



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (03): 574-588.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.050
闵婕1( ), 刘晓煌2,3(
), 刘晓煌2,3( ), 肖粤新2,4,5, 李洪宇2,3, 雒新萍2,3, 王然2,3, 邢莉圆2,3, 王超3, 赵宏慧3
), 肖粤新2,4,5, 李洪宇2,3, 雒新萍2,3, 王然2,3, 邢莉圆2,3, 王超3, 赵宏慧3
出版日期:2024-06-10
发布日期:2024-07-04
通讯作者:
刘晓煌,男,博士,正高级工程师,1972年出生,新疆维吾尔自治区“天池英才”引进计划人才,主要从事自然资源观测研究。Email: liuxh19972004@163.com。
作者简介:闵婕,女,硕士研究生,1999年出生,主要从事自然资源学、地理信息系统和遥感技术应用研究。Email:17856001096@163.com。
基金资助:
MIN Jie1( ), LIU Xiaohuang2,3(
), LIU Xiaohuang2,3( ), XIAO Yuexin2,4,5, LI Hongyu2,3, LUO Xinping2,3, WANG Ran2,3, XING Liyuan2,3, WANG Chao3, ZHAO Honghui3
), XIAO Yuexin2,4,5, LI Hongyu2,3, LUO Xinping2,3, WANG Ran2,3, XING Liyuan2,3, WANG Chao3, ZHAO Honghui3
Online:2024-06-10
Published:2024-07-04
摘要:
探析碳储量的时空格局演化规律,对新安江流域生态环境保护、土地利用方式优化具有积极反馈作用。基于2000—2020年土地利用数据,采用InVEST模型对2000—2020年新安江流域土地利用变化及碳储量变化情况进行分析,同时运用PLUS模型预测不同发展情景下2040年新安江流域碳储量分布。结果显示:(1)土地利用变化直接影响研究区的碳储量。2000—2020年,新安江流域建设用地扩张602.707 km2,林地、耕地、草地和灌木分别减少615.225 km2、42.640 km2、3.021 km2和0.296 km2,碳储量减少4.937×106 t;碳储量与土地利用空间分布一致,碳储量较高区域的建设用地少、生态用地集聚连片且分布较多。(2)2040年多情景模拟显示,整体土地利用格局一致,局部变化明显。城镇发展、自然发展和耕地保护情景碳储量分别下降7.540×106 t、7.544×106 t和11.302×106 t,其中在生态保护情景下,碳储量下降最少(7.130×106 t)。(3)碳储量空间分异受地形、生态和人为因素影响。地理探测器表明,NDVI(0.561)和NPP(0.398)的解释力显著高于其他因子,是新安江流域碳储量空间分异的主要驱动因子。不同影响因子间的交互作用强于单一因子,其中NDVI与坡度的协同影响类型最强(0.652)。研究结果表明,采取城镇发展和生态保护政策可控制碳储量减少,在未来规划中,应保护生态用地,控制建设用地扩张,以提高碳储量水平。
中图分类号:
闵婕, 刘晓煌, 肖粤新, 李洪宇, 雒新萍, 王然, 邢莉圆, 王超, 赵宏慧. 基于PLUS模型和InVEST模型的新安江流域生态系统碳储量时空变化分析与预测[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 574-588.
MIN Jie, LIU Xiaohuang, XIAO Yuexin, LI Hongyu, LUO Xinping, WANG Ran, XING Liyuan, WANG Chao, ZHAO Honghui. Analysis and Predictions of the Spatiotemporal Variations of Ecosystem Carbon Storages in the Xin’an River Basin Based on PLUS and InVEST Models[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(03): 574-588.
