23 | 0.00 | 0.026 63 | 0.001 20 | 33 | 198 | 166 | 12 | 169 | 8 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-23 | 35 | 190 | 657 | 0.29 | 0.049 74 | 0.004 33 | 0.00 | 0.040 22 | 0.001 95 | 183 | 189 | 259 | 17 | 254 | 12 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-24 | 14 | 99 | 236 | 0.42 | 0.057 37 | 0.006 18 | 0.01 | 0.043 76 | 0.001 86 | 506 | 239 | 297 | 22 | 276 | 12 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-25 | 39 | 350 | 499 | 0.70 | 0.053 65 | 0.005 65 | 0.01 | 0.063 13 | 0.002 20 | 367 | 245 | 399 | 33 | 395 | 13 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-26 | 3 | 0.364 | 1 | 0.33 | 0.733 64 | 0.145 15 | 0.15 | 1.069 70 | 0.314 97 | — | — | 4 814 | 245 | 4 689 | 981 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-27 | 3 | 4 | 345 | 0.01 | 0.073 19 | 0.043 23 | 0.04 | 0.009 96 | 0.001 11 | 1 020 | 882 | 74 | 40 | 64 | 7 | 117 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-28 | 9 | 75 | 139 | 0.54 | 0.054 79 | 0.008 22 | 0.01 | 0.051 89 | 0.003 06 | 467 | 338 | 326 | 38 | 326 | 19 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-29 | 1 | 0.004 3 | 0.183 0 | 0.02 | 0.607 43 | 0.117 76 | 0.12 | 1.016 82 | 0.181 23 | 4 526 | 315 | 4 822 | 260 | 4 522 | 579 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-30 | 28 | 146 | 387 | 0.38 | 0.056 14 | 0.006 63 | 0.01 | 0.063 83 | 0.003 00 | 457 | 265 | 405 | 33 | 399 | 18 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-31 | 212 | 565 | 6 281 | 0.09 | 0.049 64 | 0.002 78 | 0.00 | 0.029 05 | 0.001 22 | 189 | 131 | 185 | 11 | 185 | 8 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-32 | 34 | 237 | 730 | 0.32 | 0.051 90 | 0.004 76 | 0.00 | 0.043 15 | 0.001 44 | 280 | 211 | 275 | 22 | 272 | 9 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-33 | 41 | 70 | 428 | 0.16 | 0.061 07 | 0.003 54 | 0.00 | 0.090 61 | 0.003 35 | 643 | 119 | 579 | 23 | 559 | 20 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-34 | 52 | 107 | 819 | 0.13 | 0.054 67 | 0.004 55 | 0.00 | 0.061 46 | 0.002 25 | 398 | 182 | 389 | 21 | 384 | 14 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-35 | 20 | 218 | 303 | 0.72 | 0.053 69 | 0.005 82 | 0.01 | 0.053 78 | 0.003 02 | 367 | 243 | 347 | 39 | 338 | 18 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-36 | 8 | 71 | 127 | 0.56 | 0.057 89 | 0.010 03 | 0.01 | 0.045 23 | 0.002 30 | 524 | 383 | 288 | 22 | 285 | 14 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-37 | 17 | 149 | 478 | 0.31 | 0.046 81 | 0.004 77 | 0.00 | 0.032 47 | 0.001 26 | 39 | 294 | 193 | 13 | 206 | 8 | 94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-38 | 81 | 218 | 507 | 0.43 | 0.066 66 | 0.003 36 | 0.00 | 0.126 57 | 0.005 00 | 828 | 106 | 796 | 33 | 768 | 29 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-39 | 16 | 129 | 286 | 0.45 | 0.054 03 | 0.004 54 | 0.00 | 0.048 82 | 0.001 61 | 372 | 189 | 312 | 19 | 307 | 10 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-40 | 13 | 90 | 211 | 0.42 | 0.052 52 | 0.006 13 | 0.01 | 0.056 74 | 0.001 86 | 309 | 268 | 348 | 31 | 356 | 11 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-41 | 172 | 78 | 542 | 0.14 | 0.108 15 | 0.005 50 | 0.01 | 0.307 11 | 0.012 97 | 1 768 | 93 | 1 773 | 53 | 1 726 | 64 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-42 | 70 | 230 | 168 | 1.37 | 0.103 34 | 0.006 50 | 0.01 | 0.299 33 | 0.012 89 | 1 685 | 117 | 1 708 | 54 | 1 688 | 64 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-43 | 23 | 147 | 248 | 0.59 | 0.056 64 | 0.004 96 | 0.00 | 0.074 59 | 0.003 29 | 476 | 164 | 477 | 33 | 464 | 20 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-44 | 64 | 401 | 656 | 0.61 | 0.059 61 | 0.010 23 | 0.01 | 0.089 41 | 0.002 62 | 591 | 380 | 569 | 70 | 552 | 15 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-45 | 93 | 231 | 381 | 0.61 | 0.146 79 | 0.009 43 | 0.01 | 0.204 09 | 0.008 01 | 2 309 | 111 | 1 679 | 49 | 1 197 | 43 | 193 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-46 | 15 | 104 | 205 | 0.51 | 0.056 47 | 0.007 08 | 0.01 | 0.060 04 | 0.003 83 | 472 | 281 | 395 | 40 | 376 | 23 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-47 | 9 | 132 | 178 | 0.74 | 0.054 46 | 0.006 86 | 0.01 | 0.040 79 | 0.002 02 | 391 | 285 | 267 | 26 | 258 | 13 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-48 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0.92 | 0.306 86 | 0.075 45 | 0.08 | 0.118 48 | 0.013 78 | 3 505 | 390 | 2 150 | 192 | 722 | 79 | 298 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-49 | 30 | 320 | 458 | 0.70 | 0.053 98 | 0.004 30 | 0.00 | 0.043 65 | 0.002 06 | 369 | 175 | 286 | 19 | 275 | 13 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-50 | 5 | 0.029 3 | 0.013 6 | 2.15 | 0.932 91 | 0.125 23 | 0.13 | 2.401 60 | 1.310 60 | — | — | 5 721 | 509 | 7 892 | 2 484 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-51 | 105 | 79 | 369 | 0.21 | 0.089 45 | 0.004 60 | 0.00 | 0.225 63 | 0.008 06 | 1 414 | 94 | 1 361 | 41 | 1 312 | 42 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-52 | 21 | 157 | 508 | 0.31 | 0.052 42 | 0.004 32 | 0.00 | 0.033 90 | 0.001 25 | 302 | 187 | 227 | 15 | 215 | 8 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-53 | 231 | 126 | 1 287 | 0.10 | 0.076 81 | 0.003 42 | 0.00 | 0.168 73 | 0.005 73 | 1 117 | 85 | 1 050 | 30 | 1 005 | 32 | 111 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-54 | 55 | 351 | 858 | 0.41 | 0.051 01 | 0.003 07 | 0.00 | 0.046 71 | 0.001 89 | 243 | 141 | 295 | 17 | 294 | 12 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-55 | 40 | 105 | 886 | 0.12 | 0.054 25 | 0.003 69 | 0.00 | 0.039 61 | 0.001 52 | 389 | 154 | 261 | 14 | 250 | 9 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-56 | 10 | 116 | 143 | 0.81 | 0.054 23 | 0.006 33 | 0.01 | 0.054 49 | 0.001 90 | 389 | 269 | 350 | 33 | 342 | 12 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-57 | 73 | 408 | 1 072 | 0.38 | 0.053 50 | 0.003 02 | 0.00 | 0.052 84 | 0.002 22 | 350 | 128 | 336 | 16 | 332 | 14 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-58 | 18 | 167 | 355 | 0.47 | 0.057 40 | 0.040 84 | 0.04 | 0.039 37 | 0.002 78 | 506 | 1 085 | 268 | 135 | 249 | 17 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-59 | 157 | 1 146 | 1 496 | 0.77 | 0.059 13 | 0.004 59 | 0.00 | 0.087 84 | 0.004 57 | 572 | 168 | 553 | 25 | 543 | 27 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-60 | 11 | 138 | 241 | 0.57 | 0.052 21 | 0.006 36 | 0.01 | 0.039 57 | 0.001 60 | 295 | 256 | 251 | 24 | 250 | 10 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-61 | 23 | 183 | 373 | 0.49 | 0.049 32 | 0.004 09 | 0.00 | 0.050 03 | 0.001 76 | 165 | 181 | 306 | 20 | 315 | 11 | 97 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-62 | 9 | 76 | 136 | 0.56 | 0.061 46 | 0.010 85 | 0.01 | 0.043 68 | 0.003 05 | 655 | 381 | 284 | 25 | 276 | 19 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-63 | 113 | 137 | 186 | 0.73 | 0.152 67 | 0.008 84 | 0.01 | 0.418 10 | 0.021 88 | 2 376 | 99 | 2 345 | 60 | 2 252 | 99 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-64 | 23 | 46 | 325 | 0.14 | 0.140 96 | 0.038 24 | 0.04 | 0.046 79 | 0.006 08 | 2 239 | 486 | 659 | 119 | 295 | 37 | 224 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-65 | 44 | 149 | 245 | 0.61 | 0.065 39 | 0.004 76 | 0.00 | 0.128 65 | 0.005 44 | 787 | 152 | 785 | 36 | 780 | 31 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-66 | 188 | 2 221 | 4 125 | 0.54 | 0.048 23 | 0.002 49 | 0.00 | 0.039 78 | 0.001 09 | 109 | 118 | 242 | 10 | 251 | 7 | 96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-67 | 7 | 60 | 109 | 0.55 | 0.054 94 | 0.008 49 | 0.01 | 0.042 34 | 0.002 17 | 409 | 352 | 267 | 20 | 267 | 13 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-68 | 11 | 47 | 134 | 0.35 | 0.107 86 | 0.013 82 | 0.01 | 0.065 14 | 0.003 13 | 1 765 | 236 | 689 | 57 | 407 | 19 | 169 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-69 | 3 | 29 | 48 | 0.61 | 0.060 89 | 0.012 64 | 0.01 | 0.050 87 | 0.002 74 | 635 | 453 | 336 | 45 | 320 | 17 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-70 | 34 | 150 | 896 | 0.17 | 0.046 96 | 0.004 13 | 0.00 | 0.029 63 | 0.001 36 | 56 | 200 | 178 | 13 | 188 | 9 | 95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-71 | 162 | 111 | 1 193 | 0.09 | 0.064 97 | 0.003 32 | 0.00 | 0.112 49 | 0.004 81 | 772 | 108 | 714 | 29 | 687 | 28 | 112 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-72 | 5 | 109 | 220 | 0.50 | 0.065 85 | 0.022 91 | 0.02 | 0.015 25 | 0.000 90 | 1 200 | 199 | 138 | 45 | 98 | 6 | 142 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-73 | 13 | 152 | 230 | 0.66 | 0.056 16 | 0.008 36 | 0.01 | 0.041 07 | 0.002 52 | 457 | 329 | 263 | 25 | 259 | 16 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-74 | 4 | 30 | 79 | 0.38 | 0.060 97 | 0.009 20 | 0.01 | 0.040 90 | 0.002 09 | 639 | 362 | 260 | 18 | 258 | 13 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-75 | 63 | 195 | 297 | 0.66 | 0.067 06 | 0.003 89 | 0.00 | 0.145 82 | 0.005 66 | 839 | 122 | 871 | 32 | 878 | 32 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-76 | 10 | 27 | 70 | 0.38 | 0.059 22 | 0.006 33 | 0.01 | 0.098 51 | 0.004 54 | 576 | 233 | 598 | 37 | 606 | 27 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
表1 点苍山变质地体三叠纪至侏罗纪沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄
Table 1 Detrital zircon U-Pb ages for the Triassic to Jurassic sedimentary rocks in the DMT
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 碳酸盐岩DC1702 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-01 | 133 | 125 | 188 | 0.67 | 0.068 85 | 0.001 50 | 1.48 | 0.155 70 | 0.001 71 | 894 | 44 | 920 | 13 | 933 | 10 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-02 | 31 | 95 | 187 | 0.51 | 0.056 30 | 0.001 98 | 0.31 | 0.040 19 | 0.000 44 | 465 | 78 | 274 | 8 | 254 | 3 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-03 | 20 | 326 | 396 | 0.82 | 0.049 98 | 0.002 75 | 0.06 | 0.008 59 | 0.000 10 | 195 | 128 | 58 | 3 | 55 | 1 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-04 | 72 | 65 | 93 | 0.70 | 0.077 01 | 0.002 03 | 1.68 | 0.158 00 | 0.001 76 | 1 121 | 20 | 1 000 | 17 | 946 | 10 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-05 | 436 | 993 | 1 871 | 0.53 | 0.097 28 | 0.006 87 | 0.58 | 0.041 37 | 0.000 50 | 1 573 | 132 | 462 | 31 | 261 | 3 | 177 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-06 | 724 | 2 916 | 1 386 | 2.10 | 0.060 49 | 0.001 30 | 0.34 | 0.040 67 | 0.000 44 | 620 | 47 | 296 | 6 | 257 | 3 | 115 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-07 | 288 | 274 | 598 | 0.46 | 0.068 89 | 0.000 96 | 1.17 | 0.122 01 | 0.002 27 | 894 | 29 | 784 | 14 | 742 | 13 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-08 | 1 030 | 4 307 | 1 455 | 2.96 | 0.083 57 | 0.001 80 | 0.37 | 0.032 42 | 0.000 32 | 1 283 | 42 | 322 | 6 | 206 | 2 | 157 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-09 | 157 | 621 | 297 | 2.09 | 0.053 61 | 0.001 56 | 0.31 | 0.042 43 | 0.000 45 | 354 | 67 | 277 | 7 | 268 | 3 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-10 | 92 | 287 | 554 | 0.52 | 0.056 29 | 0.001 36 | 0.32 | 0.041 54 | 0.000 42 | 465 | 54 | 284 | 6 | 262 | 3 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-11 | 39 | 147 | 176 | 0.84 | 0.053 06 | 0.002 12 | 0.29 | 0.040 39 | 0.000 48 | 332 | 91 | 261 | 9 | 255 | 3 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-12 | 440 | 399 | 763 | 0.52 | 0.069 36 | 0.000 91 | 1.51 | 0.157 66 | 0.001 86 | 909 | 58 | 935 | 11 | 944 | 10 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-13 | 159 | 76 | 149 | 0.51 | 0.108 65 | 0.001 47 | 4.35 | 0.290 16 | 0.002 79 | 1 777 | 29 | 1 702 | 12 | 1 642 | 14 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-14 | 325 | 1 254 | 1 051 | 1.19 | 0.060 03 | 0.005 07 | 0.31 | 0.039 44 | 0.000 52 | 606 | 184 | 270 | 6 | 249 | 3 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-15 | 272 | 143 | 283 | 0.51 | 0.105 96 | 0.001 43 | 3.53 | 0.241 56 | 0.004 35 | 1 731 | 30 | 1 534 | 17 | 1 395 | 23 | 124 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-16 | 53 | 10 | 290 | 0.03 | 0.068 57 | 0.001 19 | 1.21 | 0.127 62 | 0.001 62 | 887 | 35 | 807 | 10 | 774 | 9 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-17 | 238 | 80 | 101 | 0.79 | 0.161 75 | 0.002 00 | 10.82 | 0.485 53 | 0.005 18 | 2 474 | 21 | 2 508 | 14 | 2 551 | 22 | 97 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-18 | 224 | 649 | 1 437 | 0.45 | 0.053 47 | 0.000 90 | 0.30 | 0.040 83 | 0.000 41 | 350 | 39 | 267 | 4 | 258 | 3 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-19 | 397 | 341 | 951 | 0.36 | 0.067 63 | 0.000 82 | 1.35 | 0.144 48 | 0.001 70 | 857 | 26 | 867 | 10 | 870 | 10 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-20 | 177 | 255 | 2 048 | 0.12 | 0.057 53 | 0.000 88 | 0.33 | 0.041 43 | 0.000 76 | 522 | 35 | 289 | 6 | 262 | 5 | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-21 | 172 | 701 | 819 | 0.86 | 0.054 04 | 0.001 13 | 0.28 | 0.038 21 | 0.000 51 | 372 | 48 | 253 | 5 | 242 | 3 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-22 | 237 | 867 | 1 022 | 0.85 | 0.051 51 | 0.000 92 | 0.29 | 0.041 54 | 0.000 43 | 265 | 43 | 262 | 4 | 262 | 3 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-23 | 11 | 33 | 66 | 0.49 | 0.060 85 | 0.003 31 | 0.35 | 0.042 19 | 0.000 67 | 635 | 112 | 303 | 13 | 266 | 4 | 114 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-24 | 80 | 299 | 286 | 1.04 | 0.052 79 | 0.001 92 | 0.30 | 0.041 37 | 0.000 43 | 320 | 116 | 267 | 9 | 261 | 3 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-25 | 86 | 33 | 288 | 0.12 | 0.106 37 | 0.001 43 | 2.10 | 0.143 02 | 0.001 92 | 1 739 | 25 | 1 149 | 13 | 862 | 11 | 133 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-26 | 184 | 590 | 952 | 0.62 | 0.056 99 | 0.000 96 | 0.32 | 0.041 20 | 0.000 54 | 500 | 37 | 284 | 5 | 260 | 3 | 109 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-27 | 47 | 188 | 147 | 1.28 | 0.055 92 | 0.002 23 | 0.30 | 0.039 39 | 0.000 48 | 450 | 117 | 270 | 10 | 249 | 3 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-28 | 344 | 283 | 1 026 | 0.28 | 0.067 37 | 0.000 84 | 1.19 | 0.127 86 | 0.001 66 | 850 | 21 | 798 | 10 | 776 | 9 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-29 | 274 | 210 | 962 | 0.22 | 0.066 38 | 0.000 87 | 1.19 | 0.128 75 | 0.002 87 | 818 | 32 | 794 | 15 | 781 | 16 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-31 | 300 | 166 | 2 267 | 0.07 | 0.059 98 | 0.000 96 | 0.70 | 0.084 56 | 0.000 85 | 611 | 34 | 540 | 6 | 523 | 5 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-32 | 452 | 1 688 | 2 665 | 0.63 | 0.065 40 | 0.001 29 | 0.31 | 0.034 28 | 0.000 34 | 787 | 41 | 277 | 5 | 217 | 2 | 127 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-33 | 60 | 174 | 450 | 0.39 | 0.051 46 | 0.001 41 | 0.30 | 0.041 56 | 0.000 42 | 261 | 63 | 265 | 6 | 262 | 3 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-34 | 34 | 197 | 195 | 1.01 | 0.075 81 | 0.003 54 | 0.26 | 0.024 52 | 0.000 32 | 1 100 | 93 | 234 | 9 | 156 | 2 | 150 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-35 | 433 | 401 | 451 | 0.89 | 0.078 64 | 0.001 87 | 1.64 | 0.148 38 | 0.001 63 | 1 165 | 46 | 986 | 11 | 892 | 9 | 111 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-36 | 268 | 345 | 352 | 0.98 | 0.065 66 | 0.001 95 | 1.18 | 0.127 42 | 0.001 15 | 794 | 63 | 790 | 10 | 773 | 7 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-37 | 121 | 416 | 688 | 0.61 | 0.050 38 | 0.001 63 | 0.30 | 0.042 00 | 0.000 43 | 213 | 44 | 265 | 5 | 265 | 3 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-38 | 383 | 111 | 498 | 0.22 | 0.151 18 | 0.004 79 | 7.31 | 0.340 40 | 0.004 65 | 2 361 | 54 | 2 150 | 17 | 1 889 | 22 | 125 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-41 | 694 | 2 777 | 1 379 | 2.01 | 0.053 18 | 0.001 83 | 0.31 | 0.041 58 | 0.000 42 | 345 | 78 | 277 | 4 | 263 | 3 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-42 | 259 | 310 | 441 | 0.70 | 0.063 66 | 0.002 09 | 1.15 | 0.128 36 | 0.001 30 | 731 | 70 | 779 | 10 | 778 | 7 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-43 | 268 | 998 | 1 249 | 0.80 | 0.049 20 | 0.001 42 | 0.29 | 0.041 48 | 0.000 36 | 167 | 73 | 257 | 4 | 262 | 2 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-44 | 323 | 358 | 350 | 1.02 | 0.073 34 | 0.001 95 | 1.39 | 0.135 50 | 0.002 47 | 1 033 | 54 | 885 | 11 | 819 | 14 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-45 | 19 | 516 | 2 245 | 0.23 | 0.047 72 | 0.002 21 | 0.02 | 0.003 72 | 0.000 06 | 87 | 104 | 25 | 1 | 24 | 1 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-46 | 589 | 2 390 | 1 429 | 1.67 | 0.049 32 | 0.001 12 | 0.29 | 0.042 37 | 0.000 45 | 161 | 54 | 260 | 4 | 268 | 3 | 97 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-47 | 108 | 414 | 546 | 0.76 | 0.057 19 | 0.003 62 | 0.28 | 0.036 25 | 0.000 44 | 498 | 139 | 251 | 8 | 230 | 3 | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-48 | 40 | 126 | 222 | 0.56 | 0.058 18 | 0.001 92 | 0.34 | 0.041 84 | 0.000 43 | 600 | 72 | 295 | 8 | 264 | 3 | 111 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-49 | 609 | 2 396 | 1 837 | 1.30 | 0.070 75 | 0.002 01 | 0.34 | 0.034 68 | 0.000 35 | 950 | 54 | 295 | 6 | 220 | 2 | 134 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-50 | 355 | 333 | 367 | 0.91 | 0.158 84 | 0.002 36 | 3.72 | 0.168 51 | 0.005 65 | 2 444 | 25 | 1 575 | 29 | 1 004 | 31 | 243 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-51 | 31 | 107 | 135 | 0.79 | 0.055 10 | 0.001 97 | 0.31 | 0.040 60 | 0.000 51 | 417 | 75 | 271 | 8 | 257 | 3 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-52 | 74 | 54 | 278 | 0.19 | 0.074 23 | 0.001 46 | 1.27 | 0.124 58 | 0.002 39 | 1 048 | 39 | 835 | 14 | 757 | 14 | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-53 | 109 | 404 | 228 | 1.77 | 0.094 44 | 0.003 88 | 0.51 | 0.038 90 | 0.000 43 | 1 517 | 77 | 416 | 14 | 246 | 3 | 169 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-54 | 79 | 293 | 337 | 0.87 | 0.051 77 | 0.001 44 | 0.30 | 0.042 06 | 0.000 44 | 276 | 65 | 266 | 6 | 266 | 3 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-55 | 96 | 310 | 454 | 0.68 | 0.072 84 | 0.002 11 | 0.36 | 0.035 97 | 0.000 38 | 1 009 | 92 | 313 | 8 | 228 | 2 | 138 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-56 | 213 | 355 | 2 081 | 0.17 | 0.057 28 | 0.001 53 | 0.33 | 0.042 08 | 0.000 74 | 502 | 59 | 287 | 6 | 266 | 5 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-57 | 78 | 229 | 204 | 1.12 | 0.072 89 | 0.004 11 | 0.50 | 0.047 97 | 0.000 60 | 1 011 | 115 | 409 | 27 | 302 | 4 | 135 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-58 | 215 | 715 | 1 282 | 0.56 | 0.052 94 | 0.001 17 | 0.28 | 0.038 63 | 0.000 28 | 328 | 50 | 252 | 5 | 244 | 2 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-59 | 227 | 396 | 697 | 0.57 | 0.132 98 | 0.008 75 | 0.89 | 0.044 50 | 0.000 87 | 2 139 | 116 | 645 | 38 | 281 | 5 | 230 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-60 | 508 | 828 | 2 262 | 0.37 | 0.068 73 | 0.000 81 | 1.13 | 0.118 62 | 0.001 31 | 900 | 25 | 767 | 9 | 723 | 8 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-61 | 34 | 140 | 129 | 1.09 | 0.056 40 | 0.003 09 | 0.28 | 0.036 48 | 0.000 50 | 478 | 120 | 253 | 12 | 231 | 3 | 109 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-62 | 219 | 189 | 542 | 0.35 | 0.072 36 | 0.001 33 | 1.23 | 0.123 05 | 0.000 98 | 996 | 33 | 814 | 10 | 748 | 6 | 109 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-63 | 725 | 737 | 1 841 | 0.40 | 0.071 15 | 0.000 77 | 1.48 | 0.150 41 | 0.001 56 | 961 | 22 | 921 | 8 | 903 | 9 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-64 | 299 | 1 160 | 748 | 1.55 | 0.054 12 | 0.001 11 | 0.32 | 0.042 60 | 0.000 49 | 376 | 46 | 280 | 5 | 269 | 3 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-65 | 229 | 189 | 373 | 0.51 | 0.078 98 | 0.001 29 | 1.67 | 0.152 23 | 0.001 28 | 1 172 | 32 | 996 | 13 | 913 | 7 | 109 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-66 | 158 | 733 | 867 | 0.85 | 0.051 96 | 0.001 07 | 0.24 | 0.033 43 | 0.000 25 | 283 | 48 | 218 | 4 | 212 | 2 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-67 | 388 | 1 616 | 744 | 2.17 | 0.068 21 | 0.002 25 | 0.38 | 0.040 19 | 0.000 40 | 876 | 69 | 326 | 9 | 254 | 2 | 128 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-68 | 63 | 242 | 286 | 0.84 | 0.052 52 | 0.001 68 | 0.29 | 0.040 55 | 0.000 45 | 309 | 77 | 262 | 8 | 256 | 3 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-69 | 386 | 1 032 | 1 007 | 1.02 | 0.062 17 | 0.001 04 | 0.67 | 0.077 50 | 0.003 04 | 680 | 37 | 522 | 19 | 481 | 18 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-71 | 287 | 307 | 662 | 0.46 | 0.069 19 | 0.001 02 | 1.24 | 0.129 66 | 0.002 22 | 906 | 63 | 819 | 13 | 786 | 13 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-72 | 333 | 459 | 381 | 1.21 | 0.068 05 | 0.001 23 | 1.16 | 0.123 22 | 0.001 04 | 870 | 38 | 780 | 11 | 749 | 6 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-73 | 76 | 309 | 380 | 0.81 | 0.054 75 | 0.001 52 | 0.29 | 0.038 96 | 0.000 35 | 467 | 61 | 262 | 7 | 246 | 2 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-74 | 803 | 582 | 1 652 | 0.35 | 0.081 38 | 0.001 09 | 1.71 | 0.154 03 | 0.003 23 | 1 231 | 26 | 1 012 | 12 | 923 | 18 | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-75 | 122 | 152 | 131 | 1.16 | 0.074 77 | 0.002 63 | 1.28 | 0.126 12 | 0.001 36 | 1 063 | 70 | 838 | 15 | 766 | 8 | 109 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-76 | 208 | 841 | 706 | 1.19 | 0.055 58 | 0.001 28 | 0.33 | 0.043 33 | 0.000 45 | 435 | 52 | 291 | 6 | 273 | 3 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-77 | 58 | 221 | 245 | 0.90 | 0.049 29 | 0.001 74 | 0.28 | 0.040 74 | 0.000 41 | 161 | 83 | 247 | 8 | 257 | 3 | 96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-78 | 13 | 37 | 53 | 0.69 | 0.065 78 | 0.003 81 | 0.46 | 0.051 07 | 0.000 89 | 798 | 122 | 386 | 20 | 321 | 5 | 120 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-81 | 963 | 758 | 3 370 | 0.22 | 0.066 95 | 0.000 81 | 1.08 | 0.116 29 | 0.001 85 | 835 | 25 | 742 | 11 | 709 | 11 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-82 | 339 | 1 150 | 1 490 | 0.77 | 0.060 83 | 0.001 57 | 0.33 | 0.039 87 | 0.000 42 | 633 | 56 | 293 | 7 | 252 | 3 | 116 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-84 | 593 | 1 866 | 2 774 | 0.67 | 0.065 26 | 0.001 79 | 0.40 | 0.044 59 | 0.000 43 | 783 | 57 | 341 | 7 | 281 | 3 | 121 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-85 | 1 042 | 2 592 | 3 974 | 0.65 | 0.093 63 | 0.010 10 | 0.66 | 0.043 28 | 0.001 05 | 1 502 | 205 | 513 | 66 | 273 | 7 | 188 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-86 | 2 079 | 6 034 | 4 774 | 1.26 | 0.074 86 | 0.001 41 | 0.00 | 0.000 00 | 0.000 00 | 1 065 | 37 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-87 | 698 | 5 241 | 4 007 | 1.31 | 0.070 53 | 0.001 39 | 0.26 | 0.026 52 | 0.000 30 | 944 | 41 | 232 | 4 | 169 | 2 | 138 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 片岩DC1703 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-01 | 46 | 154 | 1 100 | 0.14 | 0.050 54 | 0.000 89 | 0.27 | 0.038 78 | 0.000 36 | 220 | 36 | 243 | 4 | 245 | 2 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-02 | 571 | 668 | 2 455 | 0.27 | 0.091 05 | 0.001 04 | 2.47 | 0.195 80 | 0.002 10 | 1 448 | 22 | 1 262 | 11 | 1 153 | 11 | 126 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-03 | 281 | 1 374 | 1 277 | 1.08 | 0.069 94 | 0.000 71 | 1.55 | 0.160 27 | 0.001 49 | 928 | 20 | 949 | 7 | 958 | 8 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-04 | 107 | 796 | 423 | 1.88 | 0.072 60 | 0.000 92 | 1.55 | 0.154 45 | 0.001 34 | 1 003 | 25 | 949 | 8 | 926 | 7 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-05 | 233 | 78 | 732 | 0.11 | 0.132 80 | 0.001 56 | 5.06 | 0.275 46 | 0.003 70 | 2 135 | 26 | 1 830 | 15 | 1 568 | 19 | 136 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-06 | 260 | 535 | 1 416 | 0.38 | 0.069 57 | 0.000 70 | 1.53 | 0.159 49 | 0.001 53 | 917 | 21 | 943 | 7 | 954 | 8 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-07 | 31 | 417 | 679 | 0.61 | 0.051 34 | 0.001 07 | 0.26 | 0.037 39 | 0.000 45 | 257 | 46 | 238 | 4 | 237 | 3 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-08 | 768 | 129 | 1 433 | 0.09 | 0.170 36 | 0.001 79 | 