



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (06): 1245-1260.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.029
寇少磊( ), 魏立勇, 张振, 李国英, 郑鑫, 路宗悦, 杨瀚文, 孟五一
), 魏立勇, 张振, 李国英, 郑鑫, 路宗悦, 杨瀚文, 孟五一
出版日期:2020-12-22
发布日期:2020-12-22
作者简介:寇少磊,男,助理工程师,1990年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事矿产调查方面的研究工作。Email:koushaolei665511@163.com。
基金资助:
KOU Shaolei( ), WEI Liyong, ZHANG Zhen, LI Guoying, ZHENG Xin, LU Zongyue, YANG Hanwen, MENG Wuyi
), WEI Liyong, ZHANG Zhen, LI Guoying, ZHENG Xin, LU Zongyue, YANG Hanwen, MENG Wuyi
Online:2020-12-22
Published:2020-12-22
摘要:
日多玛花岗闪长岩体位于西秦岭中段美武岩体附近,对该岩体进行了岩相学、锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学方面的研究。日多玛花岗闪长岩体含有较丰富的暗色微粒包体,花岗闪长岩和暗色微粒包体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄分别为(236.8±3.6) Ma(MSWD=4.1)和(242.7±1.6) Ma(MSWD=1.4),属于印支早期。日多玛岩体具有富钾(2.58%~2.75%)、富碱(Na2O+K2O=5.57%~5.76%)、弱过铝质(A/CNK=1.48~1.51)特征,属于高钾钙碱性I型花岗岩类。日多玛岩体稀土元素表现为轻重稀土元素分馏较明显(LREE/HREE=10.4~11.9)、呈右倾特征,具有中等Eu负异常(δEu=0.68~0.81),岩石富集K、Rb、Ba、Th和U等大离子亲石元素,明显亏损Nb、Ta、Ti和P等高场强元素。岩石地球化学特征表明,日多玛花岗闪长岩来源于下地壳高钾玄武质岩石的部分熔融。此外,花岗闪长岩体具有较高的Mg#(57~61)、Cr(149×10-6~185×10-6)和Ni(36×10-6~47×10-6),显示有少量幔源物质加入,暗色微粒包体可能代表了这种幔源岩浆。结合区域地质背景分析,认为日多玛花岗闪长岩体形成于后碰撞构造环境,可能与俯冲洋壳的断离作用有关。
中图分类号:
寇少磊, 魏立勇, 张振, 李国英, 郑鑫, 路宗悦, 杨瀚文, 孟五一. 西秦岭中段日多玛岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1245-1260.
KOU Shaolei, WEI Liyong, ZHANG Zhen, LI Guoying, ZHENG Xin, LU Zongyue, YANG Hanwen, MENG Wuyi. Zircon U-Pb Ages, Geochemical Characteristics and Tectonic Implications of the Riduoma Granodiorite in the Middle Section of Western Qinling Orogen[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(06): 1245-1260.

图1 西秦岭造山带((a),据冯益民等[7],有修改)及研究区地质简图((b),据骆必继[16],有修改)
Fig.1 Simplified geological map of the Western Qingling Orogen ((a), modified after Feng et al.[7]) and the study area ((b), modified after Luo et al.[16])

图2 日多玛花岗闪长岩、暗色微粒包体野外及镜下照片 (a)花岗闪长岩体;(b)暗色微粒包体;(c)、(e)单偏光和正交偏光镜下花岗闪长岩特征;(d)、(f)单偏光和正交偏光镜下暗色微粒包体特征;(g)外接触带附近烘烤边;(h)外接触带附近绿泥石化现象;Q. 石英;Bi. 黑云母;Pl. 斜长石;Alf. 碱性长石;Am. 角闪石
Fig.2 Photos of Riduoma granodiorite and mafic microgranular enclaves in the field and microscopic photos

图5 暗色微粒包体(样品BTTW8)锆石的阴极发光(CL)图像和其表面年龄(Ma)
Fig.5 Cathodoluminescence (CL) images and the ages (Ma) of representative zircons from mafic microgranular enclaves
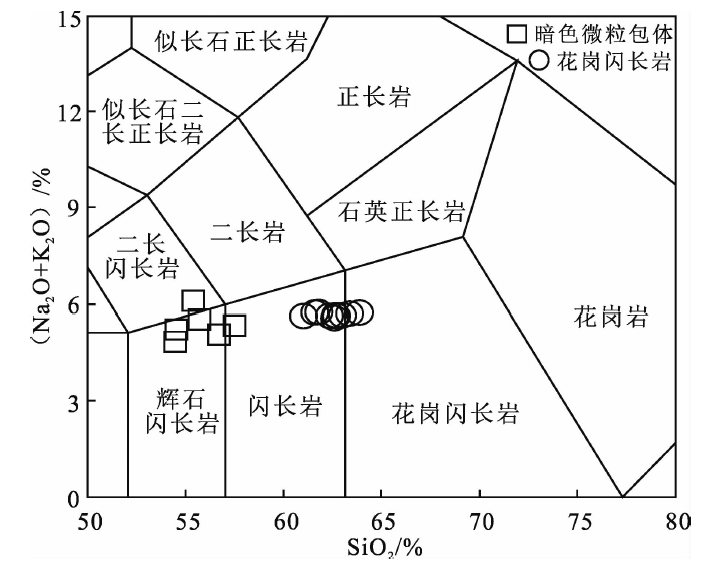
图7 花岗闪长岩和暗色微粒包体的SiO2-(Na2O +K2O)图解(底图据Middlemost[21])
Fig.7 SiO2-(Na2O+K2O) plot for the Riduoma granodiorite and mafic microgranular enclaves (base map after Middlemost[21])
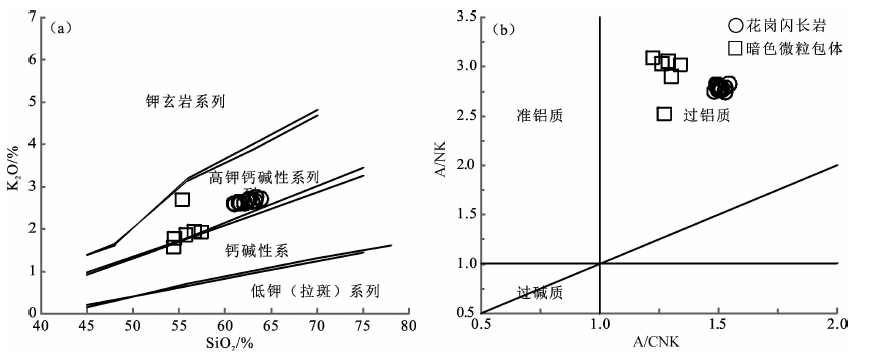
图8 岩体和暗色微粒包体岩石系列判别图((a)底图据Rickwood[22])和岩石铝饱和指数判别图((b)底图据Maniar等[23])
Fig.8 SiO2-K2O plot ((a) base map after Rickwood[22]) and A/CNK-A/NK plot (b) (base map after Maniar et al[23]) for the intrusion and mafic microgranular enclaves
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | TiO2 | MnO | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | Mg# | ALK | Na2O/K2O | δ | A/NK | A/CNK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RD01HX1 | 62.19 | 15.71 | 5.96 | 3.53 | 4.74 | 3.04 | 2.60 | 0.59 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.65 | 99.19 | 58 | 5.64 | 1.17 | 1.65 | 2.79 | 1.52 |
| RD01HX2 | 63.37 | 15.75 | 6.23 | 3.51 | 4.53 | 3.02 | 2.75 | 0.58 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.67 | 100.58 | 57 | 5.77 | 1.10 | 1.63 | 2.73 | 1.53 |
| RD01HX3 | 63.85 | 15.92 | 5.58 | 3.61 | 4.72 | 3.08 | 2.68 | 0.59 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.51 | 100.73 | 60 | 5.77 | 1.15 | 1.59 | 2.76 | 1.52 |
| RD01HX4 | 62.94 | 15.83 | 6.15 | 3.61 | 4.82 | 3.06 | 2.64 | 0.60 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.53 | 100.36 | 58 | 5.69 | 1.16 | 1.63 | 2.78 | 1.51 |
| RD01HX5 | 62.51 | 15.67 | 5.32 | 3.54 | 4.55 | 2.91 | 2.66 | 0.60 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.84 | 98.78 | 61 | 5.57 | 1.09 | 1.59 | 2.81 | 1.55 |
| RD01HX6 | 63.26 | 15.87 | 5.47 | 3.60 | 4.67 | 3.04 | 2.66 | 0.60 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.60 | 99.96 | 61 | 5.70 | 1.14 | 1.60 | 2.79 | 1.53 |
| RD01HX7 | 62.61 | 15.60 | 5.61 | 3.66 | 4.84 | 2.99 | 2.69 | 0.59 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.68 | 99.46 | 60 | 5.69 | 1.11 | 1.65 | 2.74 | 1.48 |
| RD01HX8 | 62.68 | 15.80 | 5.42 | 3.58 | 4.81 | 3.03 | 2.71 | 0.59 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.65 | 99.45 | 61 | 5.74 | 1.12 | 1.67 | 2.76 | 1.50 |
| RD02HX5 | 61.64 | 16.04 | 5.66 | 3.71 | 4.99 | 3.15 | 2.60 | 0.61 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.50 | 99.10 | 60 | 5.75 | 1.21 | 1.78 | 2.79 | 1.49 |
| RD02HX6 | 61.45 | 15.99 | 6.20 | 3.69 | 5.04 | 3.09 | 2.61 | 0.61 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.48 | 99.36 | 58 | 5.70 | 1.19 | 1.76 | 2.81 | 1.49 |
| RD02HX7 | 61.03 | 15.78 | 6.19 | 3.70 | 4.92 | 3.04 | 2.58 | 0.62 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.47 | 98.51 | 58 | 5.62 | 1.18 | 1.75 | 2.81 | 1.50 |
