



现代地质 ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (02): 271-283.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.02.03
秦锦华1,2( ), 刘翠1(
), 刘翠1( ), 邓晋福1, 段培新1, 郭娜3
), 邓晋福1, 段培新1, 郭娜3
收稿日期:2018-03-21
修回日期:2018-11-20
出版日期:2019-05-08
发布日期:2019-05-08
通讯作者:
刘翠
作者简介:刘 翠,女,副教授,1973年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事岩浆作用与成矿方向研究。Email: liucui@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
QIN Jinhua1,2( ), LIU Cui1(
), LIU Cui1( ), DENG Jinfu1, DUAN Peixin1, GUO Na3
), DENG Jinfu1, DUAN Peixin1, GUO Na3
Received:2018-03-21
Revised:2018-11-20
Online:2019-05-08
Published:2019-05-08
Contact:
LIU Cui
摘要:
碱性暗色矿物作为具有特殊指示意义的矿物,其存在对岩浆演化过程具有重要的意义。毛家屯花岗岩体位于兴蒙造山带东部的小兴安岭—张广才岭南段,岩体内部发育碱性暗色矿物。以毛家屯岩体内部发育的碱性暗色矿物为研究对象,进行了矿物学和矿物化学电子探针分析。研究表明,碱性角闪石的类型为铁-镁铝钠闪石,具有富碱,尤其富钠、富硅、富铁、贫钙、镁、钛等特征。辉石的类型为霓辉石,化学特征上高硅-高钠,高铁,低钛、镁、铝、锰。碱性暗色矿物主岩为碱性岩,成因类型为铝质A型花岗岩类。毛家屯花岗岩碱性角闪石具有很低的M值,证明其来源于地壳物质的熔融。毛家屯花岗岩中碱性角闪石的特征指示,在结晶过程中,岩浆体系处于封闭还原条件,且岩体从中央到边部存在偏酸性和偏基性组分分带现象。结合前人的同位素和年代学方面的分析资料,认为毛家屯碱性花岗岩形成于造山后期伸展转换环境中。
中图分类号:
秦锦华, 刘翠, 邓晋福, 段培新, 郭娜. 黑龙江省毛家屯花岗岩中碱性暗色矿物特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(02): 271-283.
QIN Jinhua, LIU Cui, DENG Jinfu, DUAN Peixin, GUO Na. Characteristics and Geological Significance of Alkaline Melano-minerals in Maojiatun Granite, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(02): 271-283.

图3 毛家屯岩体野外及显微照片 (a)岩体全貌图;(b)毛家屯花岗岩针柱状的暗色矿物;(c)、(d)碱性花岗岩镜下照片;Q.石英;Pl.斜长石;Kfs.钾长石;Aeg.霓辉石;Arf.钠铁闪石
Fig.3 Field photos and microphotographs of the Maojiatun granite intrusion
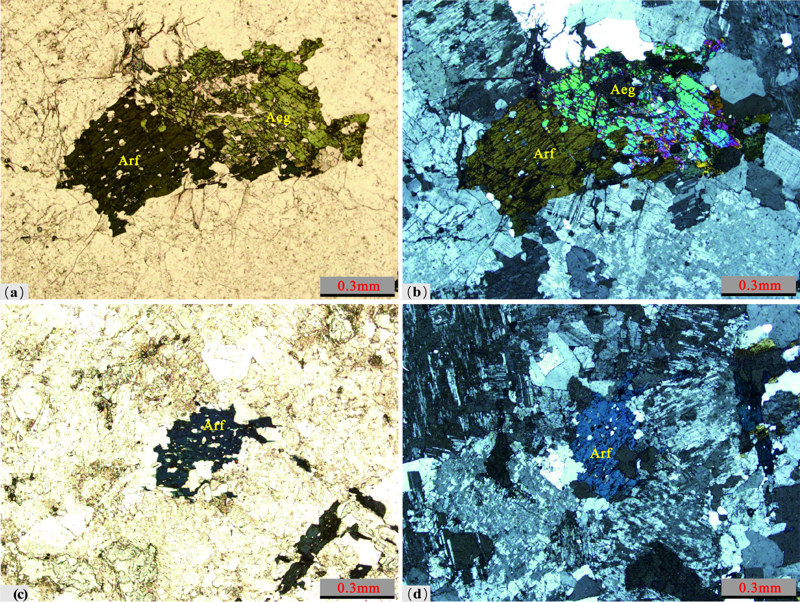
图4 毛家屯花岗岩中碱性暗色矿物镜下照片 (a)、(b)角闪石和辉石的交生关系;(c)、(d)蓝色角闪石;黄色虚线为角闪石和辉石接触边界;Arf.钠铁闪石;Aeg.霓辉石
Fig.4 Microphotographs of alkaline melano minerals in the Maojiatun granite
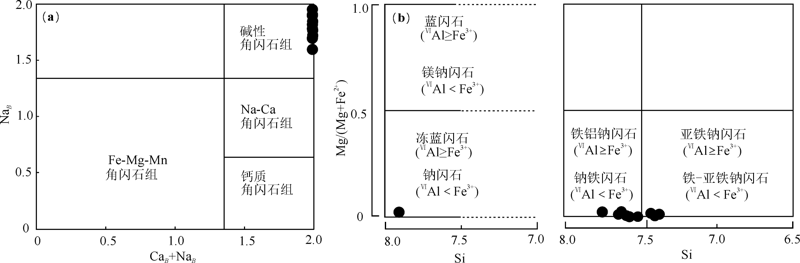
图6 角闪石的(CaB+NaB)-NaB图解((a)底图据Leake等[15])和Mg/(Mg+Fe2+)-Si图解((b)底图据Leake等[16])
Fig.6 (NaB+CaB)-NaB((a) base map after Leake et al.[15])and Mg/(Mg+Fe2+)-Si diagram of amphibole ((b)base map after Leake et al.[16])
| 测试点号 | wB/% | T占位 | C占位 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | Si | ⅣAl | Ti | 总计 | ⅥAl | Ti | |
| MJT1-1 | 49.00 | 1.39 | 0.51 | 34.35 | 1.04 | 0.06 | 1.12 | 7.58 | 1.95 | 7.64 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 7.89 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT1-2 | 48.71 | 1.28 | 0.56 | 34.32 | 1.17 | 0.01 | 1.11 | 7.76 | 2.15 | 7.59 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 7.84 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT1-3 | 49.82 | 1.33 | 0.41 | 33.72 | 1.08 | 0.13 | 0.84 | 7.74 | 2.21 | 7.74 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 7.97 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT1-4 | 48.87 | 1.45 | 0.42 | 