



现代地质 ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (02): 422-430.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.02.17
收稿日期:2018-02-17
修回日期:2019-01-20
出版日期:2019-05-08
发布日期:2019-05-08
作者简介:盛益之,男,博士,1989年出生,地下水科学与工程专业,主要从事土壤与地下水污染相关研究。Email: shengyz0330@163.com。
基金资助:
SHENG Yizhi( ), ZHANG Xu, ZHAI Xiaobo, LI Guanghe
), ZHANG Xu, ZHAI Xiaobo, LI Guanghe
Received:2018-02-17
Revised:2019-01-20
Online:2019-05-08
Published:2019-05-08
摘要:
选取某农药厂旧厂区为试验场地,考察化学氧化技术异位处理地下水非水相有机污染物的运行效果。基于小试研究,确定高锰酸钾、高铁酸钾、芬顿试剂以及次氯酸钠4种氧化剂在中试试验中的适宜投加量。中试结果表明,当进水流量为1.0 m3/h时,不同氧化剂对于常规水质指标及特征有机污染物的去除效果存在差异性。总体而言,四种氧化剂对于中长链石油烃类污染物(C10—C36)的去除率可达20%~70%,但对氯代烷烃类污染物的去除效果低于20%;高铁酸钾和次氯酸钠分别对于苯酚类和多环芳烃类污染物的去除效果较好(70%~100%);芬顿试剂对各类污染物均有显著氧化效果,其中对于短链石油烃(C6—C9,去除率20%~40%)、苯系物(去除率40%~90%)的去除效果高于其他三种氧化剂。研究不同氧化剂对于多组分有机污染地下水的处理效果,为将化学氧化技术应用于此类污染场地提供了理论和技术支持。
中图分类号:
盛益之, 张旭, 翟晓波, 李广贺. 化学氧化技术异位处理地下水非水相有机污染物中试研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(02): 422-430.
SHENG Yizhi, ZHANG Xu, ZHAI Xiaobo, LI Guanghe. Ex-situ Chemical Oxidation Treatment for Non-aqueous Liquid Contaminated Groundwater: A Pilot Study[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(02): 422-430.
| 测试指标 | 检出值(检出率/%) | 测试指标 | 检出值(检出率/%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.55±0.17 (100) | 苯/(μg/L) | 2.68±0.71 (77) | |
| SS/(mg/L) | 224.83±47.97 (100) | 甲苯/(μg/L) | 3.73±2.10 (77) | |
| 浊度/(NTU) | 159.20±47.65 (100) | 乙苯/(μg/L) | 0.16±0.03 (46) | |
| COD/(mg/L) | 155.44±30.33 (100) | 二甲苯/(μg/L) | 0.23±0.04 (62) | |
| BOD/(mg/L) | 10.60±9.71 (100) | 1,2-二氯乙烷/(μg/L) | 17.58±4.26 (100) | |
| 总磷/(mg/L) | 4.05±0.80 (100) | 2-甲基苯酚/(μg/L) | 2.75±1.36 (54) | |
| 总氮/(mg/L) | 18.39±2.62 (100) | 3,4-甲基苯酚/(μg/L) | 2.27±0.46 (77) | |
| 氨氮/(mg/L) | 8.43±0.82 (100) | 萘/(μg/L) | 75.33±60.50 (77) | |
| C6—C9/(μg/L) | 28.94±9.50 (100) | 2-甲基萘/(μg/L) | 302.27±257.31 (62) | |
| C10—C14/(μg/L) | 695.73±231.20 (100) | 芴/(μg/L) | 1.38±0.44 (85) | |
| C15—C28/(μg/L) | 397.60±48.58 (100) | 菲/(μg/L) | 1.10±0.05 (31) | |
| C29—C36/(μg/L) | 66.83±20.23 (83) | 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯/(μg/L) | 23.54±15.65 (31) | |
表1 污染场地地下水水质特征
Table 1 Characteristics of groundwater quality at the contaminated site
| 测试指标 | 检出值(检出率/%) | 测试指标 | 检出值(检出率/%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.55±0.17 (100) | 苯/(μg/L) | 2.68±0.71 (77) | |
| SS/(mg/L) | 224.83±47.97 (100) | 甲苯/(μg/L) | 3.73±2.10 (77) | |
| 浊度/(NTU) | 159.20±47.65 (100) | 乙苯/(μg/L) | 0.16±0.03 (46) | |
| COD/(mg/L) | 155.44±30.33 (100) | 二甲苯/(μg/L) | 0.23±0.04 (62) | |
| BOD/(mg/L) | 10.60±9.71 (100) | 1,2-二氯乙烷/(μg/L) | 17.58±4.26 (100) | |
