



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (03): 637-646.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.03.05
蒋天宇1( ), 余涛1,2(
), 余涛1,2( ), 侯青叶3, 戚洪彬1, 王珏3, 马旭东3, 杨忠芳3
), 侯青叶3, 戚洪彬1, 王珏3, 马旭东3, 杨忠芳3
收稿日期:2020-11-13
修回日期:2021-01-06
出版日期:2021-06-23
发布日期:2021-06-24
通讯作者:
余涛
作者简介:余 涛,男,副研究员,1979年出生,地球化学专业,主要从事环境化学与生态地球化学的教学与研究。Email: yutao@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
JIANG Tianyu1( ), YU Tao1,2(
), YU Tao1,2( ), HOU Qingye3, QI Hongbin1, WANG Jue3, MA Xudong3, YANG Zhongfang3
), HOU Qingye3, QI Hongbin1, WANG Jue3, MA Xudong3, YANG Zhongfang3
Received:2020-11-13
Revised:2021-01-06
Online:2021-06-23
Published:2021-06-24
Contact:
YU Tao
摘要:
硒是生态环境中重要的微量元素之一,如何准确评估其生物有效性一直存在争议。在四川省广安市邻水县采集了60套农作物及其根系土样品,分析其Se含量和理化性质。同时基于梯度扩散膜技术对土壤有效Se含量进行分析,并对土壤有效Se含量的影响因素进行探究。结果表明,研究区土壤Se含量为0.15~2.42 mg/kg,均值为0.48 mg/kg,不同类型土壤Se含量差异明显,石灰土(1.06 mg/kg)>黄壤(0.78 mg/kg)>紫色土(0.28 mg/kg)>水稻土(0.27 mg/kg)。石灰土和黄壤有机质含量和总铁(TFe2O3)含量明显高于其他类型土壤。研究区内不同类型土壤的DGT-Se明显不同,与土壤Se含量分布相反。相关性分析表明土壤DGT-Se与Se含量、TFe2O3含量、S含量、有机质含量、pH值、Al2O3含量显著相关,受理化性质影响导致不同类型土壤中DGT-Se的差异。水稻根系土壤DGT-Se与水稻籽实Se含量显著正相关,用DGT可以较好地表达水稻-根系土系统中土壤Se的生物有效性。基于DGT技术评估预测区域尺度农业土壤有效Se含量时,需充分考虑土壤类型及其理化性质。
中图分类号:
蒋天宇, 余涛, 侯青叶, 戚洪彬, 王珏, 马旭东, 杨忠芳. 基于DGT技术对土壤硒生物有效性及其影响因素的分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 637-646.
JIANG Tianyu, YU Tao, HOU Qingye, QI Hongbin, WANG Jue, MA Xudong, YANG Zhongfang. Analysis of Soil Selenium Bioavailability and Its Influencing Factors Based on DGT Technology[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(03): 637-646.
| 指标 | 分析方法 | 检出限 |
|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | XRF | 0.05* |
| TFe2O3 | XRF | 0.05* |
| pH | pH/ISE | 0.1** |
| N | 加浓碱蒸馏-硼酸吸收-容量法 | 20 |
| P | XRF | 10 |
| S | XRF | 50 |
| Se | AFS/ICP-MS | 0.01 |
| Corg | 重铬酸钾氧化-容量法 | 0.1* |
| Mn | AFS | 10 |
表1 各指标分析方法及检测限(单位: mg/kg)
Table 1 Detection limit and analysis methods (unit: mg/kg)
| 指标 | 分析方法 | 检出限 |
|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | XRF | 0.05* |
| TFe2O3 | XRF | 0.05* |
| pH | pH/ISE | 0.1** |
| N | 加浓碱蒸馏-硼酸吸收-容量法 | 20 |
| P | XRF | 10 |
| S | XRF | 50 |
| Se | AFS/ICP-MS | 0.01 |
| Corg | 重铬酸钾氧化-容量法 | 0.1* |
| Mn | AFS | 10 |
| 样品类型 | 样品数/个 | 最小值/ (mg/kg) | 最大值/ (mg/kg) | 算术平均值/ (mg/kg) | 标准偏差/ (mg/kg) | 标准误差 | 中位数/ (mg/kg) | 分布情况 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤 | 60 | 0.15 | 2.42 | 0.48 | 0.47 | 0.06 | 0.30 | 符合正态分布 |
| 玉米籽实 | 31 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 符合正态分布 |
| 水稻籽实 | 29 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 符合正态分布 |
表2 土壤及农作物中硒含量
Table 2 Selenium content in soil and crops