34.22 | 1.23 | - | 1.09 | 7.73 | 2.01 | 7.61 | 0.08 | 0.17 | 7.86 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT2-1 | 48.79 | 1.34 | 0.45 | 34.84 | 1.28 | 0.01 | 1.21 | 7.77 | 1.86 | 7.55 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 7.79 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT2-2 | 48.87 | 1.27 | 0.40 | 34.42 | 1.16 | 0.11 | 1.11 | 7.80 | 2.20 | 7.59 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 7.81 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT3-1 | 51.15 | 0.71 | 1.41 | 35.36 | 0.70 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 7.04 | 1.18 | 7.87 | 0.13 | 0 | 8.00 | 0.13 | 0.08 |
| MJT3-2 | 48.66 | 0.70 | 1.42 | 36.05 | 1.01 | 0.13 | 0.32 | 8.08 | 1.22 | 7.44 | 0.26 | 0.08 | 7.78 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT6-1 | 49.37 | 1.26 | 1.13 | 35.15 | 1.13 | 0.07 | 0.68 | 7.25 | 1.46 | 7.64 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 8.00 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT6-2 | 49.74 | 1.30 | 0.91 | 34.46 | 1.27 | 0.14 | 0.36 | 7.69 | 1.47 | 7.68 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 7.99 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT12-3 | 48.06 | 0.96 | 1.36 | 35.74 | 1.18 | 0.19 | 1.24 | 7.34 | 1.28 | 7.42 | 0.25 | 0.11 | 7.78 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT13-1 | 48.63 | 1.14 | 1.20 | 34.42 | 1.14 | 0.24 | 2.00 | 7.63 | 1.35 | 7.45 | 0.22 | 0.13 | 7.80 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT13-2 | 48.18 | 1.24 | 1.22 | 35.00 | 1.05 | 0.28 | 1.87 | 7.72 | 1.38 | 7.37 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 7.73 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT13-3 | 49.78 | 0.93 | 1.27 | 34.82 | 0.84 | 0.27 | 1.29 | 7.11 | 1.30 | 7.67 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 8.00 | 0 | 0.01 |
| 测试点号 | C占位 | B占位 | A占位 | 占位 总量 | |||||||||||
| Fe3+ | Mg | Fe2+ | Mn | 总计 | Mg | Fe2+ | Mn | Ca | Na | 总计 | Na | K | 总计 | ||
| MJT1-1 | 0 | 0.01 | 4.48 | 0.14 | 4.63 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.19 | 1.81 | 2 | 0.48 | 0.39 | 0.87 | 15.39 |
| MJT1-2 | 0 | 0 | 4.47 | 0.15 | 4.63 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.19 | 1.81 | 2 | 0.53 | 0.43 | 0.96 | 15.43 |
| MJT1-3 | 0 | 0.03 | 4.38 | 0.14 | 4.55 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.14 | 1.86 | 2 | 0.47 | 0.44 | 0.91 | 15.44 |
| MJT1-4 | 0 | 0 | 4.46 | 0.16 | 4.62 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.18 | 1.82 | 2 | 0.52 | 0.40 | 0.92 | 15.40 |
| MJT2-1 | 0 | 0 | 4.51 | 0.17 | 4.68 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.20 | 1.80 | 2 | 0.53 | 0.37 | 0.90 | 15.37 |