| RD02HX8 | 61.09 | 15.99 | 6.10 | 3.73 | 4.99 | 3.11 | 2.59 | 0.62 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.53 | 98.94 | 59 | 5.70 | 1.20 | 1.80 | 2.81 | 1.50 |
| BTHX1 | 54.52 | 15.71 | 7.82 | 7.21 | 7.23 | 3.42 | 1.78 | 0.64 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 1.67 | 100.20 | 68 | 5.20 | 1.93 | 2.35 | 3.02 | 1.26 |
| BTHX2 | 55.38 | 15.46 | 7.96 | 6.51 | 6.00 | 3.43 | 2.70 | 0.72 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 1.65 | 100.00 | 66 | 6.13 | 1.27 | 3.04 | 2.52 | 1.27 |
| BTHX3 | 54.47 | 14.91 | 8.60 | 7.39 | 7.37 | 3.25 | 1.57 | 0.70 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 1.11 | 99.60 | 67 | 4.82 | 2.07 | 2.03 | 3.09 | 1.22 |
| BTHX4 | 55.71 | 15.94 | 7.68 | 6.58 | 6.72 | 3.66 | 1.85 | 0.70 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 1.22 | 100.30 | 67 | 5.51 | 1.98 | 2.38 | 2.90 | 1.30 |
| BTHX5 | 56.67 | 15.50 | 7.98 | 6.76 | 6.93 | 3.14 | 1.95 | 0.65 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.86 | 100.70 | 67 | 5.09 | 1.61 | 1.89 | 3.05 | 1.29 |
| BTHX6 | 57.48 | 15.99 | 6.96 | 5.77 | 6.64 | 3.37 | 1.93 | 0.72 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.96 | 100.00 | 66 | 5.30 | 1.75 | 1.94 | 3.02 | 1.34 |
表2 日多玛花岗闪长岩和暗色微粒包体主量元素(wB/%)元素分析结果
Table 2 Contents of major elements (wt.%) of the Riduoma granodiorite and mafic microgranular enclaves
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | TiO2 | MnO | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | Mg# | ALK | Na2O/K2O | δ | A/NK | A/CNK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RD01HX1 | 62.19 | 15.71 | 5.96 | 3.53 | 4.74 | 3.04 | 2.60 | 0.59 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.65 | 99.19 | 58 | 5.64 | 1.17 | 1.65 | 2.79 | 1.52 |
| RD01HX2 | 63.37 | 15.75 | 6.23 | 3.51 | 4.53 | 3.02 | 2.75 | 0.58 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.67 | 100.58 | 57 | 5.77 | 1.10 | 1.63 | 2.73 | 1.53 |
| RD01HX3 | 63.85 | 15.92 | 5.58 | 3.61 | 4.72 | 3.08 | 2.68 | 0.59 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.51 | 100.73 | 60 | 5.77 | 1.15 | 1.59 | 2.76 | 1.52 |
| RD01HX4 | 62.94 | 15.83 | 6.15 | 3.61 | 4.82 | 3.06 | 2.64 | 0.60 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.53 | 100.36 | 58 | 5.69 | 1.16 | 1.63 | 2.78 | 1.51 |
| RD01HX5 | 62.51 | 15.67 | 5.32 | 3.54 | 4.55 | 2.91 | 2.66 | 0.60 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.84 | 98.78 | 61 | 5.57 | 1.09 | 1.59 | 2.81 | 1.55 |
| RD01HX6 | 63.26 | 15.87 | 5.47 | 3.60 | 4.67 | 3.04 | 2.66 | 0.60 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.60 | 99.96 | 61 | 5.70 | 1.14 | 1.60 | 2.79 | 1.53 |
| RD01HX7 | 62.61 | 15.60 | 5.61 | 3.66 | 4.84 | 2.99 | 2.69 | 0.59 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.68 | 99.46 | 60 | 5.69 | 1.11 | 1.65 | 2.74 | 1.48 |
| RD01HX8 | 62.68 | 15.80 | 5.42 | 3.58 | 4.81 | 3.03 | 2.71 | 0.59 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.65 | 99.45 | 61 | 5.74 | 1.12 | 1.67 | 2.76 | 1.50 |
| RD02HX5 | 61.64 | 16.04 | 5.66 | 3.71 | 4.99 | 3.15 | 2.60 | 0.61 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.50 | 99.10 | 60 | 5.75 | 1.21 | 1.78 | 2.79 | 1.49 |
| RD02HX6 | 61.45 | 15.99 | 6.20 | 3.69 | 5.04 | 3.09 | 2.61 | 0.61 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.48 | 99.36 | 58 | 5.70 | 1.19 | 1.76 | 2.81 | 1.49 |
| RD02HX7 | 61.03 | 15.78 | 6.19 | 3.70 | 4.92 | 3.04 | 2.58 | 0.62 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.47 | 98.51 | 58 | 5.62 | 1.18 | 1.75 | 2.81 | 1.50 |
| RD02HX8 | 61.09 | 15.99 | 6.10 | 3.73 | 4.99 | 3.11 | 2.59 | 0.62 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.53 | 98.94 | 59 | 5.70 | 1.20 | 1.80 | 2.81 | 1.50 |
| BTHX1 | 54.52 | 15.71 | 7.82 | 7.21 | 7.23 | 3.42 | 1.78 | 0.64 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 1.67 | 100.20 | 68 | 5.20 | 1.93 | 2.35 | 3.02 | 1.26 |
| BTHX2 | 55.38 | 15.46 | 7.96 | 6.51 | 6.00 | 3.43 | 2.70 | 0.72 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 1.65 | 100.00 | 66 | 6.13 | 1.27 | 3.04 | 2.52 | 1.27 |
| BTHX3 | 54.47 | 14.91 | 8.60 | 7.39 | 7.37 | 3.25 | 1.57 | 0.70 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 1.11 | 99.60 | 67 | 4.82 | 2.07 | 2.03 | 3.09 | 1.22 |
| BTHX4 | 55.71 | 15.94 | 7.68 | 6.58 | 6.72 | 3.66 | 1.85 | 0.70 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 1.22 | 100.30 | 67 | 5.51 | 1.98 | 2.38 | 2.90 | 1.30 |
| BTHX5 | 56.67 | 15.50 | 7.98 | 6.76 | 6.93 | 3.14 | 1.95 | 0.65 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.86 | 100.70 | 67 | 5.09 | 1.61 | 1.89 | 3.05 | 1.29 |
| BTHX6 | 57.48 | 15.99 | 6.96 | 5.77 | 6.64 | 3.37 | 1.93 | 0.72 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.96 | 100.00 | 66 | 5.30 | 1.75 | 1.94 | 3.02 | 1.34 |
| 样品编号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | LREE | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RD01HX1 | 31.90 | 63.50 | 6.78 | 25.25 | 4.79 | 1.02 | 4.18 | 0.63 | 3.26 | 0.65 | 1.81 | 0.28 | 1.75 | 0.25 | 16.60 | 133.24 | |||||||||||||||
