



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (03): 636-647.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.033
陈武迪1,2,3( ), 刘晓煌3,4(
), 刘晓煌3,4( ), 李洪宇3,4, 雒新萍3,4, 王然3,4, 邢莉圆3,4, 白亚楠1, 王超3,4, 赵宏慧3,4
), 李洪宇3,4, 雒新萍3,4, 王然3,4, 邢莉圆3,4, 白亚楠1, 王超3,4, 赵宏慧3,4
出版日期:2024-06-10
发布日期:2024-07-04
通讯作者:
刘晓煌,男,正高级工程师,1972年出生,新疆维吾尔自治区“天池英才”引进计划人才,主要从事自然资源观测研究。Email: liuxh19972004@163.com。
作者简介:陈武迪,男,硕士研究生,2000年出生,主要从事资源与环境、自然资源观测研究。Email:1830708775@qq.com。
基金资助:
CHEN Wudi1,2,3( ), LIU Xiaohuang3,4(
), LIU Xiaohuang3,4( ), LI Hongyu3,4, LUO Xinping3,4, WANG Ran3,4, XING Liyuan3,4, BAI Yanan1, WANG Chao3,4, ZHAO Honghui3,4
), LI Hongyu3,4, LUO Xinping3,4, WANG Ran3,4, XING Liyuan3,4, BAI Yanan1, WANG Chao3,4, ZHAO Honghui3,4
Online:2024-06-10
Published:2024-07-04
摘要:
产水服务是重要的生态系统服务功能之一,评估产水服务空间分异特征、明确不同自然资源分区的关键驱动因子,是维系新疆生态安全和可持续发展的关键。本研究利用InVEST模型模拟新疆1990—2018年产水服务时空变化,选择气候、土壤、地形、土地利用等因子,采用地理探测器开展产水服务空间异质性归因分析。结果表明:(1)1990—2018年新疆产水总量变化为524.39×108~683.42×108 m3,高值区集中在阿尔泰山、准噶尔盆地西部山地及天山山地等地区。(2)研究区不同地类的产水能力不同,其中荒漠和林地的产水能力最高,草地和水体与湿地其次,耕地和建设用地产水能力最差。(3)在新疆全域,气候类因子的解释能力最强,尤其是年总降水量因子,解释能力达到0.9以上;不同自然资源分区,产水服务空间分异的主要驱动因子存在明显差异,但年总降水量因子仍为第一主导因子。(4)因子的交互作用对产水服务的空间分布解释能力大于单个因子的解释能力,气候因子与地形因子的交互作用解释能力最强,其次是气候因子与土地利用因子的交互。因此,新疆产水服务的维持与保护工作应充分考虑气候、地形、土地利用等因素,制定合理的水资源管理和保护措施。
中图分类号:
陈武迪, 刘晓煌, 李洪宇, 雒新萍, 王然, 邢莉圆, 白亚楠, 王超, 赵宏慧. 基于InVEST模型的新疆1990—2018年产水服务时空变化及驱动因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 636-647.
CHEN Wudi, LIU Xiaohuang, LI Hongyu, LUO Xinping, WANG Ran, XING Liyuan, BAI Yanan, WANG Chao, ZHAO Honghui. Spatiotemporal Changes and Driving Factors of Water Yield Service Based on InVEST Model in Xinjiang from 1990 to 2018[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(03): 636-647.

