



现代地质 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (04): 631-645.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2018.04.01
收稿日期:2018-01-08
修回日期:2018-03-04
出版日期:2018-08-10
发布日期:2018-09-19
作者简介:刘 军,男,副研究员,博士,1983年出生,矿床学专业,主要从事热液矿床流体演化与成因研究。Email: junliu@yeah.net。
基金资助:
LIU Jun1( ), LIU Fuxing2, LI Shenghui2, DUAN Chao1
), LIU Fuxing2, LI Shenghui2, DUAN Chao1
Received:2018-01-08
Revised:2018-03-04
Online:2018-08-10
Published:2018-09-19
摘要:
辽宁小佟家堡子金矿床位于华北克拉通北缘。矿区出露地层为元古宇辽河群大石桥组大理岩和盖县组片岩,断裂构造控制着矿体的产出。矿石类型包括石英脉型和蚀变岩型。围岩蚀变类型有硅化、绢云母化和碳酸盐化。成矿过程划分为早、中、晚3个阶段,依次为石英±黄铁矿阶段、石英-多金属硫化物阶段和石英-碳酸盐阶段,金主要沉淀于石英-多金属硫化物阶段。流体包裹体研究表明,小佟家堡子矿床发育富液两相包裹体、富气两相包裹体、含CO2包裹体和纯CO2包裹体。成矿早阶段石英中仅见富液两相包裹体,包裹体均一温度介于311~408 ℃之间,盐度介于5.9%~14.3% NaCl eqv之间;成矿中阶段石英中发育富液两相包裹体、富气两相包裹体、含CO2包裹体和纯CO2包裹体,包裹体均一温度介于268~376 ℃之间,盐度介于4.1%~13.0% NaCl eqv之间;成矿晚阶段石英中仅见富液两相包裹体,均一温度介于201~254 ℃之间,盐度介于1.6%~7.6% NaCl eqv之间。成矿流体具中温、低盐度、富CO2的特征,属于H2O-NaCl±CO2体系。流体不混溶作用是金沉淀的主要机制。成矿流体的δ18OW值为0.3‰~2.3‰,δDW值为-99.8‰~-96.2‰,表明成矿流体以岩浆水为主,混合部分变质水和大气降水。金属硫化物的δ34S值介于+4.6‰~+12.9‰。金属硫化物的铅同位素比值变化较小,206Pb/204Pb=17.671~18.361,207Pb/204Pb=15.569~15.659,208Pb/204Pb=37.695~37.937。S-Pb同位素组成表明成矿物质主要来自辽河群变质岩和晚三叠世岩浆岩。黄铁矿中流体包裹体3He/4He值为0.27~0.53 Ra,地幔流体参与成矿作用的比例为2.9%~5.8%,地壳流体占主导地位。
中图分类号:
刘军, 刘福兴, 李生辉, 段超. 辽宁省小佟家堡子金矿床流体包裹体及同位素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 631-645.
LIU Jun, LIU Fuxing, LI Shenghui, DUAN Chao. Fluid Inclusions and Isotopic Geochemistry Characteristics of the Xiaotongjiapuzi Gold Deposit, Liaoning Province, China[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(04): 631-645.

