



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (01): 74-87.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.004
马佳怡1( ), 谢淑云1(
), 谢淑云1( ), 张默海1, 焦存礼2, 韩俊3, 鲍征宇1, 邬铁4, 张海5
), 张默海1, 焦存礼2, 韩俊3, 鲍征宇1, 邬铁4, 张海5
收稿日期:2018-10-13
修回日期:2019-07-10
出版日期:2020-03-05
发布日期:2020-03-07
通讯作者:
谢淑云
作者简介:谢淑云,女,教授,1976年出生,地球化学专业,主要从事碳酸盐岩储层溶解动力学与覆盖区地球化学找矿及定量地球化学的研究工作。Email: tinaxie@cug.edu.cn。基金资助:
MA Jiayi1( ), XIE Shuyun1(
), XIE Shuyun1( ), ZHANG Mohai1, JIAO Cunli2, HAN Jun3, BAO Zhengyu1, WU Tie4, ZHANG Hai5
), ZHANG Mohai1, JIAO Cunli2, HAN Jun3, BAO Zhengyu1, WU Tie4, ZHANG Hai5
Received:2018-10-13
Revised:2019-07-10
Online:2020-03-05
Published:2020-03-07
Contact:
XIE Shuyun
摘要:
白云岩化流体性质与成岩作用是近年来碳酸盐岩成岩作用研究的热点,研究白云岩的成因有利于进一步认识白云岩储层的形成机制并为优质储层的预测提供依据。通过岩石学、矿物学(X射线衍射)、地球化学(微量元素、稀土元素、碳氧同位素)方法,系统研究湖北秭归地区灯影组不同类型白云岩的成因,并分析了可能的白云岩化模式。样品的微量元素特征显示,秭归地区白云岩未受到陆源碎屑物质的影响,形成于气候干旱、海水咸度较大且氧化的沉积环境中;Sr含量特征显示白云岩发生了较为彻底的白云岩化,其成岩环境为温度较高的埋藏环境,成岩过程中未受到淋滤作用的影响;秭归地区白云岩化流体主要来源于海水。结合蒸发白云岩(萨布哈)及埋藏白云岩化模式解释了秭归地区泥微晶白云岩及晶粒白云岩的形成过程。
中图分类号:
马佳怡, 谢淑云, 张默海, 焦存礼, 韩俊, 鲍征宇, 邬铁, 张海. 湖北秭归地区震旦系灯影组白云岩地球化学特征及其成因意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 74-87.
MA Jiayi, XIE Shuyun, ZHANG Mohai, JIAO Cunli, HAN Jun, BAO Zhengyu, WU Tie, ZHANG Hai. Geochemical Features and Genesis of Dolomite in Sinian Dengying Formation of Zigui Area, Hubei Province[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(01): 74-87.
| 样品编号 | 分类 | 层位 | 晶粒大小/mm | 岩石学特征 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WTZG-4 | 泥微晶白云岩 | 蛤蟆井段 | <0.01 | 泥微晶白云岩,灰白色,含硅质条带 |
| WTZG-11 | 石板滩段 | <0.01 | 泥微晶白云岩 | |
| WTZG-5 | 晶粒白云岩 | 蛤蟆井段 | 0.25~0.50 | 中晶白云岩 |
| WTZG-14 | 蛤蟆井段 | 0.01~0.25 | 粉-细晶白云岩,具平直晶面,半自形晶结构 | |
| WTZG-12 | 石板滩段 | 0.01~0.05 | 粉晶白云岩 | |
| TYZG-3 | 石板滩段 | 0.01~0.05 | 硅质粉晶白云岩,含少量石英脉 | |
| TYZG-17 | 石板滩段 | 0.01~0.05 | 粉晶白云岩,可见缝合线 | |
| TYZG-20 | 石板滩段 | 0.25~1.00 | 中-粗晶白云岩,具非平直晶面,它形晶结构 | |
| WTZG-8 | 白马沱段 | 0.05~0.50 | 细晶白云岩,具非平直晶面,半自形-它形结构 | |
| WTZG-10 | 白马沱段 | 0.25~0.50 | 中晶白云岩,具平直晶面,半自形晶结构 | |
| TYZG-4 | 白马沱段 | 0.05~0.50 | 细-中晶白云岩,具平直晶面,半自形-它形结构 | |
| TYZG-26 | 白马沱段 | 0.05~0.50 | 细-中晶白云岩,具非平直晶面,半自形晶结构 | |
| WTZG-6 | 灰岩 | 石板滩段 | 灰岩,可见较多的方解石脉 | |
| WTZG-13 | 灰岩,含生物碎屑 | |||
| TYZG-18 | 灰岩,方解石碎片定向排列 |
表1 秭归地区灯影组碳酸盐岩样品岩石学特征
Table 1 Petrology characteristics of carbonate samples from Dengying Formation in Zigui
| 样品编号 | 分类 | 层位 | 晶粒大小/mm | 岩石学特征 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WTZG-4 | 泥微晶白云岩 | 蛤蟆井段 | <0.01 | 泥微晶白云岩,灰白色,含硅质条带 |
| WTZG-11 | 石板滩段 | <0.01 | 泥微晶白云岩 | |
| WTZG-5 | 晶粒白云岩 | 蛤蟆井段 | 0.25~0.50 | 中晶白云岩 |
| WTZG-14 | 蛤蟆井段 | 0.01~0.25 | 粉-细晶白云岩,具平直晶面,半自形晶结构 | |
| WTZG-12 | 石板滩段 | 0.01~0.05 | 粉晶白云岩 | |
| TYZG-3 | 石板滩段 | 0.01~0.05 | 硅质粉晶白云岩,含少量石英脉 | |
| TYZG-17 | 石板滩段 | 0.01~0.05 | 粉晶白云岩,可见缝合线 | |
| TYZG-20 | 石板滩段 | 0.25~1.00 | 中-粗晶白云岩,具非平直晶面,它形晶结构 | |
| WTZG-8 | 白马沱段 | 0.05~0.50 | 细晶白云岩,具非平直晶面,半自形-它形结构 | |
| WTZG-10 | 白马沱段 | 0.25~0.50 | 中晶白云岩,具平直晶面,半自形晶结构 | |
| TYZG-4 | 白马沱段 | 0.05~0.50 | 细-中晶白云岩,具平直晶面,半自形-它形结构 | |
| TYZG-26 | 白马沱段 | 0.05~0.50 | 细-中晶白云岩,具非平直晶面,半自形晶结构 | |
| WTZG-6 | 灰岩 | 石板滩段 | 灰岩,可见较多的方解石脉 | |
