



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (04): 1078-1087.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.030
唐世琪1( ), 卢振权2(
), 卢振权2( ), 程斌3, 廖泽文3, 刘晖2, 王婷2, 范东稳2, 张富贵1
), 程斌3, 廖泽文3, 刘晖2, 王婷2, 范东稳2, 张富贵1
收稿日期:2019-11-08
修回日期:2020-04-22
出版日期:2021-08-10
发布日期:2021-09-08
通讯作者:
卢振权
作者简介:卢振权,男,研究员,1972年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,从事天然气水合物地质地球化学勘查等研究。Email: luzhq@vip.sina.com。基金资助:
TANG Shiqi1( ), LU Zhenquan2(
), LU Zhenquan2( ), CHENG Bin3, LIAO Zewen3, LIU Hui2, WANG Ting2, FAN Dongwen2, ZHANG Fugui1
), CHENG Bin3, LIAO Zewen3, LIU Hui2, WANG Ting2, FAN Dongwen2, ZHANG Fugui1
Received:2019-11-08
Revised:2020-04-22
Online:2021-08-10
Published:2021-09-08
Contact:
LU Zhenquan
摘要:
南祁连盆地木里坳陷部署的多个天然气水合物钻孔钻遇不同程度的水合物与油气显示伴生现象,指示该地区具有良好的油气勘探前景,有必要对已发现油气显示进行来源分析。由于水合物钻孔深度有限,针对DK-9孔4组油气显示样品,在开展现有烃源岩油源对比基础上,选取中侏罗统、上三叠统各5组代表性低熟烃源岩样品进行热模拟实验,模拟深部烃源岩生、排烃过程,将新生烃类再次与油气显示进行对比,进一步探究油气显示来源。结果显示,油气显示可分为两类(Ⅰ和Ⅱ),第Ⅰ类油气显示遭受生物降解作用,成熟度稍高,第Ⅱ类油气显示成熟度稍低;现有烃源岩主要分为三种类型(Ⅰ—Ⅲ),分别对应深度163.30~207.42 m、 207.42~348.50 m、357.90~586.50 m。结合常规油源对比、热模拟实验与地质条件分析,最终推测第Ⅰ类油气显示主要与第Ⅰ类烃源岩同源;第Ⅱ类油气显示主要与第Ⅱ类烃源岩同源,此外可能还有第Ⅲ类烃源岩或更深层烃源岩的贡献,即其母质来源既与中侏罗统烃源岩有关又与上三叠统烃源岩有关。
中图分类号:
唐世琪, 卢振权, 程斌, 廖泽文, 刘晖, 王婷, 范东稳, 张富贵. 南祁连盆地木里坳陷油气来源分析:基于DK-9孔岩心样品热模拟实验[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 1078-1087.
TANG Shiqi, LU Zhenquan, CHENG Bin, LIAO Zewen, LIU Hui, WANG Ting, FAN Dongwen, ZHANG Fugui. Source Analysis of Oil and Gas Indication in Muli Depression of South Qilian Basin:A Thermal Simulation Case Study of DK-9 Core[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(04): 1078-1087.