| RD01HX2 | 31.90 | 63.00 | 7.04 | 25.05 | 4.36 | 1.03 | 3.94 | 0.59 | 3.14 | 0.61 | 1.68 | 0.26 | 1.69 | 0.25 | 15.40 | 132.38 | |||||||||||||||
| RD01HX3 | 33.60 | 66.40 | 7.45 | 27.89 | 4.91 | 1.11 | 3.90 | 0.60 | 3.19 | 0.62 | 1.77 | 0.28 | 1.76 | 0.27 | 15.80 | 141.36 | |||||||||||||||
| RD01HX4 | 32.00 | 63.60 | 7.13 | 27.16 | 4.89 | 1.12 | 4.19 | 0.62 | 3.23 | 0.58 | 1.57 | 0.25 | 1.60 | 0.25 | 15.90 | 135.90 | |||||||||||||||
| RD01HX5 | 32.10 | 63.40 | 7.02 | 26.80 | 4.71 | 1.10 | 4.05 | 0.60 | 2.91 | 0.56 | 1.60 | 0.25 | 1.62 | 0.25 | 15.80 | 135.13 | |||||||||||||||
| RD01HX6 | 33.90 | 67.20 | 7.43 | 28.39 | 4.89 | 1.11 | 4.24 | 0.61 | 3.03 | 0.58 | 1.65 | 0.26 | 1.67 | 0.26 | 16.40 | 142.92 | |||||||||||||||
| RD01HX7 | 36.20 | 71.70 | 7.87 | 30.22 | 5.36 | 1.22 | 4.25 | 0.63 | 3.38 | 0.65 | 1.83 | 0.29 | 1.88 | 0.28 | 16.90 | 152.57 | |||||||||||||||
| RD01HX8 | 35.00 | 68.50 | 7.69 | 28.45 | 4.75 | 1.01 | 4.12 | 0.61 | 3.29 | 0.65 | 1.79 | 0.28 | 1.80 | 0.27 | 15.80 | 145.40 | |||||||||||||||
| RD02HX5 | 32.70 | 62.80 | 6.99 | 26.20 | 4.52 | 1.08 | 4.06 | 0.59 | 3.11 | 0.60 | 1.63 | 0.24 | 1.51 | 0.23 | 14.90 | 134.29 | |||||||||||||||
| RD02HX6 | 34.40 | 67.70 | 7.65 | 28.51 | 4.91 | 1.16 | 3.99 | 0.57 | 3.05 | 0.60 | 1.65 | 0.26 | 1.67 | 0.25 | 15.10 | 144.33 | |||||||||||||||
| RD02HX7 | 26.50 | 52.90 | 6.12 | 23.01 | 4.12 | 1.04 | 3.62 | 0.53 | 2.70 | 0.51 | 1.35 | 0.20 | 1.32 | 0.20 | 13.00 | 113.69 | |||||||||||||||
| RD02HX8 | 31.90 | 62.60 | 7.17 | 27.04 | 4.84 | 1.21 | 4.29 | 0.62 | 3.25 | 0.62 | 1.63 | 0.24 | 1.53 | 0.24 | 15.50 | 134.76 | |||||||||||||||
| BTHX1 | 19.25 | 44.78 | 6.10 | 24.61 | 5.92 | 1.10 | 5.26 | 0.93 | 5.24 | 1.02 | 2.79 | 0.44 | 2.69 | 0.41 | 26.97 | 101.76 | |||||||||||||||
| BTHX2 | 29.84 | 70.70 | 8.76 | 33.75 | 6.74 | 0.92 | 5.86 | 0.96 | 5.30 | 1.05 | 2.88 | 0.46 | 2.96 | 0.45 | 28.69 | 150.70 | |||||||||||||||
| BTHX3 | 22.71 | 54.82 | 7.47 | 28.94 | 6.38 | 1.11 | 5.47 | 0.92 | 4.92 | 0.95 | 2.53 | 0.40 | 2.40 | 0.36 | 24.80 | 121.43 | |||||||||||||||
| BTHX4 | 27.30 | 66.40 | 8.15 | 30.47 | 6.29 | 1.00 | 5.53 | 0.88 | 4.71 | 0.92 | 2.54 | 0.40 | 2.53 | 0.40 | 25.08 | 139.61 | |||||||||||||||
| BTHX5 | 25.75 | 64.96 | 8.20 | 30.70 | 6.34 | 1.14 | 5.45 | 0.87 | 4.71 | 0.91 | 2.50 | 0.40 | 2.49 | 0.38 | 24.47 | 137.10 | |||||||||||||||
| BTHX6 | 27.85 | 71.69 | 9.17 | 36.19 | 7.65 | 1.28 | 6.34 | 1.02 | 5.17 | 1.04 | 2.84 | 0.44 | 2.58 | 0.38 | 28.49 | 153.84 | |||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | HREE | LREE/ HREE | ∑REE | (La/ Yb)N | (La/ Sm)N | (Gd/ Yb)N | δEu | δCe | Ba | Be | Co | Cr | Cs | Cu | Ga | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX1 | 12.81 | 10.40 | 146.05 | 13.08 | 4.30 | 1.98 | 0.68 | 1.01 | 629.00 | 2.98 | 16.70 | 158.00 | 9.78 | 10.30 | 21.20 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX2 | 12.16 | 10.89 | 144.54 | 13.54 | 4.72 | 1.93 | 0.75 | 0.99 | 598.00 | 2.89 | 15.60 | 156.00 | 9.31 | 10.90 | 19.40 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX3 | 12.39 | 11.41 | 153.75 | 13.69 | 4.30 | 1.83 | 0.75 | 0.99 | 595.00 | 2.36 | 14.10 | 152.00 | 12.00 | 10.50 | 19.20 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX4 | 12.29 | 11.06 | 148.19 | 14.35 | 4.22 | 2.17 | 0.74 | 0.99 | 593.00 | 2.69 | 16.00 | 175.00 | 13.50 | 12.90 | 20.30 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX5 | 11.84 | 11.41 | 146.97 | 14.21 | 4.40 | 2.07 | 0.75 | 0.99 | 587.00 | 2.39 | 16.50 | 164.00 | 9.16 | 11.30 | 19.50 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX6 | 12.30 | 11.62 | 155.22 | 14.56 | 4.30 | 2.10 | 0.73 | 0.99 | 626.00 | 2.67 | 14.40 | 168.00 | 12.60 | 25.50 | 20.30 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX7 | 13.19 | 11.57 | 165.76 | 13.81 | 4.36 | 1.87 | 0.76 | 0.99 | 665.00 | 2.58 | 16.10 | 185.00 | 10.90 | 12.50 | 21.10 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX8 | 12.81 | 11.35 | 158.21 | 13.95 | 4.30 | 1.89 | 0.68 | 0.98 | 591.00 | 2.54 | 16.10 | 176.00 | 9.48 | 24.90 | 18.80 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD02HX5 | 11.97 | 11.22 | 146.26 | 15.53 | 4.67 | 2.22 | 0.76 | 0.97 | 594.00 | 2.57 | 14.30 | 158.00 | 10.30 | 12.70 | 19.10 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD02HX6 | 12.04 | 11.99 | 156.37 | 14.78 | 4.30 | 1.98 | 0.78 | 0.98 | 601.00 | 2.42 | 15.90 | 167.00 | 10.50 | 42.40 | 20.30 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD02HX7 | 10.43 | 10.90 | 124.12 | 14.40 | 4.15 | 2.27 | 0.81 | 0.98 | 539.00 | 2.35 | 13.80 | 149.00 | 9.71 | 27.50 | 18.60 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD02HX8 | 12.42 | 10.85 | 147.18 | 14.96 | 4.25 | 2.32 | 0.79 | 0.97 | 642.00 | 2.64 | 16.10 | 172.00 | 11.20 | 38.20 | 21.60 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX1 | 18.79 | 5.42 | 120.55 | 5.13 | 2.10 | 1.62 | 0.59 | 1.01 | 356.49 | 2.69 | 22.11 | 410.50 | 21.85 | 9.85 | 19.58 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX2 | 19.92 | 7.57 | 170.62 | 7.24 | 2.86 | 1.64 | 0.44 | 1.06 | 544.59 | 3.21 | 22.03 | 293.55 | 16.25 | 32.75 | 