10.76 | 0.458 32 | 0.004 06 | 2 561 | 23 | 2 503 | 10 | 2 432 | 18 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-09 | 181 | 274 | 932 | 0.29 | 0.075 26 | 0.000 97 | 1.77 | 0.170 75 | 0.001 79 | 1 076 | 26 | 1 034 | 9 | 1 016 | 10 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-10 | 469 | 534 | 1 238 | 0.43 | 0.113 77 | 0.001 37 | 4.89 | 0.312 55 | 0.003 39 | 1 861 | 22 | 1 800 | 9 | 1 753 | 17 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-11 | 544 | 1 337 | 3 252 | 0.41 | 0.072 14 | 0.000 95 | 1.44 | 0.144 63 | 0.002 08 | 991 | 27 | 904 | 9 | 871 | 12 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-12 | 555 | 582 | 832 | 0.70 | 0.184 93 | 0.002 15 | 12.61 | 0.494 91 | 0.005 32 | 2 698 | 19 | 2 651 | 13 | 2 592 | 23 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-13 | 70 | 538 | 273 | 1.97 | 0.072 56 | 0.000 97 | 1.52 | 0.152 39 | 0.001 66 | 1 011 | 26 | 939 | 9 | 914 | 9 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-14 | 237 | 332 | 1 989 | 0.17 | 0.062 59 | 0.000 83 | 0.94 | 0.108 92 | 0.001 10 | 694 | 30 | 672 | 6 | 666 | 6 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-15 | 186 | 287 | 1 769 | 0.16 | 0.060 02 | 0.000 77 | 0.80 | 0.096 39 | 0.000 87 | 606 | 28 | 595 | 5 | 593 | 5 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-16 | 37 | 218 | 831 | 0.26 | 0.054 59 | 0.001 55 | 0.30 | 0.039 27 | 0.000 57 | 394 | 63 | 263 | 8 | 248 | 4 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-17 | 709 | 1 264 | 2 557 | 0.49 | 0.159 30 | 0.001 63 | 4.91 | 0.222 74 | 0.004 01 | 2 450 | 17 | 1 804 | 18 | 1 296 | 21 | 189 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-18 | 128 | 131 | 950 | 0.14 | 0.073 34 | 0.000 94 | 1.24 | 0.123 12 | 0.001 40 | 1 033 | 26 | 821 | 8 | 749 | 8 | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-19 | 361 | 246 | 1 381 | 0.18 | 0.089 39 | 0.001 10 | 2.86 | 0.231 86 | 0.002 36 | 1 413 | 24 | 1 370 | 9 | 1 344 | 12 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-20 | 185 | 297 | 562 | 0.53 | 0.101 98 | 0.001 31 | 3.65 | 0.260 29 | 0.002 97 | 1 661 | 24 | 1 561 | 10 | 1 491 | 15 | 111 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-21 | 39 | 731 | 749 | 0.98 | 0.053 53 | 0.001 17 | 0.28 | 0.038 32 | 0.000 47 | 350 | 48 | 253 | 5 | 242 | 3 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-22 | 53 | 174 | 494 | 0.35 | 0.062 58 | 0.001 11 | 0.80 | 0.093 32 | 0.001 13 | 694 | 38 | 598 | 7 | 575 | 7 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-23 | 141 | 472 | 623 | 0.76 | 0.076 53 | 0.001 10 | 1.84 | 0.174 72 | 0.002 58 | 1 109 | 30 | 1 061 | 11 | 1 038 | 14 | 107 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-24 | 264 | 242 | 418 | 0.58 | 0.171 74 | 0.002 24 | 11.47 | 0.485 03 | 0.004 94 | 2 576 | 22 | 2 562 | 11 | 2 549 | 21 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-25 | 35 | 181 | 808 | 0.22 | 0.051 77 | 0.001 02 | 0.28 | 0.039 62 | 0.000 42 | 276 | 46 | 253 | 4 | 250 | 3 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-26 | 88 | 339 | 282 | 1.20 | 0.087 17 | 0.001 25 | 2.62 | 0.217 58 | 0.002 29 | 1 365 | 27 | 1 305 | 11 | 1 269 | 12 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-27 | 13 | 145 | 203 | 0.71 | 0.133 44 | 0.012 07 | 0.99 | 0.047 27 | 0.001 30 | 2 144 | 159 | 698 | 56 | 298 | 8 | 234 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-28 | 367 | 161 | 1 919 | 0.08 | 0.075 40 | 0.001 11 | 1.86 | 0.179 22 | 0.002 10 | 1 080 | 30 | 1 067 | 10 | 1 063 | 11 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-29 | 217 | 316 | 680 | 0.47 | 0.093 41 | 0.001 13 | 3.41 | 0.264 77 | 0.002 60 | 1 496 | 24 | 1 506 | 9 | 1 514 | 13 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-30 | 574 | 1 000 | 936 | 1.07 | 0.161 44 | 0.002 07 | 9.41 | 0.423 41 | 0.005 27 | 2 472 | 21 | 2 379 | 12 | 2 276 | 24 | 109 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-31 | 324 | 329 | 1 808 | 0.18 | 0.071 45 | 0.000 86 | 1.60 | 0.162 85 | 0.001 80 | 970 | 24 | 972 | 8 | 973 | 10 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-32 | 174 | 178 | 823 | 0.22 | 0.075 72 | 0.000 93 | 1.97 | 0.189 15 | 0.001 91 | 1 087 | 30 | 1 107 | 8 | 1 117 | 10 | 97 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-33 | 219 | 501 | 1 141 | 0.44 | 0.071 64 | 0.000 81 | 1.61 | 0.162 55 | 0.001 63 | 976 | 22 | 972 | 7 | 971 | 9 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-34 | 46 | 66 | 259 | 0.25 | 0.073 06 | 0.001 28 | 1.59 | 0.157 29 | 0.001 72 | 1 017 | 31 | 965 | 12 | 942 | 10 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-35 | 266 | 650 | 1 361 | 0.48 | 0.071 40 | 0.000 82 | 1.61 | 0.163 18 | 0.001 55 | 969 | 23 | 974 | 8 | 974 | 9 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-36 | 73 | 564 | 1 306 | 0.43 | 0.057 34 | 0.001 13 | 0.38 | 0.047 54 | 0.000 55 | 506 | 43 | 324 | 5 | 299 | 3 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-37 | 77 | 271 | 1 678 | 0.16 | 0.052 25 | 0.000 78 | 0.31 | 0.042 47 | 0.000 41 | 298 | 35 | 271 | 3 | 268 | 3 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-38 | 31 | 355 | 488 | 0.73 | 0.053 95 | 0.001 20 | 0.38 | 0.051 01 | 0.000 66 | 369 | 50 | 326 | 6 | 321 | 4 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-39 | 28 | 90 | 663 | 0.14 | 0.053 58 | 0.001 97 | 0.28 | 0.038 69 | 0.000 97 | 354 | 51 | 254 | 7 | 245 | 6 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-40 | 328 | 513 | 1 403 | 0.37 | 0.078 93 | 0.001 05 | 2.17 | 0.199 36 | 0.002 40 | 1 170 | 27 | 1 171 | 10 | 1 172 | 13 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-41 | 185 | 316 | 956 | 0.33 | 0.073 05 | 0.001 05 | 1.67 | 0.165 81 | 0.001 93 | 1 017 | 29 | 997 | 10 | 989 | 11 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-42 | 65 | 114 | 272 | 0.42 | 0.077 22 | 0.001 32 | 2.14 | 0.201 14 | 0.002 07 | 1 128 | 34 | 1 161 | 12 | 1 181 | 11 | 95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-43 | 181 | 1 213 | 1 917 | 0.63 | 0.056 38 | 0.000 83 | 0.59 | 0.076 61 | 0.000 84 | 478 | 31 | 474 | 6 | 476 | 5 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-44 | 331 | 378 | 812 | 0.47 | 0.110 04 | 0.001 21 | 5.07 | 0.334 43 | 0.004 08 | 1 811 | 20 | 1 832 | 11 | 1 860 | 20 | 97 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-45 | 638 | 256 | 1 225 | 0.21 | 0.159 76 | 0.001 95 | 9.42 | 0.427 59 | 0.003 69 | 2 453 | 21 | 2 380 | 12 | 2 295 | 17 | 107 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-46 | 356 | 1 039 | 2 126 | 0.49 | 0.074 33 | 0.001 15 | 1.46 | 0.143 00 | 0.003 06 | 1 050 | 30 | 912 | 13 | 862 | 17 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-47 | 419 | 368 | 1 177 | 0.31 | 0.105 15 | 0.001 23 | 4.46 | 0.307 52 | 0.004 80 | 1 717 | 22 | 1 723 | 14 | 1 729 | 24 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-48 | 79 | 202 | 503 | 0.40 | 0.066 62 | 0.001 07 | 1.23 | 0.133 53 | 0.001 74 | 828 | 34 | 812 | 10 | 808 | 10 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-49 | 95 | 597 | 552 | 1.08 | 0.065 03 | 0.001 02 | 1.09 | 0.121 88 | 0.001 64 | 776 | 33 | 749 | 9 | 741 | 9 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-50 | 139 | 226 | 234 | 0.97 | 0.140 18 | 0.001 81 | 8.11 | 0.420 30 | 0.004 85 | 2 229 | 22 | 2 243 | 12 | 2 262 | 22 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-51 | 76 | 951 | 1 361 | 0.70 | 0.061 08 | 0.001 40 | 0.37 | 0.044 24 | 0.000 48 | 643 | 55 | 320 | 5 | 279 | 3 | 115 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-52 | 181 | 471 | 1 172 | 0.40 | 0.080 39 | 0.001 51 | 1.51 | 0.131 93 | 0.004 58 | 1 206 | 37 | 935 | 27 | 799 | 26 | 117 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-53 | 26 | 204 | 293 | 0.70 | 0.056 87 | 0.001 37 | 0.55 | 0.070 12 | 0.000 84 | 487 | 54 | 444 | 9 | 437 | 5 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-54 | 539 | 611 | 1 339 | 0.46 | 0.115 46 | 0.001 07 | 5.15 | 0.323 97 | 0.003 65 | 1 887 | 18 | 1 845 | 9 | 1 809 | 18 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-55 | 125 | 414 | 1 521 | 0.27 | 0.054 66 | 0.000 78 | 0.55 | 0.073 12 | 0.000 70 | 398 | 33 | 445 | 5 | 455 | 4 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-56 | 50 | 307 | 574 | 0.53 | 0.056 50 | 0.001 23 | 0.56 | 0.072 52 | 0.000 85 | 472 | 44 | 454 | 8 | 451 | 5 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-57 | 54 | 421 | 769 | 0.55 | 0.054 56 | 0.001 10 | 0.42 | 0.056 67 | 0.001 07 | 394 | 44 | 359 | 7 | 355 | 7 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-58 | 363 | 786 | 1 718 | 0.46 | 0.071 93 | 0.000 98 | 1.75 | 0.177 28 | 0.002 12 | 983 | 23 | 1 028 | 8 | 1 052 | 12 | 93 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-59 | 25 | 221 | 527 | 0.42 | 0.051 26 | 0.001 29 | 0.28 | 0.040 20 | 0.000 49 | 254 | 57 | 252 | 5 | 254 | 3 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-60 | 282 | 1 210 | 5 342 | 0.23 | 0.051 86 | 0.000 87 | 0.34 | 0.047 91 | 0.000 71 | 280 | 39 | 299 | 4 | 302 | 4 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-61 | 130 | 1 096 | 1 022 | 1.07 | 0.058 33 | 0.000 84 | 0.74 | 0.092 63 | 0.001 17 | 543 | 31 | 564 | 6 | 571 | 7 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-62 | 43 | 298 | 855 | 0.35 | 0.051 51 | 0.001 04 | 0.31 | 0.044 16 | 0.000 56 | 265 | 46 | 278 | 6 | 279 | 3 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-63 | 69 | 5 871 | 13 304 | 0.44 | 0.045 51 | 0.000 84 | 0.03 | 0.004 52 | 0.000 05 | — | — | 28 | 1 | 29 | 0 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-64 | 380 | 141 | 2 183 | 0.06 | 0.071 14 | 0.000 78 | 1.60 | 0.163 37 | 0.001 87 | 961 | 22 | 971 | 8 | 975 | 10 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-65 | 109 | 186 | 257 | 0.72 | 0.102 52 | 0.001 30 | 4.61 | 0.326 22 | 0.003 59 | 1 670 | 24 | 1 751 | 11 | 1 820 | 17 | 92 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-66 | 16 | 171 | 125 | 1.36 | 0.058 48 | 0.001 68 | 0.67 | 0.083 74 | 0.001 10 | 546 | 63 | 521 | 11 | 518 | 7 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-67 | 55 | 526 | 438 | 1.20 | 0.058 82 | 0.000 96 | 0.73 | 0.089 99 | 0.001 18 | 561 | 35 | 555 | 7 | 555 | 7 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-68 | 204 | 772 | 2 418 | 0.32 | 0.054 78 | 0.000 72 | 0.56 | 0.074 88 | 0.000 86 | 467 | 30 | 454 | 4 | 466 | 5 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-69 | 171 | 430 | 801 | 0.54 | 0.073 42 | 0.000 94 | 1.78 | 0.175 71 | 0.002 31 | 1 026 | 26 | 1 038 | 10 | 1 044 | 13 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-70 | 173 | 215 | 871 | 0.25 | 0.072 90 | 0.001 42 | 1.75 | 0.174 75 | 0.002 27 | 1 013 | 39 | 1 028 | 10 | 1 038 | 12 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-71 | 74 | 157 | 908 | 0.17 | 0.055 56 | 0.000 76 | 0.57 | 0.074 78 | 0.000 73 | 435 | 1 | 460 | 5 | 465 | 4 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-72 | 55 | 511 | 578 | 0.89 | 0.055 95 | 0.000 97 | 0.56 | 0.072 08 | 0.000 81 | 450 | 37 | 449 | 6 | 449 | 5 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-73 | 68 | 294 | 792 | 0.37 | 0.055 07 | 0.000 88 | 0.56 | 0.073 59 | 0.000 73 | 417 | 31 | 451 | 6 | 458 | 4 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-74 | 176 | 330 | 750 | 0.44 | 0.076 17 | 0.000 87 | 2.05 | 0.194 86 | 0.002 02 | 1 100 | 24 | 1 132 | 9 | 1 148 | 11 | 96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-75 | — | — | — | — | 0.059 92 | 0.005 68 | 0.46 | 0.057 91 | 0.003 01 | 611 | 203 | 387 | 31 | 363 | 18 | 107 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-76 | 68 | 209 | 831 | 0.25 | 0.055 05 | 0.000 86 | 0.55 | 0.072 12 | 0.000 78 | 413 | 31 | 443 | 5 | 449 | 5 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-77 | 31 | 363 | 608 | 0.60 | 0.052 31 | 0.000 98 | 0.29 | 0.040 71 | 0.000 37 | 298 | 43 | 261 | 4 | 257 | 2 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-78 | 22 | 204 | 422 | 0.48 | 0.050 03 | 0.001 43 | 0.30 | 0.043 90 | 0.000 70 | 198 | 67 | 268 | 7 | 277 | 4 | 97 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-79 | 98 | 250 | 371 | 0.67 | 0.077 85 | 0.001 05 | 2.21 | 0.206 19 | 0.002 64 | 1 143 | 27 | 1 184 | 9 | 1 208 | 14 | 95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-80 | 178 | 889 | 691 | 1.29 | 0.071 50 | 0.000 86 | 1.78 | 0.180 03 | 0.002 88 | 972 | 25 | 1 037 | 11 | 1 067 | 16 | 91 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-81 | 42 | 430 | 432 | 1.00 | 0.059 64 | 0.001 29 | 0.57 | 0.069 35 | 0.000 89 | 591 | 46 | 457 | 8 | 432 | 5 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-82 | 263 | 485 | 1 316 | 0.37 | 0.071 21 | 0.000 80 | 1.67 | 0.169 42 | 0.001 89 | 965 | 23 | 996 | 8 | 1 009 | 10 | 96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-83 | 91 | 411 | 433 | 0.95 | 0.069 96 | 0.000 99 | 1.50 | 0.155 80 | 0.001 61 | 928 | 34 | 932 | 9 | 933 | 9 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-84 | 153 | 624 | 1 860 | 0.34 | 0.055 88 | 0.000 86 | 0.57 | 0.073 49 | 0.000 86 | 456 | 33 | 455 | 5 | 457 | 5 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-85 | 322 | 2 219 | 3 587 | 0.62 | 0.058 26 | 0.000 72 | 0.58 | 0.072 68 | 0.000 75 | 539 | 21 | 467 | 5 | 452 | 4 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-86 | 58 | 398 | 1 334 | 0.30 | 0.058 29 | 0.001 17 | 0.31 | 0.038 15 | 0.000 40 | 539 | 44 | 273 | 5 | 241 | 2 | 113 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-87 | 276 | 515 | 1 397 | 0.37 | 0.073 15 | 0.000 99 | 1.72 | 0.170 68 | 0.001 97 | 1 018 | 32 | 1 017 | 9 | 1 016 | 11 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-88 | 628 | 502 | 1 563 | 0.32 | 0.116 07 | 0.001 29 | 5.45 | 0.339 83 | 0.003 80 | 1 898 | 20 | 1 892 | 11 | 1 886 | 18 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-89 | 340 | 328 | 872 | 0.38 | 0.113 17 | 0.001 42 | 5.09 | 0.326 23 | 0.003 56 | 1 851 | 23 | 1 834 | 10 | 1 820 | 17 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-90 | 119 | 164 | 394 | 0.42 | 0.091 46 | 0.001 34 | 3.21 | 0.254 06 | 0.002 73 | 1 457 | 28 | 1 459 | 11 | 1 459 | 14 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-91 | 152 | 511 | 1 360 | 0.38 | 0.060 58 | 0.000 81 | 0.81 | 0.097 29 | 0.000 97 | 633 | 30 | 604 | 6 | 599 | 6 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-92 | 435 | 251 | 2 496 | 0.10 | 0.070 75 | 0.000 92 | 1.58 | 0.162 08 | 0.001 67 | 950 | 26 | 963 | 8 | 968 | 9 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-93 | 193 | 191 | 404 | 0.47 | 0.128 58 | 0.001 79 | 6.79 | 0.383 34 | 0.004 80 | 2 080 | 24 | 2 085 | 14 | 2 092 | 22 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-94 | 82 | 337 | 983 | 0.34 | 0.056 27 | 0.000 87 | 0.57 | 0.073 67 | 0.000 85 | 461 | 35 | 459 | 6 | 458 | 5 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-95 | 1 260 | 183 | 2 217 | 0.08 | 0.161 84 | 0.001 82 | 10.94 | 0.490 23 | 0.005 52 | 2 476 | 18 | 2 518 | 12 | 2 572 | 24 | 96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-96 | 88 | 226 | 743 | 0.30 | 0.061 37 | 0.000 89 | 0.88 | 0.103 92 | 0.001 08 | 654 | 31 | 641 | 7 | 637 | 6 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-97 | 1 919 | 2 484 | 2 395 | 1.04 | 0.199 56 | 0.002 55 | 15.02 | 0.546 42 | 0.005 37 | 2 833 | 21 | 2 817 | 11 | 2 810 | 22 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-98 | 67 | 333 | 825 | 0.40 | 0.055 05 | 0.001 07 | 0.52 | 0.069 24 | 0.000 78 | 413 | 44 | 428 | 7 | 432 | 5 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-99 | 44 | 229 | 1 010 | 0.23 | 0.051 24 | 0.001 09 | 0.28 | 0.039 11 | 0.000 43 | 250 | 44 | 247 | 4 | 247 | 3 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-100 | 174 | 442 | 586 | 0.75 | 0.082 82 | 0.001 18 | 2.61 | 0.229 30 | 0.002 68 | 1 265 | 28 | 1 304 | 11 | 1 331 | 14 | 95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 变质砂岩DC1801 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-01 | 2 | 0.090 5 | 1 | 0.10 | 0.764 47 | 0.161 08 | 0.16 | 0.818 10 | 0.197 02 | — | — | 4 840 | 354 | 3 854 | 699 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-02 | 27 | 68 | 161 | 0.43 | 0.067 29 | 0.010 37 | 0.01 | 0.138 15 | 0.009 53 | 856 | 326 | 864 | 93 | 834 | 54 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-03 | 112 | 51 | 669 | 0.08 | 0.070 73 | 0.003 24 | 0.00 | 0.154 69 | 0.004 34 | 950 | 93 | 955 | 28 | 927 | 24 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-04 | 9 | 92 | 137 | 0.67 | 0.053 93 | 0.016 99 | 0.02 | 0.054 34 | 0.002 00 | 369 | 587 | 359 | 104 | 341 | 12 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-05 | 28 | 16 | 144 | 0.11 | 0.135 31 | 0.013 03 | 0.01 | 0.188 03 | 0.010 52 | 2 168 | 169 | 1 554 | 75 | 1 111 | 57 | 195 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-06 | 11 | 0.281 | 2 | 0.18 | 1.647 83 | 0.514 46 | 0.51 | 1.375 95 | 0.415 09 | — | — | 5 596 | 451 | 5 579 | 1 126 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-07 | 17 | 244 | 313 | 0.78 | 0.055 26 | 0.010 85 | 0.01 | 0.044 37 | 0.002 40 | 433 | 376 | 290 | 31 | 280 | 15 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-08 | 13 | 82 | 229 | 0.36 | 0.050 69 | 0.007 54 | 0.01 | 0.048 83 | 0.002 25 | 233 | 306 | 314 | 37 | 307 | 14 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-09 | 24 | 205 | 389 | 0.53 | 0.056 52 | 0.011 07 | 0.01 | 0.054 70 | 0.001 44 | 472 | 385 | 372 | 66 | 343 | 9 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-10 | 9 | 196 | 449 | 0.44 | 0.046 94 | 0.006 63 | 0.01 | 0.017 38 | 0.000 59 | 56 | 298 | 112 | 15 | 111 | 4 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-11 | 41 | 695 | 2 702 | 0.26 | 0.053 64 | 0.008 94 | 0.01 | 0.014 60 | 0.000 85 | 367 | 328 | 107 | 11 | 93 | 5 | 114 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-12 | 89 | 88 | 123 | 0.71 | 0.194 39 | 0.010 32 | 0.01 | 0.538 47 | 0.027 15 | 2 780 | 87 | 2 801 | 57 | 2 777 | 114 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-13 | 42 | 36 | 143 | 0.25 | 0.100 51 | 0.004 96 | 0.00 | 0.259 51 | 0.007 23 | 1 635 | 93 | 1 575 | 38 | 1 487 | 37 | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-14 | 20 | 120 | 336 | 0.36 | 0.052 84 | 0.004 62 | 0.00 | 0.051 16 | 0.001 97 | 320 | 200 | 323 | 20 | 322 | 12 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-15 | 22 | 150 | 403 | 0.37 | 0.051 88 | 0.004 85 | 0.00 | 0.042 02 | 0.001 99 | 280 | 215 | 270 | 20 | 265 | 12 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-16 | 92 | 120 | 290 | 0.42 | 0.152 43 | 0.016 73 | 0.02 | 0.257 29 | 0.024 15 | 2 373 | 188 | 1 935 | 163 | 1 476 | 124 | 161 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-17 | 7 | 71 | 105 | 0.68 | 0.052 59 | 0.007 35 | 0.01 | 0.051 15 | 0.002 76 | 322 | 289 | 316 | 30 | 322 | 17 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-18 | 42 | 104 | 209 | 0.50 | 0.069 35 | 0.004 83 | 0.00 | 0.151 00 | 0.006 79 | 909 | 144 | 935 | 42 | 907 | 38 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-19 | 13 | 68 | 127 | 0.54 | 0.053 22 | 0.006 08 | 0.01 | 0.083 69 | 0.002 90 | 339 | 266 | 507 | 40 | 518 | 17 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-20 | 4 | 22 | 78 | 0.29 | 0.052 26 | 0.009 30 | 0.01 | 0.035 20 | 0.002 01 | 298 | 361 | 229 | 29 | 223 | 13 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-21 | 84 | 230 | 380 | 0.61 | 0.069 86 | 0.005 76 | 0.01 | 0.157 39 | 0.006 26 | 924 | 169 | 960 | 36 | 942 | 35 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-22 | 50 | 402 | 1 712 | 0.23 | 0.046 52 | 0.004 23 | 0.00 | 0.026 63 | 0.001 20 | 33 | 198 | 166 | 12 | 169 | 8 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-23 | 35 | 190 | 657 | 0.29 | 0.049 74 | 0.004 33 | 0.00 | 0.040 22 | 0.001 95 | 183 | 189 | 259 | 17 | 254 | 12 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-24 | 14 | 99 | 236 | 0.42 | 0.057 37 | 0.006 18 | 0.01 | 0.043 76 | 0.001 86 | 506 | 239 | 297 | 22 | 276 | 12 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-25 | 39 | 350 | 499 | 0.70 | 0.053 65 | 0.005 65 | 0.01 | 0.063 13 | 0.002 20 | 367 | 245 | 399 | 33 | 395 | 13 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-26 | 3 | 0.364 | 1 | 0.33 | 0.733 64 | 0.145 15 | 0.15 | 1.069 70 | 0.314 97 | — | — | 4 814 | 245 | 4 689 | 981 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-27 | 3 | 4 | 345 | 0.01 | 0.073 19 | 0.043 23 | 0.04 | 0.009 96 | 0.001 11 | 1 020 | 882 | 74 | 40 | 64 | 7 | 117 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-28 | 9 | 75 | 139 | 0.54 | 0.054 79 | 0.008 22 | 0.01 | 0.051 89 | 0.003 06 | 467 | 338 | 326 | 38 | 326 | 19 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-29 | 1 | 0.004 3 | 0.183 0 | 0.02 | 0.607 43 | 0.117 76 | 0.12 | 1.016 82 | 0.181 23 | 4 526 | 315 | 4 822 | 260 | 4 522 | 579 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-30 | 28 | 146 | 387 | 0.38 | 0.056 14 | 0.006 63 | 0.01 | 0.063 83 | 0.003 00 | 457 | 265 | 405 | 33 | 399 | 18 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-31 | 212 | 565 | 6 281 | 0.09 | 0.049 64 | 0.002 78 | 0.00 | 0.029 05 | 0.001 22 | 189 | 131 | 185 | 11 | 185 | 8 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-32 | 34 | 237 | 730 | 0.32 | 0.051 90 | 0.004 76 | 0.00 | 0.043 15 | 0.001 44 | 280 | 211 | 275 | 22 | 272 | 9 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-33 | 41 | 70 | 428 | 0.16 | 0.061 07 | 0.003 54 | 0.00 | 0.090 61 | 0.003 35 | 643 | 119 | 579 | 23 | 559 | 20 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-34 | 52 | 107 | 819 | 0.13 | 0.054 67 | 0.004 55 | 0.00 | 0.061 46 | 0.002 25 | 398 | 182 | 389 | 21 | 384 | 14 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-35 | 20 | 218 | 303 | 0.72 | 0.053 69 | 0.005 82 | 0.01 | 0.053 78 | 0.003 02 | 367 | 243 | 347 | 39 | 338 | 18 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-36 | 8 | 71 | 127 | 0.56 | 0.057 89 | 0.010 03 | 0.01 | 0.045 23 | 0.002 30 | 524 | 383 | 288 | 22 | 285 | 14 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-37 | 17 | 149 | 478 | 0.31 | 0.046 81 | 0.004 77 | 0.00 | 0.032 47 | 0.001 26 | 39 | 294 | 193 | 13 | 206 | 8 | 94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-38 | 81 | 218 | 507 | 0.43 | 0.066 66 | 0.003 36 | 0.00 | 0.126 57 | 0.005 00 | 828 | 106 | 796 | 33 | 768 | 29 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-39 | 16 | 129 | 286 | 0.45 | 0.054 03 | 0.004 54 | 0.00 | 0.048 82 | 0.001 61 | 372 | 189 | 312 | 19 | 307 | 10 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-40 | 13 | 90 | 211 | 0.42 | 0.052 52 | 0.006 13 | 0.01 | 0.056 74 | 0.001 86 | 309 | 268 | 348 | 31 | 356 | 11 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-41 | 172 | 78 | 542 | 0.14 | 0.108 15 | 0.005 50 | 0.01 | 0.307 11 | 0.012 97 | 1 768 | 93 | 1 773 | 53 | 1 726 | 64 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-42 | 70 | 230 | 168 | 1.37 | 0.103 34 | 0.006 50 | 0.01 | 0.299 33 | 0.012 89 | 1 685 | 117 | 1 708 | 54 | 1 688 | 64 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-43 | 23 | 147 | 248 | 0.59 | 0.056 64 | 0.004 96 | 0.00 | 0.074 59 | 0.003 29 | 476 | 164 | 477 | 33 | 464 | 20 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-44 | 64 | 401 | 656 | 0.61 | 0.059 61 | 0.010 23 | 0.01 | 0.089 41 | 0.002 62 | 591 | 380 | 569 | 70 | 552 | 15 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-45 | 93 | 231 | 381 | 0.61 | 0.146 79 | 0.009 43 | 0.01 | 0.204 09 | 0.008 01 | 2 309 | 111 | 1 679 | 49 | 1 197 | 43 | 193 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-46 | 15 | 104 | 205 | 0.51 | 0.056 47 | 0.007 08 | 0.01 | 0.060 04 | 0.003 83 | 472 | 281 | 395 | 40 | 376 | 23 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-47 | 9 | 132 | 178 | 0.74 | 0.054 46 | 0.006 86 | 0.01 | 0.040 79 | 0.002 02 | 391 | 285 | 267 | 26 | 258 | 13 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-48 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0.92 | 0.306 86 | 0.075 45 | 0.08 | 0.118 48 | 0.013 78 | 3 505 | 390 | 2 150 | 192 | 722 | 79 | 298 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-49 | 30 | 320 | 458 | 0.70 | 0.053 98 | 0.004 30 | 0.00 | 0.043 65 | 0.002 06 | 369 | 175 | 286 | 19 | 275 | 13 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Pb/ (μg/g) | Th/ (μg/g) | U/ (μg/g) | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 207Pb/235U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 谐和度/ % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-50 | 5 | 0.029 3 | 0.013 6 | 2.15 | 0.932 91 | 0.125 23 | 0.13 | 2.401 60 | 1.310 60 | — | — | 