



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (05): 1450-1458.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.048
杨琼1( ), 杨忠芳1(
), 杨忠芳1( ), 季峻峰2, 刘旭1, 季文兵3, 王珏1, 吴天生4, 王磊5
), 季峻峰2, 刘旭1, 季文兵3, 王珏1, 吴天生4, 王磊5
收稿日期:2020-11-10
修回日期:2021-04-06
出版日期:2021-10-10
发布日期:2021-11-04
通讯作者:
杨忠芳
作者简介:杨忠芳,女,教授,博士生导师,1961年出生,地球化学专业,主要从事生态地球化学与教学工作。Email: zfyang01@126.com。基金资助:
YANG Qiong1( ), YANG Zhongfang1(
), YANG Zhongfang1( ), JI Junfeng2, LIU Xu1, JI Wenbing3, WANG Jue1, WU Tiansheng4, WANG Lei5
), JI Junfeng2, LIU Xu1, JI Wenbing3, WANG Jue1, WU Tiansheng4, WANG Lei5
Received:2020-11-10
Revised:2021-04-06
Online:2021-10-10
Published:2021-11-04
Contact:
YANG Zhongfang
摘要:
岩溶地质高背景区土壤中普遍存在的铁锰结核对重金属的赋存状态和有效性有重要影响。选择广西贵港覃塘岩溶地质高背景区富含铁锰结核的表层土壤(0~20 cm)为研究对象,筛分出不同粒径的铁锰结核(10~120目)和细粒径土壤(<120目)样品进行化学分析,针对以下三个方面开展研究:(1)重金属(As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Pb和Zn)在铁锰结核和细粒径土壤中的分布分配规律和铁氧化物矿物的组成;(2)铁氧化物矿物对富含铁锰结核的土壤中Cd等重金属富集的影响;(3)重金属在富含铁锰结核的土壤中的赋存机制。研究发现,铁锰结核中的Fe和Mn以及Cd等重金属含量随着粒径的增大而不断增加,说明Cd等重金属元素更倾向于在大粒径铁锰结核中富集;土壤中Cd等重金属总量的约90%赋存在结核中,表明研究区土壤中重金属主要以结核形式赋存;富含铁锰结核的土壤中赤铁矿和针铁矿的平均含量分别为0.61%和4.94%,且结核粒径越大,针铁矿和赤铁矿含量越高;除Hg外,Cd等重金属含量与针铁矿和赤铁矿的含量均呈现极显著正相关,与赤铁矿的相关性稍优于针铁矿,表明铁氧化物矿物与富含铁锰结核土壤中的Cd等重金属元素富集密切相关。铁锰结核的存在既能促进Cd等重金属在土壤中的富集,又能降低土壤中重金属的生物有效性,研究结果为解释岩溶地质高背景区土壤Cd等重金属元素高含量、低生物有效性提供了理论依据。
中图分类号:
杨琼, 杨忠芳, 季峻峰, 刘旭, 季文兵, 王珏, 吴天生, 王磊. 广西贵港岩溶地质高背景区富含铁锰结核土壤的矿物学与重金属地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1450-1458.
YANG Qiong, YANG Zhongfang, JI Junfeng, LIU Xu, JI Wenbing, WANG Jue, WU Tiansheng, WANG Lei. Characteristics of Mineralogy and Heavy Metal Geochemistry in Ferromanganese Nodule Rich Soils with High Geochemical Background from Guigang, Guangxi[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(05): 1450-1458.