| MJT2-2 | 0 | 0.03 | 4.47 | 0.15 | 4.65 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.18 | 1.82 | 2 | 0.53 | 0.44 | 0.97 | 15.44 |
| MJT3-1 | 0 | 0 | 4.55 | 0.09 | 4.85 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 1.95 | 2 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.38 | 15.23 |
| MJT3-2 | 0 | 0.03 | 4.61 | 0.13 | 4.77 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 1.95 | 2 | 0.45 | 0.24 | 0.69 | 15.24 |
| MJT6-1 | 0 | 0.02 | 4.55 | 0.15 | 4.72 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.11 | 1.89 | 2 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.58 | 15.29 |
| MJT6-2 | 0 | 0.03 | 4.45 | 0.17 | 4.65 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.06 | 1.94 | 2 | 0.36 | 0.29 | 0.65 | 15.29 |
| MJT12-3 | 0 | 0.04 | 4.62 | 0.15 | 4.81 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.21 | 1.79 | 2 | 0.40 | 0.25 | 0.66 | 15.25 |
| MJT13-1 | 0 | 0.05 | 4.41 | 0.15 | 4.61 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.33 | 1.67 | 2 | 0.59 | 0.26 | 0.86 | 15.26 |
| MJT13-2 | 0 | 0.06 | 4.48 | 0.14 | 4.68 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.31 | 1.69 | 2 | 0.60 | 0.27 | 0.86 | 15.27 |
| MJT13-3 | 0 | 0.06 | 4.49 | 0.11 | 4.66 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.21 | 1.79 | 2 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.59 | 15.26 |
表1 毛家屯花岗岩中角闪石电子探针分析计算结果
Table 1 EPMA results of amphibole in the Maojiatun granite
| 测试点号 | wB/% | T占位 | C占位 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | Si | ⅣAl | Ti | 总计 | ⅥAl | Ti | |
| MJT1-1 | 49.00 | 1.39 | 0.51 | 34.35 | 1.04 | 0.06 | 1.12 | 7.58 | 1.95 | 7.64 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 7.89 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT1-2 | 48.71 | 1.28 | 0.56 | 34.32 | 1.17 | 0.01 | 1.11 | 7.76 | 2.15 | 7.59 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 7.84 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT1-3 | 49.82 | 1.33 | 0.41 | 33.72 | 1.08 | 0.13 | 0.84 | 7.74 | 2.21 | 7.74 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 7.97 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT1-4 | 48.87 | 1.45 | 0.42 | 34.22 | 1.23 | - | 1.09 | 7.73 | 2.01 | 7.61 | 0.08 | 0.17 | 7.86 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT2-1 | 48.79 | 1.34 | 0.45 | 34.84 | 1.28 | 0.01 | 1.21 | 7.77 | 1.86 | 7.55 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 7.79 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT2-2 | 48.87 | 1.27 | 0.40 | 34.42 | 1.16 | 0.11 | 1.11 | 7.80 | 2.20 | 7.59 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 7.81 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT3-1 | 51.15 | 0.71 | 1.41 | 35.36 | 0.70 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 7.04 | 1.18 | 7.87 | 0.13 | 0 | 8.00 | 0.13 | 0.08 |