图2 新疆土地利用类型及自然资源三级区划(1990—2018年) X11.阿尔泰山与塔城盆地北部高覆盖草原地区;X12.阿尔泰山与塔城盆地中部低覆盖草原地区;X13.阿尔泰山与塔城盆地南部低覆盖草原地区;X21.准噶尔盆地沙地地区;X22.准噶尔盆地高覆盖草原旱地地区;X23.准噶尔盆地戈壁地区;X31.伊犁盆地高覆盖草原旱地地区;X41.塔克拉玛干沙漠荒漠地区;X42.塔里木平原高覆盖草原地区;X51.吐鲁番盆地沙地地区;X61.南疆荒漠地区;Ⅺ11.昆仑高山西部中覆盖草原积雪地区;Ⅺ12.昆仑高山东部低覆盖草原戈壁地区;下文同
Fig.2 Land-use types and three-level divisions of the natural resources in Xinjiang (from 1990 to 2018)
| 类型 | 影响因子 | 空间分辨率 (km×km) | 时间范围 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 气候 | 年均温(℃) | 1×1 | 1990—2018 | 国家青藏高原科学数据中心 https://data.tpdc.ac.cn |
| 年总降水量(mm) | 1×1 | 1990—2018 | ||
| 年实际蒸散量(mm) | 1×1 | 1990—2018 | ||
| 年潜在蒸散量(mm) | 1×1 | 1990—2018 | ||
| 地形地貌 | 高程(m) | 1×1 | — | 地理空间数据云 |
| 坡度(°) | 1×1 | — | 国家青藏高原科学数据中心 https://data.tpdc.ac.cn | |
| 植被 | NDVI | 1×1 | 1990—2018 | 国家青藏高原科学数据中心 https://data.tpdc.ac.cn |
| 土壤 | 土壤类型 | 1×1 | — | 中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心 http://www.resdc.cn |
| 土地利用 | 土地利用类型 | 1×1 | 1990、2000、2010、2018 |
表1 新疆产水服务空间分异影响因子及数据信息
Table 1 Influencing factors and data information of the spatial differentiation of water production service in Xinjiang
| 类型 | 影响因子 | 空间分辨率 (km×km) | 时间范围 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 气候 | 年均温(℃) | 1×1 | 1990—2018 | 国家青藏高原科学数据中心 https://data.tpdc.ac.cn |
| 年总降水量(mm) | 1×1 | 1990—2018 | ||
| 年实际蒸散量(mm) | 1×1 | 1990—2018 | ||
| 年潜在蒸散量(mm) | 1×1 | 1990—2018 | ||
| 地形地貌 | 高程(m) | 1×1 | — | 地理空间数据云 |
| 坡度(°) | 1×1 | — | 国家青藏高原科学数据中心 https://data.tpdc.ac.cn | |
| 植被 | NDVI | 1×1 | 1990—2018 | 国家青藏高原科学数据中心 https://data.tpdc.ac.cn |
| 土壤 | 土壤类型 | 1×1 | — | 中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心 http://www.resdc.cn |
| 土地利用 | 土地利用类型 | 1×1 | 1990、2000、2010、2018 |

图5 1990—2018年均产水量、年均降水量、产水总量和年均实际蒸散量的变化
Fig.5 Changes of annual average water yields, annual average precipitation, total water yield, and annual average actual evapotranspiration from 1990 to 2018
| 土地利用类型 | X11 | X12 | X13 | X22 | X31 | X42 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 荒漠 | 0.27 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.29 | 0.43 |
| 建设用地 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.02 |
| 水体与湿地 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.15 |
| 草地 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.10 |
| 林地 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.28 |
| 耕地 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.03 |
表2 三级区划不同土地利用类型产水能力
Table 2 Water yield capacity of different land-use types in three-level division
