



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (04): 981-996.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.103
收稿日期:2020-08-14
修回日期:2020-11-12
出版日期:2021-08-10
发布日期:2021-09-08
通讯作者:
康志强
作者简介:康志强,男,教授,博士生导师,1979年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事岩石、矿床地球化学研究。Email: zk99201@163.com。基金资助:
LIU Dongmei1( ), KANG Zhiqiang1,2(
), KANG Zhiqiang1,2( ), YANG Feng1,2, LI Daixian1
), YANG Feng1,2, LI Daixian1
Received:2020-08-14
Revised:2020-11-12
Online:2021-08-10
Published:2021-09-08
Contact:
KANG Zhiqiang
摘要:
印支期桂西南地区处于多板块构造交汇地带,其岩浆构造演化存在很大的争议。对桂西南十万大山盆地两侧酸性火山岩进行了系统的锆石年代学、全岩地球化学及Sr-Nd同位素地球化学研究。结果表明,十万大山盆地两侧酸性火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为240.5~248.4 Ma,形成于早三叠世。岩性主要为流纹岩,具有高SiO2、K2O、Al2O3及低的CaO、MgO特征,A/CNK=1.17~1.25,属于强过铝质高钾钙碱性-钾玄质系列岩石。微量元素整体上富集Rb、Th、U、Zr、Hf,而Sr、Nb、Ti和P元素亏损,稀土元素配分模式表现为轻稀土元素富集右倾型,轻、重稀土元素分馏显著,Eu中等负异常(δEu值为0.44~0.73);Sr-Nd同位素特征显示,样品具有较高的Sr初始值(0.706 21~0.719 51),低的εNd(t)值(-10.67~-9.72),其模式年龄为1.85~1.96 Ga,显示源区可能主要为古元古代的壳源物质。结合前人研究结果,认为研究区流纹岩是华南板块与印支地块后碰撞或碰撞晚期挤压热应力松弛的间隙环境下古老地壳变质泥岩部分熔融的产物。
中图分类号:
刘冬梅, 康志强, 杨锋, 李岱鲜. 桂西南早中生代流纹岩年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 981-996.
LIU Dongmei, KANG Zhiqiang, YANG Feng, LI Daixian. Geochronology and Geochemistry of Early Mesozoic Rhyolite in Southwestern Guangxi and Its Geological Significance[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(04): 981-996.

图1 华南板块和印支地块地质图(a)及桂西南早中生代酸性火山岩分布简图(b)((a)底图据文献[31];(b)底图据文献[24, 32])
Fig.1 Sketch map of the South China and Indosinian blocks ((a), modified from reference [31]) and simplified geologic map of southwestern Guangxi ((b), modified from references[24, 32])

图3 样品18DX-02((a)为正交偏光,(b)为单偏光)和18JZ-01镜下显微照片((c)为正交偏光,(d)为单偏光) Pl.斜长石;Qtz.石英
Fig.3 Microscopic photographs of sample 18DX-02 ((a), crossed polar; (b), plane polar) and sample 18JZ-01 ((c), crossed polar; (d), plane polar)
| 分析点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 同位素年龄/Ma | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Th | U | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | |||
| 18DX-02-01 | 14.89 | 125 | 305 | 0.41 | 0.320 3 | 0.020 9 | 0.040 1 | 0.001 4 | 282 | 16 | 253 | 9 | |
| 18DX-02-03 | 26.21 | 244 | 547 | 0.45 | 0.270 4 | 0.016 3 | 0.039 3 | 0.001 3 | 243 | 13 | 249 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-05 | 35.64 | 433 | 714 | 0.61 | 0.267 6 | 0.016 4 | 0.038 9 | 0.001 3 | 241 | 13 | 246 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-08 | 40.04 | 299 | 852 | 0.35 | 0.278 8 | 0.014 2 | 0.038 8 | 0.001 2 | 250 | 11 | 245 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-11 | 44.40 | 270 | 1 004 | 0.27 | 0.277 7 | 0.014 8 | 0.038 8 | 0.001 3 | 249 | 12 | 245 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-13 | 32.67 | 324 | 682 | 0.48 | 0.304 6 | 0.016 4 | 0.039 9 | 0.001 3 | 270 | 13 | 252 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-16 | 52.52 | 261 | 1 155 | 0.23 | 0.313 4 | 0.014 6 | 0.039 8 | 0.001 3 | 277 | 11 | 252 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-17 | 37.20 | 235 | 838 | 0.28 | 0.309 5 | 0.016 6 | 0.038 5 | 0.001 3 | 274 | 13 | 243 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-18 | 32.41 | 339 | 678 | 0.50 | 0.288 4 | 0.016 6 | 0.039 3 | 0.001 3 | 257 | 13 | 249 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-19 | 34.07 | 340 | 728 | 0.47 | 0.270 8 | 0.015 5 | 0.038 7 | 0.001 3 | 243 | 12 | 245 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-23 | 38.62 | 227 | 857 | 0.26 | 0.313 4 | 0.017 6 | 0.040 0 | 0.001 3 | 277 | 14 | 253 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-24 | 68.65 | 863 | 1373 | 0.63 | 0.291 6 | 0.013 5 | 0.040 0 | 0.001 3 | 260 | 11 | 253 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-27 | 40.67 | 451 | 833 | 0.54 | 0.309 6 | 0.017 1 | 0.039 9 | 0.001 3 | 274 | 13 | 252 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-28 | 28.62 | 286 | 605 | 0.47 | 0.270 1 | 0.017 6 | 0.038 6 | 0.001 3 | 243 | 14 | 244 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-29 | 65.49 | 226 | 1 488 | 0.15 | 0.294 1 | 0.012 6 | 0.038 9 | 0.001 2 | 262 | 10 | 246 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-01 | 13.93 | 79 | 298 | 0.26 | 0.255 2 | 0.010 1 | 0.036 3 | 0.001 1 | 231 | 8 | 230 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-02 | 12.25 | 69 | 258 | 0.27 | 0.256 9 | 0.011 1 | 0.036 7 | 0.001 2 | 232 | 9 | 232 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-04 | 8.24 | 87 | 158 | 0.55 | 0.261 7 | 0.012 4 | 0.037 2 | 0.001 2 | 236 | 10 | 235 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-05 | 18.25 | 52 | 382 | 0.14 | 0.269 7 | 0.010 5 | 0.038 1 | 0.001 2 | 242 | 8 | 241 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-06 | 12.71 | 133 | 247 | 0.54 | 0.260 1 | 0.011 3 | 0.036 9 | 0.001 2 | 235 | 9 | 234 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-07 | 21.72 | 141 | 476 | 0.30 | 0.264 6 | 0.010 0 | 0.035 0 | 0.001 1 | 238 | 8 | 222 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-10 | 15.52 | 100 | 339 | 0.30 | 0.261 2 | 0.010 5 | 0.037 0 | 0.001 2 | 236 | 8 | 234 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-11 | 13.84 | 98 | 289 | 0.34 | 0.273 9 | 0.011 3 | 0.038 6 | 0.001 2 | 246 | 9 | 244 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-12 | 16.15 | 113 | 337 | 0.33 | 0.287 9 | 0.012 0 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 257 | 9 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-13 | 14.95 | 78 | 320 | 0.24 | 0.275 3 | 0.011 4 | 0.038 8 | 0.001 2 | 247 | 9 | 245 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-14 | 9.80 | 73 | 203 | 0.36 | 0.276 0 | 0.013 9 | 0.039 0 | 0.001 3 | 247 | 11 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-15 | 13.89 | 83 | 296 | 0.28 | 0.257 4 | 0.010 6 | 0.037 7 | 0.001 2 | 233 | 9 | 239 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-16 | 10.77 | 78 | 219 | 0.35 | 0.279 6 | 0.012 0 | 0.038 0 | 0.001 2 | 250 | 9 | 241 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-18 | 12.81 | 73 | 273 | 0.27 | 0.258 8 | 0.010 8 | 0.036 4 | 0.001 2 | 234 | 9 | 230 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-19 | 11.70 | 54 | 247 | 0.22 | 0.263 1 | 0.011 9 | 0.037 5 | 0.001 2 | 237 | 10 | 237 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-20 | 6.64 | 37 | 133 | 0.27 | 0.290 2 | 0.017 3 | 0.040 2 | 0.001 5 | 259 | 14 | 254 | 9 | |
| 18JZ-01-21 | 10.27 | 53 | 223 | 0.24 | 0.258 5 | 0.011 5 | 0.036 7 | 0.001 2 | 233 | 9 | 232 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-22 | 10.39 | 55 | 221 | 0.25 | 0.259 4 | 0.011 6 | 0.038 1 | 0.001 2 | 234 | 9 | 241 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-23 | 10.84 | 72 | 222 | 0.33 | 0.275 4 | 0.012 5 | 0.038 7 | 0.001 2 | 247 | 10 | 245 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-24 | 18.29 | 103 | 400 | 0.26 | 0.270 6 | 0.011 2 | 0.037 7 | 0.001 2 | 243 | 9 | 239 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-26 | 12.25 | 82 | 266 | 0.31 | 0.275 3 | 0.011 8 | 0.038 8 | 0.001 2 | 247 | 9 | 245 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-27 | 11.53 | 111 | 230 | 0.48 | 0.269 1 | 0.011 3 | 0.040 3 | 0.001 3 | 242 | 9 | 254 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-28 | 11.76 | 70 | 247 | 0.28 | 0.280 3 | 0.011 5 | 0.040 5 | 0.001 3 | 251 | 9 | 256 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-29 | 15.58 | 106 | 338 | 0.31 | 0.256 7 | 0.010 1 | 0.039 2 | 0.001 2 | 232 | 8 | 248 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-30 | 8.29 | 47 | 176 | 0.27 | 0.281 5 | 0.012 3 | 0.040 8 | 0.001 3 | 252 | 10 | 258 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-01 | 28.25 | 181 | 604 | 0.30 | 0.271 4 | 0.011 1 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 244 | 9 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-02 | 31.78 | 179 | 689 | 0.26 | 0.264 0 | 0.010 5 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 238 | 8 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-03 | 40.73 | 402 | 813 | 0.49 | 0.279 1 | 0.011 0 | 0.039 4 | 0.001 2 | 250 | 9 | 249 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-05 | 74.04 | 475 | 1 576 | 0.30 | 0.272 7 | 0.009 8 | 0.039 0 | 0.001 2 | 245 | 8 | 247 | 7 | |
| 分析点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 同位素年龄/Ma | |||||||||
| Pb | Th | U | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | |||
| 18JZ-03-06 | 27.30 | 156 | 594 | 0.26 | 0.272 6 | 0.011 8 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 245 | 9 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-07 | 41.99 | 222 | 901 | 0.25 | 0.271 3 | 0.010 8 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 244 | 9 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-08 | 28.16 | 146 | 602 | 0.24 | 0.260 0 | 0.011 8 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 235 | 9 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-09 | 39.15 | 218 | 841 | 0.26 | 0.265 6 | 0.010 5 | 0.039 2 | 0.001 2 | 239 | 8 | 248 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-10 | 67.11 | 279 | 1 466 | 0.19 | 0.271 5 | 0.009 9 | 0.038 3 | 0.001 2 | 244 | 8 | 242 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-03-11 | 21.94 | 189 | 435 | 0.43 | 0.276 9 | 0.012 6 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 248 | 10 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-12 | 51.99 | 348 | 1 085 | 0.32 | 0.285 2 | 0.010 8 | 0.037 9 | 0.001 2 | 255 | 9 | 240 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-03-13 | 31.69 | 203 | 663 | 0.31 | 0.292 7 | 0.012 3 | 0.039 0 | 0.001 2 | 261 | 10 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-15 | 40.96 | 143 | 881 | 0.16 | 0.275 1 | 0.010 9 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 3 | 247 | 9 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-16 | 37.82 | 276 | 787 | 0.35 | 0.281 3 | 0.011 2 | 0.039 0 | 0.001 2 | 252 | 9 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-17 | 50.56 | 342 | 1 078 | 0.32 | 0.274 1 | 0.010 5 | 0.038 0 | 0.001 2 | 246 | 8 | 240 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-03-18 | 55.39 | 381 | 1 156 | 0.33 | 0.280 6 | 0.011 1 | 0.039 0 | 0.001 2 | 251 | 9 | 246 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-19 | 35.39 | 240 | 731 | 0.33 | 0.280 8 | 0.011 8 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 251 | 9 | 247 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-03-21 | 22.82 | 248 | 453 | 0.55 | 0.281 9 | 0.014 0 | 0.039 2 | 0.001 3 | 252 | 11 | 248 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-22 | 34.20 | 179 | 719 | 0.25 | 0.284 8 | 0.011 3 | 0.038 9 | 0.001 2 | 254 | 9 | 246 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-03-25 | 55.50 | 184 | 1 209 | 0.15 | 0.269 5 | 0.009 9 | 0.038 5 | 0.001 2 | 242 | 8 | 244 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-03-26 | 50.46 | 333 | 1 049 | 0.32 | 0.272 9 | 0.011 0 | 0.038 8 | 0.001 2 | 245 | 9 | 246 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-03-29 | 27.91 | 149 | 595 | 0.25 | 0.268 5 | 0.011 2 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 242 | 9 | 247 | 8 | |
