



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (06): 1193-1204.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.06.079
王爱1( ), 钟大康2,3(
), 钟大康2,3( ), 刘忠群1, 王威4, 杜红权4, 周志恒2,3, 唐自成2,3
), 刘忠群1, 王威4, 杜红权4, 周志恒2,3, 唐自成2,3
收稿日期:2019-10-11
修回日期:2019-12-25
出版日期:2020-12-22
发布日期:2020-12-22
通讯作者:
钟大康
作者简介:钟大康,男,教授,博士生导师,工学博士,1961年出生,沉积学专业,主要从事储层地质学及沉积岩石学方面的教学及研究。Email:zhongdakang@263.net.基金资助:
WANG Ai1( ), ZHONG Dakang2,3(
), ZHONG Dakang2,3( ), LIU Zhongqun1, WANG Wei4, DU Hongquan4, ZHOU Zhiheng2,3, TANG Zicheng2,3
), LIU Zhongqun1, WANG Wei4, DU Hongquan4, ZHOU Zhiheng2,3, TANG Zicheng2,3
Received:2019-10-11
Revised:2019-12-25
Online:2020-12-22
Published:2020-12-22
Contact:
ZHONG Dakang
摘要:
基于薄片观察、扫描电镜和物性测试等数据,分析了川东北元坝西地区须三段致密砂岩岩石学特征、成岩作用、孔隙类型和物性特征,建立其成岩序列和孔隙演化过程,为须三段致密砂岩的勘探开发提供思路。研究表明元坝西须三段主要由龙门山二叠系和三叠系碳酸盐岩母岩提供物源,发育辫状河三角洲平原—前缘细中粒钙屑致密砂岩,经历的成岩作用主要包括压实作用和压溶作用、方解石胶结作用、重结晶作用、溶蚀作用和破裂作用;其孔隙类型为晶间微孔隙、裂缝与溶蚀孔隙,孔隙度为0.41%~7.16%,渗透率为0.001 2×10-3~533.59×10-3 μm2。钙屑砂岩高钙屑含量的成分特殊性造成了典型的“强胶结强重结晶弱压实弱溶蚀”成岩特征,埋藏成岩的特殊性导致了钙屑砂岩孔隙和物性的特殊性。早期强烈钙质胶结导致钙屑砂岩压实作用弱,原生孔隙几乎损失殆尽,进一步导致其溶蚀作用也很弱;后期钙屑中的泥晶藻屑砂屑发生强重结晶作用形成晶间微孔,平均孔隙度只有2.0%,物性较差;钙屑砂岩的主要碎屑颗粒和胶结物均为具有脆性特征的碳酸盐矿物,在构造运动作用下容易产生裂缝,形成裂缝沟通大量的重结晶微孔、粒间溶孔、残余粒间孔的孔隙系统。
中图分类号:
王爱, 钟大康, 刘忠群, 王威, 杜红权, 周志恒, 唐自成. 川东北元坝西地区须三段钙屑致密砂岩储层成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1193-1204.
WANG Ai, ZHONG Dakang, LIU Zhongqun, WANG Wei, DU Hongquan, ZHOU Zhiheng, TANG Zicheng. Diagenesis and Porosity Evolution of Calcareous Sandstone Reservoirs of Xu-3 Member in Western Yuanba of Northeastern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(06): 1193-1204.
