



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (06): 1261-1276.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.072
郭娜1( ), 刘翠2, 崔龙1, 姚薇1, 李国英1, 甘黎明1, 黄勇3
), 刘翠2, 崔龙1, 姚薇1, 李国英1, 甘黎明1, 黄勇3
收稿日期:2018-10-26
修回日期:2019-06-10
出版日期:2020-12-22
发布日期:2020-12-22
作者简介:郭 娜,女,助理工程师,硕士研究生,1986年出生,地质工程专业,主要从事岩浆作用与资源环境方面的研究。Email:380403034@qq.com。
基金资助:
GUO Na1( ), LIU Cui2, CUI Long1, YAO Wei1, LI Guoying1, GAN Liming1, HUANG Yong3
), LIU Cui2, CUI Long1, YAO Wei1, LI Guoying1, GAN Liming1, HUANG Yong3
Received:2018-10-26
Revised:2019-06-10
Online:2020-12-22
Published:2020-12-22
摘要:
甘肃马坞金矿床位于西秦岭岷礼成矿带东段,中川岩体外接触带,属于微细浸染型金矿床,达中型规模。针对矿区发育的火成岩开展野外地质学、岩相学、年代学和地球化学等研究,以揭示致矿火成岩组合及其特征,进而探讨岩石成因及金矿形成的地质背景等。野外观察显示马坞矿区金矿脉常与煌斑岩脉、石英闪长岩脉及细晶岩脉等相伴生或相互穿切,说明金矿与上述脉岩的形成时间近乎一致,故认为该脉岩群为致矿火成岩组合。马坞矿区煌斑岩和花岗质脉岩LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年结果表明其形成于(153.5±3.5)~(154.9±0.9)Ma,推测金矿可能形成于晚侏罗世。该脉岩群具有宽广的SiO2、K2O、Na2O、TFeO和MgO含量,属于不同的岩性,且来自不同的岩浆源区,因此属于宽谱系岩墙群,指示其形成于造山带岩石圈拆沉作用所引发的伸展环境中。脉岩和金矿赋存于以中川岩体为代表的花岗质岩基及其围岩,表明其形成于西秦岭造山运动后期的大规模岩浆活动及岩基隆升之后,属于岩基后成矿作用的产物。
中图分类号:
郭娜, 刘翠, 崔龙, 姚薇, 李国英, 甘黎明, 黄勇. 西秦岭岷礼成矿带马坞金矿致矿火成岩组合与成矿地质背景[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1261-1276.
GUO Na, LIU Cui, CUI Long, YAO Wei, LI Guoying, GAN Liming, HUANG Yong. Igneous Assemblage and Metallogenic Background of the Mawu Gold Deposit in the Min-Li Ore Belt of the Western Qinling Orogen[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(06): 1261-1276.

图2 马坞矿区地质简图[18] 1.第四系;2. 下石炭统巴都组;3. 舒家坝群何家店组第四岩性段;4. 舒家坝群何家店组第三岩性段;5. 舒家坝群何家店组第二岩性段;6. 舒家坝群何家店组第一岩性段;7. 黑云母花岗岩;8.煌斑岩(突出煌斑岩脉与金矿体的关系,图中将大面积出露的煌斑岩脉进行了放大标示,未标示的区域不表示没有煌斑岩出露,而是分布比较分散);9. 矿化体位置及编号;10. 石英脉;11. 断裂带位置及编号;12. 地层界限
Fig.2 Geological sketch map of Mawu deposit [18]

图4 马坞矿区脉岩手标本及镜下照片 (a)、(b) MW-001;(c)、(d) MW-002;(e)、(f) MW-003;(g)、(h) MW-004;(i)、(j) MW-005;(k)、(l) MW-006;Am.角闪石;Pl. 斜长石;Kfs. 碱性长石;Bt. 黑云母;Qz. 石英;Va. 球颗;Cal. 方解石;Me. 金属矿物
Fig.4 Hand specimen and microscopic photos of magmatic dikes from the Mawu deposit
| 样品 | 采样点 | 原名称 | 本文定名 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | K2O+ Na2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | K2O/ Na2O | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW-001 | 马坞金矿床 | 煌斑岩 | 煌斑岩 | 53.62 | 0.79 | 14.70 | 2.80 | 1.78 | 0.22 | 3.84 | 5.72 | 2.30 | 3.10 | 5.4 | 0.24 | 10.77 | 99.86 | 1.35 | 本文 |
| MW-002 | 马坞金矿床 | 煌斑岩 | 煌斑岩 | 46.07 | 0.91 | 12.54 | 3.23 | 5.35 | 0.13 | 11.73 | 6.64 | 2.50 | 2.24 | 4.74 | 0.31 | 7.75 | 99.40 | 0.90 | 本文 |
| MW-003 | 马坞金矿床 | 石英闪长岩 | 石英闪长岩 | 47.44 | 0.94 | 14.32 | 1.60 | 5.22 | 0.12 | 5.43 | 7.05 | 0.70 | 2.80 | 3.50 | 0.17 | 14.05 | 99.84 | 4.00 | 本文 |
| MW-004 | 马坞金矿床 | 煌斑岩 | 煌斑岩 | 44.35 | 0.78 | 12.40 | 2.24 | 5.45 | 0.14 | 9.52 | 8.35 | 2.08 | 1.53 | 3.61 | 0.29 | 12.43 | 99.56 | 0.74 | 本文 |
| MW-005 | 马坞金矿床 | 煌斑岩 | 煌斑岩 | 49.21 | 0.79 | 13.59 | 1.67 | 6.38 | 0.11 | 8.66 | 5.72 | 1.01 | 1.24 | 2.25 | 0.15 | 11.29 | 99.82 | 1.29 | 本文 |
| MW-006 | 马坞金矿床 | 石英闪长岩 | 石英闪长岩 | 43.96 | 0.85 | 12.38 | 0.54 | 5.90 | 0.14 | 6.88 | 7.49 | 1.54 | 1.31 | 2.85 | 0.30 | 18.46 | 99.74 | 0.85 | 本文 |
| 08-49h | 中川岩体 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 68.93 | 0.44 | 15.60 | 0.47 | 2.24 | 0.06 | 0.95 | 2.60 | 3.63 | 3.83 | 7.46 | 0.17 | 0.74 | 99.78 | 1.06 | 李婷等,2012[ |
| 08-50h | 中川岩体 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 70.13 | 0.49 | 14.40 | 0.66 | 2.37 | 0.06 | 1.07 | 2.63 | 3.46 | 3.34 | 6.80 | 0.19 | 0.72 | 99.79 | 0.97 | 李婷等,2012[ |
| 10 | 中川岩体 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 70.88 | 0.33 | 14.08 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.77 | 1.50 | 3.55 | 4.52 | 8.07 | 0.15 | — | 99.80 | 1.27 | 李婷等,2012[ |
| 12 | 中川岩体 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 71.34 | 0.26 | 14.66 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.50 | 1.04 | 3.99 | 4.70 | 8.69 | 0.12 | — | 99.81 | 1.18 | 李婷等,2012[ |
