



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (06): 1458-1472.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.061
杨少航1,2( ), 罗良1,2(
), 罗良1,2( ), 马诗杰1,2, 薛萌1,2, 曾联波1,2, 聂舟3, 犹钰玲1,2, 周杨帆1,2
), 马诗杰1,2, 薛萌1,2, 曾联波1,2, 聂舟3, 犹钰玲1,2, 周杨帆1,2
出版日期:2024-12-10
发布日期:2024-12-09
通信作者:
罗良,男,副教授,1982年出生,主要从事含油气盆地构造分析的研究工作。Email:luoliang1225@163.com。作者简介:杨少航,男,硕士研究生,1998年出生,主要从事含油气盆地构造分析的研究工作。Email:shyangsgsg@163.com。
YANG Shaohang1,2( ), LUO Liang1,2(
), LUO Liang1,2( ), MA Shijie1,2, XUE Meng1,2, ZENG Lianbo1,2, NIE Zhou3, YOU Yuling1,2, ZHOU Yangfan1,2
), MA Shijie1,2, XUE Meng1,2, ZENG Lianbo1,2, NIE Zhou3, YOU Yuling1,2, ZHOU Yangfan1,2
Published:2024-12-10
Online:2024-12-09
摘要:
长宁地区位于四川盆地南部,区内上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统龙马溪组页岩品质较高,具有良好的生储盖条件。显生宙经历了多期伸展、挤压与走滑变形及强烈抬升剥蚀作用,致使页岩气保存条件十分复杂。本文从该区构造特征、构造演化出发,明确各项构造因素对页岩气保存条件的影响机制,并提出构造因素影响页岩气保存条件的综合定量评价方法,预测有利勘探区域。研究结果表明:长宁地区主要发育NE向和NW向两组构造,均为基底卷入断层上盘发育的相关褶皱,对应的主要形成期分别为燕山早期和燕山晚期,且部分NE向构造于喜山期受到走滑改造。构造改造时间、抬升剥蚀、地层倾角、多尺度断层-裂缝和现今地应力方向是影响长宁地区五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气保存条件的主要构造因素。基于各项构造要素对页岩气保存的影响,提出适用于长宁地区的页岩保存条件定量评价方法。评价结果显示,建武向斜页岩气保存条件最好,天宫堂背斜次之,双龙向斜与罗场向斜较差。
中图分类号:
杨少航, 罗良, 马诗杰, 薛萌, 曾联波, 聂舟, 犹钰玲, 周杨帆. 川南长宁地区构造变形特征及对页岩气保存条件的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(06): 1458-1472.
YANG Shaohang, LUO Liang, MA Shijie, XUE Meng, ZENG Lianbo, NIE Zhou, YOU Yuling, ZHOU Yangfan. Structural Deformation and Shale Gas Preservation Conditions in the Changning Area of the Southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(06): 1458-1472.