表1 桂西南早中生代酸性火山岩锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测定结果
Table 1 Zircons U-Th-Pb dating results of the Early Mesozoic felsic volcanic rocks from southwestern Guangxi
| 分析点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 同位素年龄/Ma | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Th | U | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | |||
| 18DX-02-01 | 14.89 | 125 | 305 | 0.41 | 0.320 3 | 0.020 9 | 0.040 1 | 0.001 4 | 282 | 16 | 253 | 9 | |
| 18DX-02-03 | 26.21 | 244 | 547 | 0.45 | 0.270 4 | 0.016 3 | 0.039 3 | 0.001 3 | 243 | 13 | 249 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-05 | 35.64 | 433 | 714 | 0.61 | 0.267 6 | 0.016 4 | 0.038 9 | 0.001 3 | 241 | 13 | 246 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-08 | 40.04 | 299 | 852 | 0.35 | 0.278 8 | 0.014 2 | 0.038 8 | 0.001 2 | 250 | 11 | 245 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-11 | 44.40 | 270 | 1 004 | 0.27 | 0.277 7 | 0.014 8 | 0.038 8 | 0.001 3 | 249 | 12 | 245 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-13 | 32.67 | 324 | 682 | 0.48 | 0.304 6 | 0.016 4 | 0.039 9 | 0.001 3 | 270 | 13 | 252 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-16 | 52.52 | 261 | 1 155 | 0.23 | 0.313 4 | 0.014 6 | 0.039 8 | 0.001 3 | 277 | 11 | 252 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-17 | 37.20 | 235 | 838 | 0.28 | 0.309 5 | 0.016 6 | 0.038 5 | 0.001 3 | 274 | 13 | 243 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-18 | 32.41 | 339 | 678 | 0.50 | 0.288 4 | 0.016 6 | 0.039 3 | 0.001 3 | 257 | 13 | 249 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-19 | 34.07 | 340 | 728 | 0.47 | 0.270 8 | 0.015 5 | 0.038 7 | 0.001 3 | 243 | 12 | 245 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-23 | 38.62 | 227 | 857 | 0.26 | 0.313 4 | 0.017 6 | 0.040 0 | 0.001 3 | 277 | 14 | 253 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-24 | 68.65 | 863 | 1373 | 0.63 | 0.291 6 | 0.013 5 | 0.040 0 | 0.001 3 | 260 | 11 | 253 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-27 | 40.67 | 451 | 833 | 0.54 | 0.309 6 | 0.017 1 | 0.039 9 | 0.001 3 | 274 | 13 | 252 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-28 | 28.62 | 286 | 605 | 0.47 | 0.270 1 | 0.017 6 | 0.038 6 | 0.001 3 | 243 | 14 | 244 | 8 | |
| 18DX-02-29 | 65.49 | 226 | 1 488 | 0.15 | 0.294 1 | 0.012 6 | 0.038 9 | 0.001 2 | 262 | 10 | 246 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-01 | 13.93 | 79 | 298 | 0.26 | 0.255 2 | 0.010 1 | 0.036 3 | 0.001 1 | 231 | 8 | 230 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-02 | 12.25 | 69 | 258 | 0.27 | 0.256 9 | 0.011 1 | 0.036 7 | 0.001 2 | 232 | 9 | 232 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-04 | 8.24 | 87 | 158 | 0.55 | 0.261 7 | 0.012 4 | 0.037 2 | 0.001 2 | 236 | 10 | 235 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-05 | 18.25 | 52 | 382 | 0.14 | 0.269 7 | 0.010 5 | 0.038 1 | 0.001 2 | 242 | 8 | 241 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-06 | 12.71 | 133 | 247 | 0.54 | 0.260 1 | 0.011 3 | 0.036 9 | 0.001 2 | 235 | 9 | 234 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-07 | 21.72 | 141 | 476 | 0.30 | 0.264 6 | 0.010 0 | 0.035 0 | 0.001 1 | 238 | 8 | 222 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-10 | 15.52 | 100 | 339 | 0.30 | 0.261 2 | 0.010 5 | 0.037 0 | 0.001 2 | 236 | 8 | 234 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-11 | 13.84 | 98 | 289 | 0.34 | 0.273 9 | 0.011 3 | 0.038 6 | 0.001 2 | 246 | 9 | 244 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-12 | 16.15 | 113 | 337 | 0.33 | 0.287 9 | 0.012 0 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 257 | 9 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-13 | 14.95 | 78 | 320 | 0.24 | 0.275 3 | 0.011 4 | 0.038 8 | 0.001 2 | 247 | 9 | 245 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-14 | 9.80 | 73 | 203 | 0.36 | 0.276 0 | 0.013 9 | 0.039 0 | 0.001 3 | 247 | 11 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-15 | 13.89 | 83 | 296 | 0.28 | 0.257 4 | 0.010 6 | 0.037 7 | 0.001 2 | 233 | 9 | 239 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-16 | 10.77 | 78 | 219 | 0.35 | 0.279 6 | 0.012 0 | 0.038 0 | 0.001 2 | 250 | 9 | 241 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-18 | 12.81 | 73 | 273 | 0.27 | 0.258 8 | 0.010 8 | 0.036 4 | 0.001 2 | 234 | 9 | 230 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-19 | 11.70 | 54 | 247 | 0.22 | 0.263 1 | 0.011 9 | 0.037 5 | 0.001 2 | 237 | 10 | 237 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-20 | 6.64 | 37 | 133 | 0.27 | 0.290 2 | 0.017 3 | 0.040 2 | 0.001 5 | 259 | 14 | 254 | 9 | |
