



现代地质 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (06): 1227-1241.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2018.06.11
何宇1( ), 章永梅1,2(
), 章永梅1,2( ), 顾雪祥1,2, 彭义伟3, 程文斌3, 王冠南1, 万阈4, 袁鹏4
), 顾雪祥1,2, 彭义伟3, 程文斌3, 王冠南1, 万阈4, 袁鹏4
收稿日期:2018-01-11
修回日期:2018-04-19
出版日期:2018-12-10
发布日期:2018-12-20
通讯作者:
章永梅,女,副教授,1984年出生,矿床学专业,主要从事矿床学与矿床地球化学研究。Email:zhangyongmei@cugb.edu.cn。
作者简介:何 宇,男,硕士研究生,1993年出生,地质工程专业,主要从事矿床学与矿床地球化学研究。Email:heyu@cugb.edu.cn。
基金资助:
HE Yu1( ), ZHANG Yongmei1,2(
), ZHANG Yongmei1,2( ), GU Xuexiang1,2, PENG Yiwei3, CHENG Wenbin3, WANG Guannan1, WAN Yu4, YUAN Peng4
), GU Xuexiang1,2, PENG Yiwei3, CHENG Wenbin3, WANG Guannan1, WAN Yu4, YUAN Peng4
Received:2018-01-11
Revised:2018-04-19
Online:2018-12-10
Published:2018-12-20
摘要:
呼斯特岩体位于新疆西天山博罗科努岛弧带中北缘,是博罗科努成矿带东段典型的与矽卡岩矿床成矿有关的中酸性杂岩体。对岩体中的二长花岗岩、花岗闪长岩和暗色包体进行了系统的矿物化学研究,探讨了岩浆的成岩演化过程以及矿物成分与成岩成矿的关系。造岩矿物的化学成分研究表明,呼斯特岩体为典型的I型花岗岩,形成于与俯冲有关的大陆边缘弧环境,成岩物质来自壳幔混源,成岩过程中经历了岩浆混合作用。岩体形成于较高温度(738~770 ℃)、较低压力(0.57~1.42 kbar,1 kbar=0.1 GPa)和高氧逸度环境。二长花岗岩和花岗闪长岩的侵位深度(2.2~4.2 km)和高氧逸度有利于可克萨拉—艾木斯呆依铁铜矿床的形成。岩石中的黑云母相对富镁且氧化系数较高,角闪石富镁、富硅且化学成分变化较大,二者均表现出与铁铜矿化有关的成分特征。岩浆混合作用与矿床的形成关系密切,对区内斑岩-矽卡岩型多金属矿床的找矿具有指示意义。
中图分类号:
何宇, 章永梅, 顾雪祥, 彭义伟, 程文斌, 王冠南, 万阈, 袁鹏. 西天山呼斯特岩体矿物化学特征及其成岩成矿意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(06): 1227-1241.
HE Yu, ZHANG Yongmei, GU Xuexiang, PENG Yiwei, CHENG Wenbin, WANG Guannan, WAN Yu, YUAN Peng. Mineral Chemistry of Husite Pluton in West Tianshan, Xinjiang and Its Implications for Petrogenesis and Mineralization[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(06): 1227-1241.

图1 呼斯特岩体区域地质简图(底图据文献 [2,9]) 1.冲洪积物;2.上石炭统科古琴山组;3.上石炭统东图津河组;4.上石炭统伊什基里克组;5.下石炭统阿克沙克组;6.下石炭统大哈拉军山组;7.上泥盆统托斯库尔他乌组;8.中泥盆统汗吉尕组;9.上志留统博罗霍洛山组上段;10.上志留统博罗霍洛山组下段;11.上志留统库茹尔组;12.中志留统基夫克组;13.下志留统尼勒克河组;14.上奥陶统呼独克达坂组;15.晚石炭世二长花岗岩;16.晚石炭世正长花岗岩;17.晚泥盆世二长花岗岩;18.晚泥盆世钾长花岗岩;19.晚泥盆世花岗闪长岩;20.晚泥盆世辉石二长闪长岩;21.晚泥盆世文象花岗岩;22.断裂;23.地质界线;24.铁矿床(点);25.铜矿床(点);26.金矿床(点);27.铅矿床(点);28.锌矿床(点)
Fig.1 Sketch regional geologic map of the Husite pluton (base map after references of [2,9])

图2 呼斯特岩体手标本及镜下照片 a.二长花岗岩;b. 二长花岗岩与暗色包体,二者具有截然的界限;c. 暗色包体,可见星散状黄铁矿;d. 花岗闪长岩;e. 二长花岗岩镜下照片(+);f、g. 二长花岗岩与暗色包体的显微界限(+),斜长石可见熔蚀结构和它形增生边;h—k. 暗色包体镜下照片(+、-),可见针状磷灰石,微粒状、细条状角闪石和黑云母,钾长石大颗粒包含角闪石、黑云母、斜长石和磷灰石等形成的嵌晶结构,角闪石包含黑云母、斜长石和磁铁矿;l. 花岗闪长岩镜下照片(+)。Py. 黄铁矿;Amp. 角闪石;Ap. 磷灰石;Bi. 黑云母;Chl. 绿泥石;Kf. 钾长石;Pl. 斜长石;Pre. 葡萄石;Qtz. 石英
Fig.2 Hand specimen photos and thin section micrographs of the Husite pluton

图3 呼斯特岩体长石、云母和角闪石分类图解(底图据文献 [27,29?-31]) a.长石分类图;b. 黑云母共生矿物图解:Ⅰ. 与角闪石共存的黑云母,Ⅱ. 不与镁铁矿物共存的黑云母,Ⅲ. 与白云母共存的黑云母,Ⅳ. 与铝硅酸盐共存的黑云母;c. 黑云母类型图;d. 云母分类图;e. 角闪石分类图
Fig.3 Classification diagrams of feldspar, mica and amphibole from the Husite pluton
| 岩性 | 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | SrO | 总量 | An | Ab | Or |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 58.20 | 0.01 | 25.74 | 0.15 | 7.97 | 7.11 | 0.22 | 0.35 | 99.75 | 37.78 | 1.24 | 60.98 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 57.72 | 0.02 | 25.90 | 0.25 | 8.20 | 6.85 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 99.58 | 39.02 | 1.98 | 58.99 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 56.74 | 0.02 | 26.59 | 0.16 | 9.32 | 6.37 | 0.33 | 0.20 | 99.73 | 43.88 | 1.85 | 54.27 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-8 | 57.55 | 0.09 | 26.06 | 0.28 | 8.52 | 6.62 | 0.31 | 0.22 | 99.65 | 40.83 | 1.77 | 57.41 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-8 | 56.41 | — | 26.52 | 0.25 | 8.65 | 6.33 | 0.40 | 0.19 | 98.75 | 42.03 | 2.31 | 55.66 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-8 | 57.56 | 0.01 | 26.24 | 0.32 | 8.59 | 6.44 | 0.31 | 0.22 | 99.69 | 41.67 | 1.79 | 56.54 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-8 | 59.44 | — | 25.57 | 0.29 | 6.97 | 7.52 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 100.24 | 33.39 | 1.43 | 65.19 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 55.17 | — | 27.57 | 0.26 | 10.63 | 5.77 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 99.90 | 49.61 | 1.67 | 48.73 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 57.10 | 0.02 | 26.18 | 0.26 | 8.95 | 6.61 | 0.41 | 0.28 | 99.81 | 41.82 | 2.28 | 55.90 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 56.39 | 0.16 | 26.46 | 0.27 | 9.84 | 6.28 | 0.39 | 0.22 | 100.01 | 45.41 | 2.14 | 52.45 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 56.65 | 0.01 | 26.03 | 0.22 | 9.13 | 6.41 | 0.42 | 0.14 | 99.01 | 43.01 | 2.36 | 54.64 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 57.06 | 0.11 | 26.61 | 0.24 | 8.90 | 6.60 | 0.33 | 0.22 | 100.07 | 41.91 | 1.85 | 56.24 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 56.82 | — | 26.39 | 0.20 | 9.22 | 6.27 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 99.47 | 44.07 | 1.71 | 54.23 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 57.90 | 0.04 | 25.53 | 0.22 | 8.18 | 6.61 | 0.37 | 0.18 | 99.03 | 39.74 | 2.14 | 58.12 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 57.29 | — | 26.10 | 0.22 | 8.71 | 6.56 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 99.33 | 41.72 | 1.43 | 56.86 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 57.15 | 0.07 | 26.61 | 0.21 | 8.57 | 6.68 | 0.31 | 0.24 | 99.84 | 40.76 | 1.76 | 57.49 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 56.43 | 0.02 | 26.90 | 0.12 | 9.10 | 6.12 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 99.23 | 44.35 | 1.68 | 53.97 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 56.27 | 0.04 | 27.17 | 0.15 | 9.44 | 5.94 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 99.45 | 46.19 | 1.22 | 52.59 |
表1 呼斯特岩体斜长石电子探针分析结果(wB/%)
Table 1 EPMA results of plagioclase from the Husite pluton(%)