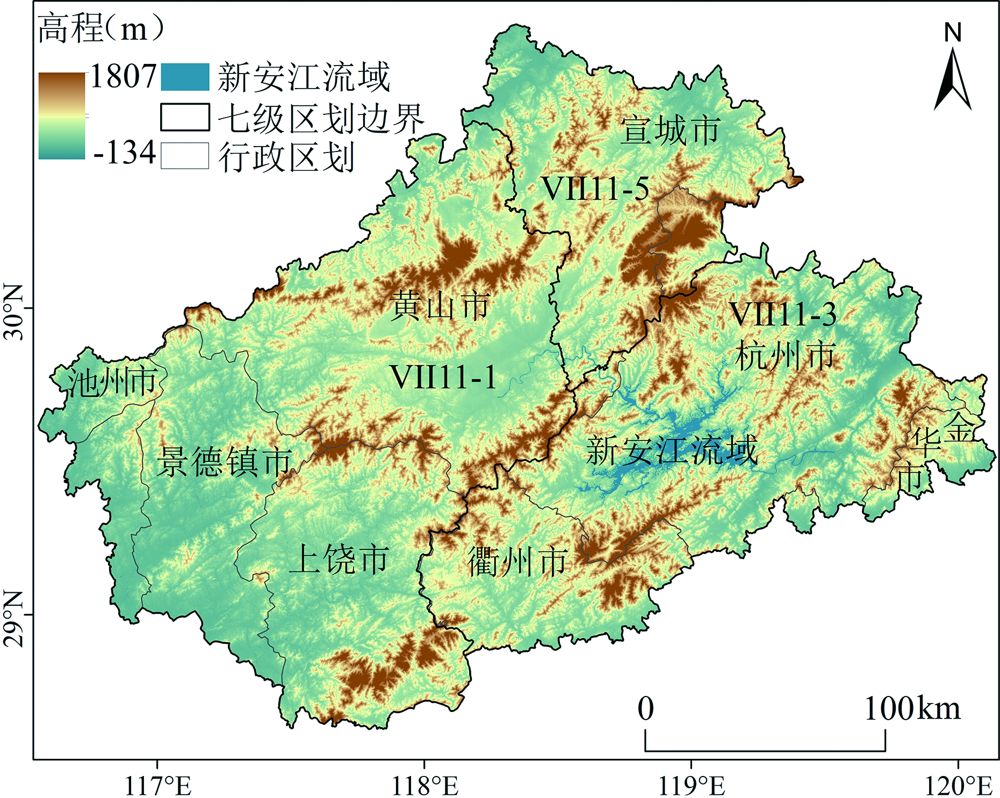
图1 新安江流域研究区划和高程分布 Ⅵ11-1.黄山市—景德镇市—上饶市西北亚热带针叶林小区;Ⅵ11-3.杭州市南—衢州市西北旱作种植小区;Ⅵ11-5.宣城市南—黄山市东北落叶阔叶灌丛小区
Fig.1 Overview of the location and elevation of the study area in the Xin’an River Basin
| 数据类型 | 数据名称 | 数据年份 | 数据精度 (m) | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土地利用 数据 | 土地利用 | 2000年、2010年、2015年和2020年 | 30 | 中国科学院资源环境科学与数据中心( |
| 气候环境 数据 | 土壤类型 | 2018年 | 30 | 国家地球系统科学数据中心土壤分中心( |
| 年平均温度 | 2020年 | 30 | 国家气象科学数据中心( | |
| 年平均降水 | 2000—2020年 | 30 | 国家气象科学数据中心( | |
| DEM高程 | 2020年 | 30 | 地理空间数据云ASTER GDEM.30M 分辨率数字高程数据( | |
| 社会经济 数据 | 坡度 | 2020年 | 30 | 利用DEM采用ArcGIS计算得到 |
| GDP | 2019年 | 1000 | 中国科学院资源环境科学与数据中心( | |
| 人口 | 2020年 | 1000 | 中国科学院资源环境科学与数据中心( | |
| 铁路距离 | 2020年 | 30 | 全国地理信息资源目录服务系统( | |
| 高速公路距离 | 2020年 | 30 | 全国地理信息资源目录服务系统( | |
| 二级道路距离 | 2020年 | 30 | 全国地理信息资源目录服务系统( | |
| 三级道路距离 | 2020年 | 30 | 全国地理信息资源目录服务系统( | |
| 四级道路距离 | 2020年 | 30 | 全国地理信息资源目录服务系统( |
表1 数据信息及来源
Table 1 Data information and sources
| 数据类型 | 数据名称 | 数据年份 | 数据精度 (m) | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土地利用 数据 | 土地利用 | 2000年、2010年、2015年和2020年 | 30 | 中国科学院资源环境科学与数据中心( |
| 气候环境 数据 | 土壤类型 | 2018年 | 30 | 国家地球系统科学数据中心土壤分中心( |
| 年平均温度 | 2020年 | 30 | 国家气象科学数据中心( | |
| 年平均降水 | 2000—2020年 | 30 | 国家气象科学数据中心( | |
| DEM高程 | 2020年 | 30 | 地理空间数据云ASTER GDEM.30M 分辨率数字高程数据( | |
| 社会经济 数据 | 坡度 | 2020年 | 30 | 利用DEM采用ArcGIS计算得到 |
| GDP | 2019年 | 1000 | 中国科学院资源环境科学与数据中心( | |
| 人口 | 2020年 | 1000 | 中国科学院资源环境科学与数据中心( | |
| 铁路距离 | 2020年 | 30 | 全国地理信息资源目录服务系统( | |
| 高速公路距离 | 2020年 | 30 | 全国地理信息资源目录服务系统( | |
| 二级道路距离 | 2020年 | 30 | 全国地理信息资源目录服务系统( | |
| 三级道路距离 | 2020年 | 30 | 全国地理信息资源目录服务系统( | |
| 四级道路距离 | 2020年 | 30 | 全国地理信息资源目录服务系统( |
| 土地利用 类型 | 地上碳密度 Cabove | 地下碳密度 Cbelow | 土壤碳密度 Csoil | 死亡有机物 碳密度Cdead |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 | 1.90 | 0.38 | 39.3 | 2.4 |
| 林地 | 32.28 | 6.57 | 63.9 | 3.8 |
| 灌木 | 14.00 | 2.40 | 66.6 | 2.5 |
| 草地 | 1.30 | 3.30 | 77.7 | 0.2 |
| 水体 | 2.30 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 未利用地 | 9.10 | 1.50 | 9.7 | 0 |
| 建设用地 | 7.60 | 4.50 | 18.1 | 0 |