| WTZG-13 | 灰岩,含生物碎屑 | |||
| TYZG-18 | 灰岩,方解石碎片定向排列 |

图2 秭归地区灯影组碳酸盐岩样品显微照片 (a)—(d)为晶粒白云岩,(e)和(f)为泥晶白云岩,(g)和(h)为灰岩;(a)WTZG-14;(b)WTZG-8;(c)TYZG-4;(d)TYZG-20;(e)、(f)WTZG-11;(g)、(h)WTZG-13
Fig.2 Micrographs of carbonate samples from Dengying Formation in Zigui
| 样品编号 | 层位 | 岩石名称 | 白云石/% | 方解石/% | 石英/% | 有序度 | d(104) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WTZG-4 | 蛤蟆井段 | 泥微晶白云岩 | 90.74 | - | 9.26 | 0.98 | 2.882 1 |
| WTZG-5 | 中晶白云岩 | 92.36 | - | 7.64 | 0.98 | 2.881 6 | |
| WTZG-14 | 粉-细晶白云岩 | 99.89 | 0.11 | - | 0.95 | 2.880 1 | |
| WTZG-6 | 石板滩段 | 灰岩 | 9.81 | 85.53 | 4.66 | - | - |
| WTZG-11 | 泥微晶白云岩 | 100.00 | - | - | 0.95 | 2.877 7 | |
| WTZG-12 | 粉晶白云岩 | 99.55 | - | 0.45 | 0.95 | 2.874 1 | |
| WTZG-13 | 灰岩 | 0.12 | 96.47 | 3.41 | - | - | |
| TYZG-3 | 硅质粉晶白云岩 | 36.66 | 63.34 | - | - | 2.880 3 | |
| TYZG-17 | 粉晶白云岩 | 99.65 | - | 0.35 | 0.95 | 2.875 9 | |
| TYZG-18 | 灰岩 | 0.18 | 86.28 | 13.55 | - | - | |
| TYZG-20 | 中-粗晶白云岩 | 100.00 | - | - | 0.95 | 2.873 2 | |
| WTZG-8 | 白马沱段 | 细-中晶白云岩 | 100.00 | - | - | 0.95 | 2.880 2 |
| WTZG-10 | 中晶白云岩 | 99.87 | - | 0.13 | 0.95 | 2.873 9 | |
| TYZG-4 | 细-中晶白云岩 | 95.37 | 3.08 | 1.56 | 0.95 | 2.880 6 | |
| TYZG-26 | 细-中晶白云岩 | 100.00 | - | - | 0.95 | 2.873 9 |
表2 秭归地区灯影组碳酸盐岩XRD矿物含量及有序度
Table 2 XRD mineral contents and ordinal degree data of carbonate samples from Dengying Formation in Zigui
| 样品编号 | 层位 | 岩石名称 | 白云石/% | 方解石/% | 石英/% | 有序度 | d(104) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WTZG-4 | 蛤蟆井段 | 泥微晶白云岩 | 90.74 | - | 9.26 | 0.98 | 2.882 1 |
| WTZG-5 | 中晶白云岩 | 92.36 | - | 7.64 | 0.98 | 2.881 6 | |
| WTZG-14 | 粉-细晶白云岩 | 99.89 | 0.11 | - | 0.95 | 2.880 1 | |
| WTZG-6 | 石板滩段 | 灰岩 | 9.81 | 85.53 | 4.66 | - | - |
| WTZG-11 | 泥微晶白云岩 | 100.00 | - | - | 0.95 | 2.877 7 | |
| WTZG-12 | 粉晶白云岩 | 99.55 | - | 0.45 | 0.95 | 2.874 1 | |
| WTZG-13 | 灰岩 | 0.12 | 96.47 | 3.41 | - | - | |
| TYZG-3 | 硅质粉晶白云岩 | 36.66 | 63.34 | - | - | 2.880 3 | |
| TYZG-17 | 粉晶白云岩 | 99.65 | - | 0.35 | 0.95 | 2.875 9 | |
| TYZG-18 | 灰岩 | 0.18 | 86.28 | 13.55 | - | - | |
| TYZG-20 | 中-粗晶白云岩 | 100.00 | - | - | 0.95 | 2.873 2 | |
| WTZG-8 | 白马沱段 | 细-中晶白云岩 | 100.00 | - | - | 0.95 | 2.880 2 |
| WTZG-10 | 中晶白云岩 | 99.87 | - | 0.13 | 0.95 | 2.873 9 | |
| TYZG-4 | 细-中晶白云岩 | 95.37 | 3.08 | 1.56 | 0.95 | 2.880 6 | |
| TYZG-26 | 细-中晶白云岩 | 100.00 | - | - | 0.95 | 2.873 9 |
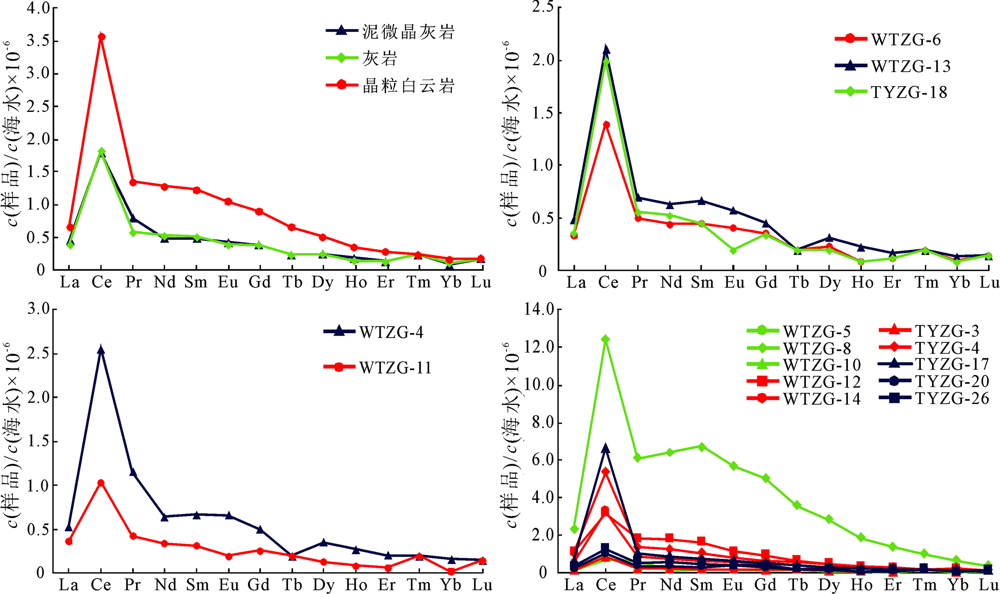
图3 秭归地区灯影组碳酸盐岩样品海水标准化稀土元素配分模式 (a)三种类型碳酸盐岩样品;(b)灰岩;(c)泥微晶白云岩;(d)晶粒白云岩
Fig.3 Seawater-normalized REE distribution patterns of carbonate samples from Dengying Formation in Zigui

图4 秭归地区灯影组白云岩海水标准化的δPr-δCe相关性图(据文献[45]修改) δCe =(Ce/Ce*)N=2×CeN/(La+Pr)N,δPr=(Pr/Pr*)N=2×PrN/(Ce+Nd)N。假设不存在PrN和NdN异常,则(Pr/Pr*)N<1,存在CeN正异常;(Ce/Ce*)N>1,存在LaN负异常
Fig.4 Seawater-normalized δCe vs. δPr diagram of dolomite from Dengying Formation in Zigui (modified from reference [45])
| 样品 | Cu | Sr | Mo | Ba | Th | U | Zr | Hf | V | Sc | V/Sc | Sr/Ba | Sr/Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WTZG-4 | 1.46 | 93.10 | 0.09 | 23.20 | 0.12 | 0.36 | 2.14 | 0.06 | 2.38 | 0.22 | 10.82 | 4.01 | 63.77 |