| ZC01/1B | 中川岩体 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 67.61 | 0.49 | 15.29 | 3.23 | — | 0.06 | 1.14 | 2.58 | 3.42 | 4.70 | 8.12 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 99.72 | 1.37 | 聂政融,2015[ |
| ZC05/1B | 中川岩体 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 68.18 | 0.47 | 15.36 | 3.13 | — | 0.06 | 1.11 | 2.50 | 3.50 | 4.46 | 7.96 | 0.19 | 0.80 | 99.78 | 1.27 | 聂政融,2015[ |
| ZC08/1B | 中川岩体 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 石英二长岩 | 65.56 | 0.61 | 15.73 | 4.15 | — | 0.08 | 1.34 | 2.48 | 3.42 | 5.07 | 8.49 | 0.22 | 1.10 | 99.73 | 1.48 | 聂政融,2015[ |
| ZC37/1B | 中川岩体 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 66.67 | 0.47 | 15.89 | 3.27 | — | 0.04 | 1.46 | 2.75 | 3.77 | 3.82 | 7.59 | 0.15 | 1.40 | 99.72 | 1.01 | 聂政融,2015[ |
| 15ZC-002 | 中川岩体 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 石英二长岩 | 63.59 | 0.52 | 17.42 | 3.26 | — | 0.06 | 1.14 | 2.65 | 3.81 | 6.10 | 9.91 | 0.19 | 0.58 | 99.32 | 1.60 | 杨尚松,2017[ |
| 13ZC-04 | 中川岩体 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 石英二长岩 | 67.41 | 0.49 | 15.54 | 4.24 | — | 0.07 | 1.10 | 2.31 | 3.30 | 4.97 | 8.27 | 0.20 | 1.28 | 100.90 | 1.51 | 杨尚松,2017[ |
| 14ZC-01 | 中川岩体 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 73.82 | 0.28 | 13.88 | 1.17 | — | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.42 | 2.96 | 5.15 | 8.11 | 0.11 | 1.37 | 99.40 | 1.74 | 杨尚松,2017[ |
| BJZ12-03 | 柏家庄岩体 | 二云母二长花岗岩 | 二云母二长花岗岩 | 74.58 | 0.17 | 13.15 | 1.30 | — | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.98 | 3.63 | 5.38 | 9.01 | 0.07 | 0.47 | 100.00 | 1.48 | 段梦,2016[ |
| BJZ12-05 | 柏家庄岩体 | 二云母二长花岗岩 | 二云母二长花岗岩 | 73.47 | 0.17 | 13.96 | 1.19 | — | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.93 | 3.46 | 5.30 | 8.76 | 0.08 | 0.59 | 99.40 | 1.53 | 段梦,2016[ |
| 13ZC-003 | 中川岩体 | 花岗岩脉 | 花岗斑岩 | 72.95 | 0.09 | 14.82 | 0.33 | — | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.42 | 7.49 | 7.91 | 0.02 | 2.98 | 99.46 | 17.83 | 杨尚松,2017[ |
| 13ZC-05 | 中川岩体 | 花岗岩脉 | 花岗斑岩 | 76.22 | 0.06 | 12.99 | 0.56 | — | 0.01 | 0.15 | 1.05 | 3.47 | 4.62 | 8.09 | 0 | 0.50 | 99.63 | 1.33 | 杨尚松,2017[ |
| LZ001 | 李坝金矿床 | 斜闪煌斑岩 | 花岗闪长斑岩 | 65.20 | 0.44 | 15.32 | 0.61 | 2.77 | 0.08 | 2.88 | 2.17 | 3.70 | 3.64 | 7.34 | 0.18 | 2.89 | 80.79 | 0.98 | 韩海涛等, 2008[ |
| LZ002 | 李坝金矿床 | 闪长细晶岩 | 石英闪长岩 | 59.28 | 0.54 | 15.56 | 0.61 | 3.95 | 0.18 | 7.48 | 2.82 | 3.40 | 1.26 | 4.66 | 0.18 | 5.11 | 80.16 | 0.37 | 韩海涛等, 2008[ |
| LZ003 | 李坝金矿床 | 花岗斑岩 | 花岗斑岩 | 70.69 | 0.31 | 16.36 | 1.01 | 1.25 | 0.20 | 1.27 | 1.16 | 3.48 | 4.16 | 7.64 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 79.53 | 1.20 | 韩海涛等, 2008[ |
表1 马坞矿区及邻区火成岩主量元素(wB/%)分析结果
Table 1 Major element compositions (%) of the magmatic rocks in/around the Mawu deposit
| 样品 | 采样点 | 原名称 | 本文定名 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | K2O+ Na2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | K2O/ Na2O | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW-001 | 马坞金矿床 | 煌斑岩 | 煌斑岩 | 53.62 | 0.79 | 14.70 | 2.80 | 1.78 | 0.22 | 3.84 | 5.72 | 2.30 | 3.10 | 5.4 | 0.24 | 10.77 | 99.86 | 1.35 | 本文 |
| MW-002 | 马坞金矿床 | 煌斑岩 | 煌斑岩 | 46.07 | 0.91 | 12.54 | 3.23 | 5.35 | 0.13 | 11.73 | 6.64 | 2.50 | 2.24 | 4.74 | 0.31 | 7.75 | 99.40 | 0.90 | 本文 |
| MW-003 | 马坞金矿床 | 石英闪长岩 | 石英闪长岩 | 47.44 | 0.94 | 14.32 | 1.60 | 5.22 | 0.12 | 5.43 | 7.05 | 0.70 | 2.80 | 3.50 | 0.17 | 14.05 | 99.84 | 4.00 | 本文 |
| MW-004 | 马坞金矿床 | 煌斑岩 | 煌斑岩 | 44.35 | 0.78 | 12.40 | 2.24 | 5.45 | 0.14 | 9.52 | 8.35 | 2.08 | 1.53 | 3.61 | 0.29 | 12.43 | 99.56 | 0.74 | 本文 |
| MW-005 | 马坞金矿床 | 煌斑岩 | 煌斑岩 | 49.21 | 0.79 | 13.59 | 1.67 | 6.38 | 0.11 | 8.66 | 5.72 | 1.01 | 1.24 | 2.25 | 0.15 | 11.29 | 99.82 | 1.29 | 本文 |
| MW-006 | 马坞金矿床 | 石英闪长岩 | 石英闪长岩 | 43.96 | 0.85 | 12.38 | 0.54 | 5.90 | 0.14 | 6.88 | 7.49 | 1.54 | 1.31 | 2.85 | 0.30 | 18.46 | 99.74 | 0.85 | 本文 |
