



现代地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (01): 77-87.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.166
远继东1,2( ), 姜正龙2, 代友旭1, 郝连成1, 张健康1, 张德程1,3, 郑立龙1(
), 姜正龙2, 代友旭1, 郝连成1, 张健康1, 张德程1,3, 郑立龙1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-05-28
修回日期:2021-11-09
出版日期:2022-02-10
发布日期:2022-03-08
通讯作者:
郑立龙
作者简介:郑立龙,男,1988年出生,构造地质学专业,主要从事海岸带综合地质调查与研究。Email: zhenglilong1020@126.com。基金资助:
YUAN Jidong1,2( ), JIANG Zhenglong2, DAI Youxu1, HAO Liancheng1, ZHANG Jiankang1, ZHANG Decheng1,3, ZHENG Lilong1(
), JIANG Zhenglong2, DAI Youxu1, HAO Liancheng1, ZHANG Jiankang1, ZHANG Decheng1,3, ZHENG Lilong1( )
)
Received:2021-05-28
Revised:2021-11-09
Online:2022-02-10
Published:2022-03-08
Contact:
ZHENG Lilong
摘要:
通过对湛江湾近海海域表层沉积物样品粒度和稀土元素(REE)测试分析,系统地研究海域沉积物稀土元素地球化学特征并探讨其物质来源。结果表明,研究区沉积物的稀土元素含量变化较大,平均值为163.23 μg/g,湾外的REE含量(168.61 μg/g)高于湾内的REE含量(142.17 μg/g);不同类型沉积物的稀土元素含量存在差异,但都表现为随沉积物粒度变细呈增长的趋势。(La/Yb)N变化范围在4.80~11.76之间,平均值为8.01;δEu变化范围为0.22~0.61,平均值为0.45;δCe变化范围为0.98~1.07,平均值为1.03;样品均具有典型的轻稀土元素(LREE)富集、重稀土元素(HREE)均一、Eu负异常明显的陆源物质特征。球粒陨石标准化配分曲线及特征参数分析显示,湛江湾沉积物与鉴江、漠阳江、珠江附近海域沉积物近似同源,物源主要来自华南大陆的花岗岩以及雷州半岛北部玄武岩和湛江组(Qp1z)、北海组(Qp2b)的松散沉积物。
中图分类号:
远继东, 姜正龙, 代友旭, 郝连成, 张健康, 张德程, 郑立龙. 湛江湾海域表层沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 77-87.
YUAN Jidong, JIANG Zhenglong, DAI Youxu, HAO Liancheng, ZHANG Jiankang, ZHANG Decheng, ZHENG Lilong. REE Characteristics in Surface Sediments of Zhanjiang Bay and their Provenance Indicating Significance[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(01): 77-87.
| 沉积物类型 | REE/(μg/g) | LREE/(μg/g) | HREE/(μg/g) | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Yb)N | δCe | δEu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 砂 (n=13) | | | | | | | | | |
| 粉砂质砂 (n=24) | | | | | | | | | |
| 砂质粉砂 (n=19) | | | | | | | | | |
| 粉砂 (n=2) | | | | | | | | | |
| 砂质泥 (n=1) | 126.19 | 111.16 | 15.03 | 7.40 | 7.10 | 3.64 | 1.35 | 1.03 | 0.58 |
| 湾内 (n=12) | | | | | | | | | |
| 湾外 (n=47) | | | | | | | | | |
| 研究区 (n=59) | | | | | | | | | |
表1 湛江湾不同沉积物类型及其REE特征参数
Table 1 REE parameters of the different sediment types in Zhanjiang Bay
