



现代地质 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (06): 1147-1156.
麦地娜·努尔太1( ), 尼加提·阿布都逊1,2, 木合塔尔·扎日1,2(
), 尼加提·阿布都逊1,2, 木合塔尔·扎日1,2( ), 吴兆宁1, 张龙1
), 吴兆宁1, 张龙1
收稿日期:2016-11-29
修回日期:2017-05-18
出版日期:2017-12-10
发布日期:2017-12-25
通讯作者:
木合塔尔·扎日,男,教授,1960年出生,构造地质学专业,主要从事区域大地构造方面的研究。Email: 作者简介:麦地娜·努尔太,女,硕士研究生,1990年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事火成岩地球化学研究。Email: madina711@163.com。
基金资助:
MADINA Nurtay1( ), NIJAT Abdurusul1,2, MUHTAR Zari1,2(
), NIJAT Abdurusul1,2, MUHTAR Zari1,2( ), WU Zhaoning1, ZHANG Long1
), WU Zhaoning1, ZHANG Long1
Received:2016-11-29
Revised:2017-05-18
Online:2017-12-10
Published:2017-12-25
摘要:
研究中天山地块卡瓦布拉克杂岩带的成因,对重建中天山南缘古生代洋陆构造格局及其演变过程具有重要意义。在查明杂岩带中-基性岩主体岩类矿物学及岩石学特征的基础上,分析了该岩类的主、微量元素和Sr-Nd-Pb同位素组成。结果显示:其属于偏基性的富钠、低钾岩石系列,富集大离子亲石元素(Rb、U、Sr)和轻稀土元素(LREE),亏损高场强元素(Nb、Ta、Zr)和重稀土元素(HREE)。全岩Sr-Nd同位素组成具有较低的锶初始比值(ISr=0.706~0.709)和较高的εNd(t)值(6.84~9.76),并具有较低的放射性成因铅同位素组成,初始铅同位素比值(206Pb/204Pb)i=18.015~18.239、(207Pb/204Pb)i=15.573~15.593、(208Pb/204Pb)i=37.871~38.207。结合前人研究成果和区域地质资料,认为其母岩浆应该来自被交代的年轻富集岩石圈地幔,代表岛弧岩浆,说明卡瓦布拉克杂岩带中-基性岩可能代表该区晚古生代岩浆弧的一部分。
中图分类号:
麦地娜·努尔太, 尼加提·阿布都逊, 木合塔尔·扎日, 吴兆宁, 张龙. 中天山卡瓦布拉克杂岩带中-基性岩的成因及其构造意义:元素地球化学和Sr-Nd-Pb同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(06): 1147-1156.
MADINA Nurtay, NIJAT Abdurusul, MUHTAR Zari, WU Zhaoning, ZHANG Long. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications of Intermediate Basic Rocks from Kawabulak Complex in Central Tianshan: Constraints from Elemental Geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb Isotopes[J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(06): 1147-1156.

图1 中亚造山带大地构造位置图(a)与研究区大地构造位置图(b)(据参考文献[8]修编) 1.吐哈地块;2.觉罗塔格构造带;3.康古尔塔格碰撞带;4.阿奇山—雅满苏构造带;5.中天山地块;6.南天山造山带;7.塔里木地块;8.敦煌地块北部活动陆缘;9.红柳河—玉石山碰撞带;10.区域性断裂:①康古尔塔格—黄山—镜儿泉断裂;②雅满苏断裂;③阿其克库都克—沙泉子断裂;④卡瓦布拉克断裂;⑤塞里克沙依—星星峡断裂;⑥辛格尔断裂;⑦红柳河断裂
Fig.1 Tectonic location of central Asian orogenic belt (a) and tectonic map of the study area (b)

图3 研究区中-基性岩镜下显微照片 (a)-(c)为正交偏光,(d)为单偏光,10×10;(a)角闪石中包有半自形板状的中长石; (b)中长石显环带结构,在中长石环带中心有次生绢云母和细粒绿帘石;(c)角闪石在一起有半自形粒状的黄铁矿,黄铁矿多呈褐铁矿化;(d)角闪石边缘被绿泥石交代;Pl.中长石;Amp.角闪石;Py.黄铁矿
Fig.3 Photomicrographs of intermediate basic rocks in the study area
| 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MgO | MnO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | LOl | Mg# | Na2O/ K2O | Na2O+ K2O | σ | A/CNK | A/NK | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KB111 | 55.84 | 0.58 | 14.83 | 5.47 | 1.85 | 0.11 | 7.77 | 6.50 | 0.40 | 0.20 | 5.82 | 25.27 | 16.14 | 6.90 | 3.71 | 0.591 | 1.342 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB211 | 49.36 | 0.52 | 18.26 | 5.98 | 7.96 | 0.10 | 13.81 | 1.74 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 1.23 | 57.09 | 5.70 | 2.04 | 0.66 | 0.649 | 5.764 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB221 | 49.68 | 0.55 | 14.30 | 7.76 | 10.35 | 0.12 | 13.14 | 1.27 | 0.39 | 0.04 | 1.71 | 57.15 | 3.24 | 1.66 | 0.41 | 0.545 | 5.731 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB411 | 52.00 | 1.07 | 17.66 | 9.21 | 4.38 | 0.16 | 8.03 | 2.98 | 1.86 | 0.36 | 1.46 | 32.24 | 1.60 | 4.84 | 2.60 | 0.826 | 2.572 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB421 | 44.41 | 1.36 | 