



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (06): 1230-1244.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.043
饶世成1( ), 王长明1,2(
), 王长明1,2( ), 贺昕宇3, 石康兴1, 祝佳萱1, 陈奇1, 段泓羽1, 李朋伟1
), 贺昕宇3, 石康兴1, 祝佳萱1, 陈奇1, 段泓羽1, 李朋伟1
收稿日期:2020-05-29
修回日期:2020-06-23
出版日期:2020-12-22
发布日期:2020-12-22
通讯作者:
王长明
作者简介:王长明,男,1974年出生,教授,博士生导师,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事矿床学研究。Email:wangcm@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
RAO Shicheng1( ), WANG Changming1,2(
), WANG Changming1,2( ), HE Xinyu3, SHI Kangxing1, ZHU Jiaxuan1, CHEN Qi1, DUAN Hongyu1, LI Pengwei1
), HE Xinyu3, SHI Kangxing1, ZHU Jiaxuan1, CHEN Qi1, DUAN Hongyu1, LI Pengwei1
Received:2020-05-29
Revised:2020-06-23
Online:2020-12-22
Published:2020-12-22
Contact:
WANG Changming
摘要:
为解析中国东部燕山期岩浆作用过程和岩石成因机理,选取熊耳山地区五丈山岩体开展岩相学、全岩主量和微量元素地球化学和全岩Sr-Nd-Pb同位素研究。五丈山岩体主要岩性为黑云角闪二长花岗岩,具有高硅(SiO2=66.44%~71.71%)、富碱(Na2O+K2O=9.8%~10.06%)、较富Al2O3(14.52%~15.63%)以及贫TFeO(1.71%~3.47%)、CaO(0.51%~2.56%)和MgO(0.19%~0.59%)等特征,为准铝质钾玄岩系列。该岩体富集LREE、K、Sr、Pb、Zr、Hf等元素,亏损HREE、Nb、Ta、Ti、P等高场强元素,具微弱Eu正异常(δEu=1.00~1.14,均值为1.07),为I型花岗岩。全岩Sr-Nd同位素分析结果显示,(87Sr/86Sr)i值较高(0.707 3~0.708 0),εNd(t)值为-20.5~-17.9,Nd的二阶段模式年龄为2 599~2 389 Ma。全岩Pb同位素组成变化范围窄(206Pb/204Pb=17.305~17.754,207Pb/204Pb=15.427~15.481,208Pb/204Pb=37.766~37.999),显示源区物质以古老的壳源物质为主。五丈山岩体具有高Sr/Y(40.85~236.72)和La/Yb(19.34~30.46)比值,显示出埃达克质岩石特征,MgO、Cr、Ni含量低,Mg#值较小。研究结果指示五丈山岩体由加厚下地壳部分熔融产生,可能与扬子板块的北向陆内俯冲有关。
中图分类号:
饶世成, 王长明, 贺昕宇, 石康兴, 祝佳萱, 陈奇, 段泓羽, 李朋伟. 豫西熊耳山地区五丈山岩体成因与构造意义:岩石地球化学和Sr-Nd-Pb同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1230-1244.
RAO Shicheng, WANG Changming, HE Xinyu, SHI Kangxing, ZHU Jiaxuan, CHEN Qi, DUAN Hongyu, LI Pengwei. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Significance of the Wuzhangshan Pluton in Xiong’ershan, Western Henan Province: Constraint from Petrogeochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb Isotopes[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(06): 1230-1244.

图1 秦岭造山带的位置图(a)、秦岭造山带构造格架图(b)、区域地质图(c)和五丈山岩体地质简图(d)(据Wang等[17]修改)
Fig.1 Location of the Qinling Orogen (a), tectonic map of the Qinling Orogen (b), regional geologic map (c) , and geologic map of the Wuzhangshan pluton (d) (modified after Wang et al.[17])

图2 五丈山岩体野外(a)、手标本(b)及镜下((c)、(d))照片 Q.石英;Or.正长石;Pl.斜长石;Pth.条纹长石;Mc.微斜长石;Hbl.角闪石
Fig.2 Field outcrop(a),hand specimens (b) and microscopic ((c), (d)) photos of the Wuzhangshan pluton
| 样品号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFeO | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSP13D721B1 | 花岗岩 | 66.44 | 0.29 | 15.17 | 3.47 | 2.50 | 1.22 | 0.05 | 0.56 | 2.56 | 4.63 | 5.17 | 0.11 |
| HSP13D722B1 | 花岗岩 | 70.03 | 0.25 | 15.22 | 1.70 | 1.49 | 0.36 | 0.04 | 0.19 | 1.50 | 4.73 | 4.98 | 0.11 |
| HSP13D723B1 | 花岗岩 | 71.71 | 0.15 | 14.83 | 2.05 | 1.34 | 0.84 | 0.03 | 0.26 | 0.51 | 4.70 | 5.33 | 0.06 |
| HSP13D724B1 | 花岗岩 | 70.01 | 0.20 | 14.52 | 1.96 | 1.70 | 0.43 | 0.05 | 0.32 | 1.77 | 4.34 | 5.31 | 0.08 |
| HSP13D725B1 | 花岗岩 | 69.57 | 0.21 | 15.22 | 2.27 | 1.52 | 0.90 | 0.04 | 0.28 | 1.69 | 4.89 | 4.81 | 0.09 |
| HSP13D726B1 | 花岗岩 | 68.04 | 0.22 | 15.63 | 2.48 | 1.60 | 1.04 | 0.05 | 0.59 | 2.00 | 4.80 | 5.26 | 0.10 |
| 样品号 | 岩性 | LOI | Total | Mg# | A/CNK | A/NK | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni |
| HSP13D721B1 | 花岗岩 | 1.92 | 100.76 | 22.34 | 0.85 | 1.15 | 5.90 | 4.30 | 4.90 | 42.40 | 2.60 | 2.50 | 1.80 |
| HSP13D722B1 | 花岗岩 | 1.42 | 100.36 | 16.60 | 0.96 | 1.15 | 6.30 | 2.50 | 3.20 | 34.70 | 3.00 | 1.20 | 1.20 |
| HSP13D723B1 | 花岗岩 | 1.01 | 100.86 | 18.47 | 1.03 | 1.10 | 3.40 | 3.10 | 2.10 | 23.50 | 2.10 | 1.10 | 1.30 |
| HSP13D724B1 | 花岗岩 | 1.70 | 100.48 | 22.54 | 0.90 | 1.13 | 4.10 | 4.70 | 3.20 | 32.10 | 2.90 | 1.60 | 1.30 |
| HSP13D725B1 | 花岗岩 | 1.62 | 100.94 | 18.04 | 0.93 | 1.15 | 4.00 | 3.40 | 3.10 | 26.90 | 2.20 | 1.10 | 1.10 |
| HSP13D726B1 | 花岗岩 | 1.17 | 100.62 | 29.78 | 0.91 | 1.15 | 5.20 | 3.40 | 3.60 | 24.60 | 2.40 | 1.90 | 1.40 |
| 样品号 | 岩性 | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | Zr | Nb | Mo | Cd | In | Sb | Cs |
| HSP13D721B1 | 花岗岩 | 8.90 | 34.0 | 19.60 | 115.00 | 1 232 | 151 | 19.50 | 0.80 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 2.70 |
| HSP13D722B1 | 花岗岩 | 6.20 | 21.0 | 18.00 | 111.00 | 947 | 199 | 21.30 | 0.60 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 1.80 |