5 721 | 509 | 7 892 | 2 484 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-51 | 105 | 79 | 369 | 0.21 | 0.089 45 | 0.004 60 | 0.00 | 0.225 63 | 0.008 06 | 1 414 | 94 | 1 361 | 41 | 1 312 | 42 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-52 | 21 | 157 | 508 | 0.31 | 0.052 42 | 0.004 32 | 0.00 | 0.033 90 | 0.001 25 | 302 | 187 | 227 | 15 | 215 | 8 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-53 | 231 | 126 | 1 287 | 0.10 | 0.076 81 | 0.003 42 | 0.00 | 0.168 73 | 0.005 73 | 1 117 | 85 | 1 050 | 30 | 1 005 | 32 | 111 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-54 | 55 | 351 | 858 | 0.41 | 0.051 01 | 0.003 07 | 0.00 | 0.046 71 | 0.001 89 | 243 | 141 | 295 | 17 | 294 | 12 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-55 | 40 | 105 | 886 | 0.12 | 0.054 25 | 0.003 69 | 0.00 | 0.039 61 | 0.001 52 | 389 | 154 | 261 | 14 | 250 | 9 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-56 | 10 | 116 | 143 | 0.81 | 0.054 23 | 0.006 33 | 0.01 | 0.054 49 | 0.001 90 | 389 | 269 | 350 | 33 | 342 | 12 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-57 | 73 | 408 | 1 072 | 0.38 | 0.053 50 | 0.003 02 | 0.00 | 0.052 84 | 0.002 22 | 350 | 128 | 336 | 16 | 332 | 14 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-58 | 18 | 167 | 355 | 0.47 | 0.057 40 | 0.040 84 | 0.04 | 0.039 37 | 0.002 78 | 506 | 1 085 | 268 | 135 | 249 | 17 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-59 | 157 | 1 146 | 1 496 | 0.77 | 0.059 13 | 0.004 59 | 0.00 | 0.087 84 | 0.004 57 | 572 | 168 | 553 | 25 | 543 | 27 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-60 | 11 | 138 | 241 | 0.57 | 0.052 21 | 0.006 36 | 0.01 | 0.039 57 | 0.001 60 | 295 | 256 | 251 | 24 | 250 | 10 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-61 | 23 | 183 | 373 | 0.49 | 0.049 32 | 0.004 09 | 0.00 | 0.050 03 | 0.001 76 | 165 | 181 | 306 | 20 | 315 | 11 | 97 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-62 | 9 | 76 | 136 | 0.56 | 0.061 46 | 0.010 85 | 0.01 | 0.043 68 | 0.003 05 | 655 | 381 | 284 | 25 | 276 | 19 | 103 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-63 | 113 | 137 | 186 | 0.73 | 0.152 67 | 0.008 84 | 0.01 | 0.418 10 | 0.021 88 | 2 376 | 99 | 2 345 | 60 | 2 252 | 99 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-64 | 23 | 46 | 325 | 0.14 | 0.140 96 | 0.038 24 | 0.04 | 0.046 79 | 0.006 08 | 2 239 | 486 | 659 | 119 | 295 | 37 | 224 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-65 | 44 | 149 | 245 | 0.61 | 0.065 39 | 0.004 76 | 0.00 | 0.128 65 | 0.005 44 | 787 | 152 | 785 | 36 | 780 | 31 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-66 | 188 | 2 221 | 4 125 | 0.54 | 0.048 23 | 0.002 49 | 0.00 | 0.039 78 | 0.001 09 | 109 | 118 | 242 | 10 | 251 | 7 | 96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-67 | 7 | 60 | 109 | 0.55 | 0.054 94 | 0.008 49 | 0.01 | 0.042 34 | 0.002 17 | 409 | 352 | 267 | 20 | 267 | 13 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-68 | 11 | 47 | 134 | 0.35 | 0.107 86 | 0.013 82 | 0.01 | 0.065 14 | 0.003 13 | 1 765 | 236 | 689 | 57 | 407 | 19 | 169 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-69 | 3 | 29 | 48 | 0.61 | 0.060 89 | 0.012 64 | 0.01 | 0.050 87 | 0.002 74 | 635 | 453 | 336 | 45 | 320 | 17 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-70 | 34 | 150 | 896 | 0.17 | 0.046 96 | 0.004 13 | 0.00 | 0.029 63 | 0.001 36 | 56 | 200 | 178 | 13 | 188 | 9 | 95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-71 | 162 | 111 | 1 193 | 0.09 | 0.064 97 | 0.003 32 | 0.00 | 0.112 49 | 0.004 81 | 772 | 108 | 714 | 29 | 687 | 28 | 112 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-72 | 5 | 109 | 220 | 0.50 | 0.065 85 | 0.022 91 | 0.02 | 0.015 25 | 0.000 90 | 1 200 | 199 | 138 | 45 | 98 | 6 | 142 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-73 | 13 | 152 | 230 | 0.66 | 0.056 16 | 0.008 36 | 0.01 | 0.041 07 | 0.002 52 | 457 | 329 | 263 | 25 | 259 | 16 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-74 | 4 | 30 | 79 | 0.38 | 0.060 97 | 0.009 20 | 0.01 | 0.040 90 | 0.002 09 | 639 | 362 | 260 | 18 | 258 | 13 | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-75 | 63 | 195 | 297 | 0.66 | 0.067 06 | 0.003 89 | 0.00 | 0.145 82 | 0.005 66 | 839 | 122 | 871 | 32 | 878 | 32 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-76 | 10 | 27 | 70 | 0.38 | 0.059 22 | 0.006 33 | 0.01 | 0.098 51 | 0.004 54 | 576 | 233 | 598 | 37 | 606 | 27 | 99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

图3 滇西点苍山变质地体三叠纪至侏罗纪沉积地层岩石学特征 (a)变质砂岩DC1801野外特征;(b)碳酸盐岩DC1702和片岩DC1703接触关系;(c)碳酸盐岩DC1702主要矿物组成;(d)片岩DC1703的矿物组成、粒状变晶结构、定向构造;Qtz. 石英;Dol. 白云石;Mus. 白云母。
Fig.3 Petrologic characteristics of the Triassic to Jurassic strata in the Diancangshan metamorphic terrane (DMT), western Yunnan
| 样品 | 年龄/Ma | 176Yb/177Hf | ±2σ | 176Lu/177Hf | ±2σ | 176Hf/177Hf | ±2σ | (176Hf/177Hf)i | εHf(t) | TDMC/Ga | TAMC/Ga |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 碳酸盐岩DC1702 | |||||||||||
| DC1702-01 | 933 | 0.035 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.001 00 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 40 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 38 | 6.91 | 1.36 | 1.18 |
| DC1702-03 | 55 | 0.132 1 | 0.002 6 | 0.003 29 | 0.000 05 | 0.283 10 | 0.000 04 | 0.283 09 | 12.59 | 0.32 | 0.09 |
| DC1702-09 | 268 | 0.102 7 | 0.000 5 | 0.002 87 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 72 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 70 | 3.50 | 1.07 | 0.87 |
| DC1702-11 | 255 | 0.078 5 | 0.002 2 | 0.002 05 | 0.000 05 | 0.282 64 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 63 | 0.48 | 1.25 | 1.06 |
| DC1702-12 | 944 | 0.046 8 | 0.002 2 | 0.001 36 | 0.000 06 | 0.282 35 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 32 | 5.05 | 1.49 | 1.32 |
| DC1702-17 | 2 474 | 0.024 1 | 0.000 4 | 0.000 76 | 0.000 01 | 0.281 39 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 35 | 5.40 | 2.65 | 2.53 |
| DC1702-18 | 246 | 0.041 9 | 0.000 9 | 0.001 20 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 71 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 71 | 3.16 | 1.07 | 0.88 |
| DC1702-21 | 242 | 0.106 5 | 0.000 7 | 0.002 37 | 0.000 06 | 0.283 32 | 0.000 75 | 0.283 31 | 24.44 | -0.30 | -0.56 |
| DC1702-22 | 262 | 0.152 0 | 0.001 4 | 0.004 11 | 0.000 04 | 0.282 77 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 75 | 4.96 | 0.97 | 0.77 |
| DC1702-24 | 261 | 0.048 6 | 0.002 0 | 0.001 46 | 0.000 05 | 0.282 39 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 38 | -8.17 | 1.80 | 1.64 |
| DC1702-28 | 776 | 0.055 9 | 0.000 8 | 0.001 52 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 84 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 81 | 18.64 | 0.50 | 0.28 |
| DC1702-29 | 781 | 0.063 6 | 0.003 3 | 0.001 95 | 0.000 07 | 0.282 65 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 62 | 11.99 | 0.92 | 0.72 |
| DC1702-31 | 523 | 0.077 7 | 0.000 4 | 0.002 58 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 47 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 45 | 0.00 | 1.48 | 1.31 |
| DC1702-33 | 262 | 0.066 6 | 0.003 6 | 0.002 15 | 0.000 13 | 0.282 56 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 55 | -2.21 | 1.42 | 1.25 |
| DC1702-36 | 773 | 0.144 9 | 0.003 8 | 0.001 81 | 0.000 08 | 0.278 44 | 0.002 77 | 0.278 42 | -137.18 | 9.64 | 9.83 |
| DC1702-37 | 265 | 0.057 6 | 0.001 7 | 0.001 97 | 0.000 05 | 0.282 26 | 0.000 04 | 0.282 25 | -12.73 | 2.08 | 1.94 |
| DC1702-41 | 263 | 0.073 9 | 0.000 5 | 0.002 00 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 67 | 0.000 04 | 0.282 66 | 1.85 | 1.17 | 0.98 |
| DC1702-42 | 778 | 0.048 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.001 69 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 31 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 29 | 0.13 | 1.67 | 1.51 |
| DC1702-43 | 262 | 0.095 3 | 0.000 9 | 0.002 70 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 70 | 0.000 04 | 0.282 69 | 2.70 | 1.11 | 0.92 |
| DC1702-46 | 268 | 0.137 0 | 0.002 1 | 0.004 05 | 0.000 06 | 0.282 69 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 67 | 2.27 | 1.14 | 0.96 |
| DC1702-51 | 257 | 0.078 3 | 0.000 9 | 0.002 44 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 72 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 71 | 3.34 | 1.07 | 0.88 |
| DC1702-54 | 266 | 0.107 8 | 0.000 7 | 0.003 32 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 66 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 65 | 1.37 | 1.20 | 1.01 |
| DC1702-58 | 244 | 0.125 2 | 0.001 7 | 0.003 82 | 0.000 03 | 0.283 57 | 0.000 85 | 0.283 55 | 32.89 | -0.85 | -1.14 |
| DC1702-63 | 903 | 0.088 0 | 0.000 7 | 0.002 73 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 39 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 35 | 4.97 | 1.46 | 1.29 |
| DC1702-64 | 269 | 0.082 5 | 0.003 9 | 0.002 20 | 0.000 07 | 0.282 12 | 0.001 40 | 0.282 11 | -17.67 | 2.39 | 2.26 |
| DC1702-66 | 212 | 0.041 8 | 0.000 5 | 0.001 34 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 32 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 32 | -11.39 | 1.96 | 1.81 |
| DC1702-72 | 749 | 0.077 9 | 0.002 5 | 0.002 54 | 0.000 07 | 0.282 41 | 0.000 05 | 0.282 37 | 2.40 | 1.50 | 1.33 |
| DC1702-77 | 257 | 0.062 0 | 0.000 6 | 0.001 78 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 63 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 62 | 0.35 | 1.26 | 1.07 |
| DC1702-81 | 709 | 0.036 4 | 0.000 3 | 0.001 14 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 43 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 42 | 3.18 | 1.42 | 1.25 |
| 片岩DC1703 | |||||||||||
| DC1703-1 | 245 | 0.022 5 | 0.000 1 | 0.000 49 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 35 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 35 | -9.69 | 1.88 | 1.73 |
| DC1703-3 | 958 | 0.024 8 | 0.000 3 | 0.000 56 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 00 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 99 | -6.59 | 2.23 | 2.09 |
| DC1703-4 | 926 | 0.011 3 | 0.000 3 | 0.000 24 | 0.000 01 | 0.281 53 | 0.000 01 | 0.281 53 | -23.53 | 3.24 | 3.15 |
| DC1703-11 | 871 | 0.030 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.000 72 | 0.000 01 | 0.281 95 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 94 | -10.19 | 2.38 | 2.25 |
| DC1703-12 | 2 698 | 0.043 0 | 0.000 6 | 0.000 99 | 0.000 01 | 0.281 08 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 03 | -1.13 | 3.22 | 3.13 |
| DC1703-15 | 593 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 12 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 31 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 31 | -3.28 | 1.74 | 1.58 |
| DC1703-16 | 248 | 0.079 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.001 80 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 35 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 34 | -9.83 | 1.89 | 1.74 |
| DC1703-20 | 1 661 | 0.032 2 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 78 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 95 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 92 | 6.90 | 1.93 | 1.78 |
| DC1703-22 | 575 | 0.025 5 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 56 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 57 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 56 | 5.26 | 1.19 | 1.00 |
| DC1703-23 | 1 109 | 0.137 9 | 0.000 8 | 0.002 83 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 40 | 0.000 04 | 0.282 34 | 9.25 | 1.35 | 1.17 |
| DC1703-25 | 250 | 0.035 5 | 0.000 6 | 0.000 78 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 31 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 31 | -11.01 | 1.97 | 1.82 |
| DC1703-26 | 1 365 | 0.025 6 | 0.000 1 | 0.000 57 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 60 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 59 | -11.69 | 2.85 | 2.74 |
| DC1703-29 | 1 496 | 0.020 7 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 45 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 99 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 97 | 5.02 | 1.92 | 1.76 |
| DC1703-31 | 973 | 0.009 8 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 22 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 09 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 08 | -2.89 | 2.01 | 1.86 |
| DC1703-33 | 971 | 0.051 7 | 0.002 1 | 0.001 05 | 0.000 05 | 0.281 90 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 88 | -10.19 | 2.46 | 2.33 |
| DC1703-34 | 942 | 0.031 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.000 68 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 75 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 74 | -15.83 | 2.78 | 2.67 |
| DC1703-38 | 321 | 0.026 8 | 0.001 3 | 0.000 78 | 0.000 04 | 0.282 73 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 72 | 5.27 | 0.99 | 0.80 |
| 样品 | 年龄/Ma | 176Yb/177Hf | ±2σ | 176Lu/177Hf | ±2σ | 176Hf/177Hf | ±2σ | (176Hf/177Hf)i | εHf(t) | TDMC/Ga | TAMC/Ga |
| DC1703-40 | 1 170 | 0.077 0 | 0.001 6 | 0.001 71 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 12 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 08 | 1.37 | 1.88 | 1.73 |
| DC1703-41 | 989 | 0.033 7 | 0.000 4 | 0.000 77 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 18 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 17 | 0.29 | 1.81 | 1.65 |
| DC1703-42 | 1 128 | 0.025 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.000 62 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 35 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 33 | 9.34 | 1.35 | 1.17 |
| DC1703-45 | 2 453 | 0.042 1 | 0.000 5 | 0.000 90 | 0.000 01 | 0.280 99 | 0.000 02 | 0.280 95 | -9.26 | 3.54 | 3.46 |
| DC1703-47 | 1 717 | 0.060 3 | 0.000 2 | 0.001 42 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 87 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 83 | 4.89 | 2.09 | 1.95 |
| DC1703-50 | 2 229 | 0.013 3 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 32 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 24 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 22 | -4.73 | 3.09 | 2.99 |
| DC1703-54 | 1 887 | 0.025 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.000 60 | 0.000 01 | 0.281 49 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 46 | -4.12 | 2.78 | 2.67 |
| DC1703-55 | 455 | 0.051 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.001 16 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 36 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 35 | -5.31 | 1.74 | 1.58 |
| DC1703-56 | 451 | 0.021 4 | 0.000 1 | 0.000 62 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 40 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 39 | -3.92 | 1.65 | 1.49 |
| DC1703-60 | 302 | 0.037 3 | 0.000 3 | 0.001 19 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 43 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 42 | -6.24 | 1.68 | 1.52 |
| DC1703-62 | 279 | 0.050 3 | 0.000 3 | 0.001 20 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 21 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 20 | -14.42 | 2.17 | 2.04 |
| DC1703-63 | 29 | 0.054 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.001 18 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 77 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 77 | 0.26 | 1.06 | 0.87 |
| DC1703-65 | 1 670 | 0.019 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.000 47 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 83 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 81 | 3.18 | 2.16 | 2.02 |
| DC1703-67 | 555 | 0.011 9 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 27 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 11 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 11 | -11.47 | 2.20 | 2.07 |
| DC1703-68 | 466 | 0.028 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.000 73 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 27 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 26 | -8.09 | 1.92 | 1.77 |
| DC1703-70 | 1 013 | 0.027 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.000 62 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 23 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 22 | 2.80 | 1.67 | 1.51 |
| DC1703-72 | 449 | 0.050 5 | 0.000 4 | 0.001 16 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 36 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 35 | -5.31 | 1.74 | 1.58 |
| DC1703-74 | 1 100 | 0.054 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.001 25 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 98 | 0.000 03 | 0.281 96 | -4.62 | 2.20 | 2.06 |
| DC1703-75 | 363 | 0.054 4 | 0.000 6 | 0.001 31 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 43 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 42 | -4.69 | 1.63 | 1.47 |
| DC1703-80 | 1 067 | 0.026 5 | 0.000 4 | 0.000 59 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 05 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 04 | -2.48 | 2.04 | 1.90 |
| DC1703-81 | 432 | 0.029 7 | 0.000 4 | 0.000 65 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 23 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 22 | -10.27 | 2.03 | 1.89 |
| DC1703-85 | 452 | 0.032 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.000 81 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 27 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 27 | -8.31 | 1.93 | 1.78 |
| DC1703-89 | 1 851 | 0.043 3 | 0.001 0 | 0.001 11 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 57 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 53 | -2.72 | 2.67 | 2.55 |
| DC1703-95 | 2 476 | 0.032 8 | 0.000 3 | 0.000 71 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 04 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 01 | -6.57 | 3.39 | 3.31 |
| DC1703-97 | 2 833 | 0.115 7 | 0.001 6 | 0.002 42 | 0.000 03 | 0.281 16 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 03 | 2.57 | 3.12 | 3.02 |
| DC1703-100 | 1 265 | 0.026 5 | 0.000 1 | 0.000 62 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 79 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 78 | -7.33 | 2.50 | 2.37 |
| 变质砂岩DC1801 | |||||||||||
| DC1801-08 | 307 | 0.058 0 | 0.000 6 | 0.001 97 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 49 | 0.000 05 | 0.282 48 | -3.65 | 1.55 | 1.38 |
| DC1801-10 | 111 | 0.028 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.000 95 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 68 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 68 | -0.86 | 1.22 | 1.04 |
| DC1801-14 | 322 | 0.025 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.000 96 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 81 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 80 | 8.17 | 0.81 | 0.61 |
| DC1801-17 | 322 | 0.039 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.001 36 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 57 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 56 | -0.49 | 1.36 | 1.18 |
| DC1801-21 | 942 | 0.029 0 | 0.000 7 | 0.000 94 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 10 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 08 | -3.66 | 2.03 | 1.88 |
| DC1801-22 | 169 | 0.040 7 | 0.000 8 | 0.001 28 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 12 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 12 | -19.33 | 2.42 | 2.29 |
| DC1801-23 | 254 | 0.052 3 | 0.000 8 | 0.001 62 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 75 | 0.000 04 | 0.282 74 | 4.38 | 1.00 | 0.80 |
| DC1801-28 | 326 | 0.072 2 | 0.001 2 | 0.002 25 | 0.000 04 | 0.282 48 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 46 | -3.76 | 1.57 | 1.40 |
| DC1801-39 | 307 | 0.035 7 | 0.000 6 | 0.000 90 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 71 | 0.000 28 | 0.282 71 | 4.48 | 1.03 | 0.84 |
| DC1801-41 | 1 726 | 0.060 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.001 82 | 0.000 01 | 0.281 53 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 47 | -7.69 | 2.88 | 2.77 |
| DC1801-52 | 215 | 0.043 3 | 0.000 4 | 0.001 29 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 53 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 53 | -3.89 | 1.49 | 1.32 |
| DC1801-54 | 294 | 0.038 2 | 0.000 4 | 0.001 15 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 36 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 35 | -8.33 | 1.83 | 1.68 |
| DC1801-56 | 342 | 0.053 1 | 0.000 1 | 0.001 64 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 95 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 94 | 13.49 | 0.49 | 0.27 |
| DC1801-60 | 250 | 0.040 7 | 0.000 5 | 0.001 25 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 66 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 66 | 1.41 | 1.18 | 1.00 |
| DC1801-62 | 276 | 0.028 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.000 94 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 75 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 74 | 5.10 | 0.97 | 0.77 |
| DC1801-63 | 2 376 | 0.043 0 | 0.000 4 | 0.001 27 | 0.000 01 | 0.281 30 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 24 | -0.93 | 2.96 | 2.86 |
| DC1801-69 | 320 | 0.038 4 | 0.000 1 | 0.001 14 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 56 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 55 | -0.66 | 1.37 | 1.19 |
| DC1801-70 | 188 | 0.050 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.001 56 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 65 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 64 | -0.45 | 1.26 | 1.07 |
| DC1801-74 | 258 | 0.106 3 | 0.001 3 | 0.002 84 | 0.000 04 | 0.283 16 | 0.000 03 | 0.283 15 | 19.00 | 0.07 | -0.17 |
| DC1801-75 | 878 | 0.033 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.000 91 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 92 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 91 | -11.20 | 2.45 | 2.32 |
表2 点苍山变质地体三叠纪至侏罗纪沉积岩碎屑锆石Lu-Hf同位素组成
Table 2 Lu-Hf isotopic data for the detrital zircons from the Triassic to Jurassic sedimentary rocks in the DMT
| 样品 | 年龄/Ma | 176Yb/177Hf | ±2σ | 176Lu/177Hf | ±2σ | 176Hf/177Hf | ±2σ | (176Hf/177Hf)i | εHf(t) | TDMC/Ga | TAMC/Ga |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 碳酸盐岩DC1702 | |||||||||||
| DC1702-01 | 933 | 0.035 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.001 00 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 40 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 38 | 6.91 | 1.36 | 1.18 |
| DC1702-03 | 55 | 0.132 1 | 0.002 6 | 0.003 29 | 0.000 05 | 0.283 10 | 0.000 04 | 0.283 09 | 12.59 | 0.32 | 0.09 |
| DC1702-09 | 268 | 0.102 7 | 0.000 5 | 0.002 87 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 72 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 70 | 3.50 | 1.07 | 0.87 |
| DC1702-11 | 255 | 0.078 5 | 0.002 2 | 0.002 05 | 0.000 05 | 0.282 64 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 63 | 0.48 | 1.25 | 1.06 |
| DC1702-12 | 944 | 0.046 8 | 0.002 2 | 0.001 36 | 0.000 06 | 0.282 35 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 32 | 5.05 | 1.49 | 1.32 |
| DC1702-17 | 2 474 | 0.024 1 | 0.000 4 | 0.000 76 | 0.000 01 | 0.281 39 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 35 | 5.40 | 2.65 | 2.53 |
| DC1702-18 | 246 | 0.041 9 | 0.000 9 | 0.001 20 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 71 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 71 | 3.16 | 1.07 | 0.88 |
| DC1702-21 | 242 | 0.106 5 | 0.000 7 | 0.002 37 | 0.000 06 | 0.283 32 | 0.000 75 | 0.283 31 | 24.44 | -0.30 | -0.56 |
| DC1702-22 | 262 | 0.152 0 | 0.001 4 | 0.004 11 | 0.000 04 | 0.282 77 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 75 | 4.96 | 0.97 | 0.77 |
| DC1702-24 | 261 | 0.048 6 | 0.002 0 | 0.001 46 | 0.000 05 | 0.282 39 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 38 | -8.17 | 1.80 | 1.64 |
| DC1702-28 | 776 | 0.055 9 | 0.000 8 | 0.001 52 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 84 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 81 | 18.64 | 0.50 | 0.28 |
| DC1702-29 | 781 | 0.063 6 | 0.003 3 | 0.001 95 | 0.000 07 | 0.282 65 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 62 | 11.99 | 0.92 | 0.72 |
| DC1702-31 | 523 | 0.077 7 | 0.000 4 | 0.002 58 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 47 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 45 | 0.00 | 1.48 | 1.31 |
