



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (03): 554-568.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.03.12
袁伟恒1,2( ), 顾雪祥2,3(
), 顾雪祥2,3( ), 章永梅2,3, 杜泽忠4, 于晓飞4, 孙海瑞4, 吕鑫4
), 章永梅2,3, 杜泽忠4, 于晓飞4, 孙海瑞4, 吕鑫4
收稿日期:2019-09-20
修回日期:2019-12-21
出版日期:2020-07-04
发布日期:2020-07-05
通讯作者:
顾雪祥
作者简介:顾雪祥,男,教授,博士生导师,1963年出生,矿床学专业,主要从事矿床学与矿床地球化学研究。Email: xuexiang_gu@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
YUAN Weiheng1,2( ), GU Xuexiang2,3(
), GU Xuexiang2,3( ), ZHANG Yongmei2,3, DU Zezhong4, YU Xiaofei4, SUN Hairui4, LÜ Xin4
), ZHANG Yongmei2,3, DU Zezhong4, YU Xiaofei4, SUN Hairui4, LÜ Xin4
Received:2019-09-20
Revised:2019-12-21
Online:2020-07-04
Published:2020-07-05
Contact:
GU Xuexiang
摘要:
小西弓金矿床位于甘肃北山造山带南部,矿体受NWW向次级断裂控制,赋矿围岩主要为中元古界西尖山群变质岩。成矿过程可分为3个阶段:石英-黄铁矿阶段(早阶段)、石英-多金属硫化物阶段(主成矿阶段)和石英-碳酸盐阶段(晚阶段)。对主成矿阶段石英中的流体包裹体、微量元素和氢、氧同位素开展研究,以期查明成矿流体性质,探讨矿床成因。主成矿阶段石英中主要发育气液两相水溶液包裹体、CO2-H2O三相包裹体和纯液相CO2包裹体,均一温度介于194~397 ℃,盐度为2.2%~8.9% NaCleqv,密度为0.63~0.98 g/cm3。利用CO2-H2O三相包裹体计算出主成矿阶段流体包裹体捕获压力为257~395 MPa,成矿深度为9.5~14.6 km。流体包裹体测温、激光拉曼光谱分析与石英微量元素特征表明,成矿流体为中高温、低盐度、中低密度的CO2-H2O-NaCl±CH4体系,且具有相对还原性的特点。主成矿阶段石英的δDV-SMOW值为-100.2‰~-75.6‰,δ18
中图分类号:
袁伟恒, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 杜泽忠, 于晓飞, 孙海瑞, 吕鑫. 甘肃北山地区小西弓金矿床成矿流体性质及矿床成因[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 554-568.
YUAN Weiheng, GU Xuexiang, ZHANG Yongmei, DU Zezhong, YU Xiaofei, SUN Hairui, LÜ Xin. Properties of Ore-forming Fluids and Genesis of the Xiaoxigong Gold Deposit in the Beishan Region, Gansu Province[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(03): 554-568.

图1 北山造山带大地构造位置示意图(A)、北山地区构造单元划分图(B)和北山地区区域地质简图(C) (图A据Kr?ner et al.[16],2008;图B据Xiao et al.[17],2010;图C据西安地质研究所,2004修改)
Fig.1 Simplified geotectonic location map of the Beishan orogenic belt (A),tectonic unit map of the Beishan area (B) and regional geological map of the Beishan area (C)
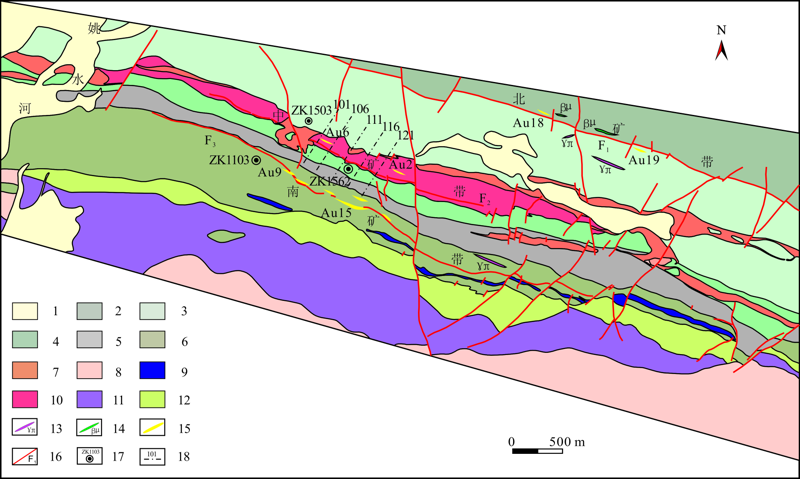
图2 小西弓金矿床地质图(据甘肃省第四地质矿产勘查院,2004修改) 1.第四系;2.西尖山群第二岩组二云石英片岩、大理岩;3.西尖山群第一岩组二云斜长石英片岩;4.西尖山群第五岩组钙质片岩、片状石英岩夹二云片岩;5.西尖山群第四岩组二岩段大理岩、中基性火山岩;6.西尖山群第四岩组一岩段二云片岩;7.石英正长斑岩;8.二长花岗岩;9.花岗岩;10.钾长花岗岩;11.石英闪长岩;12.蚀变石英闪长岩;13.花岗斑岩脉;14.辉绿岩脉;15.金矿体;16.断裂;17.钻孔位置及编号;18.勘探线及编号。
Fig.2 Geological map of the Xiaoxigong gold deposit

图3 小西弓金矿床矿体特征 A.北矿带地表采坑,矿体走向285°~ 295°,向北或向南陡倾;B.北矿带矿脉中间较为破碎,两侧见较强的硅化;C.中矿带Au2矿体,走向约290°,整体向北倾,近于直立;D.中矿带矿体中夹宽约20 cm的含金石英脉,石英脉走向与矿体走向一致;E.南矿带露天采坑,矿体沿走向呈舒缓-弯曲状延伸。
Fig.3 Ore body characteristics of the Xiaoxigong gold deposit
| 测点 | 矿物 | As | Se | Fe | S | Au | Ag | Zn | Bi | Ni | Te | Cd | Sn | 总量 | Ag/Au | 金成色 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 银金矿 | — | — | 0.99 | 0.31 | 54.64 | 42.13 | 0.14 | 0.54 | — | 0.10 | — | — | 98.85 | 0.77 | 565 |
| 2 | 银金矿 | 0.49 | — | 0.94 | 0.46 | 56.39 | 40.88 | — | 0.28 | 0.09 | 0.15 | — | 0.08 | 99.76 | 0.72 | 580 |
| 3 | 银金矿 | — | — | 0.27 | 0.33 | 49.93 | 47.77 | — | 0.36 | — | 0.11 | — | — | 98.77 | 0.96 | 511 |
| 4 | 自然金 | — | — | 0.33 | 0.23 | 82.51 | 15.20 | — | 0.30 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 98.96 | 0.18 | 844 |
| 5 | 金银矿 | — | — | 0.74 | 0.30 | 40.78 | 56.80 | — | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.11 | — | 99.22 | 1.39 | 418 |
| 6 | 自然金 | — | — | 0.09 | 0.04 | 86.83 | 11.43 | — | 0.52 | — | — | — | — | 98.91 | 0.13 | 884 |
| 7 | 自然金 | — | 0.06 | 0.84 | 0.16 | 86.47 | 11.01 | — | 0.72 | 0.22 | — | — | — | 99.48 | 0.13 | 887 |
表1 小西弓金矿床金矿物电子探针分析结果(wB/%)
Table 1 Results of electron probe analysis for the gold minerals in the Xiaoxigong gold deposit
| 测点 | 矿物 | As | Se | Fe | S | Au | Ag | Zn | Bi | Ni | Te | Cd | Sn | 总量 | Ag/Au | 金成色 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 银金矿 | — | — | 0.99 | 0.31 | 54.64 | 42.13 | 0.14 | 0.54 | — | 0.10 | — | — | 98.85 | 0.77 | 565 |
| 2 | 银金矿 | 0.49 | — | 0.94 | 0.46 | 56.39 | 40.88 | — | 0.28 | 0.09 | 0.15 | — | 0.08 | 99.76 | 0.72 | 580 |
| 3 | 银金矿 | — | — | 0.27 | 0.33 | 49.93 | 47.77 | — | 0.36 | — | 0.11 | — | — | 98.77 | 0.96 | 511 |
| 4 | 自然金 | — | — | 0.33 | 0.23 | 82.51 | 15.20 | — | 0.30 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 98.96 | 0.18 | 844 |
| 5 | 金银矿 | — | — | 0.74 | 0.30 | 40.78 | 56.80 | — | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.11 | — | 99.22 | 1.39 | 418 |
| 6 | 自然金 | — | — | 0.09 | 0.04 | 86.83 | 11.43 | — | 0.52 | — | — | — | — | 98.91 | 0.13 | 884 |
| 7 | 自然金 | — | 0.06 | 0.84 | 0.16 | 86.47 | 11.01 | — | 0.72 | 0.22 | — | — | — | 99.48 | 0.13 | 887 |

图5 小西弓金矿床成矿阶段划分 A.石英-多金属硫化物脉切穿并错断早阶段较为纯净的石英细脉;B.石英-方解石脉,含少量萤石矿物;C.方解石脉切穿早阶段纯净的石英脉;D.晚阶段方解石脉切穿石英-多金属硫化物脉;C-D在透射偏光显微镜正交偏光下拍摄;Q.石英;Cal.方解石;Py.黄铁矿;Fl.萤石。
Fig.5 Mineralization stages of the Xiaoxigong gold deposit