| 08-49h | 中川岩体 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 68.93 | 0.44 | 15.60 | 0.47 | 2.24 | 0.06 | 0.95 | 2.60 | 3.63 | 3.83 | 7.46 | 0.17 | 0.74 | 99.78 | 1.06 | 李婷等,2012[ |
| 08-50h | 中川岩体 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 70.13 | 0.49 | 14.40 | 0.66 | 2.37 | 0.06 | 1.07 | 2.63 | 3.46 | 3.34 | 6.80 | 0.19 | 0.72 | 99.79 | 0.97 | 李婷等,2012[ |
| 10 | 中川岩体 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 70.88 | 0.33 | 14.08 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.77 | 1.50 | 3.55 | 4.52 | 8.07 | 0.15 | — | 99.80 | 1.27 | 李婷等,2012[ |
| 12 | 中川岩体 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 71.34 | 0.26 | 14.66 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.50 | 1.04 | 3.99 | 4.70 | 8.69 | 0.12 | — | 99.81 | 1.18 | 李婷等,2012[ |
| ZC01/1B | 中川岩体 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 67.61 | 0.49 | 15.29 | 3.23 | — | 0.06 | 1.14 | 2.58 | 3.42 | 4.70 | 8.12 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 99.72 | 1.37 | 聂政融,2015[ |
| ZC05/1B | 中川岩体 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 68.18 | 0.47 | 15.36 | 3.13 | — | 0.06 | 1.11 | 2.50 | 3.50 | 4.46 | 7.96 | 0.19 | 0.80 | 99.78 | 1.27 | 聂政融,2015[ |
| ZC08/1B | 中川岩体 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 石英二长岩 | 65.56 | 0.61 | 15.73 | 4.15 | — | 0.08 | 1.34 | 2.48 | 3.42 | 5.07 | 8.49 | 0.22 | 1.10 | 99.73 | 1.48 | 聂政融,2015[ |
| ZC37/1B | 中川岩体 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 66.67 | 0.47 | 15.89 | 3.27 | — | 0.04 | 1.46 | 2.75 | 3.77 | 3.82 | 7.59 | 0.15 | 1.40 | 99.72 | 1.01 | 聂政融,2015[ |
| 15ZC-002 | 中川岩体 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 石英二长岩 | 63.59 | 0.52 | 17.42 | 3.26 | — | 0.06 | 1.14 | 2.65 | 3.81 | 6.10 | 9.91 | 0.19 | 0.58 | 99.32 | 1.60 | 杨尚松,2017[ |
| 13ZC-04 | 中川岩体 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 石英二长岩 | 67.41 | 0.49 | 15.54 | 4.24 | — | 0.07 | 1.10 | 2.31 | 3.30 | 4.97 | 8.27 | 0.20 | 1.28 | 100.90 | 1.51 | 杨尚松,2017[ |
| 14ZC-01 | 中川岩体 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 73.82 | 0.28 | 13.88 | 1.17 | — | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.42 | 2.96 | 5.15 | 8.11 | 0.11 | 1.37 | 99.40 | 1.74 | 杨尚松,2017[ |
| BJZ12-03 | 柏家庄岩体 | 二云母二长花岗岩 | 二云母二长花岗岩 | 74.58 | 0.17 | 13.15 | 1.30 | — | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.98 | 3.63 | 5.38 | 9.01 | 0.07 | 0.47 | 100.00 | 1.48 | 段梦,2016[ |
| BJZ12-05 | 柏家庄岩体 | 二云母二长花岗岩 | 二云母二长花岗岩 | 73.47 | 0.17 | 13.96 | 1.19 | — | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.93 | 3.46 | 5.30 | 8.76 | 0.08 | 0.59 | 99.40 | 1.53 | 段梦,2016[ |
| 13ZC-003 | 中川岩体 | 花岗岩脉 | 花岗斑岩 | 72.95 | 0.09 | 14.82 | 0.33 | — | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.42 | 7.49 | 7.91 | 0.02 | 2.98 | 99.46 | 17.83 | 杨尚松,2017[ |
| 13ZC-05 | 中川岩体 | 花岗岩脉 | 花岗斑岩 | 76.22 | 0.06 | 12.99 | 0.56 | — | 0.01 | 0.15 | 1.05 | 3.47 | 4.62 | 8.09 | 0 | 0.50 | 99.63 | 1.33 | 杨尚松,2017[ |
| LZ001 | 李坝金矿床 | 斜闪煌斑岩 | 花岗闪长斑岩 | 65.20 | 0.44 | 15.32 | 0.61 | 2.77 | 0.08 | 2.88 | 2.17 | 3.70 | 3.64 | 7.34 | 0.18 | 2.89 | 80.79 | 0.98 | 韩海涛等, 2008[ |
| LZ002 | 李坝金矿床 | 闪长细晶岩 | 石英闪长岩 | 59.28 | 0.54 | 15.56 | 0.61 | 3.95 | 0.18 | 7.48 | 2.82 | 3.40 | 1.26 | 4.66 | 0.18 | 5.11 | 80.16 | 0.37 | 韩海涛等, 2008[ |
| LZ003 | 李坝金矿床 | 花岗斑岩 | 花岗斑岩 | 70.69 | 0.31 | 16.36 | 1.01 | 1.25 | 0.20 | 1.27 | 1.16 | 3.48 | 4.16 | 7.64 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 79.53 | 1.20 | 韩海涛等, 2008[ |
| 样品 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/ HREE | (La/ Yb)N | (La/ Sm)N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW-001 | 38.60 | 71.20 | 8.25 | 30.00 | 5.34 | 1.41 | 4.36 | 0.61 | 3.12 | 0.55 | 1.49 | 0.23 | 1.42 | 0.21 | 14.30 | 181.10 | 154.83 | 26.27 | 5.89 | 18.31 | 4.55 |
| MW-002 | 36.60 | 65.60 | 7.97 | 30.50 | 5.87 | 2.52 | 4.95 | 0.71 | 3.80 | 0.69 | 1.85 | 0.29 | 1.74 | 0.26 | 20.20 | 183.57 | 149.11 | 34.47 | 4.33 | 14.20 | 3.93 |