| HSP13D723B1 | 花岗岩 | 4.20 | 18.0 | 16.10 | 110.00 | 552 | 168 | 18.10 | 0.60 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 1.10 |
| HSP13D724B1 | 花岗岩 | 5.70 | 27.0 | 18.20 | 123.00 | 625 | 141 | 23.50 | 1.40 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 1.10 |
| HSP13D725B1 | 花岗岩 | 5.00 | 19.0 | 17.10 | 104.00 | 904 | 189 | 20.70 | 0.60 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.70 |
| HSP13D726B1 | 花岗岩 | 6.30 | 24.0 | 16.90 | 116.00 | 4 190 | 164 | 21.10 | 0.50 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.80 |
| 样品号 | 岩性 | Ba | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Tl | Pb | Bi | Th | U | Y | La |
| HSP13D721B1 | 花岗岩 | 3 768 | 4.80 | 0.90 | 1.80 | 0 | 0.50 | 32.10 | - | 35.20 | 7.10 | 21.70 | 46.80 |
| HSP13D722B1 | 花岗岩 | 2 445 | 6.30 | 0.90 | 0.60 | 0 | 0.50 | 38.10 | - | 24.60 | 3.50 | 14.30 | 37.20 |
| HSP13D723B1 | 花岗岩 | 1 457 | 5.90 | 0.80 | 1.40 | 0 | 0.40 | 18.70 | - | 18.50 | 2.90 | 11.40 | 27.00 |
| HSP13D724B1 | 花岗岩 | 2 200 | 5.20 | 1.00 | 1.50 | <0.002 | 0.50 | 28.10 | 0.10 | 21.80 | 4.20 | 15.30 | 42.00 |
| HSP13D725B1 | 花岗岩 | 2 005 | 6.20 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0 | 0.40 | 31.10 | - | 25.30 | 3.10 | 10.60 | 39.60 |
| HSP13D726B1 | 花岗岩 | 2 580 | 5.20 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0 | 0.50 | 30.60 | - | 19.30 | 6.00 | 17.70 | 42.50 |
| 样品号 | 岩性 | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb |
| HSP13D721B1 | 花岗岩 | 79.10 | 8.56 | 29.90 | 4.94 | 1.72 | 4.11 | 0.68 | 3.63 | 0.72 | 2.23 | 0.35 | 2.42 |
| HSP13D722B1 | 花岗岩 | 63.60 | 6.89 | 24.30 | 3.74 | 1.26 | 3.28 | 0.49 | 2.55 | 0.49 | 1.39 | 0.23 | 1.49 |
| HSP13D723B1 | 花岗岩 | 43.00 | 4.37 | 14.90 | 2.45 | 0.76 | 2.10 | 0.32 | 1.87 | 0.38 | 1.24 | 0.21 | 1.52 |
| HSP13D724B1 | 花岗岩 | 63.50 | 6.38 | 22.70 | 3.33 | 1.17 | 3.10 | 0.48 | 2.58 | 0.48 | 1.55 | 0.28 | 1.94 |
| HSP13D725B1 | 花岗岩 | 58.50 | 5.99 | 19.80 | 3.07 | 1.00 | 2.50 | 0.37 | 1.89 | 0.34 | 1.06 | 0.19 | 1.30 |
| HSP13D726B1 | 花岗岩 | 64.30 | 6.54 | 22.70 | 3.60 | 1.16 | 3.22 | 0.54 | 2.82 | 0.58 | 1.89 | 0.31 | 2.05 |
| 样品号 | 岩性 | Lu | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | δEu | δCe | ||||
| HSP13D721B1 | 花岗岩 | 0.35 | 185.51 | 171.02 | 14.49 | 11.80 | 13.04 | 1.14 | 0.90 | ||||
| HSP13D722B1 | 花岗岩 | 0.23 | 147.13 | 136.99 | 10.14 | 13.50 | 16.83 | 1.08 | 0.91 | ||||
| HSP13D723B1 | 花岗岩 | 0.25 | 100.37 | 92.48 | 7.89 | 11.72 | 11.98 | 1.00 | 0.88 | ||||
| HSP13D724B1 | 花岗岩 | 0.31 | 149.79 | 139.08 | 10.71 | 12.98 | 14.60 | 1.10 | 0.85 | ||||
| HSP13D725B1 | 花岗岩 | 0.21 | 135.82 | 127.96 | 7.86 | 16.28 | 20.54 | 1.07 | 0.83 | ||||
| HSP13D726B1 | 花岗岩 | 0.33 | 152.54 | 140.80 | 11.74 | 11.99 | 13.98 | 1.02 | 0.85 |
表1 五丈山岩体主量(wB/%)、微量和稀土元素(wB/10-6)分析结果
Table 1 Major (%) ,trace element and REEs (10-6) contents of granite samples from the Wuzhangshan pluton
| 样品号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFeO | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSP13D721B1 | 花岗岩 | 66.44 | 0.29 | 15.17 | 3.47 | 2.50 | 1.22 | 0.05 | 0.56 | 2.56 | 4.63 | 5.17 | 0.11 |
| HSP13D722B1 | 花岗岩 | 70.03 | 0.25 | 15.22 | 1.70 | 1.49 | 0.36 | 0.04 | 0.19 | 1.50 | 4.73 | 4.98 | 0.11 |
| HSP13D723B1 | 花岗岩 | 71.71 | 0.15 | 14.83 | 2.05 | 1.34 | 0.84 | 0.03 | 0.26 | 0.51 | 4.70 | 5.33 | 0.06 |
| HSP13D724B1 | 花岗岩 | 70.01 | 0.20 | 14.52 | 1.96 | 1.70 | 0.43 | 0.05 | 0.32 | 1.77 | 4.34 | 5.31 | 0.08 |
| HSP13D725B1 | 花岗岩 | 69.57 | 0.21 | 15.22 | 2.27 | 1.52 | 0.90 | 0.04 | 0.28 | 1.69 | 4.89 | 4.81 | 0.09 |
| HSP13D726B1 | 花岗岩 | 68.04 | 0.22 | 15.63 | 2.48 | 1.60 | 1.04 | 0.05 | 0.59 | 2.00 | 4.80 | 5.26 | 0.10 |
| 样品号 | 岩性 | LOI | Total | Mg# | A/CNK | A/NK | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni |
| HSP13D721B1 | 花岗岩 | 1.92 | 100.76 | 22.34 | 0.85 | 1.15 | 5.90 | 4.30 | 4.90 | 42.40 | 2.60 | 2.50 | 1.80 |
| HSP13D722B1 | 花岗岩 | 1.42 | 100.36 | 16.60 | 0.96 | 1.15 | 6.30 | 2.50 | 3.20 | 34.70 | 3.00 | 1.20 | 1.20 |
| HSP13D723B1 | 花岗岩 | 1.01 | 100.86 | 18.47 | 1.03 | 1.10 | 3.40 | 3.10 | 2.10 | 23.50 | 2.10 | 1.10 | 1.30 |
| HSP13D724B1 | 花岗岩 | 1.70 | 100.48 | 22.54 | 0.90 | 1.13 | 4.10 | 4.70 | 3.20 | 32.10 | 2.90 | 1.60 | 1.30 |
| HSP13D725B1 | 花岗岩 | 1.62 | 100.94 | 18.04 | 0.93 | 1.15 | 4.00 | 3.40 | 3.10 | 26.90 | 2.20 | 1.10 | 1.10 |
| HSP13D726B1 | 花岗岩 | 1.17 | 100.62 | 29.78 | 0.91 | 1.15 | 5.20 | 3.40 | 3.60 | 24.60 | 2.40 | 1.90 | 1.40 |