| 序号 | 粒径/目 | pH | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | Mn | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10~20 | 6.52 | 30.73 | 22.87 | 1 807 | 85.7 | 6.152 | 1 520 | 67 | 0.501 | 179 | 124.5 | 791 |
| 2 | 20~40 | 6.40 | 34.24 | 14.78 | 1 487 | 40.8 | 3.870 | 757 | 58 | 0.486 | 156 | 95.3 | 622 |
| 3 | 40~60 | 6.39 | 34.88 | 11.83 | 1 341 | 35.1 | 3.458 | 544 | 56 | 0.493 | 152 | 87.9 | 588 |
| 4 | 60~80 | 6.48 | 35.41 | 10.75 | 1 338 | 30.3 | 3.402 | 449 | 59 | 0.512 | 153 | 85.4 | 575 |
| 5 | 80~100 | 6.50 | 34.72 | 10.13 | 1 227 | 27.8 | 3.080 | 398 | 55 | 0.467 | 143 | 79.2 | 547 |
| 6 | 100~120 | 6.52 | 35.37 | 9.87 | 1 252 | 27.8 | 3.302 | 366 | 58 | 0.483 | 148 | 82.0 | 557 |
| 7 | <120 | 6.45 | 35.06 | 9.69 | 1 222 | 28.7 | 3.067 | 355 | 59 | 0.536 | 143 | 81.2 | 538 |
| 平均值 | 6.48* | 34.34 | 12.85 | 1 382 | 39.5 | 3.762 | 627 | 59 | 0.497 | 153 | 90.8 | 603 | |
表1 不同粒径铁锰结核理化性质及重金属元素含量
Table 1 The chemical properties and heavy metal concentrations in ferromanganese nodules of different sizes
| 序号 | 粒径/目 | pH | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | Mn | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10~20 | 6.52 | 30.73 | 22.87 | 1 807 | 85.7 | 6.152 | 1 520 | 67 | 0.501 | 179 | 124.5 | 791 |
| 2 | 20~40 | 6.40 | 34.24 | 14.78 | 1 487 | 40.8 | 3.870 | 757 | 58 | 0.486 | 156 | 95.3 | 622 |
| 3 | 40~60 | 6.39 | 34.88 | 11.83 | 1 341 | 35.1 | 3.458 | 544 | 56 | 0.493 | 152 | 87.9 | 588 |
| 4 | 60~80 | 6.48 | 35.41 | 10.75 | 1 338 | 30.3 | 3.402 | 449 | 59 | 0.512 | 153 | 85.4 | 575 |
| 5 | 80~100 | 6.50 | 34.72 | 10.13 | 1 227 | 27.8 | 3.080 | 398 | 55 | 0.467 | 143 | 79.2 | 547 |
| 6 | 100~120 | 6.52 | 35.37 | 9.87 | 1 252 | 27.8 | 3.302 | 366 | 58 | 0.483 | 148 | 82.0 | 557 |
| 7 | <120 | 6.45 | 35.06 | 9.69 | 1 222 | 28.7 | 3.067 | 355 | 59 | 0.536 | 143 | 81.2 | 538 |
| 平均值 | 6.48* | 34.34 | 12.85 | 1 382 | 39.5 | 3.762 | 627 | 59 | 0.497 | 153 | 90.8 | 603 | |
| 序号 | 粒径/目 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10~20 | 56.8 | 48.2 | 59.4 | 38.2 | 34.7 | 38.5 | 42.8 | 41.7 |
| 2 | 20~40 | 16.6 | 18.6 | 18.1 | 20.1 | 20.6 | 20.5 | 20.0 | 20.1 |
| 3 | 40~60 | 11.5 | 13.4 | 10.5 | 15.6 | 16.8 | 16.1 | 14.9 | 15.3 |
| 4 | 60~80 | 4.7 | 6.3 | 4.1 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 7.8 | 6.9 | 7.1 |
| 5 | 80~100 | 2.3 | 3.1 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 4.1 | 3.9 | 3.5 | 3.7 |
| 6 | 100~120 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 1.3 | 2.9 | 3.0 | 2.8 | 2.5 | 2.6 |
| 7 | <120 | 6.4 | 8.1 | 4.7 | 11.3 | 12.5 | 10.4 | 9.4 | 9.6 |
表2 不同粒径铁锰结核中重金属元素的PQ值(%)
Table 2 PQ values of heavy metals in ferromanganese nodules of different sizes (%)
| 序号 | 粒径/目 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10~20 | 56.8 | 48.2 | 59.4 | 38.2 | 34.7 | 38.5 | 42.8 | 41.7 |
| 2 | 20~40 | 16.6 | 18.6 | 18.1 | 20.1 | 20.6 | 20.5 | 20.0 | 20.1 |
| 3 | 40~60 | 11.5 | 13.4 | 10.5 | 15.6 | 16.8 | 16.1 | 14.9 | 15.3 |
| 4 | 60~80 | 4.7 | 6.3 | 4.1 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 7.8 | 6.9 | 7.1 |
| 5 | 80~100 | 2.3 | 3.1 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 4.1 | 3.9 | 3.5 | 3.7 |
| 6 | 100~120 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 1.3 | 2.9 | 3.0 | 2.8 | 2.5 | 2.6 |