| 样品 类型 | 样品编号 | 深度/m | 层位 | 岩性及描述 | 烃源岩 类别 | 样品 类型 | 样品编号 | 深度/m | 层位 | 岩性及描述 | 烃源岩 类别 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 烃 源 岩 | DK9-M-008 | 163.30 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅰ | 烃 源 岩 | DK9-M-36 | 335.70 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅱ |
| DK9-M-10 | 172.10 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅰ | DK9-M-39 | 348.50 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅱ | ||
| DK9-M-12 | 190.00 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅰ | DK9-M-41 | 357.90 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-14 | 199.74 | 中侏罗统 | 深灰色泥岩 | Ⅰ | DK9-M-42 | 375.80 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-16 | 207.42 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅰ | DK9-M-43 | 382.70 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-18 | 227.30 | 中侏罗统 | 深灰色泥岩 | Ⅱ | DK9-M-44 | 405.40 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-21 | 250.20 | 中侏罗统 | 深灰色泥岩 | Ⅱ | DK9-M-48 | 441.00 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-23 | 260.40 | 中侏罗统 | 深灰色泥岩 | Ⅱ | DK9-M-51 | 476.40 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-26 | 273.20 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅱ | DK9-M-53 | 536.50 | 上三叠统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-29 | 285.80 | 中侏罗统 | 深灰-灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅱ | DK9-M-006 | 543.50 | 上三叠统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-31 | 294.60 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅱ | DK9-M-54 | 558.70 | 上三叠统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-33 | 303.72 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅱ | DK9-M-55 | 584.00 | 上三叠统 | 灰黑色含粉砂泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-34 | 326.90 | 中侏罗统 | 深灰-灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅱ | DK9-C-008 | 586.50 | 上三叠统 | 煤 | Ⅲ | ||
| 油气 显示 | DK9-O-01 | 160.51 | 中侏罗统 | 砂岩,褐色油浸 | 油气 显示 | DK9-O-18 | 360.93 | 中侏罗统 | 砂岩,大面积油浸 | ||
| DK9-O-09 | 237.15 | 中侏罗统 | 砂岩,褐色油浸 | DK9-O-19 | 366.90 | 中侏罗统 | 砂岩,大面积油浸 | ||||
表1 DK-9钻孔样品信息
Table 1 Sample information from borehole DK-9
| 样品 类型 | 样品编号 | 深度/m | 层位 | 岩性及描述 | 烃源岩 类别 | 样品 类型 | 样品编号 | 深度/m | 层位 | 岩性及描述 | 烃源岩 类别 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 烃 源 岩 | DK9-M-008 | 163.30 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅰ | 烃 源 岩 | DK9-M-36 | 335.70 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅱ |
| DK9-M-10 | 172.10 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅰ | DK9-M-39 | 348.50 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅱ | ||
| DK9-M-12 | 190.00 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅰ | DK9-M-41 | 357.90 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-14 | 199.74 | 中侏罗统 | 深灰色泥岩 | Ⅰ | DK9-M-42 | 375.80 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-16 | 207.42 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅰ | DK9-M-43 | 382.70 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-18 | 227.30 | 中侏罗统 | 深灰色泥岩 | Ⅱ | DK9-M-44 | 405.40 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-21 | 250.20 | 中侏罗统 | 深灰色泥岩 | Ⅱ | DK9-M-48 | 441.00 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-23 | 260.40 | 中侏罗统 | 深灰色泥岩 | Ⅱ | DK9-M-51 | 476.40 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-26 | 273.20 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅱ | DK9-M-53 | 536.50 | 上三叠统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-29 | 285.80 | 中侏罗统 | 深灰-灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅱ | DK9-M-006 | 543.50 | 上三叠统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-31 | 294.60 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅱ | DK9-M-54 | 558.70 | 上三叠统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-33 | 303.72 | 中侏罗统 | 灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅱ | DK9-M-55 | 584.00 | 上三叠统 | 灰黑色含粉砂泥岩 | Ⅲ | ||
| DK9-M-34 | 326.90 | 中侏罗统 | 深灰-灰黑色泥岩 | Ⅱ | DK9-C-008 | 586.50 | 上三叠统 | 煤 | Ⅲ | ||
| 油气 显示 | DK9-O-01 | 160.51 | 中侏罗统 | 砂岩,褐色油浸 | 油气 显示 | DK9-O-18 | 360.93 | 中侏罗统 | 砂岩,大面积油浸 | ||
| DK9-O-09 | 237.15 | 中侏罗统 | 砂岩,褐色油浸 | DK9-O-19 | 366.90 | 中侏罗统 | 砂岩,大面积油浸 | ||||
| 样品编号 | 深度/m | 层位 | 岩性 | TOC/% | RO/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DK9-M-16 | 207.42 | 泥岩 | 2.96 | 0.83 | |
| DK9-M-26 | 273.20 | 泥岩 | 4.23 | 0.68 | |
| DK9-M-41 | 357.90 | 中侏罗统 | 泥岩 | 18.15 | 0.62 |
| DK9-M-44 | 405.40 | 泥岩 | 0.45 | 0.66 | |
| DK9-M-51 | 476.40 | 泥岩 | 1.50 | 0.62 | |
| DK9-M-53 | 536.50 | 泥岩 | 3.33 | 0.61 | |
| DK9-M-006 | 543.50 | 泥岩 | 2.16 | 0.64 | |
| DK9-M-54 | 558.70 | 上三叠统 | 泥岩 | 0.85 | 0.68 |
| DK9-M-55 | 584.00 | 泥岩 | 2.89 | 0.69 | |
| DK9-C-008 | 586.50 | 煤 | 42.21 | 0.65 |