| 样品号 | 岩性 | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | Zr | Nb | Mo | Cd | In | Sb | Cs |
| HSP13D721B1 | 花岗岩 | 8.90 | 34.0 | 19.60 | 115.00 | 1 232 | 151 | 19.50 | 0.80 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 2.70 |
| HSP13D722B1 | 花岗岩 | 6.20 | 21.0 | 18.00 | 111.00 | 947 | 199 | 21.30 | 0.60 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 1.80 |
| HSP13D723B1 | 花岗岩 | 4.20 | 18.0 | 16.10 | 110.00 | 552 | 168 | 18.10 | 0.60 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 1.10 |
| HSP13D724B1 | 花岗岩 | 5.70 | 27.0 | 18.20 | 123.00 | 625 | 141 | 23.50 | 1.40 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 1.10 |
| HSP13D725B1 | 花岗岩 | 5.00 | 19.0 | 17.10 | 104.00 | 904 | 189 | 20.70 | 0.60 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.70 |
| HSP13D726B1 | 花岗岩 | 6.30 | 24.0 | 16.90 | 116.00 | 4 190 | 164 | 21.10 | 0.50 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.80 |
| 样品号 | 岩性 | Ba | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Tl | Pb | Bi | Th | U | Y | La |
| HSP13D721B1 | 花岗岩 | 3 768 | 4.80 | 0.90 | 1.80 | 0 | 0.50 | 32.10 | - | 35.20 | 7.10 | 21.70 | 46.80 |
| HSP13D722B1 | 花岗岩 | 2 445 | 6.30 | 0.90 | 0.60 | 0 | 0.50 | 38.10 | - | 24.60 | 3.50 | 14.30 | 37.20 |
| HSP13D723B1 | 花岗岩 | 1 457 | 5.90 | 0.80 | 1.40 | 0 | 0.40 | 18.70 | - | 18.50 | 2.90 | 11.40 | 27.00 |
| HSP13D724B1 | 花岗岩 | 2 200 | 5.20 | 1.00 | 1.50 | <0.002 | 0.50 | 28.10 | 0.10 | 21.80 | 4.20 | 15.30 | 42.00 |
| HSP13D725B1 | 花岗岩 | 2 005 | 6.20 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0 | 0.40 | 31.10 | - | 25.30 | 3.10 | 10.60 | 39.60 |
| HSP13D726B1 | 花岗岩 | 2 580 | 5.20 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0 | 0.50 | 30.60 | - | 19.30 | 6.00 | 17.70 | 42.50 |
| 样品号 | 岩性 | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb |
| HSP13D721B1 | 花岗岩 | 79.10 | 8.56 | 29.90 | 4.94 | 1.72 | 4.11 | 0.68 | 3.63 | 0.72 | 2.23 | 0.35 | 2.42 |
| HSP13D722B1 | 花岗岩 | 63.60 | 6.89 | 24.30 | 3.74 | 1.26 | 3.28 | 0.49 | 2.55 | 0.49 | 1.39 | 0.23 | 1.49 |
| HSP13D723B1 | 花岗岩 | 43.00 | 4.37 | 14.90 | 2.45 | 0.76 | 2.10 | 0.32 | 1.87 | 0.38 | 1.24 | 0.21 | 1.52 |
| HSP13D724B1 | 花岗岩 | 63.50 | 6.38 | 22.70 | 3.33 | 1.17 | 3.10 | 0.48 | 2.58 | 0.48 | 1.55 | 0.28 | 1.94 |
| HSP13D725B1 | 花岗岩 | 58.50 | 5.99 | 19.80 | 3.07 | 1.00 | 2.50 | 0.37 | 1.89 | 0.34 | 1.06 | 0.19 | 1.30 |
| HSP13D726B1 | 花岗岩 | 64.30 | 6.54 | 22.70 | 3.60 | 1.16 | 3.22 | 0.54 | 2.82 | 0.58 | 1.89 | 0.31 | 2.05 |
| 样品号 | 岩性 | Lu | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | δEu | δCe | ||||
| HSP13D721B1 | 花岗岩 | 0.35 | 185.51 | 171.02 | 14.49 | 11.80 | 13.04 | 1.14 | 0.90 | ||||
| HSP13D722B1 | 花岗岩 | 0.23 | 147.13 | 136.99 | 10.14 | 13.50 | 16.83 | 1.08 | 0.91 | ||||
| HSP13D723B1 | 花岗岩 | 0.25 | 100.37 | 92.48 | 7.89 | 11.72 | 11.98 | 1.00 | 0.88 | ||||
| HSP13D724B1 | 花岗岩 | 0.31 | 149.79 | 139.08 | 10.71 | 12.98 | 14.60 | 1.10 | 0.85 | ||||
| HSP13D725B1 | 花岗岩 | 0.21 | 135.82 | 127.96 | 7.86 | 16.28 | 20.54 | 1.07 | 0.83 | ||||
| HSP13D726B1 | 花岗岩 | 0.33 | 152.54 | 140.80 | 11.74 | 11.99 | 13.98 | 1.02 | 0.85 |
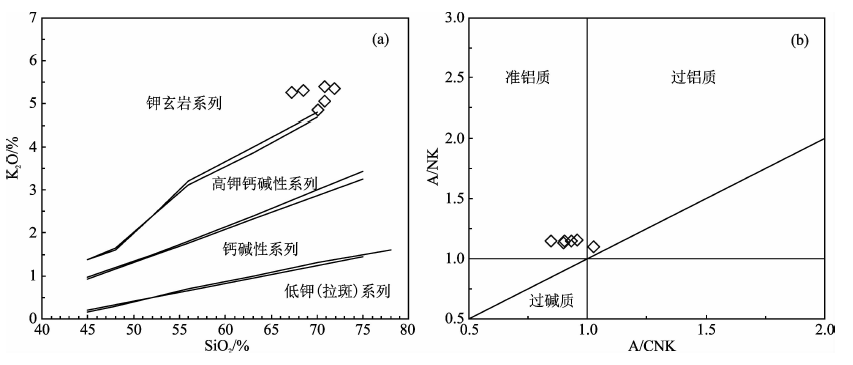
图4 五丈山岩体分类图解 (a)SiO2-K2O图解(底图据Peccerillo 和Taylor[42]);(b)A/CNK-A/NK图解(底图据Maniar和Piccoli[43])
Fig.4 Petrological discrimination diagrams for the Wuzhangshan pluton
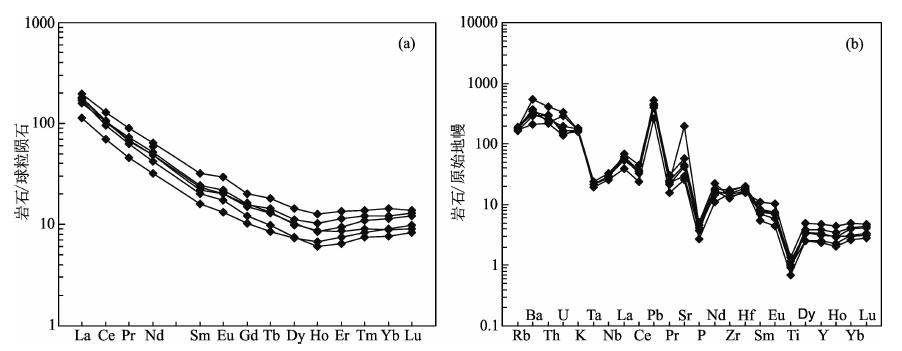
图5 五丈山岩体稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(球粒陨石和原始地幔值引自Sun 和 McDonough[44])
Fig. 5 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle (PM)-normalized multi-element spider diagram (b) for the Wuzhangshan pluton(Chondrite and PM normalizing values from Sun and McDonough[44] )
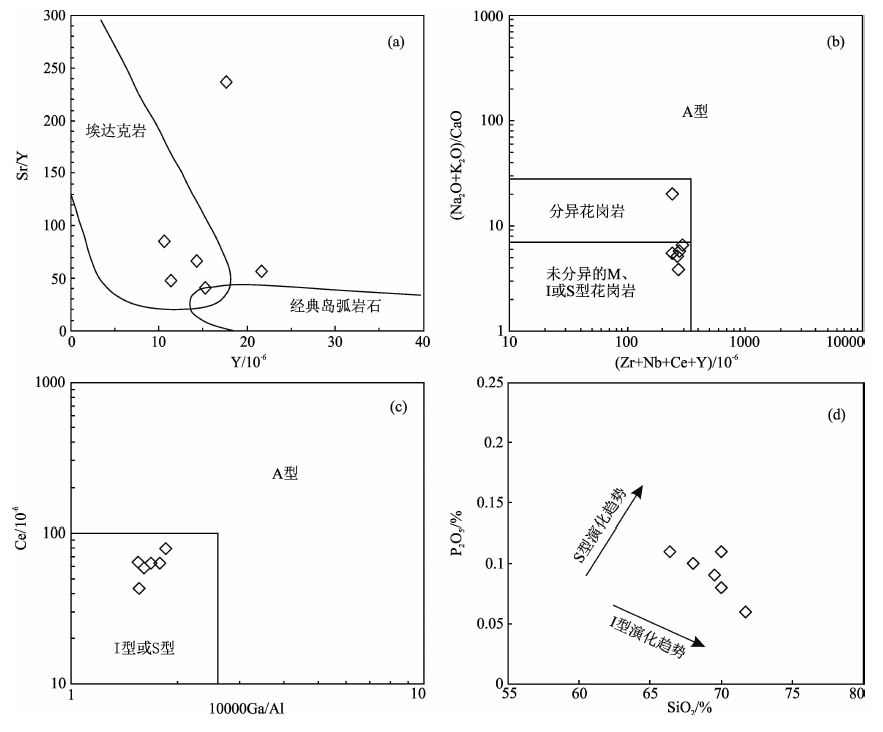
图6 五丈山岩体成因类型判别图解 (a)埃达克质岩石判别图解(底图据Defant和Drummond[45]);(b)(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-(Na2O+K2O)/CaO图解;(c)10000 Ga/Al-Ce图解((b)和(c)底图据Whalen等[46]);(d)SiO2-P2O5图解
Fig.6 Petrogenetic discrimination diagrams for the Wuzhangshan pluton
| 样品 | Rb/ 10-6 | Sr/ 10-6 | 87Rb/ 86Sr | 87Sr/ 86Sr(2σ) | (87Sr/ 86Sr)i | Sm/ 10-6 | Nd/ 10-6 | 147Sm/ 144Nd | 143Nd/ 144Nd(2σ) | εNd(0) | εNd(t) | TDM/ Ma | Ma | (143Nd/ 144Nd)i |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSP13D721B1 | 115 | 1 232 | 0.270 1 | 0.708 354 (10) | 0.707 78 | 4.94 | 29.9 | 0.099 9 | 0.511 549 (8) | -21.2 | -19.4 | 2 139 | 2 513 | 0.511 451 |