| 沉积物类型 | REE/(μg/g) | LREE/(μg/g) | HREE/(μg/g) | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Yb)N | δCe | δEu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 砂 (n=13) | | | | | | | | | |
| 粉砂质砂 (n=24) | | | | | | | | | |
| 砂质粉砂 (n=19) | | | | | | | | | |
| 粉砂 (n=2) | | | | | | | | | |
| 砂质泥 (n=1) | 126.19 | 111.16 | 15.03 | 7.40 | 7.10 | 3.64 | 1.35 | 1.03 | 0.58 |
| 湾内 (n=12) | | | | | | | | | |
| 湾外 (n=47) | | | | | | | | | |
| 研究区 (n=59) | | | | | | | | | |

图3 研究区表层沉积物平均粒径( X ¯)、REE特征参数分布图
Fig.3 Distribution patterns for the average grain size ( X ¯) and REE parameters of the surface sediments from the study area
| 沉积物类型 | REE/(μg/g) | LREE/(μg/g) | HREE/(μg/g) | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | δCe | δEu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 本文 | 163.23 | 145.12 | 18.11 | 7.91 | 8.01 | 1.03 | 0.45 |
| 湛江湾[ | 193.63 | 174.18 | 19.45 | 8.95 | 12.09 | 1.00 | 0.59 |
| 湛江湾[ | 198.19 | 179.50 | 18.69 | 9.60 | 11.42 | 1.02 | 0.69 |
| 鉴江[ | 187.36 | 168.35 | 19.01 | 8.86 | 9.49 | 0.61 | 0.99 |
| 雷州半岛近海[ | 175.40 | 159.05 | 16.35 | 9.21 | 11.22 | 0.96 | 0.57 |
| 黄河[ | 137.76 | 122.66 | 15.10 | 8.12 | 9.53 | 0.91 | 0.66 |
| 长江[ | 167.10 | 149.49 | 17.61 | 8.49 | 10.91 | 0.90 | 0.68 |
| 伶仃洋[ | 279.21 | 256.68 | 22.53 | 11.39 | 14.70 | 1.08 | 0.64 |
| 中国南海[ | 116.27 | 103.77 | 12.50 | 8.30 | 8.61 | 1.04 | 0.65 |
| 中国黄土[ | 155.31 | 138.01 | 17.30 | 7.98 | 8.08 | 1.08 | 0.65 |
| 中国浅海[ | 157.06 | 142.97 | 14.09 | 10.15 | 10.11 | 1.03 | 0.57 |
| 中国土壤[ | 155.95 | 140.79 | 15.16 | 9.29 | 10.87 | 0.99 | 0.59 |
| UCC[ | 146.37 | 132.48 | 13.89 | 9.54 | 9.19 | 1.06 | 0.65 |
| 深海沉积物[ | 125.93 | 88.16 | 37.77 | 2.33 | 1.77 | 0.66 | 0.75 |
表2 研究区与其他地区沉积物REE特征参数
Table 2 REE parameters of sediments in the study area and other areas
| 沉积物类型 | REE/(μg/g) | LREE/(μg/g) | HREE/(μg/g) | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | δCe | δEu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 本文 | 163.23 | 145.12 | 18.11 | 7.91 | 8.01 | 1.03 | 0.45 |
| 湛江湾[ | 193.63 | 174.18 | 19.45 | 8.95 | 12.09 | 1.00 | 0.59 |
| 湛江湾[ | 198.19 | 179.50 | 18.69 | 9.60 | 11.42 | 1.02 | 0.69 |
| 鉴江[ | 187.36 | 168.35 | 19.01 | 8.86 | 9.49 | 0.61 | 0.99 |
| 雷州半岛近海[ | 175.40 | 159.05 | 16.35 | 9.21 | 11.22 | 0.96 | 0.57 |