表2 热模拟实验样品基本特征
Table 2 Characteristics of the samples for the thermalsimulation
| 样品编号 | 深度/m | 层位 | 岩性 | TOC/% | RO/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DK9-M-16 | 207.42 | 泥岩 | 2.96 | 0.83 | |
| DK9-M-26 | 273.20 | 泥岩 | 4.23 | 0.68 | |
| DK9-M-41 | 357.90 | 中侏罗统 | 泥岩 | 18.15 | 0.62 |
| DK9-M-44 | 405.40 | 泥岩 | 0.45 | 0.66 | |
| DK9-M-51 | 476.40 | 泥岩 | 1.50 | 0.62 | |
| DK9-M-53 | 536.50 | 泥岩 | 3.33 | 0.61 | |
| DK9-M-006 | 543.50 | 泥岩 | 2.16 | 0.64 | |
| DK9-M-54 | 558.70 | 上三叠统 | 泥岩 | 0.85 | 0.68 |
| DK9-M-55 | 584.00 | 泥岩 | 2.89 | 0.69 | |
| DK9-C-008 | 586.50 | 煤 | 42.21 | 0.65 |
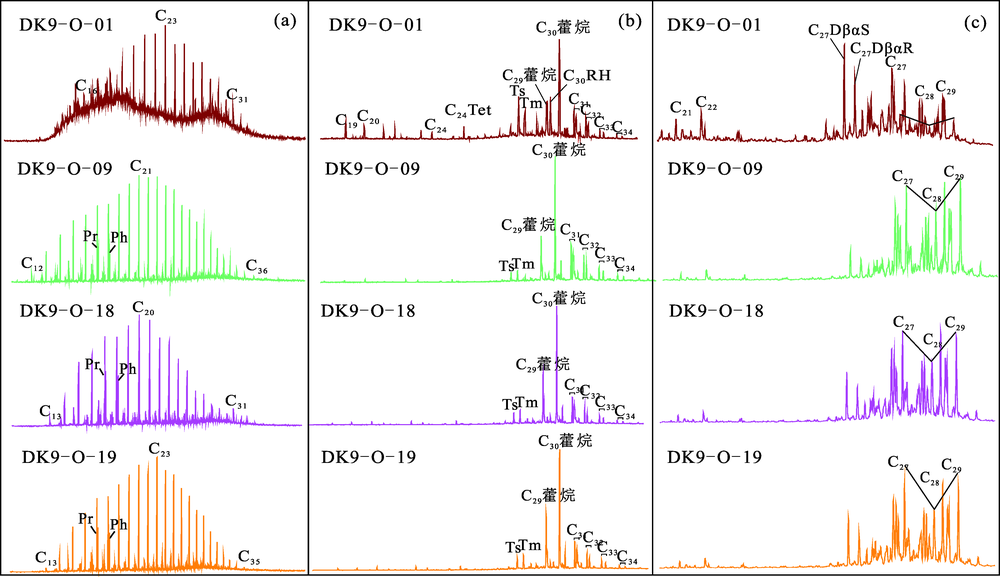
图2 DK-9孔油气显示正构烷烃(a)、萜烷(b)和甾烷(c)特征
Fig.2 Characteristics of N-alkanes (a), terpane (b) and sterane (c) of the oil and gas indications from borehole DK-9
| 样号 | Pr/Ph | Ts/ (Ts+Tm) | C30RH/ C29(H+Ts) | C29(H+Ts)/ C30H | C27D/ C27-29-St | C27αααR/ C27-St | C28αααR/ C28-St | C29αααR/ C29-St | C29-S/ (S+R) | C29-ββ/ (αα+ββ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DK9-O-01 | 1.42 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.78 | 0.32 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.60 | 0.63 |
| DK9-O-09 | 0.92 | 0.44 | 0.09 | 0.46 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.45 | 0.40 |
| DK9-O-18 | 1.06 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 0.58 | 0.09 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.50 | 0.41 |
| DK9-O-19 | 1.11 | 0.41 | 0.07 | 0.60 | 0.09 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.49 | 0.40 |
表3 DK-9孔油气显示的部分生物标志化合物参数
Table 3 Major biomarker compound parameters of oil and gas indications from borehole DK-9
| 样号 | Pr/Ph | Ts/ (Ts+Tm) | C30RH/ C29(H+Ts) | C29(H+Ts)/ C30H | C27D/ C27-29-St | C27αααR/ C27-St | C28αααR/ C28-St | C29αααR/ C29-St | C29-S/ (S+R) | C29-ββ/ (αα+ββ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DK9-O-01 | 1.42 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.78 | 0.32 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.60 | 0.63 |
| DK9-O-09 | 0.92 | 0.44 | 0.09 | 0.46 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.45 | 0.40 |
| DK9-O-18 | 1.06 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 0.58 | 0.09 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.50 | 0.41 |
| DK9-O-19 | 1.11 | 0.41 | 0.07 | 0.60 | 0.09 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.49 | 0.40 |