图1 辽东半岛区域地质和主要金矿床分布简图(据文献[19]修改) 1.中生代花岗岩;2.面理化的侏罗纪花岗岩;3.元古宙花岗岩;4.镁铁质-超镁铁质岩石;5.白垩纪陆相沉积岩;6.侏罗纪火山岩;7.石炭系—二叠系;8.寒武系—奥陶系;9.新元古代碳酸盐岩、砂岩、石英岩和板岩;10.古元古代板岩、大理岩和变泥质岩(辽河群);11.古元古代镁铁质岩浆弧带:超镁铁质岩、镁铁质岩、片麻岩、硅质岩和变泥质岩;12.片麻状混合岩和基底片麻岩;13.断裂;14.地质界线;15.金矿床:?分水金矿;?白云金矿;?小佟家堡子金矿;?石庙子金矿;?王家崴子金矿;?猫岭金矿;?塔岭金矿;?五龙金矿;?四道沟金矿
Fig.1 Sketch geological map of the Liaodong Peninsula, showing distribution of major gold deposits in the Liaodong Peninsula(modified after reference [19])

图5 小佟家堡子金矿床典型矿石照片 (a)石英-黄铁矿脉;(b)石英-黄铁矿-方铅矿-闪锌矿脉;(c)石英-黄铁矿-毒砂-方铅矿脉;(d)石英-碳酸盐脉;(e)石英-多金属硫化物脉中半自形-他形黄铁矿、针状毒砂;(f)石英-多金属硫化物脉中方铅矿和闪锌矿交代黄铁矿;Apy.毒砂;Py.黄铁矿;Gn.方铅矿;Sp.闪锌矿;Cal.方解石;Q.石英
Fig.5 Photographs and photomicrographs of ores from the Xiaotongjiapuzi gold deposit

图6 小佟家堡子金矿床代表性流体包裹体照片 (a)Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型包裹体共存;(b)Ⅱ型、Ⅲ型和Ⅳ型包裹体共存;(c)Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型包裹体共存;(d)Ⅰ型和Ⅳ型包裹体共存
Fig.6 Photomicrographs of representative fluid inclusions from the Xiaotongjiapuzi gold deposit
| 成矿 阶段 | 包裹体 类型 | 测试 数量 | 大小/ μm | 气液比/ % | ?(CO2)/ % | ℃ | tm(ice)/ ℃ | tm (cla)/ ℃ | ℃ | th/ ℃ | 盐度/% NaCl eqv | 密度/ (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早 | I | 84 | 4~7 | 10~30 | -10.3~-3.6 | 311~408 | 5.9~14.3 | 0.67~0.79 | ||||
| 中 | Ⅰ | 99 | 4~9 | 10~40 | -9.1~-2.6 | 268~371 | 4.3~13.0 | 0.71~0.88 | ||||
| Ⅱ | 12 | 4~8 | 55~75 | -5.8~-3.9 | 341~361 | 6.3~9.0 | 0.67~0.71 | |||||
| Ⅲ | 14 | 4~7 | 55~85 | -57.1~-56.7 | 6.5~7.9 | 11.5~15.2 | 323~376 | 4.1~6.5 | 0.92~0.94 | |||
| Ⅳ | 14 | 4~8 | -57.0~-56.7 | 11.4~15.1 | ||||||||
| 晚 | Ⅰ | 54 | 4~7 | 10~30 | -4.8~-0.9 | 201~254 | 1.6~7.6 | 0.82~0.90 |
表1 小佟家堡子矿床流体包裹体显微测温及相关参数
Table 1 Microthermometry data and relative parameters of fluid inclusions in the Xiaotongjiapuzi deposit
| 成矿 阶段 | 包裹体 类型 | 测试 数量 | 大小/ μm | 气液比/ % | ?(CO2)/ % | ℃ | tm(ice)/ ℃ | tm (cla)/ ℃ | ℃ | th/ ℃ | 盐度/% NaCl eqv | 密度/ (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早 | I | 84 | 4~7 | 10~30 | -10.3~-3.6 | 311~408 | 5.9~14.3 | 0.67~0.79 | ||||
| 中 | Ⅰ | 99 | 4~9 | 10~40 | -9.1~-2.6 | 268~371 | 4.3~13.0 | 0.71~0.88 | ||||