图2 长宁地区过NW向构造典型地震剖面解释图(剖面位置见图1) (a) 过天宫堂背斜NE向剖面;(b) 过长宁背斜-建武向斜NE向剖面
Fig.2 Interpretation of typical seismic sections across the NW-direction structures in Changning (seeing Fig.1 for the location of sections)

图3 长宁地区过NE向构造典型地震剖面解释图(剖面位置见图1)
Fig.3 Interpretation of typical seismic sections across the NE-direction structures in Changning (seeing Fig.1 for the location of section)

图7 长宁地区野外与岩心裂缝照片 (a) 顺层剪切裂缝野外照片;(b) 穿层剪切裂缝野外照片;(c) 层内张裂缝野外照片;(d) 顺层剪切裂缝岩心照片;(e) 穿层剪切裂缝岩心照片;(f) 层内张裂缝岩心照片
Fig.7 Photos of field and core fractures in Changning

图8 长宁地区不同级次断层与测试产量的关系图 (a) 一级断层与测试产量的关系;(b) 二级断层与测试产量的关系;(c) 三级断层与测试产量的关系;(d) 四级断层与测试产量的关系
Fig.8 Relationships between different fault scales and production testing in Changning
| 井位 | 测试产量 (m3/t) | 距一级断 层(km) | 距二级断 层(km) | 距三级断 层(km) | 距四级断 层(km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 宁208 | 0.1 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 2.1 | 7.0 |
| 宁217 | 11.1 | 0.5 | 2.9 | 0.3 | 4.4 |
| 宁216 | 20.3 | 1.3 | 0.8 | 2.8 | 0.5 |
| 宁225 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.5 |
| 宁215 | 6.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 0.6 |
| 宁224 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 4.3 | 5.8 | 2.9 |
| 宁203 | 1.3 | 7.0 | 6.3 | 2.3 | 3.0 |
| 宁209 | 1.3 | 6.0 | 5.3 | 1.3 | 0.2 |
| 宜202 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 20.3 | 6.4 | 2.2 |
| 宁201 | 1.7 | 6.0 | 3.8 | 2.2 | 1.9 |
| 宁228 | 1.9 | 10.4 | 3.3 | 4.1 | 2.7 |
| 宁214 | 24.7 | 4.3 | 4.3 | 4.2 | 5.6 |
| 宁213 | 21.9 | 2.9 | 6.5 | 0.7 | 9.1 |
| 宁222 | 10.1 | 6.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 5.6 |
| 宁211 | 10.2 | 9.3 | 9.6 | 2.8 | 1.3 |
表1 长宁地区部分井测试产量及其距各级断层的距离统计
Table 1 Statistics of production testing from selected wells in Changning and their distances from faults at various levels
| 井位 | 测试产量 (m3/t) | 距一级断 层(km) | 距二级断 层(km) | 距三级断 层(km) | 距四级断 层(km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 宁208 | 0.1 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 2.1 | 7.0 |
| 宁217 | 11.1 | 0.5 | 2.9 | 0.3 | 4.4 |
| 宁216 | 20.3 | 1.3 | 0.8 | 2.8 | 0.5 |
| 宁225 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.5 |
| 宁215 | 6.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 0.6 |
| 宁224 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 4.3 | 5.8 | 2.9 |
| 宁203 | 1.3 | 7.0 | 6.3 | 2.3 | 3.0 |
| 宁209 | 1.3 | 6.0 | 5.3 | 1.3 | 0.2 |
| 宜202 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 20.3 | 6.4 | 2.2 |
| 宁201 | 1.7 | 6.0 | 3.8 | 2.2 | 1.9 |
| 宁228 | 1.9 | 10.4 | 3.3 | 4.1 | 2.7 |
| 宁214 | 24.7 | 4.3 | 4.3 | 4.2 | 5.6 |
| 宁213 | 21.9 | 2.9 | 6.5 | 0.7 | 9.1 |
| 宁222 | 10.1 | 6.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 5.6 |
| 宁211 | 10.2 | 9.3 | 9.6 | 2.8 | 1.3 |
| 构造 单元 | 钻井 | 裂缝密度(条/m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穿层剪 切裂缝 | 顺层剪 切裂缝 | 层内张 开裂缝 | 总密度 | ||