| 总磷/(mg/L) | 4.05±0.80 (100) | 2-甲基苯酚/(μg/L) | 2.75±1.36 (54) | |
| 总氮/(mg/L) | 18.39±2.62 (100) | 3,4-甲基苯酚/(μg/L) | 2.27±0.46 (77) | |
| 氨氮/(mg/L) | 8.43±0.82 (100) | 萘/(μg/L) | 75.33±60.50 (77) | |
| C6—C9/(μg/L) | 28.94±9.50 (100) | 2-甲基萘/(μg/L) | 302.27±257.31 (62) | |
| C10—C14/(μg/L) | 695.73±231.20 (100) | 芴/(μg/L) | 1.38±0.44 (85) | |
| C15—C28/(μg/L) | 397.60±48.58 (100) | 菲/(μg/L) | 1.10±0.05 (31) | |
| C29—C36/(μg/L) | 66.83±20.23 (83) | 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯/(μg/L) | 23.54±15.65 (31) | |
| 指标 | Ⅲ类 标准 | 荷兰 干涉值 | 新泽西 州标准 | 超标 率/% | 最大超 标倍数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总石油烃/(μg/L) | 600 | 69.2 | 7.2 | ||
| 苯/(μg/L) | 10 | 30 | 23.1 | 11.7 | |
| 甲苯/(μg/L) | 700 | 1 000 | 0 | ||
| 乙苯/(μg/L) | 300 | 150 | 0 | ||
| 二甲苯/(μg/L) | 500 | 70 | 0 | ||
| 1,2-二氯乙烷/(μg/L) | 30 | 23.1 | 1.4 | ||
| 苯酚/(μg/L) | 2 000 | 0 | |||
| 3,4-甲基苯酚/(μg/L) | 70 | 0 | |||
| 萘/(μg/L) | 100 | 100 | 15.4 | 5.6 | |
| 2-甲基萘/(μg/L) | 30 | 30.1 | 48.3 | ||
| 芴/(μg/L) | 280 | 0 | |||
| 菲/(μg/L) | 5 | 0 | |||
| 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯/(μg/L) | 6 | 0 |
表2 污染场地地下水特征有机污染物现状评价
Table 2 Groundwater quality assessment of the targeted organic contaminants at the contaminated site
| 指标 | Ⅲ类 标准 | 荷兰 干涉值 | 新泽西 州标准 | 超标 率/% | 最大超 标倍数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总石油烃/(μg/L) | 600 | 69.2 | 7.2 | ||
| 苯/(μg/L) | 10 | 30 | 23.1 | 11.7 | |
| 甲苯/(μg/L) | 700 | 1 000 | 0 | ||
| 乙苯/(μg/L) | 300 | 150 | 0 | ||
| 二甲苯/(μg/L) | 500 | 70 | 0 | ||
| 1,2-二氯乙烷/(μg/L) | 30 | 23.1 | 1.4 | ||
| 苯酚/(μg/L) | 2 000 | 0 | |||
| 3,4-甲基苯酚/(μg/L) | 70 | 0 | |||
| 萘/(μg/L) | 100 | 100 | 15.4 | 5.6 | |
| 2-甲基萘/(μg/L) | 30 | 30.1 | 48.3 | ||
| 芴/(μg/L) | 280 | 0 | |||
| 菲/(μg/L) | 5 | 0 | |||
| 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯/(μg/L) | 6 | 0 |
| 氧化剂 | 反应方程 | 标准电极 电势/V |
|---|---|---|
| 高锰酸盐 | 0.59 | |
| 高铁酸盐 | 0.70 | |
| 过氧化氢 | 0.88 | |
| 次氯酸盐 | ClO- + H2O + 2e → Cl- + 2OH- | 0.90 |
表3 常见氧化剂在地下水环境中的标准电极电势[8, 15-16]
Table 3 Standard electrode potential of common oxidants in groundwater environment
| 氧化剂 | 反应方程 | 标准电极 电势/V |
|---|---|---|
| 高锰酸盐 | 0.59 | |
| 高铁酸盐 | 0.70 | |
| 过氧化氢 | 0.88 | |
| 次氯酸盐 | ClO- + H2O + 2e → Cl- + 2OH- | 0.90 |
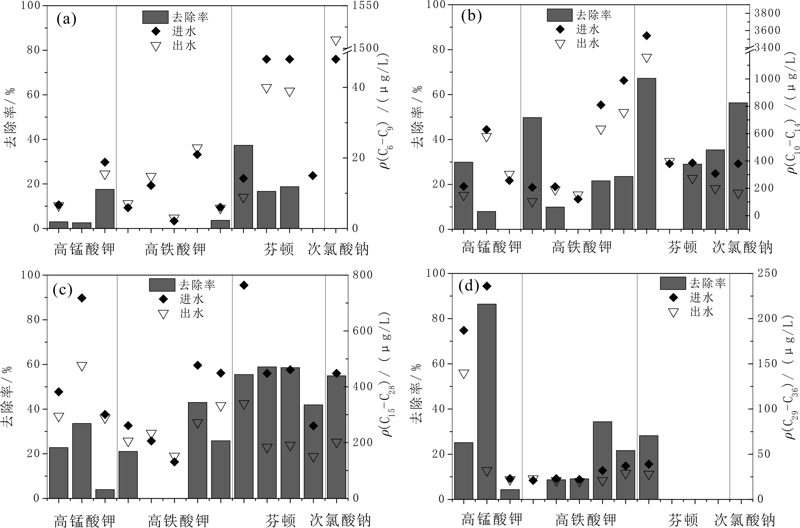
图4 不同氧化剂对场地地下水总石油烃类污染物的去除效果 (a)C6—C9;(b)C10—C14;(c)C15—C28;(d)C29—C36
Fig.4 Removal efficiency of petroleum hydrocarbons using different oxidants for onsite groundwater treatment
| [1] |
HOU Y, ZHANG T Z. Evaluation of major polluting accidents in China—Results and perspectives[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009,168(2/3):670-673.