| 18JZ-01-21 | 10.27 | 53 | 223 | 0.24 | 0.258 5 | 0.011 5 | 0.036 7 | 0.001 2 | 233 | 9 | 232 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-22 | 10.39 | 55 | 221 | 0.25 | 0.259 4 | 0.011 6 | 0.038 1 | 0.001 2 | 234 | 9 | 241 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-23 | 10.84 | 72 | 222 | 0.33 | 0.275 4 | 0.012 5 | 0.038 7 | 0.001 2 | 247 | 10 | 245 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-24 | 18.29 | 103 | 400 | 0.26 | 0.270 6 | 0.011 2 | 0.037 7 | 0.001 2 | 243 | 9 | 239 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-01-26 | 12.25 | 82 | 266 | 0.31 | 0.275 3 | 0.011 8 | 0.038 8 | 0.001 2 | 247 | 9 | 245 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-27 | 11.53 | 111 | 230 | 0.48 | 0.269 1 | 0.011 3 | 0.040 3 | 0.001 3 | 242 | 9 | 254 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-28 | 11.76 | 70 | 247 | 0.28 | 0.280 3 | 0.011 5 | 0.040 5 | 0.001 3 | 251 | 9 | 256 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-29 | 15.58 | 106 | 338 | 0.31 | 0.256 7 | 0.010 1 | 0.039 2 | 0.001 2 | 232 | 8 | 248 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-01-30 | 8.29 | 47 | 176 | 0.27 | 0.281 5 | 0.012 3 | 0.040 8 | 0.001 3 | 252 | 10 | 258 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-01 | 28.25 | 181 | 604 | 0.30 | 0.271 4 | 0.011 1 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 244 | 9 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-02 | 31.78 | 179 | 689 | 0.26 | 0.264 0 | 0.010 5 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 238 | 8 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-03 | 40.73 | 402 | 813 | 0.49 | 0.279 1 | 0.011 0 | 0.039 4 | 0.001 2 | 250 | 9 | 249 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-05 | 74.04 | 475 | 1 576 | 0.30 | 0.272 7 | 0.009 8 | 0.039 0 | 0.001 2 | 245 | 8 | 247 | 7 | |
| 分析点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 同位素年龄/Ma | |||||||||
| Pb | Th | U | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | |||
| 18JZ-03-06 | 27.30 | 156 | 594 | 0.26 | 0.272 6 | 0.011 8 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 245 | 9 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-07 | 41.99 | 222 | 901 | 0.25 | 0.271 3 | 0.010 8 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 244 | 9 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-08 | 28.16 | 146 | 602 | 0.24 | 0.260 0 | 0.011 8 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 235 | 9 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-09 | 39.15 | 218 | 841 | 0.26 | 0.265 6 | 0.010 5 | 0.039 2 | 0.001 2 | 239 | 8 | 248 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-10 | 67.11 | 279 | 1 466 | 0.19 | 0.271 5 | 0.009 9 | 0.038 3 | 0.001 2 | 244 | 8 | 242 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-03-11 | 21.94 | 189 | 435 | 0.43 | 0.276 9 | 0.012 6 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 248 | 10 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-12 | 51.99 | 348 | 1 085 | 0.32 | 0.285 2 | 0.010 8 | 0.037 9 | 0.001 2 | 255 | 9 | 240 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-03-13 | 31.69 | 203 | 663 | 0.31 | 0.292 7 | 0.012 3 | 0.039 0 | 0.001 2 | 261 | 10 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-15 | 40.96 | 143 | 881 | 0.16 | 0.275 1 | 0.010 9 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 3 | 247 | 9 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-16 | 37.82 | 276 | 787 | 0.35 | 0.281 3 | 0.011 2 | 0.039 0 | 0.001 2 | 252 | 9 | 247 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-17 | 50.56 | 342 | 1 078 | 0.32 | 0.274 1 | 0.010 5 | 0.038 0 | 0.001 2 | 246 | 8 | 240 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-03-18 | 55.39 | 381 | 1 156 | 0.33 | 0.280 6 | 0.011 1 | 0.039 0 | 0.001 2 | 251 | 9 | 246 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-19 | 35.39 | 240 | 731 | 0.33 | 0.280 8 | 0.011 8 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 251 | 9 | 247 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-03-21 | 22.82 | 248 | 453 | 0.55 | 0.281 9 | 0.014 0 | 0.039 2 | 0.001 3 | 252 | 11 | 248 | 8 | |
| 18JZ-03-22 | 34.20 | 179 | 719 | 0.25 | 0.284 8 | 0.011 3 | 0.038 9 | 0.001 2 | 254 | 9 | 246 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-03-25 | 55.50 | 184 | 1 209 | 0.15 | 0.269 5 | 0.009 9 | 0.038 5 | 0.001 2 | 242 | 8 | 244 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-03-26 | 50.46 | 333 | 1 049 | 0.32 | 0.272 9 | 0.011 0 | 0.038 8 | 0.001 2 | 245 | 9 | 246 | 7 | |
| 18JZ-03-29 | 27.91 | 149 | 595 | 0.25 | 0.268 5 | 0.011 2 | 0.039 1 | 0.001 2 | 242 | 9 | 247 | 8 | |
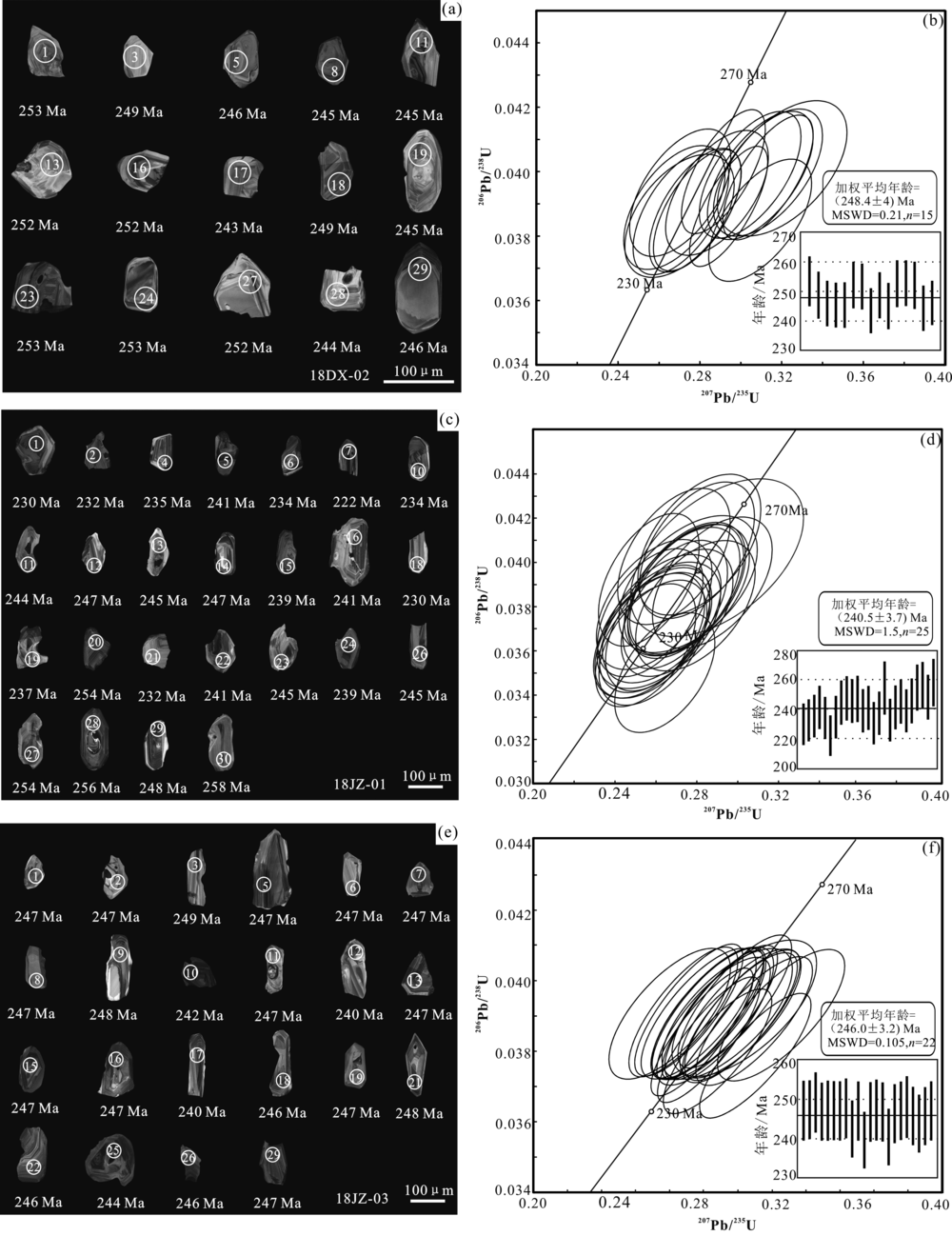
图4 研究区火山岩锆石CL图像(a)(c)(e)及U-Pb年龄谐和图(b)(d)(f) (a)(b)样品18DX-02;(c)(d)样品18JZ-01;(d)(f)样品18JZ-03。白色实心圆圈代表U-Pb年龄测试激光剥蚀点位;圆圈中数字为分析点号,编号同表1,锆石下方年龄为206Pb/238U表面年龄
Fig.4 CL images (a)(c)(e) and zircon U-Pb concordia diagrams (b)(d)(f) of volcanic rocks from the study area
| 样品号 | 地层 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3T | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18DX-01 | 板八组 | 72.65 | 0.61 | 13.43 | 3.96 | 0.05 | 0.94 | 1.53 | 3.10 | 3.32 | 0.12 | 1.16 | 100.88 |
| 18DX-02 | 板八组 | 71.14 | 0.57 | 12.81 | 3.89 | 0.05 | 0.83 | 1.38 | 1.38 | 5.49 | 0.12 | 1.44 | 99.10 |
| 18DX-03 | 板八组 | 71.72 | 0.57 | 13.36 | 4.08 | 0.05 | 0.91 | 1.24 | 1.84 | 5.35 | 0.12 | 1.32 | 100.58 |
| 18JZ-01 | 北泗组 | 71.43 | 0.71 | 13.05 | 4.04 | 0.02 | 1.20 | 1.36 | 2.13 | 4.53 | 0.13 | 2.22 | 100.83 |
| 18JZ-02 | 北泗组 | 70.38 | 0.69 | 12.69 | 5.88 | 0.03 | 1.09 | 0.96 | 2.10 | 4.59 | 0.13 | 2.28 | 100.82 |
| 18JZ-03 | 北泗组 | 70.11 | 0.70 | 12.66 | 6.10 | 0.04 | 1.26 | 1.27 | 2.10 | 4.45 | 0.13 | 2.11 | 100.94 |
| 样品号 | 地层 | A/CNK | A/NK | Mg# | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn |
| 18DX-01 | 板八组 | 1.17 | 1.54 | 35.62 | 44.75 | 3.50 | 15.56 | 41.71 | 22.83 | 11.66 | 10.82 | 18.90 | 91.55 |
| 18DX-02 | 板八组 | 1.19 | 1.56 | 33.21 | 38.14 | 2.04 | 15.82 | 40.66 | 21.35 | 9.54 | 10.73 | 18.48 | 81.65 |