| 土地利用类型 | X11 | X12 | X13 | X22 | X31 | X42 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 荒漠 | 0.27 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.29 | 0.43 |
| 建设用地 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.02 |
| 水体与湿地 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.15 |
| 草地 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.10 |
| 林地 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.28 |
| 耕地 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.03 |
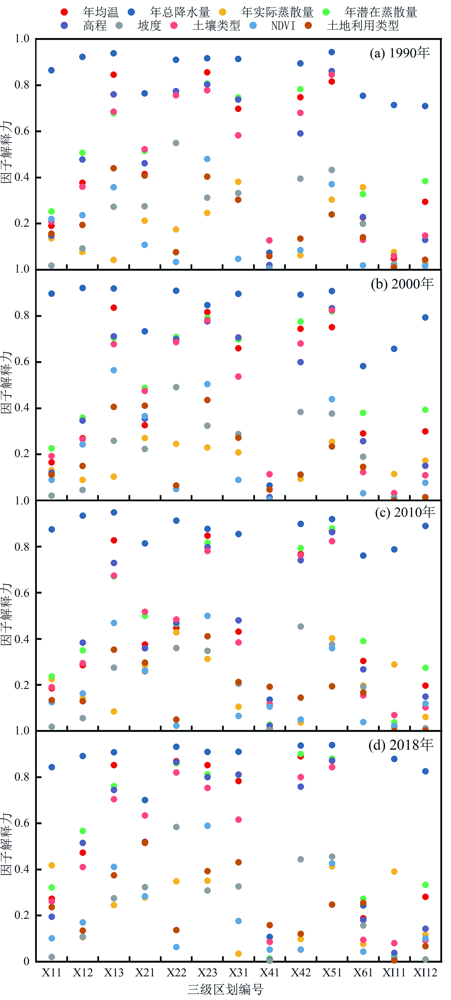
图8 新疆不同分区各因子对产水服务空间异质性的影响程度(三级区划编号见图2)
Fig.8 Analysis of factors influencing the spatial diversity of water yield services in the sub-regions of Xinjiang
| 分区编号 | 第一主导因子 | 第二主导因子 | 第三主导因子 |
|---|---|---|---|
| X11 | 实际蒸散量∩潜在蒸散量(0.59) | 温度∩实际蒸散量(0.55) | 实际蒸散量∩高程(0.50) |
| X12 | 实际蒸散量∩高程(0.7) | 实际蒸散量∩潜在蒸散量(0.65) | 温度∩实际蒸散量(0.64) |
| X13 | 实际蒸散量∩高程(0.83) | 实际蒸散量∩NDVI(0.55) | 实际蒸散量∩土地利用类型(0.49) |
| X22 | 坡度∩土地利用类型(0.58) | 坡度∩NDVI(0.56) | 实际蒸散量∩土地利用类型(0.38) |
| X31 | 土壤类型∩NDVI(0.63) | 实际蒸散量∩土地利用类型(0.46) | 实际蒸散量∩坡度(0.43) |
| X42 | 温度∩实际蒸散量(0.84) | 实际蒸散量∩高程(0.78) | 坡度∩NDVI(0.54) |
| X61 | 年总降水量∩土地利用类型(0.88) | 年总降水量∩NDVI(0.71) | 实际蒸散量∩土壤类型(0.55) |
| XI11 | 年总降水量∩土地利用类型(0.84) | 年总降水量∩坡度(0.82) | 温度∩年总降水量(0.81) |
| XI12 | 年总降水量∩土地利用类型(0.91) | 潜在蒸散量∩NDVI(0.52) | 温度∩NDVI(0.49) |
| 新疆全域 | 潜在蒸散量∩高程(0.75) | 潜在蒸散量∩NDVI(0.70) | 年均温∩NDVI(0.66) |
表3 不同自然资源分区产水量影响因子交互作用探测(1990、2000、2010、2018年4年平均值,分区编号见图2)
Table 3 Interaction detection of water yield influencing factors in different natural resource partitions (average values of years 1990, 2000, 2010 and 2018)
| 分区编号 | 第一主导因子 | 第二主导因子 | 第三主导因子 |
|---|---|---|---|
| X11 | 实际蒸散量∩潜在蒸散量(0.59) | 温度∩实际蒸散量(0.55) | 实际蒸散量∩高程(0.50) |
| X12 | 实际蒸散量∩高程(0.7) | 实际蒸散量∩潜在蒸散量(0.65) | 温度∩实际蒸散量(0.64) |
| X13 | 实际蒸散量∩高程(0.83) | 实际蒸散量∩NDVI(0.55) | 实际蒸散量∩土地利用类型(0.49) |
| X22 | 坡度∩土地利用类型(0.58) | 坡度∩NDVI(0.56) | 实际蒸散量∩土地利用类型(0.38) |
| X31 | 土壤类型∩NDVI(0.63) | 实际蒸散量∩土地利用类型(0.46) | 实际蒸散量∩坡度(0.43) |
| X42 | 温度∩实际蒸散量(0.84) | 实际蒸散量∩高程(0.78) | 坡度∩NDVI(0.54) |
| X61 | 年总降水量∩土地利用类型(0.88) | 年总降水量∩NDVI(0.71) | 实际蒸散量∩土壤类型(0.55) |
| XI11 | 年总降水量∩土地利用类型(0.84) | 年总降水量∩坡度(0.82) | 温度∩年总降水量(0.81) |
| XI12 | 年总降水量∩土地利用类型(0.91) | 潜在蒸散量∩NDVI(0.52) | 温度∩NDVI(0.49) |
| 新疆全域 | 潜在蒸散量∩高程(0.75) | 潜在蒸散量∩NDVI(0.70) | 年均温∩NDVI(0.66) |
| [1] | DAILY G C. Nature’s services:societal dependence on natural ecosystems (1997)[M]// The Future of Nature. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2017: 454-464. |
| [2] |
傅伯杰, 周国逸, 白永飞, 等. 中国主要陆地生态系统服务功能与生态安全[J]. 地球科学进展, 2009, 24(6): 571-576.