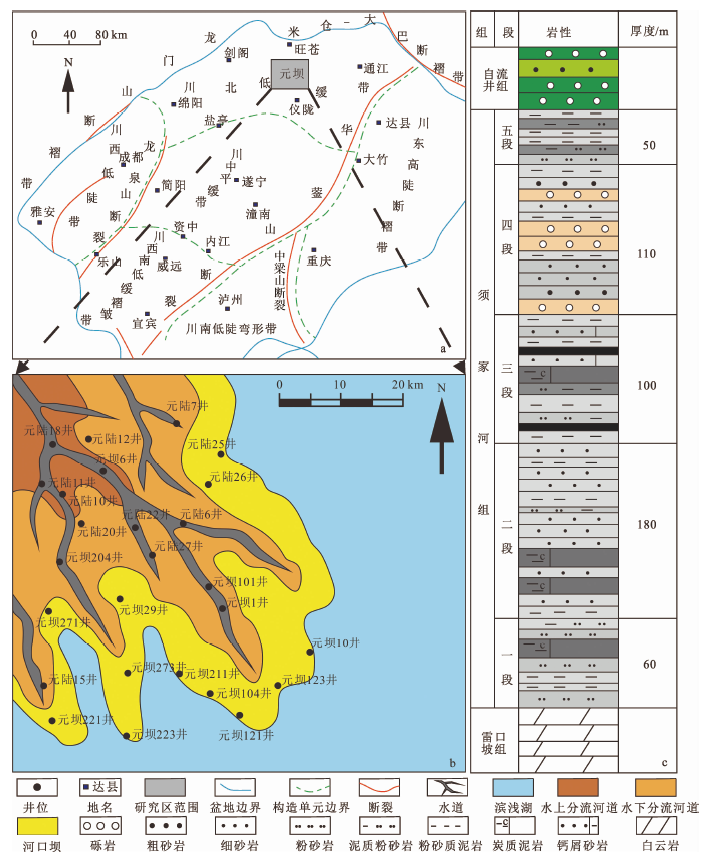
图1 研究区沉积构造背景及地层特征(据王威,2013;杜红权,2016;李军,2016;唐自成,2019;有修改[4,7-6,27]) a.工区构造位置;b.须三段沉积相图;c.须家河组综合柱状图
Fig.1 Sedimentary tectonic background and stratigraphic features of the study area (after Wang Wei, 2013; Du Hongquan, 2016; Li Jun, 2016; Tang Zicheng, 2019[4,7-6,27])

图3 元坝西须三段钙屑砂岩岩石学特征 a.钙屑含量高,石英零星分布,元坝221井,4 332.00 m,×100,正交光;b.钙屑含量高,偶见发育卡式双晶的长石,元坝224,4 346.00 m,×100,正交光;c.灰岩岩屑和白云岩岩屑,元坝271井,4 113.00 m,×100,正交光;d.含翁格达藻屑灰岩砾石,龙门山工农镇野外剖面,×100,单偏光;e.含砂盘虫灰岩砾石,龙门山工农镇野外剖面,×100,单偏光;f.可见千枚岩岩屑,元坝224井,4 344.00 m,×100,正交光;g.黏土杂基含量低,元坝272井,4 324.33 m,×100,单偏光;h.钙质胶结广泛发育,元坝271,4 095.66 m,×100,正交光;i.偶见发育石英次生加大,元坝271,4 096.00 m,×100,正交光
Fig.3 Lithological characteristics of the Xu-3 tight sandstones from western Yuanba
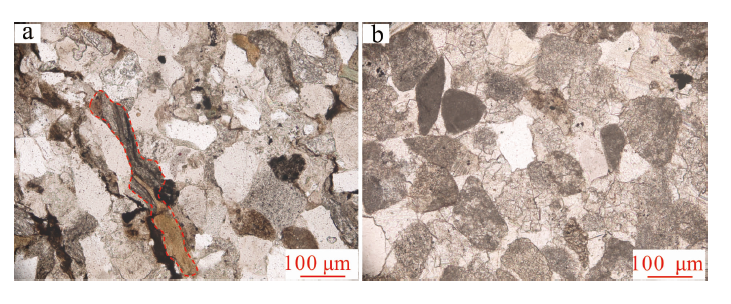
图4 元坝西须三段钙屑砂岩压实作用特征 a.塑性颗粒轻微变形,元坝6井,4 294.69m,×100,正交偏光;b.岩石内部颗粒呈点—线接触,元陆22井,4 161.78m,×100,单偏光
Fig.4 Characteristics of compaction of the Xu-3 tight sandstones from western Yuanba

图6 元坝西须三段钙屑砂岩压溶作用特征 元陆15井,4 275.21 m,压溶缝及沿压溶缝发育的粒间溶孔,×100,单偏光
Fig.6 Characteristics of pressure solution in the Xu-3 tight sandstones from western Yuanba
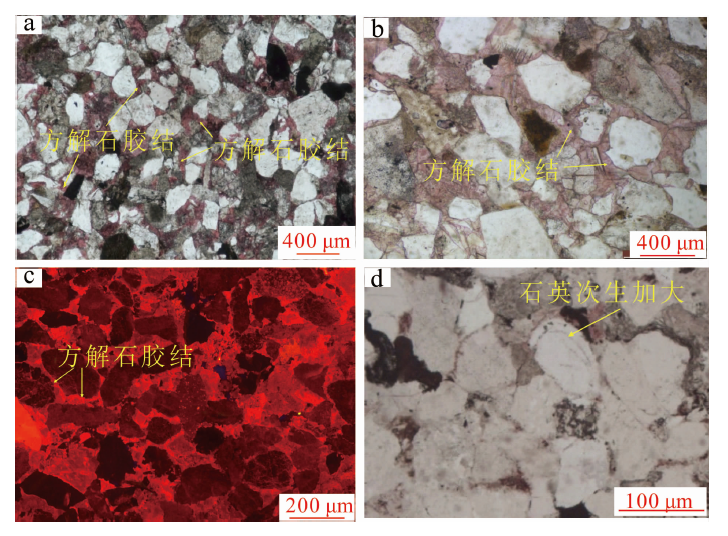
图7 元坝西须三段钙屑砂岩胶结作用特征 a.硒素红染色后的方解石胶结,孔隙式胶结,元陆4井,4 456.60 m,×50,单偏光;b.硒素红染色后的方解石胶结,基底式胶结,元陆4井,4 456.70 m,×100,单偏光;c.橘红色的早期方解石胶结物,元坝271井,4 095.66 m,×100,阴极发光;d.石英次生加大,元陆4井,4 458.00 m,×200,单偏光
Fig.7 Characteristics of cement in the Xu-3 tight sandstones from western Yuanba
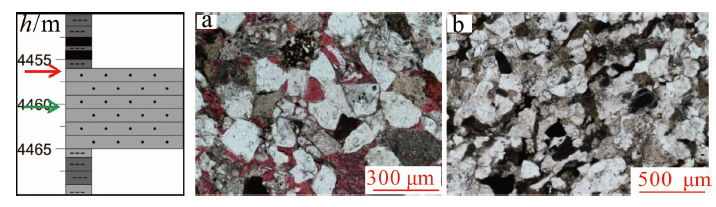
图8 元坝西须三段钙屑砂岩方解石胶结分布特征 a.厚层砂体顶部的方解石胶结发育,孔隙式胶结,元陆4井,4 457.10 m,×100,单偏光;b.厚层砂体中部的方解石胶结不发育,元陆4井,4 460.30 m,×50,单偏光;红色箭头是a薄片取样位置,绿色箭头是b薄片取样位置
Fig.8 Distribution characteristics of calcite cement in the Xu-3 tight sandstones from western Yuanba

图9 元坝西须三段钙屑砂岩重结晶作用特征 a.钙屑重结晶,元陆18井,4 526.49 m,×100,单偏光;b.钙屑重结晶,元陆12井,4 315 m,×100,单偏光