DOI URL |
| [2] | XUE P, ZENG W. Trends of environmental accidents and impact factors in China[J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering in China, 2011,5(2):266-276. |
| [3] |
YAO H, ZHANG T, LIU B, et al. Analysis of surface water pollution accidents in China: characteristics and lessons for risk management[J]. Environmental Management, 2016,57(4):868-878.
URL PMID |
| [4] | SHENG Y, TIAN X, WANG G, et al. Bacterial diversity and biogeochemical processes of oil-contaminated groundwater, Bao-ding, North China[J]. Geomicrobiology, 2016,33(6):537-551. |
| [5] |
ZHANG Q, WANG G, SUGIURA N, et al. Distribution of petroleum hydrocarbons in soils and the underlying unsaturated subsurface at an abandoned petrochemical site, North China[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2013,28(4):2185-2191.
DOI URL |
| [6] | 王平, 黄爽兵, 韩占涛, 等. 基于溶质运移模拟的某化工场地污染物对拟建水库污染风险预测[J]. 现代地质, 2015,29(2):307-315. |
| [7] | 张丹, 张旭, 李广贺, 等. Fenton试剂快速氧化处理事故场地地下水中的硝基苯[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016,10(7):3439-3444. |
| [8] | NYER E K. Groundwater Treatment Technology[M]. 3rd ed. New York:Van Nostrand Reinhold, 2009: 104-119. |
| [9] | 蔡婧怡, 陈宗宇, 蔡五田, 等. 某石化污染场地含水层自然降解BTEX能力评估[J]. 现代地质, 2015,29(2):383-389. |
| [10] | 翟晓波, 盛益之, 张旭, 等. 混凝-气浮工艺处理有机物污染地下水现场中试试验[J]. 化工环保, 2018,38(1):33-39. |
| [11] |
HE L, HUANG G H, ZENG G M, et al. An integrated simulation, inference, and optimization method for identifying groundwater remediation strategies at petroleum-contaminated aquifers in western Canada[J]. Water Research, 2008,42(10/11):2629-2639.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
TRUEX M, JOHNSON C, MACBETH T, et al. Performance assessment of pump-and-treat systems[J]. Ground Water Monitoring and Remediation, 2017,37(3):28-44.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MACKAY D, MCHERRY J A. Groundwater contamination: pump-and-treat remediation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1989,23(6):630-636.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 万鹏, 张旭, 李广贺, 等. 基于模拟-优化模型的某场地污染地下水抽水方案设计[J]. 环境科学研究, 2016,29(11):1608-1616. |
| [15] | TSAI T T, KAO C M, YEH T Y, et al. Chemical oxidation of chlorinated solvents in contaminated groundwater: review[J]. Practice Periodical of Hazardous Toxic & Radioactive Waste Mana-gement, 2008,12(12):116-126. |
| [16] | 王东升, 李文涛, 杨晓芳, 等. 高铁酸盐: 一种绿色的多功能水处理剂[J]. 应用化学, 2016,33(11):1221-1233. |
| [17] | 尹贞, 廖书林, 马强, 等. 化学氧化技术在地下水修复中的应用[J]. 环境工程学报, 2015,9(10):4910-4914. |
| [18] | 田璐, 杨琦, 尚海涛. 高锰酸钾降解地下水中PCE的研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2009,3(8):1355-1359. |
| [19] |
JOUSSE E, ATTEIA O, HOHENER P, et al. Removal of NAPL from columns by oxidation, sparging, surfactant and thermal treatment[J]. Chemosphere, 2017,188:182-189.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] | 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M].4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002: 1-295. |
| [21] |
BROWN D G, GUPTA L, KIM T H, et al. Comparative assessment of coal tars obtained from 10 former manufactured gas plant sites in the Eastern United States[J]. Chemosphere, 2006,65(9):1562-1569.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] |
COULON F, ORSI R, TURNER C, et al. Understanding the fate and transport of petroleum hydrocarbons from coal tar within Gasholders[J]. Environment International, 2009,35(2):248-252.