| MJT3-2 | 48.66 | 0.70 | 1.42 | 36.05 | 1.01 | 0.13 | 0.32 | 8.08 | 1.22 | 7.44 | 0.26 | 0.08 | 7.78 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT6-1 | 49.37 | 1.26 | 1.13 | 35.15 | 1.13 | 0.07 | 0.68 | 7.25 | 1.46 | 7.64 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 8.00 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT6-2 | 49.74 | 1.30 | 0.91 | 34.46 | 1.27 | 0.14 | 0.36 | 7.69 | 1.47 | 7.68 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 7.99 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT12-3 | 48.06 | 0.96 | 1.36 | 35.74 | 1.18 | 0.19 | 1.24 | 7.34 | 1.28 | 7.42 | 0.25 | 0.11 | 7.78 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT13-1 | 48.63 | 1.14 | 1.20 | 34.42 | 1.14 | 0.24 | 2.00 | 7.63 | 1.35 | 7.45 | 0.22 | 0.13 | 7.80 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT13-2 | 48.18 | 1.24 | 1.22 | 35.00 | 1.05 | 0.28 | 1.87 | 7.72 | 1.38 | 7.37 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 7.73 | 0 | 0 |
| MJT13-3 | 49.78 | 0.93 | 1.27 | 34.82 | 0.84 | 0.27 | 1.29 | 7.11 | 1.30 | 7.67 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 8.00 | 0 | 0.01 |
| 测试点号 | C占位 | B占位 | A占位 | 占位 总量 | |||||||||||
| Fe3+ | Mg | Fe2+ | Mn | 总计 | Mg | Fe2+ | Mn | Ca | Na | 总计 | Na | K | 总计 | ||
| MJT1-1 | 0 | 0.01 | 4.48 | 0.14 | 4.63 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.19 | 1.81 | 2 | 0.48 | 0.39 | 0.87 | 15.39 |
| MJT1-2 | 0 | 0 | 4.47 | 0.15 | 4.63 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.19 | 1.81 | 2 | 0.53 | 0.43 | 0.96 | 15.43 |
| MJT1-3 | 0 | 0.03 | 4.38 | 0.14 | 4.55 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.14 | 1.86 | 2 | 0.47 | 0.44 | 0.91 | 15.44 |
| MJT1-4 | 0 | 0 | 4.46 | 0.16 | 4.62 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.18 | 1.82 | 2 | 0.52 | 0.40 | 0.92 | 15.40 |
| MJT2-1 | 0 | 0 | 4.51 | 0.17 | 4.68 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.20 | 1.80 | 2 | 0.53 | 0.37 | 0.90 | 15.37 |
| MJT2-2 | 0 | 0.03 | 4.47 | 0.15 | 4.65 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.18 | 1.82 | 2 | 0.53 | 0.44 | 0.97 | 15.44 |
| MJT3-1 | 0 | 0 | 4.55 | 0.09 | 4.85 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 1.95 | 2 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.38 | 15.23 |
| MJT3-2 | 0 | 0.03 | 4.61 | 0.13 | 4.77 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 1.95 | 2 | 0.45 | 0.24 | 0.69 | 15.24 |
| MJT6-1 | 0 | 0.02 | 4.55 | 0.15 | 4.72 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.11 | 1.89 | 2 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.58 | 15.29 |