| 岩性 | 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | SrO | 总量 | An | Ab | Or |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 58.20 | 0.01 | 25.74 | 0.15 | 7.97 | 7.11 | 0.22 | 0.35 | 99.75 | 37.78 | 1.24 | 60.98 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 57.72 | 0.02 | 25.90 | 0.25 | 8.20 | 6.85 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 99.58 | 39.02 | 1.98 | 58.99 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 56.74 | 0.02 | 26.59 | 0.16 | 9.32 | 6.37 | 0.33 | 0.20 | 99.73 | 43.88 | 1.85 | 54.27 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-8 | 57.55 | 0.09 | 26.06 | 0.28 | 8.52 | 6.62 | 0.31 | 0.22 | 99.65 | 40.83 | 1.77 | 57.41 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-8 | 56.41 | — | 26.52 | 0.25 | 8.65 | 6.33 | 0.40 | 0.19 | 98.75 | 42.03 | 2.31 | 55.66 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-8 | 57.56 | 0.01 | 26.24 | 0.32 | 8.59 | 6.44 | 0.31 | 0.22 | 99.69 | 41.67 | 1.79 | 56.54 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-8 | 59.44 | — | 25.57 | 0.29 | 6.97 | 7.52 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 100.24 | 33.39 | 1.43 | 65.19 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 55.17 | — | 27.57 | 0.26 | 10.63 | 5.77 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 99.90 | 49.61 | 1.67 | 48.73 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 57.10 | 0.02 | 26.18 | 0.26 | 8.95 | 6.61 | 0.41 | 0.28 | 99.81 | 41.82 | 2.28 | 55.90 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 56.39 | 0.16 | 26.46 | 0.27 | 9.84 | 6.28 | 0.39 | 0.22 | 100.01 | 45.41 | 2.14 | 52.45 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 56.65 | 0.01 | 26.03 | 0.22 | 9.13 | 6.41 | 0.42 | 0.14 | 99.01 | 43.01 | 2.36 | 54.64 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 57.06 | 0.11 | 26.61 | 0.24 | 8.90 | 6.60 | 0.33 | 0.22 | 100.07 | 41.91 | 1.85 | 56.24 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 56.82 | — | 26.39 | 0.20 | 9.22 | 6.27 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 99.47 | 44.07 | 1.71 | 54.23 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 57.90 | 0.04 | 25.53 | 0.22 | 8.18 | 6.61 | 0.37 | 0.18 | 99.03 | 39.74 | 2.14 | 58.12 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 57.29 | — | 26.10 | 0.22 | 8.71 | 6.56 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 99.33 | 41.72 | 1.43 | 56.86 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 57.15 | 0.07 | 26.61 | 0.21 | 8.57 | 6.68 | 0.31 | 0.24 | 99.84 | 40.76 | 1.76 | 57.49 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 56.43 | 0.02 | 26.90 | 0.12 | 9.10 | 6.12 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 99.23 | 44.35 | 1.68 | 53.97 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 56.27 | 0.04 | 27.17 | 0.15 | 9.44 | 5.94 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 99.45 | 46.19 | 1.22 | 52.59 |
| 岩性 | 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | SrO | F | 总量 | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 37.59 | 5.16 | 13.56 | 18.21 | 0.29 | 13.15 | — | 0.11 | 9.28 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 97.91 | 2.79 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 37.19 | 5.20 | 13.80 | 18.75 | 0.35 | 12.42 | — | 0.11 | 9.46 | 0.12 | 0.40 | 97.80 | 2.78 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 36.78 | 5.14 | 13.50 | 18.86 | 0.31 | 12.84 | — | 0.16 | 9.30 | 0.19 | 0.36 | 97.44 | 2.76 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 36.62 | 5.18 | 14.02 | 17.94 | 0.24 | 12.46 | — | 0.30 | 9.31 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 96.43 | 2.76 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 37.37 | 4.85 | 13.42 | 18.75 | 0.17 | 12.75 | — | 0.21 | 9.20 | 0.16 | 0.25 | 97.13 | 2.80 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 36.26 | 4.39 | 13.63 | 17.92 | 0.25 | 13.05 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 8.74 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 94.87 | 2.78 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-8 | 37.13 | 4.84 | 13.72 | 18.75 | 0.31 | 12.60 | — | 0.14 | 9.55 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 97.31 | 2.78 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 37.61 | 4.54 | 13.52 | 17.63 | 0.29 | 13.13 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 9.26 | 0.10 | 0.30 | 96.49 | 2.82 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 36.59 | 4.33 | 13.94 | 18.15 | 0.23 | 12.74 | — | 0.30 | 8.73 | 0.09 | 0.30 | 95.40 | 2.78 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 36.93 | 4.55 | 13.61 | 18.06 | 0.22 | 12.82 | — | 0.18 | 9.13 | 0.11 | 0.39 | 96.00 | 2.80 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 37.83 | 4.59 | 13.27 | 17.91 | 0.24 | 12.92 | — | 0.28 | 9.41 | 0.07 | 0.24 | 96.76 | 2.84 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 37.07 | 5.23 | 13.76 | 19.56 | 0.28 | 12.30 | — | 0.18 | 9.24 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 97.93 | 2.77 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 36.65 | 4.64 | 13.53 | 19.64 | 0.33 | 12.62 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 8.73 | 0.10 | 0.27 | 96.84 | 2.77 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 36.34 | 4.46 | 14.19 | 19.76 | 0.27 | 12.72 | — | 0.19 | 8.59 | 0.13 | 0.34 | 96.99 | 2.74 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 36.83 | 4.40 | 14.15 | 19.88 | 0.35 | 12.29 | — | 0.29 | 8.97 | 0.10 | 0.26 | 97.52 | 2.76 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 36.56 | 5.16 | 13.78 | 16.84 | 0.32 | 12.51 | — | 0.14 | 9.63 | 0.08 | 0.21 | 95.23 | 2.78 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 37.15 | 4.77 | 13.90 | 17.55 | 0.36 | 12.84 | 0.04 | 0.31 | 9.11 | 0.13 | 0.26 | 96.42 | 2.79 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 37.08 | 5.25 | 13.76 | 16.98 | 0.25 | 12.84 | — | 0.16 | 9.27 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 95.92 | 2.79 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 35.27 | 4.69 | 14.59 | 18.32 | 0.48 | 13.05 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 8.25 | 0.12 | 0.24 | 95.24 | 2.69 |
| 岩性 | 样号 | AlⅣ | AlⅥ | Ti | Fe3+ | Fe2+ | Mn | Mg | Ca | Na | K | T | p | D |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 1.19 | 0 | 0.29 | 0.49 | 0.64 | 0.02 | 1.46 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.88 | 764 | 0.66 | 2.51 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 1.22 | 0 | 0.29 | 0.47 | 0.71 | 0.02 | 1.38 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.90 | 762 | 0.83 | 3.14 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 1.20 | 0 | 0.29 | 0.55 | 0.64 | 0.02 | 1.44 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.89 | 762 | 0.71 | 2.68 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 1.24 | 0.01 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.70 | 0.02 | 1.40 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.90 | 765 | 1.02 | 3.86 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 1.19 | 0 | 0.27 | 0.45 | 0.73 | 0.01 | 1.43 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.88 | 755 | 0.65 | 2.47 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 1.22 | 0.01 