表2 研究区土地利用类型各组成部分的碳密度(t/hm2)
Table 2 Carbon density of land-use type components in the study area (t/hm2)
| 土地利用 类型 | 地上碳密度 Cabove | 地下碳密度 Cbelow | 土壤碳密度 Csoil | 死亡有机物 碳密度Cdead |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 | 1.90 | 0.38 | 39.3 | 2.4 |
| 林地 | 32.28 | 6.57 | 63.9 | 3.8 |
| 灌木 | 14.00 | 2.40 | 66.6 | 2.5 |
| 草地 | 1.30 | 3.30 | 77.7 | 0.2 |
| 水体 | 2.30 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 未利用地 | 9.10 | 1.50 | 9.7 | 0 |
| 建设用地 | 7.60 | 4.50 | 18.1 | 0 |
| 地类 | 自然发展情景 | 城镇发展情景 | 耕地保护情景 | 生态保护情景 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | ||||
| a | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| b | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| c | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| d | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |||
| e | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |||
| f | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |||
| g | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
表3 多情景转移矩阵设置
Table 3 Multiple scene transfer matrix setting
| 地类 | 自然发展情景 | 城镇发展情景 | 耕地保护情景 | 生态保护情景 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | ||||
| a | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| b | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| c | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| d | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |||
| e | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |||
| f | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |||
| g | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 判据 | 交互作用 |
|---|---|
| 非线性减弱 | |
| 单因子非线性减弱 | |
| 双因子增强 | |
| 独立 | |
| 非线性增强 |
表4 自变量对因变量的交互作用方式
Table 4 Types of interaction between the two covariates
| 判据 | 交互作用 |
|---|---|
| 非线性减弱 | |
| 单因子非线性减弱 | |
| 双因子增强 | |
| 独立 | |
| 非线性增强 |

图3 新安江流域耕地、林地和建设用地面积增长的驱动因子贡献度 (a)新安江流域耕地增长的主要驱动因子为年平均降水、坡度和高程;(b)新安江流域林地增长的主要驱动因子为年平均气温、年平均降水和GDP;(c)新安江流域建设用地增长的主要驱动因子为GDP、距政府距离和坡度
Fig.3 Contribution of drivers to the growth of cropland, forest, and built-up areas in the Xin’an River Basin