| MJT6-2 | 0 | 0.03 | 4.45 | 0.17 | 4.65 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.06 | 1.94 | 2 | 0.36 | 0.29 | 0.65 | 15.29 |
| MJT12-3 | 0 | 0.04 | 4.62 | 0.15 | 4.81 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.21 | 1.79 | 2 | 0.40 | 0.25 | 0.66 | 15.25 |
| MJT13-1 | 0 | 0.05 | 4.41 | 0.15 | 4.61 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.33 | 1.67 | 2 | 0.59 | 0.26 | 0.86 | 15.26 |
| MJT13-2 | 0 | 0.06 | 4.48 | 0.14 | 4.68 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.31 | 1.69 | 2 | 0.60 | 0.27 | 0.86 | 15.27 |
| MJT13-3 | 0 | 0.06 | 4.49 | 0.11 | 4.66 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.21 | 1.79 | 2 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.59 | 15.26 |
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Cr2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | 总量 | Si | ⅥAl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MJT12-1 | 52.48 | 0.29 | 0.35 | 0.57 | 0 | 29.88 | 0.42 | 0.01 | 3.64 | 12.19 | 0.01 | 99.84 | 2.13 | 0.01 |
| MJT12-2 | 52.06 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0 | 30.36 | 0.33 | 0.07 | 3.14 | 12.66 | 0.02 | 99.18 | 2.13 | 0.01 |
| 样品编号 | Ti | Cr | Fe3+ | Fe2+ | Mn | Mg | Ca | Na | Li | 阳离子总量 | Wo | En | Fs | Ac |
| MJT12-1 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.83 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.95 | 0 | 3.54 | 0.05 | 13.48 | 86.46 | 41.05 |
| MJT12-2 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.91 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.14 | 1.01 | 0 | 3.54 | 0.36 | 11.64 | 87.99 | 43.14 |
表2 毛家屯花岗岩体辉石电子探针分析计算结果(wB/%)
Table 2 EPMA results of pyroxene in the Maojiatun granite(%)
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Cr2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | 总量 | Si | ⅥAl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MJT12-1 | 52.48 | 0.29 | 0.35 | 0.57 | 0 | 29.88 | 0.42 | 0.01 | 3.64 | 12.19 | 0.01 | 99.84 | 2.13 | 0.01 |
| MJT12-2 | 52.06 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0 | 30.36 | 0.33 | 0.07 | 3.14 | 12.66 | 0.02 | 99.18 | 2.13 | 0.01 |
| 样品编号 | Ti | Cr | Fe3+ | Fe2+ | Mn | Mg | Ca | Na | Li | 阳离子总量 | Wo | En | Fs | Ac |
| MJT12-1 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.83 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.95 | 0 | 3.54 | 0.05 | 13.48 | 86.46 | 41.05 |
| MJT12-2 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.91 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.14 | 1.01 | 0 | 3.54 | 0.36 | 11.64 | 87.99 | 43.14 |
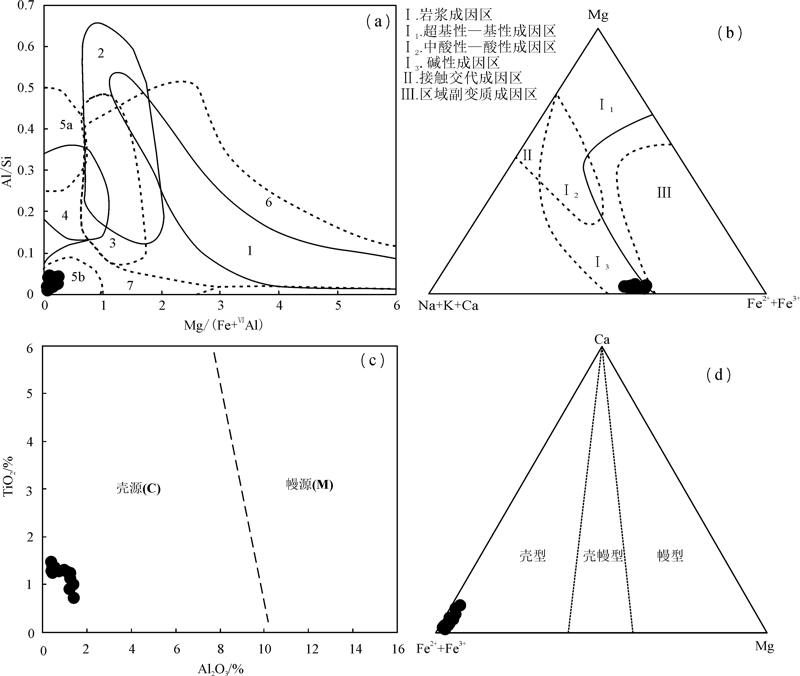
图9 角闪石Al/Si-Mg/(Fe+ⅥAl)((a)底图据薛君治等[25],1986)、Mg-(Na+K+Ca)-(Fe2++Fe3+)((b)底图据陈光远[20],1987)、Al2O3-TiO2图解((c)底图据姜常义等[26],1984)和Ca-(Fe2++Fe3+)-Mg图解((d)底图据谢应雯等[4],1990) 1.超基性岩浆角闪石;2.基性岩浆角闪石;3.中性岩浆角闪石;4.酸性岩浆角闪石;5.碱性岩浆角闪石;6.接触交代角闪石;7.区域副变质角闪石