| WTZG-5 | 0.77 | 89.50 | 0.10 | 7.84 | <0.05 | 0.63 | 0.92 | <0.05 | 3.19 | 0.10 | 31.90 | 11.42 | 116.23 |
| WTZG-6 | 1.01 | 1 323.00 | 0.14 | 20.60 | 0.08 | 1.76 | 1.51 | <0.05 | 7.22 | <0.05 | 288.80 | 64.22 | 1 309.90 |
| WTZG-8 | 1.22 | 99.60 | 1.00 | 457.00 | <0.05 | 7.73 | 1.99 | <0.05 | 29.00 | <0.05 | 1 160.00 | 0.22 | 81.64 |
| WTZG-10 | 0.35 | 32.10 | 0.11 | 3.28 | <0.05 | 0.26 | 0.14 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 1.00 | 9.79 | 91.71 |
| WTZG-11 | 0.73 | 39.80 | 0.12 | 4.88 | <0.05 | 0.93 | 0.39 | <0.05 | 2.05 | <0.05 | 82.00 | 8.16 | 54.52 |
| WTZG-12 | 1.86 | 47.30 | 0.17 | 5.49 | 0.15 | 0.76 | 2.10 | 0.06 | 4.26 | 0.34 | 12.53 | 8.62 | 25.43 |
| WTZG-13 | 1.82 | 1 360.0 | 0.19 | 9.25 | 0.12 | 3.78 | 2.21 | <0.05 | 9.02 | <0.05 | 360.80 | 147.03 | 747.25 |
| WTZG-14 | 4.52 | 77.90 | 0.11 | 6.04 | 0.28 | 0.61 | 2.42 | 0.06 | 5.47 | <0.05 | 218.80 | 12.90 | 17.23 |
| TYZG-3 | 1.06 | 52.60 | 0.20 | 21.10 | 0.07 | 0.82 | 2.57 | 0.05 | 4.27 | 2.35 | 1.82 | 2.49 | 49.62 |
| TYZG-4 | 2.08 | 92.40 | 0.22 | 132.00 | 0.88 | 4.40 | 11.8 | 0.15 | 85.4 | 3.35 | 25.49 | 0.70 | 44.42 |
| TYZG-17 | 1.79 | 76.20 | 0.30 | 8.87 | 0.67 | 2.23 | 4.70 | 0.11 | 6.60 | 3.34 | 1.98 | 8.59 | 42.57 |
| TYZG-18 | 1.06 | 1 663.00 | 0.18 | 11.00 | 0.11 | 1.34 | 1.59 | <0.05 | 7.03 | 2.49 | 2.82 | 151.18 | 1 568.87 |
| TYZG-20 | 0.21 | 34.00 | 0.05 | 2.43 | <0.05 | 0.34 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 2.54 | 0.07 | 13.99 | 161.90 |
| TYZG-26 | 0.10 | 40.00 | <0.05 | 2.31 | <0.05 | 0.17 | 0.49 | <0.05 | 0.13 | 3.10 | 0.04 | 17.32 | 400.00 |
| 灰岩(n=3) | 1.30 | 1 448.67 | 0.17 | 13.62 | 0.10 | 2.29 | 1.77 | 0.03 | 7.76 | 0.85 | 9.16 | 106.39 | 1 117.22 |
| 泥微晶白云岩 (n=2) | 1.10 | 66.45 | 0.11 | 14.04 | 0.07 | 0.65 | 1.27 | 0.04 | 2.22 | 0.12 | 18.08 | 4.73 | 60.68 |
| 晶粒白云岩 (n=10) | 1.40 | 64.16 | 0.23 | 64.64 | 0.22 | 1.80 | 2.74 | 0.06 | 13.85 | 1.52 | 9.12 | 0.99 | 45.96 |
| 大陆上地壳 | 28.00 | 320.00 | 1.10 | 624.00 | 10.50 | 2.70 | 193.00 | 5.30 | 97.00 | 14.00 | 6.93 | 0.51 | 11.43 |
表3 秭归地区灯影组碳酸盐岩微量元素测试结果(μg/g)
Table 3 Trace element analysis results of carbonate samples from Dengying Formation in Zigui (μg/g)
| 样品 | Cu | Sr | Mo | Ba | Th | U | Zr | Hf | V | Sc | V/Sc | Sr/Ba | Sr/Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WTZG-4 | 1.46 | 93.10 | 0.09 | 23.20 | 0.12 | 0.36 | 2.14 | 0.06 | 2.38 | 0.22 | 10.82 | 4.01 | 63.77 |
| WTZG-5 | 0.77 | 89.50 | 0.10 | 7.84 | <0.05 | 0.63 | 0.92 | <0.05 | 3.19 | 0.10 | 31.90 | 11.42 | 116.23 |
| WTZG-6 | 1.01 | 1 323.00 | 0.14 | 20.60 | 0.08 | 1.76 | 1.51 | <0.05 | 7.22 | <0.05 | 288.80 | 64.22 | 1 309.90 |
| WTZG-8 | 1.22 | 99.60 | 1.00 | 457.00 | <0.05 | 7.73 | 1.99 | <0.05 | 29.00 | <0.05 | 1 160.00 | 0.22 | 81.64 |
| WTZG-10 | 0.35 | 32.10 | 0.11 | 3.28 | <0.05 | 0.26 | 0.14 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 1.00 | 9.79 | 91.71 |
| WTZG-11 | 0.73 | 39.80 | 0.12 | 4.88 | <0.05 | 0.93 | 0.39 | <0.05 | 2.05 | <0.05 | 82.00 | 8.16 | 54.52 |