图4 新安江流域耕地、林地、建设用地增加区域与其最高贡献度因子叠加栅格图 (a)耕地与最高贡献度因子年平均降水叠加栅格图,绿色表示耕地扩张区域;(b)林地与最高贡献度因子年平均气温叠加栅格图,绿色表示林地扩张区域;(c)建设用地与最高贡献度因子年平均降水叠加栅格图,绿色表示建设用地扩张区域
Fig.4 Increasing areas of cultivated land, forest and built-up land in the Xin’an River Basin, superimposed on their highest contributing factors

图5 2000—2020年新安江流域碳储量变化图 (a)2000年至2020年三个小区总储量变化趋势图;(b)2000年至2020年黄山市—景德镇市—上饶市西北亚热带针叶林小区耕地、林地和建设用地碳储量变化趋势图;(c)2000年至2020年杭州市南—衢州市西北旱作种植小区耕地、林地和建设用地碳储量变化趋势图;(d)2000年至2020年宣城市南—黄山市东北落叶阔叶灌丛小区耕地、林地和建设用地碳储量变化趋势图
Fig.5 Carbon storage changes in the Xin’an River Basin from 2000 to 2020

图7 新安江流域2040年不同情景土地利用分布 (a)2040年自然发展情景下不同土地利用空间分布及转移矩阵弦图;(b)2040年城镇发展情景不同土地利用空间分布及转移矩阵弦图;(c)2040年耕地保护情景不同土地利用空间分布及转移矩阵弦图;(d)2040年生态保护情景不同土地利用空间分布及转移矩阵弦图
Fig.7 Distribution of different land-use scenarios in the Xin’an River Basin in 2040
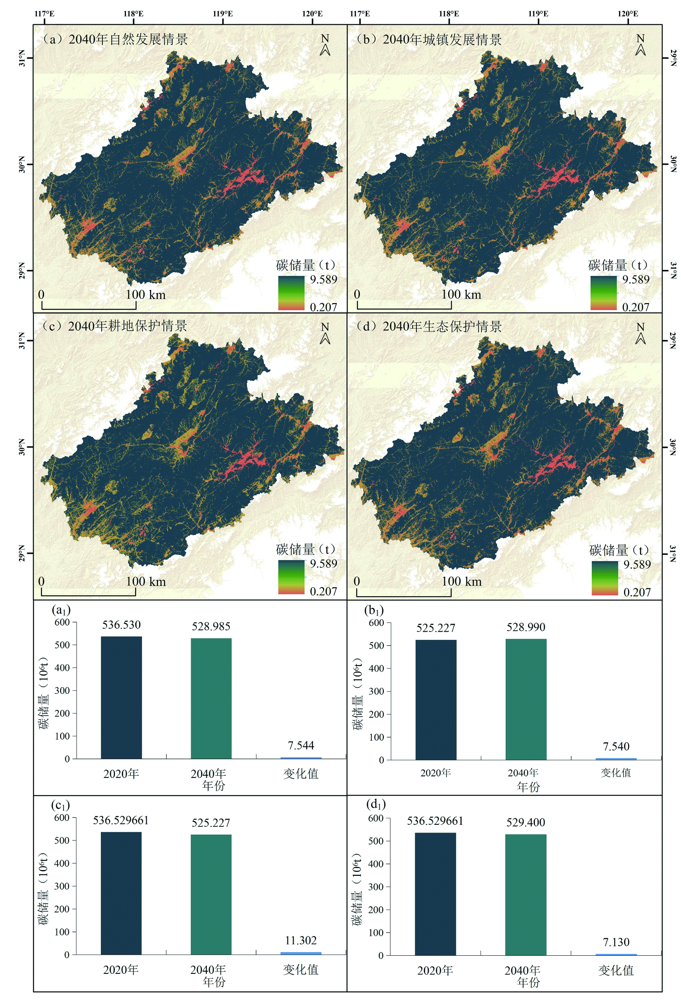
图8 新安江流域2020—2040年碳储量空间分布 (a)2040年自然发展情景碳储量空间分布;(b)2040年城镇发展情景碳储量空间分布;(c)2040年耕地保护情景碳储量空间分布;(d)2040年生态保护情景碳储量空间分布;(a1)2020年到2040年自然发展情景碳储量变化值图;(b1)2020年到2040年城镇发展情景碳储量变化值图;(c1)2020年到2040年耕地保护情景碳储量变化值图;(d)2020年到2040年生态保护情景碳储量变化值图
Fig.8 Spatial distribution of carbon storages in the Xin’an River Basin from 2020 to 2040

图9 新安江流域2020年碳储量各驱动因子交互作用探测结果 X1.坡向;X2.高程;X3.植被净初级生产力;X4.植被覆盖指数;X5.夜间灯光数据;X6.年降水量;X7.坡向;X8.年均气温;X9.年均蒸散量
Fig.9 Detection results of the interactions of the drivers for carbon storages in the Xin’an River Basin in 2020
| [1] | 邵壮, 陈然, 赵晶, 等. 基于FLUS与InVEST模型的北京市生态系统碳储量时空演变与预测[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(23): 9456-9469. |
| [2] | 罗丹, 周忠发, 陈全, 等. 喀斯特地区碳储量对土地利用模式的响应: 以南北盘江流域为例[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(9): 3500-3516. |
| [3] | HOU G L, DELANG C O, LU X X, et al. A meta-analysis of changes in soil organic carbon stocks after afforestation with deci-duous broadleaved, sempervirent broadleaved, and conifer tree species[J]. Annals of Forest Science, 2020, 77(4): 92. |
| [4] | 李春亮, 王翔, 张炜, 等. 黄土高原西段表层土壤有机碳储量及时空变化规律[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(2): 655-661. |