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.65 | 0.02 | 1.49 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.85 | 749 | 0.92 | 3.48 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-8 | 1.21 | 0 | 0.27 | 0.43 | 0.74 | 0.02 | 1.41 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.91 | 754 | 0.81 | 3.08 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 1.18 | 0.02 | 0.26 | 0.38 | 0.73 | 0.02 | 1.47 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.89 | 751 | 0.71 | 2.70 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 1.22 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.44 | 0.72 | 0.02 | 1.45 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.85 | 744 | 1.04 | 3.94 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 1.20 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.42 | 0.73 | 0.01 | 1.45 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.88 | 750 | 0.83 | 3.14 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 1.17 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.80 | 0.02 | 1.44 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.90 | 751 | 0.57 | 2.16 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 1.21 | 0 | 0.29 | 0.52 | 0.70 | 0.02 | 1.37 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.88 | 760 | 0.80 | 3.04 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 1.21 | 0 | 0.26 | 0.55 | 0.69 | 0.02 | 1.42 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.84 | 748 | 0.77 | 2.90 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 1.26 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.02 | 1.43 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.83 | 742 | 1.11 | 4.19 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 1.24 | 0.02 | 0.25 | 0.48 | 0.77 | 0.02 | 1.38 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.86 | 738 | 1.05 | 3.97 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 1.22 | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.71 | 0.02 | 1.42 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.94 | 768 | 0.96 | 3.62 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 1.21 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.72 | 0.02 | 1.44 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.87 | 757 | 0.93 | 3.50 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 1.21 | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.42 | 0.66 | 0.02 | 1.44 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.89 | 770 | 0.87 | 3.30 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 1.31 | 0.01 | 0.27 | 0.69 | 0.48 | 0.03 | 1.49 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.80 | 755 | 1.42 | 5.38 |
表2 呼斯特岩体黑云母电子探针分析结果(wB/%)
Table 2 EPMA results of biotite from the Husite pluton(%)
| 岩性 | 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | SrO | F | 总量 | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 37.59 | 5.16 | 13.56 | 18.21 | 0.29 | 13.15 | — | 0.11 | 9.28 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 97.91 | 2.79 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 37.19 | 5.20 | 13.80 | 18.75 | 0.35 | 12.42 | — | 0.11 | 9.46 | 0.12 | 0.40 | 97.80 | 2.78 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 36.78 | 5.14 | 13.50 | 18.86 | 0.31 | 12.84 | — | 0.16 | 9.30 | 0.19 | 0.36 | 97.44 | 2.76 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 36.62 | 5.18 | 14.02 | 17.94 | 0.24 | 12.46 | — | 0.30 | 9.31 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 96.43 | 2.76 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 37.37 | 4.85 | 13.42 | 18.75 | 0.17 | 12.75 | — | 0.21 | 9.20 | 0.16 | 0.25 | 97.13 | 2.80 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 36.26 | 4.39 | 13.63 | 17.92 | 0.25 | 13.05 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 8.74 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 94.87 | 2.78 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-8 | 37.13 | 4.84 | 13.72 | 18.75 | 0.31 | 12.60 | — | 0.14 | 9.55 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 97.31 | 2.78 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 37.61 | 4.54 | 13.52 | 17.63 | 0.29 | 13.13 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 9.26 | 0.10 | 0.30 | 96.49 | 2.82 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 36.59 | 4.33 | 13.94 | 18.15 | 0.23 | 12.74 | — | 0.30 | 8.73 | 0.09 | 0.30 | 95.40 | 2.78 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 36.93 | 4.55 | 13.61 | 18.06 | 0.22 | 12.82 | — | 0.18 | 9.13 | 0.11 | 0.39 | 96.00 | 2.80 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 37.83 | 4.59 | 13.27 | 17.91 | 0.24 | 12.92 | — | 0.28 | 9.41 | 0.07 | 0.24 | 96.76 | 2.84 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 37.07 | 5.23 | 13.76 | 19.56 | 0.28 | 12.30 | — | 0.18 | 9.24 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 97.93 | 2.77 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 36.65 | 4.64 | 13.53 | 19.64 | 0.33 | 12.62 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 8.73 | 0.10 | 0.27 | 96.84 | 2.77 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 36.34 | 4.46 | 14.19 | 19.76 | 0.27 | 12.72 | — | 0.19 | 8.59 | 0.13 | 0.34 | 96.99 | 2.74 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 36.83 | 4.40 | 14.15 | 19.88 | 0.35 | 12.29 | — | 0.29 | 8.97 | 0.10 | 0.26 | 97.52 | 2.76 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 36.56 | 5.16 | 13.78 | 16.84 | 0.32 | 12.51 | — | 0.14 | 9.63 | 0.08 | 0.21 | 95.23 | 2.78 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 37.15 | 4.77 | 13.90 | 17.55 | 0.36 | 12.84 | 0.04 | 0.31 | 9.11 | 0.13 | 0.26 | 96.42 | 2.79 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 37.08 | 5.25 | 13.76 | 16.98 | 0.25 | 12.84 | — | 0.16 | 9.27 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 95.92 | 2.79 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 35.27 | 4.69 | 14.59 | 18.32 | 0.48 | 13.05 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 8.25 | 0.12 | 0.24 | 95.24 | 2.69 |