| 天宫堂 背斜 | 宜202 | 0.19 | 0.59 | 2.28 | 3.05 |
| 宁西202 | 7.00 | 2.00 | 1.69 | 10.69 | |
| 双龙向斜 | 宁219 | 1.58 | 0.24 | 1.26 | 3.08 |
| 罗场向斜 | 宁218 | 1.05 | 0.53 | 0.81 | 2.39 |
| 宁228 | 0.36 | 0.21 | 0.53 | 1.10 | |
| 建武向斜 | 宁213 | 0.50 | / | 4.03 | 4.54 |
| 宁216 | 0.92 | 0.04 | 0.63 | 1.60 | |
| 宁227 | 0.47 | 0.16 | / | 0.63 | |
表2 长宁地区典型井裂缝密度统计
Table 2 Statistics of fracture density from typical wells in the Changning
| 构造 单元 | 钻井 | 裂缝密度(条/m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穿层剪 切裂缝 | 顺层剪 切裂缝 | 层内张 开裂缝 | 总密度 | ||
| 天宫堂 背斜 | 宜202 | 0.19 | 0.59 | 2.28 | 3.05 |
| 宁西202 | 7.00 | 2.00 | 1.69 | 10.69 | |
| 双龙向斜 | 宁219 | 1.58 | 0.24 | 1.26 | 3.08 |
| 罗场向斜 | 宁218 | 1.05 | 0.53 | 0.81 | 2.39 |
| 宁228 | 0.36 | 0.21 | 0.53 | 1.10 | |
| 建武向斜 | 宁213 | 0.50 | / | 4.03 | 4.54 |
| 宁216 | 0.92 | 0.04 | 0.63 | 1.60 | |
| 宁227 | 0.47 | 0.16 | / | 0.63 | |

图9 长宁地区龙马溪组多尺度断层-裂缝、地层倾角与现今最大主应力方向分布
Fig.9 Distribution map of multi-scale fault and fracture systems in the Longmaxi Formation, including stratigraphic inclination and the current maximum principal stress direction in Changning
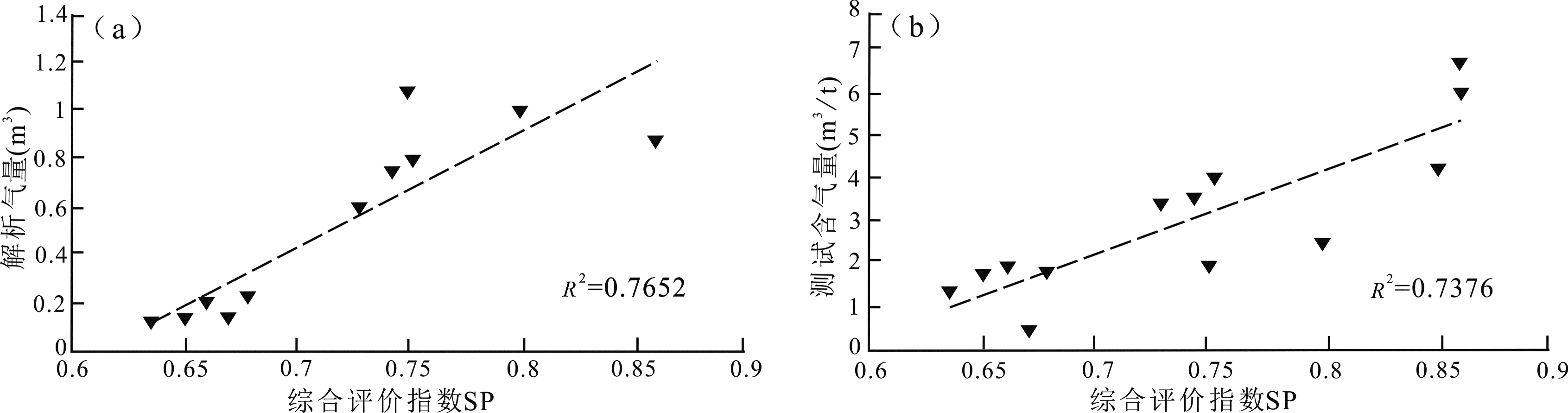
图10 长宁地区部分井解析气及测试含气量与综合评价指数SP关系 (a) 解析气与综合评价指数SP关系;(b) 测试含气量与综合评价指数SP关系
Fig.10 Analytical gas and test gas content for some wells in Changning, and the SP relationship between these values and the comprehensive evaluation index
| 评价参 数指标 | 构造改 造时间 | 剥蚀量 | 构造 样式 | 地层 倾角 | Ⅰ、Ⅱ 级断层 密度 | 目的层 底界 埋深 | 距剥蚀 线距离 | 距Ⅰ、Ⅱ 级断层 的距离 | 裂缝密度 | 现金地应 力与断层 夹角 | 综合评 价指数 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 层内张裂 缝密度 | 穿层剪切 裂缝密度 | |||||||||||
| 建武向斜 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.75 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.75 | 0.9 |
| 天宫堂背斜 | 0.75 | 0.50 | 1 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.75 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.85 |
| 罗场向斜 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.65 |
| 双龙向斜 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.6875 |
表4 长宁地区不同构造单元龙马溪组页岩气保存条件评价指数
Table 4 Evaluation index for shale gas preservation conditions across different structural units in the Longmaxi Formation, Changning
| 评价参 数指标 | 构造改 造时间 | 剥蚀量 | 构造 样式 | 地层 倾角 | Ⅰ、Ⅱ 级断层 密度 | 目的层 底界 埋深 | 距剥蚀 线距离 | 距Ⅰ、Ⅱ 级断层 的距离 | 裂缝密度 | 现金地应 力与断层 夹角 | 综合评 价指数 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 层内张裂 缝密度 | 穿层剪切 裂缝密度 | |||||||||||
| 建武向斜 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.75 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.75 | 0.9 |
| 天宫堂背斜 | 0.75 | 0.50 | 1 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.75 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.85 |
| 罗场向斜 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.65 |
| 双龙向斜 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.6875 |
| [1] |
邹才能, 赵群, 董大忠, 等. 页岩气基本特征、主要挑战与未来前景[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(12): 1781-1796.