| MW-003 | 30.80 | 56.70 | 6.55 | 24.40 | 4.69 | 1.27 | 4.25 | 0.67 | 4.06 | 0.77 | 2.18 | 0.37 | 2.24 | 0.33 | 19.80 | 159.08 | 124.42 | 34.66 | 3.59 | 9.29 | 4.13 |
| MW-004 | 40.80 | 71.80 | 8.15 | 31.20 | 5.64 | 2.10 | 4.94 | 0.71 | 3.79 | 0.66 | 1.87 | 0.30 | 1.84 | 0.28 | 18.80 | 192.82 | 159.68 | 33.14 | 4.82 | 14.97 | 4.55 |
| MW-005 | 22.90 | 43.00 | 5.27 | 20.70 | 3.95 | 1.10 | 3.53 | 0.58 | 3.26 | 0.65 | 1.86 | 0.29 | 1.93 | 0.28 | 17.80 | 127.10 | 96.89 | 30.21 | 3.21 | 8.01 | 3.65 |
| MW-006 | 39.10 | 70.00 | 8.26 | 30.90 | 5.72 | 1.61 | 4.89 | 0.68 | 3.66 | 0.62 | 1.78 | 0.28 | 1.66 | 0.25 | 17.70 | 187.17 | 155.66 | 31.50 | 4.94 | 15.84 | 4.30 |
| 08-49h | 24.40 | 43.40 | 5.05 | 19.50 | 4.56 | 1.25 | 3.59 | 0.60 | 3.38 | 0.63 | 1.70 | 0.25 | 1.55 | 0.26 | 18.60 | 128.72 | 98.16 | 30.56 | 3.21 | 10.61 | 3.37 |
| 08-50h | 40.10 | 75.50 | 7.79 | 28.30 | 5.82 | 1.15 | 4.29 | 0.67 | 3.55 | 0.63 | 1.72 | 0.24 | 1.46 | 0.25 | 19.30 | 190.77 | 158.66 | 32.11 | 4.94 | 18.52 | 4.33 |
| ZC01/1B | 63.90 | 112.70 | 11.43 | 36.70 | 5.89 | 1.27 | 4.24 | 0.62 | 3.00 | 0.46 | 1.16 | 0.17 | 1.22 | 0.21 | 14.40 | 257.37 | 231.89 | 25.48 | 9.10 | 35.31 | 6.82 |
| ZC05/1B | 28.70 | 54.00 | 6.57 | 26.10 | 5.46 | 1.17 | 3.91 | 0.64 | 3.23 | 0.58 | 1.64 | 0.23 | 1.71 | 0.23 | 16.70 | 150.87 | 122.00 | 28.87 | 4.23 | 11.32 | 3.31 |
| ZC08/1B | 34.60 | 63.90 | 7.03 | 25.10 | 5.29 | 0.97 | 4.67 | 0.73 | 3.25 | 0.69 | 1.92 | 0.29 | 2.07 | 0.30 | 21.70 | 172.51 | 136.89 | 35.62 | 3.84 | 11.27 | 4.11 |
| ZC37/1B | 36.20 | 60.20 | 6.14 | 18.00 | 3.26 | 0.83 | 2.91 | 0.40 | 1.85 | 0.37 | 1.16 | 0.17 | 1.31 | 0.19 | 11.90 | 144.89 | 124.63 | 20.26 | 6.15 | 18.63 | 6.98 |
| 15ZC-002 | 46.86 | 95.52 | 9.54 | 33.60 | 6.36 | 1.67 | 5.50 | 0.73 | 3.91 | 0.70 | 1.95 | 0.26 | 1.68 | 0.23 | 20.81 | 229.32 | 193.55 | 35.77 | 5.41 | 18.81 | 4.63 |
| 13ZC-04 | 60.80 | 107.00 | 12.10 | 44.40 | 7.67 | 1.38 | 6.13 | 0.97 | 4.51 | 0.81 | 2.26 | 0.38 | 2.41 | 0.34 | 23.50 | 274.66 | 233.35 | 41.31 | 5.65 | 17.01 | 4.99 |
| 14ZC-01 | 45.25 | 81.28 | 9.61 | 30.24 | 5.14 | 0.86 | 3.84 | 0.46 | 1.92 | 0.33 | 0.91 | 0.12 | 0.83 | 0.13 | 9.04 | 189.96 | 172.38 | 17.58 | 9.81 | 36.76 | 5.54 |
| BJZ12-03 | 36.40 | 70.20 | 7.30 | 24.70 | 4.60 | 0.50 | 3.90 | 0.60 | 3.80 | 0.80 | 2.50 | 0.40 | 2.30 | 0.30 | 25.10 | 183.40 | 143.70 | 39.70 | 3.62 | 10.67 | 4.98 |
| BJZ12-04 | 27.80 | 56.50 | 6.00 | 20.60 | 3.90 | 0.30 | 3.10 | 0.50 | 2.60 | 0.50 | 1.50 | 0.20 | 1.40 | 0.20 | 15.50 | 140.60 | 115.10 | 25.50 | 4.51 | 13.39 | 4.48 |
| BJZ12-05 | 32.30 | 66.50 | 7.10 | 24.40 | 4.50 | 0.30 | 3.50 | 0.50 | 2.80 | 0.50 | 1.60 | 0.20 | 1.50 | 0.20 | 16.90 | 162.80 | 135.10 | 27.70 | 4.88 | 14.52 | 4.52 |
| 样品 | (La/ Lu)N | (Ce/ Yb)N | δEu | δCe | Co | Ni | Hf | Rb | Nb | Sr | Ta | Th | V | U | Cu | Zr | Pb | Zn | Cr | 资料来源 | |
| MW-001 | 19.79 | 12.94 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 17.80 | 32.80 | 4.64 | 122.00 | 15.30 | 365.00 | 1.00 | 12.10 | 106.00 | 3.21 | 17.00 | 168.00 | 6.79 | 27.30 | 109.00 | 本文 | |
| MW-002 | 14.93 | 9.76 | 1.39 | 0.89 | 51.20 | 217.00 | 3.26 | 92.10 | 13.40 | 740.00 | 0.62 | 9.35 | 208.00 | 3.42 | 32.50 | 139.00 | 8.05 | 87.40 | 793.00 | 本文 | |
| MW-003 | 9.92 | 6.55 | 0.85 | 0.92 | 31.90 | 105.00 | 4.14 | 148.00 | 14.00 | 337.00 | 0.87 | 7.11 | 151.00 | 1.83 | 39.90 | 155.00 | 6.87 | 115.00 | 206.00 | 本文 | |
| MW-004 | 15.73 | 10.11 | 1.19 | 0.90 | 39.50 | 158.00 | 3.34 | 49.70 | 12.80 | 636.00 | 0.66 | 10.40 | 167.00 | 4.04 | 37.40 | 132.00 | 11.27 | 66.40 | 621.00 | 本文 | |
| MW-005 | 8.72 | 5.77 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 42.60 | 215.00 | 3.91 | 57.30 | 12.10 | 244.00 | 0.74 | 6.82 | 127.00 | 1.59 | 44.50 | 149.00 | 14.81 | 79.60 | 387.00 | 本文 | |
| MW-006 | 16.57 | 10.88 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 35.70 | 156.00 | 3.73 | 74.00 | 14.20 | 711.00 | 0.72 | 8.97 | 154.00 | 3.13 | 10.90 | 155.00 | 27.13 | 73.50 | 549.00 | 本文 | |