| [5] | 张立, 金晶泽, 姜侠, 等. 1986—2019年黑龙江省松嫩平原表层土壤有机碳变化及固碳潜力估算[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(4): 914-922. |
| [6] | PONGRATZ J, REICK C, RADDATZ T, et al. A reconstruction of global agricultural areas and land cover for the last millennium[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2008, 22(3): GB3018. |
| [7] |
张平平, 李艳红, 殷浩然, 等. 中国南北过渡带生态系统碳储量时空变化及动态模拟[J]. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(5): 1183-1197.
DOI |
| [8] | 蒋烨林, 王让会, 彭擎, 等. 干旱区景观格局演变及碳收支状况研究: 以塔里木盆地为例[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2019, 35(7): 875-884. |
| [9] | TAO Y, TIAN L, WANG C, et al. Dynamic simulation of land use and land cover and its effect on carbon storage in the Nanjing metropolitan circle under different development scenarios[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 2023, 11: 1102015. |
| [10] | 郎燕, 刘宁, 刘世荣. 气候和土地利用变化影响下生态屏障带水土流失趋势研究[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(13): 5106-5117. |
| [11] | GAO J, WANG L C. Embedding spatiotemporal changes in carbon storage into urban agglomeration ecosystem management—a case study of the Yangtze River Delta, China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 237: 117764. |
| [12] | 张徐, 李云霞, 吕春娟, 等. 基于InVEST模型的生态系统服务功能应用研究进展[J]. 生态科学, 2022, 41(1): 237-242. |
| [13] | 刘洋, 张军, 周冬梅, 等. 基于InVEST模型的疏勒河流域碳储量时空变化研究[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(10): 4052-4065. |
| [14] |
张世伟, 魏璐瑶, 金星星, 等. 基于FLUS-UGB的县域土地利用模拟及城镇开发边界划定研究[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2020, 22(9): 1848-1859.
DOI |
| [15] | 张志堂. 上海城市典型绿地的碳汇估算[J]. 绿色科技, 2017(15): 60-62. |
| [16] | MURTALA D L. pngAH A M, FIRUZ R M, et al. Exploring urban tree diversity and carbon stocks in Zaria Metropolis, North Western Nigeria[J]. Applied Geography, 2021, 127(1):102385. |
| [17] | LPATOVL D N, SHCHEGLOV A I, MANAKHOV D V, et al. Spatial variation of organic carbon stocks in peat soils and Gleyzems in the northeast of Sakhalin Island[J]. Eurasian Soil Science, 54(2): 226-237. |
| [18] |
张桂莲. 基于遥感估算的上海城市森林碳储量空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1777-1786.