| 岩性 | 样号 | AlⅣ | AlⅥ | Ti | Fe3+ | Fe2+ | Mn | Mg | Ca | Na | K | T | p | D |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 1.19 | 0 | 0.29 | 0.49 | 0.64 | 0.02 | 1.46 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.88 | 764 | 0.66 | 2.51 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 1.22 | 0 | 0.29 | 0.47 | 0.71 | 0.02 | 1.38 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.90 | 762 | 0.83 | 3.14 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 1.20 | 0 | 0.29 | 0.55 | 0.64 | 0.02 | 1.44 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.89 | 762 | 0.71 | 2.68 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 1.24 | 0.01 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.70 | 0.02 | 1.40 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.90 | 765 | 1.02 | 3.86 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 1.19 | 0 | 0.27 | 0.45 | 0.73 | 0.01 | 1.43 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.88 | 755 | 0.65 | 2.47 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 1.22 | 0.01 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.65 | 0.02 | 1.49 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.85 | 749 | 0.92 | 3.48 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-8 | 1.21 | 0 | 0.27 | 0.43 | 0.74 | 0.02 | 1.41 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.91 | 754 | 0.81 | 3.08 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 1.18 | 0.02 | 0.26 | 0.38 | 0.73 | 0.02 | 1.47 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.89 | 751 | 0.71 | 2.70 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 1.22 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.44 | 0.72 | 0.02 | 1.45 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.85 | 744 | 1.04 | 3.94 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 1.20 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.42 | 0.73 | 0.01 | 1.45 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.88 | 750 | 0.83 | 3.14 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 1.17 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.80 | 0.02 | 1.44 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.90 | 751 | 0.57 | 2.16 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 1.21 | 0 | 0.29 | 0.52 | 0.70 | 0.02 | 1.37 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.88 | 760 | 0.80 | 3.04 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 1.21 | 0 | 0.26 | 0.55 | 0.69 | 0.02 | 1.42 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.84 | 748 | 0.77 | 2.90 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 1.26 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.02 | 1.43 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.83 | 742 | 1.11 | 4.19 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 1.24 | 0.02 | 0.25 | 0.48 | 0.77 | 0.02 | 1.38 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.86 | 738 | 1.05 | 3.97 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 1.22 | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.71 | 0.02 | 1.42 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.94 | 768 | 0.96 | 3.62 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 1.21 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.72 | 0.02 | 1.44 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.87 | 757 | 0.93 | 3.50 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 1.21 | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.42 | 0.66 | 0.02 | 1.44 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.89 | 770 | 0.87 | 3.30 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 1.31 | 0.01 | 0.27 | 0.69 | 0.48 | 0.03 | 1.49 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.80 | 755 | 1.42 | 5.38 |
| 岩性 | 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | SrO | F | 总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 50.59 | 0.83 | 4.26 | 14.83 | 0.51 | 14.32 | 11.24 | 0.94 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 98.01 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 44.57 | 2.15 | 8.82 | 15.09 | 0.38 | 12.15 | 11.49 | 1.76 | 0.97 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 97.75 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 50.67 | 0.69 | 3.94 | 13.98 | 0.28 | 14.89 | 11.69 | 0.81 | 0.47 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 97.74 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 48.67 | 1.03 | 5.42 | 16.58 | 0.56 | 12.76 | 11.09 | 1.11 | 0.51 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 98.10 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 46.72 | 1.19 | 7.60 | 16.82 | 0.63 | 11.55 | 11.03 | 1.51 | 0.75 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 98.05 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 47.01 | 1.51 | 6.97 | 16.07 | 0.48 | 12.02 | 11.37 | 1.41 | 0.63 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 97.72 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-8 | 50.52 | 0.77 | 4.82 | 12.92 | 0.42 | 15.25 | 11.38 | 0.94 | 0.38 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 97.74 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 52.14 | 0.51 | 3.58 | 12.26 | 0.42 | 15.75 | 12.20 | 0.72 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 98.17 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 48.00 | 1.41 | 5.33 | 15.97 | 0.76 | 12.89 | 11.06 | 1.49 | 0.51 | 0.14 | 0.22 | 97.78 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 46.52 | 1.37 | 7.07 | 15.53 | 0.39 | 12.36 | 11.06 | 1.84 | 0.70 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 97.19 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 47.97 | 1.22 | 5.48 | 15.24 | 0.65 | 12.81 | 11.64 | 1.35 | 0.53 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 97.11 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 49.88 | 0.94 | 4.23 | 14.83 | 0.61 | 13.84 | 11.19 | 0.97 | 0.34 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 97.06 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 44.53 | 1.68 | 8.33 | 16.92 | 0.44 | 10.87 | 11.51 | 1.65 | 0.95 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 97.11 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 46.87 | 1.42 | 6.83 | 16.24 | 0.44 | 12.07 | 11.44 | 1.48 | 0.69 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 97.81 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 47.41 | 1.07 | 6.54 | 14.31 | 0.53 | 13.70 | 11.86 | 1.37 | 0.69 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 97.76 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 47.76 | 1.36 | 6.30 | 13.13 | 0.51 | 13.86 | 11.91 | 1.34 | 0.63 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 97.13 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 44.39 | 2.16 | 8.45 | 15.56 | 0.56 | 11.59 | 11.76 | 1.90 | 0.78 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 97.43 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 45.58 | 1.72 | 8.30 | 13.69 | 0.51 | 12.62 | 12.06 | 1.55 | 0.85 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 97.05 |