| 08-49h | 10.05 | 7.24 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 87.40 | 3.17 | 4.53 | 189.00 | 16.10 | 364.00 | 1.91 | 10.80 | 29.60 | 5.76 | 4.63 | 170.00 | 33.10 | 61.80 | 9.57 | 李婷等,2012[ | |
| 08-50h | 17.18 | 13.38 | 0.67 | 0.97 | 121.00 | 3.78 | 5.00 | 165.00 | 17.20 | 332.00 | 1.69 | 16.80 | 34.00 | 1.93 | 4.94 | 190.00 | 28.40 | 66.90 | 11.90 | 李婷等,2012[ | |
| ZC01/1B | 32.59 | 23.89 | 0.74 | 0.93 | 4.30 | 3.00 | 6.60 | 164.80 | 16.60 | 436.50 | 1.10 | 21.90 | 36.00 | 4.30 | 4.10 | 242.20 | 6.70 | 58.00 | 13.68 | 聂政融,2015[ | |
| ZC05/1B | 13.36 | 8.17 | 0.74 | 0.91 | 5.30 | 2.80 | 5.00 | 194.30 | 16.00 | 377.00 | 1.50 | 17.20 | 34.00 | 6.90 | 3.60 | 203.80 | 6.80 | 52.00 | <10.00 | 聂政融,2015[ | |
| ZC08/1B | 12.35 | 7.98 | 0.58 | 0.93 | 5.80 | 3.90 | 6.80 | 240.10 | 23.80 | 379.50 | 1.80 | 16.30 | 45.00 | 5.40 | 3.90 | 272.40 | 4.40 | 77.00 | 13.68 | 聂政融,2015[ | |
| ZC37/1B | 20.40 | 11.89 | 0.81 | 0.89 | 6.30 | 8.10 | 4.80 | 130.40 | 10.50 | 464.60 | 0.80 | 11.90 | 50.00 | 2.70 | 3.30 | 181.20 | 4.20 | 31.00 | 20.53 | 聂政融,2015[ | |
| 15ZC-002 | 21.82 | 14.71 | 0.84 | 1.03 | 133.12 | 15.79 | 5.23 | 232.40 | 21.64 | 493.00 | 1.80 | 12.43 | 41.32 | 3.60 | 4.70 | 209.76 | 28.96 | 74.62 | 20.18 | 杨尚松,2017[ | |
| 13ZC-04 | 19.15 | 11.48 | 0.60 | 0.90 | 107.00 | 20.40 | 8.95 | 213.00 | 20.10 | 345.00 | 2.21 | 22.90 | 35.90 | 8.61 | 2 531.00 | 305.00 | 110.00 | 2 045.00 | 13.50 | 杨尚松,2017[ | |
| 14ZC-01 | 37.28 | 25.33 | 0.57 | 0.90 | 1.25 | 2.12 | 12.22 | 317.10 | 14.04 | 114.50 | 1.83 | 24.61 | 28.92 | 9.96 | 7.86 | 464.40 | 26.50 | 22.15 | 5.54 | 杨尚松,2017[ | |
| BJZ12-03 | 12.99 | 7.89 | 0.35 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.90 | 3.40 | 425.80 | 24.40 | 105.60 | 1.60 | 23.60 | 12.30 | 3.60 | 2.70 | 144.30 | 27.80 | 71.70 | 3.10 | 段梦,2016[ | |
| BJZ12-04 | 14.89 | 10.44 | 0.26 | 1.01 | 0.50 | 0.90 | 2.10 | 424.60 | 22.50 | 56.00 | 1.50 | 17.50 | 4.40 | 3.30 | 1.10 | 78.90 | 29.50 | 61.90 | 2.70 | 段梦,2016[ | |
| BJZ12-05 | 17.30 | 11.47 | 0.22 | 1.01 | 0.40 | 2.00 | 2.70 | 460.60 | 25.20 | 56.00 | 1.50 | 20.30 | 3.70 | 7.50 | 1.00 | 105.80 | 31.30 | 84.10 | 2.90 | 段梦,2016[ | |
表2 马坞矿区及邻区火成岩微量、稀土元素(wB/10-6)分析结果
Table 2 Trace element compositions (10-6) of the magmatic rocks in/around the Mawu deposit
| 样品 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/ HREE | (La/ Yb)N | (La/ Sm)N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW-001 | 38.60 | 71.20 | 8.25 | 30.00 | 5.34 | 1.41 | 4.36 | 0.61 | 3.12 | 0.55 | 1.49 | 0.23 | 1.42 | 0.21 | 14.30 | 181.10 | 154.83 | 26.27 | 5.89 | 18.31 | 4.55 |
| MW-002 | 36.60 | 65.60 | 7.97 | 30.50 | 5.87 | 2.52 | 4.95 | 0.71 | 3.80 | 0.69 | 1.85 | 0.29 | 1.74 | 0.26 | 20.20 | 183.57 | 149.11 | 34.47 | 4.33 | 14.20 | 3.93 |
| MW-003 | 30.80 | 56.70 | 6.55 | 24.40 | 4.69 | 1.27 | 4.25 | 0.67 | 4.06 | 0.77 | 2.18 | 0.37 | 2.24 | 0.33 | 19.80 | 159.08 | 124.42 | 34.66 | 3.59 | 9.29 | 4.13 |
| MW-004 | 40.80 | 71.80 | 8.15 | 31.20 | 5.64 | 2.10 | 4.94 | 0.71 | 3.79 | 0.66 | 1.87 | 0.30 | 1.84 | 0.28 | 18.80 | 192.82 | 159.68 | 33.14 | 4.82 | 14.97 | 4.55 |
| MW-005 | 22.90 | 43.00 | 5.27 | 20.70 | 3.95 | 1.10 | 3.53 | 0.58 | 3.26 | 0.65 | 1.86 | 0.29 | 1.93 | 0.28 | 17.80 | 127.10 | 96.89 | 30.21 | 3.21 | 8.01 | 3.65 |
| MW-006 | 39.10 | 70.00 | 8.26 | 30.90 | 5.72 | 1.61 | 4.89 | 0.68 | 3.66 | 0.62 | 1.78 | 0.28 | 1.66 | 0.25 | 17.70 | 187.17 | 155.66 | 31.50 | 4.94 | 15.84 | 4.30 |
| 08-49h | 24.40 | 43.40 | 5.05 | 19.50 | 4.56 | 1.25 | 3.59 | 0.60 | 3.38 | 0.63 | 1.70 | 0.25 | 1.55 | 0.26 | 18.60 | 128.72 | 98.16 | 30.56 | 3.21 | 10.61 | 3.37 |
| 08-50h | 40.10 | 75.50 | 7.79 | 28.30 | 5.82 | 1.15 | 4.29 | 0.67 | 3.55 | 0.63 | 1.72 | 0.24 | 1.46 | 0.25 | 19.30 | 190.77 | 158.66 | 32.11 | 4.94 | 18.52 | 4.33 |
| ZC01/1B | 63.90 | 112.70 | 11.43 | 36.70 | 5.89 | 1.27 | 4.24 | 0.62 | 3.00 | 0.46 | 1.16 | 0.17 | 1.22 | 0.21 | 14.40 | 257.37 | 231.89 | 25.48 | 9.10 | 35.31 | 6.82 |