| HSP13D722B1 | 111 | 947 | 0.339 1 | 0.708 026 (16) | 0.707 30 | 3.74 | 24.3 | 0.093 0 | 0.511 621 (10) | -19.8 | -17.9 | 1 928 | 2 389 | 0.511 530 |
| HSP13D723B1 | 110 | 552 | 0.576 6 | 0.709 258 (11) | 0.708 03 | 2.45 | 14.9 | 0.099 4 | 0.511 494 (6) | -22.3 | -20.5 | 2 203 | 2 599 | 0.511 396 |
| HSP13D724B1 | 123 | 625 | 0.569 5 | 0.709 105 (11) | 0.707 89 | 3.33 | 22.7 | 0.088 7 | 0.511 584 (7) | -20.6 | -18.5 | 1 906 | 2 441 | 0.511 497 |
| HSP13D725B1 | 104 | 904 | 0.332 9 | 0.708 203 (12) | 0.707 49 | 3.07 | 19.8 | 0.093 7 | 0.511 545 (6) | -21.3 | -19.4 | 2 034 | 2 510 | 0.511 453 |
| HSP13D726B1 | 116 | 4 190 | 0.080 1 | 0.708 226 (18) | 0.708 06 | 3.60 | 22.7 | 0.095 9 | 0.511 528 (8) | -21.7 | -19.7 | 2 094 | 2 540 | 0.511 434 |
表2 五丈山岩体样品Sr-Nd同位素组成
Table 2 Sr-Nd isotope compositions of samples from the Wuzhangshan pluton
| 样品 | Rb/ 10-6 | Sr/ 10-6 | 87Rb/ 86Sr | 87Sr/ 86Sr(2σ) | (87Sr/ 86Sr)i | Sm/ 10-6 | Nd/ 10-6 | 147Sm/ 144Nd | 143Nd/ 144Nd(2σ) | εNd(0) | εNd(t) | TDM/ Ma | Ma | (143Nd/ 144Nd)i |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSP13D721B1 | 115 | 1 232 | 0.270 1 | 0.708 354 (10) | 0.707 78 | 4.94 | 29.9 | 0.099 9 | 0.511 549 (8) | -21.2 | -19.4 | 2 139 | 2 513 | 0.511 451 |
| HSP13D722B1 | 111 | 947 | 0.339 1 | 0.708 026 (16) | 0.707 30 | 3.74 | 24.3 | 0.093 0 | 0.511 621 (10) | -19.8 | -17.9 | 1 928 | 2 389 | 0.511 530 |
| HSP13D723B1 | 110 | 552 | 0.576 6 | 0.709 258 (11) | 0.708 03 | 2.45 | 14.9 | 0.099 4 | 0.511 494 (6) | -22.3 | -20.5 | 2 203 | 2 599 | 0.511 396 |
| HSP13D724B1 | 123 | 625 | 0.569 5 | 0.709 105 (11) | 0.707 89 | 3.33 | 22.7 | 0.088 7 | 0.511 584 (7) | -20.6 | -18.5 | 1 906 | 2 441 | 0.511 497 |
| HSP13D725B1 | 104 | 904 | 0.332 9 | 0.708 203 (12) | 0.707 49 | 3.07 | 19.8 | 0.093 7 | 0.511 545 (6) | -21.3 | -19.4 | 2 034 | 2 510 | 0.511 453 |
| HSP13D726B1 | 116 | 4 190 | 0.080 1 | 0.708 226 (18) | 0.708 06 | 3.60 | 22.7 | 0.095 9 | 0.511 528 (8) | -21.7 | -19.7 | 2 094 | 2 540 | 0.511 434 |
| 样品 | 含量/10-6 | 同位素比值 | 初始铅同位素比值 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Th | U | 208Pb/204Pb (2σ) | 207Pb/204Pb (2σ) | 206Pb/204Pb (2σ) | (206Pb/ 204Pb)i | (207Pb/ 204Pb)i | (208Pb/ 204Pb)i | |||
| HSP13D721B1 | 32.1 | 35.2 | 7.12 | 37.869(4) | 15.442(2) | 17.524(1) | 17.215 | 15.427 | 37.327 | ||
| HSP13D722B1 | 38.1 | 24.6 | 3.54 | 37.766(3) | 15.427(1) | 17.384(1) | 17.164 | 15.416 | 36.994 | ||
| HSP13D723B1 | 18.7 | 18.5 | 2.86 | 37.885(4) | 15.444(2) | 17.754(2) | 17.518 | 15.432 | 36.861 | ||
| HSP13D724B1 | 28.1 | 21.8 | 4.16 | 37.981(5) | 15.470(2) | 17.709(2) | 17.418 | 15.455 | 37.109 | ||
| HSP13D725B1 | 31.1 | 25.3 | 3.09 | 37.905(5) | 15.457(2) | 17.503(2) | 17.317 | 15.448 | 37.152 | ||
| HSP13D726B1 | 30.6 | 19.3 | 5.97 | 37.854(4) | 15.436(2) | 17.477(2) | 17.005 | 15.412 | 36.869 | ||
表3 五丈山岩体样品Pb同位素组成
Table 3 Pb isotope compositions of samples from the Wuzhangshan pluton
| 样品 | 含量/10-6 | 同位素比值 | 初始铅同位素比值 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Th | U | 208Pb/204Pb (2σ) | 207Pb/204Pb (2σ) | 206Pb/204Pb (2σ) | (206Pb/ 204Pb)i | (207Pb/ 204Pb)i | (208Pb/ 204Pb)i | |||
| HSP13D721B1 | 32.1 | 35.2 | 7.12 | 37.869(4) | 15.442(2) | 17.524(1) | 17.215 | 15.427 | 37.327 | ||
| HSP13D722B1 | 38.1 | 24.6 | 3.54 | 37.766(3) | 15.427(1) | 17.384(1) | 17.164 | 15.416 | 36.994 | ||
| HSP13D723B1 | 18.7 | 18.5 | 2.86 | 37.885(4) | 15.444(2) | 17.754(2) | 17.518 | 15.432 | 36.861 | ||
| HSP13D724B1 | 28.1 | 21.8 | 4.16 | 37.981(5) | 15.470(2) | 17.709(2) | 17.418 | 15.455 | 37.109 | ||
| HSP13D725B1 | 31.1 | 25.3 | 3.09 | 37.905(5) | 15.457(2) | 17.503(2) | 17.317 | 15.448 | 37.152 | ||
| HSP13D726B1 | 30.6 | 19.3 | 5.97 | 37.854(4) | 15.436(2) | 17.477(2) | 17.005 | 15.412 | 36.869 | ||
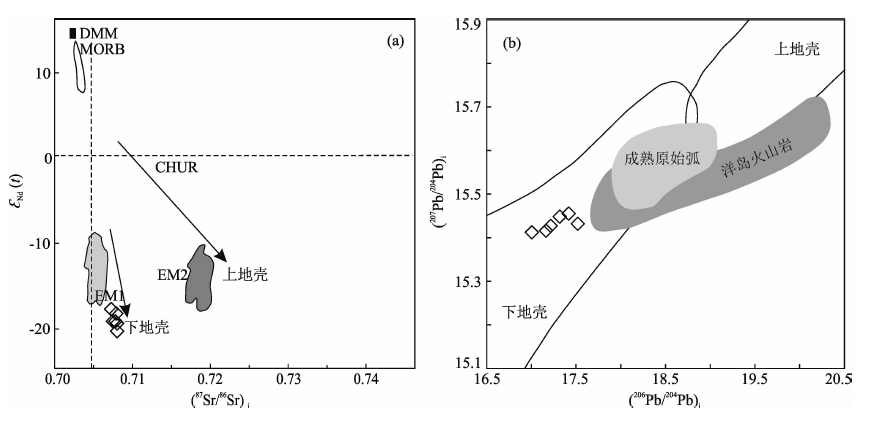
图7 五丈山岩体源区判别图解 (a)(87Sr/86Sr)i-εNd(t)图解;(b)(206Pb/204Pb)i-(207Pb/204Pb)i图解。DMM(亏损地幔)、MORB(大洋中脊玄武岩)、EM1(富集地幔1)和EM2(富集地幔2)数据引自Zindler和Hart[57],上地壳数据引自Weaver[58],下地壳数据引自Othman等[59],CHUR为球粒陨石均一源储;底图据Zartman和Doe[60]
Fig.7 Source region discrimination diagrams of the Wuzhangshan pluton
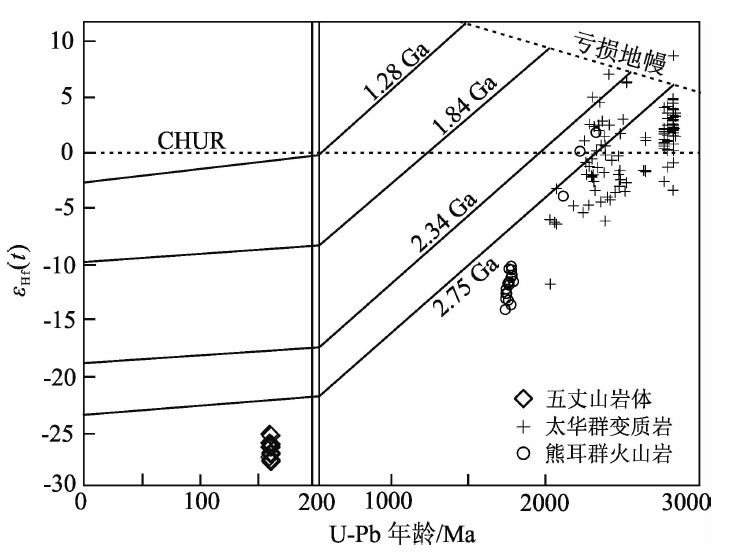
图8 五丈山岩体U-Pb年龄与εHf(t)关系图解 五丈山岩体数据来自Wang等[20];熊耳群火山岩数据来自Wang等[61]和Wang等[62];太华群变质岩数据来自Xu等[63]和第五春荣等[38]
Fig.8 Plot of U-Pb age vs. εHf(t) for the Wuzhangshan pluton
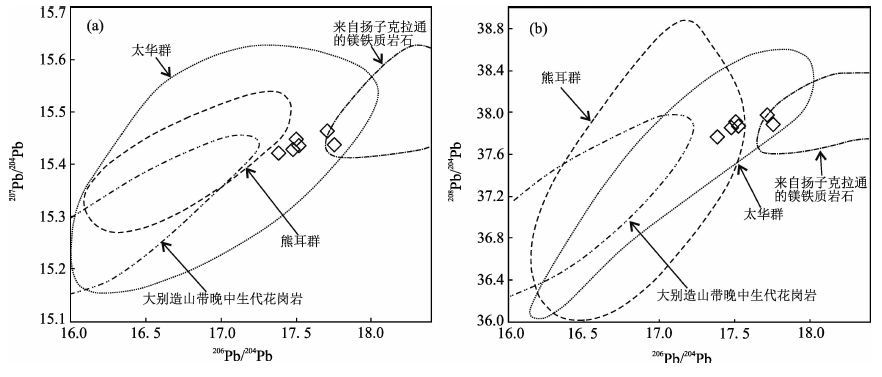
图9 五丈山岩体Pb同位素图解(熊耳群、太华群、大别造山带晚中生代花岗岩和扬子克拉通的镁铁质岩石数据范围据Zou等[26])