| 岩性 | 样号 | Si | AlⅣ | AlⅥ | Ti | Fe3+ | Fe2+ | Mn | Mg | Ca | Sr | Na | K |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 7.27 | 0.72 | 0 | 0.09 | 0.75 | 1.03 | 0.06 | 3.07 | 1.73 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.06 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 6.61 | 1.39 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 0.39 | 1.48 | 0.05 | 2.69 | 1.83 | 0.01 | 0.51 | 0.18 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 7.32 | 0.67 | 0 | 0.08 | 0.57 | 1.12 | 0.03 | 3.21 | 1.81 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.09 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 7.09 | 0.91 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.76 | 1.26 | 0.07 | 2.77 | 1.73 | 0.01 | 0.31 | 0.10 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 6.87 | 1.13 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.61 | 1.46 | 0.08 | 2.53 | 1.74 | 0.01 | 0.43 | 0.14 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 6.94 | 1.07 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.45 | 1.54 | 0.06 | 2.64 | 1.80 | 0.01 | 0.40 | 0.12 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-8 | 7.24 | 0.76 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.68 | 0.87 | 0.05 | 3.26 | 1.75 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.07 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 7.46 | 0.54 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.35 | 1.12 | 0.05 | 3.36 | 1.87 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.05 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 7.05 | 0.92 | 0 | 0.16 | 0.65 | 1.31 | 0.09 | 2.82 | 1.74 | 0.01 | 0.42 | 0.10 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 6.90 | 1.10 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.46 | 1.47 | 0.05 | 2.73 | 1.76 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 0.13 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 7.11 | 0.89 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.35 | 1.54 | 0.08 | 2.83 | 1.85 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.10 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 7.27 | 0.73 | 0 | 0.10 | 0.66 | 1.15 | 0.08 | 3.01 | 1.75 | 0.01 | 0.27 | 0.06 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 6.71 | 1.30 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.33 | 1.80 | 0.06 | 2.44 | 1.86 | 0.01 | 0.48 | 0.18 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 6.93 | 1.08 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.44 | 1.56 | 0.06 | 2.66 | 1.81 | 0.01 | 0.42 | 0.13 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 6.94 | 1.06 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.49 | 1.26 | 0.07 | 2.99 | 1.86 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.13 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 7.03 | 0.97 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.26 | 1.36 | 0.06 | 3.04 | 1.88 | 0.01 | 0.38 | 0.12 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 6.65 | 1.35 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 1.74 | 0.07 | 2.59 | 1.89 | 0.01 | 0.55 | 0.15 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 6.78 | 1.22 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 1.59 | 0.06 | 2.80 | 1.92 | 0.01 | 0.45 | 0.16 |
表3 呼斯特岩体角闪石电子探针分析结果(wB/%)
Table 3 EPMA results of amphibole from the Husite pluton(%)
| 岩性 | 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | SrO | F | 总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 50.59 | 0.83 | 4.26 | 14.83 | 0.51 | 14.32 | 11.24 | 0.94 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 98.01 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 44.57 | 2.15 | 8.82 | 15.09 | 0.38 | 12.15 | 11.49 | 1.76 | 0.97 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 97.75 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 50.67 | 0.69 | 3.94 | 13.98 | 0.28 | 14.89 | 11.69 | 0.81 | 0.47 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 97.74 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 48.67 | 1.03 | 5.42 | 16.58 | 0.56 | 12.76 | 11.09 | 1.11 | 0.51 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 98.10 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 46.72 | 1.19 | 7.60 | 16.82 | 0.63 | 11.55 | 11.03 | 1.51 | 0.75 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 98.05 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 47.01 | 1.51 | 6.97 | 16.07 | 0.48 | 12.02 | 11.37 | 1.41 | 0.63 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 97.72 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-8 | 50.52 | 0.77 | 4.82 | 12.92 | 0.42 | 15.25 | 11.38 | 0.94 | 0.38 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 97.74 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 52.14 | 0.51 | 3.58 | 12.26 | 0.42 | 15.75 | 12.20 | 0.72 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 98.17 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 48.00 | 1.41 | 5.33 | 15.97 | 0.76 | 12.89 | 11.06 | 1.49 | 0.51 | 0.14 | 0.22 | 97.78 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 46.52 | 1.37 | 7.07 | 15.53 | 0.39 | 12.36 | 11.06 | 1.84 | 0.70 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 97.19 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 47.97 | 1.22 | 5.48 | 15.24 | 0.65 | 12.81 | 11.64 | 1.35 | 0.53 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 97.11 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 49.88 | 0.94 | 4.23 | 14.83 | 0.61 | 13.84 | 11.19 | 0.97 | 0.34 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 97.06 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 44.53 | 1.68 | 8.33 | 16.92 | 0.44 | 10.87 | 11.51 | 1.65 | 0.95 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 97.11 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 46.87 | 1.42 | 6.83 | 16.24 | 0.44 | 12.07 | 11.44 | 1.48 | 0.69 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 97.81 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 47.41 | 1.07 | 6.54 | 14.31 | 0.53 | 13.70 | 11.86 | 1.37 | 0.69 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 97.76 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 47.76 | 1.36 | 6.30 | 13.13 | 0.51 | 13.86 | 11.91 | 1.34 | 0.63 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 97.13 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 44.39 | 2.16 | 8.45 | 15.56 | 0.56 | 11.59 | 11.76 | 1.90 | 0.78 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 97.43 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 45.58 | 1.72 | 8.30 | 13.69 | 0.51 | 12.62 | 12.06 | 1.55 | 0.85 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 97.05 |