17.99 | 11.55 | 6.00 | 0.16 | 12.23 | 2.31 | 1.13 | 0.23 | 2.04 | 34.20 | 2.04 | 3.45 | 8.45 | 0.664 | 3.596 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB611 | 43.80 | 1.54 | 17.02 | 11.51 | 7.35 | 0.17 | 12.68 | 1.99 | 0.68 | 0.51 | 2.19 | 38.99 | 2.93 | 2.68 | 8.93 | 0.630 | 4.263 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | LREE | HREE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB111 | 29.755 | 28.722 | 26.737 | 24.775 | 20.941 | 19.093 | 17.100 | 14.904 | 13.528 | 12.693 | 12.290 | 11.373 | 11.489 | 11.630 | 150.024 | 105.006 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB211 | 24.624 | 24.023 | 22.295 | 21.126 | 17.556 | 16.190 | 14.676 | 12.850 | 11.654 | 10.756 | 10.138 | 9.035 | 8.746 | 8.315 | 125.814 | 86.170 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB221 | 17.232 | 17.056 | 16.093 | 15.593 | 13.804 | 13.562 | 11.825 | 10.845 | 10.150 | 9.633 | 9.275 | 8.573 | 8.359 | 8.094 | 93.339 | 76.753 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB411 | 81.848 | 74.020 | 62.189 | 52.934 | 37.176 | 28.128 | 26.706 | 21.727 | 18.780 | 17.286 | 16.580 | 15.333 | 15.118 | 14.992 | 336.295 | 146.522 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB421 | 42.608 | 41.601 | 38.358 | 36.158 | 28.967 | 24.621 | 22.316 | 18.524 | 15.992 | 14.647 | 13.680 | 12.055 | 11.500 | 10.929 | 212.313 | 119.643 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB611 | 48.979 | 53.301 | 52.968 | 52.505 | 42.654 | 33.031 | 32.983 | 26.594 | 22.772 | 20.618 | 18.937 | 16.196 | 15.071 | 13.850 | 283.438 | 167.020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | ΣREE | LREE/ HREE | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | K | La | Ce | Pb | Pr | Sr | P | Nd | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB111 | 255.029 | 1.428 | 20.953 | 6.148 | 12.400 | 23.034 | 6.100 | 6.476 | 19.275 | 10.883 | 10.494 | 17.987 | 10.000 | 8.216 | 15.484 | 9.256 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB211 | 211.984 | 1.46 | 10.313 | 19.582 | 7.286 | 16.167 | 5.720 | 7.040 | 10.935 | 9.006 | 8.777 | 23.453 | 8.339 | 27.095 | 2.978 | 7.893 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB221 | 170.092 | 1.216 | 20.033 | 15.476 | 3.698 | 10.266 | 3.678 | 5.016 | 14.288 | 6.302 | 6.232 | 24.213 | 6.019 | 18.513 | 2.120 | 5.826 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB411 | 482.817 | 2.295 | 134.533 | 56.273 | 65.535 | 81.330 | 13.185 | 14.638 | 67.958 | 29.935 | 27.045 | 50.360 | 23.260 | 34.513 | 19.251 | 19.776 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB421 | 331.956 | 1.774 | 55.200 | 27.897 | 33.484 | 47.616 | 8.100 | 9.297 | 41.295 | 15.583 | 15.200 | 59.693 | 14.346 | 35.668 | 12.051 | 13.509 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB611 | 450.458 | 1.697 | 21.567 | 21.091 | 16.994 | 21.911 | 9.660 | 9.956 | 24.353 | 17.914 | 19.475 | 40.813 | 19.811 | 34.191 | 27.022 | 19.616 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | Zr | Hf | Sm | Eu | Ti | Gd | Tb | Dy | Y | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Sr/Y | La/Yb | Lu/Yb | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB111 | 6.434 | 5.825 | 7.892 | 7.191 | 4.357 | 6.460 | 5.630 | 5.098 | 4.963 | 4.821 | 4.644 | 4.265 | 4.429 | 4.376 | 7.66 | 3.61 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB211 | 4.234 | 4.040 | 6.616 | 6.097 | 3.255 | 5.544 | 4.855 | 4.392 | 3.661 | 4.086 | 3.831 | 3.388 | 3.371 | 3.129 | 34.25 | 3.93 | 0.14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB221 | 2.399 | 2.675 | 5.202 | 5.108 | 3.371 | 4.467 | 4.097 | 3.825 | 3.235 | 3.659 | 3.505 | 3.215 | 3.222 | 3.046 | 26.48 | 2.87 | 0.14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB411 | 13.078 | 10.551 | 14.010 | 10.594 | 6.496 | 10.088 | 8.208 | 7.077 | 6.070 | 6.566 | 6.265 | 5.750 | 5.828 | 5.641 | 26.31 | 7.55 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB421 | 7.056 | 6.266 | 10.916 | 9.273 | 8.269 | 8.430 | 6.998 | 6.027 | 4.981 | 5.564 | 5.169 | 4.521 | 4.433 | 4.113 | 33.14 | 5.17 | 0.14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB611 | 5.378 | 5.455 | 16.074 | 12.440 | 9.316 | 12.460 | 10.046 | 8.582 | 6.926 | 7.832 | 7.155 | 6.074 | 5.810 | 5.212 | 22.85 | 4.53 | 0.14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
表1 卡瓦布拉克杂岩带中-基性岩的主量元素(%)、稀土元素和微量元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 1 Chemical composition of major (%),REE and trace elements(10-6) of intermediate basic rocks in the Kawabulak complex
| 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MgO | MnO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | LOl | Mg# | Na2O/ K2O | Na2O+ K2O | σ | A/CNK | A/NK | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KB111 | 55.84 | 0.58 | 14.83 | 5.47 | 1.85 | 0.11 | 7.77 | 6.50 | 0.40 | 0.20 | 5.82 | 25.27 | 16.14 | 6.90 | 3.71 | 0.591 | 1.342 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB211 | 49.36 | 0.52 | 18.26 | 5.98 | 7.96 | 0.10 | 13.81 | 1.74 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 1.23 | 57.09 | 5.70 | 2.04 | 0.66 | 0.649 | 5.764 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB221 | 49.68 | 0.55 | 14.30 | 7.76 | 10.35 | 0.12 | 13.14 | 1.27 | 0.39 | 0.04 | 1.71 | 57.15 | 3.24 | 1.66 | 0.41 | 0.545 | 5.731 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB411 | 52.00 | 1.07 | 17.66 | 9.21 | 4.38 | 0.16 | 8.03 | 2.98 | 1.86 | 0.36 | 1.46 | 32.24 | 1.60 | 4.84 | 2.60 | 0.826 | 2.572 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB421 | 44.41 | 1.36 | 17.99 | 11.55 | 6.00 | 0.16 | 12.23 | 2.31 | 1.13 | 0.23 | 2.04 | 34.20 | 2.04 | 3.45 | 8.45 | 0.664 | 3.596 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB611 | 43.80 | 1.54 | 17.02 | 11.51 | 7.35 | 0.17 | 12.68 | 1.99 | 0.68 | 0.51 | 2.19 | 38.99 | 2.93 | 2.68 | 8.93 | 0.630 | 4.263 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | LREE | HREE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB111 | 29.755 | 28.722 | 26.737 | 24.775 | 20.941 | 19.093 | 17.100 | 14.904 | 13.528 | 12.693 | 12.290 | 11.373 | 11.489 | 11.630 | 150.024 | 105.006 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB211 | 24.624 | 24.023 | 22.295 | 21.126 | 17.556 | 16.190 | 14.676 | 12.850 | 11.654 | 10.756 | 10.138 | 9.035 | 8.746 | 8.315 | 125.814 | 86.170 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB221 | 17.232 | 17.056 | 16.093 | 15.593 | 13.804 | 