| 黄河[ | 137.76 | 122.66 | 15.10 | 8.12 | 9.53 | 0.91 | 0.66 |
| 长江[ | 167.10 | 149.49 | 17.61 | 8.49 | 10.91 | 0.90 | 0.68 |
| 伶仃洋[ | 279.21 | 256.68 | 22.53 | 11.39 | 14.70 | 1.08 | 0.64 |
| 中国南海[ | 116.27 | 103.77 | 12.50 | 8.30 | 8.61 | 1.04 | 0.65 |
| 中国黄土[ | 155.31 | 138.01 | 17.30 | 7.98 | 8.08 | 1.08 | 0.65 |
| 中国浅海[ | 157.06 | 142.97 | 14.09 | 10.15 | 10.11 | 1.03 | 0.57 |
| 中国土壤[ | 155.95 | 140.79 | 15.16 | 9.29 | 10.87 | 0.99 | 0.59 |
| UCC[ | 146.37 | 132.48 | 13.89 | 9.54 | 9.19 | 1.06 | 0.65 |
| 深海沉积物[ | 125.93 | 88.16 | 37.77 | 2.33 | 1.77 | 0.66 | 0.75 |
| REE | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Yb)N | δCe | δEu | | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REE | 1.00 | |||||||
| LREE/HREE | 0.50** | 1.00 | ||||||
| (La/Yb)N | 0.50** | 0.98** | 1.00 | |||||
| (La/Sm)N | 0.35** | 0.70** | 0.65** | 1.00 | ||||
| (Gd/Yb)N | 0.46** | 0.86** | 0.93** | 0.34** | 1.00 | |||
| δCe | -0.08 | -0.02 | -0.06 | -0.07 | -0.01 | 1.00 | ||
| δEu | -0.14 | 0.26 | 0.29* | -0.02 | 0.40** | 0.14 | 1.00 | |
| | 0.53** | 0.46** | 0.47** | 0.20 | 0.50** | 0.08 | 0.60** | 1.00 |
表3 研究区表层沉积物稀土元素特征参数相关性分析(n=59)
Table 3 Pearson correlation matrix of REE parameters with the average grain size ( X ¯) (n=59)
| REE | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Yb)N | δCe | δEu | | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REE | 1.00 | |||||||
| LREE/HREE | 0.50** | 1.00 | ||||||
| (La/Yb)N | 0.50** | 0.98** | 1.00 | |||||
| (La/Sm)N | 0.35** | 0.70** | 0.65** | 1.00 | ||||
| (Gd/Yb)N | 0.46** | 0.86** | 0.93** | 0.34** | 1.00 | |||
| δCe | -0.08 | -0.02 | -0.06 | -0.07 | -0.01 | 1.00 | ||
| δEu | -0.14 | 0.26 | 0.29* | -0.02 | 0.40** | 0.14 | 1.00 | |
| | 0.53** | 0.46** | 0.47** | 0.20 | 0.50** | 0.08 | 0.60** | 1.00 |

图5 湛江湾表层沉积物稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线(a)和不同类型沉积物稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线(b)(底图据文献[30])
Fig.5 Chondrite-normalized REE distribution patterns of the samples (a) and different sediment types (b) of surface sediments in Zhanjiang Bay (base map after ref. [30])
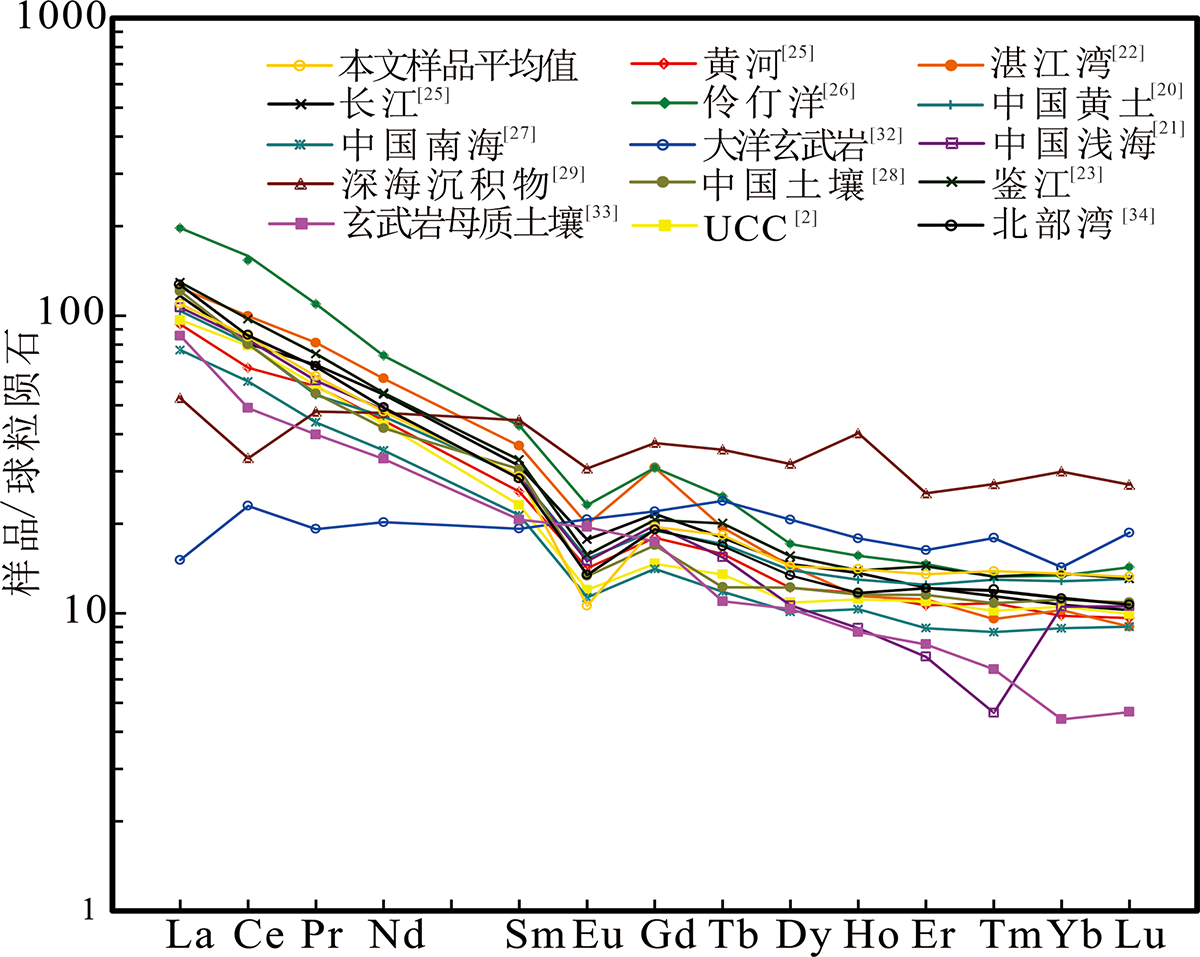
图6 研究区沉积物与潜在物源的球粒陨石标准化配分曲线(底图据文献[30])