| 样品类型 | 样品数/个 | 最小值/ (mg/kg) | 最大值/ (mg/kg) | 算术平均值/ (mg/kg) | 标准偏差/ (mg/kg) | 标准误差 | 中位数/ (mg/kg) | 分布情况 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤 | 60 | 0.15 | 2.42 | 0.48 | 0.47 | 0.06 | 0.30 | 符合正态分布 |
| 玉米籽实 | 31 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 符合正态分布 |
| 水稻籽实 | 29 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 符合正态分布 |
| 土壤 类型 | 样品 数/个 | 黏土 含量/% | 有机质 含量/% | pH | S含量/ 10-6 | Al2O3 含量/% | P含量/ 10-6 | TFe2O3 含量/% | Mn含量/ 10-6 | N含量/ 10-6 | Se含量/ 10-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄壤 | 15 | 29.73±9.48 | 5.20±4.65 | 6.05±1.09 | 1 294±1 406 | 13.71±1.82 | 778±284 | 6.12±2.14 | 562±300 | 1 915±817 | 0.78±0.59 |
| 石灰土 | 6 | 22.46±6.07 | 5.57±4.26 | 5.18±1.00 | 2 433±4 879 | 15.62±2.16 | 1 082±451 | 9.27±3.79 | 713±519 | 2 049±902 | 1.06±0.78 |
| 水稻土 | 6 | 29.58±7.58 | 2.14±0.57 | 5.70±1.19 | 512±325 | 15.50±0.41 | 513±135 | 5.88±0.29 | 516±142 | 1 179±303 | 0.27±0.07 |
| 紫色土 | 33 | 27.90±7.61 | 2.08±0.71 | 5.60±0.90 | 378±197 | 15.08±1.42 | 563±178 | 5.25±0.99 | 481±193 | 1 228±386 | 0.28±0.09 |
| 全部样品 | 60 | 27.98±8.05 | 3.21±3.06 | 5.68±0.99 | 826±1720 | 14.84±1.66 | 664±290 | 5.93±2.06 | 528±267 | 1 477±665 | 0.48±0.47 |
表3 研究区土壤理化指标
Table 3 Soil physical and chemical indicators in the study area
| 土壤 类型 | 样品 数/个 | 黏土 含量/% | 有机质 含量/% | pH | S含量/ 10-6 | Al2O3 含量/% | P含量/ 10-6 | TFe2O3 含量/% | Mn含量/ 10-6 | N含量/ 10-6 | Se含量/ 10-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄壤 | 15 | 29.73±9.48 | 5.20±4.65 | 6.05±1.09 | 1 294±1 406 | 13.71±1.82 | 778±284 | 6.12±2.14 | 562±300 | 1 915±817 | 0.78±0.59 |
| 石灰土 | 6 | 22.46±6.07 | 5.57±4.26 | 5.18±1.00 | 2 433±4 879 | 15.62±2.16 | 1 082±451 | 9.27±3.79 | 713±519 | 2 049±902 | 1.06±0.78 |
| 水稻土 | 6 | 29.58±7.58 | 2.14±0.57 | 5.70±1.19 | 512±325 | 15.50±0.41 | 513±135 | 5.88±0.29 | 516±142 | 1 179±303 | 0.27±0.07 |
| 紫色土 | 33 | 27.90±7.61 | 2.08±0.71 | 5.60±0.90 | 378±197 | 15.08±1.42 | 563±178 | 5.25±0.99 | 481±193 | 1 228±386 | 0.28±0.09 |
| 全部样品 | 60 | 27.98±8.05 | 3.21±3.06 | 5.68±0.99 | 826±1720 | 14.84±1.66 | 664±290 | 5.93±2.06 | 528±267 | 1 477±665 | 0.48±0.47 |
| 黏土含量 | 有机质 | pH | Se | N | P | S | Mn | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DGT-Se | -0.116 | 0.308* | -0.283* | 0.360** | 0.227 | 0.173 | 0.630** | 0.072 | 0.332* | 0.424** |
表4 土壤DGT-Se与土壤理化指标相关系数
Table 4 Correlation between soil DGT-Se and soil physical and chemical indicators
| 黏土含量 | 有机质 | pH | Se | N | P | S | Mn | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DGT-Se | -0.116 | 0.308* | -0.283* | 0.360** | 0.227 | 0.173 | 0.630** | 0.072 | 0.332* | 0.424** |
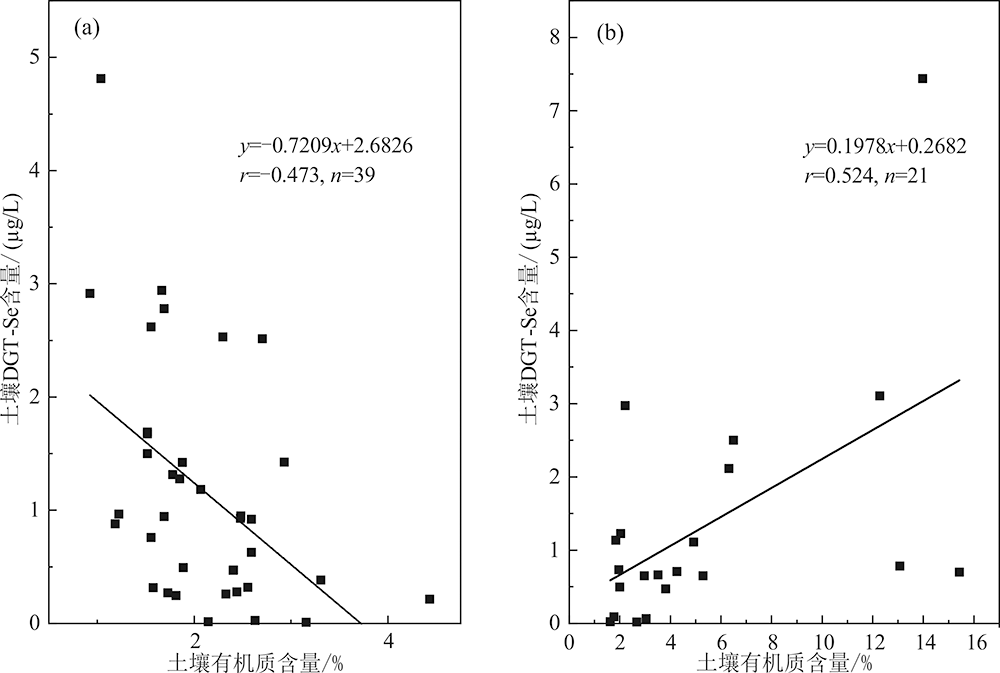
图6 土壤DGT-Se含量与有机质含量的相关性 (a)水稻土和紫色土;(b)石灰土和黄壤
Fig.6 The correlation between soil DGT-Se and soil organic matter content (a) Paddy soil and purple soil; (b) lime soil and yellow soil