DOI |
| [2] | 董大忠, 王玉满, 李新景, 等. 中国页岩气勘探开发新突破及发展前景思考[J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(1): 19-32. |
| [3] |
马新华, 谢军. 川南地区页岩气勘探开发进展及发展前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(1): 161-169.
DOI |
| [4] |
王玉满, 董大忠, 李建忠, 等. 川南下志留统龙马溪组页岩气储层特征[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(4): 551-561.
DOI |
| [5] | 李东升, 高平, 盖海峰, 等. 川东南地区龙马溪组页岩有机质纳米孔隙结构表征[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(5): 1293-1305. |
| [6] | 张国伟, 郭安林, 王岳军, 等. 中国华南大陆构造与问题[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2013, 43(10): 1553-1582. |
| [7] | 徐政语, 姚根顺, 梁兴, 等. 扬子陆块下古生界页岩气保存条件分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2015, 37(4): 407-417. |
| [8] | 刘树根, 王一刚, 孙玮, 等. 拉张槽对四川盆地海相油气分布的控制作用[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 43(1): 1-23. |
| [9] | DAI J X, ZOU C N, LIAO S M, et al. Geochemistry of the extremely high thermal maturity Longmaxi shale gas, southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2014, 74: 3-12. |
| [10] | HOU Y G, ZHANG K P, WANG F R, et al. Structural evolution of organic matter and implications for graphitization in over-mature marine shales, South China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 109: 304-316. |
| [11] | 邹才能, 董大忠, 王玉满, 等. 中国页岩气特征、挑战及前景(一)[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(6): 689-701. |
| [12] | 楼章华, 张欣柯, 吴宇辰, 等. 四川盆地南川地区及邻区页岩气保存差异的流体响应特征[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2023, 13(4):451-458. |
| [13] |
马永生, 蔡勋育, 赵培荣. 中国页岩气勘探开发理论认识与实践[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(4): 561-574.
DOI |
| [14] |
何登发, 鲁人齐, 黄涵宇, 等. 长宁页岩气开发区地震的构造地质背景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(5): 993-1006.
DOI |
| [15] | 韩倩. 川南长宁背斜构造几何学特征及形成演化[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2020. |
| [16] | 姚金鹏, 陈伟. 川南长宁背斜形成的几何运动学分析[J]. 化工设计通讯, 2021, 47(3): 191-192. |
| [17] | 张岳桥, 董树文, 李建华, 等. 中生代多向挤压构造作用与四川盆地的形成和改造[J]. 中国地质, 2011, 38(2): 233-250. |
| [18] | 邓宾, 刘树根, 刘顺, 等. 四川盆地地表剥蚀量恢复及其意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 36(6): 675-686. |
| [19] | RICHARDSON N J, DENSMORE A L, SEWARD D, et al. Extraordinary denudation in the Sichuan Basin: Insights from low-temperature thermochronology adjacent to the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth), 2008, 113(4): B04409. |
| [20] | TIAN Y T, KOHN B, QIU N, et al. Eocene to Miocene out-of-sequence deformation in the eastern Tibetan Plateau: Insights from shortening structures in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth), 2018, 123: 1840-1855. |
| [21] | 罗志立, 龙学明. 龙门山造山带崛起和川西陆前盆地沉降[J]. 四川地质学报, 1992, 12(1): 1-17. |
| [22] |
陈尚斌, 朱炎铭, 王红岩, 等. 四川盆地南缘下志留统龙马溪组页岩气储层矿物成分特征及意义[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(5): 775-782.