Fig.6 Chondrite-normalized REE distribution patterns of the samples in Zhanjiang Bay and potential sediment pro-venances(base map after ref.[30])
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 湾内 | 2.14 | 2.03 | 2.01 | 2.11 | 2.46 | 1.90 | 2.68 | 2.78 | 2.76 | 2.65 | 2.62 | 2.89 | 2.74 | 2.76 |
| 湾外 | 3.52 | 3.33 | 3.36 | 3.42 | 3.91 | 2.38 | 4.21 | 4.33 | 4.31 | 4.15 | 4.06 | 4.52 | 4.29 | 4.46 |
表4 湛江湾表层沉积物稀土元素富集因子(EF)
Table 4 Enrichment factor (EF) of REE in surface sediments of Zhanjiang Bay
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 湾内 | 2.14 | 2.03 | 2.01 | 2.11 | 2.46 | 1.90 | 2.68 | 2.78 | 2.76 | 2.65 | 2.62 | 2.89 | 2.74 | 2.76 |
| 湾外 | 3.52 | 3.33 | 3.36 | 3.42 | 3.91 | 2.38 | 4.21 | 4.33 | 4.31 | 4.15 | 4.06 | 4.52 | 4.29 | 4.46 |
| 物源区 | 搬运区 | 沉积区 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 华南花岗岩 | 雷州北部玄武岩 | 北海组 | 湛江组 | 鉴江 | 漠阳江 | 珠江 | 西江 | 海南岛东北部 |
| 0.174 | 0.242 | 0.138 | 0.206 | 0.019 | 0.015 | 0.020 | 0.033 | 0.000 5 |
表5 湛江湾表层沉积物中REE判别函数(DF)
Table 5 Discrimination function (DF) values for REE of sediments in Zhanjiang Bay
| 物源区 | 搬运区 | 沉积区 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 华南花岗岩 | 雷州北部玄武岩 | 北海组 | 湛江组 | 鉴江 | 漠阳江 | 珠江 | 西江 | 海南岛东北部 |
| 0.174 | 0.242 | 0.138 | 0.206 | 0.019 | 0.015 | 0.020 | 0.033 | 0.000 5 |
| [1] | 王中刚, 于学元, 赵振华. 稀土元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989: 1-153. |
| [2] | TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1985: 1-312. |
| [3] | 刘士林, 刘蕴华, 林舸, 等. 渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷新近系泥岩稀土元素地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2006, 20(3): 449-456. |
| [4] | 周国华, 孙彬彬, 刘占元, 等. 中国东部主要河流稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5): 1028-1042. |
| [5] | 张楠, 王淑红, 陈翰, 等. 南海北部近海陆架表层沉积物类型及其稀土元素特征[J]. 矿物学报, 2014, 34(4): 503-511. |
| [6] | 赵一阳, 王金土, 秦朝阳, 等. 中国大陆架海底沉积物中的稀土元素[J]. 沉积学报, 1990, 8(1): 37-43. |
| [7] | 蓝先洪. 中国海区海底沉积物稀土元素地球化学[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2000, 19(10): 4-6. |
| [8] | 徐方建, 李安春, 徐兆凯, 等. 东海内陆架沉积物稀土元素地球化学特征及物源意义[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2009, 27(4): 574-582. |
| [9] | 吴梦霜, 邵磊, 庞雄, 等. 南海北部深水区沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(4): 672-678. |