DOI |
| [19] |
刘孟竹, 王彦芳, 裴宏伟. 退耕还林(草)背景下中国北方农牧交错带土地利用及碳储量变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 174-182.
DOI |
| [20] | 唐志明, 刘炳响, 屈宇. 河北太行山区典型水土保持林乔木层生物量及碳储量研究[J]. 林业资源管理, 2020(1): 102-107, 135. |
| [21] | 李茂娟, 李天奇, 朱文博, 等. 基于InVEST模型的太行山区生态系统碳储量多维变化研究[J]. 河南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 51(6): 631-642, 684. |
| [22] | 余健, 童秋英, 朱波. 改进CA-Markov模型的武汉市土地利用变化模拟[J]. 测绘科学, 2020, 45(6): 165-171. |
| [23] |
刘强, 杨众养, 陈毅青, 等. 基于CA-Markov多情景模拟的海南岛土地利用变化及其生态环境效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1522-1531.
DOI |
| [24] | 李媛洁, 叶长盛, 黄小兰. 基于CLUE-S模型的南昌市“三生” 空间时空演变及情景模拟研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 2021, 28(5): 325-332. |
| [25] |
王旭东, 姚尧, 任书良, 等. 耦合FLUS和Markov的快速发展城市土地利用空间格局模拟方法[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2022, 24(1): 100-113.
DOI |
| [26] |
王旭, 马伯文, 李丹, 等. 基于FLUS模型的湖北省生态空间多情景模拟预测[J]. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(1): 230-242.
DOI |
| [27] | 林彤, 杨木壮, 吴大放, 等. 基于InVEST-PLUS模型的碳储量空间关联性及预测: 以广东省为例[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(10): 4827-4839. |
| [28] | 刘涛, 刘晓龙, 郭利彪, 等. 基于Markov-PLUS和InVEST模型的锡林郭勒草原碳储量变化预测[J]. 草原与草坪, 2023, 43(2): 1-12. |
| [29] | 王佳楠, 张志. 基于Markov-PLUS模型的柴北缘土地利用变化及模拟分析[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2022, 37(3): 139-148, 179. |
| [30] | 王洁宁, 王文超, 海蒙蒙. 基于PLUS模型的山东省土地利用变化模拟分析[J]. 国土与自然资源研究, 2022(6): 1-8. |
| [31] | 王子尧, 黄楚梨, 李倞, 等. 耦合InVEST-HFI-PLUS模型的生态分区规划与动态评估: 以博尔塔拉蒙古自治州为例[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(14): 5789-5798. |
| [32] | 张子凡, 张海燕, 刘晓煌, 等. 华北地区自然资源综合区划的动态变化特征[J]. 中国地质调查, 2021, 8(2): 92-99. |
| [33] | 黄莉, 刘晓煌, 刘玖芬, 等. 长时间尺度下自然资源动态综合区划理论与实践研究: 以青藏高原为例[J]. 中国地质调查, 2021, 8(2): 109-117. |
| [34] | 赖明, 吴淑玉, 张海燕, 等. 基于综合区划的中国西南地区自然资源动态变化特征分析[J]. 中国地质调查, 2021, 8(2): 83-91. |
| [35] | 郑艺文, 张海燕, 刘晓洁, 等. 1990—2018年东北地区综合区划下自然资源动态变化特征分析[J]. 中国地质调查, 2021, 8(2): 100-108. |
| [36] |
姜正龙, 王兵, 姜玲秀, 等. 中国海岸带自然资源区划研究[J]. 资源科学, 2020, 42(10): 1900-1910.
DOI |
| [37] |
刘晓煌, 刘晓洁, 程书波, 等. 中国自然资源要素综合观测网络构建与关键技术[J]. 资源科学, 2020, 42(10): 1849-1859.