| 18DX-03 | 板八组 | 1.20 | 1.51 | 34.22 | 30.84 | 2.58 | 16.98 | 41.25 | 21.65 | 8.98 | 11.65 | 19.94 | 92.41 |
| 18JZ-01 | 北泗组 | 1.20 | 1.55 | 40.96 | 32.45 | 2.43 | 14.30 | 31.35 | 13.43 | 8.06 | 6.58 | 20.07 | 145.40 |
| 18JZ-02 | 北泗组 | 1.25 | 1.50 | 30.17 | 29.91 | 2.38 | 14.78 | 30.07 | 12.79 | 8.30 | 6.26 | 19.75 | 68.80 |
| 18JZ-03 | 北泗组 | 1.19 | 1.53 | 32.48 | 31.12 | 2.42 | 15.26 | 30.32 | 13.06 | 11.08 | 6.82 | 20.63 | 110.20 |
| 样品号 | 地层 | Ga | Rb | Sr | Zr | Nb | Mo | In | Cs | Ba | Hf | Ta | W |
| 18DX-01 | 板八组 | 19.46 | 170.90 | 100.10 | 292.50 | 15.59 | 1.57 | 0.09 | 7.25 | 528.10 | 7.26 | 1.38 | 72.65 |
| 18DX-02 | 板八组 | 20.11 | 292.00 | 93.74 | 303.70 | 15.11 | 1.07 | 0.07 | 12.98 | 654.00 | 7.37 | 1.53 | 55.03 |
| 18DX-03 | 板八组 | 19.70 | 286.90 | 72.21 | 287.20 | 14.85 | 1.82 | 0.08 | 9.22 | 578.60 | 6.96 | 1.81 | 48.25 |
| 18JZ-01 | 北泗组 | 21.51 | 221.50 | 77.75 | 411.20 | 15.66 | 1.01 | 0.08 | 7.10 | 552.00 | 9.81 | 1.24 | 37.70 |
| 18JZ-02 | 北泗组 | 21.61 | 225.10 | 65.83 | 392.20 | 15.55 | 1.47 | 0.09 | 9.01 | 664.40 | 9.49 | 1.23 | 28.79 |
| 18JZ-03 | 北泗组 | 22.01 | 218.50 | 78.52 | 390.10 | 15.46 | 0.83 | 0.08 | 9.57 | 693.90 | 9.31 | 1.21 | 45.94 |
| 样品号 | 地层 | Tl | Pb | Bi | Th | U | Ti | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm |
| 18DX-01 | 板八组 | 0.76 | 25.33 | 0.31 | 22.15 | 4.75 | 3 633 | 52.68 | 54.60 | 97.53 | 12.30 | 45.04 | 8.92 |
| 18DX-02 | 板八组 | 1.25 | 27.48 | 0.26 | 20.88 | 4.60 | 3 411 | 48.06 | 46.87 | 84.30 | 10.57 | 38.78 | 7.83 |
| 18DX-03 | 板八组 | 1.16 | 29.75 | 0.40 | 20.13 | 4.45 | 3 424 | 47.70 | 49.82 | 87.59 | 11.02 | 40.20 | 7.98 |
| 18JZ-01 | 北泗组 | 0.88 | 36.76 | 0.17 | 19.74 | 4.07 | 4 264 | 42.51 | 44.44 | 75.17 | 9.26 | 33.95 | 6.82 |
| 18JZ-02 | 北泗组 | 0.98 | 24.43 | 0.23 | 19.19 | 4.03 | 4 144 | 48.78 | 45.37 | 81.70 | 9.99 | 36.80 | 7.63 |
| 18JZ-03 | 北泗组 | 0.92 | 27.14 | 0.23 | 19.15 | 3.87 | 4 220 | 44.78 | 46.23 | 80.64 | 9.99 | 37.25 | 7.60 |
| 样品号 | 地层 | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | REE | δEu | |
| 18DX-01 | 板八组 | 1.28 | 8.96 | 1.44 | 8.20 | 1.55 | 4.72 | 0.71 | 4.66 | 0.65 | 250.56 | 0.44 | |
| 18DX-02 | 板八组 | 1.34 | 7.90 | 1.28 | 7.40 | 1.43 | 4.33 | 0.66 | 4.44 | 0.62 | 217.73 | 0.52 | |
| 18DX-03 | 板八组 | 1.28 | 8.12 | 1.30 | 7.35 | 1.40 | 4.29 | 0.65 | 4.32 | 0.60 | 225.93 | 0.49 | |
| 18JZ-01 | 北泗组 | 1.65 | 7.04 | 1.19 | 6.98 | 1.35 | 4.19 | 0.66 | 4.55 | 0.65 | 197.90 | 0.73 | |
| 18JZ-02 | 北泗组 | 1.70 | 7.66 | 1.32 | 7.96 | 1.55 | 4.86 | 0.75 | 5.10 | 0.73 | 213.10 | 0.68 | |
| 18JZ-03 | 北泗组 | 1.71 | 7.57 | 1.22 | 7.16 | 1.41 | 4.64 | 0.71 | 4.86 | 0.70 | 211.69 | 0.69 |
表2 桂西南早中生代酸性火山岩主量(wB/%)、微量(wB/10-6)和稀土元素(wB/10-6)分析结果
Table 2 Major elements (%), trace elements (10-6) and REEs(10-6) compositional data of the Early Mesozoic felsic volcanic rocks from southwestern Guangxi
| 样品号 | 地层 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3T | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18DX-01 | 板八组 | 72.65 | 0.61 | 13.43 | 3.96 | 0.05 | 0.94 | 1.53 | 3.10 | 3.32 | 0.12 | 1.16 | 100.88 |
| 18DX-02 | 板八组 | 71.14 | 0.57 | 12.81 | 3.89 | 0.05 | 0.83 | 1.38 | 1.38 | 5.49 | 0.12 | 1.44 | 99.10 |
| 18DX-03 | 板八组 | 71.72 | 0.57 | 13.36 | 4.08 | 0.05 | 0.91 | 1.24 | 1.84 | 5.35 | 0.12 | 1.32 | 100.58 |
| 18JZ-01 | 北泗组 | 71.43 | 0.71 | 13.05 | 4.04 | 0.02 | 1.20 | 1.36 | 2.13 | 4.53 | 0.13 | 2.22 | 100.83 |
| 18JZ-02 | 北泗组 | 70.38 | 0.69 | 12.69 | 5.88 | 0.03 | 1.09 | 0.96 | 2.10 | 4.59 | 0.13 | 2.28 | 100.82 |
| 18JZ-03 | 北泗组 | 70.11 | 0.70 | 12.66 | 6.10 | 0.04 | 1.26 | 1.27 | 2.10 | 4.45 | 0.13 | 2.11 | 100.94 |
| 样品号 | 地层 | A/CNK | A/NK | Mg# | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn |
| 18DX-01 | 板八组 | 1.17 | 1.54 | 35.62 | 44.75 | 3.50 | 15.56 | 41.71 | 22.83 | 11.66 | 10.82 | 18.90 | 91.55 |
| 18DX-02 | 板八组 | 1.19 | 1.56 | 33.21 | 38.14 | 2.04 | 15.82 | 40.66 | 21.35 | 9.54 | 10.73 | 18.48 | 81.65 |
| 18DX-03 | 板八组 | 1.20 | 1.51 | 34.22 | 30.84 | 2.58 | 16.98 | 41.25 | 21.65 | 8.98 | 11.65 | 19.94 | 92.41 |
| 18JZ-01 | 北泗组 | 1.20 | 1.55 | 40.96 | 32.45 | 2.43 | 14.30 | 31.35 | 13.43 | 8.06 | 6.58 | 20.07 | 145.40 |
| 18JZ-02 | 北泗组 | 1.25 | 1.50 | 30.17 | 29.91 | 2.38 | 14.78 | 30.07 | 12.79 | 8.30 | 6.26 | 19.75 | 68.80 |
| 18JZ-03 | 北泗组 | 1.19 | 1.53 | 32.48 | 31.12 | 2.42 | 15.26 | 30.32 | 13.06 | 11.08 | 6.82 | 20.63 | 110.20 |
| 样品号 | 地层 | Ga | Rb | Sr | Zr | Nb | Mo | In | Cs | Ba | Hf | Ta | W |
| 18DX-01 | 板八组 | 19.46 | 170.90 | 100.10 | 292.50 | 15.59 | 1.57 | 0.09 | 7.25 | 528.10 | 7.26 | 1.38 | 72.65 |
| 18DX-02 | 板八组 | 20.11 | 292.00 | 93.74 | 303.70 | 15.11 | 1.07 | 0.07 | 12.98 | 654.00 | 7.37 | 1.53 | 55.03 |
| 18DX-03 | 板八组 | 19.70 | 286.90 | 72.21 | 287.20 | 14.85 | 1.82 | 0.08 | 9.22 | 578.60 | 6.96 | 1.81 | 48.25 |
| 18JZ-01 | 北泗组 | 21.51 | 221.50 | 77.75 | 411.20 | 15.66 | 1.01 | 0.08 | 7.10 | 552.00 | 9.81 | 1.24 | 37.70 |
| 18JZ-02 | 北泗组 | 21.61 | 225.10 | 65.83 | 392.20 | 15.55 | 1.47 | 0.09 | 9.01 | 664.40 | 9.49 | 1.23 | 28.79 |
| 18JZ-03 | 北泗组 | 22.01 | 218.50 | 78.52 | 390.10 | 15.46 | 0.83 | 0.08 | 9.57 | 693.90 | 9.31 | 1.21 | 45.94 |
| 样品号 | 地层 | Tl | Pb | Bi | Th | U | Ti | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm |
| 18DX-01 | 板八组 | 0.76 | 25.33 | 0.31 | 22.15 | 4.75 | 3 633 | 52.68 | 54.60 | 97.53 | 12.30 | 45.04 | 8.92 |
| 18DX-02 | 板八组 | 1.25 | 27.48 | 0.26 | 20.88 | 4.60 | 3 411 | 48.06 | 46.87 | 84.30 | 10.57 | 38.78 | 7.83 |