DOI |
| [3] | COSTANZA R, D’ARGE R, DE GROOT R, et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital[J]. Nature, 1997, 387: 253-260. |
| [4] | 陈武迪, 刘晓煌, 李洪宇, 等. 新疆天山1990—2050年生态系统服务功能及安全格局[J/OL]. 中国地质. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.1167.P.20240226.1737.006. |
| [5] | CHEN Q R, XU X, WU M Y, et al. Assessing the water conservation function based on the InVEST model: Taking Poyang Lake region as an example[J]. Land, 2022, 11(12): 2228. |
| [6] | 徐飞, 焦玉国, 唐丽伟, 等. 泰安市山水林田湖草生态修复区生态脆弱性评价与生态修复对策研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(4): 892-902. |
| [7] | 王思源, 赵敏敏, 闫晶, 等. 川藏铁路西藏昌都段生态保护重要性评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(1): 234-243. |
| [8] |
AHMED M AA, ABD-ELRAHMAN A, ESCOBEDO F J, et al. Spatially-explicit modeling of multi-scale drivers of aboveground forest biomass and water yield in watersheds of the Southeastern United States[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 199: 158-171.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
黄欣, 彭双云, 王哲, 等. 基于地理探测器的云南省生态系统产水服务的空间异质性及驱动因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(10): 2813-2821.
DOI |
| [10] |
杨洁, 谢保鹏, 张德罡. 基于InVEST模型的黄河流域产水量时空变化及其对降水和土地利用变化的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(8): 2731-2739.
DOI |
| [11] |
刘美娟, 仲俊涛, 王蓓, 等. 基于InVEST模型的青海湖流域产水功能时空变化及驱动因素分析[J]. 地理科学, 2023, 43(3): 411-422.
DOI |
| [12] | HU W M, LI G, GAO Z H, et al. Assessment of the impact of the Poplar Ecological Retreat Project on water conservation in theDongting Lake wetland region using the InVEST model[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 733: 139423. |
| [13] | 王云飞, 叶爱中, 乔飞, 等. 水源涵养内涵及估算方法综述[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2021, 19(6): 1041-1071. |
| [14] |
XU W H, XIAO Y, ZHANG J J, et al. Strengthening protected areas for biodiversity and ecosystem services in China[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(7): 1601-1606.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | ZHANG B, LI W H, XIE G D, et al. Water conservation of forest ecosystem in Beijing and its value[J]. Ecological Economics, 2010, 69(7): 1416-1426. |
| [16] | ŠATALOVÁ B, KENDERESSY P. Assessment of water retention function as tool to improve integrated watershed management (case study of Poprad River Basin, Slovakia)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 599/600: 1082-1089. |
| [17] | BAI Y, OCHUODHO T O, YANG J. Impact of land use and climate change on water-related ecosystem services in Kentucky,USA[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2019, 102: 51-64. |
| [18] | CHIANG L C, LIN Y P, HUANG T, et al. Simulation of ecosystem service responses to multiple disturbances from an earthquake and several typhoons[J]. Landscape and Urban Planning, 2014, 122: 41-55. |
| [19] | LI J H, ZHOU K C, XIE B G, et al. Impact of landscape pattern change on water-related ecosystem services: Comprehensive analysis based on heterogeneity perspective[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 133: 108372. |
| [20] | LI M Y, LIANG D, XIA J, et al. Evaluation of water conservation function of Danjiang River Basin in Qinling Mountains, China based on InVEST model[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 286: 112212. |
| [21] |
王亚慧, 戴尔阜, 马良, 等. 横断山区产水量时空分布格局及影响因素研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(2): 371-386.
DOI |
| [22] |
林峰, 陈兴伟, 姚文艺, 等. 基于SWAT模型的森林分布不连续流域水源涵养量多时间尺度分析[J]. 地理学报, 2020, 75(5): 1065-1078.