| [1] |
TERRY N, ZAYED A M, DE SOUZA M P, et al. Selenium in higher plants[J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 2000, 51:401-432.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
SUPRIATION S, WENG L P, COMANS R N J. Selenium speciation and extractability in Dutch agricultural soils[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 532:368-382.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
MATOS R P, LIMA V M P, WINDMOLLER C C, et al. Correlation between the natural levels of selenium and soil physicochemical characteristics from the Jequitinhonha Valley (MG), Brazil[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 172:195-202.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LYONS G H, GENC Y, SOOLE K, et al. Selenium increases seed production in Brassica[J]. Plant and Soil, 2009, 318(1/2): 73-80.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
NGIGI P B, DU LAING G, MASINDE P W, et al. Selenium deficiency risk in central Kenya highlands: an assessment from the soil to the body[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2020, 42(7): 2233-2250.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
TSIOUBRI M, GASPARATOS D, ECONOMOU-ELIOPOULOS M. Selenium uptake by lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) and berseem (Trifolium alexandrinum L.) as affected by the application of sodium selenate, soil acidity and organic matter content[J]. Plants, 2020, 9(5): 605.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HE Y Z, XIANG Y J, ZHOU Y Y, et al. Selenium contamination, consequences and remediation techniques in water and soils: A review[J]. Environmental Research, 2018, 164:288-301.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
SUN H B. Association of soil selenium, strontium, and magnesium concentrations with Parkinson’s disease mortality rates in the USA[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2018, 40(1): 349-357.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 曾庆良, 余涛, 王锐. 土壤硒含量影响因素及富硒土地资源区划研究——以湖北恩施沙地为例[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(1): 105-112. |
| [10] |
YU T, YANG Z F, LV Y Y, et al. The origin and geochemical cycle of soil selenium in a Se-rich area of China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 139:97-108.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
DINH Q T, CUI Z W, HUANG J, et al. Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health: A review[J]. Environment International, 2018, 112:294-309.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ERMAKOV V, JOVANOVIC L. Selenium deficiency as a consequence of human activity and its correction[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2010, 107(2): 193-199.