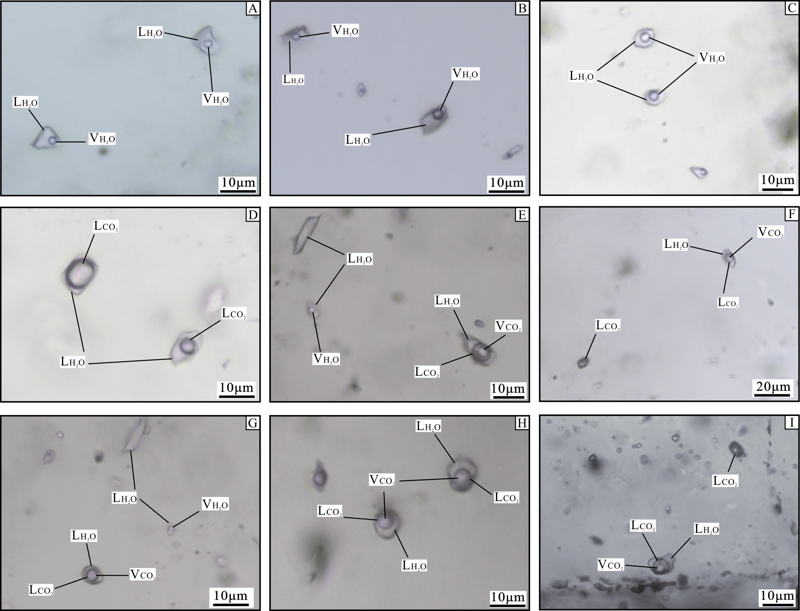

图6 小西弓金矿床流体包裹体显微照片 A.气液两相水溶液包裹体;B、C.气液两相水溶液包裹体,呈负晶形,沿生长环带分布;D.CO2-H2O包裹体,室温下呈两相,且充填度变化较大;E.CO2-H2O三相包裹体,与纯液相水溶液包裹体、气液两相水溶液包裹体共存;F.CO2-H2O三相包裹体,与纯液相CO2包裹体共存;G.CO2-H2O三相包裹体,与纯液相水溶液包裹体共存;H.CO2-H2O三相包裹体,室温下呈现双眼皮结构;I .CO2-H2O三相包裹体,与纯液相CO2包裹体、气液两相水溶液包裹体共存;LH2O.液相水;VH2O.气相水;LCO2.液相CO2;VCO2.气相CO2。
Fig.6 Microphotographs of fluid inclusions in the Xiaoxigong gold deposit
| 类型 | CO2固相初熔温度/℃ | 笼合物熔化温度/℃ | 部分均一温度/℃ | 冰点温度/℃ | 完全均一温度/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围/测定数/均值 | 范围/测定数/均值 | 范围/测定数/均值 | 范围/测定数/均值 | 范围/测定数/均值 | |
| Ⅰ型 | -5.8~-1.5/52/-3.9 | 194~397/106/315 | |||
| Ⅱ型 | -60.1~-56.3/25/-58.3 | 7.4~8.9/16/7.9 | 16.5~26.8/28/21.7 | 261~389/28/320 | |
| Ⅲ型 | -59.7~-56.8/11/-58.5 | 17.5~19.4/11/17.9 |
表2 小西弓金矿床主成矿阶段流体包裹体显微测温结果
Table 2 Microthermometric results of fluid inclusions in the main ore stage of the Xiaoxigong gold deposit
| 类型 | CO2固相初熔温度/℃ | 笼合物熔化温度/℃ | 部分均一温度/℃ | 冰点温度/℃ | 完全均一温度/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围/测定数/均值 | 范围/测定数/均值 | 范围/测定数/均值 | 范围/测定数/均值 | 范围/测定数/均值 | |
| Ⅰ型 | -5.8~-1.5/52/-3.9 | 194~397/106/315 | |||
| Ⅱ型 | -60.1~-56.3/25/-58.3 | 7.4~8.9/16/7.9 | 16.5~26.8/28/21.7 | 261~389/28/320 | |
| Ⅲ型 | -59.7~-56.8/11/-58.5 | 17.5~19.4/11/17.9 |
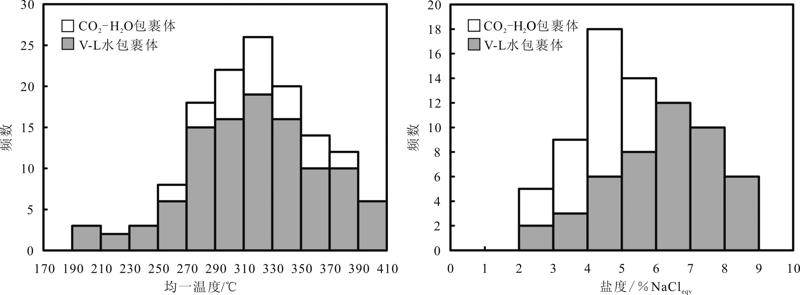
图7 小西弓金矿床主成矿阶段流体包裹体均一温度和盐度频数直方图
Fig.7 Histograms of homogenization temperature and salinity of fluid inclusions in the main ore stage of the Xiaoxigong gold deposit
| 包裹体 类型 | 密度/(g/cm3) | 压力/MPa | 深度/km | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 | 测定数 | 均值 | 范围 | 测定数 | 均值 | 范围 | 测定数 | 均值 | |||
| Ⅰ型 | 0.63~0.92 | 41 | 0.76 | ||||||||
| Ⅱ型 | 0.89~0.98 | 17 | 0.92 | 256.9~395.0 | 17 | 330 | 9.5~14.6 | 17 | 12.2 | ||
| Ⅲ型 | 0.67~0.82 | 11 | 0.75 | ||||||||
表3 小西弓金矿床主成矿阶段成矿流体密度、压力及深度
Table 3 Fluid density, pressure and depth in the main ore stage of the Xiaoxigong gold deposit
| 包裹体 类型 | 密度/(g/cm3) | 压力/MPa | 深度/km | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 | 测定数 | 均值 | 范围 | 测定数 | 均值 | 范围 | 测定数 | 均值 | |||
| Ⅰ型 | 0.63~0.92 | 41 | 0.76 | ||||||||
| Ⅱ型 | 0.89~0.98 | 17 | 0.92 | 256.9~395.0 | 17 | 330 | 9.5~14.6 | 17 | 12.2 | ||
| Ⅲ型 | 0.67~0.82 | 11 | 0.75 | ||||||||

图8 小西弓金矿床主成矿阶段流体包裹体激光拉曼光谱图 A、B.气液两相水溶液包裹体成分主要为H2O;C、D.CO2-H2O三相包裹体成分主要为H2O和CO2,含少量CH4;E、F.纯液相CO2包裹体中含一定量CH4。
Fig.8 Laser Raman spectra of fluid inclusions in the main ore stage of the Xiaoxigong gold deposit
| 样品号 | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | Y | Mo | Cd | In | Sb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BD-5 | 1.890 | 0.074 | 0.426 | 2.050 | 4.16 | 0.095 | 0.168 | 0.525 | 3.340 | 0.598 | 4.370 | 2.110 | 0.046 | 0.006 | 0.019 | <0.002 | 0.107 |
| BD-6 | 1.430 | 0.004 | 0.189 | 0.121 | 3.09 | 0.015 | 0.075 | 0.604 | 0.556 | 0.033 | 0.171 | 2.390 | 0.174 | 0.005 | 0.010 | <0.002 | 0.069 |
| BD-7 | 0.665 | 0.002 | 0.541 | 0.035 | 2.95 | 0.013 | 0.192 | 0.104 | 0.481 | 0.015 | 0.031 | 6.210 | 0.252 | 0.004 | 0.015 | 0.002 | 0.079 |
| BD-8 | 0.967 | 0.008 | 0.047 | 0.037 | 3.11 | 0.009 | 0.045 | 0.112 | 0.695 | 0.005 | 0.034 | 0.842 | 0.020 | 0.002 | <0.002 | <0.002 | 0.076 |
| ND-1 | 0.062 | 0.011 | 0.298 | 0.038 | 4.11 | 0.009 | 0.136 | 0.075 | 0.703 | 0.009 | 0.031 | 2.000 | 0.215 | 0.003 | 0.003 | <0.002 | 0.135 |
| ND-4 | 0.102 | 0.003 | 8.490 | 0.385 | 3.23 | 0.026 | 0.091 | 0.155 | 0.691 | 0.042 | 0.129 | 0.980 | 0.034 | 0.002 | 0.007 | <0.002 | 0.077 |
| ND-16 | 0.265 | 0.063 | 0.383 | 1.180 | 3.45 | 0.185 | 0.231 | 1.770 | 4.590 | 0.359 | 1.180 | 4.570 | 1.030 | 0.043 | 0.015 | <0.002 | 0.122 |
| ND-23 | 0.109 | 0.002 | 0.198 | 0.247 | 3.26 | 0.047 | 0.133 | 0.190 | 0.577 | 0.032 | 0.141 | 1.610 | 0.220 | 0.014 | 0.003 | <0.002 | 0.070 |
| ZD-4 | 1.510 | 0.110 | 0.277 | 1.130 | 3.34 | 0.203 | 0.110 | 0.146 | 1.570 | 0.547 | 4.190 | 2.080 | 0.989 | 0.022 | 0.011 | 0.005 | 0.465 |
| ZD-6 | 1.180 | 0.182 | 0.375 | 1.660 | 4.10 | 0.161 | 0.192 | 0.398 | 2.720 | 0.485 | 6.680 | 1.040 | 1.660 | 0.081 | 0.017 | 0.011 | 0.342 |
| ZD-8 | 2.050 | 0.163 | 0.330 | 1.430 | 3.11 | 0.172 | 0.201 | 0.103 | 1.780 | 0.761 | 5.270 | 9.630 | 1.370 | 0.069 | 0.036 | 0.005 | 0.618 |
| ZD-9 | 2.800 | 0.265 | 0.638 | 2.480 | 3.50 | 0.350 | 0.172 | 0.158 | 20.100 | 1.480 | 10.500 | 3.360 | 2.630 | 0.082 | 0.382 | 0.015 | 0.660 |
| 样品号 | Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | W |
| BD-5 | 0.152 | 14.300 | 0.044 | 0.082 | 0.010 | 0.031 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.367 |
| BD-6 | 0.028 | 1.210 | 0.048 | 0.089 | 0.011 | 0.040 | 0.013 | 0.005 | 0.013 | 0.003 | 0.020 | 0.005 | 0.016 | 0.004 | 0.019 | 0.003 | 0.041 |