DOI |
| [23] | 夏瑞, 张永勇, 张远, 等. 基于分布式水文模型的流域水源涵养功能计算[M]// 2018年中国环境科学学会科学技术年会论文集(第二卷). 北京:中国环境科学学会, 2018: 1087-1094. |
| [24] | 刘娅, 朱文博, 韩雅, 等. 基于SOFM神经网络的京津冀地区水源涵养功能分区[J]. 环境科学研究, 2015, 28(3): 369-376. |
| [25] | 朱丽亚, 胡克, 孙爽, 等. 基于InVEST模型的辽宁省海岸带碳储量时空变化研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(1): 96-104. |
| [26] |
包玉斌, 李婷, 柳辉, 等. 基于InVEST模型的陕北黄土高原水源涵养功能时空变化[J]. 地理研究, 2016, 35(4): 664-676.
DOI |
| [27] |
朱志洪, 周本智, 王懿祥, 等. 近30年千岛湖流域产水量时空变化及其影响因子分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(3): 111-119.
DOI |
| [28] |
王劲峰, 徐成东. 地理探测器: 原理与展望[J]. 地理学报, 2017, 72(1): 116-134.
DOI |
| [29] | 马良, 金陶陶, 文一惠, 等. InVEST模型研究进展[J]. 生态经济, 2015, 31(10): 126-131, 179. |
| [30] | 乔亚军, 张慧, 韩晓盈, 等. 基于地理空间角度的黑龙江省水源涵养功能变化的驱动因素分析[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(7): 2711-2721. |
| [31] | 李婧昕, 许尔琪, 张红旗. 关键驱动力作用下的新疆生态系统服务时空格局分析[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2019, 40(5): 9-20. |
| [32] | 郑艺文, 刘晓煌, 熊茂秋, 等. 1990—2018年新疆“三生” 用地时空变化特征及其碳排放效应[J]. 草业科学, 2022, 39(12): 2565-2577. |
| [33] |
阿迪来·乌甫, 玉素甫江·如素力, 热伊莱·卡得尔, 等. 基于MODIS数据的新疆地表蒸散量时空分布及变化趋势分析[J]. 地理研究, 2017, 36(7): 1245-1256.
DOI |
| [34] |
张海燕, 樊江文, 黄麟, 等. 中国自然资源综合区划理论研究与技术方案[J]. 资源科学, 2020, 42(10): 1870-1882.
DOI |
| [35] | 刘晓煌, 刘晓洁, 江东, 等. 全球视角下的中国自然资源区划[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2023. |
| [36] |
戴尔阜, 王亚慧. 横断山区产水服务空间异质性及归因分析[J]. 地理学报, 2020, 75(3): 607-619.
DOI |
| [37] | GAO J, SHI Y, ZHANG H, et al. China regional 250m norma-lized difference vegetation index data set (2000-2022)[EB/DB]. National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center, 2023. https://doi.org/10.11888/Terre.tpdc.300328. https://cstr.cn/18406.11.Terre.tpdc.300328. |
| [38] | PENG S. 1-km monthly mean temperature dataset for china (1901—2022)[EB/DB]. National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center, 2019. https://doi.org/10.11888/Meteoro.tpdc.270961. |
| [39] | PENG S. 1-km monthly precipitation dataset for China (1901-2022)[EB/DB]. National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center, 2020. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3185722. |
| [40] | TANG G. Digital elevation model of China (1 km) [EB/DB]. National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center, 2019. |
| [41] | MA N, JOZSEF S, ZHANG Y, et al. Terrestrial evapotranspiration dataset across China (1982-2017)[EB/DB]. National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center, 2019. https://doi.org/10.11888/AtmosPhys.tpe.249493.file. |
| [42] | PENG S. 1 km monthly potential evapotranspiration dataset in China (1990-2022)[EB/DB]. National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center, 2022. https://doi.org/10.11866/db.loess.2021.001 |
| [43] | BUDYKO M I. Climate and Life[M]. New York, Academic Press:1974. |
| [44] | ZHANG L, DAWES W R, WALKER G R. Response of mean annual evapotranspiration to vegetation changes at catchment scale[J]. Water Resources Research, 2001, 37(3): 701-708. |
| [45] | WANG J F, LI X H, CHRISTAKOS G, et al. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun region, China[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2010, 24(1): 107-127. |