Fig.9 Al/Si-Mg/(Fe+AlⅥ)(a), Mg-(Na+K+Ca)-(Fe2++Fe3+)(b), Al2O3-TiO2(c) and Ca-(Fe2++Fe3+)-Mg(d) diagrams of amphibole
| 样品号 | MJT1-1 | MJT1-2 | MJT1-3 | MJT1-4 | MJT2-2 | MJT3-1 | MJT3-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔNNO | -4.14 | -4.12 | -4.04 | -3.78 | -3.93 | -4.08 | -3.78 |
| 样品号 | MJT6-1 | MJT6-2 | MJT12-3 | MJT2-1 | MJT13-1 | MJT13-2 | MJT13-3 |
| ΔNNO | -3.93 | -4.08 | -4.06 | -3.98 | -4.00 | -4.01 | -3.92 |
表3 角闪石ΔNNO计算结果
Table 3 ΔNNO calculation results of amphiboles
| 样品号 | MJT1-1 | MJT1-2 | MJT1-3 | MJT1-4 | MJT2-2 | MJT3-1 | MJT3-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔNNO | -4.14 | -4.12 | -4.04 | -3.78 | -3.93 | -4.08 | -3.78 |
| 样品号 | MJT6-1 | MJT6-2 | MJT12-3 | MJT2-1 | MJT13-1 | MJT13-2 | MJT13-3 |
| ΔNNO | -3.93 | -4.08 | -4.06 | -3.98 | -4.00 | -4.01 | -3.92 |

图10 温度-氧逸度图解 实线为氧缓冲线,据Eugster等,1962[32];虚线为毛家屯岩体中碱性角闪石的氧逸度;IQF.铁-石英-铁橄榄石组合;IM.自然铁-磁铁矿组合;IW.自然铁-方铁矿组合;WM.方铁矿-磁铁矿组合;NNO.镍-氧化镍组合;MH.磁铁矿-赤铁矿组合
Fig.10 Temperature vs. oxygen fugacity diagram
| [1] |
EBY G N, WOOLLEY A R, DIN V, et al. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of nepheline syenites:Kasungu-Chipala, Ilomba, and Ulindi Nepheline Syenite Intrusions,North Nyasa Alkaline Province,Malawi[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1998,39(8):1405-1424.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 韦栋梁, 夏斌, 张玉泉, 等. 滇西卓潘—六合碱性岩的辉石成分及其岩石化学特征[J]. 矿物岩石, 2005,5(2):15-19. |
| [3] | 夏斌, 李建峰, 张玉泉, 等. 江苏省东海县片麻状碱性花岗岩的成因及年代学研究[J]. 地质科学, 2009,44(1):213-230. |
| [4] | 谢应雯, 张玉泉. 横断山区花岗岩类中角闪石的标型特征及其成因意义[J]. 矿物学报, 1990,10(1) : 95-105. |
| [5] | 谢应雯, 张玉泉. 青藏高原东部及邻区富碱侵入岩中的角闪石和辉石[J]. 矿物学报, 1998,18(1):90-96. |
| [6] | 赵广涛, 王文正. 崂山花岗岩中角闪石成分的变化及其意义[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 1998,28(4):609-614. |
| [7] | 金秉福, 岳伟, 王昆山. 黄河沉积中角闪石矿物晶体化学特征和成因分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2013,35(1):131-143. |
| [8] | 赵斌. 在高温高压条件下合成纤维状碱性角闪石的实验研究[J]. 地球化学, 1973(2):113-130. |
| [9] | 杨富贵, 王中刚, 刘丛强, 等. 西北准噶尔地区碱性花岗岩体中角闪石的地质地球化学意义[J]. 矿物学报, 1999,19(1):70-76. |
| [10] |
WU F Y, SUN D Y, LI H, et al. A-type granites in Northeastern China: Age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002,187(1/2):143-173.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 林强, 葛文春, 吴福元, 等. 大兴安岭中生代花岗岩类的地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2004,20(3):403-412. |
| [12] | 尹京武, 邵兴坤, 杨海涛, 等. 新疆拜城波孜果尔碱性岩中副矿物的特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2013,32(2):337-352. |
| [13] | 郑巧荣. 由电子探针分析值计算Fe3+和Fe2+[J]. 矿物学报, 1983,3(1):57-64. |
| [14] | 李胜荣. 结晶学与矿物学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2008: 1-346. |