| 7 | <120 | 6.4 | 8.1 | 4.7 | 11.3 | 12.5 | 10.4 | 9.4 | 9.6 |
| 序号 | 粒径/目 | 赤铁矿Hm | 针铁矿Gt | Hm/TFe2O3 | Gt/TFe2O3 | (Hm+Gt)/TFe2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10~20 | 1.48 | 11.70 | 6.47 | 51.16 | 57.63 |
| 2 | 20~40 | 0.70 | 4.98 | 4.75 | 33.69 | 38.43 |
| 3 | 40~60 | 0.47 | 3.77 | 3.96 | 31.84 | 35.79 |
| 4 | 60~80 | 0.42 | 3.53 | 3.90 | 32.81 | 36.71 |
| 5 | 80~100 | 0.44 | 3.88 | 4.38 | 38.31 | 42.69 |
| 6 | 100~120 | 0.42 | 3.72 | 4.24 | 37.72 | 41.96 |
| 7 | <120 | 0.35 | 2.99 | 3.66 | 30.88 | 34.53 |
| 平均含量 | 0.61 | 4.94 | 4.48 | 36.63 | 41.11 | |
表3 不同粒径铁锰结核赤铁矿和针铁矿含量(%)
Table 3 Contents of hematite (Hm) and goethite (Gt) in ferromanganese nodules of different sizes(%)
| 序号 | 粒径/目 | 赤铁矿Hm | 针铁矿Gt | Hm/TFe2O3 | Gt/TFe2O3 | (Hm+Gt)/TFe2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10~20 | 1.48 | 11.70 | 6.47 | 51.16 | 57.63 |
| 2 | 20~40 | 0.70 | 4.98 | 4.75 | 33.69 | 38.43 |
| 3 | 40~60 | 0.47 | 3.77 | 3.96 | 31.84 | 35.79 |
| 4 | 60~80 | 0.42 | 3.53 | 3.90 | 32.81 | 36.71 |
| 5 | 80~100 | 0.44 | 3.88 | 4.38 | 38.31 | 42.69 |
| 6 | 100~120 | 0.42 | 3.72 | 4.24 | 37.72 | 41.96 |
| 7 | <120 | 0.35 | 2.99 | 3.66 | 30.88 | 34.53 |
| 平均含量 | 0.61 | 4.94 | 4.48 | 36.63 | 41.11 | |
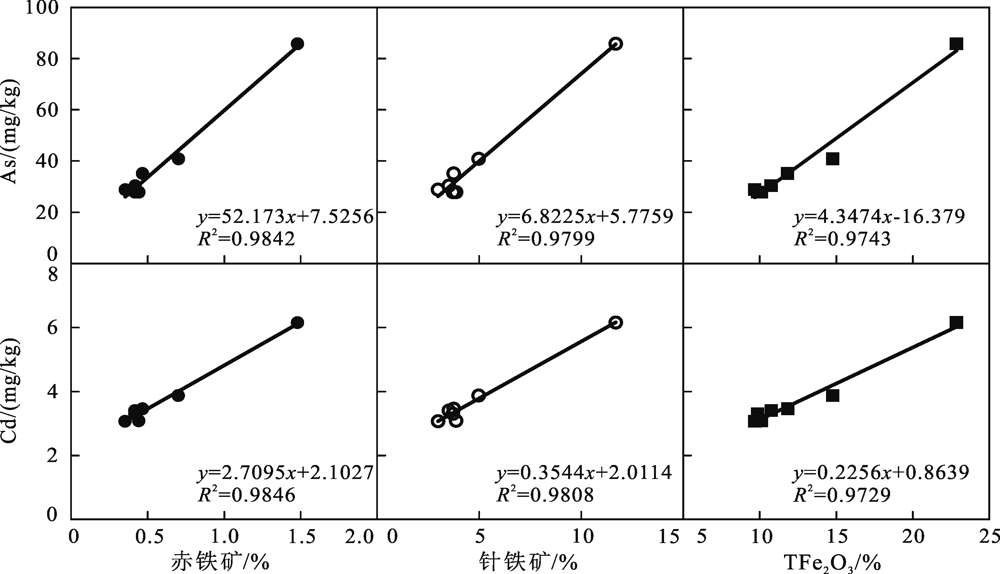
图3 不同粒径结核中As、Cd元素含量与赤铁矿、针铁矿、TFe2O3含量散点图
Fig.3 Scatter plots of As and Cd elements, and hematite, goethite and TFe2O3 in ferromanganese nodules of different sizes

图4 不同粒径结核中Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Pb和Zn元素含量与赤铁矿、针铁矿、TFe2O3含量散点图
Fig.4 Scatter plots of Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb and Zn and hematite, goethite and TFe2O3 in ferromanganese nodules of different sizes
| [1] | 温琰茂, 曾水泉, 潘树荣, 等. 中国东部石灰岩土壤元素含量分异规律研究[J]. 地理科学, 1994, 14(1):16-21. |
| [2] | 赵中秋, 后立胜, 蔡运龙. 西南喀斯特地区土壤退化过程与机理探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(3):185-189. |
| [3] | 王世杰, 季宏兵, 欧阳自远, 等. 碳酸盐岩风化成土作用的初步研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1999, 29(5):441-449. |
| [4] | 李德文, 崔之久, 刘耕年, 等. 岩溶风化壳形成演化及其循环意义[J]. 中国岩溶, 2001, 20(3):183-188. |
| [5] | 杨琼, 侯青叶, 顾秋蓓, 等. 广西武鸣县典型土壤剖面Se的地球化学特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(2):455-462. |
| [6] |
PALUMBO B, BELLANCA A, NERI R, et al. Trace metal partitioning in Fe-Mn nodules from Sicilian soils, Italy[J]. Chemical Geology, 2001, 173(4):257-269.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
GIRAO R D O, MOREIRA L J D S, GIRAO A L D A, et al. Soil genesis and iron nodules in a karst environment of the Apodi Plateau[J]. Revista Ciencia Agronomica, 2014, 45(4):683-695.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LATRILLE C, ELSASS F, OORT F V, et al. Physical speciation of trace metals in Fe-Mn concretions from a rendzic lithosol developed on Sinemurian limestones (France)[J]. Geoderma, 2001, 100(1/2):127-146.
DOI URL |
| [9] | BAKKER A P D, TOKASHIKI Y, ARACHCHI L P V. Mineralogy of Okinawan terrestrial Fe/Mn nodules and their surrounding soils[J]. Clay Science, 2003, 12(3):121-130. |
| [10] |
FENG J L. Behaviour of rare earth elements and yttrium in ferromanganese concretions, gibbsite spots, and the surrounding terra rossa over dolomite during chemical weathering[J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 271(3/4):112-132.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