| [10] | 密蓓蓓, 张勇, 梅西, 等. 中国东部海域表层沉积物稀土元素赋存特征及物源探讨[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(5): 1530-1541. |
| [11] | 王兆生, 张盈, 张振国, 等. 南海表层沉积物稀土元素分布特征及资源前景[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2020, 38(6): 808-815. |
| [12] | 颜彬, 苗莉, 黄蔚霞, 等. 广东近岸海湾表层沉积物的稀土元素特征及其物源示踪[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(2): 67-79. |
| [13] | 张际标, 姚兼辉, 陈春亮, 等. 湛江东海岛潮间带表层沉积物粒度的分布及与环境要素的相关性[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2015, 34(1): 49-56. |
| [14] | 曹瀚升, 邓忆雯, 陈法锦, 等. 湛江湾表层沉积物微量元素特征及生态风险评价[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2020, 39(2): 71-77. |
| [15] |
张乔民, 郑德延. 湛江港潮汐汊道落潮三角洲沉积动力过程[J]. 地理学报, 1995, 50(5): 421-429.
DOI |
| [16] | 韩志远, 谢华亮, 李怀远, 等. 湛江湾口外落潮三角洲演变特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2021, 37(1): 45-50. |
| [17] | 陈碧珊, 陈诗敏, 何炽鹏. 雷州半岛红树林湿地表层沉积物粒度分布特征[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(1): 198-205. |
| [18] | 广东省地质矿产局. 广东省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1988: 264-272. |
| [19] | 梁俊平. 广东省湛江地区第四纪更新世地层[J]. 广东地质, 1992, 7(4): 21-34. |
| [20] | 文启忠, 刁桂仪, 潘景瑜, 等. 黄土高原黄土的平均化学成分与地壳克拉克值的类比[J]. 土壤学报, 1996, 33(3): 225-231. |
| [21] | 赵一阳, 鄢明才. 中国浅海沉积物地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1994: 1-200. |
| [22] | 张际标, 杨波, 陈涛, 等. 湛江湾沉积物稀土元素分布特征及物源分析[M]// “一带一路” 战略与海洋科技创新:中国海洋学会2015年学术年会. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2015: 223-230. |
| [23] |
WANG S, ZHANG N, CHEN H, et al. The surface sediment types and their rare earth element characteristics from the continental shelf of the northern South China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 88: 185-202.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 颜彬, 陈亮, 李团结. 雷州半岛近海表层沉积物的稀土元素组成及物源指示意义[M]//热带海洋科学学术研讨会暨第八届广东海洋湖沼学会、第七届广东海洋学会会员代表大会论文及摘要汇编. 湛江: 广东海洋湖沼学会, 广东海洋学会,中国海洋学会热带海洋分会, 2013: 523-535. |
| [25] | 杨守业, 李从先. 长江与黄河沉积物REE地球化学及示踪作用[J]. 地球化学, 1999, 28(4): 374-380. |
| [26] | 刘岩, 张祖麟, 洪华生. 珠江口伶仃洋海区表层沉积物稀土元素分布特征及配分模式[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(1): 109-114. |
| [27] | 朱赖民, 高志友, 尹观, 等. 南海表层沉积物的稀土和微量元素的丰度及其空间变化[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(11): 2963-2980. |