| BD-7 | 0.028 | 0.383 | 0.04 | 0.090 | 0.012 | 0.046 | 0.014 | 0.005 | 0.013 | 0.004 | 0.025 | 0.008 | 0.033 | 0.008 | 0.078 | 0.022 | 0.047 |
| BD-8 | 0.023 | 0.569 | 0.022 | 0.037 | 0.004 | 0.017 | 0.004 | <0.002 | 0.003 | <0.002 | 0.003 | <0.002 | 0.002 | <0.002 | <0.002 | <0.002 | 0.064 |
| ND-1 | 0.016 | 0.351 | 0.107 | 0.211 | 0.029 | 0.110 | 0.024 | 0.005 | 0.026 | 0.005 | 0.029 | 0.006 | 0.018 | 0.003 | 0.018 | 0.003 | 0.040 |
| ND-4 | 0.012 | 1.190 | 0.024 | 0.039 | 0.003 | 0.015 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | <0.002 | 0.005 | <0.002 | 0.003 | <0.002 | 0.002 | <0.002 | 0.046 |
| ND-16 | 0.039 | 7.170 | 0.538 | 1.220 | 0.167 | 0.642 | 0.149 | 0.036 | 0.126 | 0.026 | 0.160 | 0.036 | 0.105 | 0.018 | 0.106 | 0.013 | 0.242 |
| ND-23 | 0.011 | 3.000 | 0.537 | 0.921 | 0.125 | 0.511 | 0.100 | 0.014 | 0.081 | 0.010 | 0.042 | 0.006 | 0.016 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 0.002 | 0.035 |
| ZD-4 | 0.165 | 4.510 | 0.547 | 1.220 | 0.180 | 0.796 | 0.266 | 0.041 | 0.199 | 0.042 | 0.215 | 0.038 | 0.099 | 0.015 | 0.073 | 0.010 | 547.000 |
| ZD-6 | 0.099 | 9.130 | 1.050 | 2.400 | 0.269 | 0.962 | 0.206 | 0.046 | 0.185 | 0.041 | 0.265 | 0.059 | 0.178 | 0.031 | 0.199 | 0.027 | 17.600 |
| ZD-8 | 0.194 | 7.350 | 1.360 | 2.980 | 0.385 | 1.440 | 0.337 | 0.046 | 0.256 | 0.050 | 0.276 | 0.051 | 0.151 | 0.024 | 0.135 | 0.019 | 251.000 |
| ZD-9 | 0.226 | 10.000 | 1.540 | 3.600 | 0.503 | 2.070 | 0.626 | 0.092 | 0.491 | 0.096 | 0.513 | 0.099 | 0.257 | 0.040 | 0.226 | 0.032 | 1 085.000 |
| 样品号 | Re | Tl | Pb | Bi | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | δEu | δCe | Y/Ho | Zr/Hf | Hf/Sm | Nb/La | Th/La |
| BD-5 | <0.002 | 0.023 | 1.890 | 0.045 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.239 | 0.017 | 0.357 | 0.016 | 1.55 | 0.89 | 23.00 | 22.31 | 3.20 | 5.43 | 0.16 |
| BD-6 | <0.002 | 0.005 | 9.620 | 0.096 | <0.002 | 0.004 | 0.006 | <0.002 | 0.037 | <0.002 | 1.16 | 0.88 | 34.80 | — | — | 0.13 | — |
| BD-7 | <0.002 | <0.002 | 0.340 | 0.007 | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.039 | <0.002 | 1.11 | 0.96 | 31.50 | — | — | 0.10 | 0.13 |
| BD-8 | <0.002 | <0.002 | 0.212 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.203 | 0.013 | 0.059 | 0.002 | 1.70 | 0.87 | — | 29.50 | 0.50 | 9.23 | 0.18 |
| ND-1 | <0.002 | <0.002 | 0.472 | 0.009 | 0.003 | 0.008 | 0.003 | <0.002 | 0.034 | <0.002 | 0.61 | 0.88 | 35.83 | — | — | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| ND-4 | <0.002 | <0.002 | 1.160 | 0.010 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.013 | 0.002 | 0.034 | <0.002 | 3.03 | 0.93 | — | — | — | 0.54 | 0.08 |
| ND-16 | <0.002 | 0.005 | 6.990 | 0.006 | 0.074 | 0.025 | 0.062 | 0.006 | 0.969 | 0.030 | 0.78 | 0.95 | 28.61 | 32.30 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.14 |
| ND-23 | <0.002 | 0.002 | 0.945 | 0.008 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.003 | <0.002 | 0.034 | <0.002 | 0.46 | 0.81 | 36.67 | — | — | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| ZD-4 | 0.007 | 0.071 | 94.100 | 2.010 | 0.098 | 0.052 | 0.195 | 0.012 | 0.968 | 0.035 | 0.52 | 0.91 | 26.03 | 27.66 | 0.13 | 0.36 | 0.18 |
| ZD-6 | <0.002 | 0.048 | 0.673 | 0.013 | 0.223 | 0.151 | 0.503 | 0.031 | 25.900 | 0.753 | 0.71 | 1.04 | 28.14 | 34.40 | 3.66 | 0.48 | 0.21 |
| ZD-8 | 0.003 | 0.046 | 55.600 | 1.660 | 0.340 | 0.074 | 0.675 | 0.041 | 1.600 | 0.059 | 0.46 | 0.96 | 26.86 | 27.12 | 0.18 | 0.50 | 0.25 |
| ZD-9 | 0.013 | 0.122 | 217.000 | 6.640 | 0.286 | 0.233 | 0.868 | 0.053 | 2.220 | 0.077 | 0.49 | 0.96 | 26.57 | 28.83 | 0.12 | 0.56 | 0.19 |
表4 小西弓金矿床主成矿阶段石英的微量元素(wB /10-6)及特征值
Table 4 Trace element concentrations and characteristic values for the main ore stage quartz of the Xiaoxigong gold deposit(10-6)
| 样品号 | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | Y | Mo | Cd | In | Sb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BD-5 | 1.890 | 0.074 | 0.426 | 2.050 | 4.16 | 0.095 | 0.168 | 0.525 | 3.340 | 0.598 | 4.370 | 2.110 | 0.046 | 0.006 | 0.019 | <0.002 | 0.107 |
| BD-6 | 1.430 | 0.004 | 0.189 | 0.121 | 3.09 | 0.015 | 0.075 | 0.604 | 0.556 | 0.033 | 0.171 | 2.390 | 0.174 | 0.005 | 0.010 | <0.002 | 0.069 |
| BD-7 | 0.665 | 0.002 | 0.541 | 0.035 | 2.95 | 0.013 | 0.192 | 0.104 | 0.481 | 0.015 | 0.031 | 6.210 | 0.252 | 0.004 | 0.015 | 0.002 | 0.079 |
| BD-8 | 0.967 | 0.008 | 0.047 | 0.037 | 3.11 | 0.009 | 0.045 | 0.112 | 0.695 | 0.005 | 0.034 | 0.842 | 0.020 | 0.002 | <0.002 | <0.002 | 0.076 |
| ND-1 | 0.062 | 0.011 | 0.298 | 0.038 | 4.11 | 0.009 | 0.136 | 0.075 | 0.703 | 0.009 | 0.031 | 2.000 | 0.215 | 0.003 | 0.003 | <0.002 | 0.135 |