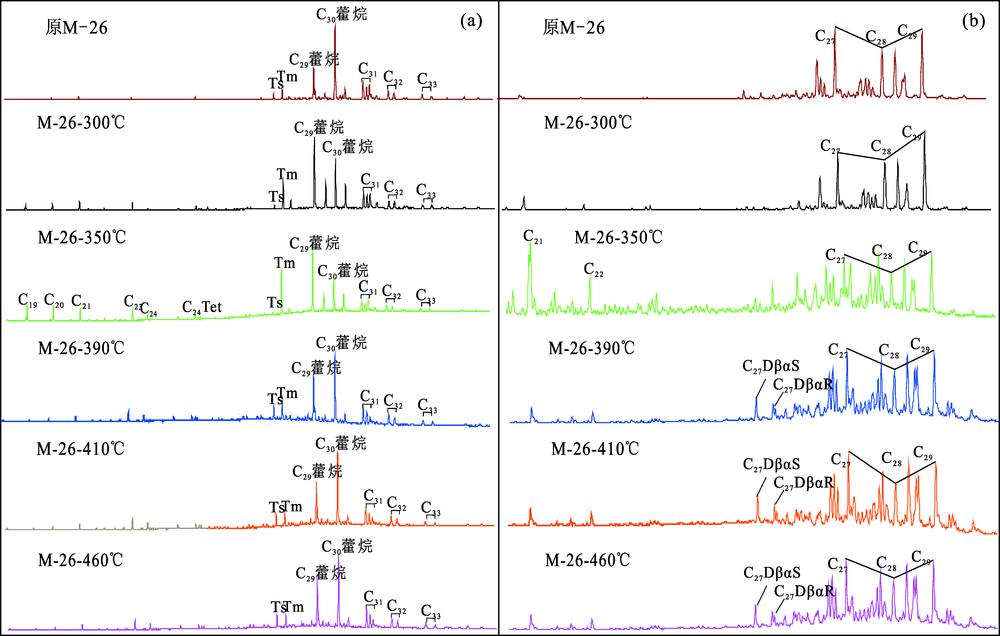
图5 DK-9孔中侏罗统样品在不同温度点下萜烷(a)与甾烷(b)特征
Fig.5 Characteristics of terpane (a) and sterane (b) of the Middle Jurassic samples from borehole DK-9 under different temperatures
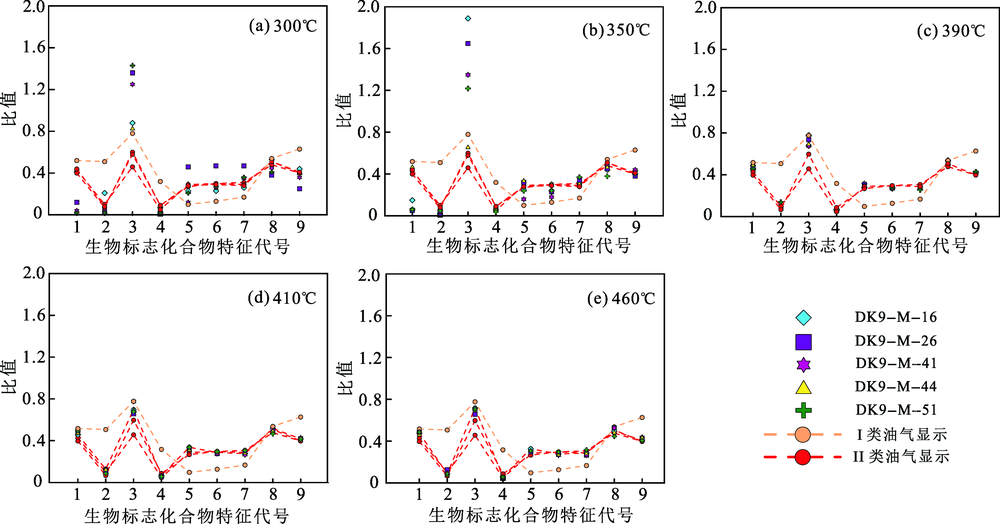
图6 不同温度点下DK-9孔中侏罗统样品与油气显示生标特征对比图 1.Ts/ (Ts+Tm); 2. C30RH /C29(H+Ts); 3. C29(H+Ts) / C30H; 4. C27D/C27-29-St; 5. C27αααR/ C27-St; 6.C28αααR/ C28-St; 7. C29αααR/ C29-St; 8. C29-S/(S+R); 9. C29-ββ/(αα+ββ)
Fig.6 Comparison between biomarker compound characteristics of Middle Jurassic samples and oil/gas indications of borehole DK-9 under different temperatures

图7 DK-9孔上三叠统试验样品在不同温度点下萜烷(a)与甾烷(b)特征
Fig.7 Characteristics of terpane (a) and sterane (b) of the Upper Triassic samples from borehole DK-9 under different temperatures
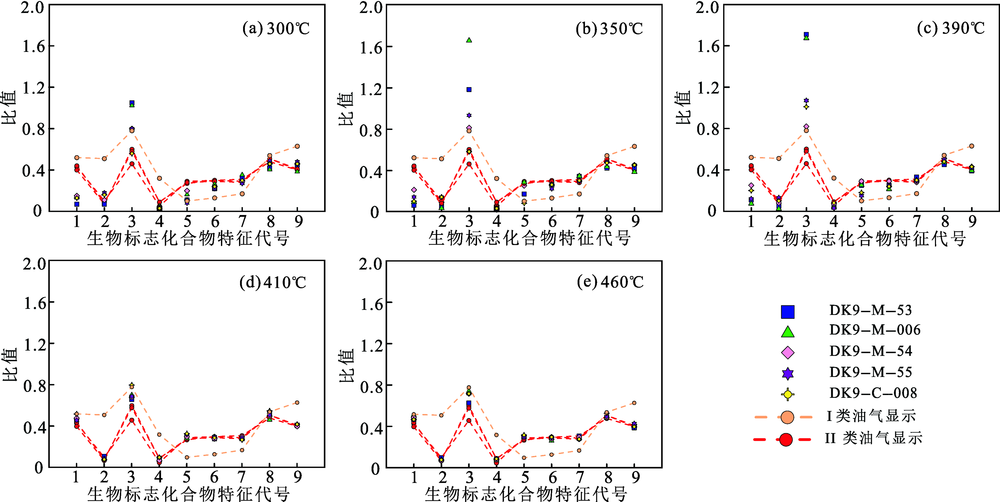
图8 不同温度下DK-9孔上三叠统样品与油气显示生标特征对比图 1.Ts/ (Ts+Tm); 2. C30RH /C29(H+Ts); 3. C29(H+Ts) / C30H; 4.C27D/C27-29-St; 5.C27αααR/ C27-St; 6.C28αααR/ C28-St; 7.C29αααR/ C29-St; 8.C29-S/(S+R); 9. C29-ββ/(αα+ββ)
Fig.8 Comparison between biomarker compound characteristics of the Upper Triassic samples and oil/gas indications the borehole DK-9 under different temperatures
| [1] | 祝有海, 张永勤, 文怀军. 祁连山冻土区天然气水合物科学钻探工程概况[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(12):1816-1822. |
| [2] | 文怀军, 卢振权, 李永红, 等. 青海木里三露天井田天然气水合物调查研究新进展[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(5):983-994. |
| [3] |
LU Z Q, ZHAI G Y, ZUO Y H, et al. The geological process for gas hydrate formation in the Qilian Mountain Permafrost[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology, 2019, 37(13):1566-1581.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LU Z Q, ZHAI G Y, ZHU Y H, et al. New discovery of the permafrost gas hydrate accumulation in Qilian Mountain, China[J]. China Geology, 2018, 1(2):306-307.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 卢振权, 祝有海, 刘晖, 等. 祁连山冻土区含天然气水合物层段的油气显示现象[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(1):231-238. |
| [6] | 卢振权, 唐世琪, 王伟超, 等. 青海木里三露天冻土天然气水合物气源性质研究[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(5):995-1001. |
| [7] | 王伟超, 卢振权, 李永红, 等. 青海木里三露天天然气水合物分布与储层特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(5):1035-1046. |
| [8] | 李永红, 王伟超, 卢振权, 等. 青海木里三露天地区天然气水合物资源量初步评价[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(5):1251-1260. |