| ZC05/1B | 28.70 | 54.00 | 6.57 | 26.10 | 5.46 | 1.17 | 3.91 | 0.64 | 3.23 | 0.58 | 1.64 | 0.23 | 1.71 | 0.23 | 16.70 | 150.87 | 122.00 | 28.87 | 4.23 | 11.32 | 3.31 |
| ZC08/1B | 34.60 | 63.90 | 7.03 | 25.10 | 5.29 | 0.97 | 4.67 | 0.73 | 3.25 | 0.69 | 1.92 | 0.29 | 2.07 | 0.30 | 21.70 | 172.51 | 136.89 | 35.62 | 3.84 | 11.27 | 4.11 |
| ZC37/1B | 36.20 | 60.20 | 6.14 | 18.00 | 3.26 | 0.83 | 2.91 | 0.40 | 1.85 | 0.37 | 1.16 | 0.17 | 1.31 | 0.19 | 11.90 | 144.89 | 124.63 | 20.26 | 6.15 | 18.63 | 6.98 |
| 15ZC-002 | 46.86 | 95.52 | 9.54 | 33.60 | 6.36 | 1.67 | 5.50 | 0.73 | 3.91 | 0.70 | 1.95 | 0.26 | 1.68 | 0.23 | 20.81 | 229.32 | 193.55 | 35.77 | 5.41 | 18.81 | 4.63 |
| 13ZC-04 | 60.80 | 107.00 | 12.10 | 44.40 | 7.67 | 1.38 | 6.13 | 0.97 | 4.51 | 0.81 | 2.26 | 0.38 | 2.41 | 0.34 | 23.50 | 274.66 | 233.35 | 41.31 | 5.65 | 17.01 | 4.99 |
| 14ZC-01 | 45.25 | 81.28 | 9.61 | 30.24 | 5.14 | 0.86 | 3.84 | 0.46 | 1.92 | 0.33 | 0.91 | 0.12 | 0.83 | 0.13 | 9.04 | 189.96 | 172.38 | 17.58 | 9.81 | 36.76 | 5.54 |
| BJZ12-03 | 36.40 | 70.20 | 7.30 | 24.70 | 4.60 | 0.50 | 3.90 | 0.60 | 3.80 | 0.80 | 2.50 | 0.40 | 2.30 | 0.30 | 25.10 | 183.40 | 143.70 | 39.70 | 3.62 | 10.67 | 4.98 |
| BJZ12-04 | 27.80 | 56.50 | 6.00 | 20.60 | 3.90 | 0.30 | 3.10 | 0.50 | 2.60 | 0.50 | 1.50 | 0.20 | 1.40 | 0.20 | 15.50 | 140.60 | 115.10 | 25.50 | 4.51 | 13.39 | 4.48 |
| BJZ12-05 | 32.30 | 66.50 | 7.10 | 24.40 | 4.50 | 0.30 | 3.50 | 0.50 | 2.80 | 0.50 | 1.60 | 0.20 | 1.50 | 0.20 | 16.90 | 162.80 | 135.10 | 27.70 | 4.88 | 14.52 | 4.52 |
| 样品 | (La/ Lu)N | (Ce/ Yb)N | δEu | δCe | Co | Ni | Hf | Rb | Nb | Sr | Ta | Th | V | U | Cu | Zr | Pb | Zn | Cr | 资料来源 | |
| MW-001 | 19.79 | 12.94 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 17.80 | 32.80 | 4.64 | 122.00 | 15.30 | 365.00 | 1.00 | 12.10 | 106.00 | 3.21 | 17.00 | 168.00 | 6.79 | 27.30 | 109.00 | 本文 | |
| MW-002 | 14.93 | 9.76 | 1.39 | 0.89 | 51.20 | 217.00 | 3.26 | 92.10 | 13.40 | 740.00 | 0.62 | 9.35 | 208.00 | 3.42 | 32.50 | 139.00 | 8.05 | 87.40 | 793.00 | 本文 | |
| MW-003 | 9.92 | 6.55 | 0.85 | 0.92 | 31.90 | 105.00 | 4.14 | 148.00 | 14.00 | 337.00 | 0.87 | 7.11 | 151.00 | 1.83 | 39.90 | 155.00 | 6.87 | 115.00 | 206.00 | 本文 | |
| MW-004 | 15.73 | 10.11 | 1.19 | 0.90 | 39.50 | 158.00 | 3.34 | 49.70 | 12.80 | 636.00 | 0.66 | 10.40 | 167.00 | 4.04 | 37.40 | 132.00 | 11.27 | 66.40 | 621.00 | 本文 | |
| MW-005 | 8.72 | 5.77 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 42.60 | 215.00 | 3.91 | 57.30 | 12.10 | 244.00 | 0.74 | 6.82 | 127.00 | 1.59 | 44.50 | 149.00 | 14.81 | 79.60 | 387.00 | 本文 | |
| MW-006 | 16.57 | 10.88 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 35.70 | 156.00 | 3.73 | 74.00 | 14.20 | 711.00 | 0.72 | 8.97 | 154.00 | 3.13 | 10.90 | 155.00 | 27.13 | 73.50 | 549.00 | 本文 | |
| 08-49h | 10.05 | 7.24 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 87.40 | 3.17 | 4.53 | 189.00 | 16.10 | 364.00 | 1.91 | 10.80 | 29.60 | 5.76 | 4.63 | 170.00 | 33.10 | 61.80 | 9.57 | 李婷等,2012[ | |
| 08-50h | 17.18 | 13.38 | 0.67 | 0.97 | 121.00 | 3.78 | 5.00 | 165.00 | 17.20 | 332.00 | 1.69 | 16.80 | 34.00 | 1.93 | 4.94 | 190.00 | 28.40 | 66.90 | 11.90 | 李婷等,2012[ | |
| ZC01/1B | 32.59 | 23.89 | 0.74 | 0.93 | 4.30 | 3.00 | 6.60 | 164.80 | 16.60 | 436.50 | 1.10 | 21.90 | 36.00 | 4.30 | 4.10 | 242.20 | 6.70 | 58.00 | 13.68 | 聂政融,2015[ | |
| ZC05/1B | 13.36 | 8.17 | 0.74 | 0.91 | 5.30 | 2.80 | 5.00 | 194.30 | 16.00 | 377.00 | 1.50 | 17.20 | 34.00 | 6.90 | 3.60 | 203.80 | 6.80 | 52.00 | <10.00 | 聂政融,2015[ | |
| ZC08/1B | 12.35 | 7.98 | 0.58 | 0.93 | 5.80 | 3.90 | 6.80 | 240.10 | 23.80 | 379.50 | 1.80 | 16.30 | 45.00 | 5.40 | 3.90 | 272.40 | 4.40 | 77.00 | 13.68 | 聂政融,2015[ | |
| ZC37/1B | 20.40 | 11.89 | 0.81 | 0.89 | 6.30 | 8.10 | 4.80 | 130.40 | 10.50 | 464.60 | 0.80 | 11.90 | 50.00 | 2.70 | 3.30 | 181.20 | 4.20 | 31.00 | 20.53 | 聂政融,2015[ | |