Fig.9 Recrystallization features of the Xu-3 tight sandstones from western Yuanba
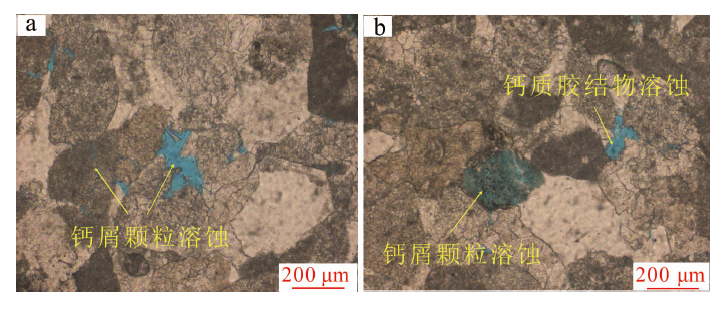
图10 元坝西须三段钙屑砂岩溶蚀作用特征 a.钙屑溶蚀,元陆15井,4 276.00 m,×100,单偏光;b.钙质胶结物溶蚀,元陆15井,4 276.00 m,×100,单偏光
Fig.10 Dissolution features of the Xu-3 tight sandstones from western Yuanba

图11 元坝西须三段钙屑砂岩破裂作用特征 a.裂缝切穿砾石,元陆6井,4 184.48 m,×100,单偏光;b.裂缝,元陆18井,4 526.23 m,×100,单偏光
Fig.11 Fracturing features of the Xu-3 tight sandstones from western Yuanba

图12 元坝西须三段钙屑砂岩原生孔与晶间微孔特征 a.原生孔隙(残余粒间孔)与溶蚀孔,元陆15井,4 275.46 m;b.钙屑重结晶微孔,元陆18井,4 564.8 m;c.钙屑重结晶微孔,元陆22井,4 257.76 m;d.胶结物晶间微孔,元陆15井,4 280.1 m
Fig.12 Characteristics of primary pores and intercrystalline micropores in the Xu-3 tight sandstones from western Yuanba
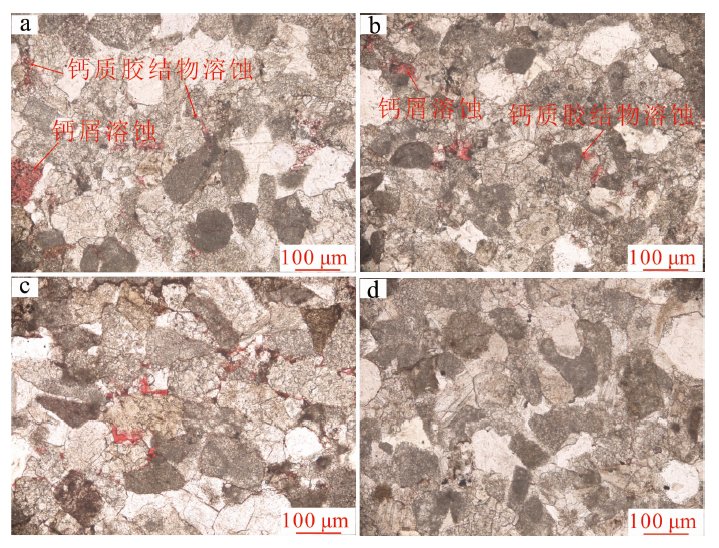
图14 元坝西须三段钙屑砂岩溶蚀孔隙特征 a.钙屑与钙质胶结物溶蚀,元陆20井,4 140.74 m,×100,单偏光;b.钙屑与钙质胶结物溶蚀,元陆18井,4 564.41 m,×100,单偏光;c.溶蚀孔隙,元陆15井,4 275.33 m,×100,单偏光;d.溶蚀孔隙不发育,元陆15井,4 279.42 m,×100,单偏光
Fig.14 Characteristics of dissolved pores in the Xu-3 tight sandstones from western Yuanba

图15 元坝西须三段钙屑砂岩裂缝特征 a.贴粒缝,元陆12井,4 315.55 m,×100,单偏光;b.构造缝,元陆15井,4 282.43 m,×100,单偏光;c.微裂缝沟通晶间的微孔,元陆15井,4 275.6 m;d.微裂缝沟通晶间的微孔隙,元陆18井,4 524.34 m
Fig.15 Characteristics of fractures in the Xu-3 tight sandstones from western Yuanba
| 孔隙类型 | 残余粒间孔 | 晶间微孔隙 | 裂缝 | 溶蚀孔隙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均孔隙度/% | 0.04 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| 总孔隙占比/% | 2.0 | 68.6 | 14.7 | 14.7 |
表1 元坝西须三段钙屑砂岩孔隙类型与总孔隙占比统计表
Table 1 Statistics of pore types and total pore ratios of the Xu-3 tight sandstones from western Yuanba
| 孔隙类型 | 残余粒间孔 | 晶间微孔隙 | 裂缝 | 溶蚀孔隙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均孔隙度/% | 0.04 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| 总孔隙占比/% | 2.0 | 68.6 | 14.7 | 14.7 |
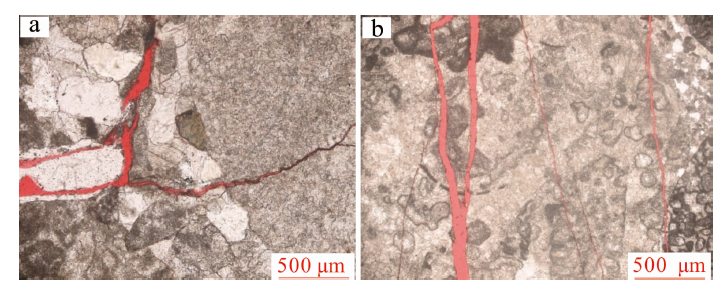
图18 元坝西须三段钙屑砂岩裂缝发育典型特征 a.裂缝沿颗粒边缘发育,元陆18井,4 579.11 m,铸体薄片,×100,单偏光;b.微裂缝切穿钙屑颗粒,元陆6井,4 184.48 m,铸体薄片,×100,单偏光