| [28] | 中国环境检测总站. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990: 88-89. |
| [29] | 王金土. 黄海表层沉积物稀土元素地球化学[J]. 地球化学, 1990, 19(1): 44-53. |
| [30] | BOYNTON W V. Cosmochemistry of the Rare Earth Elements: Meteorite Studies[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984: 63-114. |
| [31] | 路远发. GeoKit:一个用VBA构建的地球化学工具软件包[J]. 地球化学, 2004, 33(5): 459-464. |
| [32] |
FREY F A, HASHIN L. Rare earths in oceanic basalts[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1964, 69(4): 775-780.
DOI URL |
| [33] | 张立娟, 李徐生, 李德成, 等. 雷州半岛玄武岩母质土壤剖面稀土元素分布及其与常量元素、粒度的关系[J]. 土壤学报, 2011, 48(1): 1-9. |
| [34] | 窦衍光, 李军, 李炎. 北部湾东部海域表层沉积物稀土元素组成及物源指示意义[J]. 地球化学, 2012, 41(2): 147-157. |
| [35] | 吴淑壮, 王淑红, 陈翰, 等. 南海西北部陆架表层沉积物稀有金属矿物及相关元素的分布特征与影响因素[J]. 矿物学报, 2016, 36(3): 429-440. |
| [36] | 杨守业, 李从先. REE示踪沉积物物源研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 1999, 14(2): 63-66. |
| [37] | 蓝先洪, 申顺喜. 南黄海中部沉积岩心的稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 海洋通报, 2002, 21(5): 46-53. |
| [38] |
SHIELDS G, STILLE P, STRAUSS H, et al. Diagenetic constraints on the use of cerium anomalies as palaeoseawater redox proxies: an isotopic and REE study of Cambrian phosphorites[J]. Chemical Geology, 2001, 175(1/2): 29-48.
DOI URL |
| [39] | 李军, 桑树勋, 林会喜, 等. 渤海湾盆地石炭二叠系稀土元素特征及其地质意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25(4): 589-596. |
| [40] | 张楠. 南海北部近海陆架表层稀有金属元素特征[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2014. |
| [41] |
XU Z, HAN G. Rare earth elements (REE) of dissolved and suspended loads in the Xijiang River, South China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2009, 24(9): 1803-1816.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
HUANG X, YU Y, LI J, et al. Geochronology and petrogenesis of the Early Paleozoic I-type granite in the Taishan area, South China: Middle-lower crustal melting during orogenic collapse[J]. Lithos, 2013, 177: 268-284.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
HUANG H, LI X, LI Z, et al. Intraplate crustal remelting as the genesis of Jurassic high-K granites in the coastal region of the Guangdong Province, SE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 74: 280-302.