| 15ZC-002 | 21.82 | 14.71 | 0.84 | 1.03 | 133.12 | 15.79 | 5.23 | 232.40 | 21.64 | 493.00 | 1.80 | 12.43 | 41.32 | 3.60 | 4.70 | 209.76 | 28.96 | 74.62 | 20.18 | 杨尚松,2017[ | |
| 13ZC-04 | 19.15 | 11.48 | 0.60 | 0.90 | 107.00 | 20.40 | 8.95 | 213.00 | 20.10 | 345.00 | 2.21 | 22.90 | 35.90 | 8.61 | 2 531.00 | 305.00 | 110.00 | 2 045.00 | 13.50 | 杨尚松,2017[ | |
| 14ZC-01 | 37.28 | 25.33 | 0.57 | 0.90 | 1.25 | 2.12 | 12.22 | 317.10 | 14.04 | 114.50 | 1.83 | 24.61 | 28.92 | 9.96 | 7.86 | 464.40 | 26.50 | 22.15 | 5.54 | 杨尚松,2017[ | |
| BJZ12-03 | 12.99 | 7.89 | 0.35 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.90 | 3.40 | 425.80 | 24.40 | 105.60 | 1.60 | 23.60 | 12.30 | 3.60 | 2.70 | 144.30 | 27.80 | 71.70 | 3.10 | 段梦,2016[ | |
| BJZ12-04 | 14.89 | 10.44 | 0.26 | 1.01 | 0.50 | 0.90 | 2.10 | 424.60 | 22.50 | 56.00 | 1.50 | 17.50 | 4.40 | 3.30 | 1.10 | 78.90 | 29.50 | 61.90 | 2.70 | 段梦,2016[ | |
| BJZ12-05 | 17.30 | 11.47 | 0.22 | 1.01 | 0.40 | 2.00 | 2.70 | 460.60 | 25.20 | 56.00 | 1.50 | 20.30 | 3.70 | 7.50 | 1.00 | 105.80 | 31.30 | 84.10 | 2.90 | 段梦,2016[ | |
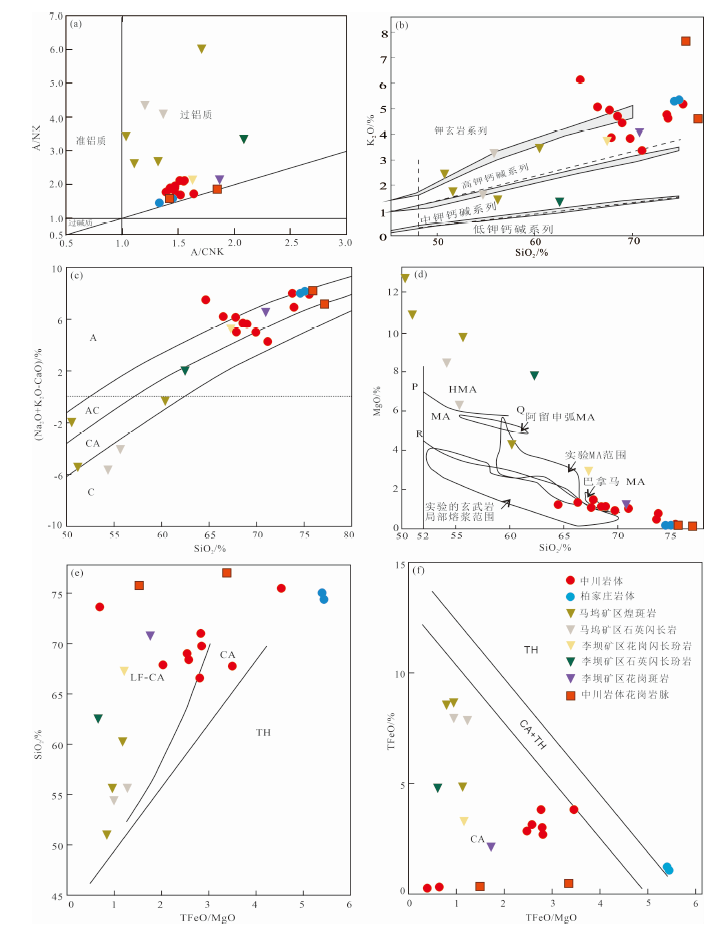
图7 马坞矿区及邻区火山岩构造环境判别图解(投图数据均来自表1) (a) A/CNK-A/NK图解(底图据文献[22]);(b) SiO2-K2O图解(底图据文献[19]);(c) SiO2-(Na2O+K2O-CaO)图解(底图据文献[22]);(d) SiO2-MgO图解(底图据文献[23]);(e) TFeO/MgO-SiO2图解(底图据文献[24]);(f) TFeO/MgO-TFeO图解(底图据文献[23]);A. 碱性系列; AC. 过碱性系列; CA. 钙碱性系列; C. 钙性系列; HMA. 高镁安山岩类; MA. 镁安山岩类; LF-CA. 低铁钙碱系列; TH. 拉斑系列
Fig.7 Tectonic discrimination diagrams of the magmatic rocks in/around the Mawu deposit
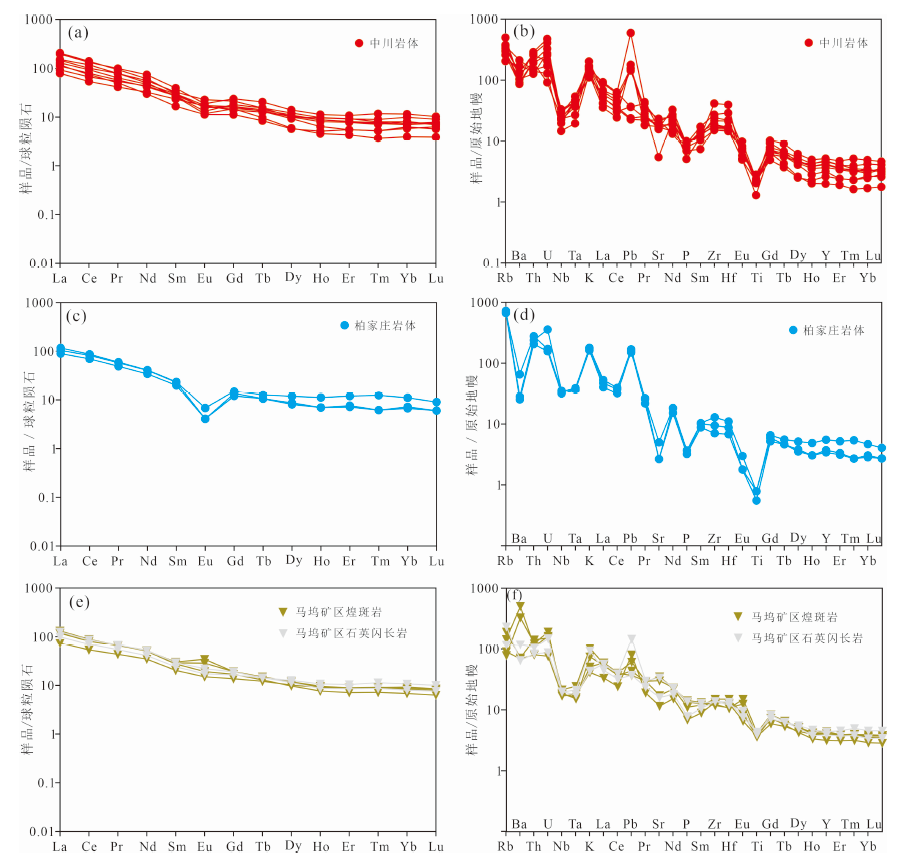
图8 稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式图和痕量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(底图分别据文献[26]和[27],投图数据均来自表2)
Fig.8 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle-normalized multi-elements spider diagrams

图10 火成岩构造环境判别图解(底图据文献[33],投图数据来自表2) (a)Yb-Ta图解;(b) (Y+Nb)-Rb图解;(c) (Yb+Ta)-Rb图解;(d) Y-Nb图解;VAG. 火山弧花岗岩区域; syn-COLG. 同碰撞花岗岩区域; WPG. 板内花岗岩区域; ORG.洋脊花岗岩区域
Fig.10 Tectonic discrimination diagrams of magmatic rocks
| [1] | 陈衍景, 张静, 张复新, 等. 西秦岭地区卡林-类卡林型金矿床及其成矿时间、构造背景和模式[J]. 地质论评, 2004,50(2):134-152. |
| [2] | 陈衍景. 秦岭印支期构造背景、岩浆活动及成矿作用[J]. 中国地质, 2010,37(4):854-865. |
| [3] | 张汉成, 肖荣阁, 王京彬, 等. 甘肃李坝金矿围岩蚀变与金成矿关系[J]. 现代地质, 2009,23(3):472-480. |
| [4] | 刘伯崇, 李康宁, 史海龙, 等. 西秦岭甘青交界一带晚三叠世火山岩岩石成因及构造指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018,32(4):704-717. |
| [5] | 曹东宏, 崔龙, 辛晓军, 等. 西秦岭马坞金矿床韧性剪切带构造控矿特征[J]. 黄金技术科学, 2016,24(6):24-31. |
| [6] | 崔龙. 甘肃省马坞金矿地质特征及成矿模式[J]. 西南科技大学学报, 2010,25(2):43-50. |
| [7] | 辛晓军, 冯永学, 吴亚谋, 等. 甘肃马坞金矿床地质特征及找矿前景探讨[J]. 黄金技术科学, 2015,23(1):40-45. |
| [8] | 孙增战. 甘肃岷县马坞金矿地球化学特征、控矿因素分析及找矿潜力[J]. 西北地质, 2011,44(4):33-43. |
| [9] | 刘坤, 刘家军, 吴杰, 等. 甘肃马坞金矿床8号矿体黄铁矿热电性特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014,28(4):711-720. |
| [10] | 刘坤, 刘家军, 吴杰, 等. 甘肃马坞金矿床成矿流体特征及地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2014,41(5):1594-1607. |
| [11] | 赵玉锁, 肖力, 王晓军, 等. 甘肃省马坞金矿地质特征及构造控矿模式[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2009,17(6):417-422. |
| [12] | 赵玉锁, 肖力, 杨鹏飞, 等. 甘肃岷县马坞金矿同位素特征与成因探讨[J]. 西北地质, 2009,42(4):30-35. |
| [13] | 穆新华, 赵文川. 甘肃省岷县马坞金矿区成矿机制及找矿方向研究[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2011,26(3):272-276. |
| [14] | 冯建忠, 汪东波, 王学明, 等. 甘肃礼县李坝大型金矿床成矿地质特征及成因[J]. 矿床地质, 2003,22(3):257-263. |
| [15] | 李婷, 徐学义, 陈隽璐, 等. 西秦岭造山带礼县地区中川岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其构造环境[J]. 地质通报, 2012,31(6):875-883. |
| [16] | 杨尚松. 西秦岭中川地区中酸性岩浆活动与金成矿作用研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017: 1-100. |
| [17] | 聂政融, 王晓霞, 柯昌辉, 等. 西秦岭中川岩体年代学、地球化学及其与金成矿的关系[J]. 矿床地质, 2014,33(2):243-244. |
| [18] | 武警黄金第五支队. 中央地质勘查基金项目“甘肃省岷县马坞矿区岩金矿普查报告”(2011621039)[R]. 西安:武警黄金第五支队, 2016: 1-105. |
| [19] | LE MAITRE R W. 火成岩分类及属于辞典[M]. 王碧香, 沈昆,毕立君,译.北京:地质出版社, 1991: 1-253. |
| [20] | 段梦. 西秦岭造山带柏家庄和闾井岩体的年代学、地球化学及地质意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016: 1-40. |