| [9] | 唐世琪, 卢振权, 王伟超, 等. 青海木里三露天冻土区天然气水合物钻孔岩心顶空气组成及指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(5):1201-1213. |
| [10] | 唐世琪, 卢振权, 饶竹, 等. 祁连山冻土区天然气水合物岩心顶空气组分与同位素的指示意义——以DK-9孔为例[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(5):961-971. |
| [11] | 卢振权, 翟刚毅, 文怀军, 等. 青海木里三露天冻土区天然气水合物形成与分布地质控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(5), 1002-1013. |
| [12] | 卢振权, 李永红, 王伟超, 等. 青海木里三露天冻土天然气水合物成藏模式研究[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(5):1014-1023. |
| [13] | 吴初国, 何贤杰, 盛昌明, 等. 能源安全综合评价方法探讨[J]. 自然资源学报, 2011, 26(6):964-970. |
| [14] | 符俊辉, 周立发. 南祁连盆地石炭—侏罗纪地层区划及石油地质特征[J]. 西北地质科学, 1998, 19(2):47-54. |
| [15] | 符俊辉, 周立发. 南祁连盆地三叠纪地层及石油地质特征[J]. 西北地质科学, 2000, 21(2):64-72. |
| [16] | 郝爱胜, 李剑, 王东良, 等. 南祁连盆地石炭系与上三叠统尕勒得寺组烃源岩地球化学特征[J]. 非常规油气, 2016, 3(1):7-13. |
| [17] | 唐世琪, 卢振权, 王伟超, 等. 青海木里三露天天然气水合物气源岩有机地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(5):1205-1213. |
| [18] | 任拥军, 纪友亮. 南祁连盆地石炭系可能烃源岩的甾萜烷地球化学特征及意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2000, 22(4):341-345. |
| [19] | 谢其锋, 周立发, 蔡元峰, 等. 南祁连盆地二叠系海相烃源岩地球化学特征及其对物源属性和古环境的约束[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(7):1288-1301. |
| [20] | 谢其锋, 周立发, 马国福, 等. 南祁连盆地三叠系烃源岩有机地球化学特征[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 47(6):1034-1040. |
| [21] | 程青松, 龚建明, 张敏, 等. 祁连山冻土区烃源岩地球化学特征及天然气水合物气源分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(5):139-147. |
| [22] | 张家政, 祝有海, 黄霞, 等. 南祁连盆地木里冻土区天然气水合物烃源岩特征及评价[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(4):634-643. |
| [23] | 龚文强, 张永生, 宋天锐, 等. 南祁连盆地木里坳陷侏罗系烃源岩生烃潜力评价[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2013, 35(3):177-179. |
| [24] |
LU Z Q, XUE X H, LIAO Z W, et al. Source rocks for gases from gas hydrate and their burial depth in the Qilian Mountain Permafrost, Qinghai: Results from thermal stimulation[J]. Energy & Fuels: 2013, 27(12):7233-7244.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 翟刚毅, 卢振权, 卢海龙, 等. 祁连山冻土区天然气水合物成矿系统[J]. 矿物岩石, 2014, 34(4):79-92. |
| [26] | 薛小花, 卢振权, 廖泽文, 等. 祁连山冻土区含天然气水合物层段岩心热模拟实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(2):413-423. |
| [27] |