| WTZG-12 | 1.86 | 47.30 | 0.17 | 5.49 | 0.15 | 0.76 | 2.10 | 0.06 | 4.26 | 0.34 | 12.53 | 8.62 | 25.43 |
| WTZG-13 | 1.82 | 1 360.0 | 0.19 | 9.25 | 0.12 | 3.78 | 2.21 | <0.05 | 9.02 | <0.05 | 360.80 | 147.03 | 747.25 |
| WTZG-14 | 4.52 | 77.90 | 0.11 | 6.04 | 0.28 | 0.61 | 2.42 | 0.06 | 5.47 | <0.05 | 218.80 | 12.90 | 17.23 |
| TYZG-3 | 1.06 | 52.60 | 0.20 | 21.10 | 0.07 | 0.82 | 2.57 | 0.05 | 4.27 | 2.35 | 1.82 | 2.49 | 49.62 |
| TYZG-4 | 2.08 | 92.40 | 0.22 | 132.00 | 0.88 | 4.40 | 11.8 | 0.15 | 85.4 | 3.35 | 25.49 | 0.70 | 44.42 |
| TYZG-17 | 1.79 | 76.20 | 0.30 | 8.87 | 0.67 | 2.23 | 4.70 | 0.11 | 6.60 | 3.34 | 1.98 | 8.59 | 42.57 |
| TYZG-18 | 1.06 | 1 663.00 | 0.18 | 11.00 | 0.11 | 1.34 | 1.59 | <0.05 | 7.03 | 2.49 | 2.82 | 151.18 | 1 568.87 |
| TYZG-20 | 0.21 | 34.00 | 0.05 | 2.43 | <0.05 | 0.34 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 2.54 | 0.07 | 13.99 | 161.90 |
| TYZG-26 | 0.10 | 40.00 | <0.05 | 2.31 | <0.05 | 0.17 | 0.49 | <0.05 | 0.13 | 3.10 | 0.04 | 17.32 | 400.00 |
| 灰岩(n=3) | 1.30 | 1 448.67 | 0.17 | 13.62 | 0.10 | 2.29 | 1.77 | 0.03 | 7.76 | 0.85 | 9.16 | 106.39 | 1 117.22 |
| 泥微晶白云岩 (n=2) | 1.10 | 66.45 | 0.11 | 14.04 | 0.07 | 0.65 | 1.27 | 0.04 | 2.22 | 0.12 | 18.08 | 4.73 | 60.68 |
| 晶粒白云岩 (n=10) | 1.40 | 64.16 | 0.23 | 64.64 | 0.22 | 1.80 | 2.74 | 0.06 | 13.85 | 1.52 | 9.12 | 0.99 | 45.96 |
| 大陆上地壳 | 28.00 | 320.00 | 1.10 | 624.00 | 10.50 | 2.70 | 193.00 | 5.30 | 97.00 | 14.00 | 6.93 | 0.51 | 11.43 |
| 样品号 | 岩性 | δ18O/‰ | δ13C/‰ | Z |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WTZG-6 | 灰岩 | -10.4 | 3.7 | 129.70 |
| WTZG-13 | 灰岩 | -8.5 | 1.9 | 126.96 |
| TYZG-18 | 灰岩 | -7.3 | 2.9 | 129.60 |
| WTZG-4 | 泥微晶白云岩 | -7.3 | -1.0 | 121.62 |
| WTZG-11 | 泥微晶白云岩 | -7.4 | 1.0 | 125.66 |
| WTZG-5 | 晶粒白云岩 | -7.3 | 4.1 | 132.06 |
| WTZG-8 | 晶粒白云岩 | -7.5 | 0.1 | 123.77 |
| WTZG-10 | 晶粒白云岩 | -8.5 | 1.9 | 126.96 |
| WTZG-14 | 晶粒白云岩 | -3.9 | 2.6 | 130.68 |
| WTZG-12 | 晶粒白云岩 | -8.5 | -5.3 | 112.21 |
| TYZG-3 | 晶粒白云岩 | -7.3 | 3.0 | 129.81 |
| TYZG-4 | 晶粒白云岩 | -7.7 | -1.3 | 120.80 |
| TYZG-17 | 晶粒白云岩 | -8.1 | 1.6 | 126.54 |
| TYZG-20 | 晶粒白云岩 | -6.4 | 2.2 | 128.62 |
| TYZG-26 | 晶粒白云岩 | -7.0 | 3.2 | 130.37 |
表4 秭归地区灯影组白云岩碳、氧同位素测试结果及Z值
Table 4 C-O isotope results and Z value of dolomite samples from Dengying Formation in Zigui
| 样品号 | 岩性 | δ18O/‰ | δ13C/‰ | Z |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WTZG-6 | 灰岩 | -10.4 | 3.7 | 129.70 |
| WTZG-13 | 灰岩 | -8.5 | 1.9 | 126.96 |
| TYZG-18 | 灰岩 | -7.3 | 2.9 | 129.60 |
| WTZG-4 | 泥微晶白云岩 | -7.3 | -1.0 | 121.62 |
| WTZG-11 | 泥微晶白云岩 | -7.4 | 1.0 | 125.66 |
| WTZG-5 | 晶粒白云岩 | -7.3 | 4.1 | 132.06 |
| WTZG-8 | 晶粒白云岩 | -7.5 | 0.1 | 123.77 |
| WTZG-10 | 晶粒白云岩 | -8.5 | 1.9 | 126.96 |
| WTZG-14 | 晶粒白云岩 | -3.9 | 2.6 | 130.68 |
| WTZG-12 | 晶粒白云岩 | -8.5 | -5.3 | 112.21 |
| TYZG-3 | 晶粒白云岩 | -7.3 | 3.0 | 129.81 |
| TYZG-4 | 晶粒白云岩 | -7.7 | -1.3 | 120.80 |
| TYZG-17 | 晶粒白云岩 | -8.1 | 1.6 | 126.54 |
| TYZG-20 | 晶粒白云岩 | -6.4 | 2.2 | 128.62 |
| TYZG-26 | 晶粒白云岩 | -7.0 | 3.2 | 130.37 |
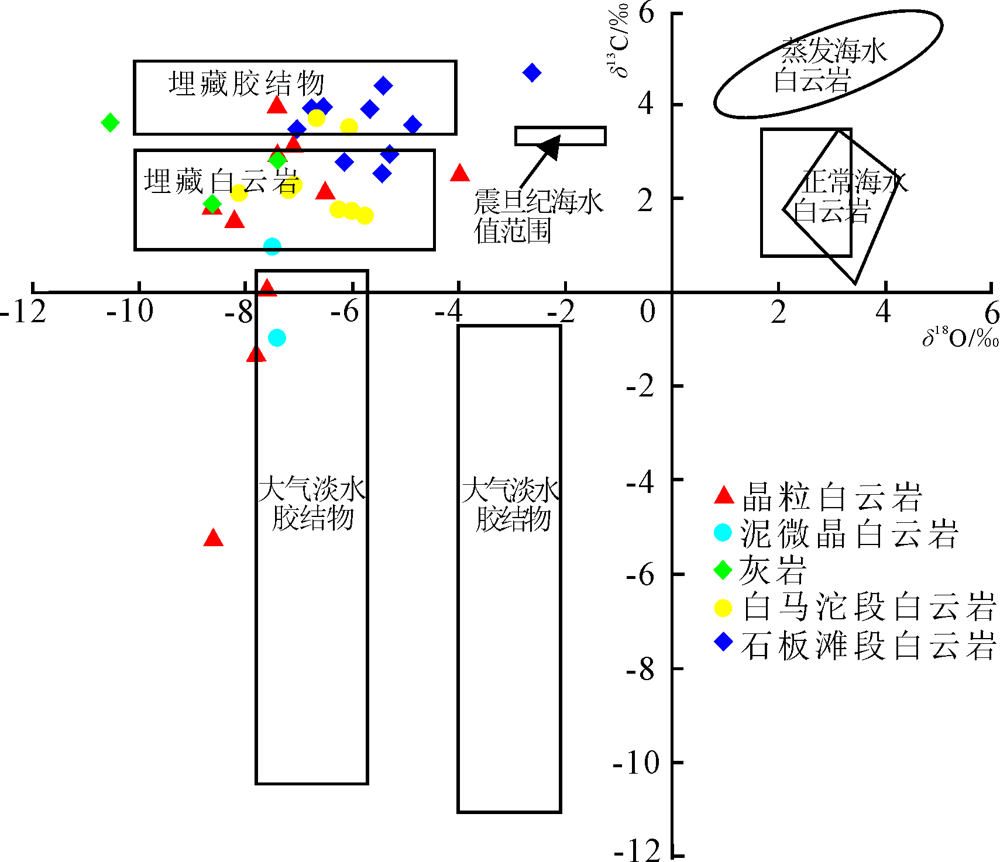
图5 秭归地区灯影组碳酸盐岩C、O同位素特征与成岩环境(据陈梅等[59]修改)