| Ⅱ | 12 | 4~8 | 55~75 | -5.8~-3.9 | 341~361 | 6.3~9.0 | 0.67~0.71 | |||||
| Ⅲ | 14 | 4~7 | 55~85 | -57.1~-56.7 | 6.5~7.9 | 11.5~15.2 | 323~376 | 4.1~6.5 | 0.92~0.94 | |||
| Ⅳ | 14 | 4~8 | -57.0~-56.7 | 11.4~15.1 | ||||||||
| 晚 | Ⅰ | 54 | 4~7 | 10~30 | -4.8~-0.9 | 201~254 | 1.6~7.6 | 0.82~0.90 |
| 样号 | 样品描述 | 成矿阶段 | 分析对象 | δDW/‰ | δ18Omineral /‰ | δ18OW/‰ | 计算温度/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LX-12 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 中 | 石英 | -96.2 | 5.7 | 0.5 | 353 |
| LX-14 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 中 | 石英 | -98.1 | 6.3 | 1.1 | 355 |
| LX-15 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 中 | 石英 | -99.8 | 5.6 | 0.3 | 351 |
| LX-16 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 中 | 石英 | -98.8 | 7.4 | 2.3 | 357 |
表2 小佟家堡子矿床氢、氧同位素组成
Table 2 H and O isotope compositions of the Xiaotongjiapuzi deposit
| 样号 | 样品描述 | 成矿阶段 | 分析对象 | δDW/‰ | δ18Omineral /‰ | δ18OW/‰ | 计算温度/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LX-12 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 中 | 石英 | -96.2 | 5.7 | 0.5 | 353 |
| LX-14 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 中 | 石英 | -98.1 | 6.3 | 1.1 | 355 |
| LX-15 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 中 | 石英 | -99.8 | 5.6 | 0.3 | 351 |
| LX-16 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 中 | 石英 | -98.8 | 7.4 | 2.3 | 357 |
| 样号 | 样品描述 | 分析矿物 | δ34S/‰ | 208Pb/204Pb | 2σ | 207Pb/204Pb | 2σ | 206Pb/204Pb | 2σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LX-1.1 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 闪锌矿 | 5.1 | 37.708 | 0.003 | 15.574 | 0.001 | 17.701 | 0.002 |
| LX-1.2 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 方铅矿 | 4.6 | 37.716 | 0.003 | 15.578 | 0.001 | 17.697 | 0.002 |
| LX-2.1 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 闪锌矿 | 6.1 | 37.804 | 0.004 | 15.605 | 0.002 | 17.729 | 0.001 |
| LX-2.2 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 方铅矿 | 5.4 | 37.695 | 0.004 | 15.569 | 0.002 | 17.690 | 0.002 |
| LX-4 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 黄铁矿 | 6.9 | 37.695 | 0.004 | 15.579 | 0.002 | 17.671 | 0.002 |