13.562 | 11.825 | 10.845 | 10.150 | 9.633 | 9.275 | 8.573 | 8.359 | 8.094 | 93.339 | 76.753 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB411 | 81.848 | 74.020 | 62.189 | 52.934 | 37.176 | 28.128 | 26.706 | 21.727 | 18.780 | 17.286 | 16.580 | 15.333 | 15.118 | 14.992 | 336.295 | 146.522 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB421 | 42.608 | 41.601 | 38.358 | 36.158 | 28.967 | 24.621 | 22.316 | 18.524 | 15.992 | 14.647 | 13.680 | 12.055 | 11.500 | 10.929 | 212.313 | 119.643 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB611 | 48.979 | 53.301 | 52.968 | 52.505 | 42.654 | 33.031 | 32.983 | 26.594 | 22.772 | 20.618 | 18.937 | 16.196 | 15.071 | 13.850 | 283.438 | 167.020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | ΣREE | LREE/ HREE | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | K | La | Ce | Pb | Pr | Sr | P | Nd | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB111 | 255.029 | 1.428 | 20.953 | 6.148 | 12.400 | 23.034 | 6.100 | 6.476 | 19.275 | 10.883 | 10.494 | 17.987 | 10.000 | 8.216 | 15.484 | 9.256 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB211 | 211.984 | 1.46 | 10.313 | 19.582 | 7.286 | 16.167 | 5.720 | 7.040 | 10.935 | 9.006 | 8.777 | 23.453 | 8.339 | 27.095 | 2.978 | 7.893 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB221 | 170.092 | 1.216 | 20.033 | 15.476 | 3.698 | 10.266 | 3.678 | 5.016 | 14.288 | 6.302 | 6.232 | 24.213 | 6.019 | 18.513 | 2.120 | 5.826 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB411 | 482.817 | 2.295 | 134.533 | 56.273 | 65.535 | 81.330 | 13.185 | 14.638 | 67.958 | 29.935 | 27.045 | 50.360 | 23.260 | 34.513 | 19.251 | 19.776 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB421 | 331.956 | 1.774 | 55.200 | 27.897 | 33.484 | 47.616 | 8.100 | 9.297 | 41.295 | 15.583 | 15.200 | 59.693 | 14.346 | 35.668 | 12.051 | 13.509 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB611 | 450.458 | 1.697 | 21.567 | 21.091 | 16.994 | 21.911 | 9.660 | 9.956 | 24.353 | 17.914 | 19.475 | 40.813 | 19.811 | 34.191 | 27.022 | 19.616 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | Zr | Hf | Sm | Eu | Ti | Gd | Tb | Dy | Y | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Sr/Y | La/Yb | Lu/Yb | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB111 | 6.434 | 5.825 | 7.892 | 7.191 | 4.357 | 6.460 | 5.630 | 5.098 | 4.963 | 4.821 | 4.644 | 4.265 | 4.429 | 4.376 | 7.66 | 3.61 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB211 | 4.234 | 4.040 | 6.616 | 6.097 | 3.255 | 5.544 | 4.855 | 4.392 | 3.661 | 4.086 | 3.831 | 3.388 | 3.371 | 3.129 | 34.25 | 3.93 | 0.14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB221 | 2.399 | 2.675 | 5.202 | 5.108 | 3.371 | 4.467 | 4.097 | 3.825 | 3.235 | 3.659 | 3.505 | 3.215 | 3.222 | 3.046 | 26.48 | 2.87 | 0.14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB411 | 13.078 | 10.551 | 14.010 | 10.594 | 6.496 | 10.088 | 8.208 | 7.077 | 6.070 | 6.566 | 6.265 | 5.750 | 5.828 | 5.641 | 26.31 | 7.55 | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB421 | 7.056 | 6.266 | 10.916 | 9.273 | 8.269 | 8.430 | 6.998 | 6.027 | 4.981 | 5.564 | 5.169 | 4.521 | 4.433 | 4.113 | 33.14 | 5.17 | 0.14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KB611 | 5.378 | 5.455 | 16.074 | 12.440 | 9.316 | 12.460 | 10.046 | 8.582 | 6.926 | 7.832 | 7.155 | 6.074 | 5.810 | 5.212 | 22.85 | 4.53 | 0.14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