| 岩性 | 样号 | Si | AlⅣ | AlⅥ | Ti | Fe3+ | Fe2+ | Mn | Mg | Ca | Sr | Na | K |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 7.27 | 0.72 | 0 | 0.09 | 0.75 | 1.03 | 0.06 | 3.07 | 1.73 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.06 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 6.61 | 1.39 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 0.39 | 1.48 | 0.05 | 2.69 | 1.83 | 0.01 | 0.51 | 0.18 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 7.32 | 0.67 | 0 | 0.08 | 0.57 | 1.12 | 0.03 | 3.21 | 1.81 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.09 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-2 | 7.09 | 0.91 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.76 | 1.26 | 0.07 | 2.77 | 1.73 | 0.01 | 0.31 | 0.10 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 6.87 | 1.13 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.61 | 1.46 | 0.08 | 2.53 | 1.74 | 0.01 | 0.43 | 0.14 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-3 | 6.94 | 1.07 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.45 | 1.54 | 0.06 | 2.64 | 1.80 | 0.01 | 0.40 | 0.12 |
| 二长花岗岩 | ZK404-8 | 7.24 | 0.76 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.68 | 0.87 | 0.05 | 3.26 | 1.75 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.07 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 7.46 | 0.54 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.35 | 1.12 | 0.05 | 3.36 | 1.87 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.05 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 7.05 | 0.92 | 0 | 0.16 | 0.65 | 1.31 | 0.09 | 2.82 | 1.74 | 0.01 | 0.42 | 0.10 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-20 | 6.90 | 1.10 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.46 | 1.47 | 0.05 | 2.73 | 1.76 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 0.13 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 7.11 | 0.89 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.35 | 1.54 | 0.08 | 2.83 | 1.85 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.10 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 7.27 | 0.73 | 0 | 0.10 | 0.66 | 1.15 | 0.08 | 3.01 | 1.75 | 0.01 | 0.27 | 0.06 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 6.71 | 1.30 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.33 | 1.80 | 0.06 | 2.44 | 1.86 | 0.01 | 0.48 | 0.18 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 16KK-22 | 6.93 | 1.08 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.44 | 1.56 | 0.06 | 2.66 | 1.81 | 0.01 | 0.42 | 0.13 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 6.94 | 1.06 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.49 | 1.26 | 0.07 | 2.99 | 1.86 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.13 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 7.03 | 0.97 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.26 | 1.36 | 0.06 | 3.04 | 1.88 | 0.01 | 0.38 | 0.12 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 6.65 | 1.35 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 1.74 | 0.07 | 2.59 | 1.89 | 0.01 | 0.55 | 0.15 |
| 暗色包体 | 16KK-8 | 6.78 | 1.22 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 1.59 | 0.06 | 2.80 | 1.92 | 0.01 | 0.45 | 0.16 |
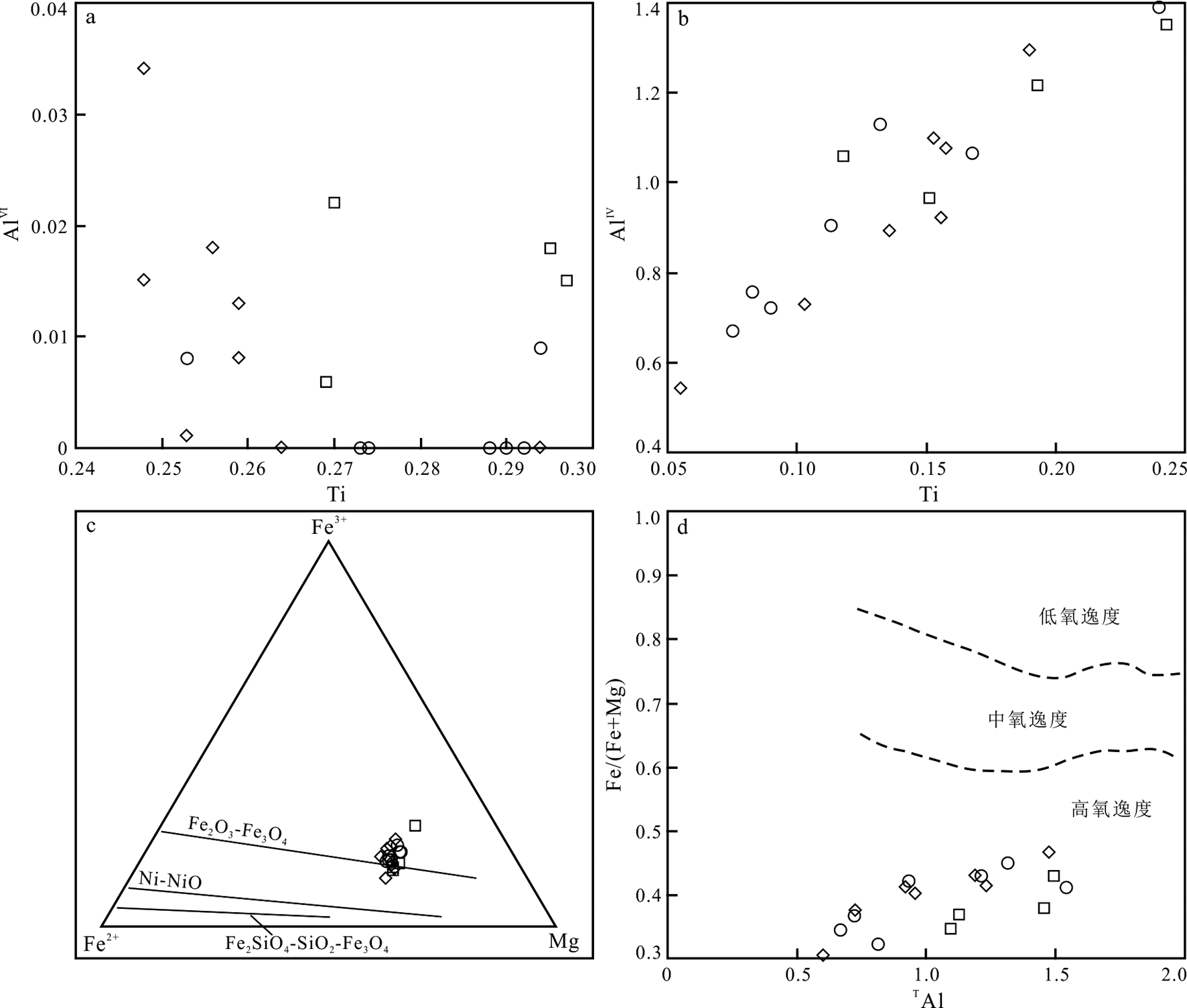
图5 黑云母Ti-AlⅥ(a)和Fe3+-Fe2+-Mg(c. 底图据文献 [11])图解以及角闪石Ti-AlⅣ(b)和TAl-Fe/(Fe+Mg)(d. 底图据文献 [16])图解(图例同图3)
Fig.5 Ti vs.AlⅥ (a) and ternary Fe3+-Fe2+-Mg diagrams of biotite (c.base map from reference[11]),Ti vs.AlⅣ(b) and TAl vs.Fe/(Fe+Mg) diagrams of amphibole (d.base map from reference[16])
| [1] |
顾雪祥, 章永梅, 彭义伟, 等. 西天山博罗科努成矿带与侵入岩有关的铁铜钼多金属成矿系统: 成岩成矿地球化学与构造-岩浆演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(5): 156-175.
DOI |
| [2] | 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 王新利, 等. 新疆西天山可克萨拉—艾木斯呆依铁铜矿床成岩成矿年代学及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(6): 195-209. |
| [3] |
ZHANG D Y, ZHANG Z C, XUE C J, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the ore-forming porphyries in the Lailisigao’er-Lamasu region of the Western Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang, NW China: Implications for petrogenesis, metallogenesis, and tectonic setting[J]. Journal of Geology, 2010, 118(5): 543-563.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 薛春纪, 陈波, 贾志业, 等. 新疆西天山莱历斯高尔—3571斑岩铜钼矿田地质地球化学和成矿年代[J]. 地学前缘, 2011, 18(1): 149-165. |
| [5] | 王新利, 顾雪祥, 彭义伟, 等. 新疆博罗科努成矿带东段矽卡岩型铁铜多金属矿床: 地质特征、成矿背景与找矿潜力[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(5): 1315-1332. |
| [6] | 何格, 顾雪祥, 王新利, 等. 新疆西天山哈勒尕提铁铜矿床流体包裹体和氢氧同位素特征及其成矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(6): 1795-1808. |
| [7] | 张东阳, 张招崇, 艾羽, 等. 西天山莱历斯高尔一带铜(钼)矿成矿斑岩体矿物学特征及其成岩成矿意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2009, 28(1): 3-16. |
| [8] | 张东阳, 张招崇, 艾羽, 等. 西天山莱历斯高尔一带铜(钼)矿成矿斑岩年代学、地球化学及其意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(6): 1319-1331. |
| [9] | 章永梅, 张力强, 高虎, 等. 新疆西天山呼斯特杂岩体岩石学、锆石U-Pb年龄及Hf同位素特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(6): 1749-1769. |
| [10] | 高景刚, 李文渊, 高云霞, 等. 西天山博罗霍洛地区晚泥盆世岩体地球化学、U-Pb年代及Sr-Nd-Pb同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(5): 1379-1390. |
| [11] | WONES D R, EUGSTER H P. Stability of biotite: Experiment, theory, and application[J]. American Mineralogist, 1965, 50(9): 1228-1272. |
| [12] |
CHIVAS A R. Goechemical evidence for magmatic fluids in porphyry copper mineralization. Part I. Mafic silicates from the Koloula Igneous Complex[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1981, 78(4): 389-403.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
HENDRY D A F, CHIVAS A R, LONG J V P, et al. Chemical differences between minerals from mineralizing and barren intrusions from some North American porphyry copper deposits[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1985, 89(4): 317-329.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HENDRY D A F, GUNOW A J, SMITH M R P, et al. Chemical differences between minerals from mineralizing and barren intrusions associated with molybdenum mineralization at Climax, Colorado[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 1988, 39(3): 251-263.