Fig. 5 C-O isotopic characteristics and diagenetic environment of carbonates from Dengying Formation in Zigui(modified from reference[59])
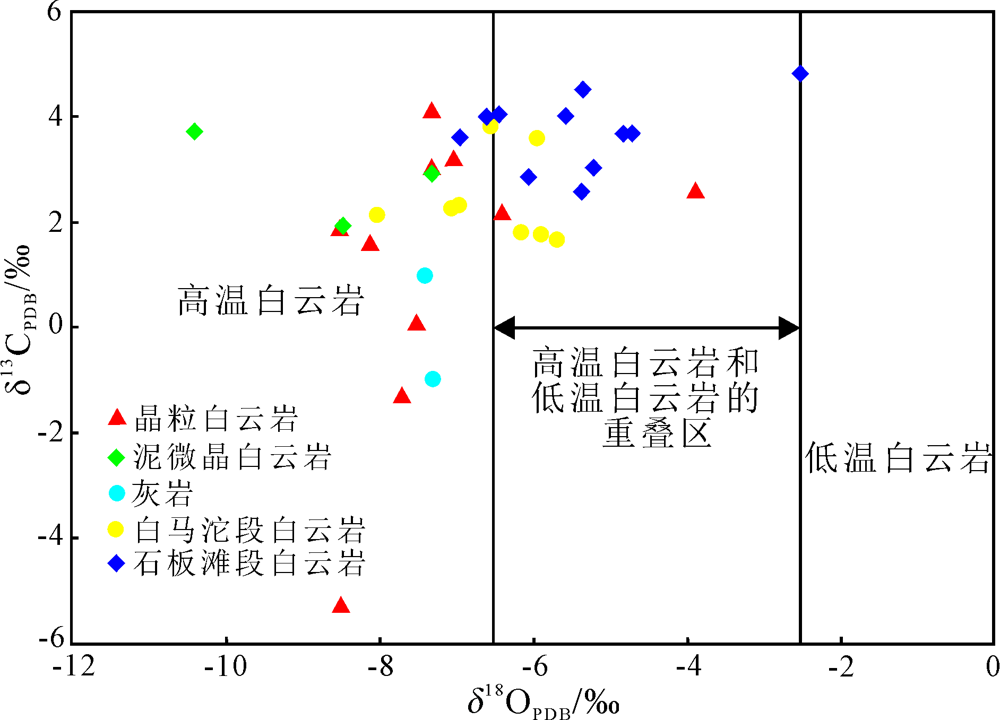
图6 秭归地区灯影组碳酸盐岩高温白云岩和低温白云岩交会图(据文献[63]修改)
Fig.6 High-temperature dolomite and low-temperature dolomite intersection diagram of carbonates from Dengying Formation in Zigui (modified from reference [63])
| 成因参数 | 泥微晶白云岩 | 晶粒白云岩 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 岩石结构 | 泥微晶结构 | 晶粒结构(粉-细- 中-粗晶) | |
| 晶体形态 | 多为半自形-它形,平直晶面-非平直晶面 | ||
| 有序度 | 0.97 | 0.96 | |
| 微量 元素 | Sr/10-6 | 66.45 | 64.93 |
| U/10-6 | 0.65 | 1.80 | |
| Mo/10-6 | 0.11 | 0.23 | |
| V/Sc | 18.08 | 9.12 | |
| Sr/Ba | 4.73 | 0.99 | |
| Sr/Cu | 60.68 | 45.96 | |
| δCe | 2.86 | 4.32 | |
| δEu | 0.99 | 0.93 | |
| δ13C/‰ | 0 | 1.20 | |
| δ18O/‰ | -7.35 | -7.20 | |
表5 秭归地区灯影组不同类型白云岩成因参数
Table 5 Genetic parameters of different types of dolomite from Dengying Formation in Zigui
| 成因参数 | 泥微晶白云岩 | 晶粒白云岩 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 岩石结构 | 泥微晶结构 | 晶粒结构(粉-细- 中-粗晶) | |
| 晶体形态 | 多为半自形-它形,平直晶面-非平直晶面 | ||
| 有序度 | 0.97 | 0.96 | |
| 微量 元素 | Sr/10-6 | 66.45 | 64.93 |
| U/10-6 | 0.65 | 1.80 | |
| Mo/10-6 | 0.11 | 0.23 | |
| V/Sc | 18.08 | 9.12 | |
| Sr/Ba | 4.73 | 0.99 | |
| Sr/Cu | 60.68 | 45.96 | |
| δCe | 2.86 | 4.32 | |
| δEu | 0.99 | 0.93 | |
| δ13C/‰ | 0 | 1.20 | |
| δ18O/‰ | -7.35 | -7.20 | |
| [1] | ZENGLER D H, DUNHAM J D, ETHINGTON R L. Concepts and Models of Dolomitization[M]. Tulsa:Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, 1980: 285-286. |
| [2] | SUN S Q. A reappraisal of dolomite abundance and occurrence in the Phanerozoic[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1994,64(7):396-404. |
| [3] | 马锋, 杨柳明, 顾家裕, 等. 世界白云岩油气田勘探综述[J]. 沉积学报, 2011,29(5):1010-1021. |
| [4] | 苏中堂. 鄂尔多斯盆地古隆起周缘马家沟组白云岩成因及成岩系统研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2011. |
| [5] | 罗平, 张静, 刘伟, 等. 中国海相碳酸盐岩油气储层基本特征[J]. 地学前缘, 2008,15(1):36-50. |
| [6] | 吴仕强, 朱井泉, 胡文瑄, 等. 塔里木盆地寒武系—奥陶系白云岩稀土元素特征及其成因意义[J]. 现代地质, 2009,23(4):638-647. |
| [7] | KENWARD P A, GOLDSTEIN R H, BROOKFIELD A E, et al. Model for how microbial methane generation can preserve early porosity in dolomite and limestone reservoirs[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012,96(3):399-413. |
| [8] | ZHAO W Z, SHEN A J, ZHENG J F, et al. The porosity origin of dolostone reservoirs in the Tarim, Sichuan and Ordos basins and its implication to reservoir prediction[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2014,57(10):2498-2511. |
| [9] | 姚根顺, 郝毅, 周进高, 等. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组储层储集空间的形成与演化[J]. 天然气工业, 2014,34(3):31-37. |
| [10] | 马永生, 郭旭升, 郭彤楼, 等. 四川盆地普光大型气田的发现与勘探启示[J]. 地质论评, 2005,51(4):477-480. |
| [11] | CHEN W. Discussing again on the source of Sinian gas pool in Weiyuan gas field in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 1992,12(6):28-32. |
| [12] | 王爱, 钟大康, 党录瑞, 等. 川东地区震旦系灯影组储层特征及其控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2015,29(6):1398-1408. |