图7 卡瓦布拉克杂岩带中-基性岩的微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(标准化数值据文献[11])
Fig.7 Primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram of intermediate basic rocks from the Kawabulak complex
| 样品号 | Rb/(μg/g) | Sr/(μg/g) | 87Rb/ 86Sr | 87Sr/86Sr ±2σ | (87Sr/ 86Sr)i | 143Nd/ 144Nd | 147Sm/ 144Nd | (143Nd/ 144Nd)i | εNd(0) | εNd(t) | TDM /Ma | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KB2-2-1 | 12.02 | 368.40 | 0.095 6 | 0.709 4±0.000 005 | 0.709 | 0.512 5 | 0.018 4 | 0.513 | -1.06 | 7.45 | 449 | |
| KB2-1-1 | 6.19 | 539.20 | 0.033 6 | 0.705 8±0.000 004 | 0.706 | 0.512 6 | 0.013 0 | 0.513 | -0.57 | 8.21 | 418 | |
| KB6-1-1 | 12.94 | 680.40 | 0.055 7 | 0.706 4±0.000 005 | 0.706 | 0.512 5 | 0.009 9 | 0.512 | -2.08 | 6.84 | 469 | |
| KB4-1-1 | 80.72 | 686.80 | 0.344 6 | 0.707 6±0.000 004 | 0.706 | 0.512 5 | 0.008 0 | 0.513 | -1.90 | 7.11 | 458 | |
| KB4-2-1 | 33.12 | 709.80 | 0.136 8 | 0.706 8±0.000 005 | 0.706 | 0.512 6 | 0.005 7 | 0.513 | 0.64 | 9.76 | 358 |
表2 卡瓦布拉克杂岩带中-基性岩Sr-Nd同位素组成
Table 2 Sr-Nd isotopic data of intermediate basic rocks in the Kawabulak complex
| 样品号 | Rb/(μg/g) | Sr/(μg/g) | 87Rb/ 86Sr | 87Sr/86Sr ±2σ | (87Sr/ 86Sr)i | 143Nd/ 144Nd | 147Sm/ 144Nd | (143Nd/ 144Nd)i | εNd(0) | εNd(t) | TDM /Ma | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KB2-2-1 | 12.02 | 368.40 | 0.095 6 | 0.709 4±0.000 005 | 0.709 | 0.512 5 | 0.018 4 | 0.513 | -1.06 | 7.45 | 449 | |
| KB2-1-1 | 6.19 | 539.20 | 0.033 6 | 0.705 8±0.000 004 | 0.706 | 0.512 6 | 0.013 0 | 0.513 | -0.57 | 8.21 | 418 | |
| KB6-1-1 | 12.94 | 680.40 | 0.055 7 | 0.706 4±0.000 005 | 0.706 | 0.512 5 | 0.009 9 | 0.512 | -2.08 | 6.84 | 469 | |
| KB4-1-1 | 80.72 | 686.80 | 0.344 6 | 0.707 6±0.000 004 | 0.706 | 0.512 5 | 0.008 0 | 0.513 | -1.90 | 7.11 | 458 | |
| KB4-2-1 | 33.12 | 709.80 | 0.136 8 | 0.706 8±0.000 005 | 0.706 | 0.512 6 | 0.005 7 | 0.513 | 0.64 | 9.76 | 358 |
| 样品号 | Pb/(μg/g) | Th/(μg/g) | U/(μg/g) | 206Pb/204Pb | 207Pb/204Pb | 208Pb/204Pb | (206Pb/204Pb)i | (207Pb/204Pb)i | (208Pb/204Pb)i |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KB2-2-1 | 3.63 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 18.478 3 | 15.604 4 | 38.315 4 | 18.235 | 15.591 | 38.207 |
| KB2-1-1 | 3.52 | 0.58 | 0.33 | 18.474 2 | 15.601 1 | 38.257 5 | 18.078 | 15.580 | 38.037 |
| KB6-1-1 | 6.12 | 1.35 | 0.44 | 18.547 9 | 15.607 3 | 38.399 2 | 18.239 | 15.591 | 38.104 |
| KB4-1-1 | 7.55 | 5.21 | 1.65 | 18.943 4 | 15.623 7 | 38.793 1 | 18.015 | 15.573 | 37.871 |
| KB4-2-1 | 8.95 | 2.66 | 0.97 | 18.669 4 | 15.617 4 | 38.482 8 | 18.211 | 15.593 | 38.085 |
表3 卡瓦布拉克杂岩带中-基性岩Pb同位素组成
Table 3 Pb isotopic compositions of intermediate basic rocks in the Kawabulak complex
| 样品号 | Pb/(μg/g) | Th/(μg/g) | U/(μg/g) | 206Pb/204Pb | 207Pb/204Pb | 208Pb/204Pb | (206Pb/204Pb)i | (207Pb/204Pb)i | (208Pb/204Pb)i |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KB2-2-1 | 3.63 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 18.478 3 | 15.604 4 | 38.315 4 | 18.235 | 15.591 | 38.207 |