| 18DX-03 | 板八组 | 1.16 | 29.75 | 0.40 | 20.13 | 4.45 | 3 424 | 47.70 | 49.82 | 87.59 | 11.02 | 40.20 | 7.98 |
| 18JZ-01 | 北泗组 | 0.88 | 36.76 | 0.17 | 19.74 | 4.07 | 4 264 | 42.51 | 44.44 | 75.17 | 9.26 | 33.95 | 6.82 |
| 18JZ-02 | 北泗组 | 0.98 | 24.43 | 0.23 | 19.19 | 4.03 | 4 144 | 48.78 | 45.37 | 81.70 | 9.99 | 36.80 | 7.63 |
| 18JZ-03 | 北泗组 | 0.92 | 27.14 | 0.23 | 19.15 | 3.87 | 4 220 | 44.78 | 46.23 | 80.64 | 9.99 | 37.25 | 7.60 |
| 样品号 | 地层 | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | REE | δEu | |
| 18DX-01 | 板八组 | 1.28 | 8.96 | 1.44 | 8.20 | 1.55 | 4.72 | 0.71 | 4.66 | 0.65 | 250.56 | 0.44 | |
| 18DX-02 | 板八组 | 1.34 | 7.90 | 1.28 | 7.40 | 1.43 | 4.33 | 0.66 | 4.44 | 0.62 | 217.73 | 0.52 | |
| 18DX-03 | 板八组 | 1.28 | 8.12 | 1.30 | 7.35 | 1.40 | 4.29 | 0.65 | 4.32 | 0.60 | 225.93 | 0.49 | |
| 18JZ-01 | 北泗组 | 1.65 | 7.04 | 1.19 | 6.98 | 1.35 | 4.19 | 0.66 | 4.55 | 0.65 | 197.90 | 0.73 | |
| 18JZ-02 | 北泗组 | 1.70 | 7.66 | 1.32 | 7.96 | 1.55 | 4.86 | 0.75 | 5.10 | 0.73 | 213.10 | 0.68 | |
| 18JZ-03 | 北泗组 | 1.71 | 7.57 | 1.22 | 7.16 | 1.41 | 4.64 | 0.71 | 4.86 | 0.70 | 211.69 | 0.69 |
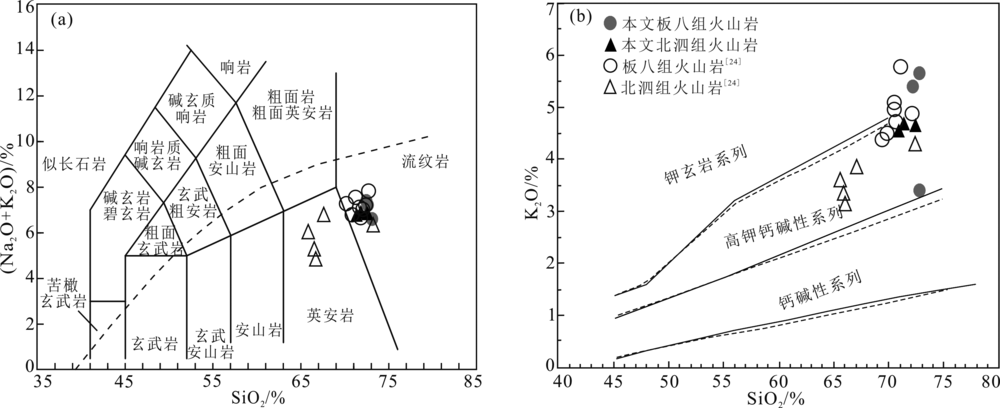
图5 桂西南早中生代酸性火山岩TAS分类图解((a),底图据文献[44])和SiO2-K2O判别图解((b),底图据文献[45])
Fig.5 TAS ((a),modified from reference [44]) and SiO2 vs. K2O ((b),modified from reference[45]) diagrams of the Early Mesozoic felsic volcanic rocks from southwestern Guangxi
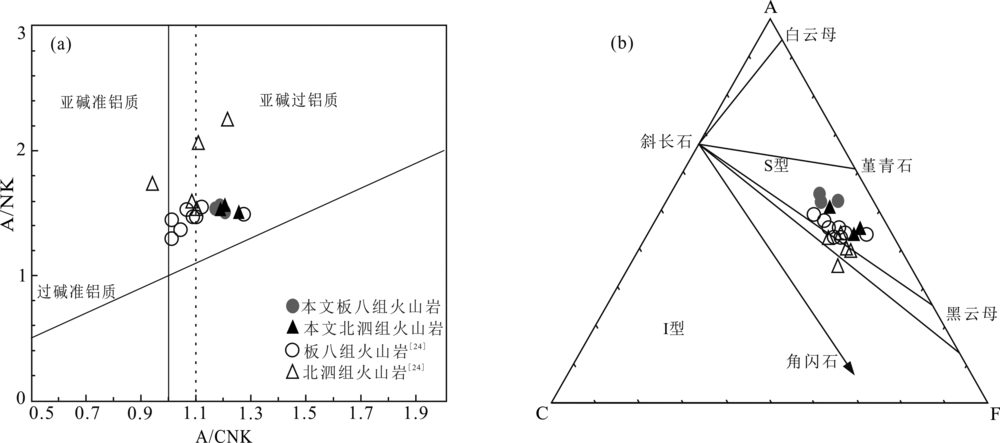
图6 桂西南早中生代酸性火山岩A/CNK-A/NK图解((a),底图据文献[46])和ACF图解((b),底图据文献[47])
Fig.6 A/CNK vs. A/NK ((a), modified from reference [46]) and ACF ((b), modified from reference[47]) diagrams of the Early Mesozoic felsic volcanic rocks from southwestern Guangxi
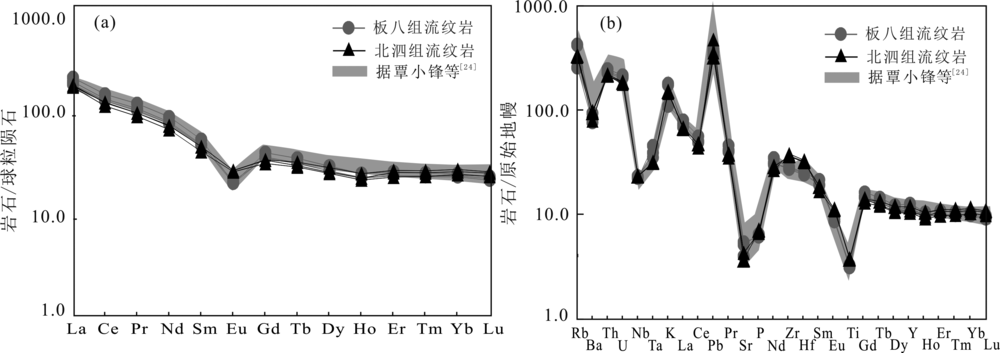
图7 桂西南早中生代酸性火山岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(球粒陨石标准化值据文献[54],原始地幔标准化值据文献[55])
Fig.7 Chondrite-normalized REE distribution patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized multi-element diagram (b) of the Early Mesozoic felsic volcanic rocks from southwestern Guangxi
| 样品编号 | Sm | Nd | Rb | Sr | 147Sm/144Nd | 143Nd/144Nd | INd | εNd(t) | 87Rb/86Sr | 87Sr/86Sr | (87Sr/86Sr)i | TDM/Ga |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18DX-02 | 7.83 | 38.8 | 292 | 93.7 | 0.121 93 | 0.511 97 | 0.511 77 | -10.67 | 9.017 38 | 0.751 38 | 0.719 51 | 1.96 |
| 18JZ-01 | 6.82 | 34.0 | 222 | 77.8 | 0.121 20 | 0.512 02 | 0.511 83 | -9.73 | 8.256 77 | 0.733 69 | 0.706 21 | 1.85 |
| 18JZ-03 | 7.60 | 37.3 | 219 | 78.5 | 0.123 11 | 0.512 02 | 0.500 82 | -9.72 | 8.072 56 | 0.735 38 | 0.707 13 | 1.90 |
表3 桂西南早中生代酸性火山岩Sr-Nd同位素分析结果
Table 3 Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of the Early Mesozoic felsic volcanic rocks from southwestern Guangxi
| 样品编号 | Sm | Nd | Rb | Sr | 147Sm/144Nd | 143Nd/144Nd | INd | εNd(t) | 87Rb/86Sr | 87Sr/86Sr | (87Sr/86Sr)i | TDM/Ga |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18DX-02 | 7.83 | 38.8 | 292 | 93.7 | 0.121 93 | 0.511 97 | 0.511 77 | -10.67 | 9.017 38 | 0.751 38 | 0.719 51 | 1.96 |
| 18JZ-01 | 6.82 | 34.0 | 222 | 77.8 | 0.121 20 | 0.512 02 | 0.511 83 | -9.73 | 8.256 77 | 0.733 69 | 0.706 21 | 1.85 |
| 18JZ-03 | 7.60 | 37.3 | 219 | 78.5 | 0.123 11 | 0.512 02 | 0.500 82 | -9.72 | 8.072 56 | 0.735 38 | 0.707 13 | 1.90 |
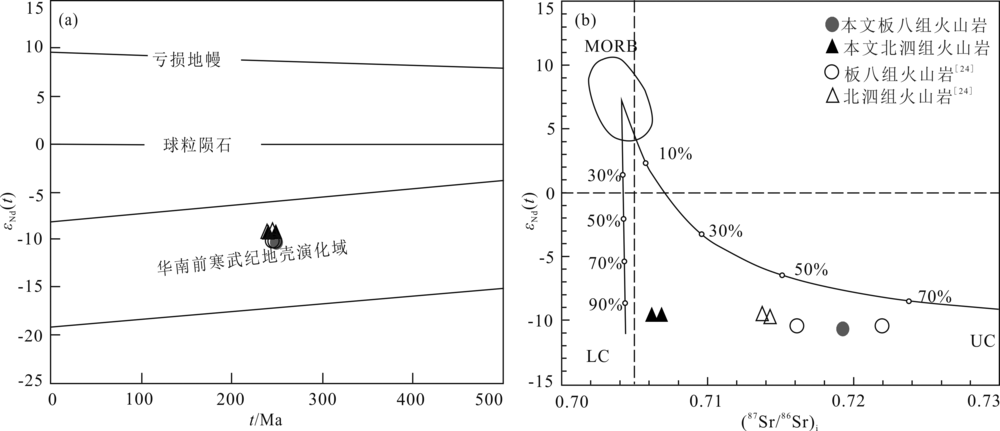
图8 桂西南早中生代酸性火山岩t -εNd(t) 图解((a),底图据文献[58])和(87Sr/86Sr)i-εNd(t)图解((b),底图据文献[59]) MORB.洋中脊玄武岩;LC.下地壳;UC.上地壳
Fig.8 t vs. εNd(t)((a),modified from reference[58])and (87Sr/86Sr)i-εNd(t) ((b),modified from reference[59]) diagrams of the Early Mesozoic felsic volcanic rocks from southwestern Guangxi
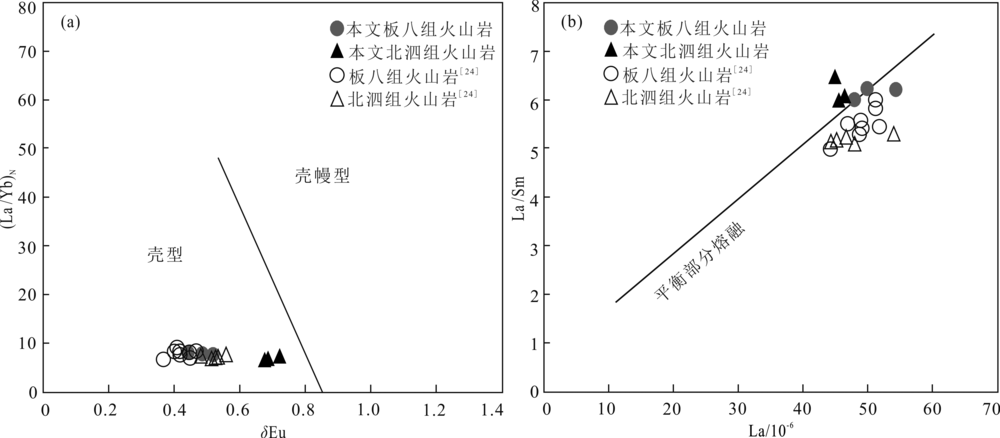
图9 桂西南早中生代酸性火山岩δEu-(La/Yb)N图解((a),底图据文献[65])和La-La/Sm图解((b),底图据文献[66])
Fig.9 δEu vs. (La/Yb)N((a),modified from reference[65]) and La vs. La/Sm ((b),modified from reference[66]) diagrams of the Early Mesozoic felsic volcanic rocks from southwestern Guangxi
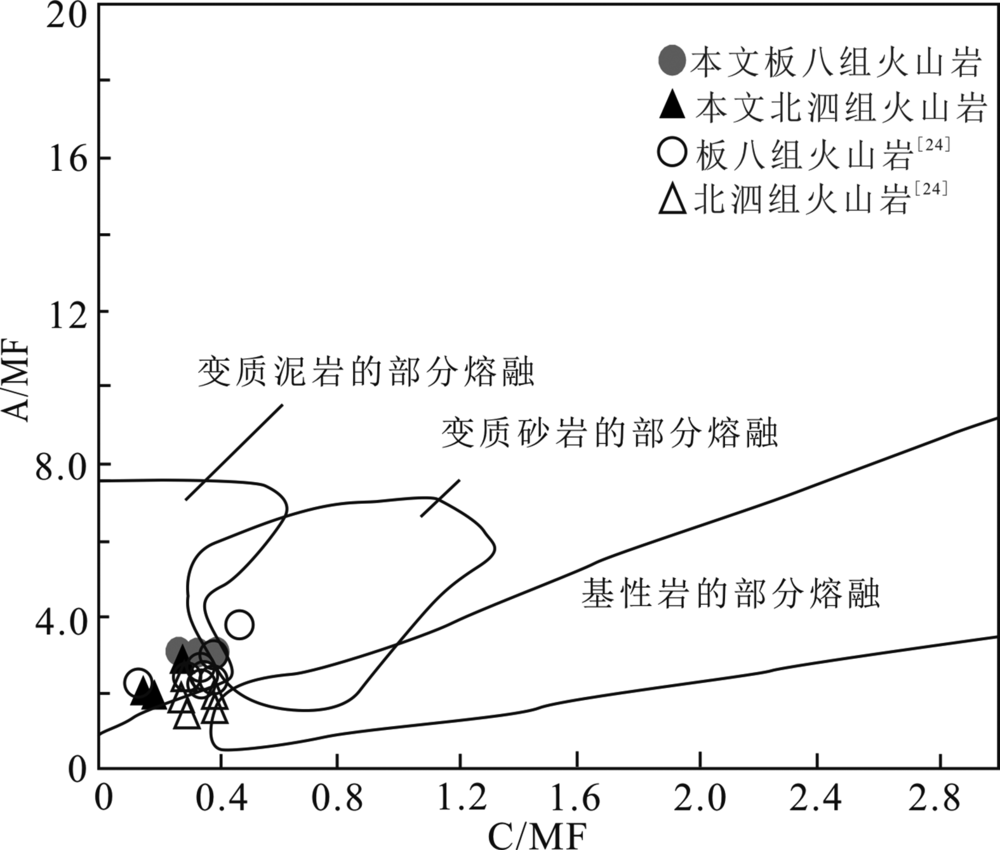
图10 桂西南早中生代酸性火山岩C/MF-A/MF图解(底图据文献[67])
Fig.10 C/MF vs. A/MF diagram of the Early Mesozoic felsic volcanic rocks from southwestern Guangxi (modified from reference[67])
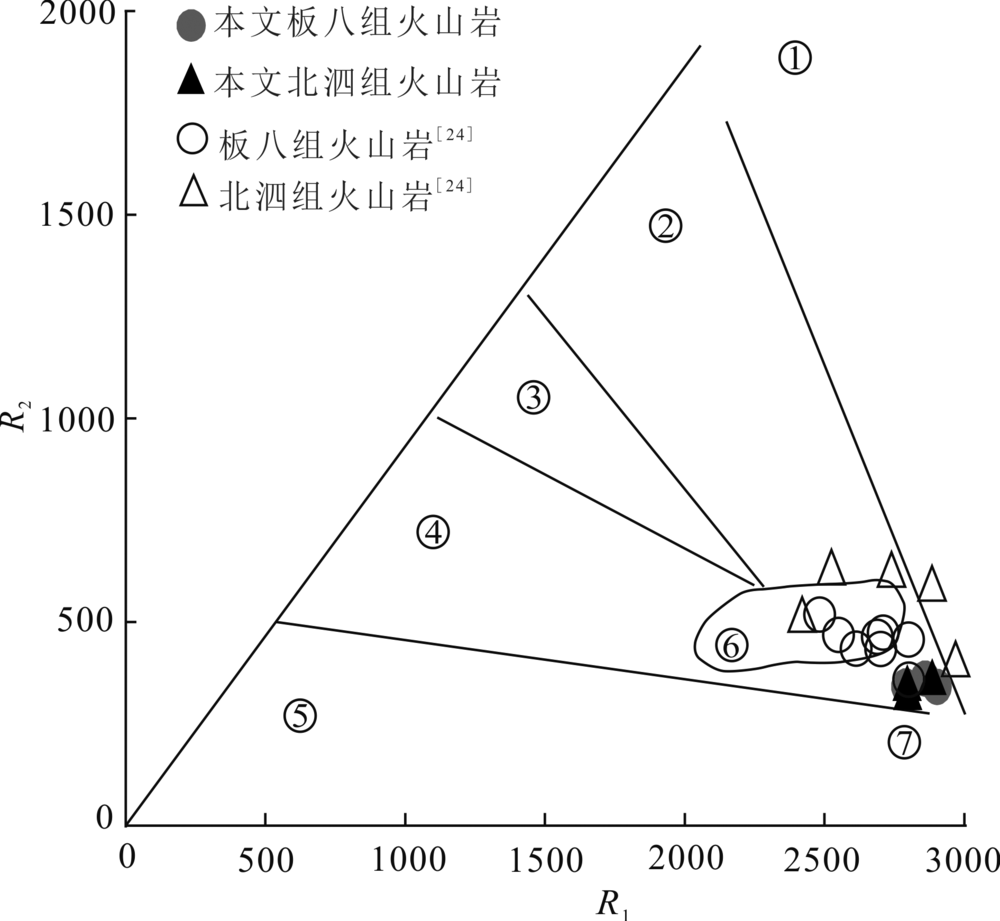
图11 桂西南早中生代酸性火山岩R1-R2图解(底图据文献[87]) ①地幔斜长花岗岩;②破坏性活动板块边缘(板块碰撞前)花岗岩;③板块碰撞后隆起期花岗岩;④晚造山期花岗岩;⑤非造山期A型花岗岩;⑥同碰撞(S型)花岗岩;⑦造山期后(A型)花岗岩;R1=1000×[4Si-11(Na+K)-2(Fe+Ti)]; R2=1000×(6Ca+2Mg+Al);R1和R2计算式中元素符号为对应阳离子比
Fig.11 R1-R2 diagrams of the Early Mesozoic felsic volcanic rocks from southwestern Guangxi(modified from reference[87])
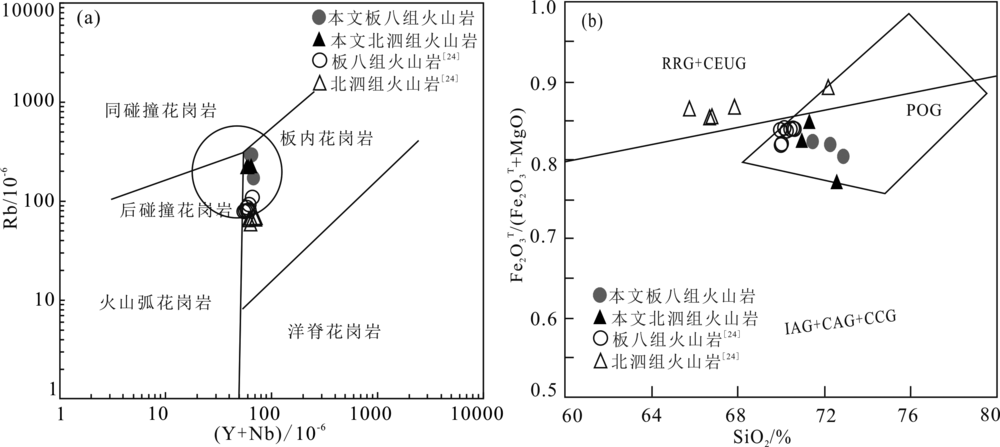
图12 桂西南早中生代酸性火山岩(Y+Nb)-Rb((a),底图据文献[88])和SiO2-Fe2O3T /( Fe2O3T+MgO) ((b),底图据文献[89])图解 IAG.岛弧花岗岩类;CAG.大陆弧花岗岩类;CCG.大陆碰撞花岗岩类;POG.造山后花岗岩类;RRG.与裂谷有关的花岗岩类;CEUG.与大陆的造陆抬升有关的花岗岩类
Fig.12 Tectonic discrimination diagrams of (Y+Nb)-Rb ((a),modified from reference [88]) and SiO2-Fe2O3T/(Fe2O3T +MgO) ((b), modified from reference[89]) of the Early Mesozoic felsic volcanic rocks from southwestern Guangxi
| [1] |
LI Z X, ZHANG L H, POWELL C M. South China in Rodinia: part of the missing link between Australia-East Antarctica and Laurentia?[J]. Geology, 1995, 23(5):407-410.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