DOI |
| [38] | 张乃夫, 刘霞, 朱继鹏, 等. 安徽新安江流域土壤侵蚀敏感性评价及空间分异特征[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2014, 12(6): 8-15. |
| [39] | 李冬花, 张晓瑶, 王咏, 等. 新安江流域生态系统服务演化过程及权衡协同关系[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(17): 6981-6993. |
| [40] | YANG J, HUANG X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2021, 13(8): 3907-3925. |
| [41] | 孙方虎, 方凤满, 洪炜林, 等. 基于PLUS和InVEST模型的安徽省碳储量演化分析与预测[J]. 水土保持学报, 2023, 37(1): 151-158. |
| [42] | 周杰, 张学儒, 牟凤云, 等. 基于CA-Markov的土壤有机碳储量空间格局重建研究: 以泛长三角地区为例[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2018, 27(7): 1565-1575. |
| [43] | 丁岳, 王柳柱, 桂峰, 等. 基于InVEST模型和PLUS模型的环杭州湾生态系统碳储量[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(6): 3343-3352. |
| [44] | 吴楠, 陈凝, 程鹏, 等. 安徽省陆地生态系统碳储量变化对未来土地覆被情景的响应[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2023, 32(2): 415-426. |
| [45] |
包玉斌, 李婷, 柳辉, 等. 基于InVEST模型的陕北黄土高原水源涵养功能时空变化[J]. 地理研究, 2016, 35(4): 664-676.
DOI |
| [46] | 张凯琪, 陈建军, 侯建坤, 等. 耦合InVEST与GeoSOS-FLUS模型的桂林市碳储量可持续发展研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(6): 2799-2809. |
| [47] | LIANG X, GUAN Q F, CLARKE K C, et al. Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model: A case study in Wuhan, China[EB/OL]. 2020. arXiv: 2010. 11541. http://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11541. |
| [48] | 陈新云, 王甜, 李宝健. 北京市西北部生态涵养区未来土地利用及生态系统服务变化情景模拟[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2021, 36(1): 86-95. |
| [49] | LI Y Y, ZHANG J B, ZHU H, et al. Soil erosion characteristics and scenario analysis in the Yellow River Basin based on PLUS and RUSLE models[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2023, 20(2): 1222. |
| [50] |
王劲峰, 徐成东. 地理探测器: 原理与展望[J]. 地理学报, 2017, 72(1): 116-134.
DOI |
| [51] |
通拉嘎, 徐新良, 付颖, 等. 地理环境因子对螺情影响的探测分析[J]. 地理科学进展, 2014, 33(5): 625-635.
DOI |
| [52] |
王成武, 罗俊杰, 唐鸿湖. 基于InVEST模型的太行山沿线地区生态系统碳储量时空分异驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 215-225.
DOI |
| [53] |
李梦华, 韩颖娟, 赵慧, 等. 基于地理探测器的宁夏植被覆盖度时空变化特征及其驱动因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1317-1325.
DOI |
| [54] | WILLCOCK S, PHILLIPS O L, PLATTS P J, et al. Towards regional, error-bounded landscape carbon storage estimates for data-deficient areas of the world[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(9): e44795. |
| [55] | ADHIKARI K, HARTEMINK A E. Digital mapping of topsoil carbon content and changes in the driftless area of Wisconsin, USA[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2015, 79(1): 155-164. |
| [56] | ADAMS A B, PONTIUS J, GALFORD G L, et al. Modeling carbon storage across a heterogeneous mixed temperate forest: The influence of forest type specificity on regional-scale carbon storage estimates[J]. Landscape Ecology, 2018, 33(4): 641-658. |
| [57] | 李瑾璞, 夏少霞, 于秀波, 等. 基于InVEST模型的河北省陆地生态系统碳储量研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2020, 36(7): 854-861. |
| [58] |
王超越, 郭先华, 郭莉, 等. 基于FLUS-InVEST的西北地区土地利用变化及其对碳储量的影响: 以呼包鄂榆城市群为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1667-1679.