URL PMID |
| [23] | VROM. Circular Values and Intervention Values for Soil Remediation Annex A: Target Values, Soil Remediation Intervention Values and Indictive Levels for Serious Contamination[M]. Amster dam: Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and Environment (VROM), 2010. |
| [24] | NJDEP. Ground Water Quality Standards Class II-A[S]. Trenton:New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection, 2018. |
| [25] | 盛益之, 王广才, 张琦伟, 等. 某污染场地周边地下水环境质量评价[J]. 现代地质, 2012,26(3):601-606. |
| [26] |
金伟, 范瑾初. 紫外吸光值(UV_(254))作为有机物替代参数的探讨[J]. 工业水处理, 1997,17(6):30-32.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
BOONRATTANAKIJ N, LU M, CANOTAI J. Iron crystallization in a fluidized-bed Fenton process[J]. Water Research, 2011,45(10):3255-3262.
URL PMID |
| [28] | 吴建新. 高铁酸盐处理制药废水的试验研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2010,26(15):79-81. |
| [29] | 周建红, 李军, 令玉林, 等. 高铁酸钾和次氯酸钠联用处理苯酚废水研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2013,33(10):27-29. |
| [30] | 杨涛. 高锰酸钾、次氯酸钠复合预氧化与常规处理工艺联用处理微污染水源水的中试研究[J]. 辽宁化工, 2006,35(4):217-218. |
| [31] | 赵丹, 阎秀兰, 廖晓勇, 等. 不同化学氧化剂对焦化污染场地苯系物的修复效果[J]. 环境科学, 2011,32(3):849-856. |
| [32] |
BERGENDAHL J, HUBBARD S, GRASSO D. Pilot-scale Fenton’s oxidation of organic contaminants in groundwater using autochthonous iron[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2003,99(1):43-56.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 王滢, 胡伟武, 陈男, 冯传平. 华北棕壤土掺砂比对渗滤系统净化污水性能的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 914-924. |
| [2] | 张卓, 陈社明, 柳富田, 高志鹏, 牛笑童. 滨海平原区深层高氟地下水富集机理:以滦河三角洲为例[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 925-932. |
| [3] | 刘圣锋, 高柏, 易玲, 方正, 史天成, 丁燕. 海拉尔盆地水环境中砷和铀的分布特征及风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 933-942. |
| [4] | 彭红明, 王占巍, 罗银飞, 袁有靖, 王万平. 基于地下水数值模拟的布哈河流域地下水可开采资源量评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 943-953. |
| [5] | 闫佰忠, 孙剑, 陈佳琦, 孙丰博, 李晓萌, 付庆杰. 基于自适应BPNN-GIS耦合的地下水源热泵适宜性分区研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 963-971. |
| [6] | 程智余, 刘瑞, 张金锋, 马海春, 王京平. 围压变化作用下基于水力开度变化的单裂隙渗流特性研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 972-976. |
| [7] | 张莉, 刘菲, 袁慧卿, 梁凯旋. 地下水抽出处理技术研究进展与展望[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 977-985. |
| [8] | 胡新宇, 申媛媛, 褚婷雯, 贺巍, 魏炜, 申晓鹏. 生态补水下的永定河流域地下水水位变化规律[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 986-993. |
| [9] | 姜哲, 周训, 陈柄桦, 陶广斌, 李状, 曹入文, 隋丽嫒. 四川康定市二道桥地区地下热水稳定同位素特征及热储温度计算[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1183-1192. |
| [10] | 赵明坤, 孙亚军, 段忠丰, 沈权伟, 路桂景. 河南漯河市明化镇组温热水地球化学特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 507-514. |
| [11] | 杨峰田, 石宇佳, 李文庆. 基于水文地球化学特征的辽宁丹东地区地热水成因模式研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 474-483. |
| [12] | 刘茂涵, 刘海燕, 张卫民, 王振, 吴通航, 王玉罡. 鄱阳湖流域赣江北支水体和沉积物中稀土元素的含量和分异特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 389-405. |
| [13] | 安国英, 郭兆成, 叶佩. 云南大理地区1989—2019年期间气候变化及对洱海水质的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 406-417. |
| [14] | 李泽岩, 曹文庚, 王卓然, 李谨丞, 任宇. 内蒙古河套灌区浅层地下水化学特征和灌溉适宜性分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 418-426. |
| [15] | 吴通航, 刘海燕, 张卫民, 孙占学, 王振, 刘茂涵. 鄱阳湖流域赣江下游水化学特征及人类健康风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 427-438. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||