DOI URL |
| [13] | JONES G D, DROZ B, GREVE P, et al. Selenium deficiency risk predicted to increase under future climate change[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(11): 2848-2853. |
| [14] | 侯佳渝, 杨耀栋, 谢薇, 等. 天津市西郊富硒土壤地球化学特征和成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(3): 618-625. |
| [15] |
DINH Q T, WANG M K, TRAN T A T, et al. Bioavailability of selenium in soil-plant system and a regulatory approach[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2019, 49(6): 443-517.
DOI URL |
| [16] | HAGAROVÁ I, ŽEMBERYOVÁ M, BAJCAN D. Sequential and single step extraction procedures used for fractionation of selenium in soil samples[J]. Chemical Papers, 2005, 59(2): 93-98. |
| [17] |
KESKINEN R, EKHOLM P, YLI-HALLA M, et al. Efficiency of different methods in extracting selenium from agricultural soils of Finland[J]. Geoderma, 2009, 153(1/2): 87-93.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
MUNIER-LAMY C, DENEUX-MUSTIN S, MUSTIN C, et al. Selenium bioavailability and uptake as affected by four different plants in a loamy clay soil with particular attention to mycorrhizae inoculated ryegrass[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2007, 97(2/3): 148-158.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ZHAO C Y, REN J G, XUE C Z, et al. Study on the relationship between soil selenium and plant selenium uptake[J]. Plant and Soil, 2005, 277(1/2): 197-206.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
PENG Q, WANG M K, CUI Z W, et al. Assessment of bioavai-lability of selenium in different plant-soil systems by diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT)[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 225:637-643.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ZHANG H, ZHAO F J, SUN B, et al. A new method to measure effective soil solution concentration predicts copper availability to plants[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2001, 35(12): 2602-2607.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
WANG P F, WANG T, YAO Y, et al. A diffusive gradient-in-thin-film technique for evaluation of the bioavailability of Cd in soil contaminated with Cd and Pb[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2016, 13(6): 556.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
TANDY S, MUNDUS S, YNGVESSON J, et al. The use of DGT for prediction of plant available copper, zinc and phosphorus in agricultural soils[J]. Plant and Soil, 2011, 346(1/2): 167-180.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
SONG N N, WANG F L, MA Y B, et al. Using DGT to assess cadmium bioavailability to ryegrass as influenced by soil properties[J]. Pedosphere, 2015, 25(6): 825-833.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
PENG Q, WANG D, WANG M, et al. Prediction of selenium uptake by pak choi in several agricultural soils based on diffusive gradients in thin-films technique and single extraction[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 256:113414.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 杨忠芳, 余涛, 李敏, 等. DZ/T 0295—2016 土地质量地球化学评价规范[S]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016: 15-17. |
| [27] |
MALIK J A, GOEL S, KAUR N, et al. Selenium antagonises the toxic effects of arsenic on mungbean (Phaseolus aureus Roxb.) plants by restricting its uptake and enhancing the antioxidative and detoxification mechanisms[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2012, 77:242-248.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 严明书, 龚媛媛, 杨乐超, 等. 重庆土壤硒的地球化学特征及经济意义[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(2): 325-330. |
| [29] |
WANG Z J, GAO Y X. Biogeochemical cycling of selenium in Chinese environments[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2001, 16(11/12): 1345-1351.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 余涛, 杨忠芳, 王锐, 等. 恩施典型富硒区土壤硒与其他元素组合特征及来源分析[J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(6): 1119-1125. |
| [31] | 谭见安. 中华人民共和国地方病与环境图集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989: 39. |
| [32] | 刘道荣, 徐虹, 周漪, 等. 浙西常山地区富硒土壤特征及成因分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(3): 658-666. |
| [33] |
WANG D, XUE M Y, WANG Y K, et al. Effects of straw amendment on selenium aging in soils: Mechanism and influential factors[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 657:871-881.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
AHMAD M, LEE S S, LEE S E, et al. Biochar-induced changes in soil properties affected immobilization/mobilization of metals/metalloids in contaminated soils[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2017, 17(3): 717-730.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
LI Z, LIANG D L, PENG Q, et al. Interaction between selenium and soil organic matter and its impact on soil selenium bioavai-lability: A review[J]. Geoderma, 2017, 295:69-79.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 吴俊. 福建省寿宁县富硒土壤地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(2): 386-391. |
| [37] |
WANG Z J, GAO Y X, BELZILE N. Microwave digestion of environmental and natural waters for selenium speciation[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2001, 73(19): 4711-4716.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
PEAK D. Adsorption mechanisms of selenium oxyanions at the aluminum oxide/water interface[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2006, 303(2): 337-345.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
LI Z, MAN N, WANG S S, et al. Selenite adsorption and desorption in main Chinese soils with their characteristics and physicochemical properties[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2015, 15(5): 1150-1158.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
JOHNSON C C, GE X, GREEN K A, et al. Selenium distribution in the local environment of selected villages of the Keshan Disease belt, Zhangjiakou District, Hebei Province, People’s Republic of China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2000, 15(3): 385-401.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
SILVA E C, WADT L H O, SILVA K E, et al. Natural variation of selenium in Brazil nuts and soils from the Amazon region[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 188:650-658.