| DC1702-33 | 262 | 0.066 6 | 0.003 6 | 0.002 15 | 0.000 13 | 0.282 56 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 55 | -2.21 | 1.42 | 1.25 |
| DC1702-36 | 773 | 0.144 9 | 0.003 8 | 0.001 81 | 0.000 08 | 0.278 44 | 0.002 77 | 0.278 42 | -137.18 | 9.64 | 9.83 |
| DC1702-37 | 265 | 0.057 6 | 0.001 7 | 0.001 97 | 0.000 05 | 0.282 26 | 0.000 04 | 0.282 25 | -12.73 | 2.08 | 1.94 |
| DC1702-41 | 263 | 0.073 9 | 0.000 5 | 0.002 00 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 67 | 0.000 04 | 0.282 66 | 1.85 | 1.17 | 0.98 |
| DC1702-42 | 778 | 0.048 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.001 69 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 31 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 29 | 0.13 | 1.67 | 1.51 |
| DC1702-43 | 262 | 0.095 3 | 0.000 9 | 0.002 70 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 70 | 0.000 04 | 0.282 69 | 2.70 | 1.11 | 0.92 |
| DC1702-46 | 268 | 0.137 0 | 0.002 1 | 0.004 05 | 0.000 06 | 0.282 69 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 67 | 2.27 | 1.14 | 0.96 |
| DC1702-51 | 257 | 0.078 3 | 0.000 9 | 0.002 44 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 72 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 71 | 3.34 | 1.07 | 0.88 |
| DC1702-54 | 266 | 0.107 8 | 0.000 7 | 0.003 32 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 66 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 65 | 1.37 | 1.20 | 1.01 |
| DC1702-58 | 244 | 0.125 2 | 0.001 7 | 0.003 82 | 0.000 03 | 0.283 57 | 0.000 85 | 0.283 55 | 32.89 | -0.85 | -1.14 |
| DC1702-63 | 903 | 0.088 0 | 0.000 7 | 0.002 73 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 39 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 35 | 4.97 | 1.46 | 1.29 |
| DC1702-64 | 269 | 0.082 5 | 0.003 9 | 0.002 20 | 0.000 07 | 0.282 12 | 0.001 40 | 0.282 11 | -17.67 | 2.39 | 2.26 |
| DC1702-66 | 212 | 0.041 8 | 0.000 5 | 0.001 34 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 32 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 32 | -11.39 | 1.96 | 1.81 |
| DC1702-72 | 749 | 0.077 9 | 0.002 5 | 0.002 54 | 0.000 07 | 0.282 41 | 0.000 05 | 0.282 37 | 2.40 | 1.50 | 1.33 |
| DC1702-77 | 257 | 0.062 0 | 0.000 6 | 0.001 78 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 63 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 62 | 0.35 | 1.26 | 1.07 |
| DC1702-81 | 709 | 0.036 4 | 0.000 3 | 0.001 14 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 43 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 42 | 3.18 | 1.42 | 1.25 |
| 片岩DC1703 | |||||||||||
| DC1703-1 | 245 | 0.022 5 | 0.000 1 | 0.000 49 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 35 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 35 | -9.69 | 1.88 | 1.73 |
| DC1703-3 | 958 | 0.024 8 | 0.000 3 | 0.000 56 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 00 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 99 | -6.59 | 2.23 | 2.09 |
| DC1703-4 | 926 | 0.011 3 | 0.000 3 | 0.000 24 | 0.000 01 | 0.281 53 | 0.000 01 | 0.281 53 | -23.53 | 3.24 | 3.15 |
| DC1703-11 | 871 | 0.030 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.000 72 | 0.000 01 | 0.281 95 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 94 | -10.19 | 2.38 | 2.25 |
| DC1703-12 | 2 698 | 0.043 0 | 0.000 6 | 0.000 99 | 0.000 01 | 0.281 08 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 03 | -1.13 | 3.22 | 3.13 |
| DC1703-15 | 593 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 12 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 31 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 31 | -3.28 | 1.74 | 1.58 |
| DC1703-16 | 248 | 0.079 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.001 80 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 35 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 34 | -9.83 | 1.89 | 1.74 |
| DC1703-20 | 1 661 | 0.032 2 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 78 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 95 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 92 | 6.90 | 1.93 | 1.78 |
| DC1703-22 | 575 | 0.025 5 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 56 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 57 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 56 | 5.26 | 1.19 | 1.00 |
| DC1703-23 | 1 109 | 0.137 9 | 0.000 8 | 0.002 83 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 40 | 0.000 04 | 0.282 34 | 9.25 | 1.35 | 1.17 |
| DC1703-25 | 250 | 0.035 5 | 0.000 6 | 0.000 78 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 31 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 31 | -11.01 | 1.97 | 1.82 |
| DC1703-26 | 1 365 | 0.025 6 | 0.000 1 | 0.000 57 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 60 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 59 | -11.69 | 2.85 | 2.74 |
| DC1703-29 | 1 496 | 0.020 7 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 45 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 99 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 97 | 5.02 | 1.92 | 1.76 |
| DC1703-31 | 973 | 0.009 8 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 22 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 09 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 08 | -2.89 | 2.01 | 1.86 |
| DC1703-33 | 971 | 0.051 7 | 0.002 1 | 0.001 05 | 0.000 05 | 0.281 90 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 88 | -10.19 | 2.46 | 2.33 |
| DC1703-34 | 942 | 0.031 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.000 68 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 75 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 74 | -15.83 | 2.78 | 2.67 |
| DC1703-38 | 321 | 0.026 8 | 0.001 3 | 0.000 78 | 0.000 04 | 0.282 73 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 72 | 5.27 | 0.99 | 0.80 |
| 样品 | 年龄/Ma | 176Yb/177Hf | ±2σ | 176Lu/177Hf | ±2σ | 176Hf/177Hf | ±2σ | (176Hf/177Hf)i | εHf(t) | TDMC/Ga | TAMC/Ga |
| DC1703-40 | 1 170 | 0.077 0 | 0.001 6 | 0.001 71 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 12 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 08 | 1.37 | 1.88 | 1.73 |
| DC1703-41 | 989 | 0.033 7 | 0.000 4 | 0.000 77 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 18 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 17 | 0.29 | 1.81 | 1.65 |
| DC1703-42 | 1 128 | 0.025 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.000 62 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 35 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 33 | 9.34 | 1.35 | 1.17 |
| DC1703-45 | 2 453 | 0.042 1 | 0.000 5 | 0.000 90 | 0.000 01 | 0.280 99 | 0.000 02 | 0.280 95 | -9.26 | 3.54 | 3.46 |
| DC1703-47 | 1 717 | 0.060 3 | 0.000 2 | 0.001 42 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 87 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 83 | 4.89 | 2.09 | 1.95 |
| DC1703-50 | 2 229 | 0.013 3 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 32 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 24 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 22 | -4.73 | 3.09 | 2.99 |
| DC1703-54 | 1 887 | 0.025 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.000 60 | 0.000 01 | 0.281 49 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 46 | -4.12 | 2.78 | 2.67 |
| DC1703-55 | 455 | 0.051 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.001 16 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 36 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 35 | -5.31 | 1.74 | 1.58 |
| DC1703-56 | 451 | 0.021 4 | 0.000 1 | 0.000 62 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 40 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 39 | -3.92 | 1.65 | 1.49 |
| DC1703-60 | 302 | 0.037 3 | 0.000 3 | 0.001 19 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 43 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 42 | -6.24 | 1.68 | 1.52 |
| DC1703-62 | 279 | 0.050 3 | 0.000 3 | 0.001 20 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 21 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 20 | -14.42 | 2.17 | 2.04 |
| DC1703-63 | 29 | 0.054 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.001 18 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 77 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 77 | 0.26 | 1.06 | 0.87 |
| DC1703-65 | 1 670 | 0.019 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.000 47 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 83 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 81 | 3.18 | 2.16 | 2.02 |
| DC1703-67 | 555 | 0.011 9 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 27 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 11 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 11 | -11.47 | 2.20 | 2.07 |
| DC1703-68 | 466 | 0.028 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.000 73 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 27 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 26 | -8.09 | 1.92 | 1.77 |
| DC1703-70 | 1 013 | 0.027 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.000 62 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 23 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 22 | 2.80 | 1.67 | 1.51 |
| DC1703-72 | 449 | 0.050 5 | 0.000 4 | 0.001 16 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 36 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 35 | -5.31 | 1.74 | 1.58 |
| DC1703-74 | 1 100 | 0.054 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.001 25 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 98 | 0.000 03 | 0.281 96 | -4.62 | 2.20 | 2.06 |
| DC1703-75 | 363 | 0.054 4 | 0.000 6 | 0.001 31 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 43 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 42 | -4.69 | 1.63 | 1.47 |
| DC1703-80 | 1 067 | 0.026 5 | 0.000 4 | 0.000 59 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 05 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 04 | -2.48 | 2.04 | 1.90 |
| DC1703-81 | 432 | 0.029 7 | 0.000 4 | 0.000 65 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 23 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 22 | -10.27 | 2.03 | 1.89 |
| DC1703-85 | 452 | 0.032 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.000 81 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 27 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 27 | -8.31 | 1.93 | 1.78 |
| DC1703-89 | 1 851 | 0.043 3 | 0.001 0 | 0.001 11 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 57 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 53 | -2.72 | 2.67 | 2.55 |
| DC1703-95 | 2 476 | 0.032 8 | 0.000 3 | 0.000 71 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 04 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 01 | -6.57 | 3.39 | 3.31 |
| DC1703-97 | 2 833 | 0.115 7 | 0.001 6 | 0.002 42 | 0.000 03 | 0.281 16 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 03 | 2.57 | 3.12 | 3.02 |
| DC1703-100 | 1 265 | 0.026 5 | 0.000 1 | 0.000 62 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 79 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 78 | -7.33 | 2.50 | 2.37 |
| 变质砂岩DC1801 | |||||||||||
| DC1801-08 | 307 | 0.058 0 | 0.000 6 | 0.001 97 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 49 | 0.000 05 | 0.282 48 | -3.65 | 1.55 | 1.38 |
| DC1801-10 | 111 | 0.028 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.000 95 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 68 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 68 | -0.86 | 1.22 | 1.04 |
| DC1801-14 | 322 | 0.025 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.000 96 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 81 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 80 | 8.17 | 0.81 | 0.61 |
| DC1801-17 | 322 | 0.039 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.001 36 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 57 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 56 | -0.49 | 1.36 | 1.18 |
| DC1801-21 | 942 | 0.029 0 | 0.000 7 | 0.000 94 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 10 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 08 | -3.66 | 2.03 | 1.88 |
| DC1801-22 | 169 | 0.040 7 | 0.000 8 | 0.001 28 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 12 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 12 | -19.33 | 2.42 | 2.29 |
| DC1801-23 | 254 | 0.052 3 | 0.000 8 | 0.001 62 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 75 | 0.000 04 | 0.282 74 | 4.38 | 1.00 | 0.80 |
| DC1801-28 | 326 | 0.072 2 | 0.001 2 | 0.002 25 | 0.000 04 | 0.282 48 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 46 | -3.76 | 1.57 | 1.40 |
| DC1801-39 | 307 | 0.035 7 | 0.000 6 | 0.000 90 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 71 | 0.000 28 | 0.282 71 | 4.48 | 1.03 | 0.84 |
| DC1801-41 | 1 726 | 0.060 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.001 82 | 0.000 01 | 0.281 53 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 47 | -7.69 | 2.88 | 2.77 |
| DC1801-52 | 215 | 0.043 3 | 0.000 4 | 0.001 29 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 53 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 53 | -3.89 | 1.49 | 1.32 |
| DC1801-54 | 294 | 0.038 2 | 0.000 4 | 0.001 15 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 36 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 35 | -8.33 | 1.83 | 1.68 |
| DC1801-56 | 342 | 0.053 1 | 0.000 1 | 0.001 64 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 95 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 94 | 13.49 | 0.49 | 0.27 |
| DC1801-60 | 250 | 0.040 7 | 0.000 5 | 0.001 25 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 66 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 66 | 1.41 | 1.18 | 1.00 |
| DC1801-62 | 276 | 0.028 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.000 94 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 75 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 74 | 5.10 | 0.97 | 0.77 |
| DC1801-63 | 2 376 | 0.043 0 | 0.000 4 | 0.001 27 | 0.000 01 | 0.281 30 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 24 | -0.93 | 2.96 | 2.86 |
| DC1801-69 | 320 | 0.038 4 | 0.000 1 | 0.001 14 | 0.000 01 | 0.282 56 | 0.000 02 | 0.282 55 | -0.66 | 1.37 | 1.19 |
| DC1801-70 | 188 | 0.050 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.001 56 | 0.000 00 | 0.282 65 | 0.000 03 | 0.282 64 | -0.45 | 1.26 | 1.07 |
| DC1801-74 | 258 | 0.106 3 | 0.001 3 | 0.002 84 | 0.000 04 | 0.283 16 | 0.000 03 | 0.283 15 | 19.00 | 0.07 | -0.17 |
| DC1801-75 | 878 | 0.033 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.000 91 | 0.000 00 | 0.281 92 | 0.000 02 | 0.281 91 | -11.20 | 2.45 | 2.32 |
| 样品 | La/ | Ce/ | Pr/ | Nd/ | Sm/ | Eu/ | Gd/ | Tb/ | Dy/ | Ho/ | Er/ | Tm/ | Yb/ | Lu/ | Eu/ Eu* | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | |||||||||||||||||||
| 碳酸盐岩DC1702 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-01 | 0.001 | 11.68 | 0.04 | 0.83 | 2.89 | 0.25 | 19.18 | 7.20 | 92.1 | 36.1 | 163.1 | 34.9 | 315.5 | 60.2 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-02 | 0.003 | 6.11 | 0.06 | 1.14 | 2.24 | 0.20 | 13.70 | 4.93 | 64.0 | 25.0 | 117.3 | 26.2 | 239.9 | 43.4 | 0.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-03 | 14.26 | 58.84 | 4.36 | 25.90 | 26.08 | 0.42 | 130.82 | 41.88 | 468.4 | 164.3 | 650.2 | 120.5 | 968.7 | 153.9 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-04 | 0.004 | 6.28 | 0.06 | 1.01 | 2.88 | 0.36 | 20.33 | 6.88 | 86.2 | 34.4 | 152.8 | 32.5 | 292.5 | 55.2 | 0.14 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-05 | 3.33 | 46.66 | 2.27 | 18.67 | 23.46 | 4.44 | 79.15 | 28.88 | 374.8 | 161.0 | 790.9 | 166.1 | 1 336.5 | 202.7 | 0.31 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-06 | 1.61 | 53.43 | 1.45 | 12.28 | 16.56 | 6.28 | 70.18 | 23.50 | 256.3 | 86.8 | 356.5 | 70.4 | 609.3 | 106.4 | 0.56 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-07 | 0.09 | 17.15 | 0.28 | 3.90 | 8.24 | 0.69 | 46.74 | 16.63 | 205.6 | 80.1 | 357.8 | 73.6 | 660.6 | 121.8 | 0.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-08 | 4.06 | 72.25 | 9.18 | 86.69 | 94.99 | 41.29 | 226.21 | 64.92 | 579.6 | 155.3 | 564.3 | 108.3 | 907.5 | 139.1 | 0.86 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-09 | 4.27 | 21.69 | 0.92 | 5.16 | 5.27 | 0.57 | 26.58 | 9.27 | 113.3 | 42.7 | 185.6 | 38.9 | 346.4 | 62.1 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-10 | 0.02 | 17.17 | 0.13 | 2.21 | 6.56 | 0.35 | 45.00 | 17.57 | 224.3 | 91.8 | 415.8 | 82.3 | 704.7 | 120.2 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-11 | 0.20 | 15.69 | 0.44 | 7.08 | 14.20 | 0.62 | 74.64 | 24.18 | 279.0 | 103.3 | 426.3 | 82.5 | 682.3 | 113.8 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-12 | 0.003 | 20.52 | 0.11 | 2.62 | 8.55 | 0.21 | 56.16 | 21.99 | 279.4 | 111.9 | 494.5 | 102.9 | 924.7 | 167.0 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-13 | 0.02 | 1.81 | 0.10 | 2.43 | 6.49 | 0.41 | 43.87 | 15.74 | 191.2 | 70.3 | 296.0 | 56.4 | 485.0 | 91.5 | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-14 | 0.07 | 90.05 | 0.35 | 6.33 | 13.68 | 1.12 | 97.09 | 37.06 | 461.5 | 176.7 | 759.3 | 152.7 | 1 270.1 | 206.0 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-15 | 0.05 | 10.30 | 0.12 | 2.13 | 3.83 | 0.57 | 21.88 | 7.65 | 94.2 | 38.6 | 183.9 | 41.0 | 395.0 | 85.2 | 0.19 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-16 | 0.04 | 1.08 | 0.07 | 1.40 | 3.70 | 1.69 | 15.88 | 4.65 | 36.2 | 9.2 | 30.9 | 5.2 | 47.0 | 10.3 | 0.67 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-17 | 0.01 | 13.74 | 0.10 | 2.39 | 3.26 | 0.90 | 16.38 | 4.84 | 54.6 | 20.9 | 98.8 | 21.7 | 209.6 | 42.9 | 0.38 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-18 | 0.92 | 30.61 | 1.29 | 12.48 | 15.11 | 4.11 | 58.34 | 21.67 | 256.8 | 97.7 | 439.3 | 91.7 | 819.6 | 146.2 | 0.42 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-19 | 0.66 | 15.41 | 0.40 | 4.37 | 8.55 | 0.14 | 53.31 | 22.26 | 282.5 | 115.2 | 532.9 | 113.0 | 1 027.0 | 188.7 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-20 | 2.70 | 28.64 | 2.76 | 20.76 | 23.18 | 9.24 | 66.58 | 22.91 | 229.2 | 68.4 | 293.5 | 69.0 | 681.7 | 123.5 | 0.72 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-21 | 55.85 | 150.83 | 14.78 | 67.45 | 32.23 | 4.64 | 113.50 | 40.15 | 457.1 | 161.9 | 665.7 | 129.0 | 1 019.2 | 168.1 | 0.23 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-22 | 0.72 | 70.25 | 0.93 | 12.69 | 25.95 | 3.16 | 139.99 | 48.44 | 562.1 | 195.1 | 777.6 | 140.7 | 1 072.7 | 159.6 | 0.16 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-23 | 28.35 | 79.79 | 7.93 | 34.40 | 10.15 | 0.62 | 24.13 | 7.41 | 82.7 | 29.5 | 125.1 | 25.6 | 223.4 | 39.8 | 0.12 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-26 | 1.56 | 41.51 | 1.34 | 10.97 | 14.54 | 2.93 | 78.38 | 30.11 | 362.4 | 137.8 | 603.6 | 120.9 | 1 027.0 | 174.5 | 0.27 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-27 | 5.14 | 41.33 | 2.68 | 24.32 | 28.44 | 1.90 | 117.96 | 33.32 | 335.3 | 113.3 | 428.5 | 77.5 | 620.5 | 105.0 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-28 | 1.35 | 18.24 | 0.76 | 5.31 | 6.40 | 0.17 | 42.47 | 17.88 | 241.3 | 100.7 | 474.6 | 103.7 | 982.0 | 187.1 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-29 | 0.24 | 12.69 | 0.23 | 2.16 | 3.57 | 0.09 | 26.28 | 11.08 | 159.7 | 68.2 | 326.2 | 73.2 | 706.2 | 132.6 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-31 | 0.68 | 14.20 | 0.77 | 4.19 | 4.68 | 0.09 | 32.04 | 15.53 | 228.3 | 96.9 | 496.3 | 121.8 | 1 257.0 | 247.4 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-32 | 5.64 | 194.78 | 9.50 | 93.28 | 120.35 | 38.66 | 349.12 | 114.12 | 1 190.4 | 379.5 | 1 472.8 | 264.5 | 1 998.2 | 288.7 | 0.58 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-33 | 0.04 | 12.06 | 0.11 | 1.21 | 2.70 | 0.33 | 14.89 | 5.71 | 68.4 | 27.3 | 126.9 | 28.8 | 276.7 | 54.3 | 0.16 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-34 | 0.09 | 23.56 | 0.10 | 2.07 | 4.12 | 1.08 | 21.00 | 6.81 | 78.2 | 29.8 | 138.1 | 29.2 | 278.6 | 58.2 | 0.35 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-35 | 0.01 | 21.49 | 0.06 | 1.33 | 2.95 | 0.27 | 16.31 | 6.46 | 81.6 | 31.8 | 156.8 | 35.1 | 334.5 | 66.3 | 0.12 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-36 | 0.41 | 18.36 | 0.37 | 4.59 | 7.21 | 2.00 | 35.23 | 11.61 | 137.9 | 51.5 | 237.1 | 50.9 | 471.9 | 96.1 | 0.38 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-37 | 0.08 | 64.68 | 0.36 | 7.02 | 13.92 | 0.98 | 68.01 | 21.84 | 250.2 | 89.0 | 386.6 | 78.0 | 659.2 | 110.8 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-38 | 0.48 | 13.34 | 0.75 | 9.47 | 24.59 | 12.64 | 119.65 | 33.95 | 273.9 | 65.1 | 210.2 | 36.4 | 306.0 | 58.4 | 0.71 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-41 | 1.22 | 52.86 | 1.24 | 10.64 | 14.50 | 5.08 | 66.76 | 22.83 | 247.9 | 83.7 | 350.8 | 71.1 | 607.3 | 103.2 | 0.50 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-42 | 11.62 | 47.15 | 3.16 | 15.17 | 5.19 | 0.90 | 19.06 | 6.72 | 84.5 | 35.3 | 181.6 | 43.0 | 427.7 | 92.1 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-43 | 0.06 | 50.68 | 0.54 | 7.44 | 15.92 | 1.31 | 104.21 | 40.64 | 530.8 | 207.1 | 930.8 | 190.1 | 1 550.9 | 247.9 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-44 | 0.02 | 18.09 | 0.07 | 1.42 | 2.91 | 0.36 | 18.19 | 6.79 | 89.4 | 36.0 | 177.8 | 39.9 | 376.5 | 71.5 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-45 | 0.01 | 2.47 | 0.03 | 0.77 | 3.66 | 0.20 | 33.16 | 12.91 | 154.8 | 55.6 | 239.8 | 48.4 | 419.6 | 79.5 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-46 | 0.22 | 113.30 | 1.63 | 24.13 | 40.12 | 1.47 | 188.45 | 61.25 | 699.9 | 247.4 | 1 079.9 | 216.9 | 1 878.9 | 330.5 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | La/ | Ce/ | Pr/ | Nd/ | Sm/ | Eu/ | Gd/ | Tb/ | Dy/ | Ho/ | Er/ | Tm/ | Yb/ | Lu/ | Eu/ Eu* | |||||||||||||||||