Fig.9 206Pb/204Pb vs. 207Pb/204Pb (a) and 206Pb/204Pb vs. 208Pb/204Pb (b) diagrams for the Wuzhangshan pluton
| 序号 | 年龄/Ma | 测试方法 | 测试矿物 | 样品点数 | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 159 | K-Ar | 全岩 | 不详 | 河南省地质矿产局[ |
| 2 | 155.4±3.5 | K-Ar | 全岩 | 不详 | 范光等[ |
| 3 | 144.7±3.4 | K-Ar | 全岩 | 不详 | 范光等[ |
| 4 | 156.8±1.2 | SHRIMP U-Pb | 锆石 | 14 | 李永峰[ |
| 5 | 156.8±3.1 | Ar-Ar | 角闪石 | 13 | Han等[ |
| 6 | 157.0±1.0 | SHRIMP U-Pb | 锆石 | 14 | Mao等[ |
| 7 | 153.6±1.3 | SHRIMP U-Pb | 锆石 | 14 | 孟芳等[ |
| 8 | 177.3±1.4 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 15 | 庞绪成等[ |
| 9 | 177.4±1.7 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 15 | 庞绪成等[ |
| 10 | 177.3±1.6 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 15 | 庞绪成等[ |
| 11 | 177.4±1.9 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 14 | 庞绪成等[ |
| 12 | 177.5±1.5 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 17 | 庞绪成等[ |
| 13 | 177.2±1.7 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 14 | 庞绪成等[ |
| 14 | 160.1±0.6 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 29 | Wang等[ |
| 15 | 159.6±1.6 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 18 | 梁涛等[ |
| 16 | 157.2±1.1 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 15 | Zou等[ |
| 17 | 156.4±1.1 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 19 | Zou等[ |
表4 五丈山岩体形成年龄
Table 4 Age data statistics for the Wuzhangshan pluton
| 序号 | 年龄/Ma | 测试方法 | 测试矿物 | 样品点数 | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 159 | K-Ar | 全岩 | 不详 | 河南省地质矿产局[ |
| 2 | 155.4±3.5 | K-Ar | 全岩 | 不详 | 范光等[ |
| 3 | 144.7±3.4 | K-Ar | 全岩 | 不详 | 范光等[ |
| 4 | 156.8±1.2 | SHRIMP U-Pb | 锆石 | 14 | 李永峰[ |
| 5 | 156.8±3.1 | Ar-Ar | 角闪石 | 13 | Han等[ |
| 6 | 157.0±1.0 | SHRIMP U-Pb | 锆石 | 14 | Mao等[ |
| 7 | 153.6±1.3 | SHRIMP U-Pb | 锆石 | 14 | 孟芳等[ |
| 8 | 177.3±1.4 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 15 | 庞绪成等[ |
| 9 | 177.4±1.7 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 15 | 庞绪成等[ |
| 10 | 177.3±1.6 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 15 | 庞绪成等[ |
| 11 | 177.4±1.9 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 14 | 庞绪成等[ |
| 12 | 177.5±1.5 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 17 | 庞绪成等[ |
| 13 | 177.2±1.7 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 14 | 庞绪成等[ |
| 14 | 160.1±0.6 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 29 | Wang等[ |
| 15 | 159.6±1.6 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 18 | 梁涛等[ |
| 16 | 157.2±1.1 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 15 | Zou等[ |
| 17 | 156.4±1.1 | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 锆石 | 19 | Zou等[ |
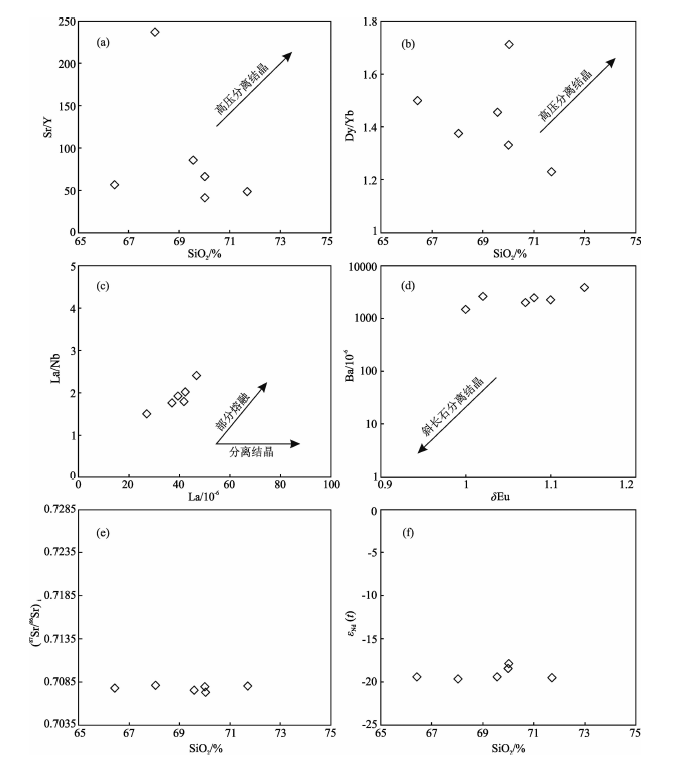
图10 五丈山岩体成因图解 (a)SiO2-Sr/Y图解;(b)SiO2-Dy/Yb图解;(c)La-La/Nb图解;(d)δEu-Ba图解;(e)SiO2-(87Sr/86Sr)i图解;(f)SiO2-εNd(t)图解
Fig.10 Petrogenetic diagrams for the Wuzhangshan pluton
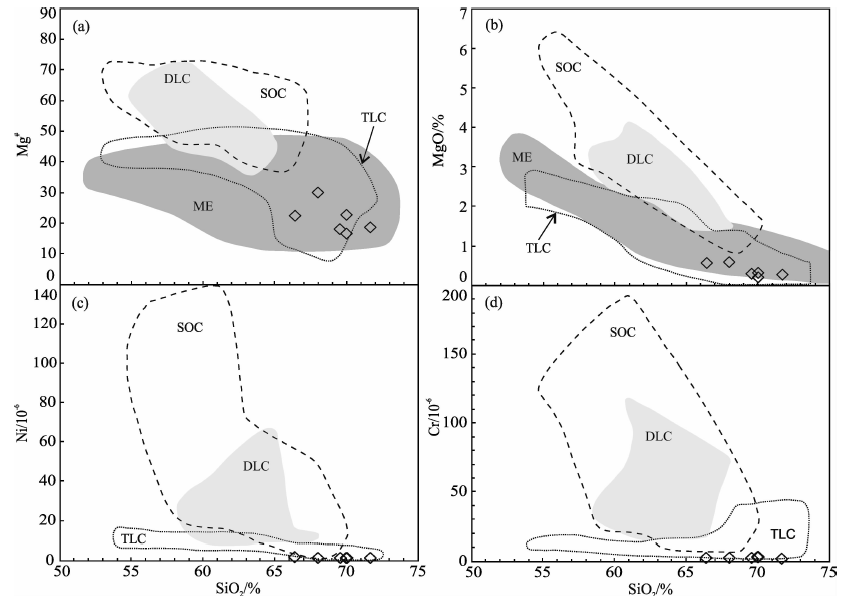
图11 埃达克质岩石成因判别图解(底图据Lu等[76]) (a)SiO2-Mg#图解;(b)SiO2-MgO图解;(c)SiO2-Ni图解;(d)SiO2-Cr图解。SOC.起源于俯冲洋壳的埃达克质岩石;DLC.起源于拆沉下地壳的埃达克质岩石;TLC.起源于加厚下地壳的埃达克质岩石;ME.变玄武岩和榴辉岩实验熔体
Fig.11 Petrogenesis discrimination diagrams of adakite rocks (after Lu et al.[76])
| [1] | 吴利仁. 中国东部中生代花岗岩类[J]. 岩石学报, 1985,1(1):1-10. |
| [2] | 王德滋, 周金城. 我国花岗岩研究的回顾与展望[J]. 岩石学报, 1999,15(2):161-169. |
| [3] | 邓晋福, 赵国春, 赵海玲, 等. 中国东部燕山期火成岩构造组合与造山-深部过程[J]. 地质论评, 2000,46(1):41-48. |
| [4] | 周新民, 李武显. 中国东南部晚中生代火成岩成因: 岩石圈消减和玄武岩底侵相结合的模式[J]. 自然科学进展, 2000,10(3):240-247. |
| [5] | 张旗, 王焰, 钱青, 等. 中国东部燕山期埃达克岩的特征及其构造-成矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2001,17(2):236-244. |
| [6] | 张旗, 王焰, 王元龙. 燕山期中国东部高原下地壳组成初探: 埃达克质岩Sr、Nd同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2001,17(4):505-513. |
| [7] | 张旗, 赵太平, 王焰, 等. 中国东部燕山期岩浆活动的几个问题[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2001,20(3):273-280. |
| [8] | 张旗, 金惟俊, 李承东, 等. 再论花岗岩按照Sr-Yb的分类标志[J]. 岩石学报, 2010,26(4):985-1015. |
| [9] | 洪迪. 中国东部中生代板内花岗岩类的成因是古太平洋板块俯冲的运动的结果[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院大学中国科学院海洋研究所, 2018: 1-62. |
| [10] | DENG J, GONG Q J, WANG C M, et al. Sequence of Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous magmatic-hydrothermal events in the Xiong’ershan region, Central China: An overview with new zircon U-Pb geochronology data on quartz porphyries[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013,79:161-172. |