| ND-4 | 0.102 | 0.003 | 8.490 | 0.385 | 3.23 | 0.026 | 0.091 | 0.155 | 0.691 | 0.042 | 0.129 | 0.980 | 0.034 | 0.002 | 0.007 | <0.002 | 0.077 |
| ND-16 | 0.265 | 0.063 | 0.383 | 1.180 | 3.45 | 0.185 | 0.231 | 1.770 | 4.590 | 0.359 | 1.180 | 4.570 | 1.030 | 0.043 | 0.015 | <0.002 | 0.122 |
| ND-23 | 0.109 | 0.002 | 0.198 | 0.247 | 3.26 | 0.047 | 0.133 | 0.190 | 0.577 | 0.032 | 0.141 | 1.610 | 0.220 | 0.014 | 0.003 | <0.002 | 0.070 |
| ZD-4 | 1.510 | 0.110 | 0.277 | 1.130 | 3.34 | 0.203 | 0.110 | 0.146 | 1.570 | 0.547 | 4.190 | 2.080 | 0.989 | 0.022 | 0.011 | 0.005 | 0.465 |
| ZD-6 | 1.180 | 0.182 | 0.375 | 1.660 | 4.10 | 0.161 | 0.192 | 0.398 | 2.720 | 0.485 | 6.680 | 1.040 | 1.660 | 0.081 | 0.017 | 0.011 | 0.342 |
| ZD-8 | 2.050 | 0.163 | 0.330 | 1.430 | 3.11 | 0.172 | 0.201 | 0.103 | 1.780 | 0.761 | 5.270 | 9.630 | 1.370 | 0.069 | 0.036 | 0.005 | 0.618 |
| ZD-9 | 2.800 | 0.265 | 0.638 | 2.480 | 3.50 | 0.350 | 0.172 | 0.158 | 20.100 | 1.480 | 10.500 | 3.360 | 2.630 | 0.082 | 0.382 | 0.015 | 0.660 |
| 样品号 | Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | W |
| BD-5 | 0.152 | 14.300 | 0.044 | 0.082 | 0.010 | 0.031 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.367 |
| BD-6 | 0.028 | 1.210 | 0.048 | 0.089 | 0.011 | 0.040 | 0.013 | 0.005 | 0.013 | 0.003 | 0.020 | 0.005 | 0.016 | 0.004 | 0.019 | 0.003 | 0.041 |
| BD-7 | 0.028 | 0.383 | 0.04 | 0.090 | 0.012 | 0.046 | 0.014 | 0.005 | 0.013 | 0.004 | 0.025 | 0.008 | 0.033 | 0.008 | 0.078 | 0.022 | 0.047 |
| BD-8 | 0.023 | 0.569 | 0.022 | 0.037 | 0.004 | 0.017 | 0.004 | <0.002 | 0.003 | <0.002 | 0.003 | <0.002 | 0.002 | <0.002 | <0.002 | <0.002 | 0.064 |
| ND-1 | 0.016 | 0.351 | 0.107 | 0.211 | 0.029 | 0.110 | 0.024 | 0.005 | 0.026 | 0.005 | 0.029 | 0.006 | 0.018 | 0.003 | 0.018 | 0.003 | 0.040 |
| ND-4 | 0.012 | 1.190 | 0.024 | 0.039 | 0.003 | 0.015 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | <0.002 | 0.005 | <0.002 | 0.003 | <0.002 | 0.002 | <0.002 | 0.046 |
| ND-16 | 0.039 | 7.170 | 0.538 | 1.220 | 0.167 | 0.642 | 0.149 | 0.036 | 0.126 | 0.026 | 0.160 | 0.036 | 0.105 | 0.018 | 0.106 | 0.013 | 0.242 |
| ND-23 | 0.011 | 3.000 | 0.537 | 0.921 | 0.125 | 0.511 | 0.100 | 0.014 | 0.081 | 0.010 | 0.042 | 0.006 | 0.016 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 0.002 | 0.035 |
| ZD-4 | 0.165 | 4.510 | 0.547 | 1.220 | 0.180 | 0.796 | 0.266 | 0.041 | 0.199 | 0.042 | 0.215 | 0.038 | 0.099 | 0.015 | 0.073 | 0.010 | 547.000 |
| ZD-6 | 0.099 | 9.130 | 1.050 | 2.400 | 0.269 | 0.962 | 0.206 | 0.046 | 0.185 | 0.041 | 0.265 | 0.059 | 0.178 | 0.031 | 0.199 | 0.027 | 17.600 |
| ZD-8 | 0.194 | 7.350 | 1.360 | 2.980 | 0.385 | 1.440 | 0.337 | 0.046 | 0.256 | 0.050 | 0.276 | 0.051 | 0.151 | 0.024 | 0.135 | 0.019 | 251.000 |
| ZD-9 | 0.226 | 10.000 | 1.540 | 3.600 | 0.503 | 2.070 | 0.626 | 0.092 | 0.491 | 0.096 | 0.513 | 0.099 | 0.257 | 0.040 | 0.226 | 0.032 | 1 085.000 |
| 样品号 | Re | Tl | Pb | Bi | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | δEu | δCe | Y/Ho | Zr/Hf | Hf/Sm | Nb/La | Th/La |
| BD-5 | <0.002 | 0.023 | 1.890 | 0.045 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.239 | 0.017 | 0.357 | 0.016 | 1.55 | 0.89 | 23.00 | 22.31 | 3.20 | 5.43 | 0.16 |
| BD-6 | <0.002 | 0.005 | 9.620 | 0.096 | <0.002 | 0.004 | 0.006 | <0.002 | 0.037 | <0.002 | 1.16 | 0.88 | 34.80 | — | — | 0.13 | — |
| BD-7 | <0.002 | <0.002 | 0.340 | 0.007 | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.039 | <0.002 | 1.11 | 0.96 | 31.50 | — | — | 0.10 | 0.13 |
| BD-8 | <0.002 | <0.002 | 0.212 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.203 | 0.013 | 0.059 | 0.002 | 1.70 | 0.87 | — | 29.50 | 0.50 | 9.23 | 0.18 |
| ND-1 | <0.002 | <0.002 | 0.472 | 0.009 | 0.003 | 0.008 | 0.003 | <0.002 | 0.034 | <0.002 | 0.61 | 0.88 | 35.83 | — | — | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| ND-4 | <0.002 | <0.002 | 1.160 | 0.010 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.013 | 0.002 | 0.034 | <0.002 | 3.03 | 0.93 | — | — | — | 0.54 | 0.08 |
| ND-16 | <0.002 | 0.005 | 6.990 | 0.006 | 0.074 | 0.025 | 0.062 | 0.006 | 0.969 | 0.030 | 0.78 | 0.95 | 28.61 | 32.30 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.14 |
| ND-23 | <0.002 | 0.002 | 0.945 | 0.008 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.003 | <0.002 | 0.034 | <0.002 | 0.46 | 0.81 | 36.67 | — | — | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| ZD-4 | 0.007 | 0.071 | 94.100 | 2.010 | 0.098 | 0.052 | 0.195 | 0.012 | 0.968 | 0.035 | 0.52 | 0.91 | 26.03 | 27.66 | 0.13 | 0.36 | 0.18 |
| ZD-6 | <0.002 | 0.048 | 0.673 | 0.013 | 0.223 | 0.151 | 0.503 | 0.031 | 25.900 | 0.753 | 0.71 | 1.04 | 28.14 | 34.40 | 3.66 | 0.48 | 0.21 |