| (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | |||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-47 | 0.36 | 34.63 | 0.52 | 6.44 | 10.36 | 1.18 | 53.97 | 19.42 | 236.7 | 91.3 | 413.5 | 83.7 | 718.2 | 130.3 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-48 | 0.09 | 14.03 | 0.16 | 2.74 | 4.82 | 0.26 | 28.43 | 9.77 | 124.2 | 46.9 | 213.5 | 41.9 | 359.8 | 67.3 | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-49 | 52.30 | 364.07 | 18.06 | 113.08 | 103.05 | 21.54 | 375.11 | 120.99 | 1 245.0 | 384.5 | 1 467.9 | 260.9 | 1 960.0 | 292.3 | 0.33 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-50 | 0.17 | 27.49 | 0.30 | 3.91 | 5.03 | 1.32 | 21.27 | 6.24 | 68.6 | 25.8 | 119.3 | 26.3 | 256.8 | 54.9 | 0.39 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-51 | 0.02 | 8.22 | 0.13 | 2.27 | 3.92 | 0.28 | 19.79 | 6.87 | 82.7 | 31.3 | 139.0 | 29.1 | 261.0 | 48.7 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-52 | 0.22 | 9.43 | 0.23 | 1.55 | 2.51 | 0.29 | 14.39 | 5.55 | 67.9 | 26.6 | 122.1 | 26.4 | 243.5 | 46.9 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-53 | 0.45 | 26.68 | 0.59 | 8.93 | 12.97 | 1.66 | 54.62 | 15.17 | 154.6 | 52.6 | 214.8 | 40.7 | 332.8 | 65.1 | 0.19 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-54 | 0.03 | 32.88 | 0.44 | 7.28 | 14.87 | 0.86 | 80.50 | 27.06 | 326.3 | 118.8 | 503.8 | 96.8 | 780.1 | 130.7 | 0.08 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-55 | 0.60 | 31.03 | 0.54 | 5.40 | 7.25 | 1.12 | 37.89 | 13.46 | 168.7 | 64.8 | 295.8 | 60.7 | 514.6 | 97.5 | 0.21 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-56 | 2.24 | 33.98 | 2.10 | 16.98 | 16.94 | 7.34 | 44.65 | 14.62 | 151.4 | 52.0 | 240.9 | 54.9 | 524.6 | 96.3 | 0.82 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-57 | 6.45 | 36.45 | 2.40 | 13.74 | 8.88 | 1.47 | 33.30 | 10.99 | 129.8 | 48.6 | 222.0 | 46.7 | 422.4 | 81.9 | 0.26 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-58 | 52.87 | 136.20 | 8.61 | 35.48 | 21.18 | 3.65 | 72.69 | 24.75 | 290.5 | 113.1 | 551.7 | 124.6 | 1 180.3 | 241.1 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-59 | 0.36 | 14.37 | 0.61 | 3.59 | 5.35 | 1.72 | 24.10 | 8.21 | 93.4 | 34.0 | 150.0 | 32.2 | 286.6 | 52.2 | 0.46 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-60 | 6.54 | 79.93 | 9.56 | 51.85 | 37.90 | 1.87 | 75.18 | 27.18 | 320.9 | 117.3 | 558.0 | 125.7 | 1 179.3 | 229.3 | 0.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-61 | 0.09 | 16.30 | 0.30 | 4.45 | 6.44 | 2.27 | 31.51 | 9.68 | 111.7 | 43.6 | 198.8 | 44.4 | 422.2 | 83.9 | 0.49 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-62 | 0.10 | 9.63 | 0.08 | 1.68 | 4.66 | 0.14 | 31.90 | 12.82 | 171.3 | 72.1 | 345.2 | 73.7 | 678.8 | 136.1 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-63 | 2.51 | 43.93 | 3.82 | 20.84 | 19.05 | 0.69 | 77.05 | 31.66 | 405.3 | 163.0 | 754.6 | 162.7 | 1 452.5 | 267.9 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-64 | 0.18 | 22.23 | 0.33 | 5.57 | 9.01 | 1.68 | 45.12 | 15.14 | 169.5 | 61.9 | 260.4 | 51.6 | 429.3 | 79.0 | 0.25 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-65 | 0.18 | 11.05 | 0.08 | 1.50 | 3.83 | 0.18 | 31.04 | 12.11 | 156.6 | 62.7 | 295.2 | 62.5 | 564.4 | 107.8 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-66 | 0.09 | 10.50 | 0.72 | 12.21 | 25.97 | 1.68 | 142.69 | 47.00 | 517.7 | 182.2 | 729.1 | 137.9 | 1 127.4 | 201.0 | 0.08 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-67 | 0.22 | 85.99 | 1.06 | 17.87 | 34.09 | 8.45 | 166.19 | 50.89 | 540.9 | 190.0 | 763.1 | 149.3 | 1 236.4 | 217.9 | 0.34 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-68 | 0.51 | 23.68 | 0.71 | 8.69 | 13.48 | 0.82 | 71.73 | 23.44 | 268.3 | 99.2 | 413.9 | 81.9 | 682.2 | 117.0 | 0.08 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-69 | 4.28 | 25.20 | 2.78 | 18.10 | 14.60 | 6.51 | 42.56 | 13.23 | 145.6 | 56.3 | 267.7 | 61.9 | 643.9 | 164.8 | 0.80 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-71 | 0.74 | 23.55 | 0.90 | 6.79 | 8.57 | 0.37 | 41.09 | 15.73 | 199.4 | 79.3 | 363.3 | 78.6 | 709.8 | 138.6 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-72 | 21.82 | 78.74 | 7.79 | 40.63 | 13.95 | 2.33 | 41.82 | 11.54 | 132.7 | 49.6 | 222.4 | 46.7 | 424.3 | 87.6 | 0.29 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-73 | 0.06 | 10.67 | 0.20 | 3.41 | 6.85 | 1.09 | 41.33 | 14.65 | 181.2 | 73.3 | 330.9 | 69.8 | 635.6 | 121.0 | 0.20 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-76 | 0.36 | 53.17 | 0.77 | 11.28 | 20.66 | 0.68 | 94.07 | 30.96 | 350.5 | 127.5 | 539.4 | 107.8 | 924.3 | 167.1 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-77 | 0.05 | 30.04 | 0.53 | 9.10 | 18.34 | 0.73 | 103.85 | 33.14 | 369.8 | 131.9 | 529.0 | 98.5 | 806.1 | 137.2 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-78 | 0.004 | 6.94 | 0.04 | 0.69 | 1.74 | 0.36 | 11.28 | 3.72 | 47.1 | 19.1 | 92.2 | 20.9 | 197.5 | 38.9 | 0.25 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-81 | 6.10 | 86.90 | 4.96 | 34.24 | 52.46 | 1.07 | 258.34 | 88.00 | 933.4 | 308.9 | 1 248.7 | 243.1 | 2 205.1 | 419.7 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-82 | 2.01 | 69.79 | 1.38 | 14.68 | 19.90 | 5.47 | 86.33 | 30.60 | 382.7 | 134.0 | 604.0 | 126.6 | 1 161.7 | 213.2 | 0.40 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-84 | 10.01 | 91.80 | 3.17 | 20.47 | 22.76 | 2.51 | 119.39 | 49.24 | 656.0 | 261.5 | 1 264.2 | 271.0 | 2 472.2 | 402.8 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-85 | 35.18 | 153.35 | 11.35 | 66.60 | 47.00 | 11.21 | 171.25 | 56.86 | 640.6 | 226.0 | 1 070.0 | 236.4 | 2 303.4 | 432.4 | 0.38 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-86 | 16.64 | 434.80 | 42.24 | 419.16 | 454.50 | 180.71 | 1 013.00 | 265.82 | 2 337.1 | 626.9 | 2 251.9 | 403.9 | 3 303.9 | 503.8 | 0.81 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-87 | 20.07 | 221.95 | 22.63 | 180.17 | 172.24 | 71.11 | 374.24 | 98.07 | 855.2 | 225.5 | 855.6 | 177.0 | 1 589.7 | 266.4 | 0.86 | |||||||||||||||||
| 糜棱岩化片岩DC1703 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-01 | 0.03 | 2.31 | 0.14 | 4.24 | 15.58 | 0.64 | 84.68 | 36.85 | 364.8 | 107.6 | 382.4 | 79.9 | 740.0 | 102.4 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-02 | 0.06 | 19.39 | 0.36 | 6.61 | 15.65 | 0.57 | 72.96 | 35.07 | 448.0 | 173.8 | 778.6 | 186.2 | 1 942.7 | 289.2 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-03 | 5.02 | 68.27 | 1.73 | 9.95 | 11.64 | 0.65 | 43.64 | 18.59 | 221.9 | 80.1 | 331.8 | 76.0 | 750.4 | 106.2 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-04 | 0.72 | 56.13 | 3.58 | 41.34 | 45.52 | 16.92 | 97.45 | 27.61 | 224.4 | 59.2 | 202.1 | 39.2 | 366.9 | 49.0 | 0.78 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-05 | 0.01 | 22.95 | 0.07 | 1.99 | 3.36 | 0.55 | 14.85 | 6.88 | 90.8 | 35.9 | 163.7 | 40.4 | 451.3 | 67.7 | 0.24 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-06 | — | 68.58 | 0.09 | 2.84 | 6.05 | 2.64 | 27.08 | 11.66 | 146.1 | 56.3 | 263.2 | 68.3 | 823.3 | 137.0 | 0.63 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-07 | 0.02 | 40.40 | 0.10 | 2.73 | 4.72 | 2.08 | 17.59 | 7.56 | 99.5 | 38.0 | 179.3 | 48.5 | 575.7 | 102.3 | 0.70 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | La/ | Ce/ | Pr/ | Nd/ | Sm/ | Eu/ | Gd/ | Tb/ | Dy/ | Ho/ | Er/ | Tm/ | Yb/ | Lu/ | Eu/ Eu* | |||||||||||||||||
| (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | |||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-08 | 0.01 | 14.63 | 0.01 | 0.78 | 1.59 | 0.66 | 8.35 | 4.45 | 61.9 | 25.3 | 120.5 | 32.0 | 368.5 | 56.1 | 0.55 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-09 | 0.47 | 8.56 | 0.82 | 12.83 | 22.48 | 1.42 | 83.76 | 35.10 | 426.8 | 152.0 | 624.2 | 143.8 | 1 448.7 | 207.8 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-10 | — | 23.89 | 0.35 | 6.69 | 13.25 | 0.82 | 46.40 | 18.51 | 213.1 | 75.6 | 304.8 | 67.7 | 676.7 | 92.4 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-11 | 0.63 | 19.92 | 1.30 | 16.04 | 27.10 | 2.01 | 82.58 | 34.07 | 398.2 | 137.7 | 594.4 | 139.5 | 1 426.5 | 209.3 | 0.13 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-12 | 0.11 | 31.68 | 1.07 | 17.06 | 32.67 | 6.49 | 115.87 | 45.20 | 512.8 | 170.6 | 675.8 | 144.3 | 1 383.9 | 190.1 | 0.32 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-15 | 0.02 | 8.05 | 0.27 | 5.70 | 15.72 | 1.15 | 58.27 | 21.11 | 180.1 | 44.4 | 140.4 | 25.7 | 224.0 | 27.5 | 0.12 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-16 | 0.20 | 3.42 | 0.29 | 4.78 | 13.77 | 0.36 | 86.14 | 48.14 | 641.7 | 249.6 | 1 086.9 | 2 47.3 | 2 498.7 | 354.5 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-17 | 2.49 | 100.69 | 4.95 | 40.02 | 40.06 | 15.24 | 80.52 | 31.33 | 315.0 | 94.8 | 365.0 | 79.3 | 738.7 | 103.1 | 0.82 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-18 | 0.03 | 2.03 | 0.14 | 2.68 | 7.14 | 0.27 | 41.52 | 24.88 | 339.8 | 132.8 | 604.0 | 144.9 | 1 456.6 | 215.4 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-19 | 0.12 | 5.02 | 0.22 | 5.69 | 19.17 | 0.60 | 76.40 | 28.16 | 237.3 | 56.2 | 165.8 | 28.1 | 228.5 | 26.8 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-20 | 3.77 | 46.15 | 1.48 | 11.42 | 11.37 | 1.24 | 47.27 | 22.29 | 296.7 | 114.7 | 511.4 | 117.6 | 1 223.2 | 176.3 | 0.16 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-21 | 1.19 | 12.62 | 1.21 | 17.86 | 34.22 | 0.95 | 133.09 | 58.75 | 673.6 | 249.6 | 1 022.4 | 229.2 | 2 265.4 | 321.0 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-22 | 0.07 | 25.53 | 0.20 | 4.89 | 10.61 | 1.48 | 38.30 | 16.90 | 186.1 | 66.1 | 263.0 | 59.1 | 596.3 | 85.6 | 0.22 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-23 | 0.37 | 29.07 | 1.72 | 32.96 | 60.08 | 13.66 | 215.02 | 89.29 | 965.9 | 317.8 | 1 213.2 | 252.2 | 2 303.4 | 307.6 | 0.37 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-24 | 0.13 | 32.37 | 0.52 | 6.14 | 7.40 | 1.31 | 18.70 | 6.64 | 68.7 | 22.8 | 97.9 | 23.0 | 255.6 | 40.6 | 0.34 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-25 | 0.05 | 2.82 | 0.16 | 4.14 | 15.94 | 0.47 | 92.50 | 53.92 | 719.3 | 281.3 | 1 248.0 | 289.2 | 2 867.4 | 412.4 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-26 | 3.28 | 174.82 | 1.05 | 10.08 | 14.21 | 3.69 | 47.79 | 19.31 | 210.9 | 74.1 | 302.0 | 67.6 | 684.4 | 101.0 | 0.43 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-27 | 421.30 | 952.83 | 114.82 | 492.09 | 85.76 | 13.92 | 88.97 | 13.26 | 112.6 | 36.2 | 156.3 | 37.6 | 419.7 | 65.6 | 0.49 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-28 | — | 2.94 | 0.04 | 1.19 | 4.54 | 0.33 | 20.03 | 9.98 | 115.2 | 40.2 | 175.6 | 44.6 | 524.1 | 85.0 | 0.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-29 | 0.01 | 35.30 | 0.10 | 2.18 | 5.36 | 1.34 | 23.75 | 11.14 | 137.1 | 49.6 | 211.8 | 48.9 | 509.4 | 75.4 | 0.36 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-30 | 0.41 | 56.84 | 2.25 | 29.75 | 38.81 | 3.87 | 111.37 | 39.97 | 422.8 | 137.2 | 520.2 | 106.8 | 1 050.2 | 142.4 | 0.18 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-31 | — | 5.15 | 0.13 | 2.58 | 8.64 | 0.26 | 40.09 | 20.19 | 214.9 | 68.2 | 245.4 | 50.5 | 479.2 | 67.7 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-32 | — | 2.97 | 0.11 | 4.26 | 12.87 | 0.31 | 64.39 | 30.92 | 359.6 | 122.2 | 464.9 | 100.4 | 981.7 | 138.6 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-33 | 0.04 | 9.81 | 0.47 | 7.91 | 17.18 | 0.75 | 61.55 | 24.83 | 242.8 | 71.7 | 250.0 | 50.1 | 443.1 | 60.3 | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-34 | 0.02 | 13.81 | 0.12 | 2.90 | 7.44 | 0.91 | 44.97 | 27.64 | 380.2 | 137.9 | 541.6 | 108.5 | 920.0 | 123.9 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-35 | — | 18.92 | 0.16 | 4.46 | 11.49 | 0.49 | 60.70 | 30.12 | 381.5 | 139.8 | 589.5 | 133.0 | 1 328.9 | 186.8 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-36 | 134.72 | 287.41 | 34.94 | 144.22 | 36.40 | 5.75 | 60.42 | 19.39 | 214.8 | 77.6 | 344.4 | 80.2 | 821.1 | 130.5 | 0.37 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-39 | 0.06 | 1.89 | 0.19 | 2.22 | 6.75 | 0.17 | 44.39 | 28.65 | 361.6 | 140.5 | 638.8 | 150.5 | 1 591.2 | 215.6 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-40 | 0.19 | 11.52 | 0.38 | 7.52 | 17.35 | 0.81 | 79.04 | 42.09 | 572.3 | 226.3 | 1 025.9 | 244.9 | 2 554.4 | 376.6 | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-41 | — | 10.41 | 0.13 | 2.86 | 7.33 | 0.25 | 37.22 | 20.51 | 276.2 | 110.5 | 489.0 | 117.6 | 1 232.5 | 179.9 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-42 | 0.01 | 20.73 | 0.21 | 4.65 | 8.58 | 2.30 | 31.40 | 13.99 | 170.3 | 63.2 | 274.6 | 65.7 | 697.3 | 104.0 | 0.43 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-43 | 0.14 | 89.40 | 0.60 | 11.03 | 18.75 | 4.94 | 65.21 | 28.21 | 358.7 | 142.6 | 650.2 | 161.8 | 1 789.2 | 280.9 | 0.43 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-44 | 0.08 | 16.76 | 0.20 | 4.59 | 12.03 | 0.94 | 55.19 | 28.52 | 358.5 | 140.4 | 604.1 | 136.3 | 1 396.8 | 206.9 | 0.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-45 | 0.01 | 21.55 | 0.42 | 7.32 | 9.26 | 2.20 | 29.61 | 11.68 | 124.4 | 41.9 | 170.1 | 39.1 | 416.9 | 61.6 | 0.41 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-46 | 1.68 | 19.94 | 2.82 | 29.08 | 39.65 | 6.03 | 123.74 | 55.77 | 629.6 | 214.1 | 854.6 | 178.8 | 1 666.8 | 234.5 | 0.26 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-47 | 0.21 | 20.71 | 0.61 | 7.42 | 10.72 | 2.02 | 41.50 | 24.38 | 337.0 | 139.6 | 648.9 | 160.8 | 1 745.8 | 259.7 | 0.29 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-48 | 0.09 | 26.64 | 0.21 | 4.83 | 14.28 | 10.08 | 58.40 | 21.68 | 190.2 | 54.8 | 191.1 | 39.0 | 382.9 | 54.3 | 1.07 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-49 | 0.03 | 299.80 | 0.52 | 13.09 | 33.82 | 14.80 | 170.89 | 77.04 | 981.6 | 374.4 | 1 541.0 | 344.9 | 3 365.3 | 503.2 | 0.60 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-50 | — | 49.99 | 0.06 | 2.53 | 4.61 | 0.98 | 16.84 | 7.28 | 84.4 | 32.8 | 142.7 | 33.9 | 365.3 | 54.8 | 0.34 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-51 | 31.16 | 143.92 | 16.88 | 103.02 | 53.25 | 2.14 | 104.85 | 37.87 | 423.4 | 153.1 | 640.6 | 137.8 | 1 336.4 | 201.8 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-52 | 7.88 | 59.35 | 6.74 | 46.63 | 30.65 | 5.92 | 62.83 | 25.74 | 303.7 | 114.3 | 507.0 | 122.5 | 1 346.0 | 206.3 | 0.41 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-53 | 0.10 | 20.59 | 0.17 | 4.14 | 12.40 | 2.28 | 50.94 | 24.65 | 300.3 | 114.7 | 501.7 | 114.2 | 1 157.1 | 175.1 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-54 | 0.06 | 8.65 | 0.27 | 5.76 | 15.17 | 0.13 | 61.60 | 28.08 | 331.4 | 119.4 | 493.5 | 108.2 | 1 050.5 | 151.0 | 0.013 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | La/ | Ce/ | Pr/ | Nd/ | Sm/ | Eu/ | Gd/ | Tb/ | Dy/ | Ho/ | Er/ | Tm/ | Yb/ | Lu/ | Eu/ Eu* | |||||||||||||||||
| (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | |||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-55 | 0.02 | 9.78 | 0.11 | 3.12 | 8.53 | 0.29 | 50.47 | 28.40 | 371.8 | 151.4 | 700.3 | 168.0 | 1 741.9 | 258.4 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-56 | 0.36 | 14.64 | 0.09 | 1.26 | 1.88 | 0.82 | 7.51 | 4.05 | 55.5 | 23.6 | 126.6 | 35.3 | 464.2 | 86.6 | 0.67 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-57 | — | 13.67 | 0.34 | 7.27 | 17.73 | 2.20 | 83.22 | 39.87 | 500.9 | 185.3 | 798.3 | 173.7 | 1 723.1 | 251.9 | 0.18 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-58 | 0.04 | 43.24 | 0.24 | 5.64 | 10.87 | 2.62 | 38.52 | 18.52 | 231.9 | 93.0 | 431.6 | 104.9 | 1 170.6 | 182.1 | 0.39 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-59 | 0.12 | 3.50 | 0.26 | 5.58 | 14.83 | 0.32 | 74.68 | 36.80 | 469.1 | 179.0 | 791.9 | 181.2 | 1 820.0 | 260.8 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-60 | — | 42.93 | 0.10 | 2.53 | 4.64 | 0.44 | 16.72 | 8.53 | 111.9 | 49.0 | 249.2 | 71.7 | 869.0 | 137.1 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-63 | 0.04 | 38.68 | 0.35 | 9.29 | 39.13 | 2.52 | 195.85 | 82.97 | 863.7 | 268.3 | 1 017.3 | 207.0 | 1 919.0 | 264.6 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-64 | 0.14 | 3.08 | 0.05 | 0.86 | 1.16 | 0.21 | 9.24 | 6.53 | 98.1 | 37.3 | 161.3 | 34.3 | 322.1 | 48.2 | 0.20 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-65 | 0.05 | 54.72 | 0.51 | 10.15 | 18.35 | 4.37 | 46.33 | 17.48 | 180.9 | 62.8 | 269.4 | 62.9 | 644.4 | 102.8 | 0.46 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-66 | 0.08 | 10.81 | 0.16 | 4.75 | 9.84 | 1.38 | 39.69 | 18.10 | 221.9 | 78.6 | 337.1 | 73.8 | 750.7 | 107.8 | 0.21 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-67 | 0.10 | 73.04 | 0.56 | 9.22 | 13.17 | 2.57 | 34.42 | 12.87 | 126.2 | 39.0 | 151.0 | 32.3 | 312.7 | 43.9 | 0.37 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-68 | 0.02 | 18.07 | 0.05 | 1.81 | 3.92 | 0.59 | 18.30 | 10.50 | 144.7 | 61.1 | 306.9 | 79.5 | 928.4 | 149.9 | 0.21 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-69 | — | 56.60 | 0.25 | 5.74 | 12.30 | 0.51 | 52.81 | 25.58 | 318.9 | 120.1 | 509.2 | 113.4 | 1 109.6 | 159.2 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-70 | — | 12.68 | 0.41 | 7.17 | 13.64 | 1.03 | 44.44 | 19.00 | 217.1 | 78.6 | 338.8 | 76.7 | 762.0 | 111.7 | 0.13 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-71 | 0.06 | 3.54 | 0.11 | 3.05 | 11.05 | 0.58 | 68.38 | 44.96 | 657.2 | 264.7 | 1 248.3 | 290.1 | 2 989.9 | 436.1 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-72 | 0.003 | 40.18 | 0.70 | 14.00 | 23.69 | 5.69 | 76.35 | 33.28 | 384.6 | 138.6 | 588.4 | 132.0 | 1 316.5 | 191.5 | 0.41 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-73 | 0.06 | 5.29 | 0.99 | 18.77 | 33.60 | 1.55 | 112.71 | 40.27 | 366.1 | 102.8 | 363.8 | 75.0 | 743.0 | 104.8 | 0.08 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-74 | 0.05 | 5.70 | 0.18 | 5.30 | 13.87 | 0.40 | 68.83 | 33.37 | 423.6 | 157.5 | 684.2 | 153.1 | 1 533.2 | 224.2 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-75 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-76 | — | 4.79 | 0.24 | 5.08 | 16.35 | 0.51 | 86.23 | 51.08 | 701.8 | 274.5 | 1 246.3 | 278.8 | 2 844.1 | 404.0 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-77 | 0.15 | 15.22 | 1.15 | 18.82 | 30.04 | 4.67 | 68.63 | 21.13 | 165.3 | 37.1 | 102.1 | 16.6 | 133.5 | 15.7 | 0.31 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-78 | 0.04 | 32.71 | 0.19 | 3.51 | 7.34 | 1.90 | 22.29 | 10.76 | 127.1 | 48.7 | 227.6 | 58.3 | 670.8 | 104.3 | 0.45 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-79 | 0.01 | 120.37 | 0.20 | 6.57 | 14.97 | 2.82 | 56.35 | 27.48 | 342.8 | 124.9 | 554.9 | 125.5 | 1 310.4 | 189.2 | 0.30 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-80 | 0.20 | 39.56 | 0.92 | 14.65 | 27.18 | 2.36 | 88.12 | 39.16 | 441.1 | 149.3 | 612.5 | 122.0 | 1 206.8 | 165.2 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-81 | 38.65 | 136.45 | 12.91 | 70.84 | 43.91 | 4.67 | 86.14 | 32.03 | 327.4 | 108.5 | 429.8 | 90.2 | 880.1 | 125.3 | 0.23 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-82 | 0.05 | 26.60 | 0.06 | 2.08 | 5.32 | 0.13 | 22.98 | 13.85 | 183.8 | 72.1 | 326.2 | 73.2 | 740.6 | 106.7 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-83 | 0.01 | 15.95 | 0.42 | 6.08 | 12.74 | 0.50 | 38.82 | 17.23 | 194.0 | 69.4 | 290.5 | 64.3 | 648.7 | 94.2 | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-84 | 0.03 | 38.82 | 0.17 | 4.19 | 10.53 | 2.00 | 49.17 | 27.52 | 382.3 | 159.7 | 786.9 | 202.7 | 2 381.6 | 380.4 | 0.27 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-87 | 0.04 | 10.85 | 0.27 | 5.11 | 16.16 | 0.32 | 71.69 | 38.77 | 468.2 | 171.1 | 717.5 | 159.8 | 1 602.6 | 216.6 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-88 | 0.03 | 10.90 | 0.26 | 6.06 | 14.89 | 0.29 | 62.67 | 32.12 | 400.1 | 153.6 | 660.6 | 149.2 | 1 471.9 | 215.6 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-89 | — | 5.99 | 0.38 | 7.94 | 17.52 | 0.27 | 76.23 | 38.96 | 478.3 | 177.4 | 731.9 | 159.6 | 1 559.1 | 225.7 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-90 | 5.85 | 16.36 | 1.45 | 9.62 | 15.96 | 1.13 | 70.33 | 27.84 | 328.2 | 121.8 | 500.5 | 110.6 | 1 114.6 | 163.2 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-91 | 0.21 | 37.28 | 0.33 | 5.15 | 10.46 | 1.89 | 40.47 | 18.61 | 213.2 | 81.0 | 355.4 | 81.3 | 859.0 | 129.3 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-92 | — | 2.58 | 0.19 | 5.41 | 22.94 | 0.87 | 85.59 | 32.70 | 256.3 | 61.5 | 184.2 | 32.4 | 282.9 | 34.6 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-93 | 0.02 | 29.38 | 0.28 | 4.06 | 8.83 | 0.50 | 33.02 | 15.25 | 187.7 | 67.6 | 288.6 | 65.2 | 666.3 | 100.2 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-94 | — | 8.66 | 0.14 | 3.13 | 8.29 | 0.71 | 43.21 | 22.51 | 305.8 | 122.5 | 556.6 | 133.2 | 1 411.9 | 212.9 | 0.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-95 | 0.04 | 5.73 | 0.05 | 1.58 | 6.79 | 0.55 | 45.60 | 28.21 | 322.4 | 99.9 | 376.2 | 78.0 | 762.9 | 109.5 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-96 | 0.06 | 17.42 | 0.61 | 12.55 | 26.94 | 1.50 | 92.44 | 39.26 | 435.2 | 150.5 | 603.2 | 130.1 | 1 262.4 | 173.3 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-97 | 0.30 | 173.27 | 1.33 | 19.43 | 30.84 | 1.03 | 113.21 | 57.27 | 702.2 | 264.7 | 1 136.8 | 250.6 | 2 436.1 | 326.5 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-98 | 0.02 | 23.85 | 0.09 | 2.03 | 5.46 | 1.14 | 23.15 | 12.21 | 157.6 | 63.1 | 303.6 | 77.0 | 867.3 | 140.2 | 0.31 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-99 | 0.04 | 2.53 | 0.16 | 3.60 | 15.18 | 0.30 | 90.06 | 54.50 | 748.4 | 297.8 | 1 333.0 | 304.3 | 3 080.0 | 431.4 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-100 | 0.01 | 68.41 | 0.09 | 3.52 | 7.59 | 0.79 | 29.48 | 15.01 | 190.1 | 73.2 | 323.6 | 76.0 | 780.0 | 117.8 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | La/ | Ce/ | Pr/ | Nd/ | Sm/ | Eu/ | Gd/ | Tb/ | Dy/ | Ho/ | Er/ | Tm/ | Yb/ | Lu/ | Eu/ Eu* | |||||||||||||||||
| (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | |||||||||||||||||||
| 变质砂岩DC1801 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-01 | — | 0.20 | — | — | 0.13 | 0.10 | 1.21 | 0.26 | 4.2 | 1.2 | 4.0 | 0.8 | 7.7 | 0.9 | 0.76 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-02 | 0.04 | 1.63 | 0.16 | 2.06 | 3.64 | 0.31 | 22.16 | 7.60 | 99.0 | 39.9 | 180.4 | 38.5 | 362.1 | 58.6 | 0.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-03 | 0.14 | 0.79 | 0.05 | 0.64 | 4.48 | 0.10 | 34.18 | 16.99 | 209.8 | 65.9 | 236.0 | 42.8 | 345.9 | 48.4 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-04 | 0.27 | 25.04 | 0.25 | 3.03 | 2.50 | 1.47 | 12.46 | 3.12 | 43.4 | 14.5 | 59.1 | 13.6 | 156.1 | 27.2 | 0.81 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-05 | — | 5.06 | — | — | 1.56 | 0.50 | 2.65 | 0.41 | 11.5 | 3.6 | 20.0 | 7.6 | 77.5 | 12.9 | 0.75 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-06 | — | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.63 | 1.56 | — | 0.30 | 0.66 | 5.0 | 2.1 | 6.3 | 1.5 | 8.7 | 1.3 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-07 | 1.55 | 52.74 | 0.82 | 5.61 | 4.94 | 2.02 | 14.37 | 5.65 | 59.9 | 21.8 | 96.8 | 22.8 | 253.9 | 40.4 | 0.73 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-10 | — | 12.44 | 0.03 | 0.93 | 2.27 | 0.14 | 11.85 | 4.48 | 53.4 | 21.2 | 95.9 | 21.5 | 217.9 | 39.6 | 0.08 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-11 | 0.08 | 21.85 | 0.25 | 0.56 | 1.83 | 0.45 | 13.26 | 4.23 | 69.0 | 27.9 | 143.7 | 37.9 | 462.3 | 110.6 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-12 | 0.03 | 26.48 | 0.11 | 1.34 | 2.66 | 0.55 | 14.57 | 4.77 | 52.8 | 17.1 | 67.9 | 12.5 | 106.0 | 19.9 | 0.27 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-13 | 0.34 | 31.86 | 0.46 | 2.64 | 4.46 | 1.74 | 9.58 | 3.04 | 30.1 | 10.3 | 49.5 | 10.6 | 102.4 | 21.4 | 0.81 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-14 | 0.06 | 10.68 | 0.14 | 0.86 | 1.62 | 0.43 | 7.73 | 2.43 | 29.8 | 12.1 | 58.5 | 14.0 | 148.0 | 33.1 | 0.37 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-15 | 10.89 | 42.16 | 3.43 | 14.96 | 5.30 | 0.88 | 17.43 | 6.04 | 81.4 | 33.5 | 162.4 | 37.2 | 368.6 | 74.5 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-16 | 98.59 | 322.94 | 34.31 | 148.50 | 33.72 | 3.98 | 56.61 | 9.13 | 82.6 | 21.1 | 82.6 | 15.6 | 162.0 | 28.4 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-17 | 78.40 | 192.26 | 24.81 | 110.16 | 23.28 | 3.48 | 37.44 | 8.69 | 90.1 | 33.7 | 147.3 | 31.7 | 304.4 | 62.0 | 0.36 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-18 | 0.07 | 3.29 | 0.29 | 5.25 | 8.64 | 0.61 | 42.20 | 14.15 | 165.0 | 58.0 | 239.6 | 47.6 | 418.5 | 72.9 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-19 | 0.01 | 5.09 | 0.06 | 1.15 | 2.78 | 0.45 | 14.84 | 5.06 | 63.4 | 23.4 | 103.4 | 22.1 | 199.1 | 38.5 | 0.21 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-20 | — | 5.17 | 0.10 | 1.88 | 5.77 | 1.59 | 34.01 | 11.40 | 139.5 | 52.9 | 224.5 | 43.5 | 364.9 | 67.8 | 0.35 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-21 | 0.66 | 10.36 | 0.60 | 5.71 | 6.19 | 0.70 | 24.56 | 7.15 | 81.6 | 28.6 | 118.0 | 23.9 | 215.9 | 39.4 | 0.17 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-22 | — | 5.99 | 0.02 | 0.78 | 4.61 | 0.79 | 36.82 | 15.41 | 221.3 | 88.4 | 416.5 | 86.1 | 805.4 | 139.5 | 0.18 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-23 | — | 9.62 | 0.05 | 1.28 | 3.11 | 0.38 | 22.10 | 7.83 | 100.9 | 40.8 | 184.0 | 39.9 | 370.8 | 72.7 | 0.14 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-24 | 0.01 | 13.63 | 0.11 | 1.45 | 3.22 | 0.07 | 20.28 | 7.53 | 86.3 | 31.9 | 132.4 | 26.5 | 233.6 | 39.4 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-25 | 8.15 | 41.91 | 2.01 | 12.15 | 8.77 | 1.04 | 35.02 | 10.99 | 127.5 | 45.4 | 194.0 | 38.7 | 352.8 | 65.4 | 0.18 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-26 | — | 0.15 | — | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.48 | 0.14 | 3.2 | 1.0 | 3.8 | 0.5 | 5.0 | 0.8 | 1.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-27 | 0.07 | 0.54 | 0.10 | — | — | — | 1.56 | 1.29 | 11.2 | 2.6 | 8.0 | 2.0 | 14.8 | 1.9 | 0.00 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-28 | 0.19 | 3.70 | 0.23 | 2.19 | 5.54 | 0.53 | 29.62 | 10.18 | 114.4 | 40.5 | 170.2 | 31.9 | 280.7 | 52.0 | 0.13 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-29 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 3.66 | 0.02 | 23.01 | 13.24 | 144.0 | 34.6 | 128.7 | 32.6 | 356.6 | 47.4 | 0.005 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-30 | 0.22 | 26.66 | 0.46 | 1.89 | 3.77 | 1.08 | 12.70 | 4.34 | 69.2 | 28.1 | 135.6 | 30.4 | 307.1 | 60.6 | 0.48 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-31 | 0.03 | 4.38 | 0.03 | 0.97 | 5.36 | 0.26 | 58.04 | 29.63 | 417.4 | 169.3 | 804.2 | 178.2 | 1 721.6 | 302.3 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-34 | 0.02 | 8.62 | 0.10 | 1.01 | 0.48 | 0.50 | 11.06 | 4.98 | 67.6 | 26.6 | 135.3 | 32.2 | 333.5 | 58.8 | 0.66 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-35 | 0.34 | 31.48 | 0.36 | 1.82 | 1.73 | 1.02 | 8.06 | 1.90 | 26.3 | 12.1 | 62.7 | 15.7 | 187.7 | 47.5 | 0.83 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-36 | — | 6.66 | 0.11 | 2.19 | 4.32 | 1.14 | 26.70 | 9.79 | 121.8 | 47.8 | 210.8 | 43.3 | 397.4 | 79.3 | 0.32 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-37 | 0.01 | 3.12 | 0.11 | 1.77 | 3.89 | 0.57 | 26.50 | 9.17 | 117.4 | 43.9 | 186.7 | 38.7 | 369.9 | 59.8 | 0.17 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-38 | 0.04 | 9.78 | 0.13 | 2.11 | 4.58 | 0.54 | 22.97 | 8.00 | 97.0 | 37.7 | 162.5 | 35.5 | 336.0 | 61.2 | 0.16 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-39 | 0.03 | 11.52 | 0.03 | 0.54 | 1.45 | 0.34 | 6.86 | 2.43 | 33.7 | 14.2 | 70.5 | 16.0 | 163.7 | 34.1 | 0.33 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-40 | — | 6.99 | — | 0.69 | 1.09 | 0.33 | 9.46 | 3.42 | 45.5 | 21.7 | 116.4 | 27.4 | 294.1 | 65.3 | 0.31 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-41 | 2.07 | 126.13 | 2.59 | 18.41 | 17.32 | 8.60 | 36.75 | 10.57 | 106.2 | 28.9 | 113.3 | 22.3 | 227.2 | 38.8 | 1.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-42 | 0.03 | 10.21 | 0.03 | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.40 | 2.09 | 0.55 | 6.2 | 2.3 | 12.5 | 3.0 | 33.2 | 7.3 | 1.14 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-43 | 0.08 | 11.70 | 0.07 | 1.72 | 3.54 | 0.62 | 20.76 | 7.37 | 91.4 | 36.7 | 164.7 | 35.6 | 326.0 | 63.7 | 0.22 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-44 | 4.24 | 200.65 | 6.21 | 39.95 | 28.23 | 8.71 | 65.56 | 19.65 | 194.2 | 58.0 | 250.9 | 49.9 | 470.8 | 73.6 | 0.62 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-45 | 0.02 | 29.30 | 0.04 | 0.95 | 0.80 | 0.55 | 7.54 | 1.79 | 27.8 | 10.9 | 56.1 | 12.5 | 133.9 | 30.0 | 0.69 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-46 | 0.47 | 19.64 | 0.26 | 1.79 | 1.49 | 0.31 | 7.91 | 3.49 | 40.2 | 16.4 | 73.4 | 16.3 | 163.1 | 31.3 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | La/ | Ce/ | Pr/ | Nd/ | Sm/ | Eu/ | Gd/ | Tb/ | Dy/ | Ho/ | Er/ | Tm/ | Yb/ | Lu/ | Eu/ Eu* | |||||||||||||||||