| [11] | DENG J, WANG C M, BAGAS L, et al. Cretaceous-Cenozoic tectonic history of the Jiaojia Fault and gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from zircon U-Pb, illite K-Ar, and apatite fission track thermochronometry[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2015,50(8):987-1006. |
| [12] | DENG J, WANG C M, BAGAS L, et al. Crustal architecture and metallogenesis in the south-eastern North China Craton[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018,182:251-272. |
| [13] | DENG J, WANG Q F. Gold mineralization in China: Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016,36:219-274. |
| [14] | HE X Y, WANG J H, WANG C M, et al. Petrogenesis, zircon U-Pb age, and geochemistry of the A-type Mogou syenite, western Henan Province: Implications for mesozoic Tectono-magmatic evolution of the Qinling orogen[J]. Journal of Earth System Science, 2016,125(3):585-603. |
| [15] | WANG C M, DENG J, ZHANG S T, et al. Metallogenic province and large scale mineralization of volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits in China[J]. Resource Geology, 2010,60(4):404-413. |
| [16] | WANG C M, DENG J, CARRANZA E J M, et al. Nature, diversity and temporal-spatial distributions of sediment-hosted Pb-Zn deposits in China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014,56:327-351. |
| [17] | WANG C M, CHEN L, BAGAS L, et al. Characterization and origin of the Taishanmiao aluminous A-type granites: Implications for Early Cretaceous lithospheric thinning at the southern margin of the North China Craton[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2016,105(5):1563-1589. |
| [18] | WANG C M, BAGAS L, LU Y J, et al. Terrane boundary and spatio-temporal distribution of ore deposits in the Sanjiang Tethyan Orogen: Insights from zircon Hf-isotopic mapping[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016,156:39-65. |
| [19] | WANG C M, LU Y J, HE X Y, et al. The Paleoproterozoic diorite dykes in the southern margin of the North China Craton: Insight into rift-related magmatism[J]. Precambrian Research, 2016,227:26-46. |
| [20] | WANG C M, DENG J, BAGAS L, et al. Zircon Hf-isotopic mapping for understanding crustal architecture and metallogenesis in the Eastern Qinling Orogen[J]. Gondwana Research, 2017,50:293-310. |
| [21] | WANG C M, BAGAS L, DENG J, et al. Crustal architecture and its controls on mineralization in the North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018,98:109-125. |
| [22] | ZHANG J, CHEN Y J, PIRAJNO F, et al. Geology, C-H-O-S-Pb isotope systematics and geochronology of the Yindongpo gold deposit, Tongbai Mountains, central China: Implication for ore genesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013,53:343-356. |
| [23] | ZHANG Z C, HOU T, SANTOSH M, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution and tectonic settings of the major iron deposits in China: An overview[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014,57:247-263. |
| [24] | 陈斌, 田伟, 翟明国, 等. 太行山和华北其它地区中生代岩浆作用的锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学特征及其岩浆成因和地球动力学意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2005,21(1):13-24. |
| [25] | 郑永飞, 徐峥, 赵子福, 等. 华北中生代镁铁质岩浆作用与克拉通减薄和破坏[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2018,48(4):379-414. |
| [26] |
ZOU S H, XU D R, DENG T, et al. Geochemical variations of the Late Mesozoic granitoids in the southern margin of North China Craton: A possible link to the tectonic transformation from compression to extension[J]. Gondwana Research, 2019,75:118-133.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 李永峰. 豫西熊耳山地区中生代花岗岩类时空演化与钼(金)成矿作用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2005: 1-135. |
| [28] |
MAO J W, XIE G Q, PIRAJNO F, et al. Late Jurassic-Cretaceous granitoid magmatism in eastern Qinling, central-eastern China: SHRIMP zircon U-Pb ages and tectonic implications[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2010,57(1):51-78.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 孟芳, 叶会寿, 高亚龙. 豫西熊耳山地区花岗岩地质特征及SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 矿床地质, 2012,31(增):591-592. |
| [30] | 梁涛, 卢仁, 罗照华. 豫西五丈山花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 地质评论, 2019,65(5):1054-1076. |
| [31] | 庞绪成, 杨春蕾, 张红军, 等. 豫西熊耳山五丈山岩体锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2016,36(4):57-65. |