| ZD-8 | 0.003 | 0.046 | 55.600 | 1.660 | 0.340 | 0.074 | 0.675 | 0.041 | 1.600 | 0.059 | 0.46 | 0.96 | 26.86 | 27.12 | 0.18 | 0.50 | 0.25 |
| ZD-9 | 0.013 | 0.122 | 217.000 | 6.640 | 0.286 | 0.233 | 0.868 | 0.053 | 2.220 | 0.077 | 0.49 | 0.96 | 26.57 | 28.83 | 0.12 | 0.56 | 0.19 |
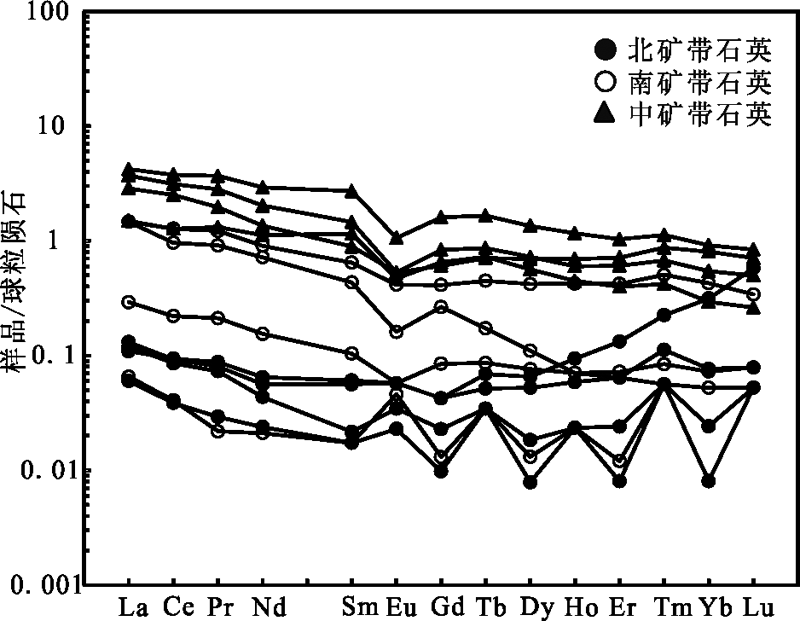
图9 小西弓金矿床主成矿阶段石英稀土元素配分型式图 (标准化数据引自Sun and Mcdonough[25], 1989)
Fig.9 REE distribution patterns of the main ore stage quartz of the Xiaoxigong gold deposit
| 序号 | 样品编号 | 岩石类型 | 测试矿物 | δDV-SMOW/‰ | δ18OV-SMOW/‰ | 平衡温度/℃ | δ18 | 数据来源 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BD-5 | 北矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -90.6 | 14.0 | 300 | 7.1 | 本文 | |||||||||
| 2 | BD-6 | 北矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -94.9 | 13.6 | 300 | 6.7 | ||||||||||
| 3 | BD-7 | 北矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -88.9 | 13.9 | 340 | 8.3 | ||||||||||
| 4 | BD-8 | 北矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -88.3 | 11.7 | 300 | 4.8 | ||||||||||
| 5 | ND-1 | 南矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -81.0 | 12.9 | 280 | 5.3 | ||||||||||
| 6 | ND-4 | 南矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -75.6 | 11.8 | 280 | 4.2 | ||||||||||
| 7 | ND-16 | 南矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -77.6 | 13.3 | 280 | 5.7 | ||||||||||
| 8 | ND-23 | 南矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -81.8 | 12.5 | 280 | 4.9 | ||||||||||
| 9 | ZD-4 | 中矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -92.9 | 12.0 | 320 | 5.8 | ||||||||||
| 10 | ZD-6 | 中矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -100.2 | 12.8 | 320 | 6.6 | ||||||||||
| 11 | ZD-8 | 中矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -95.7 | 13.3 | 320 | 7.1 | ||||||||||
| 12 | ZD-9 | 中矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -94.3 | 13.2 | 320 | 7.0 | ||||||||||
| 13 | XXG9901 | 早期含金黄铜矿-石英脉 | 石英 | -115.9 | 10.9 | 285 | 3.5 | 聂凤军等[ | |||||||||
| 14 | XXG9902 | 早期含金黄铜矿-石英脉 | 石英 | -103.0 | 12.5 | 300 | 5.6 | ||||||||||
| 15 | XXG9903 | 晚期含金多金属硫化物-石英脉 | 石英 | -90.6 | 13.9 | 280 | 6.3 | ||||||||||
| 16 | XXG9904 | 晚期含金多金属硫化物-石英脉 | 石英 | -115.0 | 9.7 | 279 | 2.0 | ||||||||||
| 17 | XXG9905 | 晚期含金多金属硫化物-石英脉 | 石英 | -109.4 | 11.6 | 270 | 3.5 | ||||||||||
| 18 | XXG9906 | 蚀变岩型 | 石英 | -83.6 | 6.6 | 248 | -2.4 | ||||||||||
| 19 | XXG9907 | 蚀变岩型 | 石英 | -82.0 | 8.5 | 274 | 0.6 | ||||||||||
| 20 | XXG9908 | 蚀变岩型 | 石英 | -83.7 | 9.3 | 268 | 1.2 | ||||||||||
| 21 | XXG9909 | 蚀变岩型 | 石英 | -82.5 | 13.1 | 276 | 5.3 | ||||||||||
| 22 | XXG9910 | 蚀变岩型 | 石英 | -94.6 | 9.9 | 254 | 1.1 | ||||||||||
| 23 | XXG05-6 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -76.0 | 12.4 | 219 | 1.8 | 胡朋[ | |||||||||
| 24 | XXG05-10 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -90.0 | 9.5 | 219 | -1.1 | ||||||||||
| 25 | XXG05-12 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -80.0 | 9.6 | 219 | -1.0 | ||||||||||
| 26 | XXG05-20 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -83.0 | 11.7 | 241.6 | 2.3 | ||||||||||
| 27 | B80-2 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -96.0 | 13.6 | 230 | 3.6 | 陈柏林[ | |||||||||
| 28 | B80-3 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -102.0 | 13.4 | 224 | 3.1 | ||||||||||
| 29 | B80-4 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -107.0 | 13.8 | 191 | 1.5 | ||||||||||
| 30 | B4 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -126.0 | 14.2 | 250 | 5.3 | ||||||||||
| 31 | B5 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -72.5 | 14.97 | 250 | 6.0 | ||||||||||
| 32 | XX-5 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -99.6 | 14.2 | 400 | 10.1 | 刘伟等[ | |||||||||
| 33 | XX-7 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -99.0 | 13.9 | 400 | 9.8 | ||||||||||
| 34 | XX-10 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -109.3 | 12.6 | 400 | 8.5 | ||||||||||
| 35 | XXG-15 | 中矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -84.0 | 13.4 | 300 | 6.5 | 朱江[ | |||||||||
| 36 | XXG-19 | 中矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -102.0 | 13.6 | 300 | 6.7 | ||||||||||
| 37 | XXG-14 | 中矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -107.0 | 13.3 | 300 | 6.4 | ||||||||||
表5 小西弓金矿床石英的氢、氧同位素组成
Table 5 Hydrogen and oxygen isotope compositions of quartz in the Xiaoxigong gold deposit
| 序号 | 样品编号 | 岩石类型 | 测试矿物 | δDV-SMOW/‰ | δ18OV-SMOW/‰ | 平衡温度/℃ | δ18 | 数据来源 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BD-5 | 北矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -90.6 | 14.0 | 300 | 7.1 | 本文 | |||||||||