| (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | |||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-47 | — | 4.52 | 0.53 | 7.55 | 15.68 | 3.83 | 57.63 | 15.17 | 134.2 | 35.2 | 108.6 | 16.9 | 157.4 | 20.3 | 0.39 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-48 | — | 0.32 | 0.01 | 0.18 | — | 0.10 | 0.50 | 0.23 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 6.2 | 1.4 | 13.8 | 4.2 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-49 | 0.07 | 17.94 | 0.18 | 3.19 | 5.60 | 1.30 | 25.13 | 7.95 | 100.6 | 38.8 | 177.2 | 37.8 | 371.3 | 72.6 | 0.33 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-50 | 0.66 | 1.11 | 0.12 | 0.50 | 0.12 | 0.26 | — | 0.01 | 0.025 18 | 0.006 59 | 0.009 35 | — | 0.1 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-51 | 0.01 | 1.79 | 0.02 | 0.52 | 1.07 | 0.03 | 11.82 | 6.20 | 86.4 | 38.7 | 183.2 | 39.3 | 373.8 | 67.4 | 0.024 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-52 | 0.04 | 3.49 | 0.13 | 2.04 | 5.62 | 0.62 | 29.87 | 11.24 | 136.1 | 50.7 | 218.4 | 43.7 | 396.8 | 71.2 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-53 | 0.01 | 7.44 | 0.07 | 1.19 | 2.23 | 0.08 | 10.29 | 3.28 | 29.5 | 8.6 | 26.5 | 4.7 | 41.9 | 7.9 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-54 | 0.07 | 9.86 | 0.08 | 1.37 | 2.12 | 0.54 | 13.93 | 5.85 | 79.7 | 32.5 | 149.3 | 33.4 | 312.4 | 57.3 | 0.30 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-55 | 0.07 | 0.85 | 0.16 | 1.47 | 4.23 | 0.09 | 33.87 | 16.24 | 243.0 | 101.6 | 478.4 | 107.2 | 995.0 | 176.1 | 0.023 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-56 | 0.49 | 20.56 | 0.32 | 3.94 | 5.45 | 1.80 | 28.65 | 8.40 | 99.4 | 38.6 | 171.5 | 36.4 | 330.0 | 69.2 | 0.44 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-57 | 4.12 | 23.53 | 2.48 | 17.64 | 10.74 | 1.69 | 27.76 | 7.77 | 88.7 | 33.6 | 146.0 | 31.1 | 293.7 | 53.2 | 0.30 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-58 | 5.87 | 33.60 | 1.19 | 8.13 | 4.48 | — | 29.60 | 8.25 | 135.6 | 50.4 | 208.9 | 45.5 | 681.7 | 64.8 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-59 | 5.03 | 86.89 | 12.47 | 94.16 | 88.63 | 37.29 | 216.49 | 72.40 | 696.6 | 204.7 | 732.4 | 134.7 | 990.6 | 170.5 | 0.82 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-60 | 0.20 | 34.77 | 0.29 | 2.86 | 4.39 | 1.44 | 14.05 | 4.36 | 55.8 | 21.0 | 92.9 | 21.3 | 196.4 | 37.0 | 0.56 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-61 | 1.12 | 19.57 | 0.70 | 4.09 | 2.57 | 0.31 | 16.58 | 7.38 | 104.4 | 45.8 | 223.9 | 51.2 | 515.1 | 104.7 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-62 | 0.03 | 9.28 | 0.04 | 0.27 | 0.80 | 0.15 | 4.25 | 1.80 | 25.1 | 11.3 | 61.0 | 16.2 | 191.6 | 43.9 | 0.24 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-63 | 0.15 | 10.07 | 0.25 | 1.85 | 2.30 | 1.56 | 9.65 | 2.57 | 28.3 | 10.6 | 49.3 | 12.3 | 136.6 | 28.9 | 1.01 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-64 | 0.82 | 2.05 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.66 | 0.27 | 13.39 | 4.79 | 62.9 | 20.7 | 89.9 | 25.6 | 271.0 | 30.4 | 0.17 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-65 | — | 12.73 | 0.06 | 1.09 | 2.60 | 1.22 | 14.82 | 5.76 | 73.9 | 28.2 | 129.3 | 29.9 | 298.2 | 54.1 | 0.60 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-66 | 0.01 | 15.91 | 0.06 | 1.92 | 10.88 | 1.71 | 84.56 | 30.33 | 382.6 | 139.5 | 559.5 | 103.3 | 870.0 | 141.1 | 0.17 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-67 | 0.003 | 7.12 | 0.02 | 0.45 | 1.80 | 0.30 | 11.64 | 4.34 | 57.8 | 24.5 | 112.0 | 23.9 | 228.2 | 46.2 | 0.20 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-68 | 4.67 | 15.55 | 0.96 | 3.46 | 1.02 | 0.16 | 3.98 | 1.64 | 20.4 | 7.6 | 34.4 | 8.5 | 82.9 | 17.2 | 0.23 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-69 | 0.005 | 5.38 | 0.03 | 0.50 | 1.07 | 0.43 | 8.59 | 3.26 | 42.5 | 17.7 | 83.3 | 18.7 | 180.3 | 37.8 | 0.44 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-70 | 0.003 | 2.55 | 0.03 | 0.54 | 2.22 | 0.35 | 22.59 | 9.96 | 135.2 | 55.9 | 248.6 | 52.7 | 473.8 | 88.4 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-71 | 1.23 | 7.07 | 0.38 | 3.22 | 5.18 | 0.20 | 28.15 | 11.77 | 161.9 | 62.3 | 296.4 | 73.2 | 767.2 | 150.2 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-72 | 0.04 | 8.55 | 0.03 | 0.57 | 1.18 | 0.30 | 8.43 | 3.32 | 46.4 | 15.3 | 72.3 | 14.9 | 152.2 | 27.7 | 0.30 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-73 | 0.05 | 12.11 | 0.14 | 2.08 | 3.59 | 0.79 | 21.29 | 7.81 | 97.9 | 40.2 | 184.4 | 40.0 | 370.7 | 71.3 | 0.27 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-74 | 0.002 | 6.49 | 0.17 | 2.87 | 6.98 | 2.08 | 41.57 | 14.43 | 177.6 | 64.9 | 268.6 | 51.7 | 435.5 | 76.3 | 0.37 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-75 | — | 3.01 | 0.26 | 3.65 | 8.49 | 0.48 | 33.28 | 9.31 | 99.7 | 34.4 | 135.0 | 26.9 | 233.6 | 41.8 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-76 | — | 13.00 | 0.09 | 1.69 | 2.27 | 1.09 | 10.01 | 3.11 | 37.9 | 14.5 | 68.3 | 15.9 | 169.0 | 34.8 | 0.70 | |||||||||||||||||
表3 点苍山变质地体三叠纪至侏罗纪沉积岩碎屑锆石稀土元素含量及Eu/Eu*比值
Table 3 REE content and Eu/Eu* ratios of the detrital zircon grains for the Triassic to Jurassic sedimentary rocks in the DMT
| 样品 | La/ | Ce/ | Pr/ | Nd/ | Sm/ | Eu/ | Gd/ | Tb/ | Dy/ | Ho/ | Er/ | Tm/ | Yb/ | Lu/ | Eu/ Eu* | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | |||||||||||||||||||
| 碳酸盐岩DC1702 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-01 | 0.001 | 11.68 | 0.04 | 0.83 | 2.89 | 0.25 | 19.18 | 7.20 | 92.1 | 36.1 | 163.1 | 34.9 | 315.5 | 60.2 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-02 | 0.003 | 6.11 | 0.06 | 1.14 | 2.24 | 0.20 | 13.70 | 4.93 | 64.0 | 25.0 | 117.3 | 26.2 | 239.9 | 43.4 | 0.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-03 | 14.26 | 58.84 | 4.36 | 25.90 | 26.08 | 0.42 | 130.82 | 41.88 | 468.4 | 164.3 | 650.2 | 120.5 | 968.7 | 153.9 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-04 | 0.004 | 6.28 | 0.06 | 1.01 | 2.88 | 0.36 | 20.33 | 6.88 | 86.2 | 34.4 | 152.8 | 32.5 | 292.5 | 55.2 | 0.14 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-05 | 3.33 | 46.66 | 2.27 | 18.67 | 23.46 | 4.44 | 79.15 | 28.88 | 374.8 | 161.0 | 790.9 | 166.1 | 1 336.5 | 202.7 | 0.31 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-06 | 1.61 | 53.43 | 1.45 | 12.28 | 16.56 | 6.28 | 70.18 | 23.50 | 256.3 | 86.8 | 356.5 | 70.4 | 609.3 | 106.4 | 0.56 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-07 | 0.09 | 17.15 | 0.28 | 3.90 | 8.24 | 0.69 | 46.74 | 16.63 | 205.6 | 80.1 | 357.8 | 73.6 | 660.6 | 121.8 | 0.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-08 | 4.06 | 72.25 | 9.18 | 86.69 | 94.99 | 41.29 | 226.21 | 64.92 | 579.6 | 155.3 | 564.3 | 108.3 | 907.5 | 139.1 | 0.86 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-09 | 4.27 | 21.69 | 0.92 | 5.16 | 5.27 | 0.57 | 26.58 | 9.27 | 113.3 | 42.7 | 185.6 | 38.9 | 346.4 | 62.1 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-10 | 0.02 | 17.17 | 0.13 | 2.21 | 6.56 | 0.35 | 45.00 | 17.57 | 224.3 | 91.8 | 415.8 | 82.3 | 704.7 | 120.2 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-11 | 0.20 | 15.69 | 0.44 | 7.08 | 14.20 | 0.62 | 74.64 | 24.18 | 279.0 | 103.3 | 426.3 | 82.5 | 682.3 | 113.8 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-12 | 0.003 | 20.52 | 0.11 | 2.62 | 8.55 | 0.21 | 56.16 | 21.99 | 279.4 | 111.9 | 494.5 | 102.9 | 924.7 | 167.0 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-13 | 0.02 | 1.81 | 0.10 | 2.43 | 6.49 | 0.41 | 43.87 | 15.74 | 191.2 | 70.3 | 296.0 | 56.4 | 485.0 | 91.5 | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-14 | 0.07 | 90.05 | 0.35 | 6.33 | 13.68 | 1.12 | 97.09 | 37.06 | 461.5 | 176.7 | 759.3 | 152.7 | 1 270.1 | 206.0 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-15 | 0.05 | 10.30 | 0.12 | 2.13 | 3.83 | 0.57 | 21.88 | 7.65 | 94.2 | 38.6 | 183.9 | 41.0 | 395.0 | 85.2 | 0.19 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-16 | 0.04 | 1.08 | 0.07 | 1.40 | 3.70 | 1.69 | 15.88 | 4.65 | 36.2 | 9.2 | 30.9 | 5.2 | 47.0 | 10.3 | 0.67 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-17 | 0.01 | 13.74 | 0.10 | 2.39 | 3.26 | 0.90 | 16.38 | 4.84 | 54.6 | 20.9 | 98.8 | 21.7 | 209.6 | 42.9 | 0.38 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-18 | 0.92 | 30.61 | 1.29 | 12.48 | 15.11 | 4.11 | 58.34 | 21.67 | 256.8 | 97.7 | 439.3 | 91.7 | 819.6 | 146.2 | 0.42 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-19 | 0.66 | 15.41 | 0.40 | 4.37 | 8.55 | 0.14 | 53.31 | 22.26 | 282.5 | 115.2 | 532.9 | 113.0 | 1 027.0 | 188.7 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-20 | 2.70 | 28.64 | 2.76 | 20.76 | 23.18 | 9.24 | 66.58 | 22.91 | 229.2 | 68.4 | 293.5 | 69.0 | 681.7 | 123.5 | 0.72 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-21 | 55.85 | 150.83 | 14.78 | 67.45 | 32.23 | 4.64 | 113.50 | 40.15 | 457.1 | 161.9 | 665.7 | 129.0 | 1 019.2 | 168.1 | 0.23 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-22 | 0.72 | 70.25 | 0.93 | 12.69 | 25.95 | 3.16 | 139.99 | 48.44 | 562.1 | 195.1 | 777.6 | 140.7 | 1 072.7 | 159.6 | 0.16 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-23 | 28.35 | 79.79 | 7.93 | 34.40 | 10.15 | 0.62 | 24.13 | 7.41 | 82.7 | 29.5 | 125.1 | 25.6 | 223.4 | 39.8 | 0.12 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-26 | 1.56 | 41.51 | 1.34 | 10.97 | 14.54 | 2.93 | 78.38 | 30.11 | 362.4 | 137.8 | 603.6 | 120.9 | 1 027.0 | 174.5 | 0.27 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-27 | 5.14 | 41.33 | 2.68 | 24.32 | 28.44 | 1.90 | 117.96 | 33.32 | 335.3 | 113.3 | 428.5 | 77.5 | 620.5 | 105.0 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-28 | 1.35 | 18.24 | 0.76 | 5.31 | 6.40 | 0.17 | 42.47 | 17.88 | 241.3 | 100.7 | 474.6 | 103.7 | 982.0 | 187.1 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-29 | 0.24 | 12.69 | 0.23 | 2.16 | 3.57 | 0.09 | 26.28 | 11.08 | 159.7 | 68.2 | 326.2 | 73.2 | 706.2 | 132.6 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-31 | 0.68 | 14.20 | 0.77 | 4.19 | 4.68 | 0.09 | 32.04 | 15.53 | 228.3 | 96.9 | 496.3 | 121.8 | 1 257.0 | 247.4 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-32 | 5.64 | 194.78 | 9.50 | 93.28 | 120.35 | 38.66 | 349.12 | 114.12 | 1 190.4 | 379.5 | 1 472.8 | 264.5 | 1 998.2 | 288.7 | 0.58 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-33 | 0.04 | 12.06 | 0.11 | 1.21 | 2.70 | 0.33 | 14.89 | 5.71 | 68.4 | 27.3 | 126.9 | 28.8 | 276.7 | 54.3 | 0.16 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-34 | 0.09 | 23.56 | 0.10 | 2.07 | 4.12 | 1.08 | 21.00 | 6.81 | 78.2 | 29.8 | 138.1 | 29.2 | 278.6 | 58.2 | 0.35 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-35 | 0.01 | 21.49 | 0.06 | 1.33 | 2.95 | 0.27 | 16.31 | 6.46 | 81.6 | 31.8 | 156.8 | 35.1 | 334.5 | 66.3 | 0.12 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-36 | 0.41 | 18.36 | 0.37 | 4.59 | 7.21 | 2.00 | 35.23 | 11.61 | 137.9 | 51.5 | 237.1 | 50.9 | 471.9 | 96.1 | 0.38 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-37 | 0.08 | 64.68 | 0.36 | 7.02 | 13.92 | 0.98 | 68.01 | 21.84 | 250.2 | 89.0 | 386.6 | 78.0 | 659.2 | 110.8 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-38 | 0.48 | 13.34 | 0.75 | 9.47 | 24.59 | 12.64 | 119.65 | 33.95 | 273.9 | 65.1 | 210.2 | 36.4 | 306.0 | 58.4 | 0.71 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-41 | 1.22 | 52.86 | 1.24 | 10.64 | 14.50 | 5.08 | 66.76 | 22.83 | 247.9 | 83.7 | 350.8 | 71.1 | 607.3 | 103.2 | 0.50 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-42 | 11.62 | 47.15 | 3.16 | 15.17 | 5.19 | 0.90 | 19.06 | 6.72 | 84.5 | 35.3 | 181.6 | 43.0 | 427.7 | 92.1 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-43 | 0.06 | 50.68 | 0.54 | 7.44 | 15.92 | 1.31 | 104.21 | 40.64 | 530.8 | 207.1 | 930.8 | 190.1 | 1 550.9 | 247.9 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-44 | 0.02 | 18.09 | 0.07 | 1.42 | 2.91 | 0.36 | 18.19 | 6.79 | 89.4 | 36.0 | 177.8 | 39.9 | 376.5 | 71.5 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-45 | 0.01 | 2.47 | 0.03 | 0.77 | 3.66 | 0.20 | 33.16 | 12.91 | 154.8 | 55.6 | 239.8 | 48.4 | 419.6 | 79.5 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-46 | 0.22 | 113.30 | 1.63 | 24.13 | 40.12 | 1.47 | 188.45 | 61.25 | 699.9 | 247.4 | 1 079.9 | 216.9 | 1 878.9 | 330.5 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | La/ | Ce/ | Pr/ | Nd/ | Sm/ | Eu/ | Gd/ | Tb/ | Dy/ | Ho/ | Er/ | Tm/ | Yb/ | Lu/ | Eu/ Eu* | |||||||||||||||||
| (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | |||||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-47 | 0.36 | 34.63 | 0.52 | 6.44 | 10.36 | 1.18 | 53.97 | 19.42 | 236.7 | 91.3 | 413.5 | 83.7 | 718.2 | 130.3 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-48 | 0.09 | 14.03 | 0.16 | 2.74 | 4.82 | 0.26 | 28.43 | 9.77 | 124.2 | 46.9 | 213.5 | 41.9 | 359.8 | 67.3 | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-49 | 52.30 | 364.07 | 18.06 | 113.08 | 103.05 | 21.54 | 375.11 | 120.99 | 1 245.0 | 384.5 | 1 467.9 | 260.9 | 1 960.0 | 292.3 | 0.33 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-50 | 0.17 | 27.49 | 0.30 | 3.91 | 5.03 | 1.32 | 21.27 | 6.24 | 68.6 | 25.8 | 119.3 | 26.3 | 256.8 | 54.9 | 0.39 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-51 | 0.02 | 8.22 | 0.13 | 2.27 | 3.92 | 0.28 | 19.79 | 6.87 | 82.7 | 31.3 | 139.0 | 29.1 | 261.0 | 48.7 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-52 | 0.22 | 9.43 | 0.23 | 1.55 | 2.51 | 0.29 | 14.39 | 5.55 | 67.9 | 26.6 | 122.1 | 26.4 | 243.5 | 46.9 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-53 | 0.45 | 26.68 | 0.59 | 8.93 | 12.97 | 1.66 | 54.62 | 15.17 | 154.6 | 52.6 | 214.8 | 40.7 | 332.8 | 65.1 | 0.19 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-54 | 0.03 | 32.88 | 0.44 | 7.28 | 14.87 | 0.86 | 80.50 | 27.06 | 326.3 | 118.8 | 503.8 | 96.8 | 780.1 | 130.7 | 0.08 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-55 | 0.60 | 31.03 | 0.54 | 5.40 | 7.25 | 1.12 | 37.89 | 13.46 | 168.7 | 64.8 | 295.8 | 60.7 | 514.6 | 97.5 | 0.21 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-56 | 2.24 | 33.98 | 2.10 | 16.98 | 16.94 | 7.34 | 44.65 | 14.62 | 151.4 | 52.0 | 240.9 | 54.9 | 524.6 | 96.3 | 0.82 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-57 | 6.45 | 36.45 | 2.40 | 13.74 | 8.88 | 1.47 | 33.30 | 10.99 | 129.8 | 48.6 | 222.0 | 46.7 | 422.4 | 81.9 | 0.26 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-58 | 52.87 | 136.20 | 8.61 | 35.48 | 21.18 | 3.65 | 72.69 | 24.75 | 290.5 | 113.1 | 551.7 | 124.6 | 1 180.3 | 241.1 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-59 | 0.36 | 14.37 | 0.61 | 3.59 | 5.35 | 1.72 | 24.10 | 8.21 | 93.4 | 34.0 | 150.0 | 32.2 | 286.6 | 52.2 | 0.46 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-60 | 6.54 | 79.93 | 9.56 | 51.85 | 37.90 | 1.87 | 75.18 | 27.18 | 320.9 | 117.3 | 558.0 | 125.7 | 1 179.3 | 229.3 | 0.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-61 | 0.09 | 16.30 | 0.30 | 4.45 | 6.44 | 2.27 | 31.51 | 9.68 | 111.7 | 43.6 | 198.8 | 44.4 | 422.2 | 83.9 | 0.49 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-62 | 0.10 | 9.63 | 0.08 | 1.68 | 4.66 | 0.14 | 31.90 | 12.82 | 171.3 | 72.1 | 345.2 | 73.7 | 678.8 | 136.1 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-63 | 2.51 | 43.93 | 3.82 | 20.84 | 19.05 | 0.69 | 77.05 | 31.66 | 405.3 | 163.0 | 754.6 | 162.7 | 1 452.5 | 267.9 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-64 | 0.18 | 22.23 | 0.33 | 5.57 | 9.01 | 1.68 | 45.12 | 15.14 | 169.5 | 61.9 | 260.4 | 51.6 | 429.3 | 79.0 | 0.25 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-65 | 0.18 | 11.05 | 0.08 | 1.50 | 3.83 | 0.18 | 31.04 | 12.11 | 156.6 | 62.7 | 295.2 | 62.5 | 564.4 | 107.8 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-66 | 0.09 | 10.50 | 0.72 | 12.21 | 25.97 | 1.68 | 142.69 | 47.00 | 517.7 | 182.2 | 729.1 | 137.9 | 1 127.4 | 201.0 | 0.08 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-67 | 0.22 | 85.99 | 1.06 | 17.87 | 34.09 | 8.45 | 166.19 | 50.89 | 540.9 | 190.0 | 763.1 | 149.3 | 1 236.4 | 217.9 | 0.34 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-68 | 0.51 | 23.68 | 0.71 | 8.69 | 13.48 | 0.82 | 71.73 | 23.44 | 268.3 | 99.2 | 413.9 | 81.9 | 682.2 | 117.0 | 0.08 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-69 | 4.28 | 25.20 | 2.78 | 18.10 | 14.60 | 6.51 | 42.56 | 13.23 | 145.6 | 56.3 | 267.7 | 61.9 | 643.9 | 164.8 | 0.80 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-71 | 0.74 | 23.55 | 0.90 | 6.79 | 8.57 | 0.37 | 41.09 | 15.73 | 199.4 | 79.3 | 363.3 | 78.6 | 709.8 | 138.6 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-72 | 21.82 | 78.74 | 7.79 | 40.63 | 13.95 | 2.33 | 41.82 | 11.54 | 132.7 | 49.6 | 222.4 | 46.7 | 424.3 | 87.6 | 0.29 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-73 | 0.06 | 10.67 | 0.20 | 3.41 | 6.85 | 1.09 | 41.33 | 14.65 | 181.2 | 73.3 | 330.9 | 69.8 | 635.6 | 121.0 | 0.20 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-76 | 0.36 | 53.17 | 0.77 | 11.28 | 20.66 | 0.68 | 94.07 | 30.96 | 350.5 | 127.5 | 539.4 | 107.8 | 924.3 | 167.1 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-77 | 0.05 | 30.04 | 0.53 | 9.10 | 18.34 | 0.73 | 103.85 | 33.14 | 369.8 | 131.9 | 529.0 | 98.5 | 806.1 | 137.2 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-78 | 0.004 | 6.94 | 0.04 | 0.69 | 1.74 | 0.36 | 11.28 | 3.72 | 47.1 | 19.1 | 92.2 | 20.9 | 197.5 | 38.9 | 0.25 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-81 | 6.10 | 86.90 | 4.96 | 34.24 | 52.46 | 1.07 | 258.34 | 88.00 | 933.4 | 308.9 | 1 248.7 | 243.1 | 2 205.1 | 419.7 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-82 | 2.01 | 69.79 | 1.38 | 14.68 | 19.90 | 5.47 | 86.33 | 30.60 | 382.7 | 134.0 | 604.0 | 126.6 | 1 161.7 | 213.2 | 0.40 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-84 | 10.01 | 91.80 | 3.17 | 20.47 | 22.76 | 2.51 | 119.39 | 49.24 | 656.0 | 261.5 | 1 264.2 | 271.0 | 2 472.2 | 402.8 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-85 | 35.18 | 153.35 | 11.35 | 66.60 | 47.00 | 11.21 | 171.25 | 56.86 | 640.6 | 226.0 | 1 070.0 | 236.4 | 2 303.4 | 432.4 | 0.38 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-86 | 16.64 | 434.80 | 42.24 | 419.16 | 454.50 | 180.71 | 1 013.00 | 265.82 | 2 337.1 | 626.9 | 2 251.9 | 403.9 | 3 303.9 | 503.8 | 0.81 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1702-87 | 20.07 | 221.95 | 22.63 | 180.17 | 172.24 | 71.11 | 374.24 | 98.07 | 855.2 | 225.5 | 855.6 | 177.0 | 1 589.7 | 266.4 | 0.86 | |||||||||||||||||
| 糜棱岩化片岩DC1703 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-01 | 0.03 | 2.31 | 0.14 | 4.24 | 15.58 | 0.64 | 84.68 | 36.85 | 364.8 | 107.6 | 382.4 | 79.9 | 740.0 | 102.4 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-02 | 0.06 | 19.39 | 0.36 | 6.61 | 15.65 | 0.57 | 72.96 | 35.07 | 448.0 | 173.8 | 778.6 | 186.2 | 1 942.7 | 289.2 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-03 | 5.02 | 68.27 | 1.73 | 9.95 | 11.64 | 0.65 | 43.64 | 18.59 | 221.9 | 80.1 | 331.8 | 76.0 | 750.4 | 106.2 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-04 | 0.72 | 56.13 | 3.58 | 41.34 | 45.52 | 16.92 | 97.45 | 27.61 | 224.4 | 59.2 | 202.1 | 39.2 | 366.9 | 49.0 | 0.78 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-05 | 0.01 | 22.95 | 0.07 | 1.99 | 3.36 | 0.55 | 14.85 | 6.88 | 90.8 | 35.9 | 163.7 | 40.4 | 451.3 | 67.7 | 0.24 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-06 | — | 68.58 | 0.09 | 2.84 | 6.05 | 2.64 | 27.08 | 11.66 | 146.1 | 56.3 | 263.2 | 68.3 | 823.3 | 137.0 | 0.63 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-07 | 0.02 | 40.40 | 0.10 | 2.73 | 4.72 | 2.08 | 17.59 | 7.56 | 99.5 | 38.0 | 179.3 | 48.5 | 575.7 | 102.3 | 0.70 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | La/ | Ce/ | Pr/ | Nd/ | Sm/ | Eu/ | Gd/ | Tb/ | Dy/ | Ho/ | Er/ | Tm/ | Yb/ | Lu/ | Eu/ Eu* | |||||||||||||||||