CHENG B, XU J B, LU Z Q, et al. Hydrocarbon source for oil and gas indication associated with gas hydrate and its significance in the Qilian Mountain permafrost, Qinghai, Northwest China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 89(1):202-215.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 卢振权, 祝有海, 张永勤, 等. 青海省祁连山冻土区天然气水合物基本地质特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(1):182-191. |
| [29] | 周幼吾, 郭东信, 邱国庆, 等. 中国冻土[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000. |
| [30] | 张雪亭, 杨生德. 青海省板块构造研究——1:100 万青海省大地构造图说明书[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007. |
| [31] | 青海省地质矿产局. 青海省岩石地层[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1997. |
| [32] |
MOLDOWAN J M, FAGO F J, CARLSON R M K, et al. Rearranged hopanes in sediments and petroleum[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1991, 55:3333-3353.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
TELNAES N, ISAKSEN G H, FARRIMOND P. Unusual triterpane distributions in lacustrine oils[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1992, 18(6):785-789.
DOI URL |
| [34] | PETERS K E, MOLDOWAN J M. The Biomarker Guide: Interpreting Molecular Fossils in Petroleum and Ancient Sediments[M]. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1993. |
| [35] | PHILIP R P, GILBERT T D. Biomarker distribution in oils predominantly derived from terrigenous source material [M]//LEYTHAEUSER D, RULLKOTTER J. Advances in Organic Geochemistry. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1986:73-84. |
| [36] |
OBERMAJER M, OSADETZ K G, FOWLER M G, et al. Delineating compositional variabilities among crude oils from central Montana, USA,using light hydrocarbon and biomarker characteristics[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2002, 33:1343-1359.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 张文正, 杨华, 侯林慧, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组不同烃源岩17α(H)-重排藿烷的分布及其地质意义[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2009, 52(7):965-974. |
| [38] |
DE LEEUW J M, COX H C, VAN GRASS G, et al. Limited double bond isomerisation and selective hydrogenation of steranes during early diagenesis[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989, 53:903-909.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
MOLDOWAN J M, SUNDARARAMAN P, SCHOELL M. Sensitivity of biomarker properties to depositional environment and/or source input in the lower Toarcian of S.W. Germany[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 10:915-926.