| LX-9 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 毒砂 | 8.7 | 37.937 | 0.004 | 15.648 | 0.001 | 17.688 | 0.002 |
| LX-22 | 蚀变岩型金矿石 | 黄铁矿 | 12.9 | 37.890 | 0.004 | 15.659 | 0.001 | 18.361 | 0.002 |
| LX-21 | 蚀变岩型金矿石 | 黄铁矿 | 10.5 | ||||||
| LX-24 | 蚀变岩型金矿石 | 黄铁矿 | 8.5 |
表3 小佟家堡子金矿床硫和铅同位素组成
Table 3 S and Pb isotopic compositions of the Xiaotongjiapuzi gold deposit
| 样号 | 样品描述 | 分析矿物 | δ34S/‰ | 208Pb/204Pb | 2σ | 207Pb/204Pb | 2σ | 206Pb/204Pb | 2σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LX-1.1 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 闪锌矿 | 5.1 | 37.708 | 0.003 | 15.574 | 0.001 | 17.701 | 0.002 |
| LX-1.2 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 方铅矿 | 4.6 | 37.716 | 0.003 | 15.578 | 0.001 | 17.697 | 0.002 |
| LX-2.1 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 闪锌矿 | 6.1 | 37.804 | 0.004 | 15.605 | 0.002 | 17.729 | 0.001 |
| LX-2.2 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 方铅矿 | 5.4 | 37.695 | 0.004 | 15.569 | 0.002 | 17.690 | 0.002 |
| LX-4 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 黄铁矿 | 6.9 | 37.695 | 0.004 | 15.579 | 0.002 | 17.671 | 0.002 |
| LX-9 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 毒砂 | 8.7 | 37.937 | 0.004 | 15.648 | 0.001 | 17.688 | 0.002 |
| LX-22 | 蚀变岩型金矿石 | 黄铁矿 | 12.9 | 37.890 | 0.004 | 15.659 | 0.001 | 18.361 | 0.002 |
| LX-21 | 蚀变岩型金矿石 | 黄铁矿 | 10.5 | ||||||
| LX-24 | 蚀变岩型金矿石 | 黄铁矿 | 8.5 |
| 样号 | 样品描述 | 40Ar/36Ar | 36Ar/38Ar | 3He/4He/10-6 | R/Ra | 40Ar/10-8 | 4He/10-8 | Hemantle/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LX-2 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 671.6±1.1 | 5.41±0.01 | 0.64±0.02 | 0.46 | 188.9 | 185.1 | 5.0 |
| LX-5 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 362.2±0.3 | 5.45±0.01 | 0.74±0.04 | 0.53 | 183.9 | 214.9 | 5.8 |
| LX-6 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 1113.1±2.6 | 5.40±0.02 | 0.67±0.06 | 0.48 | 239.8 | 226.9 | 5.2 |
| LX-8 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 612.6±0.7 | 5.35±0.01 | 0.38±0.02 | 0.27 | 273.8 | 536.3 | 2.9 |