| 2 | BD-6 | 北矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -94.9 | 13.6 | 300 | 6.7 | ||||||||||
| 3 | BD-7 | 北矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -88.9 | 13.9 | 340 | 8.3 | ||||||||||
| 4 | BD-8 | 北矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -88.3 | 11.7 | 300 | 4.8 | ||||||||||
| 5 | ND-1 | 南矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -81.0 | 12.9 | 280 | 5.3 | ||||||||||
| 6 | ND-4 | 南矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -75.6 | 11.8 | 280 | 4.2 | ||||||||||
| 7 | ND-16 | 南矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -77.6 | 13.3 | 280 | 5.7 | ||||||||||
| 8 | ND-23 | 南矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -81.8 | 12.5 | 280 | 4.9 | ||||||||||
| 9 | ZD-4 | 中矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -92.9 | 12.0 | 320 | 5.8 | ||||||||||
| 10 | ZD-6 | 中矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -100.2 | 12.8 | 320 | 6.6 | ||||||||||
| 11 | ZD-8 | 中矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -95.7 | 13.3 | 320 | 7.1 | ||||||||||
| 12 | ZD-9 | 中矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -94.3 | 13.2 | 320 | 7.0 | ||||||||||
| 13 | XXG9901 | 早期含金黄铜矿-石英脉 | 石英 | -115.9 | 10.9 | 285 | 3.5 | 聂凤军等[ | |||||||||
| 14 | XXG9902 | 早期含金黄铜矿-石英脉 | 石英 | -103.0 | 12.5 | 300 | 5.6 | ||||||||||
| 15 | XXG9903 | 晚期含金多金属硫化物-石英脉 | 石英 | -90.6 | 13.9 | 280 | 6.3 | ||||||||||
| 16 | XXG9904 | 晚期含金多金属硫化物-石英脉 | 石英 | -115.0 | 9.7 | 279 | 2.0 | ||||||||||
| 17 | XXG9905 | 晚期含金多金属硫化物-石英脉 | 石英 | -109.4 | 11.6 | 270 | 3.5 | ||||||||||
| 18 | XXG9906 | 蚀变岩型 | 石英 | -83.6 | 6.6 | 248 | -2.4 | ||||||||||
| 19 | XXG9907 | 蚀变岩型 | 石英 | -82.0 | 8.5 | 274 | 0.6 | ||||||||||
| 20 | XXG9908 | 蚀变岩型 | 石英 | -83.7 | 9.3 | 268 | 1.2 | ||||||||||
| 21 | XXG9909 | 蚀变岩型 | 石英 | -82.5 | 13.1 | 276 | 5.3 | ||||||||||
| 22 | XXG9910 | 蚀变岩型 | 石英 | -94.6 | 9.9 | 254 | 1.1 | ||||||||||
| 23 | XXG05-6 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -76.0 | 12.4 | 219 | 1.8 | 胡朋[ | |||||||||
| 24 | XXG05-10 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -90.0 | 9.5 | 219 | -1.1 | ||||||||||
| 25 | XXG05-12 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -80.0 | 9.6 | 219 | -1.0 | ||||||||||
| 26 | XXG05-20 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -83.0 | 11.7 | 241.6 | 2.3 | ||||||||||
| 27 | B80-2 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -96.0 | 13.6 | 230 | 3.6 | 陈柏林[ | |||||||||
| 28 | B80-3 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -102.0 | 13.4 | 224 | 3.1 | ||||||||||
| 29 | B80-4 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -107.0 | 13.8 | 191 | 1.5 | ||||||||||
| 30 | B4 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -126.0 | 14.2 | 250 | 5.3 | ||||||||||
| 31 | B5 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -72.5 | 14.97 | 250 | 6.0 | ||||||||||
| 32 | XX-5 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -99.6 | 14.2 | 400 | 10.1 | 刘伟等[ | |||||||||
| 33 | XX-7 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -99.0 | 13.9 | 400 | 9.8 | ||||||||||
| 34 | XX-10 | 石英脉型 | 石英 | -109.3 | 12.6 | 400 | 8.5 | ||||||||||
| 35 | XXG-15 | 中矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -84.0 | 13.4 | 300 | 6.5 | 朱江[ | |||||||||
| 36 | XXG-19 | 中矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -102.0 | 13.6 | 300 | 6.7 | ||||||||||
| 37 | XXG-14 | 中矿带石英脉型 | 石英 | -107.0 | 13.3 | 300 | 6.4 | ||||||||||

图10 小西弓金矿床成矿流体δ18O-δD图解(底图据Craig[33], 1961;Taylor[34], 1974; Sheppard et al.[35], 1986修改)
Fig.10 Plots of δ18O-δD for the ore-forming fluids in the Xiaoxigong gold deposit
| 特征 | 小西弓金矿床 | 造山型金矿床 |
|---|---|---|
| 构造背景 | 北山造山带挤压形成的韧性剪切带中 | 汇聚板块边缘或陆内碰撞造山带 |
| 控矿构造 | NWW向次级断裂、韧性剪切带 | 区域断裂或者韧性剪切带的次级构造 |
| 赋矿围岩 | 中元古界西尖山群中浅变质岩 | 绿片岩相-角闪岩相变质地体 |
| 矿体形态 | 脉状、透镜体状 | 一般以脉状、似层状为主 |
| 矿石组分 | 以黄铁矿和毒砂为主(≤ 5%),脉石矿物主要为石英 | 含有≤ 3%~ 5%的硫化物,脉石矿物以石英为主 |
| 围岩蚀变 | 硅化、绢云母化、萤石化、碳酸盐化 | 硅化、绢云母化、碳酸盐化、绿泥石化等 |
| 成矿流体成分 | CO2-H2O-NaCl±CH4体系 | CO2-H2O-NaCl,含CH4及少量N2 |
| 成矿流体温度、盐度 | 194~397 ℃,2.2%~8.9% NaCleqv | 200~500 ℃,3%~10%NaCleqv |
| 成矿流体来源 | 以变质水为主 | 变质水 |
| 成矿时间 | 与造山作用时间基本吻合(284~276 Ma) | 与造山作用同时或稍晚于造山作用 |
表6 小西弓金矿床与典型造山型金矿床特征对比
Table 6 Comparison of characteristics between the Xiaoxigong gold deposit and typical orogenic gold deposits
| 特征 | 小西弓金矿床 | 造山型金矿床 |
|---|---|---|
| 构造背景 | 北山造山带挤压形成的韧性剪切带中 | 汇聚板块边缘或陆内碰撞造山带 |
| 控矿构造 | NWW向次级断裂、韧性剪切带 | 区域断裂或者韧性剪切带的次级构造 |
| 赋矿围岩 | 中元古界西尖山群中浅变质岩 | 绿片岩相-角闪岩相变质地体 |
| 矿体形态 | 脉状、透镜体状 | 一般以脉状、似层状为主 |
| 矿石组分 | 以黄铁矿和毒砂为主(≤ 5%),脉石矿物主要为石英 | 含有≤ 3%~ 5%的硫化物,脉石矿物以石英为主 |
| 围岩蚀变 | 硅化、绢云母化、萤石化、碳酸盐化 | 硅化、绢云母化、碳酸盐化、绿泥石化等 |