DOI URL |
| [15] | ABDEL-RAHMAN A F M. Nature of biotites from alkaline, calc-alkaline, and peraluminous magmas[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1994, 35(2): 1025-1029. |
| [16] |
ANDERSON J L, SMITH D R. The effects of temperature and $f_{o_{2}}$ on the Al-in-hornblende barometer[J]. American Mineralogist, 1995, 80(5/6): 549-559.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SELBY D, NESBITT B E. Chemical composition of biotite from the Casino porphyry Cu-Au-Mo mineralization, Yukon, Canada: evaluation of magmatic and hydrothermal fluid chemistry[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000, 171(1): 77-93.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
HENRY D J, GUIDOTTI C V, THOMSON J A. The Ti-saturation surface for low-to-medium pressure metapelitic biotites: Implications for geothermometry and Ti-substitution mechanisms[J]. American Mineralogist, 2005, 90(3): 316-328.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
UCHIDA E, ENDO S, MAKINO M. Relationship between solidification depth of granitic rocks and formation of hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Resource Geology, 2007, 57(1): 47-56.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 高俊, 何国琦, 李茂松. 西天山造山带的构造变形特征研究[J]. 地球学报, 1997, 18(1): 1-10. |
| [21] | 高俊, 钱青, 龙灵利, 等. 西天山的增生造山过程[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(12): 1804-1816. |
| [22] | 冯京, 薛春纪, 吴淦国. 西天山莱历斯高尔—达巴特一带与斑岩相关的铜钼金矿产预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011: 1-317. |
| [23] |
RIEDER M, CAVAZZINI M, D’YAKONOV G, et al. Nomenclature of the micas[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 1999, 63(2): 267-296.
DOI URL |
| [24] | DYMEK R F. Titanium, aluminum and interlayer cation substitutions in biotite from high-grade gneisses, west Greenland[J]. American Mineralogist, 1983, 68(9/10), 880-899. |
| [25] |
YAVUZ F. Evaluating micas in petrologic and metallogenic aspect: I-definitions and structure of the computer program MICA+[J]. Computers and Geosciences, 2003, 29(10): 1203-1213.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
KUMAR S, PATHAK M. Mineralogy and geochemistry of biotites from Proterozoic granitoids of western Arunachal Himalaya: Evidence of bimodal granitogeny and tectonic affinity[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 2010, 75(5): 715-730.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ALBUQUERQUE C A R D. Geochemistry of biotites from granitic rocks, Northern Portugal[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1973, 37(7): 1779-1802.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
PARSAPOOR A, KHALILI M, TEPLEY F, et al. Mineral chemistry and isotopic composition of magmatic, re-equilibrated and hydrothermal biotites from Darreh-Zar porphyry copper deposit, Kerman (Southeast of Iran)[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 66: 200-218.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
NACHIT H, IBHI A, ABIA E H, et al. Discrimination between primary magmatic biotites, reequilibrated biotites and neoformed biotites[J]. Comptes Rendus-Géoscience, 2005, 337(16): 1415-1420.
DOI URL |
| [30] | FOSTER M D. Interpretation of the composition of trioctahedral micas[J]. United States Geological Survey Professional Paper, 1960, 354-B: 11-49. |
| [31] | LEAKE B E, WOOLLEY A R, ARPS C E S, et al. Nomenclature of amphiboles: Report of the subcommittee on amphiboles of the International Mineralogical Association, Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 1997, 35(1): 219-237. |
| [32] | SCHUMACHER J C. Nomenclature of amphiboles appendix 2: The estimation of ferric iron in the electron-microprobe analysis of amphiboles[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 1997, 35(1): 238-246. |
| [33] | YAVUZ F. WinAmphcal: A Windows program for the IMA04 amphibole classification[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems, 2013, 8(1): 1-12. |
| [34] | 周作侠. 侵入岩的镁铁云母化学成分特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 1988, 4(3): 63-73. |
| [35] | WHALEN J B, CHAPPELL B W. Opaque mineralogy and mafic mineral chemistry of I-and S-type granites of the Lachlan Fold Belt, southeast Australia[J]. American Mineralogist, 1988, 73(3): 281-296. |
| [36] |
SHABANI A A T, LALONDE A E, WHALEN J B. Composition of biotite from granitic rocks of the Canadian Appalachian orogen: A potential tectonomagmatic indicator?[J]. Canadian Mineralogist, 2003, 41(3): 1381-1396.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 肖庆辉, 邓晋福, 马大铨. 花岗岩研究思维与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002: 1-294. |
| [38] | 周作侠. 湖北丰山洞岩体成因探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 1986, 2(1): 59-70. |
| [39] | 丁孝石. 西藏中南部花岗岩类中云母矿物标型特征及其地质意义[M]// 中国地质科学院矿床研究所. 中国地质科学院矿床地质研究所文集. 北京: 地质出版社, 1988: 33-50. |
| [40] | 陈光远, 孙岱生, 邵伟. 胶东郭家岭花岗闪长岩成因矿物学与金矿化[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1993: 1-131. |
| [41] |
ANNEN C, BLUNDY J D, SPARKS R S J. The genesis of intermediate and silicic magmas in deep crustal hot zones[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2006, 47(3): 505-539.
DOI URL |
| [42] | HAMMARSTROM J M, ZEN E. Aluminum in hornblende: an empirical igneous geobarometer[J]. American Mineralogist, 1986, 71(11): 1297-1313. |
| [43] |
SCHMIDT M W. Amphibole composition in tonalite as a function of pressure: An experimental calibration of the Al-in-hornblende barometer[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1992, 110(2/3): 304-310.