DOI |
| [23] | 邓宾. 四川盆地中—新生代盆-山结构与油气分布[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2013. |
| [24] | 胡召齐, 朱光, 刘国生, 等. 川东“侏罗山式” 褶皱带形成时代: 不整合面的证据[J]. 地质论评, 2009, 55(1): 32-42. |
| [25] | SHEN C B, MEI L F, XU S H. Fission track dating of Mesozoic sandstones and its tectonic significance in the Eastern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2009, 44(9/10): 945-949. |
| [26] | 梅廉夫, 刘昭茜, 汤济广, 等. 湘鄂西—川东中生代陆内递进扩展变形: 来自裂变径迹和平衡剖面的证据[J]. 地球科学, 2010, 35(2): 161-174. |
| [27] | SHI H C, SHI X B, GLASMACHER U A, et al. The evolution of eastern Sichuan Basin, Yangtze Block since Cretaceous: Constraints from low temperature thermochronology[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 116: 208-221. |
| [28] | 张岳桥, 赵越, 董树文, 等. 中国东部及邻区早白垩世裂陷盆地构造演化阶段[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(3): 123-133. |
| [29] | 唐永, 周立夫, 陈孔全, 等. 川东南构造应力场地质分析及构造变形成因机制讨论[J]. 地质论评, 2018, 64(1): 15-28. |
| [30] | 张经国, 陈伟, 孟立丰. 长宁页岩气田建武向斜构造解析及成因机制[J]. 化工设计通讯, 2021, 47(3): 193-194. |
| [31] | 王二七, 尹纪云. 川西南新生代构造作用以及四川原型盆地的破坏[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 39(3): 359-367. |
| [32] | WILSON C J L, FOWLER A P. Denudational response to surface uplift in East Tibet: Evidence from apatite fission-track thermochronology[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2011, 123(9/10): 1966-1987. |
| [33] | WANG E, MENG K, SU Z, et al. Block rotation: Tectonic response of the Sichuan Basin to the southeastward growth of the Tibetan Plateau along the Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang fault[J]. Tecto-nics, 2014, 33(5): 686-718. |
| [34] | 张梦琳, 李郭琴, 何嘉, 等. 川西南缘天宫堂构造奥陶系五峰组—志留系龙马溪组页岩气富集主控因素[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(2): 141-151. |
| [35] | 刘树根, 孙玮, 钟勇, 等. 四川海相克拉通盆地显生宙演化阶段及其特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(4): 1058-1072. |
| [36] | 汤济广, 汪凯明, 秦德超, 等. 川东南南川地区构造变形与页岩气富集[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 11-21. |
| [37] | 覃作鹏, 刘树根, 邓宾, 等. 川东南构造带中新生代多期构造特征及演化[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 40(6): 703-711. |
| [38] |
王学军, 杨志如, 韩冰. 四川盆地叠合演化与油气聚集[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(3): 161-173.