Fig.18 Typical fracture development characteristics of the Xu-3 tight sandstones from western Yuanba

图19 元坝西须三段钙屑砂岩孔隙系统典型特征 元陆6井,4 182.98 m,发育重结晶微孔、粒间溶孔和残余粒间孔,也可见微裂缝和缝合线发育,×100,单偏光
Fig.19 Typical pore system characteristics of the Xu-3 tight sandstones from western Yuanba
| [1] | 邹才能, 陶士振, 侯连华, 等. 非常规油气地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011: 50-83. |
| [2] | 贾承造, 郑民, 张永峰. 中国非常规油气资源与勘探开发前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012,39(2):129-136. |
| [3] | 邹才能, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等. 常规与非常规油气聚集类型、特征、机理及展望——以中国致密油和致密气为例[J]. 石油学报, 2012,33(2):173-187. |
| [4] | 王威, 岳全玲. 四川盆地北部须家河组致密砂岩储层成因机制[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2012,35(1):13-17. |
| [5] | 张莉, 邹华耀, 郝芳, 等. 川东北元坝地区须家河组储层特征与超致密成因探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2017,91(9):2105-2118. |
| [6] | 李军, 胡东风, 邹华耀, 等. 四川盆地元坝—通南巴地区须家河组致密砂岩储层成岩—成藏耦合关系[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016,27(7):1164-1178. |
| [7] | 杜红权, 王威, 周霞, 等. 川东北元坝地区须三段钙屑砂砾岩储层特征及控制因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016,37(4):565-571. |
| [8] | 王威. 高能河道砂体特征及勘探意义——以元坝地区须三段为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2013,35(6):657-661. |
| [9] | 肖开华, 李宏涛, 贾爽. 川东北元坝地区须三段钙屑砂岩储层特征及控气因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014,35(5):654-660. |
| [10] | 曾小英, 张小青, 钟玉梅. 川西坳陷中段须家河组四段钙屑砂岩气层的成因[J]. 沉积学报, 2007,25(6):84-90. |
| [11] | 黎静容, 李毓, 程洪亮, 等. 元坝地区须三段沉积特征[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2013,28(5):43-50. |
| [12] | 郝景宇. 川东北地区须家河组沉积与层序特征精细研究[D]. 武汉:长江大学, 2012. |
| [13] | 曾韬. 川东北元坝地区须三段沉积相及沉积演化[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2014(4):468-475. |
| [14] | 张冲, 谢润成, 周文, 等. 川东北元坝地区须三段致密储集层裂缝特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2014,35(4):395-398. |