DOI URL |
| [42] | TOLU J, THIRY Y, BUENO M, et al. Distribution and speciation of ambient selenium in contrasted soils, from mineral to organic rich[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 479:93-101. |
| [43] |
MULLER J, ABDELOUAS A, RIBET S, et al. Sorption of selenite in a multi-component system using the “dialysis membrane” method[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2012, 27(12): 2524-2532.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
ÁVILA P A, FAQUIN V, ÁVILA F W, et al. Phosphorus and sulfur in a tropical soil and their effects on growth and selenium accumulation in Leucaena leucocephala(Lam.) de Wit[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27:44060-44072.
DOI URL |
| [45] | 陈怀满. 环境土壤学[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 176-188. |
| [1] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [2] | 梁鸣, 高文, 罗先熔, 王晓东, 刘秀娟, 陈皓, 刘攀峰, 竹峰, 李伟. 冀北高尖子地区土壤地球化学特征及其找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1567-1579. |
| [3] | 刘永林, 赵家宇, 刘怡, 吴梅, 肖慧娴, 刘丁慧, 田兴磊. 重庆侏罗纪地层区土壤硒含量分异:以江津和石柱地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1644-1654. |
| [4] | 李楠, 曹明杰, 郝喆, 侯永莉, 陈红丹, 张颖. 基于不同土地利用方式的土壤重金属污染与潜在风险评价:以辽河流域(浑太水系)山水林田湖草沙一体化保护和修复工程为例[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1655-1664. |
| [5] | 王倩, 金晓媚, 张绪财, 殷秀兰, 金爱芳, 罗绪富. 河北省张承地区2001—2020年植被动态变化及驱动因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 881-891. |
| [6] | 钱信禹, 边小卫, 张亚峰, 王颖维, 杨运军, 游军. 丹江源地区地质建造对土壤和植被生态空间格局的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 903-913. |
| [7] | 王滢, 胡伟武, 陈男, 冯传平. 华北棕壤土掺砂比对渗滤系统净化污水性能的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 914-924. |
| [8] | 韩宝华, 段星星, 何峻岭, 阿地来·赛提尼亚孜, 王翠翠, 董越. 甘肃白银东大沟地区土壤镉地球化学特征及生态风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 745-757. |
| [9] | 胡永浩, 段星星, 夏昭德, 韩宝华. 玉米根际土壤细菌群落对不同程度镉污染的响应: 以甘肃省白银市四龙镇地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 758-766. |
| [10] | 王东晓, 袁德志. 锶在土壤-作物中迁移富集机制及作物富锶标准探讨:以河南固始史河一带为例[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 767-777. |
| [11] | 胡庆海, 王学求, 韩志轩, 成晓梦, 吴慧, 田密, 刘福田, 孙彬彬, 陈卫明, 杜雪苗, 刘彬, 崔邢涛. 京津冀地区永清县土壤重金属地球化学特征及绿色食品产地的土壤质量评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 778-789. |
| [12] | 杜古尔·卫卫, 石海涛, 邢浩, 娄雪聪, 胡宏利, 布龙巴特. 新疆戈壁荒漠区典型露天煤矿土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 790-800. |
| [13] | 李慧, 温汉辉, 蔡立梅, 徐耀辉, 罗杰, 梅敬娴, 徐述邦. 广东省揭阳市揭东区微量元素分布特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(01): 208-216. |
| [14] | 周墨, 梁晓红, 张明, 文帮勇, 唐志敏, 湛龙. 南京市溧水区表层土壤锗地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(01): 217-226. |
| [15] | 刘同, 刘传朋, 康鹏宇, 赵秀芳, 邓俊, 王凯凯. 山东省沂南县东部土壤重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1173-1182. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||