| KB2-1-1 | 3.52 | 0.58 | 0.33 | 18.474 2 | 15.601 1 | 38.257 5 | 18.078 | 15.580 | 38.037 |
| KB6-1-1 | 6.12 | 1.35 | 0.44 | 18.547 9 | 15.607 3 | 38.399 2 | 18.239 | 15.591 | 38.104 |
| KB4-1-1 | 7.55 | 5.21 | 1.65 | 18.943 4 | 15.623 7 | 38.793 1 | 18.015 | 15.573 | 37.871 |
| KB4-2-1 | 8.95 | 2.66 | 0.97 | 18.669 4 | 15.617 4 | 38.482 8 | 18.211 | 15.593 | 38.085 |
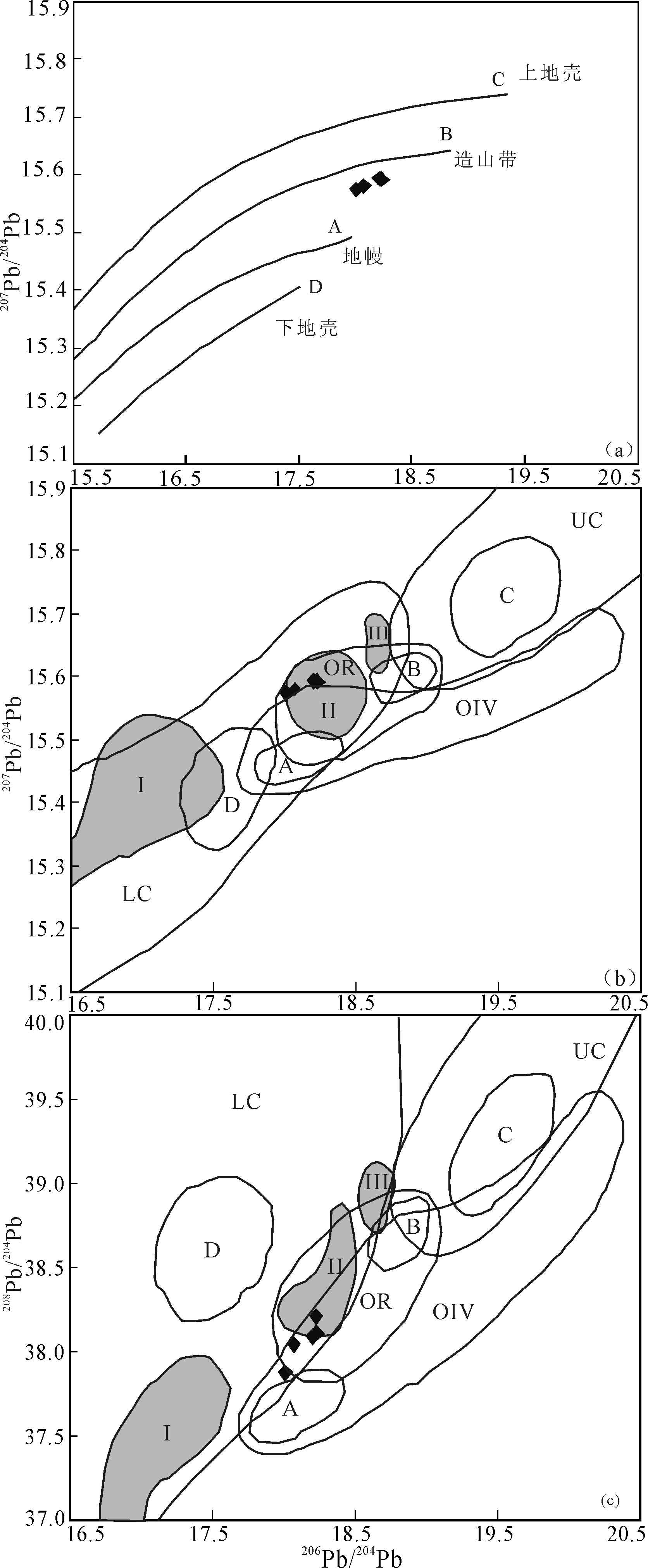
图10 卡瓦布拉克杂岩带中-基性岩Pb同位素图解 (a)206Pb/204Pb-207Pb/204Pb构造图解(底图据Zartman等 [15]);(b)206Pb/204Pb-207Pb/204Pb源区判别图;(c)206Pb/204Pb-208Pb/204Pb源区判别图;Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ分区引自文献[16];A、B、C、D分区引自文献[17],分别代表地幔、造山带、上部地壳和下部地壳;UC.上地壳;LC.下地壳;OR.造山带;OIV.洋岛火山岩
Fig.10 Pb isotopic compositions diagram of intermediate basic rocks in the Kawabulak complex
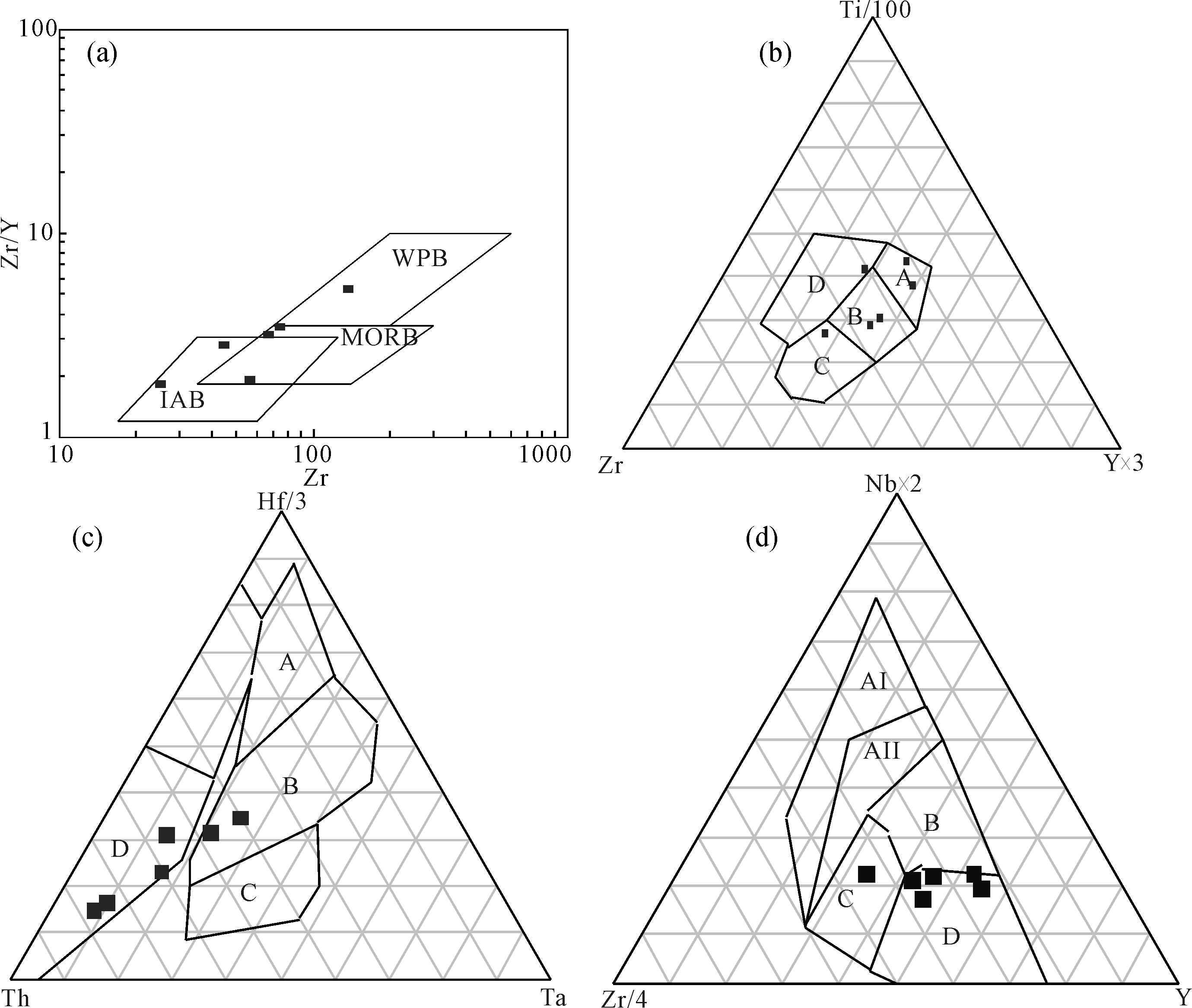
图11 卡瓦布拉克杂岩带中-基性岩微量元素构造环境判别图 (a)底图据文献[18]:IAB.岛弧拉斑玄武岩;MORB.大洋中脊玄武岩;WPB.板内玄武岩。 (b) 底图据文献[21]:A.岛弧拉斑玄武岩;B.MORB、岛弧拉斑玄武岩和钙碱性玄武岩;C.钙碱性玄武岩;D.板内玄武岩。 (c) 底图据文献[21]:A.N-MORB;B.E-MORB和板内拉斑玄武岩;C.板内碱性玄武岩;D.火山弧玄武岩。(d) 底图据文献[21];AI区,板内碱性玄武岩;AII区,板内碱性和拉斑玄武岩;B区,E-MORB;C区,火山弧玄武岩和板内拉斑玄武岩;D区,火山弧玄武岩
Fig.11 Trace element diagrams for discrimination of structural environments of intermediate basic rocks in the Kawabulak complex
| [1] | 周海. 星星峡地区晚古生代侵入岩及星星峡杂岩的再厘定——对中天山地块属性及其晚古生代构造格架的探讨[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2014. |
| [2] |
XIAO W J, ZHANG L C, QIN K Z, et al. Paleozoic accretionary and collisional tectonics of the Eastern Tianshan(China) : implication for the continental growth of central Asia[J]. American Journal of Science, 2004, 304: 370-395.
DOI URL |
| [3] | SENGOR A M C, NATALIN B A, BURTMAN U S. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Paleozoic crustal growth in Eurasia[J]. Nature, 1993, 364: 209-304. |
| [4] | 李锦轶. 国土资源大调查项目“东天山构造格架研究”研究报告[R]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2002. |
| [5] | 尼加提·阿布都逊, 木合塔尔·扎日, 吴兆宁, 等. 中天山卡瓦布拉克杂岩带中闪长岩的锆石U-Pb 年龄及Hf同位素特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015, 45(6):1702-1712. |
| [6] | 彭明兴, 钟春根, 左琼华, 等. 东天山卡瓦布拉克地区片麻状花岗岩形成时代及地质意义[J]. 新疆地质, 2012, 30(1):12-18. |
| [7] | 田少亭, 彭明兴, 张雄华, 等. 中天山卡瓦布拉克地区中元古代卡瓦布拉克群硅质岩成因[J]. 新疆地质, 2012, 30(4):309-403. |
| [8] | 孙桂华, 李锦轶, 王德贵, 等. 东天山阿其克库都克断裂南侧花岗岩和花岗岩闪长岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(8): 945-952. |
| [9] |
IRVINE T N, BARAGAR W R A. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1971, 8: 523-548.
DOI URL |
| [10] | ROLLINSON H R. Using Geochemical Data:Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation[M]. New York: Longman Scientific and Technical Press, 1993:1-35. |
| [11] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implication for mantle composition and Processes[M]// SAUNDERSA D, NORRYM J.Magmatism in the Ocean Basin. London:Geological Society of London, Special Publication, 1989: 313-346. |
| [12] |
木合塔尔·扎日, 尼加提·阿布都逊, 吴兆宁, 等. 觉罗塔格南缘石炭系火山岩地球化学特征及其对古亚洲洋南缘构造演化的指示意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(1):238-250.
DOI |
| [13] |
ALLEGRE C J, MINSTER J F. Quantitative method of trace element behavior in magmatic processes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1978, 38: 1-25.