18.55 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX3 | 17.96 | 6.76 | 139.39 | 6.80 | 2.30 | 1.89 | 0.56 | 1.03 | 335.88 | 2.69 | 26.93 | 452.49 | 18.41 | 91.59 | 19.79 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX4 | 17.91 | 7.80 | 157.51 | 7.73 | 2.80 | 1.80 | 0.51 | 1.08 | 475.83 | 3.26 | 24.65 | 280.73 | 17.09 | 39.18 | 20.94 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX5 | 17.72 | 7.74 | 154.82 | 7.41 | 2.62 | 1.81 | 0.58 | 1.09 | 491.49 | 3.00 | 23.45 | 349.70 | 13.67 | 59.41 | 19.92 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX6 | 19.81 | 7.76 | 173.66 | 7.75 | 2.35 | 2.03 | 0.55 | 1.09 | 461.79 | 3.24 | 21.97 | 287.66 | 13.12 | 29.43 | 21.95 | ||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Hf | Li | Nb | Ni | Pb | Rb | Sc | Sr | Ta | Th | U | V | Zn | Zr | Sr/Y | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX1 | 4.64 | 50.00 | 12.10 | 40.10 | 20.70 | 108.00 | 14.40 | 399.00 | 0.80 | 11.10 | 1.36 | 75.00 | 65.60 | 155.00 | 24.04 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX2 | 4.46 | 48.30 | 10.80 | 38.90 | 21.20 | 115.00 | 13.00 | 375.00 | 0.74 | 11.90 | 1.30 | 72.00 | 62.60 | 159.00 | 24.35 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX3 | 4.96 | 49.60 | 11.00 | 35.40 | 17.70 | 117.00 | 12.70 | 395.00 | 0.85 | 12.30 | 1.52 | 71.20 | 49.20 | 161.00 | 25.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX4 | 4.89 | 50.10 | 11.70 | 46.60 | 18.60 | 121.00 | 12.50 | 359.00 | 0.83 | 11.30 | 1.91 | 74.20 | 56.80 | 176.00 | 22.58 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX5 | 5.13 | 50.30 | 11.30 | 40.40 | 18.20 | 113.00 | 12.20 | 381.00 | 0.80 | 12.20 | 2.40 | 74.20 | 57.00 | 185.00 | 24.11 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX6 | 5.44 | 54.90 | 11.60 | 39.10 | 14.90 | 122.00 | 12.80 | 400.00 | 0.82 | 12.50 | 1.93 | 76.40 | 49.40 | 197.00 | 24.39 | ||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Hf | Li | Nb | Ni | Pb | Rb | Sc | Sr | Ta | Th | U | V | Zn | Zr | Sr/Y | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX7 | 5.34 | 53.00 | 11.80 | 44.30 | 21.40 | 124.00 | 14.10 | 418.00 | 0.89 | 13.40 | 1.62 | 80.50 | 58.50 | 180.00 | 24.73 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX8 | 5.30 | 47.60 | 10.80 | 41.10 | 20.20 | 123.00 | 13.10 | 376.00 | 0.79 | 13.20 | 1.91 | 75.60 | 55.10 | 180.00 | 23.80 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD02HX5 | 4.37 | 46.90 | 10.60 | 38.00 | 20.00 | 119.00 | 12.20 | 380.00 | 0.76 | 13.00 | 1.57 | 72.80 | 52.40 | 157.00 | 25.50 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD02HX6 | 4.97 | 41.90 | 10.70 | 39.30 | 17.40 | 110.00 | 13.60 | 393.00 | 0.76 | 12.40 | 1.56 | 80.30 | 51.60 | 170.00 | 26.03 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD02HX7 | 4.18 | 38.60 | 9.93 | 36.40 | 14.90 | 101.00 | 11.40 | 345.00 | 0.65 | 9.28 | 1.18 | 71.70 | 48.90 | 151.00 | 26.54 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD02HX8 | 5.05 | 43.30 | 11.30 | 41.50 | 17.60 | 116.00 | 13.90 | 403.00 | 0.76 | 11.30 | 1.33 | 83.20 | 56.50 | 184.00 | 26.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX1 | 3.85 | 47.00 | 10.58 | 87.27 | 16.79 | 108.67 | 19.07 | 321.29 | 0.61 | 4.92 | 1.19 | 108.72 | 65.80 | 130.24 | 11.91 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX2 | 4.18 | 52.48 | 11.77 | 59.48 | 13.07 | 135.07 | 19.57 | 264.58 | 0.79 | 5.61 | 1.34 | 110.52 | 55.71 | 140.34 | 9.22 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX3 | 4.11 | 50.36 | 10.15 | 87.13 | 20.97 | 87.07 | 19.31 | 303.24 | 0.56 | 4.87 | 1.18 | 123.66 | 86.48 | 145.24 | 12.23 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX4 | 3.76 | 68.18 | 11.88 | 80.60 | 18.00 | 111.07 | 20.94 | 335.64 | 0.79 | 5.40 | 1.34 | 106.83 | 65.88 | 135.63 | 13.38 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX5 | 3.79 | 58.76 | 10.46 | 71.59 | 23.53 | 88.54 | 20.47 | 351.88 | 0.96 | 4.15 | 1.10 | 102.51 | 87.08 | 125.24 | 14.38 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX6 | 4.31 | 55.26 | 13.17 | 56.70 | 28.46 | 88.49 | 24.36 | 428.26 | 0.90 | 5.32 | 1.05 | 115.11 | 81.74 | 147.49 | 15.03 | ||||||||||||||||
表3 日多玛花岗闪长岩和暗色微粒包体微量元素和稀土元素分析结果(wB/10-6)
Table 3 Contents of trace elements and REE of the Riduoma granodiorite and mafic microgranular enclaves(10-6)
| 样品编号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | LREE | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RD01HX1 | 31.90 | 63.50 | 6.78 | 25.25 | 4.79 | 1.02 | 4.18 | 0.63 | 3.26 | 0.65 | 1.81 | 0.28 | 1.75 | 0.25 | 16.60 | 133.24 | |||||||||||||||
| RD01HX2 | 31.90 | 63.00 | 7.04 | 25.05 | 4.36 | 1.03 | 3.94 | 0.59 | 3.14 | 0.61 | 1.68 | 0.26 | 1.69 | 0.25 | 15.40 | 132.38 | |||||||||||||||
| RD01HX3 | 33.60 | 66.40 | 7.45 | 27.89 | 4.91 | 1.11 | 3.90 | 0.60 | 3.19 | 0.62 | 1.77 | 0.28 | 1.76 | 0.27 | 15.80 | 141.36 | |||||||||||||||
| RD01HX4 | 32.00 | 63.60 | 7.13 | 27.16 | 4.89 | 1.12 | 4.19 | 0.62 | 3.23 | 0.58 | 1.57 | 0.25 | 1.60 | 0.25 | 15.90 | 135.90 | |||||||||||||||