| [15] | 王杰, 秦建中, 刘文汇, 等. 川东北元坝地区中生代构造与动态热演化史——磷灰石、锆石(U-Th)/He定年分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2012,34(1):19-24. |
| [16] | 黄进腊, 张哨楠, 刘成川, 等. 川东北元坝地区须家河组断层预测及发育特征[J]. 天然气技术与经济, 2013,7(3):3-6. |
| [17] | 盘昌林. 四川盆地元坝地区上三叠统须家河组天然气成藏条件研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2011. |
| [18] | 秦华, 肖伟. 川东北元坝地区须家河组凝缩层的归属及成因[J]. 天然气技术与经济, 2010,4(3):11-13. |
| [19] | 何志勇, 刘海涛, 肖伟, 等. 四川盆地元坝地区下侏罗统介壳灰岩储层分布预测[J]. 现代地质, 2017,31(1):144-151. |
| [20] | TIAN Y, KOHN B P, ZHU C, et al. Post-orogenic evolution of the Mesozoic Micang Shan Foreland Basin system, central China[J]. Basin Research, 2012,24(1):70-90. |
| [21] | ENKELMANN E, RATSCHBACHER L, JONCKHEERE R, et al. Cenozoic exhumation and deformation of northeastern Tibet and the Qinling: Is Tibetan lower crustal flow diverging around the Sichuan Basin?[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2006,118(5/6):651-671. |
| [22] |
YIN A, HARRISON T M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000,28:211-280.
DOI URL |
| [23] | 黄仁春. 川东北元坝地区雷口坡组天然气来源与成藏分析[J]. 现代地质, 2014,28(2):412-418. |
| [24] | 张峰. 川东北地区上三叠统须家河组层序岩相古地理研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2011. |
| [25] |
赵宗举, 朱琰, 李大成, 等. 中国南方构造形变对油气藏的控制作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2002,23(1):19-25.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 陈龙博, 何登发, 王贝, 等. 川东北地区通南巴背斜中三叠世以来构造变形时间厘定及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2017,41(3):433-445. |
| [27] | 唐自成, 钟大康, 王威, 等. 川东北元坝地区须家河组三段钙屑砂岩孔隙类型及地质意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019,40(5):1137-1147. |
| [28] |
TAN X, XIA Q, CHEN J, et al. Basin-scale sand deposition in the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation of the Sichuan Basin, Southwest China: Sedimentary framework and conceptual model[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2013,24(1):89-103.