DOI URL |
| [14] | RUDNICK R, GAO S. The role of lower crustal recycling in continent formation[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochima Acta, 2003, 67:1-10. |
| [15] |
ZARTMAN Robert E, HAINES Sara M. The plimbo tectonic model for Pb isotopic systematics among major terrestrial reservoirs-A case for bi-direction transport[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1988, 52(6): 1327-1339.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 邓晋福, 邱瑞照, 肖庆辉, 等. 对流地幔输入大陆与大陆成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 2003, 21(1):24-31. |
| [17] | 卢欣祥, 于在平, 冯有利, 等. 东秦岭深源浅成型花岗岩的成矿作用及地质构造背景[J]. 矿床地质, 2002, 21(2):168-178. |
| [18] | 曹锐, 木合塔尔·扎日, 陈斌, 等. 东天山板块缝合带石炭纪火山岩地球化学和Sr-Nd同位素特征及其大地构造意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(2):400-409. |
| [19] | DUPUY C, DOSTAL J, MARCELOT G, et al. Geochemistry of basalts from central and southern New Hebrides arc: implication for their source rock composition[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1982, 60(2): 207-225. |
| [20] | 陈斌, 贺敬博, 陈长健, 等. 东天山白石泉镁铁-超镁铁杂岩体的Nd-Sr-Os同位素成分及其对岩浆演化的意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(1):294-302. |
| [21] | 马星华, 陈斌, 王超, 等. 早古生代古亚洲洋俯冲作用: 来自新疆哈尔里克侵入岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学和 Sr-Nd 同位素证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(1):89-104. |
| [22] | 李春昱, 王荃, 刘雪亚, 等. 亚洲大地构造图说明说[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1981:1-20. |
| [23] | 马瑞士, 舒良树, 孙家齐. 东天山构造演化与成矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997:1-20. |
| [24] | 马瑞士, 王赐银, 叶尚夫, 等. 东天山构造格架及地壳演化[M]. 南京: 南京大学出版社, 1993:1-22. |
| [25] | 顾连兴, 杨浩, 陶仙聪, 等. 中天山东段花岗岩类铷-锶年代学及构造演化[J]. 桂林冶金地质学院学报, 1990, 10(1):49-55. |
| [26] | 杨浩, 顾连兴, 严正富. 中天山尾亚杂岩体的铅同位素组成特征[J]. 铀矿地质, 1990, 6(3):156-162. |
| [27] | 姜常义, 吴文奎, 杨复, 等. 天山加里东晚期构造运动及其地质意义[J]. 西安地质学院学报, 1993, 15(4):41-46. |
| [28] | 朱永峰, 宋彪. 新疆天格尔糜棱岩化花岗岩的岩石学及其SHRIMP年代学研究:兼论花岗岩中热液锆石边的定年[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(1):135-144. |
| [29] | 左国朝, 刘义科, 张招崇, 等. 中亚地区中、南天山造山带构造演化及成矿背景分析[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(1):1-14. |
| [30] | 贺振宇, 张泽明, 宗克清, 等. 星星峡石英闪长质片麻岩的锆石年代学:对天山造山带构造演化及基底归属的意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(6):1857-1874. |
| [31] | 尼加提·阿布都逊, 木合塔尔·扎日,贾晓亮.新疆南天山东段早石炭世—早二叠世花岗岩类及其对南天山洋闭合时间的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(2):263-273. |
| [32] | 张亚峰, 蔺新望, 王星, 等. 阿尔泰造山带南缘昆格依特岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石成因及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(1):16-28. |
| [33] | 陈岳龙, 王忠, 罗照华, 等. 康定杂岩Rb-Sr、Sm-Nd同位素系统及其意义[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(5):707-714. |
| [34] | 曲凯, 董国臣, 李胜荣, 等. 太行山木吉村斑岩铜(钼)矿床岩石地球化学、Sr-Nd-Pb同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(3):449-460. |
| [35] | 褚少雄, 刘建明, 徐九华, 等. 黑龙江三矿沟铁铜矿床花岗闪长岩锆石 U-Pb 定年、岩石成因及构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(2):433-50. |
| [36] | 段志明, 张玉修, 祝向平, 等. 松潘—甘孜南部玛孜措石英闪长岩的地球化学特征、同位素年龄及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(12):1874-1886. |
| [37] | 黄博涛, 贺振宇, 宗克清, 等. 新疆阿拉塔格地区新元古代花岗片麻岩的锆石U-Pb定年与Hf同位素:对中天山地块前寒武纪地壳演化的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2014, 59(3):287-296. |
| [38] | 李光来, 华仁民, 胡东泉, 等. 赣南地区石雷石英闪长岩的成因:岩石化学、副矿物微量元素、 锆石U-Pb年代学与Sr-Nd-Hf同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(3):903-918. |
| [39] | 李秋根, 刘树文, 宋彪, 等. 中天山东段中元古代晚期—古生代构造-热事件:SHRIMP锆石年代学证据[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(2):175-184. |
| [40] | 李佐臣, 裴先治, 刘站庆, 等. 东昆仑南缘布青山构造混杂岩带哥日卓托闪长岩体年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(8):1089-1103. |
| [41] | 刘建峰, 迟效国, 张兴洲, 等. 内蒙古西乌旗南部石炭纪石英闪长岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(3):365-376. |
| [42] | 屈翠侠, 杨兴科, 易鹏飞, 等. 巴里坤塔格晚古生代侵入岩岩石地球化学与Sr-Nd-Pb同位素特征[J]. 西北地质, 2015, 48(2):17-30. |
| [43] | 施文翔, 廖群安, 胡远清, 等. 东天山地区中天山地块内中元古代花岗岩的特征及地质意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2010, 29(1):29-37. |
| [44] | 修群业, 于海峰, 李铨, 等. 卡瓦布拉克群花岗岩闪长岩单颗粒锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 新疆地质, 2002, 20(4):335-337. |
| [45] | 颜代蓉, 邓晓东, 胡浩, 等. 鄂东南地区阮家湾和犀牛山花岗闪长岩的时代、成因及成矿和找矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(10):3373-3388. |
| [46] | 杨承海, 许文良, 杨德彬, 等. 鲁西中生代高Mg闪长岩的成因:年代学与岩石地球化学证据[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2006, 31(1):81-92. |
| [47] | 杨天南, 李锦轶, 孙桂花, 等. 中天山早泥盆世陆弧:来自花岗质糜棱岩地球化学及SHRIMP-U/Pb定年的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(1):41-48. |
| [48] | 姚磊, 谢桂青, 吕志成, 等. 鄂东南程潮铁矿床花岗质岩和闪长岩的岩体时代、成因及其地质意义——锆石年龄、地球化学和Hf同位素新证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2013, 43(5):1393-1422. |
| [49] | 张遵忠, 顾连兴, 吴昌志, 等. 中天山东段尾亚印支早—中期石英闪长岩—陆内俯冲与原生下陆壳部分熔融[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(9):1420-1434. |
| [50] |
ALLEN M B, WINDLEY B F, ZHANG C. Palaeozoic collisional tectonics and magmatism of the Chinese Tien Shan, central Asia[J]. Tectonophysics, 1993, 220: 89-115.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
DEFANT M J, DRUMMOND M S. Derivation of some modern magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347: 662-665.