| [15] | LEAKE B E, WOOLEY A R, ARPS C E S, et al. Nomenclature of amphiboles:Report of the Subcommittee on Amphiboles of the International Mineralogical Association, Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names[J]. American Mineralogist, 1997,82(9):1019-1037. |
| [16] |
LEAKE B E, WOOLLEY A R, BIRCH W D, et al. Nomenclature of amphiboles:Additions and revisions to the International Mineralogical Association’ amphibole nomenclature[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 2004,68(1):209-215.
DOI URL |
| [17] | MORIMOTO N, 黄婉康. 辉石命名法[J]. 矿物学报, 1988,8(4):3-19. |
| [18] | 马莲花, 蔡永丰, 刘希军, 等. 云南个旧卡房锡矿田花岗岩黑云母矿物化学特征及其成岩成矿意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 2018,24(5):68-77. |
| [19] |
WASTON E B, HARRISON T M. Zircon saturation revisited: temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983,64(2):295-304.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 陈光远. 成因矿物学与找矿矿物学[M]. 重庆: 重庆出版社, 1988: 1-50. |
| [21] | RIDOLFI F, PUERINI M, RENZULLI A, et al. The magmatic feeding system of El Reventador volcano (Sub-Andean zone, Ecuador) constrained by texture, mineralogy and thermobarometry of the 2002 erupted products[J]. Journal of Volcanology & Geothermal Research, 2008,176(1):94-106. |
| [22] | 刘昌实, 陈小明, 陈培荣, 等. A型岩套的分类、判别标志和成因[J]. 高校地质学报, 2003,9(4):573-591. |
| [23] | 李小伟, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 等. 关于A型花岗岩判别过程中若干问题的讨论[J]. 地质通报, 2010,29(增刊1):278-285. |
| [24] | 林培英, 邰道乾, 鄂安元. 内蒙其特敖包的镁钠铁闪石的研究[J]. 地质论评, 1986,32(6):532-540. |
| [25] | 薛君治, 白学让, 陈武. 成因矿物学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1990: 1-161. |
| [26] | 姜常义, 安三元. 论火成岩中钙质角闪石的化学组成特征及其岩石学意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 1984(3):4-12. |
| [27] | STRECK M J, DUNGAN M A, BUSSY F, et al. Mineral inventory of continuously erupting basaltic andesites at Arenal volcano,Costa Rica: implications for interpreting monotonous,crystal-rich,mafic arc stratigraphies[J]. Journal of Volcanology & Geothermal Research, 2005,140(1/3):133-155. |
| [28] | 许继锋. 米仓山碱性岩中的主要矿物研究及其成因信息[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 1993(3):269-278. |
| [29] | 王方正. 岩石物理化学[M]. 郑州: 河南科学技术出版社, 1987: 1-334. |
| [30] | RIDOLFI F, RENZULLI A, PUERINI M. Stability and chemical equilibrium of amphibole in calc-alkaline magmas: an overview, new thermobarometric formulations and application to subduction-related volcanoes[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 2010,160(1):45-66. |
| [31] |
ERNST W G, LIU J. Experimental phase-equilibrium study of Al-and Ti-contents of calcic amphibole in MORB—a semiquantitative thermobarometer[J]. American Mineralogist, 1998,83(9/10):952-969.