| LX-9 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 681.9±1.4 | 5.41±0.02 | 0.73±0.02 | 0.52 | 155.5 | 167.8 | 5.7 |
表4 小佟家堡子金矿床黄铁矿中流体包裹体He、Ar同位素组成
Table 4 Helium and argon isotopic components of the inclusion-trapped fluid in pyrite from the Xiaotongjiapuzi gold deposit
| 样号 | 样品描述 | 40Ar/36Ar | 36Ar/38Ar | 3He/4He/10-6 | R/Ra | 40Ar/10-8 | 4He/10-8 | Hemantle/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LX-2 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 671.6±1.1 | 5.41±0.01 | 0.64±0.02 | 0.46 | 188.9 | 185.1 | 5.0 |
| LX-5 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 362.2±0.3 | 5.45±0.01 | 0.74±0.04 | 0.53 | 183.9 | 214.9 | 5.8 |
| LX-6 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 1113.1±2.6 | 5.40±0.02 | 0.67±0.06 | 0.48 | 239.8 | 226.9 | 5.2 |
| LX-8 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 612.6±0.7 | 5.35±0.01 | 0.38±0.02 | 0.27 | 273.8 | 536.3 | 2.9 |
| LX-9 | 石英-多金属硫化物脉 | 681.9±1.4 | 5.41±0.02 | 0.73±0.02 | 0.52 | 155.5 | 167.8 | 5.7 |
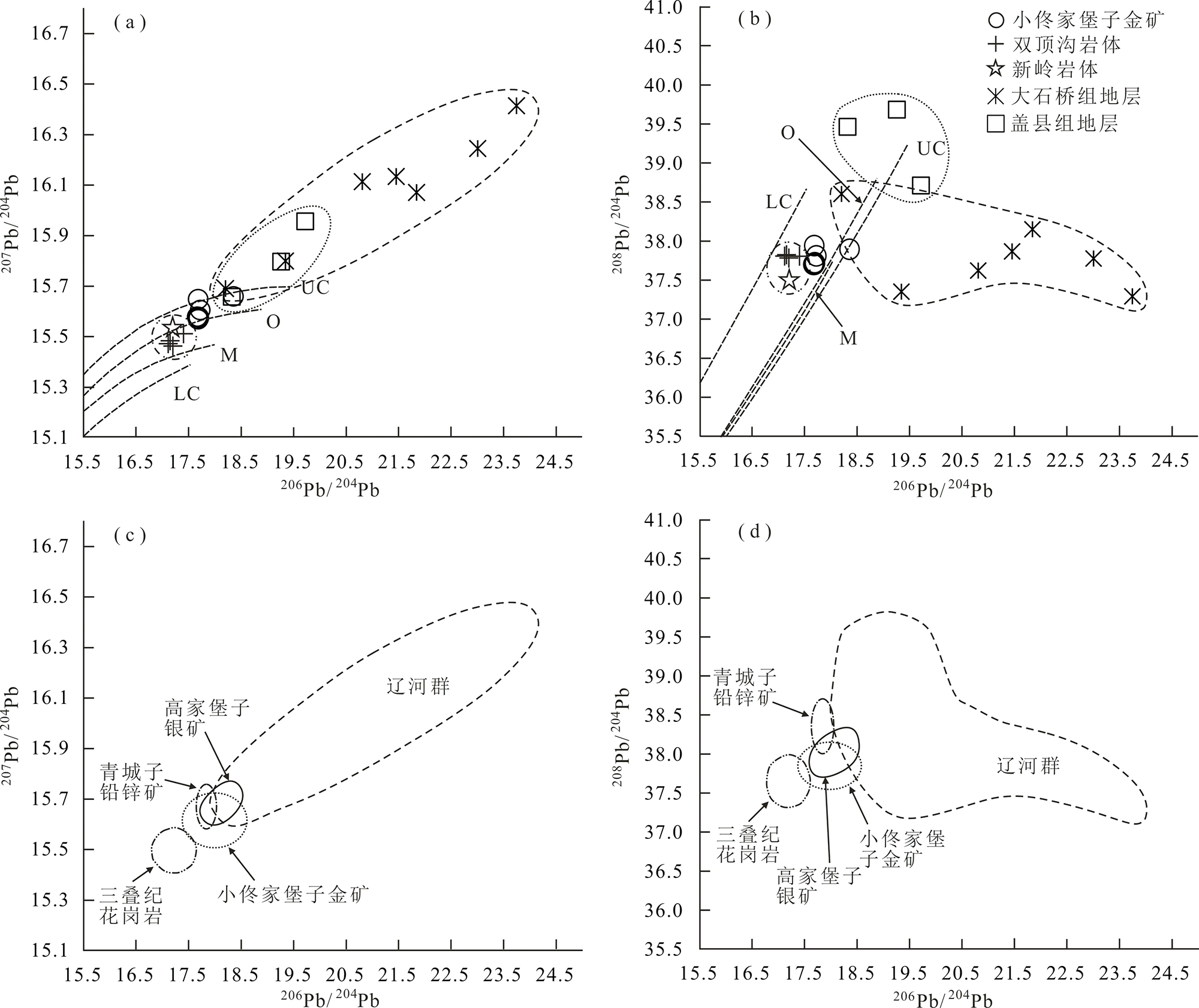
图12 小佟家堡子金矿床((a)、(b))及青城子铅锌金银矿集区铅同位素组成图解((c)、(d))(据文献[48]修改) 晚三叠世花岗岩(双顶沟和新岭岩体)及辽河群变质岩(盖县组和大石桥组变质岩)Pb同位素数据引自文献[6,49];青城子地区铅锌矿和高家堡子银矿中金属硫化物Pb同位素数据引自文献[49]
Fig.12 Pb isotopic evolution diagrams of the Xiaotongjiapuzi gold deposit ((a),(b)) and Qingchengzi Pb-Zn-Au-Ag ore concentration area ((c), (d)) (modified after reference [48])
| [1] | 涂光炽. 中国层控矿床地球化学.第一卷[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984:137-138. |
| [2] | 方如恒. 中朝古元古代层控铅锌矿床类型及其比较[J]. 辽宁地质, 1999, 16(1):43-56. |
| [3] | 刘先利, 姜瑛, 刘志远. 青城子矿田高家堡子大型金银矿床地质特征及成矿机制[J]. 辽宁地质, 2000, 17(2):121-127. |
| [4] | 魏民. 青城子矿田金、银矿床基本特征及成因探讨[M]// 中国地质调查局. 辽吉地区地质与成矿研讨会论文集. 北京: 地质出版社, 2001:137-145. |
| [5] | 倪培, 徐克勤. 辽东半岛地质演化及金矿床的成因[J]. 矿床地质, 1993, 12(3):231-244. |
| [6] |
YU G, CHEN J F, XUE C J, et al. Geochronological framework and Pb, Sr isotope geochemistry of the Qingchengzi Pb-Zn-Ag-Au orefield, Northeastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2009, 35: 367-382.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 杨利亚, 杨立强, 袁万明, 等. 造山型金矿成矿流体来源与演化的氢-氧同位素示踪:夹皮沟金矿带例析[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(11):4025-4035. |