| [13] | 邹才能, 杜金虎, 徐春春, 等. 四川盆地震旦系—寒武系特大型气田形成分布、资源潜力及勘探发现[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014,41(3):278-293. |
| [14] | 魏国齐, 王志宏, 李剑, 等. 四川盆地震旦系、寒武系烃源岩特征、资源潜力与勘探方向[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017,28(1):1-13. |
| [15] | 刘树根, 黄文明, 张长俊, 等. 四川盆地白云岩成因的研究现状及存在问题[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2008,20(2):6-15. |
| [16] | 郭战峰, 陈绵琨, 付宜兴, 等. 鄂西渝东地区震旦、寒武系天然气成藏条件[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2008,30(4):39-42. |
| [17] | 胡晓凤. 湘鄂西地区油气藏类型及勘探方向[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2002,23(3):300-302. |
| [18] | 陈洪德, 庞林, 倪新锋, 等. 中上扬子地区海相油气勘探前景[J]. 石油实验地质, 2007,29(1):13-18. |
| [19] | 王自强, 尹崇玉, 高林志, 等. 湖北宜昌峡东地区震旦系层型剖面化学地层特征及其国际对比[J]. 地质论评, 2002,48(4):408-415. |
| [20] | 杨剑, 丁莲芳. 湖北秭归庙河震旦系陡山沱组—灯影组界线层元素地球化学异常[J]. 地质学报, 1998,72(2):96. |
| [21] | 杨剑, 丁莲芳, 李勇. 湖北秭归庙河震旦系陡山沱组—灯影组界线层内微球粒的发现及意义[J]. 成都理工学院学报, 2000,27(1):22-25. |
| [22] | 张林, 李建明, 万琳. 宜昌莲沱上震旦统灯影组沉积相与储层特征分析[J]. 油气地球物理, 2009,7(4):34-37. |
| [23] | 李旭兵, 王传尚, 刘安. 雪峰山西侧秭归—五峰段海相层系油气地质条件研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2009,31(2):197-201. |
| [24] | 李嵘, 张娣, 赵瞻, 等. 雪峰山西侧重点白云岩储层成岩、储集特征及质量影响因素[J]. 地质通报, 2012,31(11):1852-1861. |
| [25] | 张学丰, 刘波, 蔡忠贤, 等. 白云岩化作用与碳酸盐岩储层物性[J]. 地质科技情报, 2010,29(3):79-85. |
| [26] | 白晓, 凌文黎, 段瑞春, 等. 扬子克拉通核部中元古代—古生代沉积地层Nd同位素演化特征及其地质意义[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2011,41(7):972-983. |
| [27] | 颜丹平, 汪新文, 刘友元. 川鄂湘边区褶皱构造样式及其成因机制分析[J]. 现代地质, 2000,14(1):37-43. |
| [28] | 徐大良, 彭练红, 刘浩, 等. 黄陵背斜中新生代多期次隆升的构造-沉积响应[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2013,29(2):90-99. |
| [29] | 熊成云, 韦昌山, 金光富, 等. 鄂西黄陵背斜地区前南华纪古构造格架及主要地质事件[J]. 地质力学学报, 2004,10(2):97-112. |
| [30] | 毛琼, 邹光富, 张洪茂, 等. 四川盆地动力学演化与油气前景探讨[J]. 天然气工业, 2006,26(11):7-10. |
| [31] | 赵自强. 长江三峡地区生物地层学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1985: 68-79. |
| [32] | 谌刚, 严春杰, 寿瑾枫, 等. 蒙脱石X射线衍射定量分析方法影响因素研究[J]. 非金属矿, 2011,34(1):60-62. |
| [33] | 刘晔, 柳小明, 胡兆初, 等. ICP-MS测定地质样品中37个元素的准确度和长期稳定性分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(5):1203-1210. |
| [34] | 蔡俊军, 卢振权, 孙青, 等. 祁连山冻土区天然气水合物伴生碳酸盐C、O 同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2013,27(6):1356-1364. |
| [35] | 胡俊杰, 李琦, 陈若瑜, 等. 羌塘盆地中、下二叠统碳酸盐岩白云石有序度控制因素研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 2014,34(2):91-95. |
| [36] | 彭俊. 川东南地区震旦系灯影组储层特征研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2010. |
| [37] | 朱同兴, 黄志英. 地质记录中的海水白云岩化作用[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 1993,13(5):16-26. |
| [38] | HECHT L, FREIBERGER R, GILG H A, et al. Rare earth element and isotope (C, O, Sr) characteristics of hydrothermal carbonates: genetic implications for dolomite-hosted talc mineralization at Gopfersgrun (Fichtelgebirge, Germany)[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999,155(1/2):115-130. |
| [39] | WANG L, HU W, WANG X, et al. Seawater normalized REE patterns of dolomites in Geshan and Panlongdong sections, China: Implications for tracing dolomitization and diagenetic fluids[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014,56(3):63-73. |