FENG J L. Trace elements in ferromanganese concretions, gibbsite spots, and the surrounding terra rossa overlying dolomite: Their mobilization, redistribution and fractionation[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2011, 108(1):99-111.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WEN Y B, LI W, YANG Z F, et al. Enrichment and source identification of Cd and other heavy metals in soils with high geochemical background in the karst region, Southwestern China[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 245:125620.
DOI URL |
| [13] | 刘旭, 顾秋蓓, 杨琼, 等. 广西象州与横县碳酸盐岩分布区土壤中Cd形态分布特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(2):374-385. |
| [14] | 苏春田, 唐健生, 邹胜章, 等. 锰元素在铁锰结核-土壤-旱地作物的分布研究[J]. 热带地理, 2011, 31(3):262-265. |
| [15] |
GAO T, KE S, WANG S J, et al. Contrasting Mg isotopic compositions between Fe-Mn nodules and surrounding soils: Accumulation of light Mg isotopes by Mg-depleted clay minerals and Fe oxides[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2018, 237:205-222.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 唐瑞玲, 王惠艳, 吕许朋, 等. 西南重金属高背景区农田系统土壤重金属生态风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(5):917-927. |
| [17] |
JI W B, YANG Z F, YU T, et al. Potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the Fe-Mn nodules in the karst area of Guangxi, Southwest China[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2021, 106(3):51-56.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LIU Q S, TORRENT J, BARRON V, et al. Quantification of hematite from the visible diffuse reflectance spectrum: effects of aluminium substitution and grain morphology[J]. Clay Minerals, 2011, 46:137-147.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
HAN J, KATZ L E. Capturing the variable reactivity of goethites in surface complexation modeling by correlating model parameters with specific surface area[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2019, 244:248-263.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 朱立军, 李景阳. 碳酸盐岩红色风化壳中的氧化铁矿物[J]. 地质科学, 2001, 36(4):395-401. |
| [21] |
ZHANG Y G, JI J F, BALSAM W L, et al. High resolution hematite and goethite records from ODP 1143, South China Sea: Co-evolution of monsoonal precipitation and El Niño over the past 600,000 years[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 264(1/2):136-150.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHOU W, CHEN L X, ZHOU M, et al. Thermal identification of goethite in soils and sediments by diffuse reflectance spectroscopy[J]. Geoderma, 2010, 155(3/4):419-425.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LONG X Y, JI J F, BARRON V, et al. Climatic thresholds for pedogenic iron oxides under aerobic conditions: Processes and their significance in paleoclimate reconstruction[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 150:264-277.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 季峻峰, 陈骏, BALSAM W, 等. 黄土剖面中赤铁矿和针铁矿的定量分析与气候干湿变化研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27(2):221-229. |
| [25] | 李风玲. 长江三角洲地区土壤中铁氧化物对重金属的富集作用[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2011. |
| [26] |