| [8] |
DENG J, WANG Q F, LI G J, et al. Tethys tectonic evolution and its bearing on the distribution of important mineral deposits in the Sanjiang region, SW China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 26: 419-437.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 刘国平, 艾永富. 辽东小佟家堡子金矿岩石地球化学及成矿条件研究[J]. 矿床地质, 1998, 17(4):289-295. |
| [10] | 刘国平, 艾永富. 辽宁小佟家堡子金矿床成矿时代探讨[J]. 矿床地质, 2002, 21(1):53-57. |
| [11] | 薛春纪, 陈毓川, 路远发, 等. 辽东青城子矿集区金、银成矿时代及地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2003, 22(2):177-184. |
| [12] | 代军治, 王可勇, 杨言辰, 等. 青城子小佟家堡子、林家金矿成矿流体特征及成矿机制[J]. 地质论评, 2006, 52(6):836-842. |
| [13] | 张森, 张迪, 沙德喜, 等. 辽东林家三道沟—小佟家堡子地区金(银)矿成矿特征及成因[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(3):725-732. |
| [14] | 王一存, 王可勇, 张淼, 等. 辽宁小佟家堡子金矿床成矿流体特征及来源讨论[J]. 地质与勘探, 2015, 51(1):79-87. |
| [15] | 路孝平, 吴福元, 林景仟, 等. 辽东半岛南部早前寒武纪花岗质岩浆作用的年代学格架[J]. 地质科学, 2004, 39(1):123-138. |
| [16] | 孟恩, 刘福来, 刘平华, 等. 辽东半岛东北部宽甸地区南辽河群沉积时限的确定及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(7):2465-2480. |
| [17] |
TANG H S, CHEN Y J, SANTOSH M, et al. C-O isotope geochemistry of the Dashiqiao magnesite belt, North China Craton: implications for the Great Oxidation Event and ore genesis[J]. Geological Journal, 2013, 48: 467-483.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 杨进辉, 吴福元, 罗清华, 等. 辽宁丹东地区侏罗纪花岗岩的变形时代:40Ar/39Ar年代学制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2004, 20(5):1205-1214. |
| [19] | 林伟, 王清晨, 王军, 等. 辽东半岛晚中生代伸展构造——华北克拉通破坏的地壳响应[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 2011, 41(5):638-653. |
| [20] |
WU F Y, YANG J H, WILDE S A, et al. Geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Jurassic granites in the Liao-dong Peninsula, NE China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005, 221: 127-156.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
WU F Y, LIN J Q, WILDE S A, et al. Nature and significance of the Early Cretaceous giant igneous event in eastern China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233: 103-119.