| [40] | KAWABE I, TORIUMI T, OHTA A, et al. Monoisotopic REE abundances in seawater and the origin of seawater tetrad effect[J]. Geochemical Journal, 1998,32:213-229. |
| [41] | LEYBOURNE M I, JOHANNESSON K H. Rare earth elements (REE) and yttrium in stream waters, stream sediments, and Fe-Mn oxyhydroxides: Fractionation, speciation, and controls over REE plus Y patterns in the surface environment[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2008,72:5962-5983. |
| [42] | 胡文瑄, 陈琪, 王小林, 等. 白云岩储层形成演化过程中不同流体作用的稀土元素判别模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2010,31(6):810-818. |
| [43] | QING H U, MOUNTJOY E W. Rare-earth element geochemistry of dolomites in the Middle Devonian Presqu’ile barrier, Western Canada Sedimentary Basin: implications for fluid-rock ratios during dolomitization[J]. Sedimentology, 1994,41:787-804. |
| [44] | BAU M. Rare-earth element mobility during hydrothermal and metamorphic fluid-rock interaction and the significance of the oxidation state of europium[J]. Chemical Geology, 1991,93(3/4):219-230. |
| [45] | WEBB G E, KAMBER B S. Rare earth elements in Holocene reefal microbialites: a new shallow seawater proxy[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000,64(9):1557-1565. |
| [46] | 朱东亚, 张殿伟, 张荣强, 等. 中国南方地区灯影组白云岩储层流体溶蚀改造机制[J]. 石油学报, 2015,36(10):1188-1198. |
| [47] | 韩银学, 李忠, 韩登林, 等. 塔里木盆地塔北东部下奥陶统基质白云岩的稀土元素特征及其成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2009,25(10):6-8. |
| [48] | BAIOUMY H, LEHMANN B. Anomalous enrichment of redox-sensitive trace elements in the marine black shales from the Duwi Formation, Egypt: Evidence for the late Cretaceous Tethys anoxia[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2017,133:7-14. |
| [49] | KIMURA H, WATANABE Y. Oceanic anoxia at the Precambrian-Cambrian boundary[J]. Geology, 2001,29(11):995-998. |
| [50] | 王鹏万, 陈子炓, 李娴静, 等. 黔南坳陷上震旦统灯影组地球化学特征及沉积环境意义[J]. 现代地质, 2011,25(6):1059-1065. |
| [51] | 倪善芹, 侯泉林, 王安建, 等. 碳酸盐岩中锶元素地球化学特征及其指示意义——以北京下古生界碳酸盐岩为例[J]. 地质学报, 2010,84(10):1510-1516. |
| [52] | RUDNICK R L, GAO S. Composition of the Continental Crust[M]. Oxford: Oxford Press, 2003: 1-10. |
| [53] | KEITH M L, WEBER J N. Carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of selected limestones and fossils[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1964,28(10/11):1787-1816. |
| [54] | DERRY L A, KETO L S, JACOBSEN S B, et al. Sr isotopic variations in Upper Proterozoic carbonates from Svalbard and East Greenland[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989,53(9):2331-2339. |
| [55] | 黄擎宇, 刘伟, 石书缘, 等. 塔中—巴麦地区下古生界不同结构类型白云岩元素地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, 2016,45(2):199-212. |
| [56] | 陈永权, 周新源, 赵葵东, 等. 塔里木盆地塔中1井藻纹层白云岩与竹叶状白云岩成因——基于岩石学、元素与同位素地球化学的厘定[J]. 地质学报, 2008,82(6):826-834. |
| [57] | 贺训云, 寿建峰, 沈安江, 等. 白云岩地球化学特征及成因——以鄂尔多斯盆地靖西马五段中组合为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014,41(3):375-384. |
| [58] | 谭盼盼, 卢振权, 王伟超, 等. 祁连山木里三露天天然气水合物层段碳酸盐矿物学地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2015,29(5):1223-1233. |