| (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | |||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-08 | 0.01 | 14.63 | 0.01 | 0.78 | 1.59 | 0.66 | 8.35 | 4.45 | 61.9 | 25.3 | 120.5 | 32.0 | 368.5 | 56.1 | 0.55 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-09 | 0.47 | 8.56 | 0.82 | 12.83 | 22.48 | 1.42 | 83.76 | 35.10 | 426.8 | 152.0 | 624.2 | 143.8 | 1 448.7 | 207.8 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-10 | — | 23.89 | 0.35 | 6.69 | 13.25 | 0.82 | 46.40 | 18.51 | 213.1 | 75.6 | 304.8 | 67.7 | 676.7 | 92.4 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-11 | 0.63 | 19.92 | 1.30 | 16.04 | 27.10 | 2.01 | 82.58 | 34.07 | 398.2 | 137.7 | 594.4 | 139.5 | 1 426.5 | 209.3 | 0.13 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-12 | 0.11 | 31.68 | 1.07 | 17.06 | 32.67 | 6.49 | 115.87 | 45.20 | 512.8 | 170.6 | 675.8 | 144.3 | 1 383.9 | 190.1 | 0.32 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-15 | 0.02 | 8.05 | 0.27 | 5.70 | 15.72 | 1.15 | 58.27 | 21.11 | 180.1 | 44.4 | 140.4 | 25.7 | 224.0 | 27.5 | 0.12 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-16 | 0.20 | 3.42 | 0.29 | 4.78 | 13.77 | 0.36 | 86.14 | 48.14 | 641.7 | 249.6 | 1 086.9 | 2 47.3 | 2 498.7 | 354.5 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-17 | 2.49 | 100.69 | 4.95 | 40.02 | 40.06 | 15.24 | 80.52 | 31.33 | 315.0 | 94.8 | 365.0 | 79.3 | 738.7 | 103.1 | 0.82 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-18 | 0.03 | 2.03 | 0.14 | 2.68 | 7.14 | 0.27 | 41.52 | 24.88 | 339.8 | 132.8 | 604.0 | 144.9 | 1 456.6 | 215.4 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-19 | 0.12 | 5.02 | 0.22 | 5.69 | 19.17 | 0.60 | 76.40 | 28.16 | 237.3 | 56.2 | 165.8 | 28.1 | 228.5 | 26.8 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-20 | 3.77 | 46.15 | 1.48 | 11.42 | 11.37 | 1.24 | 47.27 | 22.29 | 296.7 | 114.7 | 511.4 | 117.6 | 1 223.2 | 176.3 | 0.16 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-21 | 1.19 | 12.62 | 1.21 | 17.86 | 34.22 | 0.95 | 133.09 | 58.75 | 673.6 | 249.6 | 1 022.4 | 229.2 | 2 265.4 | 321.0 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-22 | 0.07 | 25.53 | 0.20 | 4.89 | 10.61 | 1.48 | 38.30 | 16.90 | 186.1 | 66.1 | 263.0 | 59.1 | 596.3 | 85.6 | 0.22 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-23 | 0.37 | 29.07 | 1.72 | 32.96 | 60.08 | 13.66 | 215.02 | 89.29 | 965.9 | 317.8 | 1 213.2 | 252.2 | 2 303.4 | 307.6 | 0.37 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-24 | 0.13 | 32.37 | 0.52 | 6.14 | 7.40 | 1.31 | 18.70 | 6.64 | 68.7 | 22.8 | 97.9 | 23.0 | 255.6 | 40.6 | 0.34 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-25 | 0.05 | 2.82 | 0.16 | 4.14 | 15.94 | 0.47 | 92.50 | 53.92 | 719.3 | 281.3 | 1 248.0 | 289.2 | 2 867.4 | 412.4 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-26 | 3.28 | 174.82 | 1.05 | 10.08 | 14.21 | 3.69 | 47.79 | 19.31 | 210.9 | 74.1 | 302.0 | 67.6 | 684.4 | 101.0 | 0.43 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-27 | 421.30 | 952.83 | 114.82 | 492.09 | 85.76 | 13.92 | 88.97 | 13.26 | 112.6 | 36.2 | 156.3 | 37.6 | 419.7 | 65.6 | 0.49 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-28 | — | 2.94 | 0.04 | 1.19 | 4.54 | 0.33 | 20.03 | 9.98 | 115.2 | 40.2 | 175.6 | 44.6 | 524.1 | 85.0 | 0.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-29 | 0.01 | 35.30 | 0.10 | 2.18 | 5.36 | 1.34 | 23.75 | 11.14 | 137.1 | 49.6 | 211.8 | 48.9 | 509.4 | 75.4 | 0.36 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-30 | 0.41 | 56.84 | 2.25 | 29.75 | 38.81 | 3.87 | 111.37 | 39.97 | 422.8 | 137.2 | 520.2 | 106.8 | 1 050.2 | 142.4 | 0.18 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-31 | — | 5.15 | 0.13 | 2.58 | 8.64 | 0.26 | 40.09 | 20.19 | 214.9 | 68.2 | 245.4 | 50.5 | 479.2 | 67.7 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-32 | — | 2.97 | 0.11 | 4.26 | 12.87 | 0.31 | 64.39 | 30.92 | 359.6 | 122.2 | 464.9 | 100.4 | 981.7 | 138.6 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-33 | 0.04 | 9.81 | 0.47 | 7.91 | 17.18 | 0.75 | 61.55 | 24.83 | 242.8 | 71.7 | 250.0 | 50.1 | 443.1 | 60.3 | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-34 | 0.02 | 13.81 | 0.12 | 2.90 | 7.44 | 0.91 | 44.97 | 27.64 | 380.2 | 137.9 | 541.6 | 108.5 | 920.0 | 123.9 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-35 | — | 18.92 | 0.16 | 4.46 | 11.49 | 0.49 | 60.70 | 30.12 | 381.5 | 139.8 | 589.5 | 133.0 | 1 328.9 | 186.8 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-36 | 134.72 | 287.41 | 34.94 | 144.22 | 36.40 | 5.75 | 60.42 | 19.39 | 214.8 | 77.6 | 344.4 | 80.2 | 821.1 | 130.5 | 0.37 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-39 | 0.06 | 1.89 | 0.19 | 2.22 | 6.75 | 0.17 | 44.39 | 28.65 | 361.6 | 140.5 | 638.8 | 150.5 | 1 591.2 | 215.6 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-40 | 0.19 | 11.52 | 0.38 | 7.52 | 17.35 | 0.81 | 79.04 | 42.09 | 572.3 | 226.3 | 1 025.9 | 244.9 | 2 554.4 | 376.6 | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-41 | — | 10.41 | 0.13 | 2.86 | 7.33 | 0.25 | 37.22 | 20.51 | 276.2 | 110.5 | 489.0 | 117.6 | 1 232.5 | 179.9 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-42 | 0.01 | 20.73 | 0.21 | 4.65 | 8.58 | 2.30 | 31.40 | 13.99 | 170.3 | 63.2 | 274.6 | 65.7 | 697.3 | 104.0 | 0.43 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-43 | 0.14 | 89.40 | 0.60 | 11.03 | 18.75 | 4.94 | 65.21 | 28.21 | 358.7 | 142.6 | 650.2 | 161.8 | 1 789.2 | 280.9 | 0.43 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-44 | 0.08 | 16.76 | 0.20 | 4.59 | 12.03 | 0.94 | 55.19 | 28.52 | 358.5 | 140.4 | 604.1 | 136.3 | 1 396.8 | 206.9 | 0.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-45 | 0.01 | 21.55 | 0.42 | 7.32 | 9.26 | 2.20 | 29.61 | 11.68 | 124.4 | 41.9 | 170.1 | 39.1 | 416.9 | 61.6 | 0.41 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-46 | 1.68 | 19.94 | 2.82 | 29.08 | 39.65 | 6.03 | 123.74 | 55.77 | 629.6 | 214.1 | 854.6 | 178.8 | 1 666.8 | 234.5 | 0.26 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-47 | 0.21 | 20.71 | 0.61 | 7.42 | 10.72 | 2.02 | 41.50 | 24.38 | 337.0 | 139.6 | 648.9 | 160.8 | 1 745.8 | 259.7 | 0.29 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-48 | 0.09 | 26.64 | 0.21 | 4.83 | 14.28 | 10.08 | 58.40 | 21.68 | 190.2 | 54.8 | 191.1 | 39.0 | 382.9 | 54.3 | 1.07 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-49 | 0.03 | 299.80 | 0.52 | 13.09 | 33.82 | 14.80 | 170.89 | 77.04 | 981.6 | 374.4 | 1 541.0 | 344.9 | 3 365.3 | 503.2 | 0.60 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-50 | — | 49.99 | 0.06 | 2.53 | 4.61 | 0.98 | 16.84 | 7.28 | 84.4 | 32.8 | 142.7 | 33.9 | 365.3 | 54.8 | 0.34 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-51 | 31.16 | 143.92 | 16.88 | 103.02 | 53.25 | 2.14 | 104.85 | 37.87 | 423.4 | 153.1 | 640.6 | 137.8 | 1 336.4 | 201.8 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-52 | 7.88 | 59.35 | 6.74 | 46.63 | 30.65 | 5.92 | 62.83 | 25.74 | 303.7 | 114.3 | 507.0 | 122.5 | 1 346.0 | 206.3 | 0.41 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-53 | 0.10 | 20.59 | 0.17 | 4.14 | 12.40 | 2.28 | 50.94 | 24.65 | 300.3 | 114.7 | 501.7 | 114.2 | 1 157.1 | 175.1 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-54 | 0.06 | 8.65 | 0.27 | 5.76 | 15.17 | 0.13 | 61.60 | 28.08 | 331.4 | 119.4 | 493.5 | 108.2 | 1 050.5 | 151.0 | 0.013 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | La/ | Ce/ | Pr/ | Nd/ | Sm/ | Eu/ | Gd/ | Tb/ | Dy/ | Ho/ | Er/ | Tm/ | Yb/ | Lu/ | Eu/ Eu* | |||||||||||||||||
| (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | |||||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-55 | 0.02 | 9.78 | 0.11 | 3.12 | 8.53 | 0.29 | 50.47 | 28.40 | 371.8 | 151.4 | 700.3 | 168.0 | 1 741.9 | 258.4 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-56 | 0.36 | 14.64 | 0.09 | 1.26 | 1.88 | 0.82 | 7.51 | 4.05 | 55.5 | 23.6 | 126.6 | 35.3 | 464.2 | 86.6 | 0.67 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-57 | — | 13.67 | 0.34 | 7.27 | 17.73 | 2.20 | 83.22 | 39.87 | 500.9 | 185.3 | 798.3 | 173.7 | 1 723.1 | 251.9 | 0.18 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-58 | 0.04 | 43.24 | 0.24 | 5.64 | 10.87 | 2.62 | 38.52 | 18.52 | 231.9 | 93.0 | 431.6 | 104.9 | 1 170.6 | 182.1 | 0.39 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-59 | 0.12 | 3.50 | 0.26 | 5.58 | 14.83 | 0.32 | 74.68 | 36.80 | 469.1 | 179.0 | 791.9 | 181.2 | 1 820.0 | 260.8 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-60 | — | 42.93 | 0.10 | 2.53 | 4.64 | 0.44 | 16.72 | 8.53 | 111.9 | 49.0 | 249.2 | 71.7 | 869.0 | 137.1 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-63 | 0.04 | 38.68 | 0.35 | 9.29 | 39.13 | 2.52 | 195.85 | 82.97 | 863.7 | 268.3 | 1 017.3 | 207.0 | 1 919.0 | 264.6 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-64 | 0.14 | 3.08 | 0.05 | 0.86 | 1.16 | 0.21 | 9.24 | 6.53 | 98.1 | 37.3 | 161.3 | 34.3 | 322.1 | 48.2 | 0.20 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-65 | 0.05 | 54.72 | 0.51 | 10.15 | 18.35 | 4.37 | 46.33 | 17.48 | 180.9 | 62.8 | 269.4 | 62.9 | 644.4 | 102.8 | 0.46 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-66 | 0.08 | 10.81 | 0.16 | 4.75 | 9.84 | 1.38 | 39.69 | 18.10 | 221.9 | 78.6 | 337.1 | 73.8 | 750.7 | 107.8 | 0.21 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-67 | 0.10 | 73.04 | 0.56 | 9.22 | 13.17 | 2.57 | 34.42 | 12.87 | 126.2 | 39.0 | 151.0 | 32.3 | 312.7 | 43.9 | 0.37 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-68 | 0.02 | 18.07 | 0.05 | 1.81 | 3.92 | 0.59 | 18.30 | 10.50 | 144.7 | 61.1 | 306.9 | 79.5 | 928.4 | 149.9 | 0.21 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-69 | — | 56.60 | 0.25 | 5.74 | 12.30 | 0.51 | 52.81 | 25.58 | 318.9 | 120.1 | 509.2 | 113.4 | 1 109.6 | 159.2 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-70 | — | 12.68 | 0.41 | 7.17 | 13.64 | 1.03 | 44.44 | 19.00 | 217.1 | 78.6 | 338.8 | 76.7 | 762.0 | 111.7 | 0.13 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-71 | 0.06 | 3.54 | 0.11 | 3.05 | 11.05 | 0.58 | 68.38 | 44.96 | 657.2 | 264.7 | 1 248.3 | 290.1 | 2 989.9 | 436.1 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-72 | 0.003 | 40.18 | 0.70 | 14.00 | 23.69 | 5.69 | 76.35 | 33.28 | 384.6 | 138.6 | 588.4 | 132.0 | 1 316.5 | 191.5 | 0.41 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-73 | 0.06 | 5.29 | 0.99 | 18.77 | 33.60 | 1.55 | 112.71 | 40.27 | 366.1 | 102.8 | 363.8 | 75.0 | 743.0 | 104.8 | 0.08 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-74 | 0.05 | 5.70 | 0.18 | 5.30 | 13.87 | 0.40 | 68.83 | 33.37 | 423.6 | 157.5 | 684.2 | 153.1 | 1 533.2 | 224.2 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-75 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-76 | — | 4.79 | 0.24 | 5.08 | 16.35 | 0.51 | 86.23 | 51.08 | 701.8 | 274.5 | 1 246.3 | 278.8 | 2 844.1 | 404.0 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-77 | 0.15 | 15.22 | 1.15 | 18.82 | 30.04 | 4.67 | 68.63 | 21.13 | 165.3 | 37.1 | 102.1 | 16.6 | 133.5 | 15.7 | 0.31 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-78 | 0.04 | 32.71 | 0.19 | 3.51 | 7.34 | 1.90 | 22.29 | 10.76 | 127.1 | 48.7 | 227.6 | 58.3 | 670.8 | 104.3 | 0.45 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-79 | 0.01 | 120.37 | 0.20 | 6.57 | 14.97 | 2.82 | 56.35 | 27.48 | 342.8 | 124.9 | 554.9 | 125.5 | 1 310.4 | 189.2 | 0.30 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-80 | 0.20 | 39.56 | 0.92 | 14.65 | 27.18 | 2.36 | 88.12 | 39.16 | 441.1 | 149.3 | 612.5 | 122.0 | 1 206.8 | 165.2 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-81 | 38.65 | 136.45 | 12.91 | 70.84 | 43.91 | 4.67 | 86.14 | 32.03 | 327.4 | 108.5 | 429.8 | 90.2 | 880.1 | 125.3 | 0.23 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-82 | 0.05 | 26.60 | 0.06 | 2.08 | 5.32 | 0.13 | 22.98 | 13.85 | 183.8 | 72.1 | 326.2 | 73.2 | 740.6 | 106.7 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-83 | 0.01 | 15.95 | 0.42 | 6.08 | 12.74 | 0.50 | 38.82 | 17.23 | 194.0 | 69.4 | 290.5 | 64.3 | 648.7 | 94.2 | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-84 | 0.03 | 38.82 | 0.17 | 4.19 | 10.53 | 2.00 | 49.17 | 27.52 | 382.3 | 159.7 | 786.9 | 202.7 | 2 381.6 | 380.4 | 0.27 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-87 | 0.04 | 10.85 | 0.27 | 5.11 | 16.16 | 0.32 | 71.69 | 38.77 | 468.2 | 171.1 | 717.5 | 159.8 | 1 602.6 | 216.6 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-88 | 0.03 | 10.90 | 0.26 | 6.06 | 14.89 | 0.29 | 62.67 | 32.12 | 400.1 | 153.6 | 660.6 | 149.2 | 1 471.9 | 215.6 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-89 | — | 5.99 | 0.38 | 7.94 | 17.52 | 0.27 | 76.23 | 38.96 | 478.3 | 177.4 | 731.9 | 159.6 | 1 559.1 | 225.7 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-90 | 5.85 | 16.36 | 1.45 | 9.62 | 15.96 | 1.13 | 70.33 | 27.84 | 328.2 | 121.8 | 500.5 | 110.6 | 1 114.6 | 163.2 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-91 | 0.21 | 37.28 | 0.33 | 5.15 | 10.46 | 1.89 | 40.47 | 18.61 | 213.2 | 81.0 | 355.4 | 81.3 | 859.0 | 129.3 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-92 | — | 2.58 | 0.19 | 5.41 | 22.94 | 0.87 | 85.59 | 32.70 | 256.3 | 61.5 | 184.2 | 32.4 | 282.9 | 34.6 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-93 | 0.02 | 29.38 | 0.28 | 4.06 | 8.83 | 0.50 | 33.02 | 15.25 | 187.7 | 67.6 | 288.6 | 65.2 | 666.3 | 100.2 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-94 | — | 8.66 | 0.14 | 3.13 | 8.29 | 0.71 | 43.21 | 22.51 | 305.8 | 122.5 | 556.6 | 133.2 | 1 411.9 | 212.9 | 0.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-95 | 0.04 | 5.73 | 0.05 | 1.58 | 6.79 | 0.55 | 45.60 | 28.21 | 322.4 | 99.9 | 376.2 | 78.0 | 762.9 | 109.5 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-96 | 0.06 | 17.42 | 0.61 | 12.55 | 26.94 | 1.50 | 92.44 | 39.26 | 435.2 | 150.5 | 603.2 | 130.1 | 1 262.4 | 173.3 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-97 | 0.30 | 173.27 | 1.33 | 19.43 | 30.84 | 1.03 | 113.21 | 57.27 | 702.2 | 264.7 | 1 136.8 | 250.6 | 2 436.1 | 326.5 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-98 | 0.02 | 23.85 | 0.09 | 2.03 | 5.46 | 1.14 | 23.15 | 12.21 | 157.6 | 63.1 | 303.6 | 77.0 | 867.3 | 140.2 | 0.31 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-99 | 0.04 | 2.53 | 0.16 | 3.60 | 15.18 | 0.30 | 90.06 | 54.50 | 748.4 | 297.8 | 1 333.0 | 304.3 | 3 080.0 | 431.4 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1703-100 | 0.01 | 68.41 | 0.09 | 3.52 | 7.59 | 0.79 | 29.48 | 15.01 | 190.1 | 73.2 | 323.6 | 76.0 | 780.0 | 117.8 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | La/ | Ce/ | Pr/ | Nd/ | Sm/ | Eu/ | Gd/ | Tb/ | Dy/ | Ho/ | Er/ | Tm/ | Yb/ | Lu/ | Eu/ Eu* | |||||||||||||||||
| (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | |||||||||||||||||||
| 变质砂岩DC1801 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-01 | — | 0.20 | — | — | 0.13 | 0.10 | 1.21 | 0.26 | 4.2 | 1.2 | 4.0 | 0.8 | 7.7 | 0.9 | 0.76 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-02 | 0.04 | 1.63 | 0.16 | 2.06 | 3.64 | 0.31 | 22.16 | 7.60 | 99.0 | 39.9 | 180.4 | 38.5 | 362.1 | 58.6 | 0.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-03 | 0.14 | 0.79 | 0.05 | 0.64 | 4.48 | 0.10 | 34.18 | 16.99 | 209.8 | 65.9 | 236.0 | 42.8 | 345.9 | 48.4 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-04 | 0.27 | 25.04 | 0.25 | 3.03 | 2.50 | 1.47 | 12.46 | 3.12 | 43.4 | 14.5 | 59.1 | 13.6 | 156.1 | 27.2 | 0.81 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-05 | — | 5.06 | — | — | 1.56 | 0.50 | 2.65 | 0.41 | 11.5 | 3.6 | 20.0 | 7.6 | 77.5 | 12.9 | 0.75 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-06 | — | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.63 | 1.56 | — | 0.30 | 0.66 | 5.0 | 2.1 | 6.3 | 1.5 | 8.7 | 1.3 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-07 | 1.55 | 52.74 | 0.82 | 5.61 | 4.94 | 2.02 | 14.37 | 5.65 | 59.9 | 21.8 | 96.8 | 22.8 | 253.9 | 40.4 | 0.73 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-10 | — | 12.44 | 0.03 | 0.93 | 2.27 | 0.14 | 11.85 | 4.48 | 53.4 | 21.2 | 95.9 | 21.5 | 217.9 | 39.6 | 0.08 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-11 | 0.08 | 21.85 | 0.25 | 0.56 | 1.83 | 0.45 | 13.26 | 4.23 | 69.0 | 27.9 | 143.7 | 37.9 | 462.3 | 110.6 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-12 | 0.03 | 26.48 | 0.11 | 1.34 | 2.66 | 0.55 | 14.57 | 4.77 | 52.8 | 17.1 | 67.9 | 12.5 | 106.0 | 19.9 | 0.27 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-13 | 0.34 | 31.86 | 0.46 | 2.64 | 4.46 | 1.74 | 9.58 | 3.04 | 30.1 | 10.3 | 49.5 | 10.6 | 102.4 | 21.4 | 0.81 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-14 | 0.06 | 10.68 | 0.14 | 0.86 | 1.62 | 0.43 | 7.73 | 2.43 | 29.8 | 12.1 | 58.5 | 14.0 | 148.0 | 33.1 | 0.37 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-15 | 10.89 | 42.16 | 3.43 | 14.96 | 5.30 | 0.88 | 17.43 | 6.04 | 81.4 | 33.5 | 162.4 | 37.2 | 368.6 | 74.5 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-16 | 98.59 | 322.94 | 34.31 | 148.50 | 33.72 | 3.98 | 56.61 | 9.13 | 82.6 | 21.1 | 82.6 | 15.6 | 162.0 | 28.4 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-17 | 78.40 | 192.26 | 24.81 | 110.16 | 23.28 | 3.48 | 37.44 | 8.69 | 90.1 | 33.7 | 147.3 | 31.7 | 304.4 | 62.0 | 0.36 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-18 | 0.07 | 3.29 | 0.29 | 5.25 | 8.64 | 0.61 | 42.20 | 14.15 | 165.0 | 58.0 | 239.6 | 47.6 | 418.5 | 72.9 | 0.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-19 | 0.01 | 5.09 | 0.06 | 1.15 | 2.78 | 0.45 | 14.84 | 5.06 | 63.4 | 23.4 | 103.4 | 22.1 | 199.1 | 38.5 | 0.21 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-20 | — | 5.17 | 0.10 | 1.88 | 5.77 | 1.59 | 34.01 | 11.40 | 139.5 | 52.9 | 224.5 | 43.5 | 364.9 | 67.8 | 0.35 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-21 | 0.66 | 10.36 | 0.60 | 5.71 | 6.19 | 0.70 | 24.56 | 7.15 | 81.6 | 28.6 | 118.0 | 23.9 | 215.9 | 39.4 | 0.17 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-22 | — | 5.99 | 0.02 | 0.78 | 4.61 | 0.79 | 36.82 | 15.41 | 221.3 | 88.4 | 416.5 | 86.1 | 805.4 | 139.5 | 0.18 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-23 | — | 9.62 | 0.05 | 1.28 | 3.11 | 0.38 | 22.10 | 7.83 | 100.9 | 40.8 | 184.0 | 39.9 | 370.8 | 72.7 | 0.14 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-24 | 0.01 | 13.63 | 0.11 | 1.45 | 3.22 | 0.07 | 20.28 | 7.53 | 86.3 | 31.9 | 132.4 | 26.5 | 233.6 | 39.4 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-25 | 8.15 | 41.91 | 2.01 | 12.15 | 8.77 | 1.04 | 35.02 | 10.99 | 127.5 | 45.4 | 194.0 | 38.7 | 352.8 | 65.4 | 0.18 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-26 | — | 0.15 | — | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.48 | 0.14 | 3.2 | 1.0 | 3.8 | 0.5 | 5.0 | 0.8 | 1.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-27 | 0.07 | 0.54 | 0.10 | — | — | — | 1.56 | 1.29 | 11.2 | 2.6 | 8.0 | 2.0 | 14.8 | 1.9 | 0.00 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-28 | 0.19 | 3.70 | 0.23 | 2.19 | 5.54 | 0.53 | 29.62 | 10.18 | 114.4 | 40.5 | 170.2 | 31.9 | 280.7 | 52.0 | 0.13 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-29 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 3.66 | 0.02 | 23.01 | 13.24 | 144.0 | 34.6 | 128.7 | 32.6 | 356.6 | 47.4 | 0.005 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-30 | 0.22 | 26.66 | 0.46 | 1.89 | 3.77 | 1.08 | 12.70 | 4.34 | 69.2 | 28.1 | 135.6 | 30.4 | 307.1 | 60.6 | 0.48 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-31 | 0.03 | 4.38 | 0.03 | 0.97 | 5.36 | 0.26 | 58.04 | 29.63 | 417.4 | 169.3 | 804.2 | 178.2 | 1 721.6 | 302.3 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-34 | 0.02 | 8.62 | 0.10 | 1.01 | 0.48 | 0.50 | 11.06 | 4.98 | 67.6 | 26.6 | 135.3 | 32.2 | 333.5 | 58.8 | 0.66 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-35 | 0.34 | 31.48 | 0.36 | 1.82 | 1.73 | 1.02 | 8.06 | 1.90 | 26.3 | 12.1 | 62.7 | 15.7 | 187.7 | 47.5 | 0.83 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-36 | — | 6.66 | 0.11 | 2.19 | 4.32 | 1.14 | 26.70 | 9.79 | 121.8 | 47.8 | 210.8 | 43.3 | 397.4 | 79.3 | 0.32 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-37 | 0.01 | 3.12 | 0.11 | 1.77 | 3.89 | 0.57 | 26.50 | 9.17 | 117.4 | 43.9 | 186.7 | 38.7 | 369.9 | 59.8 | 0.17 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-38 | 0.04 | 9.78 | 0.13 | 2.11 | 4.58 | 0.54 | 22.97 | 8.00 | 97.0 | 37.7 | 162.5 | 35.5 | 336.0 | 61.2 | 0.16 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-39 | 0.03 | 11.52 | 0.03 | 0.54 | 1.45 | 0.34 | 6.86 | 2.43 | 33.7 | 14.2 | 70.5 | 16.0 | 163.7 | 34.1 | 0.33 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-40 | — | 6.99 | — | 0.69 | 1.09 | 0.33 | 9.46 | 3.42 | 45.5 | 21.7 | 116.4 | 27.4 | 294.1 | 65.3 | 0.31 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-41 | 2.07 | 126.13 | 2.59 | 18.41 | 17.32 | 8.60 | 36.75 | 10.57 | 106.2 | 28.9 | 113.3 | 22.3 | 227.2 | 38.8 | 1.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-42 | 0.03 | 10.21 | 0.03 | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.40 | 2.09 | 0.55 | 6.2 | 2.3 | 12.5 | 3.0 | 33.2 | 7.3 | 1.14 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-43 | 0.08 | 11.70 | 0.07 | 1.72 | 3.54 | 0.62 | 20.76 | 7.37 | 91.4 | 36.7 | 164.7 | 35.6 | 326.0 | 63.7 | 0.22 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-44 | 4.24 | 200.65 | 6.21 | 39.95 | 28.23 | 8.71 | 65.56 | 19.65 | 194.2 | 58.0 | 250.9 | 49.9 | 470.8 | 73.6 | 0.62 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-45 | 0.02 | 29.30 | 0.04 | 0.95 | 0.80 | 0.55 | 7.54 | 1.79 | 27.8 | 10.9 | 56.1 | 12.5 | 133.9 | 30.0 | 0.69 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-46 | 0.47 | 19.64 | 0.26 | 1.79 | 1.49 | 0.31 | 7.91 | 3.49 | 40.2 | 16.4 | 73.4 | 16.3 | 163.1 | 31.3 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | La/ | Ce/ | Pr/ | Nd/ | Sm/ | Eu/ | Gd/ | Tb/ | Dy/ | Ho/ | Er/ | Tm/ | Yb/ | Lu/ | Eu/ Eu* | |||||||||||||||||
| (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | |||||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-47 | — | 4.52 | 0.53 | 7.55 | 15.68 | 3.83 | 57.63 | 15.17 | 134.2 | 35.2 | 108.6 | 16.9 | 157.4 | 20.3 | 0.39 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-48 | — | 0.32 | 0.01 | 0.18 | — | 0.10 | 0.50 | 0.23 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 6.2 | 1.4 | 13.8 | 4.2 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-49 | 0.07 | 17.94 | 0.18 | 3.19 | 5.60 | 1.30 | 25.13 | 7.95 | 100.6 | 38.8 | 177.2 | 37.8 | 371.3 | 72.6 | 0.33 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-50 | 0.66 | 1.11 | 0.12 | 0.50 | 0.12 | 0.26 | — | 0.01 | 0.025 18 | 0.006 59 | 0.009 35 | — | 0.1 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-51 | 0.01 | 1.79 | 0.02 | 0.52 | 1.07 | 0.03 | 11.82 | 6.20 | 86.4 | 38.7 | 183.2 | 39.3 | 373.8 | 67.4 | 0.024 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-52 | 0.04 | 3.49 | 0.13 | 2.04 | 5.62 | 0.62 | 29.87 | 11.24 | 136.1 | 50.7 | 218.4 | 43.7 | 396.8 | 71.2 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-53 | 0.01 | 7.44 | 0.07 | 1.19 | 2.23 | 0.08 | 10.29 | 3.28 | 29.5 | 8.6 | 26.5 | 4.7 | 41.9 | 7.9 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-54 | 0.07 | 9.86 | 0.08 | 1.37 | 2.12 | 0.54 | 13.93 | 5.85 | 79.7 | 32.5 | 149.3 | 33.4 | 312.4 | 57.3 | 0.30 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-55 | 0.07 | 0.85 | 0.16 | 1.47 | 4.23 | 0.09 | 33.87 | 16.24 | 243.0 | 101.6 | 478.4 | 107.2 | 995.0 | 176.1 | 0.023 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-56 | 0.49 | 20.56 | 0.32 | 3.94 | 5.45 | 1.80 | 28.65 | 8.40 | 99.4 | 38.6 | 171.5 | 36.4 | 330.0 | 69.2 | 0.44 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-57 | 4.12 | 23.53 | 2.48 | 17.64 | 10.74 | 1.69 | 27.76 | 7.77 | 88.7 | 33.6 | 146.0 | 31.1 | 293.7 | 53.2 | 0.30 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-58 | 5.87 | 33.60 | 1.19 | 8.13 | 4.48 | — | 29.60 | 8.25 | 135.6 | 50.4 | 208.9 | 45.5 | 681.7 | 64.8 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-59 | 5.03 | 86.89 | 12.47 | 94.16 | 88.63 | 37.29 | 216.49 | 72.40 | 696.6 | 204.7 | 732.4 | 134.7 | 990.6 | 170.5 | 0.82 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-60 | 0.20 | 34.77 | 0.29 | 2.86 | 4.39 | 1.44 | 14.05 | 4.36 | 55.8 | 21.0 | 92.9 | 21.3 | 196.4 | 37.0 | 0.56 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-61 | 1.12 | 19.57 | 0.70 | 4.09 | 2.57 | 0.31 | 16.58 | 7.38 | 104.4 | 45.8 | 223.9 | 51.2 | 515.1 | 104.7 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-62 | 0.03 | 9.28 | 0.04 | 0.27 | 0.80 | 0.15 | 4.25 | 1.80 | 25.1 | 11.3 | 61.0 | 16.2 | 191.6 | 43.9 | 0.24 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-63 | 0.15 | 10.07 | 0.25 | 1.85 | 2.30 | 1.56 | 9.65 | 2.57 | 28.3 | 10.6 | 49.3 | 12.3 | 136.6 | 28.9 | 1.01 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-64 | 0.82 | 2.05 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.66 | 0.27 | 13.39 | 4.79 | 62.9 | 20.7 | 89.9 | 25.6 | 271.0 | 30.4 | 0.17 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-65 | — | 12.73 | 0.06 | 1.09 | 2.60 | 1.22 | 14.82 | 5.76 | 73.9 | 28.2 | 129.3 | 29.9 | 298.2 | 54.1 | 0.60 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-66 | 0.01 | 15.91 | 0.06 | 1.92 | 10.88 | 1.71 | 84.56 | 30.33 | 382.6 | 139.5 | 559.5 | 103.3 | 870.0 | 141.1 | 0.17 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-67 | 0.003 | 7.12 | 0.02 | 0.45 | 1.80 | 0.30 | 11.64 | 4.34 | 57.8 | 24.5 | 112.0 | 23.9 | 228.2 | 46.2 | 0.20 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-68 | 4.67 | 15.55 | 0.96 | 3.46 | 1.02 | 0.16 | 3.98 | 1.64 | 20.4 | 7.6 | 34.4 | 8.5 | 82.9 | 17.2 | 0.23 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-69 | 0.005 | 5.38 | 0.03 | 0.50 | 1.07 | 0.43 | 8.59 | 3.26 | 42.5 | 17.7 | 83.3 | 18.7 | 180.3 | 37.8 | 0.44 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-70 | 0.003 | 2.55 | 0.03 | 0.54 | 2.22 | 0.35 | 22.59 | 9.96 | 135.2 | 55.9 | 248.6 | 52.7 | 473.8 | 88.4 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-71 | 1.23 | 7.07 | 0.38 | 3.22 | 5.18 | 0.20 | 28.15 | 11.77 | 161.9 | 62.3 | 296.4 | 73.2 | 767.2 | 150.2 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-72 | 0.04 | 8.55 | 0.03 | 0.57 | 1.18 | 0.30 | 8.43 | 3.32 | 46.4 | 15.3 | 72.3 | 14.9 | 152.2 | 27.7 | 0.30 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-73 | 0.05 | 12.11 | 0.14 | 2.08 | 3.59 | 0.79 | 21.29 | 7.81 | 97.9 | 40.2 | 184.4 | 40.0 | 370.7 | 71.3 | 0.27 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-74 | 0.002 | 6.49 | 0.17 | 2.87 | 6.98 | 2.08 | 41.57 | 14.43 | 177.6 | 64.9 | 268.6 | 51.7 | 435.5 | 76.3 | 0.37 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-75 | — | 3.01 | 0.26 | 3.65 | 8.49 | 0.48 | 33.28 | 9.31 | 99.7 | 34.4 | 135.0 | 26.9 | 233.6 | 41.8 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| DC1801-76 | — | 13.00 | 0.09 | 1.69 | 2.27 | 1.09 | 10.01 | 3.11 | 37.9 | 14.5 | 68.3 | 15.9 | 169.0 | 34.8 | 0.70 | |||||||||||||||||