| RD01HX5 | 32.10 | 63.40 | 7.02 | 26.80 | 4.71 | 1.10 | 4.05 | 0.60 | 2.91 | 0.56 | 1.60 | 0.25 | 1.62 | 0.25 | 15.80 | 135.13 | |||||||||||||||
| RD01HX6 | 33.90 | 67.20 | 7.43 | 28.39 | 4.89 | 1.11 | 4.24 | 0.61 | 3.03 | 0.58 | 1.65 | 0.26 | 1.67 | 0.26 | 16.40 | 142.92 | |||||||||||||||
| RD01HX7 | 36.20 | 71.70 | 7.87 | 30.22 | 5.36 | 1.22 | 4.25 | 0.63 | 3.38 | 0.65 | 1.83 | 0.29 | 1.88 | 0.28 | 16.90 | 152.57 | |||||||||||||||
| RD01HX8 | 35.00 | 68.50 | 7.69 | 28.45 | 4.75 | 1.01 | 4.12 | 0.61 | 3.29 | 0.65 | 1.79 | 0.28 | 1.80 | 0.27 | 15.80 | 145.40 | |||||||||||||||
| RD02HX5 | 32.70 | 62.80 | 6.99 | 26.20 | 4.52 | 1.08 | 4.06 | 0.59 | 3.11 | 0.60 | 1.63 | 0.24 | 1.51 | 0.23 | 14.90 | 134.29 | |||||||||||||||
| RD02HX6 | 34.40 | 67.70 | 7.65 | 28.51 | 4.91 | 1.16 | 3.99 | 0.57 | 3.05 | 0.60 | 1.65 | 0.26 | 1.67 | 0.25 | 15.10 | 144.33 | |||||||||||||||
| RD02HX7 | 26.50 | 52.90 | 6.12 | 23.01 | 4.12 | 1.04 | 3.62 | 0.53 | 2.70 | 0.51 | 1.35 | 0.20 | 1.32 | 0.20 | 13.00 | 113.69 | |||||||||||||||
| RD02HX8 | 31.90 | 62.60 | 7.17 | 27.04 | 4.84 | 1.21 | 4.29 | 0.62 | 3.25 | 0.62 | 1.63 | 0.24 | 1.53 | 0.24 | 15.50 | 134.76 | |||||||||||||||
| BTHX1 | 19.25 | 44.78 | 6.10 | 24.61 | 5.92 | 1.10 | 5.26 | 0.93 | 5.24 | 1.02 | 2.79 | 0.44 | 2.69 | 0.41 | 26.97 | 101.76 | |||||||||||||||
| BTHX2 | 29.84 | 70.70 | 8.76 | 33.75 | 6.74 | 0.92 | 5.86 | 0.96 | 5.30 | 1.05 | 2.88 | 0.46 | 2.96 | 0.45 | 28.69 | 150.70 | |||||||||||||||
| BTHX3 | 22.71 | 54.82 | 7.47 | 28.94 | 6.38 | 1.11 | 5.47 | 0.92 | 4.92 | 0.95 | 2.53 | 0.40 | 2.40 | 0.36 | 24.80 | 121.43 | |||||||||||||||
| BTHX4 | 27.30 | 66.40 | 8.15 | 30.47 | 6.29 | 1.00 | 5.53 | 0.88 | 4.71 | 0.92 | 2.54 | 0.40 | 2.53 | 0.40 | 25.08 | 139.61 | |||||||||||||||
| BTHX5 | 25.75 | 64.96 | 8.20 | 30.70 | 6.34 | 1.14 | 5.45 | 0.87 | 4.71 | 0.91 | 2.50 | 0.40 | 2.49 | 0.38 | 24.47 | 137.10 | |||||||||||||||
| BTHX6 | 27.85 | 71.69 | 9.17 | 36.19 | 7.65 | 1.28 | 6.34 | 1.02 | 5.17 | 1.04 | 2.84 | 0.44 | 2.58 | 0.38 | 28.49 | 153.84 | |||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | HREE | LREE/ HREE | ∑REE | (La/ Yb)N | (La/ Sm)N | (Gd/ Yb)N | δEu | δCe | Ba | Be | Co | Cr | Cs | Cu | Ga | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX1 | 12.81 | 10.40 | 146.05 | 13.08 | 4.30 | 1.98 | 0.68 | 1.01 | 629.00 | 2.98 | 16.70 | 158.00 | 9.78 | 10.30 | 21.20 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX2 | 12.16 | 10.89 | 144.54 | 13.54 | 4.72 | 1.93 | 0.75 | 0.99 | 598.00 | 2.89 | 15.60 | 156.00 | 9.31 | 10.90 | 19.40 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX3 | 12.39 | 11.41 | 153.75 | 13.69 | 4.30 | 1.83 | 0.75 | 0.99 | 595.00 | 2.36 | 14.10 | 152.00 | 12.00 | 10.50 | 19.20 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX4 | 12.29 | 11.06 | 148.19 | 14.35 | 4.22 | 2.17 | 0.74 | 0.99 | 593.00 | 2.69 | 16.00 | 175.00 | 13.50 | 12.90 | 20.30 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX5 | 11.84 | 11.41 | 146.97 | 14.21 | 4.40 | 2.07 | 0.75 | 0.99 | 587.00 | 2.39 | 16.50 | 164.00 | 9.16 | 11.30 | 19.50 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX6 | 12.30 | 11.62 | 155.22 | 14.56 | 4.30 | 2.10 | 0.73 | 0.99 | 626.00 | 2.67 | 14.40 | 168.00 | 12.60 | 25.50 | 20.30 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX7 | 13.19 | 11.57 | 165.76 | 13.81 | 4.36 | 1.87 | 0.76 | 0.99 | 665.00 | 2.58 | 16.10 | 185.00 | 10.90 | 12.50 | 21.10 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX8 | 12.81 | 11.35 | 158.21 | 13.95 | 4.30 | 1.89 | 0.68 | 0.98 | 591.00 | 2.54 | 16.10 | 176.00 | 9.48 | 24.90 | 18.80 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD02HX5 | 11.97 | 11.22 | 146.26 | 15.53 | 4.67 | 2.22 | 0.76 | 0.97 | 594.00 | 2.57 | 14.30 | 158.00 | 10.30 | 12.70 | 19.10 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD02HX6 | 12.04 | 11.99 | 156.37 | 14.78 | 4.30 | 1.98 | 0.78 | 0.98 | 601.00 | 2.42 | 15.90 | 167.00 | 10.50 | 42.40 | 20.30 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD02HX7 | 10.43 | 10.90 | 124.12 | 14.40 | 4.15 | 2.27 | 0.81 | 0.98 | 539.00 | 2.35 | 13.80 | 149.00 | 9.71 | 27.50 | 18.60 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD02HX8 | 12.42 | 10.85 | 147.18 | 14.96 | 4.25 | 2.32 | 0.79 | 0.97 | 642.00 | 2.64 | 16.10 | 172.00 | 11.20 | 38.20 | 21.60 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX1 | 18.79 | 5.42 | 120.55 | 5.13 | 2.10 | 1.62 | 0.59 | 1.01 | 356.49 | 2.69 | 22.11 | 410.50 | 21.85 | 9.85 | 19.58 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX2 | 19.92 | 7.57 | 170.62 | 7.24 | 2.86 | 1.64 | 0.44 | 1.06 | 544.59 | 3.21 | 22.03 | 293.55 | 16.25 | 32.75 | 18.55 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX3 | 17.96 | 6.76 | 139.39 | 6.80 | 2.30 | 1.89 | 0.56 | 1.03 | 335.88 | 2.69 | 26.93 | 452.49 | 18.41 | 91.59 | 19.79 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX4 | 17.91 | 7.80 | 157.51 | 7.73 | 2.80 | 1.80 | 0.51 | 1.08 | 475.83 | 3.26 | 24.65 | 280.73 | 17.09 | 39.18 | 20.94 