| [21] | 韩海涛, 刘继顺, 王志平, 等. 李坝—赵沟金矿床煌斑岩(脉岩)与金矿关系[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2008,23(1):43-47. |
| [22] | MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1989,101:635-643. |
| [23] | ARCULUS R. Use and abuse of the terms calcalkaline and calcalkalic[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2003,44(5):929-935. |
| [24] | 邓晋福, 刘翠, 冯艳芳, 等. 高镁安山岩/闪长岩类(HMA)和镁安山岩/闪长岩类(MA) :与洋俯冲作用相关的两类典型的火成岩[J]. 中国地质, 2010,37(4):1112-1118. |
| [25] | 黑慧欣, 罗照华, 李德东, 等. 宽成分谱系岩墙群的岩石成因及其构造与成矿意义[J]. 地质通报, 2015,34(2/3):229-250. |
| [26] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London,Special Publications, 1989,42(1):313-345. |
| [27] | BOYNTON W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite Studies[M]//HENDERSON P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam:Elsevier, 1984: 63-114. |
| [28] | 罗照华, 魏阳, 辛厚田, 等. 造山后脉岩组合的岩石成因——对岩石圈拆沉作用的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2006,22(6):1672-1684. |
| [29] | EL-SAYED M M. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the post-orogenic bimodal dyke swarms in NW Sinai,Egypt: constraints on the magmatic-tectonic processes during the Late Precambrian[J]. Chemie Der Ered—Geochemistry, 2006,66(2):129-141. |
| [30] | FÉMÉNIAS O, BERZA T, TATU M, et al. Nature and significance of a Cambro-Ordovician high-K,calc-alkaline sub-volcanic suite: the late-to post-orogenic Motru Dyke Swarm (Southern Carpathians, Romania)[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2008,97:479-496. |
| [31] | 薛怀民, 董树文, 马芳, 等. 安徽庐枞火山岩盆地橄榄玄粗岩系的地球化学特征及其对下杨子地区晚中生代岩石圈减薄机制的约束[J]. 地质学报, 2010,84(5):664-681. |
| [32] | 邓晋福, 肖庆辉, 苏尚国, 等. 火成岩组合与构造环境:讨论[J]. 高校地质学报, 2007,11(3):392-402. |
| [33] | PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984,25:956-983. |
| [34] | 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 等. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 1-855. |
| [1] | 陈世明, 杨镇熙, 雷自强, 康维良, 张晶, 赵青虎. 甘肃北山前红泉地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1513-1524. |
| [2] | 刘永彪, 李省晔, 赵吉昌, 樊新祥, 杨镇熙, 陈海云. 岩屑测量在甘肃北山水系沉积物测量弱异常区的找矿效果:以盐池黑山南金矿的发现为例[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1525-1537. |
| [3] | 王斌, 宋伊圩, 孙彪, 杨可, 马振宇, 康成鑫, 张旺, 蒋东祥, 唐源壑, 杨洋, 姬省军, 牛秋生. 甘肃寨上金矿南矿带构造叠加晕实用模型及深部找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1504-1514. |
| [4] | 王玉平, 吴文彬, 刘永俊, 李海洋, 王晓亮, 李超. 辽东岫岩地区晚侏罗世侵入岩的年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 955-967. |
| [5] | 王浩杰, 孙萍, 韩帅, 张帅, 李晓斌, 王涛, 辛鹏, 郭强. 甘肃通渭“9·14”常河滑坡成因机理[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 732-743. |
| [6] | 王伟, 王生云, 刘涛, 李天石, 陈云杰, 马骊, 赵如意, 宋振涛. 甘肃红石泉伟晶岩型铀矿床地质、地球化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(02): 244-253. |
| [7] | 杜佰松, 申俊峰, 秦玉良, 刘海明, 刘圣强, 徐立为, 牛刚, 欧阳尔彪. 甘肃省沃尔给花岗岩体中黑云母的成分对其岩体碱度的响应及成岩成矿意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(04): 672-682. |
| [8] | 王磊,杨建国,王小红,齐琦,张洲远, 张乐,谢燮,杨涛,杨生飞,胡兆国. 甘肃北山炭山子—黄草泉一带水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿远景[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(6): 1276-1284. |
| [9] | 鲁艳明, 专少鹏, 所承逊, 殷敏. 内蒙古阿鲁科尔沁地区晚侏罗世侵入岩年代学、地球化学特征及成矿潜力[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 981-993. |
| [10] | 孙娅琴,田淑芳,王兴振,高雅洁. 基于光谱匹配的热红外高光谱数据岩性分类研究[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(1): 239-246. |
| [11] | 谢燮,杨建国,王小红,王磊,江磊,姜安定. 甘肃北山红柳沟基性-超基性岩体岩石成因及成矿条件[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(6): 1259-1270. |
| [12] | 刘坤,刘家军,吴杰,刘冲昊,杨尚松,辛晓军,李渊. 甘肃马坞金矿床8号矿体黄铁矿热电性特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(4): 711-720. |
| [13] | 韦红钢. 铀在北山花岗岩中的吸附迁移影响因素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(4): 823-828. |
| [14] | 谢裕江, 刘高, 李高勇. 甘肃兰州黄河北岸疏松砂岩成因[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(4): 705-711. |
| [15] | 李士彬, 宋谢炎, 胡瑞忠, 陈列锰. 甘肃金川Ⅱ号岩浆硫化物含矿岩体岩浆演化过程探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(4): 703-711. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||