LI M, XI X H, XIAO G Y, et al. National multi-purpose regional geochemical survey in China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 139(1):21-30.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 中华人民共和国国土资源部. DZ/T 0258—2014 多目标区域地球化学调查规范 (1:250 000)[S]. 北京: 全国国土资源标准化技术委员会, 2014. |
| [28] |
MEHRA O P, JACKSON M L. Iron oxide removal from soils and clays by a dithionite-citrate system buffered with sodium bicarbonate[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 1960, 7(1):317-327.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
JI J F, BALSAM W, CHEN J, et al. Rapid and quantitative measurement of hematite and goethite in the Chinese loess-paleosol sequence by diffuse reflectance spectroscopy[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 2002, 50(2):208-216.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 郑国东. 广西北部湾地区表层土壤重金属分布特征及其影响因素研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学 (北京), 2016. |
| [31] |
YANG Q, YANG Z F, FILIPPELLI G M, et al. Distribution and secondary enrichment of heavy metal elements in karstic soils with high geochemical background in Guangxi, China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2021, 567:120081.
DOI URL |
| [32] | 谌建国, 刘云华, 许俊文. 广西两种三水铝石铝土矿成矿的差异性[J]. 地学前缘, 1999, 6(增):251-256. |
| [33] | 张颖异, 程相利, 齐渊洪, 等. 广西贵港高铁型铝土矿的矿物学特征研究[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2015, 35(5):52-55. |
| [34] | 郑国东, 覃建勋, 付伟, 等. 广西北部湾地区表层土壤As分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2018, 48(1):181-192. |
| [35] | 李永华, 王五一, 谭文峰, 等. 土壤铁锰结核中生命有关元素的化学地理特征[J]. 地理研究, 2001, 20(5):609-615. |
| [36] | 苏春田, 唐健生, 单海平, 等. 黎塘岩溶区土壤铁锰结核的地球化学特征研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2008, 27(1):43-49. |
| [37] |
CHRISTL I, KRETZSCHMAR R. Interaction of copper and fulvic acid at the hematite-water interface[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(20):3435-3442.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
STICHER H, HOINS U, CHARLETHANS L. Ligand effect on the adsorption of heavy metals: the sulfate-Cadmium-Goethite case[J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 1993, 68(1/2):241-255.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
HIEMSTRA T, RIEMSDIJK W H V. A surface structural approach to ion adsorption: the charge distribution (CD) model[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1996, 179(2):488-508.
DOI URL |
| [40] | WEERASOORIYA R, TOBSCHALL H J. Modeling the Cd(II) adsorption onto goethite[J]. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry Reviews, 1999, 68(1/2):169-177. |
| [41] |
SWEDLUND P J, WEBSTER J G, MISKELLY G M. Goethite adsorption of Cu(II), Pb(II), Cd(II), and Zn(II) in the presence of sulfate: properties of the ternary complex[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73(6):1548-1562.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
MANGOLD J E, CHANG M P, LILJESTRAND H M, et al. Surface complexation modeling of Hg(II) adsorption at the goethite/water interface using the Charge Distribution Multi-Site Complexation (CD-MUSIC) model[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2014, 418:147-161.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
JEON B H, DEMPSEY B A, BURGOS W D, et al. Sorption kinetics of Fe(II), Zn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cd(II), and Fe(II)/Me(II) onto hematite[J]. Water Research, 2003, 37(17):4135-4142.