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX5 | 17.72 | 7.74 | 154.82 | 7.41 | 2.62 | 1.81 | 0.58 | 1.09 | 491.49 | 3.00 | 23.45 | 349.70 | 13.67 | 59.41 | 19.92 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX6 | 19.81 | 7.76 | 173.66 | 7.75 | 2.35 | 2.03 | 0.55 | 1.09 | 461.79 | 3.24 | 21.97 | 287.66 | 13.12 | 29.43 | 21.95 | ||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Hf | Li | Nb | Ni | Pb | Rb | Sc | Sr | Ta | Th | U | V | Zn | Zr | Sr/Y | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX1 | 4.64 | 50.00 | 12.10 | 40.10 | 20.70 | 108.00 | 14.40 | 399.00 | 0.80 | 11.10 | 1.36 | 75.00 | 65.60 | 155.00 | 24.04 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX2 | 4.46 | 48.30 | 10.80 | 38.90 | 21.20 | 115.00 | 13.00 | 375.00 | 0.74 | 11.90 | 1.30 | 72.00 | 62.60 | 159.00 | 24.35 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX3 | 4.96 | 49.60 | 11.00 | 35.40 | 17.70 | 117.00 | 12.70 | 395.00 | 0.85 | 12.30 | 1.52 | 71.20 | 49.20 | 161.00 | 25.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX4 | 4.89 | 50.10 | 11.70 | 46.60 | 18.60 | 121.00 | 12.50 | 359.00 | 0.83 | 11.30 | 1.91 | 74.20 | 56.80 | 176.00 | 22.58 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX5 | 5.13 | 50.30 | 11.30 | 40.40 | 18.20 | 113.00 | 12.20 | 381.00 | 0.80 | 12.20 | 2.40 | 74.20 | 57.00 | 185.00 | 24.11 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX6 | 5.44 | 54.90 | 11.60 | 39.10 | 14.90 | 122.00 | 12.80 | 400.00 | 0.82 | 12.50 | 1.93 | 76.40 | 49.40 | 197.00 | 24.39 | ||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Hf | Li | Nb | Ni | Pb | Rb | Sc | Sr | Ta | Th | U | V | Zn | Zr | Sr/Y | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX7 | 5.34 | 53.00 | 11.80 | 44.30 | 21.40 | 124.00 | 14.10 | 418.00 | 0.89 | 13.40 | 1.62 | 80.50 | 58.50 | 180.00 | 24.73 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD01HX8 | 5.30 | 47.60 | 10.80 | 41.10 | 20.20 | 123.00 | 13.10 | 376.00 | 0.79 | 13.20 | 1.91 | 75.60 | 55.10 | 180.00 | 23.80 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD02HX5 | 4.37 | 46.90 | 10.60 | 38.00 | 20.00 | 119.00 | 12.20 | 380.00 | 0.76 | 13.00 | 1.57 | 72.80 | 52.40 | 157.00 | 25.50 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD02HX6 | 4.97 | 41.90 | 10.70 | 39.30 | 17.40 | 110.00 | 13.60 | 393.00 | 0.76 | 12.40 | 1.56 | 80.30 | 51.60 | 170.00 | 26.03 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD02HX7 | 4.18 | 38.60 | 9.93 | 36.40 | 14.90 | 101.00 | 11.40 | 345.00 | 0.65 | 9.28 | 1.18 | 71.70 | 48.90 | 151.00 | 26.54 | ||||||||||||||||
| RD02HX8 | 5.05 | 43.30 | 11.30 | 41.50 | 17.60 | 116.00 | 13.90 | 403.00 | 0.76 | 11.30 | 1.33 | 83.20 | 56.50 | 184.00 | 26.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX1 | 3.85 | 47.00 | 10.58 | 87.27 | 16.79 | 108.67 | 19.07 | 321.29 | 0.61 | 4.92 | 1.19 | 108.72 | 65.80 | 130.24 | 11.91 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX2 | 4.18 | 52.48 | 11.77 | 59.48 | 13.07 | 135.07 | 19.57 | 264.58 | 0.79 | 5.61 | 1.34 | 110.52 | 55.71 | 140.34 | 9.22 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX3 | 4.11 | 50.36 | 10.15 | 87.13 | 20.97 | 87.07 | 19.31 | 303.24 | 0.56 | 4.87 | 1.18 | 123.66 | 86.48 | 145.24 | 12.23 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX4 | 3.76 | 68.18 | 11.88 | 80.60 | 18.00 | 111.07 | 20.94 | 335.64 | 0.79 | 5.40 | 1.34 | 106.83 | 65.88 | 135.63 | 13.38 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX5 | 3.79 | 58.76 | 10.46 | 71.59 | 23.53 | 88.54 | 20.47 | 351.88 | 0.96 | 4.15 | 1.10 | 102.51 | 87.08 | 125.24 | 14.38 | ||||||||||||||||
| BTHX6 | 4.31 | 55.26 | 13.17 | 56.70 | 28.46 | 88.49 | 24.36 | 428.26 | 0.90 | 5.32 | 1.05 | 115.11 | 81.74 | 147.49 | 15.03 | ||||||||||||||||
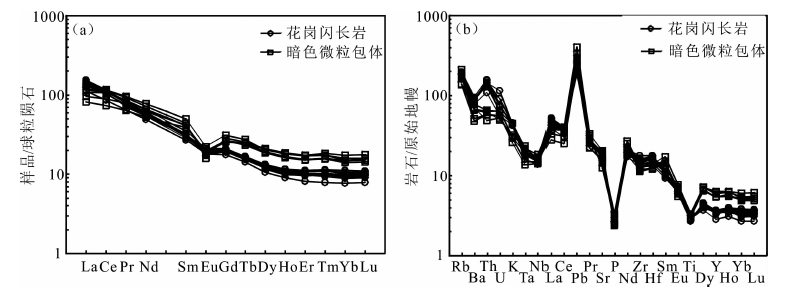
图10 日多玛花岗闪长岩和暗色微粒包体稀土元素配分模式图(a)和微量元素蛛网图(b)(球粒陨石、原始地幔数据来自文献[24])
Fig.10 Chondrite-normalized REE pattern (a) and primitive mantle-normalized multi-element spidergram (b) for the Ri-duoma granodiorite and mafic microgranular enclaves (primitive-mantle and chondrite normalizing data after reference [24])
| [1] | RUDNICK R, GAO S. Composition of the continental crust[M]//RUDNICK R L. Treatise on Geochemistry.Amsterdam:Elsevier, 2003,3:1-64. |
| [2] | 邓晋福, 莫宣学, 罗熙, 等. 火成岩构造组合与壳-幔成矿系统[J]. 地学前缘, 1999,6(2):259-269. |
| [3] | MO X X, NIU Y L, DONG G C, et al. Contribution of syncollisional felsic magmatism tocontinental crust growth:A case study of the Paleogene Linzizong volcanic Succession in southern Tibet[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008,250(1/4):49-67. |
| [4] | GOLDFARB R J, TAYLOR R D, Collins G S, et al. Phanerozoic continental growth and gold metallogeny of Asia[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014,25(1):48-102. |
| [5] | XIONG X, ZHU L M, ZHANG G W, et al. Geology and geochemistry of the Triassic Wenquan Mo-deposit and Mo-mineralized granite in the Western Qinling Orogen,China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016,30:159-178. |