DOI |
| [52] | PAPP R P, SHIMIZU N, NORMAN M D. Reaction between slab-derived melts and peridotite in the mantle wedge: experimental constraints at 3.8 GPa[J]. Geochemical Geology, 1999, 160(4):335-356. |
| [53] |
PAPP R P, WATSON E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8-32 kbar: implication for continental growth and crust-mantle recyling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4): 891-931.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
RINGWOOD A E. Slab-mantle interactions: 3. Petrogenisis of interplate magmas and structure of the upper mantle[J]. Chemical Geology, 1990, 82: 187-207.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
WINDLEY B F, ALLEN M B, ZHANG C et al. Paleozoic accretion and Cenozoic redeformation of the Chinese Tien Shan Range, Central Asia[J]. Geology, 1990, 18(2): 128-131.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
MA Xuxuan, SHU Liangshu, JOSEPH G. The Paleozoic evolution of Central Tianshan: Geochemical and geochronological evidence[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25: 797-819.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
MA Xuxuan, SHU Liangshu, SANTOSH M, et al. Paleoproterozoic collisional orogeny in Central Tianshan: Assembling the Tarim Block within the Columbia supercontinent[J]. Precambrian Research, 2013, 228: 1-19.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
HAN B F, WANG S G, JAHN B M, et al. Depleted-mantle source for the Ulungur River A-type granites from North Xinjiang, China: geochemistry and Nd-Sr isotopic evidence, and implications for Phanerozoic crustal growth[J]. Chemical Geology, 1997, 138(3): 135-159.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
HAN B F, GUO Q H. Late Carboniferous collision between theTarim and Kazakhstan Yili terranes in the western segment of th South Tian Shan Orogen, Central Asia, and implications for the Northern Xinjiang, western China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2011, 109(3): 74-93.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
XIAO W, WINDLEY B F, ALLEN M B, et al. Paleozoic multiple accretionary and collisional tectonics of the Chinese Tianshan orogentic collage[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23(4): 1316-1314.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [2] | 韩飞, 宋元宝, 张伟, 李道凌, 黄永高, 李应栩, 贾小川, 杨学俊, 杨青松, 宋旭波, 卢柳. 西藏冈底斯南木林地区晚三叠世中酸性岩浆作用及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 547-561. |
| [3] | 李文霞, 赵志丹, 王晓丽, 严溶, 路远发. 西藏日喀则蛇绿岩镁铁质岩石Re-Os同位素特征及意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1503-1512. |
| [4] | 张志平, 钟康惠, 单树成, 郑鑫, 黄浩震, 严钊. 新特提斯洋晚白垩世演化特点:来自泽当共国日二长花岗岩年代学、地球化学及Sr-Nd同位素证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1194-1205. |
| [5] | 饶世成, 王长明, 贺昕宇, 石康兴, 祝佳萱, 陈奇, 段泓羽, 李朋伟. 豫西熊耳山地区五丈山岩体成因与构造意义:岩石地球化学和Sr-Nd-Pb同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1230-1244. |
| [6] | 于立栋, 于学峰, 李大鹏, 刘强, 刘家军, 舒磊, 尉鹏飞. 鲁西临朐铁寨杂岩体锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 418-430. |
| [7] | 岳相元, 杨波, 周雄, 龚大兴, 叶亚康, 谭红旗, 周玉, 朱志敏. 川西地区热达门石英闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄和岩石地球化学特征:岩石成因与构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(05): 1015-1024. |
| [8] | 朱伯鹏, 秦纪华, 何斌, 张汉青, 吴晓贵. 阿尔泰巴利尔斯河一带岩体LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石成因及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 680-691. |
| [9] | 朱玉娣, 代堰锫, 王丽丽, 李同柱, 张惠华, 沈战武. 松潘—甘孜造山带南缘江浪穹窿文家坪花岗岩成因及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(01): 16-27. |
| [10] | 李研, 王建, 孙德有, 陈德兵, 韩志滨, 崔家瑞. 内蒙古海拉尔北部八大关地区花岗岩的成岩时代、地球化学特征与成因[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(02): 234-245. |
| [11] | 谢燮,杨建国,王小红,王磊,江磊,姜安定. 甘肃北山红柳沟基性-超基性岩体岩石成因及成矿条件[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(6): 1259-1270. |
| [12] | 蔡春红,赵国春,任留东,李崇,关家敏. 辽西建平杂岩中新太古代变质基性岩的地球化学、年代学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(4): 844-854. |
| [13] | 黄丁伶,朱洛婷,侯青叶,王瑾,刘金宝,陈岳龙,王忠,李大鹏. 内蒙古维拉斯托矿区花岗岩类地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(6): 1122-1137. |
| [14] | 曲凯,董国臣,李胜荣,申俊峰,王艳娟,王霞,罗薇. 太行山木吉村斑岩铜(钼)矿床岩石地球化学、Sr-Nd-Pb同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(3): 449-460. |
| [15] | 李良林,周汉文,陈植华,王锦荣,陈正华,肖依. 福建太姥山地区和鼓山地区A型花岗岩对比及其地球动力学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(3): 509-524. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||