YE M F, LI X H, LI W X, et al. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb geochronological and whole rock geochemical evidence for an early Neoproterozoic Sibaoan magmatic arc along the southeastern margin of the Yangtze Block[J]. Gondwana Research, 2007, 12(1/2):144-156.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ZHAO G C, CAWOOD P A. Tectonothermal evolution of the Mayuan assemblage in the Cathaysia Block: implications for Neoproterozoic collision-related assembly of the South China craton[J]. American Journal of Science, 1999, 299(4):309-339.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZHAO J H, ZHOU M F, YAN D P, et al. Reappraisal of the ages of Neoproterozoic strata in South China: No connection with the Grenvillian orogeny[J]. Geology, 2011, 39(4):299-302.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 张岳桥, 徐先兵, 贾东, 等. 华南早中生代从印支期碰撞构造体系向燕山期俯冲构造体系转换的形变记录[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(1):234-247. |
| [6] | 陈培荣, 周新民, 张文兰, 等. 南岭东段燕山早期正长岩-花岗岩杂岩的成因和意义[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2004, 34(6):493-503. |
| [7] | 陈卫锋, 陈培荣, 周新民, 等. 湖南阳明山岩体的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及成因研究[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(7):1065-1077. |
| [8] | GILDER S A, GILL J, COE R S, et al. Isotopic and paleomagnetic constraints on the Mesozoic tectonic evolution of south China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1996, 101(B7):16137-16154. |
| [9] |
LI X H. Cretaceous magmatism and lithospheric extension in Southeast China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2000, 18(3):293-305.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
WANG J, LI X H, DUAN T Z, et al. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating for the Cangshuipu volcanic rocks and its implications for the lower boundary age of the Nanhua strata in South China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(16):1663-1669.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
CHEN J F, JAHN B M. Crustal evolution of southeastern China: Nd and Sr isotopic evidence[J]. Tectonophysics, 1998, 284(1/2):101-133.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 梁新权, 李献华, 丘元禧, 等. 华南印支期碰撞造山——十万大山盆地构造和沉积学证据[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2005, 29(1):99-112. |
| [13] | 徐先兵, 张岳桥, 贾东, 等. 华南早中生代大地构造过程[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(3):573-593. |
| [14] | 赵越, 徐刚, 张拴宏, 等. 燕山运动与东亚构造体制的转变[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(3):319-328. |
| [15] | 董树文, 张岳桥, 龙长兴, 等. 中国侏罗纪构造变革与燕山运动新诠释[J]. 地质学报, 2007, 81(11):1449-1461. |
| [16] | 舒良树. 华南构造演化的基本特征[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(7):1035-1053. |
| [17] | 张岳桥, 董树文, 李建华, 等. 华南中生代大地构造研究新进展[J]. 地球学报, 2012, 33(3):257-279. |
| [18] | 周新民. 对华南花岗岩研究的若干思考[J]. 高校地质学报, 2003, 9(4):556-565. |
| [19] |
CHEN C H, HSIEH P S, LEE C Y, et al. Two episodes of the Indosinian thermal event on the South China Block:Constraints from LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon and electron microprobe monazite ages of the Darongshan S-type granitic suite[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011, 19(4):1008-1023.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 邓希光, 陈志刚, 李献华, 等. 桂东南地区大容山—十万大山花岗岩带SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年[J]. 地质论评, 2004, 50(4):426-432. |
| [21] | 林伟, FAURE M, LEPVRIER C, 等. 华南板块南缘早中生代的逆冲推覆构造及其相关的动力学背景[J]. 地质科学, 2011, 46(1):134-145. |
| [22] | 汪洋, 邓晋福. 广西南部三叠纪强过铝质火成岩岩石化学特征的动力学意义[J]. 地质地球化学, 2003, 31(4):35-42. |
| [23] | 王磊, 龙文国, 周岱, 等. 桂东南大容山晚二叠世花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(8):1291-1303. |
| [24] | 覃小锋, 王宗起, 张英利, 等. 桂西南早中生代酸性火山岩年代学和地球化学:对钦-杭结合带西南段构造演化的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(3):794-808. |
| [25] | 赵亮, 郭锋, 范蔚茗, 等. 广西十万大山地壳演化:来自印支期花岗岩中麻粒岩包体锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素记录[J]. 科学通报, 2010, 55(15):1489-1500. |
| [26] | 焦淑娟, 郭敬辉, 彭松柏. 华南大容山—十万大山花岗岩体中石榴石成因以及麻粒岩包体变质作用研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(5):1740-1758. |
| [27] | 王文宝, 李建华, 辛宇佳, 等. 华南大容山—十万大山花岗岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(2):179-194. |
| [28] |
LI Z X, LI X H. Formation of the 1 300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China a flat-slab subduction model[J]. Geology, 2007, 35:179-182.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
CHU Y, FAURE M, LIN W, et al. Tectonics of the Middle Triassic intracontinental Xuefengshan Belt, South China: new insights from structural and chronological constraints on the basal decollement zone[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2012, 101(8):2125-2150.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 梁金城, 邓继新, 陈懋弘, 等. 桂西南早三叠世中酸性火山岩及其构造环境[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2001, 25(2):141-148. |
| [31] |
WANG Y J, ZHANG A M, FAN W M, et al. Petrogenesis of Late Triassic post-collisional basaltic rocks of the Lancangjiang tectonic zone,southwest China,and tectonic implications for the evolution of the eastern Paleotethys: Geochronological and geochemical constraints[J]. Lithos, 2010, 120(3/4):529-546.
DOI URL |
| [32] | 杨明桂, 梅勇文. 钦-杭古板块结合带与成矿带的主要特征[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 1997, 13(3):52-59. |
| [33] | 广西壮族自治区地质矿产局. 广西壮族自治区区域地质志 [M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1985:1-853. |
| [34] | 杨丽贞, 陈兆福, 白艳萍. 广西南部中生代火山岩[J]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1997:1-47. |
| [35] |
LIU Y, GAO S, HU Z, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the trans-north China Orogen:U-Pb dating,Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2):537-571.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
ANDERSEN T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1/2):59-79.