| [6] | 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 等. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 1-855. |
| [7] | 冯益民, 曹宣铎, 张二朋, 等. 西秦岭造山带结构造山过程及动力学[M]. 西安: 西安地图出版社, 2003: 1-263. |
| [8] | CAO X F, LÜ X B, YAO S Z, et al. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon geochronology,geochemistry and kinetics of the Wenquan ore-bearing granites from West Qinling,China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2010,43(1):120-131. |
| [9] | QIN J F, LAI S C, DIWU C R, et al. Magma mixing origin for the post-collisional adakitic monzogranite of the Triassic Yangba pluton, Northwestern margin of the South China block:Geochemistry,Sr-Nd isotopic,zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic evidences[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2010,159(3):389-409. |
| [10] | QIN J F, LAI S C, GRAPES R, et al. Geochemical evidence for origin of magma mixing for the Triassic monzonitic granite and its enclaves at Mishuling in the Qinling orogen(Central China)[J]. Lithos, 2009,112(3/4):259-276. |
| [11] | QIN J F, LAI S C, GRAPES R, et al. Origin of Late Triassic high-Mg adakitic granitoid rocks from the Dongjiangkou area,Qinling orogen,central China:Implications for subduction of continental crust[J]. Lithos, 2010,120(3/4):347-367. |
| [12] | QIN J F, LAI S C, LI Y F. Slab breakoff model for the Triassic post-collisional adakitic granitoids in the Qinling Orogen,Central China:Zircon U-Pb ages,geochemistry,and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic constraints[J]. International Geology Review, 2008,50(12):1080-1104. |
| [13] | QIN J F, LAI S C, WANG J, et al. High-Mg# adakitic tonalite from the Xichahe area,South Qinling orogenic belt(Central China):Petrogenesis and geological implications[J]. International Geology Review, 2007,49(12):1145-1158. |
| [14] | ZHANG H F, XIAO L, ZHANG L, et al. Geochemical and Pb-Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of Indosinian granitoids from the Bikou block,northwest of the Yangtze plate:Constraints on petrogenesis,nature of deep crust and geodynamics[J]. Science in China:Series D, 2007,50(7):972-983. |
| [15] | 张成立, 王涛, 王晓霞, 等. 秦岭造山带早中生代花岗岩成因及其构造环境[J]. 高校地质学报, 2008,14(3):304-316. |
| [16] | 骆必继, 张宏飞, 肖尊奇. 西秦岭印支早期美武岩体的岩石成因及其构造意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2012,19(3):199-211. |
| [17] | 金维浚, 张旗, 何登发, 等. 西秦岭埃达克岩的SHRIMP定年及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2005,21(3):959-966. |
| [18] | 杨瀚文, 申俊峰, 魏立勇, 等. 西秦岭西段共和盆地周缘西功卡花岗闪长岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018,32(2):316-327. |
| [19] | YUAN H, GAO S, LIU X, et al. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geostandards & Geoanalytical Research, 2010,28(3):353-370. |
| [20] | 刘晔, 柳小明, 胡兆初, 等. ICP-MS测定地质样品中37个元素的准确度和长期稳定性分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(5):1203-1210. |
| [21] | MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994,37(3/4):215-224. |
| [22] | RICKWOOD P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989,22(4):247-263. |
| [23] | MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989,101(5):635-643. |
| [24] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematic of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 1989,42(1):313-345. |
| [25] | CHAPPELL B W. Two contrasting granite types[J]. Pacific Geology, 1974,8:173-174. |
| [26] | COLLINS W J, BEAMS S D, WHITE A J R. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia[J]. Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982,80(2):189-200. |
| [27] | WILSON M. Igneous Petrogenesis[M]. London:Unwin Hyman, 1989: 1-464. |
| [28] | THOMPSON R N, MORRISOB M A, HENDRY G L, et al. An assessment of the relative roles of a crust and mantle in magma genesis:an elemental approach[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A-Mathematical.Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1984,A310:549-590. |
| [29] | SISSON T W, RATAJESKI K, HANKINS W B, et al. Voluminous granitic magma from common basaltic sources[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2005,148(6):635-661. |
| [30] | 张宏飞, 靳兰兰, 张利, 等. 西秦岭花岗岩类地球化学和Pb-Sr-Nd同位素组成对基底性质及其构造属性的限制[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 2005,35(10):914-926. |
| [31] | RAPP R P, SHIMIZU N, NORMAN M D, et al. Reaction between slab-derived melts and peridotite in the mantle wedge:Experimental constraints at 3.8GPa[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999,160(4):335-356. |
| [32] | RAPP R P, WATSON E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8-32 kbar:Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995,36(4):891. |
| [33] | RUSHMER T. Partial melting of two amphibolites:Contrasting experimental results under fluid-absent conditions[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1991,107(1):41-59. |
| [34] | 李曙光, 孙卫东, 张国伟, 等. 南秦岭勉略构造带黑沟峡变质火山岩的年代学和地球化学:古生代洋盆及其闭合时代的证据[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 1996,26(3):223-230. |
| [35] | 任纪舜. 昆仑-秦岭造山系的几个问题[J]. 西北地质, 2004,37(1):1-5. |