| 成矿流体成分 | CO2-H2O-NaCl±CH4体系 | CO2-H2O-NaCl,含CH4及少量N2 |
| 成矿流体温度、盐度 | 194~397 ℃,2.2%~8.9% NaCleqv | 200~500 ℃,3%~10%NaCleqv |
| 成矿流体来源 | 以变质水为主 | 变质水 |
| 成矿时间 | 与造山作用时间基本吻合(284~276 Ma) | 与造山作用同时或稍晚于造山作用 |
| [1] | 肖文交, 舒良树, 高俊, 等. 中亚造山带大陆动力学过程与成矿作用[J]. 新疆地质, 2008,26(1):4-8. |
| [2] | 毛启贵. 北山及邻区古生代—早中生代增生与碰撞大地构造格局[D]. 北京: 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所, 2008: 1-227. |
| [3] | 蔡志慧, 许志琴, 何碧竹, 等. 东天山—北山造山带中大型韧性剪切带属性及形成演化时限与过程[J]. 岩石学报, 2012,28(6):1875-1895. |
| [4] | 潘小菲, 刘伟. 甘肃—新疆北山成矿带典型矿床成矿流体研究进展及成矿作用探讨[J]. 地球学报, 2010,31(4):507-518. |
| [5] | 陈柏林, 吴淦国, 叶德金, 等. 北山地区金矿类型、成矿规律和找矿方向[J]. 地质力学学报, 2001,7(3):217-223. |
| [6] | 郭晓东, 金宝义, 徐燕夫, 等. 甘肃小西弓金矿地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 黄金地质, 2002,8(3):33-37. |
| [7] | 李奋其, 王成善. 甘肃小西弓金矿地质地球化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 矿物岩石, 2003,23(1):65-69. |
| [8] | 聂凤军, 江思宏, 胡朋, 等. 甘肃小西弓金矿床成矿物质来源和含矿流体运移轨迹同位素示踪[J]. 地质地球化学, 2003,31(4):1-10. |
| [9] | 江思宏. 北山地区岩浆活动与金的成矿作用[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2004: 1-166. |
| [10] | 刘伟, 潘小菲. 新疆—甘肃北山金矿南带的成矿流体演化和成矿机制[J]. 岩石学报, 2006,22(1):171-188. |
| [11] | 朱江. 北山造山带南带构造-岩浆建造与金多金属成矿 [D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2013: 1-184. |
| [12] | 孙新春, 张雨莲, 高永伟. 甘蒙北山北带古生代地壳演化与成矿作用[J]. 甘肃地质, 2011,20(2):45-50. |
| [13] | 左国朝, 何国琦. 北山板块构造及成矿规律 [M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1990: 1-226. |
| [14] | 刘雪亚, 王荃. 中国西部北山造山带的大地构造及其演化[C]// 中国地质科学院地质研究所.中国地质科学院地质研究所文集(28).北京:中国地质学会, 1995: 42-53. |
| [15] | 陈柏林. 北山南带韧性剪切带构造与金矿成矿动力学 [M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 2003, 1-127. |
| [16] | KRÖNER A, HEGNER E, LEHMANN B, et al. Palaeozoic arc magmatism in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt of Kazakhstan: SHRIMP zircon ages and whole-rock Nd isotopic systematics[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008,32(2):118-130. |
| [17] | XIAO W J, MAO Q G, WINDLEY B F, et al. Paleozoic multiple accretionary and collisional processes of the Beishan orogenic collage[J]. American Journal of Science, 2011,310(10):1553-1594. |
| [18] | CLAYTON R N, MAYEDA T K. The use of bromine pentafluoride in the extraction of oxygen from oxides and silicates for isotopic analysis[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1963,27(1):43-52. |
| [19] | COLEMAN M L, SHEPHERD T J, DURHAM J J, et al. Reduction of water with zinc for hydrogen isotope analysis[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1982,54(6):993-995. |
| [20] | ROEDDER E. Fluid Inclusions: Reviews in Mineralogy[M]. Washington: Mineralogical Society of America, 1984: 1-644. |
| [21] | 卢焕章, 范宏瑞, 倪培, 等. 流体包裹体 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004: 208-222. |
| [22] | HALL D L, STERNER S M, BODNAR R J. Freezing point depression of NaCl-KCl-H2O[J]. Economic Geology, 1988,83(1):197-202. |
| [23] | 刘斌, 段光贤. NaCl-H2O 溶液包裹体的密度式和等容式及其应用[J]. 矿物学报, 1987(4):59-66. |
| [24] | BROWN P E. FLINCOR:A microcomputer program for the reduction and investigation of fluid-inclusion data[J]. American Mineralogist, 1989,74(11) : 1390-1393. |
| [25] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systema-tics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London, Special Publications, 1989,42(1):313-345. |
| [26] | NORMAN D I, LANDIS G P. Source of mineralizing components in hydrothermal ore fluids as evidenced by 87Sr/86Sr and stable isotope data from the Pasto Bueno deposit, Peru [J]. Economic Geology, 1983,78:451-465. |
| [27] | 毕献武, 胡瑞忠, 彭建堂, 等. 黄铁矿微量元素地球化学特征及其对成矿流体性质的指示[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2004,23(1):1-4. |
| [28] | 胡朋. 北山南带构造岩浆演化与金的成矿作用[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2007: 1-142. |
| [29] | BAU M, DULSKI P. Comparing yttrium and rare earths in hydrothermal fluids from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge: implications for Y and REE behaviour during near-vent mixing and for the Y/Ho ratio of Proterozoic seawater[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999,155(1):77-90. |
| [30] | 陈衍景, 倪培, 范宏瑞, 等. 不同类型热液金矿系统的流体包裹体特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(9):2085-2108. |
| [31] | ZHU J, LÜ X B, PENG S G. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating, geochemistry and tectonic implications of the Neoproterozoic Xiaoxigong granite at Dunhuang block, northeastern Tarim, NW China[J]. Geosciences Journal, 2015,19(4):697-708. |
| [32] | 朱江, 吕新彪, 彭三国, 等. 甘肃北山小西弓金矿区石英正长斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2015,34(8):1460-1469. |
| [33] |
CRAIG H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters[J]. Science, 1961,133(3465):1702-1703.