DOI URL |
| [44] | RIEMSDIJK W H V, HIEMSTRA T. Chapter 8 The CD-MUSIC model as a framework for interpreting ion adsorption on metal (hydr) oxide surfaces[J]. Interface Science and Technology, 2006, 11:251-268. |
| [45] |
ELZINGA E J, KRETZSCHMAR R. In situ ATR-FTIR spectroscopic analysis of the co-adsorption of orthophosphate and Cd(II) onto hematite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2013, 117(5):53-64.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
KHORSHIDI N, AZADMEHR A R. Characterization and adsorption properties of oxalate-loaded hematite composite for Cd (II) and Pb (II) adsorption: equilibrium models, thermodynamic, and kinetic studies[J]. Separation Science and Technology, 2016, 51(13):2122-2137.
DOI URL |
| [47] | GAILLARDET J, VIERS J, DUPRE B. Trace elements in river waters[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2014, 7:195-235. |
| [1] | 李楠, 曹明杰, 郝喆, 侯永莉, 陈红丹, 张颖. 基于不同土地利用方式的土壤重金属污染与潜在风险评价:以辽河流域(浑太水系)山水林田湖草沙一体化保护和修复工程为例[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1655-1664. |
| [2] | 胡庆海, 王学求, 韩志轩, 成晓梦, 吴慧, 田密, 刘福田, 孙彬彬, 陈卫明, 杜雪苗, 刘彬, 崔邢涛. 京津冀地区永清县土壤重金属地球化学特征及绿色食品产地的土壤质量评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 778-789. |
| [3] | 杜古尔·卫卫, 石海涛, 邢浩, 娄雪聪, 胡宏利, 布龙巴特. 新疆戈壁荒漠区典型露天煤矿土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 790-800. |
| [4] | 刘同, 刘传朋, 康鹏宇, 赵秀芳, 邓俊, 王凯凯. 山东省沂南县东部土壤重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1173-1182. |
| [5] | 朱英海, 施泽明, 王新宇, 张凯亮, 朱伯丞. 攀西大梁子铅锌矿区水系沉积物重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 923-932. |
| [6] | 郭正材, 郭华明, 魏亮, 高志鹏. 河北保定典型污灌区土壤Cu吸附特性研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 524-532. |
| [7] | 乔雯, 王议, 张德强, 殷秀兰, 白光宇, 何培雍. 某矿区土壤重金属分布特征及来源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 543-551. |
| [8] | 黄勇, 段续川, 袁国礼, 李欢, 张沁瑞. 北京市延庆区土壤重金属元素地球化学特征及其来源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 634-644. |
| [9] | 朱超, 文美兰, 刘攀峰, 陈斌艳, 鲍厚银, 赵银强, 陈昊, 杨奕波. 桂林灵川县典型有机水稻田重金属元素分布特征及污染评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1433-1440. |
| [10] | 李金哲, 刘宁强, 龚庆杰, 李承柱. 广东汕头市内海湾沉积物重金属环境质量调查与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1441-1449. |
| [11] | 成晓梦, 吴超, 孙彬彬, 贺灵, 曾道明. 浙江中部典型黑色岩系分布区土壤-作物富硒特征与重金属风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 425-433. |
| [12] | 唐瑞玲, 王惠艳, 吕许朋, 徐进力, 徐仁廷, 张富贵. 西南重金属高背景区农田系统土壤重金属生态风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 917-927. |
| [13] | 汤世凯, 张杰, 于晓静, 陶志斌, 李金鹏. 山东丁字湾海域沉积物重金属含量、分布及与粒径之间的关系研究[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 928-935. |
| [14] | 赵秀芳, 王艺璇, 张永帅, 王燕燕. 山东安丘地区土壤-小麦系统重金属等元素间的相互作用[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 936-944. |
| [15] | 李博, 杨忠芳, 季文兵, 余涛, 侯青叶, 何海云, 张起钻, 吴天生, 覃建勋. 典型岩溶区硫化物矿床——广西贵港锡基坑铅锌矿开采的生态效应[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 957-969. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||