DOI URL |
| [37] | LUDWIG K R. User’s Manual for Isoplot 3.00:A Geochronolo-gical Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley :Berkeley Geo chronology Center, 2003: 20-35. |
| [38] |
YUAN H L, GAO S, LIU X M, et al. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2004, 28(3):353-370.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
WANG X L, ZHOU J C, QIU J S, et al. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Neoproterozoic igneous rocks from Northern Guangxi,South China:Implications for tectonic evolution[J]. Precambrian Research, 2006, 145(1/2) : 111-130.
DOI URL |
| [40] | 刘颖, 刘海臣, 李献华. 用ICP-MS准确测定岩石样品中的40余种微量元素[J]. 地球化学, 1996, 25(6):552-558. |
| [41] | 梁细荣, 韦刚健, 李献华, 等. 利用MC-ICPMS精确测定143Nd/144Nd和Sm/Nd比值[J]. 地球化学, 2003, 32(1):91-96. |
| [42] |
SYLVESTER P J. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45(1/2/3/4):29-44.
DOI URL |
| [43] | 凌洪飞, 沈渭洲, 邓平, 等. 粤北帽峰花岗岩体地球化学特征及成因研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(3):677-687. |
| [44] |
BAS M J L, MAITRE R W L, STRECKEISEN A, et al. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali-silica diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1986, 27(3):745-750.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
MIYASHIRO A. Volcanic rock series in island arcs and active continental margins[J]. American Journal of Science, 1974, 274(4):321-355.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of grani-toids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101:635-643.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
WHITE A J R, CHAPPELL B W. Ultrametamorphism and granitoid genesis[J]. Tectonophysics, 1977, 43(1/2):7-22.
DOI URL |
| [48] | 曹延, 康志强, 许继峰, 等. 拉萨地块西部狮泉河地区典中组火山岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(5):1573-1592. |
| [49] | ROLLISON H R. 岩石地球化学 [M].杨学明,杨晓勇,译. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2000:179-205. |
| [50] | 于小亮, 蔡成龙, 张世龙, 等. 南祁连野牛脊山地区早志留世侵入岩的岩石成因:岩石地球化学和锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年代学制约[J]. 西北地质, 2018, 51(4):133-146. |
| [51] | 杜云, 罗小亚, 黄革非, 等. 湖南塔山岩体岩石学、地球化学、U-Pb年代学特征及其形成构造背景[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(6):50-61. |
| [52] | 刘一鸣, 李才, 王明, 等. 藏北羌塘盆地望湖岭组流纹岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2014, 33(11):1759-1767. |
| [53] | 穆可斌, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 南秦岭白龙江群中花岗岩脉群年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(3):111-135. |
| [54] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalt:implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345.
DOI URL |
| [55] | TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evolution,An Examination of the Geochemical Record Preserved in Sedimentary Rocks[M]. Oxford:Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1985: 1-312. |
| [56] | 陈强. 福建顺昌三连甫地区早泥盆世花岗岩的发现及形成构造环境[J]. 福建地质, 2019, 38(3):155-168. |
| [57] | 吴锁平, 吴才来, 陈其龙, 等. Sr-Nd同位素初始比值和Nd模式年龄的误差估算[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(7):1030-1038. |
| [58] | 孙涛, 周新民, 陈培荣, 等. 南岭东段中生代强过铝花岗岩成因及其大地构造意义[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2003, 33(12):1209-1218. |
| [59] |
ZINDLER A, HART S. Chemical geodynamics[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1986, 14(1):493-571.
DOI URL |
| [60] | 李宁波, 单强, 张永平, 等. 西天山阿吾拉勒地区A型流纹斑岩的初步研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2012, 36(4):624-633. |
| [61] | 魏永峰, 肖倩茹, 李有波, 等. 西藏纳木错早白垩世流纹岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(3):487-500. |
| [62] | 迟清华, 鄢明才. 应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册 [M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 103-104. |
| [63] | 张永明, 裴先治, 李佐臣, 等. 青海南山地区加里东期强过铝质花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(5):742-756. |
| [64] | 程银行, 李影, 刘永顺, 等. 松辽盆地西缘早白垩世伸展事件:流纹岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学研究[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(12):3492-3507. |
| [65] | 王中刚, 于学元, 赵振华. 稀土元素地球化学 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989:1-515. |
| [66] | 康志强, 许继峰, 王保弟, 等. 拉萨地块北部去申拉组火山岩:班公湖-怒江特提斯洋南向俯冲的产物?[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(10):3106-3116. |
| [67] | 赵宏刚, 梁积伟, 王驹, 等. 甘肃北山南带沙枣园复式岩体年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(2):396-425. |
| [68] | 陈泽超, 林伟, MICHEL Faure, 等. 越南东北部早中生代构造事件的年代学约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(5):1825-1840. |
| [69] |
ZHAO L, GUO F, FAN W M, et al. Origin of the granulite enclaves in Indo-Sinian peraluminous granites, South China and its implication for crustal anataxis[J]. Lithos, 2012, 150:209-226.
DOI URL |
| [70] | 汪绍年. 广西大容山-十万大山岩带中花岗岩类特征及成因[J]. 岩石学报, 1991, 7(2):73-80. |
| [71] |
LIANG X Q, LI X H. Late Permian to Middle Triassic sedimentary records in Shiwandashan Basin: Implication for the Indosinian Yunkai Orogenic Belt,South China[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2005, 177(3/4):297-320.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
HU L S, CAWOOD P A, DU Y S, et al. Detrital records for Upper Permian-Lower Triassic succession in the Shiwandashan Basin, South China and implication for Permo-Triassic (Indosinian) orogeny[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 98:152-166.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
DE LEPVRIER C, MALUSKI H, VAN VUONG N, et al. Indosinian NW trending shear zones within the Truong Son belt (Vietnam):40Ar-39Ar Triassic ages and Cretaceous to Cenozoic overprints[J]. Tectonophysics, 1997, 283(1/2/3/4):105-128.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
NGOCNAM T. Thermotectonic events from Early Proterozoic to Miocene in the Indochina craton: Implication of K-Ar ages in Vietnam[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 1998, 16:475-484.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
CARTER A, ROQUES D, BRISTOW C. Understanding Mesozoic accretion in Southeast Asia:Significance of Triassic thermotectonism (Indosinian orogeny) in Vietnam[J]. Geology, 2001, 29(3):211-214.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
MALUSKI H, LEPVRIER C, JOLIVET L, et al. Ar-Ar and fission-track ages in the Song Chay Massif: Early Triassic and Cenozoic tectonics in northern Vietnam[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2001, 19(1/2):233-248.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
LAN C Y, CHUNG S L, SHEN J S, et al. Geochemical and Sr-Nd isotopic characteristics of granitic rocks from northern Vietnam[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2000, 18:267-280.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
LAN C Y, CHUNG S L, VAN LONG T, et al. Geochemical and Sr-Nd isotopic constraints from the Kontum massif,central Vietnam on the crustal evolution of the Indochina block[J]. Precambrian Research, 2003, 122(1/2/3/4):7-27.
DOI URL |
| [79] | 王岳军, ZHANG H Y, 范蔚茗, 等. 湖南印支期过铝质花岗岩的形成:岩浆底侵与地壳加厚热效应的数值模拟[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2002, 32(6):491-499. |
| [80] |
PATINO DOUCE A E, HUMPHREYS E D, DANA JOHNSTON A D. Anatexis and metamorphism in tectonically thickened continental crust exemplified by the Sevier hinterland,western North America[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1990, 97(3/4):290-315.
DOI URL |
| [81] | 谢才富, 朱金初, 丁式江, 等. 琼中海西期钾玄质侵入岩的厘定及其构造意义[J]. 科学通报, 2006, 51(16):1944-1954. |
| [82] | 王强, 赵振华, 简平, 等. 武夷山洋坊霓辉石正长岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其构造意义[J]. 科学通报, 2003, 48(14):1582-1588. |
| [83] |
LIEGEOIS J P, NAVEZ J, HERTOGEN J, et al. Contrasting origin of post-collisional high-K calc-alkaline and shoshonitic versus alkaline and peralkaline granitoids: The use of sliding norma-lization[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45(1/2/3/4):1-28.
DOI URL |
| [84] | 郭春丽, 陈毓川, 蔺志永, 等. 赣南印支期柯树岭花岗岩体SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学、锆石Hf同位素特征及成因探讨[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2011, 30(4):567-580. |
| [85] | 袁永盛, 刘胜, 南争路, 等. 桂东南永安岩体锆石U-Pb测年、Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2018, 37(6):869-883. |
| [86] | 倪战旭, 潘罗忠, 李翠萍, 等. 桂东南六陈中酸性侵入岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年、岩石学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 矿产与地质, 2019, 33(1):96-105. |
| [87] |
BATCHELOR R A, BOWDEN P. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters[J]. Chemical Geology, 1985, 48(1/2/3/4):43-55.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4):956-983.
DOI URL |
| [89] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of grani-toids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5) : 635-643.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 朱拓, 何登洋, 黄雅琪, 邱昆峰. 华北克拉通胶莱盆地马山地区粗面英安岩磷灰石U-Pb年代学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 117-127. |
| [2] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [3] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [4] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [5] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [6] | 张靓, 陈奇, 高添, 李雯, 钱金龙, 刘俐君, 王长明. 三江特提斯马厂箐斑岩铜钼矿床成矿时间尺度探讨:来自石英中Ti-Al扩散年代学的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1509-1523. |
| [7] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [8] | 梁鸣, 高文, 罗先熔, 王晓东, 刘秀娟, 陈皓, 刘攀峰, 竹峰, 李伟. 冀北高尖子地区土壤地球化学特征及其找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1567-1579. |
| [9] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [10] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [11] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [12] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [13] | 可行, 赵青芳, 吴飘, 杨传胜, 廖晶, 龚建明. 胶莱盆地东北部白垩系烃源岩特征与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1358-1368. |
| [14] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [15] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||