DOI URL |
| [32] | EUGSTER H P, WONES D R. Stability relations of the ferruginous biotite,Annite[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1962,3(1):2648-2697. |
| [33] | 王濮, 潘兆橹, 翁玲宝. 系统矿物学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1982: 1-263. |
| [34] | 邵济安. 中朝板块北缘中段地壳演化[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1991: 1-139. |
| [35] | 童英, 洪大卫, 王涛, 等. 中蒙边境中段花岗岩时空分布特征及构造和找矿意义[J]. 地球学报, 2010,31(3):395-412. |
| [36] | 许文良, 王枫, 裴福萍, 等. 中国东北中生代构造体制与区域成矿背景:来自中生代火山岩组合时空变化的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2013,29(2):339-353. |
| [37] |
EBY G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992,20(7):641.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
BONIN B. A-type granites and related rocks; evolution of a concept,problems and prospects[J]. Lithos, 2007,97:1-29.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王亿, 李立兴, 李厚民, 李小赛, 马兰晶, 邢玉亮, 孙欣宇, 戴阳, 王小慧. 冀北招兵沟铁磷矿床成矿时代及成因研究[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 46-55. |
| [2] | 侯婷婷, 姚玉增, 付建飞, 刘静, 张永利, 郭荣荣. 辽宁弓长岭富铁矿成矿过程元素迁移特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 56-67. |
| [3] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [4] | 胡生平, 韩善楚, 张洪求, 张勇, 潘家永, 钟福军, 卢建研, 李惟鑫. 庐枞盆地西湾铅锌矿床黄铁矿微量元素组成特征及成矿启示[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 183-197. |
| [5] | 刘金波, 张德贤, 胡子奇, 陈绍炜, 谢小雨. 豫西熊耳山蒿坪沟Ag-Au-Pb-Zn多金属矿床闪锌矿矿物学和微量元素组成特征及其成矿启示[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 198-213. |
| [6] | 周小蓉, 陈石, 张新顺, 丁宝通, 宋兴国, 潘楚琦, 彭梓俊. 南乍得盆地Doseo坳陷背形负花状构造成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1146-1154. |
| [7] | 于景维, 丁韦, 张欣, 祁利祺, 黄舒雅, 张智越, 张以勒. 准噶尔盆地AH5井区八道湾组碳酸盐胶结物成因及对储层影响分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1336-1344. |
| [8] | 周洪福, 方甜, 夏晨皓, 冉涛, 徐如阁, 张景华. 工程扰动诱发川西杜米滑坡复活变形特征及机理分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 1044-1053. |
| [9] | 曾帅, 马志刚, 赵聪, 杨磊, 张肃, 董继红, 梁京涛, 鄢圣武. 青藏高原东部大渡河流域太平桥乡古滑坡群复活特征多源遥感识别[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 994-1003. |
| [10] | 韩飞, 宋元宝, 张伟, 李道凌, 黄永高, 李应栩, 贾小川, 杨学俊, 杨青松, 宋旭波, 卢柳. 西藏冈底斯南木林地区晚三叠世中酸性岩浆作用及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 547-561. |
| [11] | 柳晨, 李江海, 王志琛. 南中国海形成演化的动力学模式分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 259-269. |
| [12] | 张银涛, 陈石, 刘强, 冯光, 谢舟, 梁鑫鑫, 李婷, 宋兴国, 康鹏飞, 彭梓俊. 塔里木盆地富满油田FⅠ19断裂发育特征及演化模式[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 283-295. |
| [13] | 唐名鹰, 华磊, 丁正江, 董振昆, 王炜晓, 翟孝志, 王汝杰, 郑成龙. 东昆仑祁漫塔格地区乌腊德石墨矿床地球化学特征及成矿机制研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1475-1485. |
| [14] | 夏锦胜, 孙莉, 张鹏, 陈昌阔, 汪君珠, 司江福. 四川坪河晶质石墨矿床地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1486-1496. |
| [15] | 李文霞, 赵志丹, 王晓丽, 严溶, 路远发. 西藏日喀则蛇绿岩镁铁质岩石Re-Os同位素特征及意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1503-1512. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||