DOI |
| [59] | 朱丽亚, 胡克, 孙爽, 等. 基于InVEST模型的辽宁省海岸带碳储量时空变化研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(1): 96-104. |
| [60] | 朱志强, 马晓双, 胡洪. 基于耦合FLUS-InVEST模型的广州市生态系统碳储量时空演变与预测[J]. 水土保持通报, 2021, 41(2): 222-229, 239. |
| [61] | 吴佩君, 刘小平, 黎夏, 等. 基于InVEST模型和元胞自动机的城市扩张对陆地生态系统碳储量影响评估: 以广东省为例[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2016, 32(5): 22-28, 36, 2. |
| [62] | 韩玉, 丁素婷, 杨太保. 山西南部中条山生态系统碳储量时空分布及驱动因素[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(3): 1298-1306. |
| [63] | HOBLEY E, WILSON B, WILKIE A, et al. Drivers of soil organic carbon storage and vertical distribution in Eastern Australia[J]. Plant and Soil, 2015, 390(1): 111-127. |
| [64] |
尤海舟, 毕君, 王超, 等. 河北小五台山不同海拔白桦林土壤有机碳密度分布特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(3): 432-437.
DOI |
| [65] | CONTOSTA A R, LERMAN S B, XIAO J F, et al. Biogeoche-mical and socioeconomic drivers of above- and below-ground carbon stocks in urban residential yards of a small city[J]. Landscape and Urban Planning, 2020, 196: 103724. |
| [66] | 杜之利, 苏彤, 葛佳敏, 等. 碳中和背景下的森林碳汇及其空间溢出效应[J]. 经济研究, 2021, 56(12): 187-202. |
| [67] | 孙毅兵. 森林生态系统土壤碳影响因素研究[J]. 林业勘查设计, 2021, 50(3): 73-75. |
| [68] | 张志国, 班高晗. 土地利用变化驱动下洛阳市生态系统碳储量时空变异[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2021, 49(14): 226-230. |
| [69] | 杨小琬, 张丽君, 秦耀辰, 等. 1995年以来黄河下游碳储量时空变化及驱动因素[J]. 河南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 52(1): 20-33. |
| [1] | 魏总, 杨朝磊, 田瑜峰, 杨金江, 黄勇, 和峰, 朱志平. 金沙江干热河谷区土壤侵蚀时空演变及其定量归因分析:以云南楚雄元谋地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 683-693. |
| [2] | 陈武迪, 刘晓煌, 李洪宇, 雒新萍, 王然, 邢莉圆, 白亚楠, 王超, 赵宏慧. 基于InVEST模型的新疆1990—2018年产水服务时空变化及驱动因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 636-647. |
| [3] | 郭佳晖, 刘晓煌, 张文博, 杨朝磊, 王然, 雒新萍, 邢莉圆, 王超, 赵宏慧. 基于InVEST模型和PLUS模型的云贵高原产水量时空变化特征分析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 624-635. |
| [4] | 郭富印, 刘晓煌, 张文博, 邢莉圆, 王然, 祖皮艳木·买买提, 雒新萍, 王超, 赵宏慧. 2000—2040年黄河流域(河南段)生境质量时空格局演变及驱动力分析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 599-611. |
| [5] | 袁江龙, 刘晓煌, 李洪宇, 邢莉圆, 雒新萍, 王然, 王超, 赵宏慧. 1990—2050年黄河中游伊洛河流域不同土地利用类型碳储量时空分异特征[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 559-573. |
| [6] | 朱丽亚, 胡克, 孙爽, 刘禹含, 梁佳欣. 基于InVEST模型的辽宁省海岸带碳储量时空变化研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 96-104. |
| [7] | 刘国栋, 戴慧敏, 杨泽, 许江, 张一鹤, 魏明辉. 三江平原土壤碳库时空变化和影响因素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 443-454. |
| [8] | 代杰瑞, 庞绪贵, 董健, 王增辉, 喻超. 山东省土壤有机碳库及其时空变化特征[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(02): 386-393. |
| [9] | 钟聪, 杨忠芳, 夏学齐, 侯青叶, 姜伟. 青海省土壤有机碳储量估算及其源汇因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5): 896-909. |
| [10] | 傅野思, 夏学齐, 杨忠芳, 李娟. 内蒙古自治区土壤有机碳库储量及分布特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5): 886-895. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||