URL PMID |
| [34] | TAYLOR H P. The application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal alteration and ore deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 1974,69(6):843-883. |
| [35] | SHEPPARD S M F, VALLEY J W, TAYLOR H P, et al. Chara-cterization and isotopic variations in natural waters[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy, 1986,16(3):165-183. |
| [36] | 曾威, 段明, 万多, 等. 河南银洞坡金矿成矿流体与矿床成因研究[J]. 现代地质, 2016,30(4):781-791. |
| [37] | BOWERS T S, HELGESON H C. Calculation of the thermodynamic and geochemical consequences of nonideal mixing in the system H2O-CO2-NaCl on phase relations in geologic systems: metamorphic equilibria at high pressures and temperatures[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1983,47(7):1247-1275. |
| [38] | COULIBALY Y, BOIRON M C, CATHELINEAU M, et al. Fluid immiscibility and gold deposition in the Birimian quartz veins of the Angovia deposit[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2008,50(2/4):234-254. |
| [39] | KLEIN E L, FUZIKAWA K. Origin of the CO2-only fluid inclusions in the Palaeoproterozoic Carará vein-quartz gold deposit, Ipitinga Auriferous District, SE-Guiana Shield, Brazil: Implications for orogenic gold mineralization[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2010,37(1):31-40. |
| [40] | 卢焕章, 池国祥, 朱笑青, 等. 造山型金矿的地质特征和成矿流体[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2018,163(2):54-75. |
| [41] | 吴程赟, 顾雪祥, 刘丽, 等. 贵州丫他卡林型金矿床流体包裹体特征及其成矿意义[J]. 现代地质, 2012,26(2):277-285. |
| [42] | 徐九华, 谢玉玲, 丁汝福, 等. CO2-CH4流体与金成矿作用:以阿尔泰山南缘和穆龙套金矿为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(8):2026-2032. |
| [43] | EVANS K A, POWELL R, HOLLAND T J B. Internally consis-tent data for sulphur-bearing phases and application to the construction of pseudosections for mafic greenschist facies rocks in Na2O-CaO-K2O-FeO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2-CO2-O-S-H2O[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2010,28(6):667-687. |
| [44] | PHILLIPS G N, POWELL R, BROWN M, et al. Formation of gold deposits: a metamorphic devolatilization model[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2010,28(6):689-718. |
| [45] | 李葆华, 李雯霞, 顾雪祥, 等. 四川丹巴燕子沟金矿床成矿流体不混溶的流体包裹体证据[J]. 地学前缘, 2014,21(5):41-49. |
| [46] | 李增达. 甘肃花牛山铅锌银多金属矿田岩浆成矿作用与找矿[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018: 1-148. |
| [1] | 王启博, 张寿庭, 唐利, 李军军, 盛渊明. 豫西杨山萤石矿床成因:萤石稀土元素组成和流体包裹体热力学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1524-1537. |
| [2] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [3] | 刘洋, 李贤庆, 赵光杰, 刘满仓, 董才源, 李谨, 肖中尧. 库车坳陷东部吐格尔明地区天然气地球化学特征及油气充注史[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 988-997. |
| [4] | 郭云成, 刘家军, 尹超, 郭梦需. 小秦岭大湖金钼矿床地质特征及成矿流体[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1536-1550. |
| [5] | 汪超, 王瑞廷, 刘云华, 薛玉山, 胡西顺, 牛亮. 陕西商南三官庙金矿床流体包裹体及C-H-O-S稳定同位素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1551-1564. |
| [6] | 常铭, 刘家军, 杨永春, 翟德高, 周淑敏, 王建平. 甘肃省鹿儿坝金矿流体包裹体研究:对流体演化和成矿机制的探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1576-1586. |
| [7] | 孙康, 曹毅, 张伟, 赵洋. 安徽青阳铜矿里钼多金属矿床地质特征及流体包裹体研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1371-1379. |
| [8] | 郝鹏, 杨纪磊, 张旭东, 臧春艳, 陈容涛, 王波, 税蕾蕾, 王思惠, 蔡涛. 基于成藏过程重建研究渤中凹陷西北缘陡坡带油气差异聚集机理[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 1124-1135. |
| [9] | 曾瑞垠, 姜华, 祝新友, 张雄, 肖剑, 吕晓强, 胡川, 杨晓坤, 李金林, 郑泽光. 云南东川铜矿床流体演化与成矿机制研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 244-257. |
| [10] | 孙可欣, 李贤庆, 魏强, 梁万乐, 张亚超, 李剑, 肖中尧. 库车坳陷克深大气田白垩系致密砂岩储层古流体地球化学特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(06): 1220-1228. |
| [11] | 刘润川, 任战利, 马侃, 张园园, 祁凯, 于春勇, 任文波, 杨燕. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部延长组油气成藏期次研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(06): 1263-1274. |
| [12] | 高丽晔, 章永梅, 顾雪祥, 刘丽, 王路智, 欧阳鑫. 内蒙古敖汉旗金路金矿床地质特征及成矿流体研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(01): 137-151. |
| [13] | 宋志娇, 陈翠华, 尹力, 张燕. 陕西马元铅锌矿床中有机质的存在及其对成矿的作用[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(06): 1272-1282. |
| [14] | 葛战林, 章永梅, 顾雪祥, 陈伟志, 徐劲驰, 武若晨, 黄岗. 新疆东准噶尔南明水金矿床成矿流体特征: 流体包裹体及氢氧同位素证据[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 887-901. |
| [15] | 徐浩, 张闯, 庞雅庆, 曹豪杰, 刘佳林, 刘文泉. 广东长排铀矿床成矿流体特征[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 902-912. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||