DOI URL |
| [29] | BEARD D C, WEYL P K. Influence of texture on porosity and permeability of unconsolidated sand[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1973,57(2):349-369. |
| [30] | HOUSEKNECHT D W. Assessing the relative importance of compaction processes and cementation to reduction of porosity in sandstones[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1987,71:633-642. |
| [31] |
LUNDEGARD P D. Sandstones porosity loss—a big picture view of the importance of compaction[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1992,62:250-260.
DOI URL |
| [32] | EHRENBERG S N. Measuring sandstone compaction from modal analyses of thin sections: how to do it and what the results mean[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1995,6:369-379. |
| [1] | 晁海德, 陈建洲, 王瑾, 李吉庆, 王国仓, 赵洪岳, 蔡廷俊, 刘立波, 李生福, 任文恺, 邱亮. 青藏高原北部东昆仑地区三叠系页岩成岩作用及其对储层的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1052-1064. |
| [2] | 于景维, 罗刚, 李斌, 潘拓, 余海涛, 况昊, 褚旭, 张晓童. 沙湾凹陷上乌尔禾组储层成岩作用及成岩相分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1095-1104. |
| [3] | 姚宗全, 于兴河, 岳红星, 德勒恰提·加娜塔依, 周隶华, 王进, 高阳. 砂砾岩储层特征及控制因素:以红山嘴地区三叠系克拉玛依组上段为例[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(06): 1188-1198. |
| [4] | 郭芪恒, 金振奎, 朱小二, 常睿, 江梦雅, 王金艺. 北京下苇甸地区寒武系张夏组鲕粒滩成岩演化与勘探前景[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(04): 820-830. |
| [5] | 何宇, 章永梅, 顾雪祥, 彭义伟, 程文斌, 王冠南, 万阈, 袁鹏. 西天山呼斯特岩体矿物化学特征及其成岩成矿意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(06): 1227-1241. |
| [6] | 郭芪恒, 金振奎, 朱小二, 王金艺. 北京下苇甸剖面张夏组鲕粒特征及其白云化机制[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 766-773. |
| [7] | 伊硕, 黄文辉, 金振奎, 高白水, 朱小二. 哈萨克斯坦Zanazor油田石炭系KT-Ⅱ碳酸盐岩层成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(04): 791-801. |
| [8] | 王晓晨, 罗静兰, 李文厚, 王若谷, 唐启银. 鄂尔多斯盆地苏77、召51区块山23段储层成岩作用与孔隙演化定量分析[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(03): 565-573. |
| [9] | 蒋威,谭先锋,王佳,付明庆,陈青,吴康军,冉天. 龙女寺东端须家河组致密砂岩成岩作用及储层形成机理[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(6): 1348-1360. |
| [10] | 乔锦杨,张英波,杨香华,王清斌,周心怀,朱红涛,王维,李欢. 黄河口凹陷莱北斜坡带玄武岩发育区砂岩成岩特征、孔隙流体及储层控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(1): 209-219. |
| [11] | 刘圣乾,姜在兴,王夏斌,陈骥,高艺,吴明昊,孙晓玮,栾天思. 辽河西部凹陷西斜坡沙四段储层特征及成岩作用对其影响[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(3): 692-701. |
| [12] | 刘永福,赵建华,范秋海,林畅松,孙琦,黄理力. 塔北隆起哈拉哈塘凹陷东河砂岩成岩作用及其控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(3): 635-644. |
| [13] | 李锟,于炳松,王黎栋,潘莹露. 塔里木盆地东南地区侏罗系低孔渗砂岩储层成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(2): 388-395. |
| [14] | 冯冲,郭彤楼,邹华耀,成晓啭. 川东北地区飞仙关组—长兴组天然气富集机制[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(4): 907-914. |
| [15] | 董果果,黄文辉,万欢,王华军. 东营凹陷北部陡坡带沙四上亚段砂砾岩储层固体-流体相互作用研究[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(4): 941-948. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||