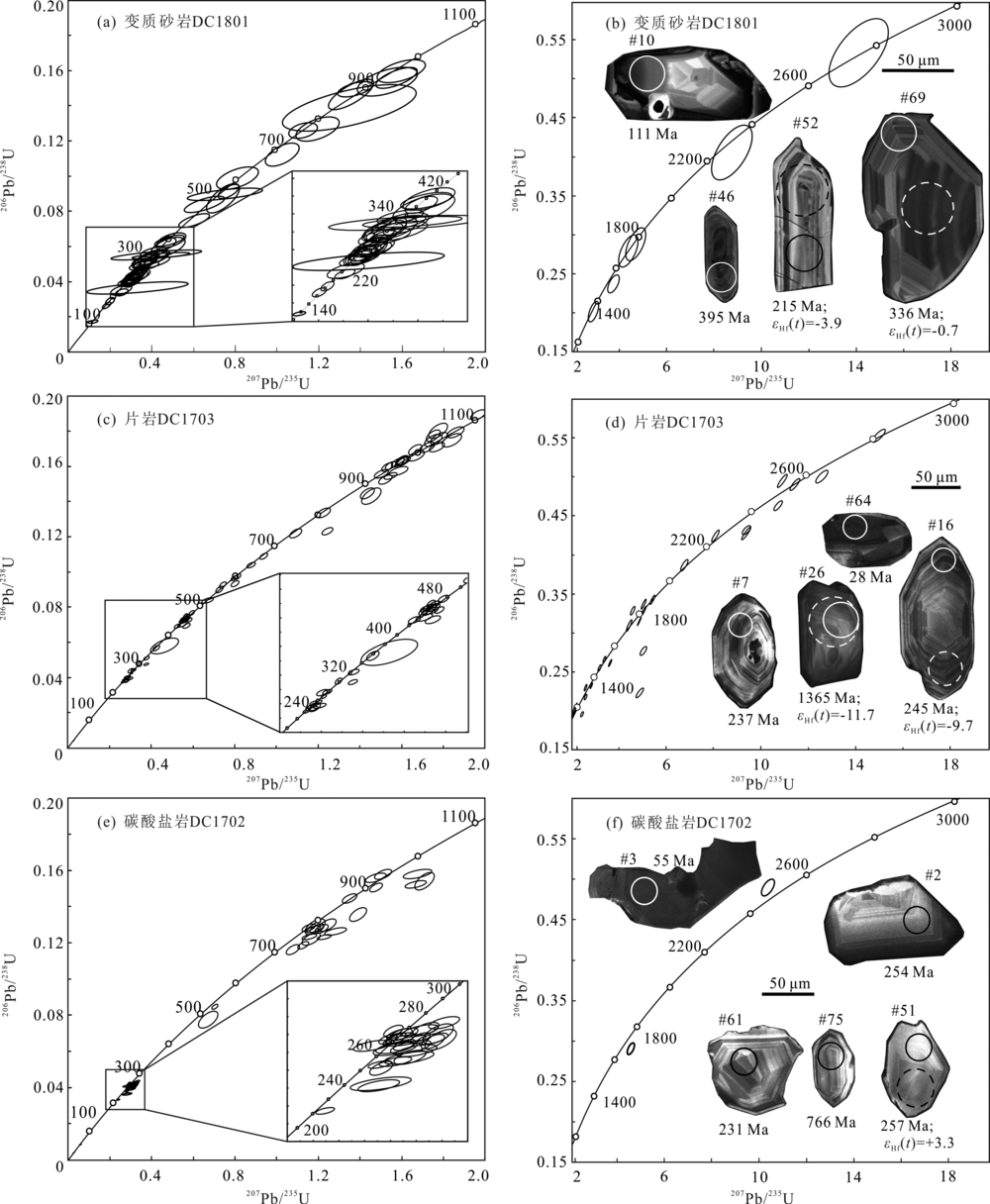
图4 滇西点苍山变质地体三叠纪至侏罗纪沉积岩碎屑锆石典型CL结构及U-Pb年龄谐和图 (a)和(b)变质砂岩DC1801;(c)和(d)片岩DC1703;(e)和(f)碳酸盐岩DC1702;锆石颗粒上黑色或白色实线代表U-Pb年龄测点位置,黑色或白色虚线代表Hf同位素测点位置;测点号及其U-Pb年龄、εHf(t)值已在相应锆石颗粒附近标出。
Fig.4 Typical zircon cathodeluminescene structures and concordia diagrams of detrital zircon U-Pb ages for the Triassic to Jurassic sedimentary rocks in the DMT, western Yunnan
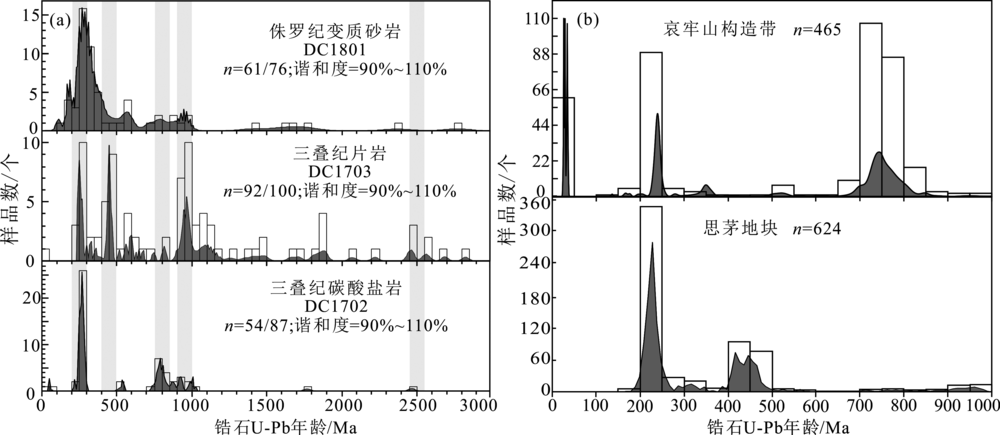
图5 滇西点苍山变质地体三叠纪至侏罗纪沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄概率密度直方图
Fig.5 (a)本文3个沉积岩样品中碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄概率密度直方图;(b)哀牢山构造带[37]和思茅地块内部主要岩浆岩年龄分布统计[19,23,36,58-61]。 Probability density histogram of detrital zircon U-Pb ages for the Triassic to Jurassic sedimentary rocks in the DMT, western Yunnan

图6 滇西点苍山变质地体三叠纪至侏罗纪沉积岩碎屑锆石Hf同位素组成 (a)碎屑锆石εHf(t) 值vs. U-Pb年龄图,哀牢山三叠纪花岗岩类εHf(t) 值[20,21,22]、印支地块三叠纪侵入岩εHf(t) 值[19,58-59]和扬子西缘新元古代侵入岩εHf(t) 值[6,30-35]分别统计自已发表文献,印支地块早古生代侵入岩εHf(t) 值根据区域岩浆岩Nd同位素[36]及大陆岩石Nd-Hf同位素相关性[62,63]计算获得;(b)点苍山变质地体三叠纪至侏罗纪沉积岩碎屑锆石与哀牢山洋演化相关岩浆记录中锆石的εHf(t) 值对比图,其中哀牢山洋演化相关岩浆记录中锆石εHf(t)值演化趋势及哀牢山洋闭合时限依据Wang等[19]。
Fig.6 Detrital zircon Hf isotopic compositions for the Triassic to Jurassic sedimentary rocks in the DMT, western Yunnan
| 年龄/Ma | 厚度/km | 平均误差 | 样本数量/个 | 样本方差 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 225 | 45.3 | 5.6 | 2 | 71.55 |
| 230 | 54.3 | 6.6 | 1 | 0.00 |
| 235 | — | — | — | — |
| 240 | 34.0 | 4.3 | 2 | 24.76 |
| 245 | 26.6 | 3.5 | 1 | 0.00 |
| 250 | 41.6 | 5.2 | 7 | 327.68 |
| 255 | 34.5 | 4.4 | 2 | 3.12 |
| 260 | 37.7 | 4.7 | 9 | 116.05 |
| 265 | 60.6 | 7.2 | 6 | 576.00 |
| 270 | 40.7 | 5.1 | 6 | 203.94 |
| 275 | 49.7 | 6.0 | 5 | 314.18 |
| 280 | 40.5 | 5.0 | 3 | 58.45 |
| 285 | 68.9 | 8.2 | 4 | 280.08 |
| 290 | 28.4 | 3.7 | 1 | 0.00 |
| 295 | 46.4 | 5.7 | 4 | 284.76 |
| 三叠纪 | 46.1 | 5.7 | 7 | 385.89 |
| 古生代 | 50.4 | 6.1 | 100 | 397.10 |
| 新元古代 | 42.3 | 5.2 | 49 | 392.32 |
| 中元古代 | 50.0 | 6.1 | 30 | 617.91 |
| 古元古代 | 44.0 | 5.4 | 12 | 514.64 |
| 新太古代 | 50.4 | 6.1 | 5 | 179.24 |
表4 不同年龄锆石样品由铕异常计算所得的地壳厚度
Table 4 Crustal thicknesses calculated from detrital zircon Eu/Eu* ratios
| 年龄/Ma | 厚度/km | 平均误差 | 样本数量/个 | 样本方差 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 225 | 45.3 | 5.6 | 2 | 71.55 |
| 230 | 54.3 | 6.6 | 1 | 0.00 |
| 235 | — | — | — | — |
| 240 | 34.0 | 4.3 | 2 | 24.76 |
| 245 | 26.6 | 3.5 | 1 | 0.00 |
| 250 | 41.6 | 5.2 | 7 | 327.68 |
| 255 | 34.5 | 4.4 | 2 | 3.12 |
| 260 | 37.7 | 4.7 | 9 | 116.05 |
| 265 | 60.6 | 7.2 | 6 | 576.00 |
| 270 | 40.7 | 5.1 | 6 | 203.94 |
| 275 | 49.7 | 6.0 | 5 | 314.18 |
| 280 | 40.5 | 5.0 | 3 | 58.45 |
| 285 | 68.9 | 8.2 | 4 | 280.08 |
| 290 | 28.4 | 3.7 | 1 | 0.00 |
| 295 | 46.4 | 5.7 | 4 | 284.76 |
| 三叠纪 | 46.1 | 5.7 | 7 | 385.89 |
| 古生代 | 50.4 | 6.1 | 100 | 397.10 |
| 新元古代 | 42.3 | 5.2 | 49 | 392.32 |
| 中元古代 | 50.0 | 6.1 | 30 | 617.91 |
| 古元古代 | 44.0 | 5.4 | 12 | 514.64 |
| 新太古代 | 50.4 | 6.1 | 5 | 179.24 |

图8 滇西点苍山变质地体三叠纪至侏罗纪沉积岩碎屑锆石物源区地壳厚度随时间演化图(a)和碎屑锆石揭示的哀牢山洋闭合阶段区域地壳加厚及随后伸展(b)
Fig.8 Crustal thickness evolution through time for the provenance areas of the Triassic to Jurassic sedimentary rocks in the DMT, western Yunnan (a) and regional crustal thickening during the closure of the Ailaoshan ocean deduced by detrital zircons (b)
| 成对样本T检验项目 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 标准误差 平均值 | 差值 95%置信区间 | t | 自由度 | 差异性(双尾) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||||
| 时代-地壳厚度 | 1 241.98 | 1 002.27 | 409.18 | 190.16 | 2 293.8 | 3.045 | 5 | 0.029 | |
表5 对不同时代地壳厚度进行统计学成对样本T检验的结果
Table 5 The results of paired sample T-test on the crustal thickness of different ages
| 成对样本T检验项目 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 标准误差 平均值 | 差值 95%置信区间 | t | 自由度 | 差异性(双尾) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||||
| 时代-地壳厚度 | 1 241.98 | 1 002.27 | 409.18 | 190.16 | 2 293.8 | 3.045 | 5 | 0.029 | |
| [1] | TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The continental crust: its composition and evolution. An examination of the geochemical record preserved in sedimentary rocks[J]. Journal of Geology, 1985, 94:57-72. |
| [2] |
HAWKESWORTH C, CAWOOD P A, KEMP T, et al. A matter of preservation[J]. Science, 2009, 323:49-50.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LANCASTER P J, STOREY C D, HAWKESWORTH C J, et al. Understanding the roles of crustal growth and preservation in the detrital zircon record[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 305(3/4):405-412.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 陈岳龙, 李大鹏, 刘长征, 等. 大兴安岭的形成与演化历史:来自河漫滩沉积物地球化学及其碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成的证据[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(1):1-14. |
| [5] |
KANG H, LI D, CHEN Y, et al. Micro-continental blocks in Gondwana assembly: Geological and geochemical evidence of the Indochina block,SE Tibetan Plateau[J]. Lithos, 2019, 326/327:460-475.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LI D, CHEN Y, HOU K, et al. Detrital zircon record of Paleozoic and Mesozoic meta-sedimentary strata in the eastern part of the Baoshan block: Implications of their provenance and the tectonic evolution of the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Lithos, 2015, 227:194-204.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LI D, CHEN Y, HOU K, et al. Origin and evolution of the Tengchong block, southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau: Zircon U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopic evidence from the (meta-) sedimentary rocks and intrusions[J]. Tectonophysics, 2016, 687:245-256.
DOI URL |
| [8] | LI D, LUO Z, CHEN Y, et al. Deciphering the origin of the Tengchong block, west Yunnan: Evidence from detrital zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes of carboniferous strata[J]. Tectonophy-sics, 2014, 614:66-77. |
| [9] |
XU B, LI D, KANG H, et al. Detrital zircon record of Cambrian (meta-)sedimentary strata in the western part of the Baoshan Block: Constraints on its eastern boundary and Early Palaeozoic palaeoposition[J]. Geological Journal, 2019, 55:3416-3429.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
BAO C, CHEN Y, LI D, et al. Provenances of the Mesozoic sedi-ments in the Ordos Basin and implications for collision between the North China Craton (NCC) and the South China Craton (SCC)[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 96:296-307.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
CHEN Y, LI D, ZHOU J, et al. U-Pb ages of zircons in Western Qinling Shan, China, and their tectonic implications[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2008, 15(4):88-107.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
CHEN Y, LI D, ZHOU J, et al. U-Pb dating, geochemistry, and tectonic implications of the Songpan-Ganzi block and the Longmen Shan, China[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2009, 43(2):77-99.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
CHEN Y, LIU F, NIE L, et al. Elemental and Sm-Nd isotopic geochemistry on detrital sedimentary rocks in the Ganzi-Songpan block and Longmen Mountains[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science in China, 2007, 1(1):60-68.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 陈岳龙, 唐金荣, 刘飞, 等. 松潘—甘孜碎屑沉积岩的地球化学与Sm-Nd同位素地球化学[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(1):109-118. |
| [15] | MALONE D, CRADDOCK J, KONSTANTINOU A, et al. Detrital zircon geology of the Bighorn dolomite, Wyoming, USA: Evidence for Trans-Hudson dust deposition on the Western Laurentian carbonate platefrom[J]. Journal of Geology, 2017, 125(2):161-169. |
| [16] |
KHELEN A C, MANIKYAMBA C, TANG L, et al. Detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology of stromatolitic carbonates from the Greenstone belts of Dharwar Craton and Cuddapah basin of Peninsular India[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2019, 11(1):229-242.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
BONEV N, FILIPOV P, RAICHEVA R, et al. Detrital zircon age and Sr isotopic constraints for a Late Palaeozoic carbonate platform in the lower Rhodope thrust system, Pirin, SW Bulgaria[J]. Geological Magazine, 2019, 156(12):2117-2124.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
METCALFE I. Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion: Tectonic and palaeogeographic evolution of eastern Tethys[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 66:1-33.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
WANG Y, QIAN X, CAWOOD P A, et al. Closure of the East Paleotethyan Ocean and amalgamation of the eastern Cimmerian and southeast Asia continental fragments[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 186:195-230.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LIU H, WANG Y, LI Z, et al. Geodynamics of the Indosinian orogeny between the South China and Indochina blocks: Insights from latest Permian-Triassic granitoids and numerical modeling[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2018, 130(7/8):1289-1306.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 冀磊, 刘福来, 王舫. 点苍山—哀牢山变质杂岩带中、北段多期花岗质岩浆事件及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(9):2957-2974. |
| [22] | 刘汇川, 王岳军, 范蔚茗, 等. 滇西哀牢山地区晚三叠世高εNd(t)-εHf(t)花岗岩的构造指示[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2014, 44(11):2373-2388. |
| [23] |
WANG Y, ZHANG A, FAN W, et al. Petrogenesis of late Triassic post-collisional basaltic rocks of the Lancangjiang tectonic zone, southwest China, and tectonic implications for the evolution of the eastern Paleotethys: Geochronological and geochemical constraints[J]. Lithos, 2010, 120(3/4):529-546.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
JIAN P, LIU D, KRÖNER A, et al. Devonian to Permian plate tectonic cycle of the Paleo-Tethys Orogen in southwest China (I): Geochemistry of ophiolites, arc/back-arc assemblages and within-plate igneous rocks[J]. Lithos, 2009, 113(3/4):748-766.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
JIAN P, LIU D, KRÖNER A, et al. Devonian to Permian plate tectonic cycle of the Paleo-Tethys Orogen in southwest China (Ⅱ): Insights from zircon ages of ophiolites, arc/back-arc assemblages and within-plate igneous rocks and generation of the Emeishan CFB province[J]. Lithos, 2009, 113(3/4):767-784.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
LAI C, MEFFRE S, CRAWFORD A J, et al. The Central Ailaoshan ophiolite and modern analogs[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 26(1):75-88.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
XIA X, NIE X, LAI C, et al. Where was the Ailaoshan Ocean and when did it open: A perspective based on detrital zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope evidence[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 36:488-502.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
LELOUP P H, KIENAST J R. High-temperature metamorphism in a major strike-slip shear zone: the Ailao Shan-Red River, People’s Republic of China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1993, 118(1/4):213-234.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
TAPPONNIER P, LACASSIN R, LELOUP P H, et al. The Ailao Shan/Red River metamorphic belt: Tertiary left-lateral shear between Indochina and South China[J]. Nature, 1990, 343:431-437.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
QI X, SANTOSH M, ZHU L, et al. Mid-Neoproterozoic arc magmatism in the northeastern margin of the Indochina block, SW China: Geochronological and petrogenetic constraints and implications for Gondwana assembly[J]. Precambrian Research, 2014, 245:207-224.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
QI X, SANTOSH M, ZHAO Y, et al. Mid-Neoproterozoic ridge subduction and magmatic evolution in the northeastern margin of the Indochina block: evidence from geochronology and geochemi-stry of calc-alkaline plutons[J]. Lithos, 2016, 248/251:138-152.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
QI X, ZENG L, ZHU L, et al. Zircon U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopic systematics of the Daping plutonic rocks: Implications for the Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the northeastern margin of the Indochina block, Southwest China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 21(1):180-193.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
CAI Y, WANG Y, CAWOOD P A, et al. Neoproterozoic crustal growth of the Southern Yangtze Block: Geochemical and zircon U-Pb geochronological and Lu-Hf isotopic evidence of Neoproterozoic diorite from the Ailaoshan zone[J]. Precambrian Research, 2015, 266:137-149.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
CAI Y, WANG Y, CAWOOD P A, et al. Neoproterozoic subduction along the Ailaoshan zone, South China: Geochronological and geochemical evidence from amphibolite[J]. Precambrian Research, 2014, 245:13-28.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
WANG Y, ZHOU Y, CAI Y, et al. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of the Ailaoshan granitic and migmatite rocks and its implications on Neoproterozoic subduction along the SW Yangtze Block[J]. Precambrian Research, 2016, 283:106-124.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
LIU H, XIA X, LAI C, et al. Break-away of South China from Gondwana: Insights from the Silurian high-Nb basalts and associated magmatic rocks in the Diancangshan-Ailaoshan fold belt (SW China)[J]. Lithos, 2018, 318/319:194-208.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
LI D, CHEN Y, KANG H, et al. Neoproterozoic continental arc system along the NW margin of Rodinia supercontinent: Constraints from geochronological and geochemical studies of Neopro-terozoic granitoids in the Diancangshan massif[J]. Lithos, 2018, 316/317:77-91.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
GUO Z, HERTOGEN J, LIU J, et al. Potassic magmatism in western Sichuan and Yunnan provinces, SE Tibet, China: Petrological and geochemical constraints on petrogenesis[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2005, 46(1):33-78.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
HUANG X, NIU Y, XU Y, et al. Mineralogical and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of post-collisional potassic and ultrapotassic rocks from western Yunnan, SW China[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(8):1617-1654.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
LIU J, CHEN X, WU W, et al. New tectono-geochronological constraints on timing of shearing along the Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone: Implications for genesis of Ailao Shan gold mineralization[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 103(1):70-86.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
LU Y, KERRICH R, CAWOOD P A, et al. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of potassic felsic intrusions in western Yunnan, SW China: Constraints on the relationship of magmatism to the Jinsha suture[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 22(2):737-747.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
LU Y, KERRICH R, MCCUAIG T C, et al. Geochemical, Sr-Nd-Pb, and zircon Hf-O isotopic compositions of Eocene-Oligocene shoshonitic and potassic adakite-like felsic intrusions in western Yunnan, SW China: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2013, 54(7):1309-1348.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
LELOUP P H, LACASSIN R, TAPPONNIER P, et al. The Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone (Yunnan, China), Tertiary transform boundary of Indochina[J]. Tectonophysics, 1995, 251(1):3-10.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
SCHÄRER U, ZHANG L S, TAPPONNIER P. Duration of strike-slip movements in large shear zones: The Red River belt, China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994, 126(4):379-397.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
ZHANG L S, SCHÄRER U. Age and origin of magmatism along the Cenozoic Red River shear belt, China[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1999, 134(1):67-85.
DOI URL |
| [46] | 宋彪, 张玉海, 万渝生, 等. 锆石SHRIMP样品靶制作、年龄测定及有关现象讨论[J]. 地质论评, 2002, 48(S1):26-30. |
| [47] | 侯可军, 李延河, 邹天人, 等. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(10):2595-2604. |
| [48] |
JACKSON S E, PEARSON N J, GRIFFIN W L, et al. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 211(1):47-69.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
LIU Y, GAO S, HU Z, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1):537-557.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
SLÁMA J, KOLER J, CONDON D J, et al. Pleovice zircon — A new natural reference material for U-Pb and Hf isotopic microana-lysis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 249(1):1-35.
DOI URL |
| [51] | LUDWIG K R. User’s Manuscript for ISOPLOT 3.6: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley:Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003: 1-55. |
| [52] |
GENG J, QIU K, GOU Z, et al. Tectonic regime switchover of Triassic Western Qinling Orogen: Constraints from LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology and Lu-Hf isotope of Dangchuan intrusive complex in Gansu, China[J]. Chemie der Erde-Geochemistry, 2017, 77(4):637-651.
DOI URL |
| [53] | 耿建珍, 李怀坤, 张健, 等. 锆石Hf同位素组成的LA-MC-ICP-MS测定[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(10):34-39. |
| [54] |
CHU N C, TAYLOR R N, CHAVAGNAC V, et al. Hf isotope ratio analysis using multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: An evaluation of isobaric interference corrections[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2002, 17(12):1567-1574.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
CORFU F, HANCHAR J M, HOSKIN P W O, et al. Atlas of zircon textures[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2003, 53:469-500.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
GEORGE G. Detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology applied to tectonics[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2014, 42:127-149.
DOI URL |
| [57] | HOSKIN P W O, SCHALTEGGER U. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis[J]. Reviews in Mine-ralogy and Geochemistry, 2003, 53:27-62. |
| [58] |
DONG G, MO X, ZHAO Z, et al. Zircon U-Pb dating and the petrological and geochemical constraints on Lincang granite in Western Yunnan, China: Implications for the closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 62:282-294.
DOI URL |
| [59] | 孔会磊, 董国臣, 莫宣学, 等. 滇西三江地区临沧花岗岩的岩石成因: 地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(5):92-106. |
| [60] | PENG T, WILDE S A, WANG Y, et al. Mid-Triassic felsic igneous rocks from the southern Lancangjiang Zone, SW China: Petrogenesis and implications for the evolution of Paleo-Tethys[J]. Lithos, 2013, 168:15-32. |
| [61] | 赵枫, 李龚健, 张鹏飞, 等. 西南三江临沧花岗岩基成因与构造启示: 元素地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(5):1397-1412. |
| [62] |
VERVOORT J D, PATCHETT P J, ALBARÈDE F, et al. Hf-Nd isotopic evolution of the lower crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2000, 181(1):115-129.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
VERVOORT J D, PATCHETT P J, BLICHERT-TOFT J, et al. Relationships between Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotopic systems in the global sedimentary system[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1999, 168(1):79-99.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
LIN T H, CHUNG S L, CHIU H Y, et al. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotope constraints from the Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone on the tectonic and crustal evolution of southwestern China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 291:23-37.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
USUKI T, LAN C, WANG K, et al. Linking the Indochina block and Gondwana during the Early Paleozoic: Evidence from U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes of detrital zircons[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 586:145-159.
DOI URL |
| [66] | 莫宣学, 路凤香, 沈上越, 等. 三江特提斯火山作用与成矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1993: 1-235. |
| [67] | 刘翠, 邓晋福, 刘俊来, 等. 哀牢山构造岩浆带晚二叠世—早三叠世火山岩特征及其构造环境[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(12):3590-3602. |
| [68] | 戚学祥, 朱路华, 李化启, 等. 青藏高原东缘哀牢山—金沙江构造带糜棱状花岗岩的LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2010, 84(3):357-369. |
| [69] | 李龚健, 王庆飞, 禹丽, 等. 哀牢山古特提斯洋缝合时限: 晚二叠世花岗岩类锆石U-Pb年代学与地球化学制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(11):3883-3900. |
| [70] | 李宝龙, 季建清, 罗清华, 等. 滇西点苍山—哀牢山隆升构造样式和隆升时限[J]. 地震地质, 2012, 34(4):696-712. |
| [71] |
UENO K, TSUTSUMI S. Lopingian (Late Permian) foraminiferal faunal succession of a Paleo-Tethyan mid-oceanic carbonate buildup: Shifodong Formation in the Changning-Menglian Belt, West Yunnan, Southwest China[J]. Island Arc, 2010, 18(1):69-93.
DOI URL |
| [72] | 莫宣学. 三江中南段火山岩—蛇绿岩与成矿 [M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998: 1-46. |
| [73] |
FAN W, WANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Paleotethyan subduction process revealed from Triassic blueschists in the Lancang tectonic belt of Southwest China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2015, 662:95-108.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
TANG M, ERDMAN M, ELDRIDGE G, et al. The redox “filter”beneath magmatic orogens and the formation of continental crust [J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(5): eaar4444. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aar4444.
DOI |
| [75] |
TANG M, LEE C-T A, COSTIN G, et al. Recycling reduced iron at the base of magmatic orogens[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2019, 528:115827.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
THOMAS J B, BODNAR R J, SHIMIZU N, et al. Determination of zircon/melt trace element partition coefficients from SIMS ana-lysis of melt inclusions in zircon[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2002, 66(16):2887-2901.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
REN M, PARKER D F, WHITE J C. Partitioning of Sr, Ba, Rb, Y, and LREE between plagioclase and peraluminous silicic magmas[J]. American Mineralogist, 2003, 88:1091-1103.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
HOLDER R M, YAKYMCHUK C, VIETE D R. Accessory mine-ral Eu anomalies in suprasolidus rocks: Beyond feldspar[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystem, 2020, 21(8): doi: 10.1029/2020gc009052.
DOI |
| [79] |
TANG M, JI W, CHU X, et al. Reconstructing crustal thickness evolution from europium anomalies in detrital zircons[J]. Geology, 2020, 49(1):76-80.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [2] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [3] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [4] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [5] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [6] | 梁鸣, 高文, 罗先熔, 王晓东, 刘秀娟, 陈皓, 刘攀峰, 竹峰, 李伟. 冀北高尖子地区土壤地球化学特征及其找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1567-1579. |
| [7] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [8] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [9] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [10] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [11] | 可行, 赵青芳, 吴飘, 杨传胜, 廖晶, 龚建明. 胶莱盆地东北部白垩系烃源岩特征与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1358-1368. |
| [12] | 李俊磊, 张绪教, 王一凡, 张向格, 王重歌, 袁晓宁, 刘心兰, 王凯雅, 饶昊舒, 刘江, 秦渊. 青海省化隆县地学研学旅行的路线规划与思考[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1411-1422. |
| [13] | 梁乾坤, 陈岳龙, 王善辉, 于洋, 杨帆. 嫩江河漫滩沉积物碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 529-546. |
| [14] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [15] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||