DOI URL |
| [22] | 吴福元, 杨进辉, 柳小明. 辽东半岛中生代花岗质岩浆作用的年代学格架[J]. 高校地质学报, 2005, 11(3):305-317. |
| [23] | 杨进辉, 吴福元. 华北东部三叠纪岩浆作用与克拉通破坏[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 2009, 39(7):910-921. |
| [24] |
LIU J L, DAVIS G A, LIN Z Y, et al. The Liaonan metamorphic core complex, Southeastern Liaoning Province, North China: A likely contributor to Cretaceous rotation of Eastern Liaoning, Korea and contiguous areas[J]. Tectonophysics, 2005, 407: 65-80.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
LIN W, FAURE M, MONIE P, et al. Polyphase Mesozoic tectonics in the eastern part of North China Block: insights from the eastern Liaoning Peninsula massif (NE China)[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2007, 280: 153-169.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
LIN W, FAURE M, PATRICK M, et al. Mesozoic extensional tectonics in Eastern Asia: the South Liaodong peninsula metamorphic core complex(NE China)[J]. Journal of Geology, 2008, 116:134-154.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 田豫才. 辽东小佟家堡子金矿床地质特征及成矿机理探讨[J]. 有色金属矿产与勘查, 1999, 8(5):264-269. |
| [28] | 代军治. 辽宁青城子地区金、银矿床成矿流体特征及成因探讨[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2005:1-106. |
| [29] | 卢焕章, 范宏瑞, 倪培, 等. 流体包裹体[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004:1-444. |
| [30] |
BODNAR R J. Revised equation and table for determining the freezing point depression of H2O-NaCl solutions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57: 683-684.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
COLLINS P L F. Gas hydrates in CO2-bearing fluid inclusions and the use of freezing data for estimation of salinity[J]. Economic Geology, 1979, 74: 1435-1444.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
CLAYTON R N, MAYEDA T K. The use of bromine pentafluoride in the extraction of oxygen from oxides and silicates for isoto-pic analysis[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1963, 27: 43-52.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
CLAYTON R N, O’NEIL J R, MAYEDA T K. Oxygen isotope exchange between quartz and water[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1972, 77: 3057-3067.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
HU R Z, TURNER G, BURNARD P G, et al. Helium and argon isotopic geochemistry of Jinding superlarge Pb-Zn deposit[J]. Science in China:Series D, 1998, 41(4): 442-448.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
PHILLIPS G N, EVANS K A. Role of CO2 in the formation of gold deposits[J]. Nature, 2004, 429: 860-863.
DOI |
| [36] |
SHEPPARD S M F. Identification of the origin of ore-forming solutions by the use of stable isotopes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1977, 7: 25-41.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
OHMOTO H. Systematics of sulfide and carbon isotopes in hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 1972, 67: 551-578.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
CHAUSSIDON M, LORAND J P. Sulphur isotope composition of orogenic spinel lherzolite massifs from Ariege(North-Eastern Pyreness,France): An ion microprobe study[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1990, 54: 2835-2846.
DOI URL |
| [39] | ROLLINSOM H R. Using Geochemical Data:Evaluation, Pre-sentation, Interpretation[M]. London: Longman Scientific and Technical Press, 1993:306-308. |
| [40] | 刘辉, 金成洙, 关广岳. 辽南猫岭金矿床的成矿物质来源及金的活化、迁移及富集机理[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 1990, 5(4):57-68. |
| [41] |
BURNARD P G, HU R, TURNER G. Mantle, crustal and atmospheric noble gases in Ailaoshan gold deposits, Yunnan Pro-vince, China[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63: 1595-1604.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
MARTY B, JAMBON A, SANO Y. Helium isotopes and CO2 in volcanic gases of Japan[J]. Chemical Geology, 1989, 76: 25-40.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
STUART F M, BURNARD P G, TAYLOR R P, et al. Resolving mantle and crustal contributions to ancient hydrothermal fluids: He-Ar isotopes in fluid inclusions from Dae Hwa W-Mo mineralization, South Korea[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59: 4663-4673.
DOI URL |
| [44] | MAMYRIN B A, TOLSTIBIN I N. Helium isotope in nature[M]//FYFE W S. Developments in Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984:1-237. |
| [45] | 徐永昌, 沈平, 陶明信, 等. 东部油气区天然气中幔源挥发分的地球化学—— I.氦资源的新类型:沉积壳层幔源氦的工业储集[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 1996, 26(1):1-8. |
| [46] | 徐永昌, 沈平, 刘文汇, 等. 天然气中稀有气体地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998:99. |
| [47] | 张乾, 潘家永, 邵树勋. 中国某些金属矿床矿石铅来源的铅同位素诠释[J]. 地球化学, 2000, 29(3):231-238. |
| [48] |
ZARTMAN R E, DOE B R. Plumbotectonics—the model[J]. Tectonophysics, 1981, 75: 135-162.