| [32] | 范宏瑞, 谢奕汉, 王英兰. 豫西花山花岗岩基岩石学和地球化学特征及其成因[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 1994,13(1):19-32. |
| [33] |
HAN Y G, ZHANG S H, FRANCO P, et al. Evolution of the Mesozoic granites in the Xiong’ershan-Waifangshan region, western Henan Province, China, and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2007,81(2):253-265.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 聂政融, 王晓霞, 柯昌辉, 等. 华北地块南缘花山、五丈山岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及成因[J]. 地质通报, 2015,34(8):1502-1516. |
| [35] | 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 等. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 1-863. |
| [36] | 陈衍景, 唐国军, PIRAJNO F, 等. 东秦岭上宫金矿流体成矿作用: 放射成因同位素地球化学研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 2004,24(3):22-27. |
| [37] | 赵太平, 徐勇航, 翟明国. 华北陆块南部元古宙熊耳群火山岩的成因与构造环境: 事实与争议[J]. 高校地质学报, 2007,13(2):191-206. |
| [38] | 第五春荣, 孙勇, 刘良, 等. 北秦岭宽坪岩群的解体及新元古代N-MORB[J]. 岩石学报, 2010,26(7):2025-2038. |
| [39] | 赵太平, 邓小芹, 胡国辉, 等. 华北克拉通古/中元古代界线和相关地质问题讨论[J]. 岩石学报, 2015,31(6):1495-1508. |
| [40] |
ANDRADE S, HYPOLITO R, ULBRICH H H G J, et al. Iron(II) oxide determination in rocks and minerals[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002,182(1):85-89.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994,37(3/4):215-224.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976,58(1):63-81.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1989,101(5):635-643.
DOI URL |
| [44] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[M]//SAUNDERS A D, NORRY M J . Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. London:Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1989: 313-345. |
| [45] |
DEFANT M J, DRUMMOND M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990,347:662-665.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987,95(4):407-419.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
FROST C D, FROST B R. On ferroan (A-type) granitoids: Their compositional variability and modes of origin[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2011,52(1):39-53.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
BONIN B. A-type granites and related rocks: Evolution of a concept, problems and prospects[J]. Lithos, 2007,97(1/2):1-29.
DOI URL |
| [49] | 吴锁平, 王梅英, 戚开静. A型花岗岩研究现状及其述评[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2007,26(1):57-66. |
| [50] | GILL R. Igneous Rocks and Processes[M]. Hoboken: Wiley-Blackwell, 2010: 1-440. |
| [51] |
GAO X Y, ZHAO T P, CHEN W T. Petrogenesis of the early Cretaceous Funiushan granites on the southern margin of the North China Craton: Implications for the Mesozoic geological evolution[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014,94:28-44.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
GAO X Y, ZHAO T P, BAO Z W, et al. Petrogenesis of the early Cretaceous intermediate and felsic intrusions at the southern margin of the North China Craton: Implications for crust-mantle interaction[J]. Lithos, 2014,206/207:65-78.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
LI N, CHEN Y J, PIRAJNO F, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating, trace element and Hf isotope geochemistry of the Heyu granite batholith, eastern Qinling, central China: Implications for Mesozoic tectono-magmatic evolution[J]. Lithos, 2012,142/143:34-47.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
WANG X X, WANG T, KE C H, et al. Nd-Hf isotopic mapping of Late Mesozoic granitoids in the East Qinling orogen, central China: Constraint on the basements of terranes and distribution of Mo mineralization[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015,103:169-183.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
ZHAO H X, JIANG S Y, FRIMMEL H E, et al. Geochemistry, geochronology and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes of two Mesozoic granitoids in the Xiaoqinling gold district: Implication for large-scale lithospheric thinning in the North China Craton[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012,294/295:173-189.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
ZHAO T P, MENG L, GAO X Y, et al. Late Mesozoic felsic magmatism and Mo-Au-Pb-Zn mineralization in the southern margin of the North China Craton: A review[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018,161:103-121.