| [59] | 陈梅, 王龙樟, 张雄, 等. C、O同位素在川东北碳酸盐岩储层研究中的应用[J]. 沉积学报, 2011,29(2):217-225. |
| [60] | 陈孝红, 李华芹, 陈立德, 等. 三峡地区震旦系碳酸盐岩碳氧同位素特征[J]. 地质论评, 2003,49(1):66-73. |
| [61] | 黄志诚, 陈智娜, 杨守业. 中国南方灯影峡期海洋碳酸盐岩原始δ13C和δ18O组成及海水温度[J]. 古地理学报, 1999,1(3):1-7. |
| [62] | MACHEL H G. Concepts and models of dolomitization: a critical reappraisal[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 2004,235(1):7-63. |
| [63] | ALLEN J R, WIGGINS W D. Dolomite Reservoirs: Geochemical Techniques for Evaluating Origin and Distribution[M]. Tulsa: AAPG, 1993: 1-109. |
| [64] | NOTHDURFT L D, WEBB G E, KAMBER B S. Rare earth element geochemistry of Late Devonian reefal carbonates, canning basin, Western Australia: Confirmation of a seawater REE proxy in ancient limestones[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004,68(2):263-283. |
| [65] | AZMY K, BRAND U, SYLVESTER P, et al. Biogenic and abiogenic low-Mg calcite (bLMC and aLMC): Evaluation of seawater-REE composition, water masses and carbonate diagenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2011,280(1):180-190. |
| [66] | LING H F, CHEN X, LI D, et al. Cerium anomaly variations in Ediacaran-earliest Cambrian carbonates from the Yangtze Gorges area, South China: Implications for oxygenation of coeval shallow seawater[J]. Precambrian Research, 2013,225(1):110-127. |
| [67] | MCLENNAN S M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: Influence of provenance and sedimentary processes[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy, 1989,21(8):169-200. |
| [68] | BUSH P. Some Aspects of the Diagenetic History of the Sabkha in Abu Dhabi, Persian Gulf[M]. Berlin: Springer, 1973: 395-407. |
| [69] | TUCKER M, WRIGHT V P. Carbonate Sedimentology[M]. Oxford:Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1990: 401-402. |
| [1] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [2] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [3] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [4] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [5] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [6] | 梁鸣, 高文, 罗先熔, 王晓东, 刘秀娟, 陈皓, 刘攀峰, 竹峰, 李伟. 冀北高尖子地区土壤地球化学特征及其找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1567-1579. |
| [7] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [8] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [9] | 谭聪, 刘策, 王铜山, 李秋芬, 朱玺, 付景龙, 姜华. 局部白云岩化作用研究:以塔里木盆地阿克苏地区蓬莱坝剖面鹰山组为例[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1182-1193. |
| [10] | 张一范, 高远, 陈积权, 黄帅, 海伦, 毋正轩, 杨柳, 董甜. 松辽盆地晚白垩世湖相白云岩碳氧同位素特征及其古环境意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1243-1253. |
| [11] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [12] | 张宇慧, 朱正平, 罗文军, 潘仁芳, 刘曦翔. 四川盆地高石梯地区震旦系灯影组四段微生物碳酸盐岩微相组合发育特征与储层主控因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1282-1292. |
| [13] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [14] | 可行, 赵青芳, 吴飘, 杨传胜, 廖晶, 龚建明. 胶莱盆地东北部白垩系烃源岩特征与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1358-1368. |
| [15] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||