| [36] | 殷鸿福, 张克信. 中央造山带的演化及其特点[J]. 地球科学, 1998,23(5):438-442. |
| [37] | 陈守建, 李荣社, 计文化, 等. 昆仑造山带二叠纪岩相古地理特征及盆山转换探讨[J]. 中国地质, 2010,37(2):374-393. |
| [38] | PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks.[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984,25(4):956-983. |
| [39] | DAVIES J H, VON BLANCKENBURG F. Slab breakoff:A model of lithosphere detachment and its test in the magmatism and deformation of collisional orogens[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1995,129:85-102. |
| [40] | VON BLANCKENBURG F, DAVIES J H. Slab breakoff:A model for syncollisional magmatism and tectonics in the Alps[J]. Tectonics, 1995,14(1):120-131. |
| [41] | ALTUNKAYNAK S. Collision-driven slab breakoff magmatism in northwestern Anatolia,Turkey[J]. Journal of Geology, 2007,115(1):63-82. |
| [42] | ALTUNKAYNAK S, DILEK Y. Timing and nature of postcollisional volcanism in western Anatolia and geodynamic implications[J]. Special Paper,Geological Society of America, 2006,409:321-351. |
| [43] | ATHERTON M P, GHANI A A. Slab breakoff:A model for Caledonian,Late Granite syn-collisional magmatism in the orthotectonic(metamorphic)zone of Scotland and Donegel,Ireland[J]. Lithos, 2002,62(3/4):65-85. |
| [44] | KOHN M J, PARKINSON C D. Petrologic case for Eocene slab breakoff during the Indo-Asian collision[J]. Geology, 2002,30(7):591-594. |
| [45] | MAHÉO G, BLICHERT-TOFT J, PIN C et al. Partial melting of mantle and crustal sources beneath south Karakorum,Pakistan:Implications for the Miocene geodynamic evolution of the India-Asia convergence zone[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2009,50(3):427-449. |
| [46] | MAHÉO G, GUILLOT S, BLICHERT-TOFT J, et al. A slab breakoff model for the Neogene thermal evolution of South Karakorum and South Tibet[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002,195(1/2):45-58. |
| [47] | BONIN B. Do coeval mafic and felsic magmas in post-collisional to within-plate regimes necessarily imply two contrasting,mantle and crustal,sources? A review[J]. Lithos, 2004,78(1/2):1-24. |
| [48] | MASSONNE H. Involvement of crustal material in delamination of the lithosphere after continent-continent collision[J]. International Geology Review, 2005,47(8):792-804. |
| [49] |
WORTEL M J R, SPAKMAN W. Subduction and slab detachment in the Mediterranean-Carpathian region[J]. Science, 2000,290:1910-1917.
DOI URL PMID |
| [50] | XIAO L, ZHANG H F, CLEMENS J D, et al. Late Triassic granitoids of the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau:Geochronology,petrogenesis and implications for tectonic evolution[J]. Lithos, 2007,96(3/4):436-452. |
| [51] | ZHANG H F, PARRISH R, ZHANG L, et al. A-type granite and adakitic magmatism association in Songpan-Garze fold belt,eastern Tibetan Plateau:Implication for lithospheric delamination[J]. Lithos, 2007,97(3/4):323-335. |
| [52] | ZHANG H F, ZHANG L, HARRIS N, et al. U/Pb zircon ages,geochemical and isotopic compositions of granitoids in Songba-Garze fold belt,eastern Tibetan Plateau:Constraints on petrogenesis and tectonic evolution of the basement[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2006,152(1):75-88. |
| [53] | 张成立, 张国伟, 宴云翔, 等. 南秦岭勉略带北光头山花岗岩体群的成因及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2005,21(3):711-720. |
| [54] | NEILSON J C, KOKELAAR B P, CROWLEY Q G. Timing,relations and cause of plutonic and volcanic activity of the Siluro-Devonian post-collision magmatic episode in the Grampian Terrane,Scotland[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2009,166(3):545-561. |
| [55] | ROGERS R D, KÁRASON H, VAN DER HISLT R D. Epeirogenic uplift above a detached slab in northern Central America[J]. Geology, 2002,30(11):1031-1034. |
| [56] | DURETZ T, GERYA T V, MAY D A. Numerical modeling of spontaneous slab breakoff and subsequent topographic response[J]. Tectonophysics, 2011,502(1/2):244-256. |
| [1] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [2] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [3] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [4] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [5] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [6] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [7] | 梁鸣, 高文, 罗先熔, 王晓东, 刘秀娟, 陈皓, 刘攀峰, 竹峰, 李伟. 冀北高尖子地区土壤地球化学特征及其找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1567-1579. |
| [8] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [9] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [10] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [11] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [12] | 可行, 赵青芳, 吴飘, 杨传胜, 廖晶, 龚建明. 胶莱盆地东北部白垩系烃源岩特征与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1358-1368. |
| [13] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [14] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [15] | 王向伟, 张保涛, 杨浩强, 韩进国. 青海省海晏县团宝山一带变质岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 586-598. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||