DOI URL |
| [57] | ZINDLER A, HART S R. Chemical geodynamics[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1986,14:493-571. |
| [58] | WEAVER B L. The origin of ocean island basalt end-member compositions: Trace element and isotopic constraints[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991,104:381-397. |
| [59] | OTHMAN D B, POLVE M, ALLGRE C J. Nd-Sr isotopic composition of granulites and constraints on the evolution of the lower continental crust[J]. Nature, 1984,307:510-515. |
| [60] | ZARTMAN R E, DOE B R. Plumbotectonics-the model[J]. Tectonophysics, 1981,75:135-162. |
| [61] | WANG X L, JIANG S Y, DAI B Z. Melting of enriched Archean subcontinental lithospheric mantle: Evidence from the ca. 1760 Ma volcanic rocks of the Xiong’er Group, southern margin of the North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2010,182(3):204-216. |
| [62] | WANG C M, HE X Y, CARRANZA E J M, et al. Paleoproterozoic volcanic rocks in the southern margin of the North China Craton, central China: Implications for the Columbia supercontinent[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2019,10(4):1543-1560. |
| [63] | XU X S, GRIFFIN W L, MA X, et al. The Taihua group on the southern margin of the North China Craton: Further insights from U-Pb ages and Hf isotope compositions of zircons[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2009,97(1/2):43-59. |
| [64] | XIONG X L, KEPPLER H, AUDETAT A, et al. Experimental constraints on rutile saturation during partial melting of metabasalt at the amphibolite to eclogite transition, with applications to TTG genesis[J]. American Mineralogist, 2009,94(8/9):1175-1186. |
| [65] | 河南省地质矿产局. 河南省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1989: 1-774. |
| [66] | 范光, 张子敏, 张邻素. 熊耳山区花岗岩特征及其与金矿化的关系[J]. 铀矿地质, 1995,11(4):207-213. |
| [67] | JIANG Y H, JIN G D, LIAO S Y, et al. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on the origin of Late Triassic granitoids from the Qinling Orogen, central China: Implications for a continental arc to continent-continent collision[J]. Lithos, 2010,117(1/4):183-197. |
| [68] | CASTILLO P R. 埃达克岩成因回顾[J]. 科学通报, 2006,51(6):617-627. |
| [69] | 王团华, 毛景文, 王彦斌. 小秦岭—熊耳山地区岩墙锆石SHRIMP年代学研究——秦岭造山带岩石圈拆沉的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2008,24(6):1273-1287. |
| [70] | XU J F, SHINJO R, DEFANT M J, et al. Origin of Mesozoic adakitic intrusive rocks in the Ningzhen area of east China: Partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust?[J]. Geology, 2002,30(12):1111-1114. |
| [71] | XU W L, WANG D Y, LIU X C, et al. Discovery of eclogite inclusions and its geological significance in early Jurassic intrusive complex in Xuzhou northern Anhui, eastern China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002,47(14):1212-1216. |
| [72] | MACPHERSON C G, DREHER S T, THIRLWALL M F. Adakites without slab melting: High pressure differentiation of island arc magma, Mindanao, the Philippines[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006,243(3/4):581-593. |
| [73] | CASTILLO P R, JANNEY P E, SOLIDUM R U. Petrology and geochemistry of Camiguin Island, southern Philippines: Insights to the source of adakites and other lavas in a complex arc setting[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1999,134(1):33-51. |
| [74] | CASTILLO P R. Adakite petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 2012,134/135:304-316. |
| [75] | 许继峰, 邬建斌, 王强, 等. 埃达克岩与埃达克质岩在中国的研究进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2014,33(1):6-13. |
| [76] | STRECK M J, LEEMAN W P, CHESLEY J. High-magnesian andesite from Mount Shasta: A product of magma mixing and contamination, not a primitive mantle melt[J]. Geology, 2007,35(4):351-354. |
| [77] | CHUNG S L, LIU D Y, JI J Q, et al. Adakites from continental collision zones: Melting of thickened lower crust beneath southern Tibet[J]. Geology, 2003,31(11):1021-1024. |
| [78] | LU Y J, KERRICH R, KEMP A I S, et al. Intracontinental Eocene-Oligocene porphyry Cu mineral systems of Yunnan, Western Yangtze Craton, China: Compositional characteristics, sources, and implications for continental collision metallogeny[J]. Economic Geology, 2013,108(7):1541-1576. |
| [79] | ZHENG J P, SUN M, LU F X, et al. Mesozoic lower crustal xenoliths and their significance in lithospheric evolution beneath the Sino-Korean Craton[J]. Tectonophysics, 2003,361(1/2):37-60. |
| [80] | ZHENG Y F, XU Z, ZHAO Z F, et al. Mesozoic mafic magmatism in North China: Implications for thinning and destruction of cratonic lithosphere[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018,61(4):353-385. |
| [81] | 张健, 余学中, 薛春纪. 东秦岭地区秦岭群与陡岭群关系判断及构造启示[J]. 现代地质, 2019,33(1):45-55. |
| [82] | 贺昕宇, 王长明, 袁继明, 等. 熊耳山—外方山矿集区中生代Au-Mo成矿系统[J]. 地学前缘, 2019,26(5):33-52. |
| [83] | 王文博, 张静, 陈良, 等. 豫西熊耳山地区上道回钼矿床地质及流体包裹体研究[J]. 现代地质, 2016,30(2):328-340. |
| [84] | 任纪舜, 陈廷愚, 牛宝贵, 等. 中国东部及邻区大陆岩石圈的构造演化与成矿[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1992: 1-203. |
| [85] | 石铨曾, 尉向东, 李明立, 等. 河南省东秦岭山脉北缘的推覆构造及伸展拆离构造[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004: 1-109. |
| [86] | 王长明, 邓军, 张寿庭. 河南熊耳山地区花山花岗岩与金矿化的关系[J]. 现代地质, 2006,20(2):315-321. |
| [87] | 毛景文, 李晓峰, 张作衡, 等. 中国东部中生代浅成热液金矿的类型、特征及其地球动力学背景[J]. 高校地质学报, 2003,9(4):620-637. |
| [88] | 周国藩. 秦巴地区地球物理场特征与地壳构造格架关系的研究[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1992: 1-87. |
| [89] | 熊小林, 刘星成, 朱志敏, 等. 华北埃达克质岩与克拉通破坏: 实验岩石学和地球化学依据[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2011,41(5):654-667. |
| [1] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [2] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [3] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [4] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [5] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [6] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [7] | 梁鸣, 高文, 罗先熔, 王晓东, 刘秀娟, 陈皓, 刘攀峰, 竹峰, 李伟. 冀北高尖子地区土壤地球化学特征及其找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1567-1579. |
| [8] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [9] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [10] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [11] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [12] | 可行, 赵青芳, 吴飘, 杨传胜, 廖晶, 龚建明. 胶莱盆地东北部白垩系烃源岩特征与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1358-1368. |
| [13] | 韩飞, 宋元宝, 张伟, 李道凌, 黄永高, 李应栩, 贾小川, 杨学俊, 杨青松, 宋旭波, 卢柳. 西藏冈底斯南木林地区晚三叠世中酸性岩浆作用及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 547-561. |
| [14] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [15] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||