DOI URL |
| [40] | BRINCAT D, ABBOTT G D. Some aspects of the molecular biogeochemistry of laminated and massive rocks from the Naples Beach Section (Santa Barbara-Ventura Basin) [M]//ISAACS C M, RULLKOTTER J. The Monterey Formation: From Rocks to Molecules. Columbia: Columbia University Press, 2001:140-149. |
| [41] | 张水昌, 梁狄刚, 张宝民, 等. 塔里木盆地海相油气的生成[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004. |
| [1] | 张舒, 张赞赞, 胡召齐, 施立胜, 周涛发, 吴明安, 杜建国. 长江中下游成矿带庐枞矿集区花岗岩型铀矿床成矿作用研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1435-1448. |
| [2] | 曹林杰, 张运周, 李四龙, 王志红, 张瑶, 张寒. 北大巴山平利县大坪—金岭重晶石矿床地球化学特征与成矿物源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1497-1502. |
| [3] | 李二庭, 马万云, 李际, 马新星, 潘长春, 曾立飞, 王明. 准噶尔盆地南缘侏罗系煤生烃热模拟实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1313-1323. |
| [4] | 杜保峰, 张荣臻, 杨长青, 李山坡, 谭和勇, 朱红运. 西藏则不吓铅锌矿床硫、铅同位素组成及对成矿物质来源的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1138-1145. |
| [5] | 郑瑞辉, 金霄, 郑铎, 李佳阳, 陈雪, 张枝焕. 基于包裹体信息分析准噶尔盆地柴窝堡凹陷芦草沟组储层油源及成藏期次[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 998-1008. |
| [6] | 朱英海, 施泽明, 王新宇, 张凯亮, 朱伯丞. 攀西大梁子铅锌矿区水系沉积物重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 923-932. |
| [7] | 乔雯, 王议, 张德强, 殷秀兰, 白光宇, 何培雍. 某矿区土壤重金属分布特征及来源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 543-551. |
| [8] | 江瑶, 刘雪敏, 李建亭, 韩志轩, 王燕燕. 铜同位素示踪覆盖区地表土壤的异常来源初探:以福建罗卜岭隐伏铜钼矿床为例[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 624-633. |
| [9] | 黄勇, 段续川, 袁国礼, 李欢, 张沁瑞. 北京市延庆区土壤重金属元素地球化学特征及其来源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 634-644. |
| [10] | 赵保具, 张艳飞, 颜开, 肖荣阁. 大兴安岭中段有色金属矿床成矿物质来源探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1380-1396. |
| [11] | 李金哲, 刘宁强, 龚庆杰, 李承柱. 广东汕头市内海湾沉积物重金属环境质量调查与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1441-1449. |
| [12] | 宿宇驰, 毛小平, 张飞, 毛珂, 卢鹏羽. 沧县隆起北部地温场特征及其主控因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 403-411. |
| [13] | 李朋飞, 刘超, 陶春军, 汪晶, 吴正. 再生铅工业园周边土壤重金属分布特征及来源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 663-671. |
| [14] | 肖晓牛, 费利东, 秦新龙, 肖娥, 刘荣芳. 闽中梅仙铅锌多金属矿区S、Pb同位素组成及对成矿物质的示踪:以丁家山和峰岩铅锌多金属矿为例[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 569-578. |
| [15] | 费利东, 肖晓牛, 肖娥, 刘军, 白涛. 滇中播卡铜矿床硫、铅同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 579-587. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||