DOI URL |
| [44] | JOHNSON M C, RUTHERFORD M J. Experimental calibration of the aluminum-in-hornblende geobarometer with application to Long Valley caldera(California) volcanic rocks[J]. Anaesthesia, 1989, 56(2): 195-195. |
| [45] | WONES D R. Significance of the assemblage titanite+magnetite+quartz in granitic rocks[J]. American Mineralogist, 1989, 74(7): 744-749. |
| [46] | 吕志成, 段国正, 董广华. 大兴安岭中南段燕山期三类不同成矿花岗岩中黑云母的化学成分特征及其成岩成矿意义[J]. 矿物学报, 2003, 23(2): 177-184. |
| [47] | 孙紫坚, 方维萱, 鲁佳, 等. 云南因民铁铜矿区辉长岩类中黑云母-金红石化特征及其指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(2):267-277. |
| [48] | 杜佰松, 申俊峰, 秦玉良, 等. 甘肃省沃尔给花岗岩体中黑云母的成分对其岩体碱度的响应及成岩成矿意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(4):672-682. |
| [49] | 程启芬, 毛建仁, 苏郁香, 等. 长江中下游中酸性侵入岩中的黑云母及其地质意义[J]. 华东地质, 1987(3): 58-72. |
| [50] | 舒全安, 陈培良, 程建荣. 鄂东铁铜矿产地质[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1992: 1-532. |
| [51] | 赵海杰, 毛景文, 向君峰, 等. 湖北铜绿山矿床石英闪长岩的矿物学及Sr-Nd-Pb同位素特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(3): 768-784. |
| [52] | 徐耀明, 蒋少涌, 朱志勇, 等. 江西九瑞矿集区成矿与未成矿中酸性侵入岩年代学、岩石化学、矿物化学特征的异同及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(12): 4291-4310. |
| [53] | 李伟, 谢桂青, 姚磊, 等. 鄂东南地区程潮大型矽卡岩型铁矿区岩体成因探讨[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(6): 1827-1855. |
| [54] | 姚洪忠, 闫峻, 刘晓强, 等. 长江中下游地区晚中生代岩浆岩氧逸度特征及意义[J]. 地质科学, 2016, 51(4): 1163-1180. |
| [55] | MEINERT L D, DIPPLE G M, NICOLESCU S. World skarn deposits[M]// GOLDFARBR J, RICHARDS. Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume. Littleton: Society of Economic Geologists, Inc, 2005: 299-336. |
| [56] |
LI J W, ZHAO X F, ZHOU M F, et al. Origin of the Tongshan-kou porphyry-skarn Cu-Mo deposit, eastern Yangtze craton, Eastern China: Geochronological, geochemical, and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2008, 43(3): 315-336.
DOI URL |
| [57] | 吕志成, 段国正, 郝立波, 等. 大兴安岭中南段燕山期两类不同成矿花岗岩类角闪石的化学成分及其成岩成矿意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2003, 23(1): 5-10. |
| [58] | PIRAJNO F. Hydrothermal Processes and Mineral Systems[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2009: 1-1250. |
| [59] | 王玉往, 王京彬, 龙灵利, 等. 岩浆混合作用的类型、标志、机制、模式及其与成矿的关系——以新疆北部为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(8): 2317-2330. |
| [60] |
HATTORI K H, KEITH J D. Contribution of mafic melt to porphyry copper mineralization: Evidence from Mount Pinatubo, Philippines, and Bingham Canyon, Utah, USA[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2001, 36(8): 799-806.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
ZHANG D H, AUDÉTAT A. What caused the formation of the Giant Bingham Canyon porphyry Cu-Mo-Au deposit? Insights from melt inclusions and magmatic sulfides[J]. Economic Geology, 2017, 112(1): 221-244.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
DU Y S. Petrological and mineralogical study of enclaves in plutons in the typical mining districts of Tongling, Anhui and its bearing on the process of magmatism-metallogeny[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 1999, 18(3): 208-218.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
MA X H, CHEN B, YANG M C. Magma mixing origin for the Aolunhua porphyry related to Mo-Cu mineralization, eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 24(3/4): 1152-1171.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 晁海德, 陈建洲, 王瑾, 李吉庆, 王国仓, 赵洪岳, 蔡廷俊, 刘立波, 李生福, 任文恺, 邱亮. 青藏高原北部东昆仑地区三叠系页岩成岩作用及其对储层的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1052-1064. |
| [2] | 于景维, 罗刚, 李斌, 潘拓, 余海涛, 况昊, 褚旭, 张晓童. 沙湾凹陷上乌尔禾组储层成岩作用及成岩相分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1095-1104. |
| [3] | 王爱, 钟大康, 刘忠群, 王威, 杜红权, 周志恒, 唐自成. 川东北元坝西地区须三段钙屑致密砂岩储层成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1193-1204. |
| [4] | 姚宗全, 于兴河, 岳红星, 德勒恰提·加娜塔依, 周隶华, 王进, 高阳. 砂砾岩储层特征及控制因素:以红山嘴地区三叠系克拉玛依组上段为例[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(06): 1188-1198. |
| [5] | 郭芪恒, 金振奎, 朱小二, 常睿, 江梦雅, 王金艺. 北京下苇甸地区寒武系张夏组鲕粒滩成岩演化与勘探前景[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(04): 820-830. |
| [6] | 刘明义, 张晶, 孟广路, 胡立. 区域地球化学评价中变异系数校正参数的意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 1074-1079. |
| [7] | 郭芪恒, 金振奎, 朱小二, 王金艺. 北京下苇甸剖面张夏组鲕粒特征及其白云化机制[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 766-773. |
| [8] | 伊硕, 黄文辉, 金振奎, 高白水, 朱小二. 哈萨克斯坦Zanazor油田石炭系KT-Ⅱ碳酸盐岩层成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(04): 791-801. |
| [9] | 王晓晨, 罗静兰, 李文厚, 王若谷, 唐启银. 鄂尔多斯盆地苏77、召51区块山23段储层成岩作用与孔隙演化定量分析[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(03): 565-573. |
| [10] | 蒋威,谭先锋,王佳,付明庆,陈青,吴康军,冉天. 龙女寺东端须家河组致密砂岩成岩作用及储层形成机理[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(6): 1348-1360. |
| [11] | 乔锦杨,张英波,杨香华,王清斌,周心怀,朱红涛,王维,李欢. 黄河口凹陷莱北斜坡带玄武岩发育区砂岩成岩特征、孔隙流体及储层控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(1): 209-219. |
| [12] | 刘圣乾,姜在兴,王夏斌,陈骥,高艺,吴明昊,孙晓玮,栾天思. 辽河西部凹陷西斜坡沙四段储层特征及成岩作用对其影响[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(3): 692-701. |
| [13] | 刘永福,赵建华,范秋海,林畅松,孙琦,黄理力. 塔北隆起哈拉哈塘凹陷东河砂岩成岩作用及其控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(3): 635-644. |
| [14] | 李锟,于炳松,王黎栋,潘莹露. 塔里木盆地东南地区侏罗系低孔渗砂岩储层成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(2): 388-395. |
| [15] | 董果果,黄文辉,万欢,王华军. 东营凹陷北部陡坡带沙四上亚段砂砾岩储层固体-流体相互作用研究[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(4): 941-948. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||