DOI URL |
| [44] | 中国科学院贵阳地球化学研究所. 华南花岗岩类的地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1979: 280-281. |
| [45] | 徐金鸿, 徐瑞松, 夏斌, 等. 广东红壤中稀土元素的含量及分布特征[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2007, 44(1): 18-21, 40. |
| [46] |
CRICHTON J G, CONDIE K C. Trace elements as source indicators in cratonic sediments: a case study from the Early Proterozoic Libby Creek Group, southeastern Wyoming[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1993, 101(3): 319-332.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
CULLERS R L. The geochemistry of shales, siltstones and sandstones of Pennsylvanian-Permian age, Colorado, USA: implications for provenance and metamorphic studies[J]. Lithos, 2000, 51(3): 181-203.
DOI URL |
| [48] | 李泽文, 栾振东, 阎军, 等. 南海北部外陆架表层沉积物粒度参数特征及物源分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2011, 35(12): 92-100. |
| [49] | 许冬, 初凤友, 李家彪, 等. 粤西-琼东北近海沉积物的运移和沉积[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(3): 905-917. |
| [50] | 杨毅, 徐艳东, 王发云, 等. 粤西沿岸流和物质输移模型研究及应用[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(19): 80-85. |
| [51] | ALLEGRE C J, MICHARD G. Introduction to Geochemistry[M]. Dordrecht: Reidel Publishing Company, 1974: 69-70. |
| [52] | 周品彰. 雷琼地区新生代玄武岩地球化学分析及岩石成因[D]. 台北: 台湾师范大学, 2010. |
| [53] | 李双林, 李绍全. 黄海YA01孔沉积物稀土元素组成与源区示踪[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(3): 51-56. |
| [1] | 王启博, 张寿庭, 唐利, 李军军, 盛渊明. 豫西杨山萤石矿床成因:萤石稀土元素组成和流体包裹体热力学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1524-1537. |
| [2] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [3] | 杜贯新, 闫百泉, 孙雨, 钱程, 秦涛, 臧延庆. 松嫩平原黑土区西北部阿荣旗地下黑土稀土元素特征及环境指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 813-820. |
| [4] | 曹玉璐, 曾宇轲, 张元元. 基于扫描电子显微镜的重矿物物源分析方法对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 475-485. |
| [5] | 刘茂涵, 刘海燕, 张卫民, 王振, 吴通航, 王玉罡. 鄱阳湖流域赣江北支水体和沉积物中稀土元素的含量和分异特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 389-405. |
| [6] | 王艺璇, 周训, 陈梦颖, 马静茹, 海阔, 肖萌, 尚子琦, 张颖, 余鸣潇. 河北北部四处温泉的水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 494-506. |
| [7] | 吴小雷, 常晋阳, 曾南石, 徐文杰, 陶明荣, 赵刚, 韩建. 辽宁红透山铜锌矿床含矿岩系地球化学特征及找矿指示[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 362-377. |
| [8] | 吴龙, 柳长峰, 刘文灿, 张宏远. 青藏高原东北缘祁连山三叠系砂岩碎屑锆石U-Pb定年及其物源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1178-1193. |
| [9] | 赵保具, 张艳飞, 颜开, 肖荣阁. 大兴安岭中段有色金属矿床成矿物质来源探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1380-1396. |
| [10] | 黎介, 刘宁强, 龚庆杰, 吴轩, 严桃桃. 基于微量元素岩性地球化学基因的构建与检验[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1459-1470. |
| [11] | 王珍珍, 李进孝, 张珂, 郭文牧, 张绍韡, 肖林. 山西西铭煤矿煤中稀土元素地球化学特征及指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 1009-1017. |
| [12] | 赵保具, 颜开, 肖荣阁. 一种稀土参数图解新方法:以内蒙古拜仁达坝-维拉斯托闪长岩成因研究为例[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 608-624. |
| [13] | 孔霄, 来风兵, 陈蜀江, 朱选. 别里库姆沙漠胡杨回涡沙丘表层沉积物粒度特征[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 657-664. |
| [14] | 龚庆杰, 吴轩, 严桃桃, 刘宁强, 李晓蕾, 李睿堃, 刘梦翔. 地球化学基因的构建与检验[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 865-882. |
| [15] | 李怡佳, 阮壮, 刘帅, 常秋红, 赖玮, 杨志辉. 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘长10-长8段物源及源区构造背景研究[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 784-799. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||