| [46] | WANG J F, HU Y. Environmental health risk detection withGeogDetector[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2012, 33: 114-115. |
| [47] | 陈晓莹. 荒漠草原两种典型土壤的水分特征及其影响因素[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2020. |
| [48] | DELPHIN S, ESCOBEDO F J, ABD-ELRAHMAN A, et al. Urbanization as a land use change driver of forest ecosystem services[J]. Land Use Policy, 2016, 54: 188-199. |
| [49] | SUN G, CALDWELL P, NOORMETS A, et al. Upscaling key ecosystem functions across the conterminous United States by a water-centric ecosystem model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2011, 116:1-16. |
| [50] | 魏培洁, 吴明辉, 贾映兰, 等. 基于InVEST模型的疏勒河上游产水量时空变化特征分析[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(15): 6418-6429. |
| [51] | LU H T, YAN Y, ZHU J Y, et al. Spatiotemporal water yield variations and influencing factors in the Lhasa River Basin, Tibetan Plateau[J]. Water, 2020, 12(5): 1498. |
| [1] | 袁江龙, 刘晓煌, 李洪宇, 邢莉圆, 雒新萍, 王然, 王超, 赵宏慧. 1990—2050年黄河中游伊洛河流域不同土地利用类型碳储量时空分异特征[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 559-573. |
| [2] | 闵婕, 刘晓煌, 肖粤新, 李洪宇, 雒新萍, 王然, 邢莉圆, 王超, 赵宏慧. 基于PLUS模型和InVEST模型的新安江流域生态系统碳储量时空变化分析与预测[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 574-588. |
| [3] | 郭富印, 刘晓煌, 张文博, 邢莉圆, 王然, 祖皮艳木·买买提, 雒新萍, 王超, 赵宏慧. 2000—2040年黄河流域(河南段)生境质量时空格局演变及驱动力分析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 599-611. |
| [4] | 郭佳晖, 刘晓煌, 张文博, 杨朝磊, 王然, 雒新萍, 邢莉圆, 王超, 赵宏慧. 基于InVEST模型和PLUS模型的云贵高原产水量时空变化特征分析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 624-635. |
| [5] | 魏总, 杨朝磊, 田瑜峰, 杨金江, 黄勇, 和峰, 朱志平. 金沙江干热河谷区土壤侵蚀时空演变及其定量归因分析:以云南楚雄元谋地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 683-693. |
| [6] | 李洪宇, 刘晓煌, 刘玖芬, 赵晓峰, 张文博, 李福杰. 基于地貌区划的新疆地表基质质地分类方案[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 706-717. |
| [7] | 赵晓峰, 刘晓煌, 刘玖芬, 李洪宇, 张文博. 基于多环境要素的新疆耕地适宜性评价[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 718-733. |
| [8] | 王晓彤, 刘军, 杨艳, 何军成. 新疆北部喇嘛苏铜矿床成矿时代与构造背景:来自石榴子石原位LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 645-661. |
| [9] | 朱丽亚, 胡克, 孙爽, 刘禹含, 梁佳欣. 基于InVEST模型的辽宁省海岸带碳储量时空变化研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 96-104. |
| [10] | 蔺新望, 王星, 陈光庭, 赵端昌, 赵江林. 新疆北部阿尔泰山东段泥盆纪岩浆活动及侵位方式的探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 514-531. |
| [11] | 柳坤峰, 冯昌荣, 翟黎明, 徐磊, 张嘉升, 王少华, 寇昕. 新疆乌恰县吾合沙鲁地区水系沉积物地球化学特征与找矿远景[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(04): 759-771. |
| [12] | 何宇, 章永梅, 顾雪祥, 彭义伟, 程文斌, 王冠南, 万阈, 袁鹏. 西天山呼斯特岩体矿物化学特征及其成岩成矿意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(06): 1227-1241. |
| [13] | 葛战林, 章永梅, 顾雪祥, 陈伟志, 徐劲驰, 武若晨, 黄岗. 新疆东准噶尔南明水金矿床成矿流体特征: 流体包裹体及氢氧同位素证据[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 887-901. |
| [14] | 刘明义, 张晶, 孟广路, 胡立. 区域地球化学评价中变异系数校正参数的意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 1074-1079. |
| [15] | 朱伯鹏, 秦纪华, 何斌, 张汉青, 吴晓贵. 阿尔泰巴利尔斯河一带岩体LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石成因及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 680-691. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||