DOI URL |
| [49] | CHEN J F, YU G, XUE C J, et al. Pb isotope geochemistry of lead, zinc, gold and silver deposit clustered region, Liaodong rift zone, northeastern China[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2005, 48(4): 467-476. |
| [50] | 芮宗瑶, 施林道, 方如恒. 华北陆块北缘及邻区有色金属矿床地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1994:1-576. |
| [51] | 段晓侠, 刘建明, 王永彬, 等. 辽宁青城子铅锌多金属矿田晚三叠世岩浆岩年代学、地球化学及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(2):595-606. |
| [1] | 王启博, 张寿庭, 唐利, 李军军, 盛渊明. 豫西杨山萤石矿床成因:萤石稀土元素组成和流体包裹体热力学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1524-1537. |
| [2] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [3] | 刘洋, 李贤庆, 赵光杰, 刘满仓, 董才源, 李谨, 肖中尧. 库车坳陷东部吐格尔明地区天然气地球化学特征及油气充注史[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 988-997. |
| [4] | 郭云成, 刘家军, 尹超, 郭梦需. 小秦岭大湖金钼矿床地质特征及成矿流体[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1536-1550. |
| [5] | 汪超, 王瑞廷, 刘云华, 薛玉山, 胡西顺, 牛亮. 陕西商南三官庙金矿床流体包裹体及C-H-O-S稳定同位素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1551-1564. |
| [6] | 常铭, 刘家军, 杨永春, 翟德高, 周淑敏, 王建平. 甘肃省鹿儿坝金矿流体包裹体研究:对流体演化和成矿机制的探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1576-1586. |
| [7] | 孙康, 曹毅, 张伟, 赵洋. 安徽青阳铜矿里钼多金属矿床地质特征及流体包裹体研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1371-1379. |
| [8] | 郝鹏, 杨纪磊, 张旭东, 臧春艳, 陈容涛, 王波, 税蕾蕾, 王思惠, 蔡涛. 基于成藏过程重建研究渤中凹陷西北缘陡坡带油气差异聚集机理[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 1124-1135. |
| [9] | 曾瑞垠, 姜华, 祝新友, 张雄, 肖剑, 吕晓强, 胡川, 杨晓坤, 李金林, 郑泽光. 云南东川铜矿床流体演化与成矿机制研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 244-257. |
| [10] | 袁伟恒, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 杜泽忠, 于晓飞, 孙海瑞, 吕鑫. 甘肃北山地区小西弓金矿床成矿流体性质及矿床成因[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 554-568. |
| [11] | 孙可欣, 李贤庆, 魏强, 梁万乐, 张亚超, 李剑, 肖中尧. 库车坳陷克深大气田白垩系致密砂岩储层古流体地球化学特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(06): 1220-1228. |
| [12] | 刘润川, 任战利, 马侃, 张园园, 祁凯, 于春勇, 任文波, 杨燕. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部延长组油气成藏期次研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(06): 1263-1274. |
| [13] | 高丽晔, 章永梅, 顾雪祥, 刘丽, 王路智, 欧阳鑫. 内蒙古敖汉旗金路金矿床地质特征及成矿流体研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(01): 137-151. |
| [14] | 宋志娇, 陈翠华, 尹力, 张燕. 陕西马元铅锌矿床中有机质的存在及其对成矿的作用[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(06): 1272-1282. |
| [15] | 葛战林, 章永梅, 顾雪祥, 陈伟志, 徐劲驰, 武若晨, 黄岗. 新疆东准噶尔南明水金矿床成矿流体特征: 流体包裹体及氢氧同位素证据[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 887-901. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||