DOI |
| [39] | 聂海宽, 包书景, 高波, 等. 四川盆地及其周缘下古生界页岩气保存条件研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(3): 280-294. |
| [40] | 胡东风, 张汉荣, 倪楷, 等. 四川盆地东南缘海相页岩气保存条件及其主控因素[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(6): 17-23. |
| [41] | 汤济广, 李豫, 汪凯明, 等. 四川盆地东南地区龙马溪组页岩气有效保存区综合评价[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(5): 15-23. |
| [42] | 王濡岳, 丁文龙, 龚大建, 等. 黔北地区海相页岩气保存条件: 以贵州岑巩区块下寒武统牛蹄塘组为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(1): 45-55. |
| [43] | 谌志远. 南方海相页岩气散失控制因素研究: 以四川盆地南缘为例[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2019. |
| [44] | 何顺, 秦启荣, 范存辉, 等. 川东南丁山地区五峰—龙马溪组页岩储层特征及影响因素[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2019, 9(4): 61-67, 78. |
| [45] | 李轲, 陈杨, 牟必鑫, 等. 西昌盆地南部地区志留系龙马溪组页岩气保存条件的评价[J]. 非常规油气, 2021, 8(1): 34-42. |
| [46] |
张海涛, 张颖, 何希鹏, 等. 渝东南武隆地区构造作用对页岩气形成与保存的影响[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2018, 23(5): 47-56.
DOI |
| [47] | 龙小军. 焦石坝地区构造变形差异及保存条件解析[J]. 非常规油气, 2018, 5(5): 28-34. |
| [48] | 曾联波, 肖淑蓉. 低渗透储集层中的泥岩裂缝储集体[J]. 石油实验地质, 1999, 21(3): 266-269. |
| [49] | 姜磊. 强改造作用下川南下古生界页岩气保存条件研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2019. |
| [50] | 周政. 长宁地区五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气富集特征研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2020. |
| [51] | LIU S G, YANG Y, DENG B, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Sichuan Basin, Southwest China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2021, 213: 103470. |
| [52] | 于俊友, 雍自权, 程凌云, 等. 强改造区龙马溪组页岩气保存条件指数评价[J]. 长江大学学报(自科版), 2015, 12(35): 1-7, 9. |
| [53] | ZENG L B, LYU W Y, LI J, et al. Natural fractures and their influence on shale gas enrichment in Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2016, 30: 1-9. |
| [54] | 梁兴, 王高成, 徐政语, 等. 中国南方海相复杂山地页岩气储层甜点综合评价技术: 以昭通国家级页岩气示范区为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(1): 33-42. |
| [55] | 唐相路, 姜振学, 张莺莺, 等. 渝东南地区页岩气富集区差异性分布成因[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 30(3): 24-30, 35, 7. |
| [56] | 张昆. 复杂构造背景海相页岩气保存机理与评价方法[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2019. |
| [57] | 黄瑞广, 罗超, 公子龙, 等. 断裂系统与页岩气保存条件之间的关系: 以泸州地区为例[J]. 山东化工, 2022, 51(5): 148-153, 158. |
| [58] | 蒋代琴, 李平平, 邹华耀. 川东北元坝地区侏罗系陆相页岩天然裂缝发育特征及其对页岩油气富集和保存的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(2):362-372. |
| [59] | 向杰, 陈尚斌, 王阳, 等. 断裂体系对页岩气保存的影响: 以滇东北地区五峰—龙马溪组为例[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(11): 3599-3612. |
| [60] | 田鹤, 曾联波, 徐翔, 等. 四川盆地涪陵地区海相页岩天然裂缝特征及对页岩气的影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(3): 474-483. |
| [61] | 俞雨溪, 王宗秀, 冯兴强, 等. 剪切作用对页岩有机质孔发育特征和吸附能力的影响[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(6): 830-839. |
| [62] | 陈永峤, 周新桂, 于兴河, 等. 断层封闭性要素与封闭效应[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(6): 38-40. |
| [63] | 陆应新, 胡望水, 汤济广, 等. 川东南丁山构造龙马溪组页岩裂缝发育与分布[J]. 长江大学学报(自科版), 2016, 13(8): 6-10, 2. |
| [1] | 史原鹏, 淡伟宁, 于福生, 王少春, 王旭峰, 田野, 冯广业, 王浩宇, 王标. 阿拉善地块雅布赖盆地“跷跷板式”负反转构造特征及成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(05): 1221-1234. |
| [2] | 焦建刚, 谭福, 李林娜, 刘健, 杨兴科, 高栋. 甘肃金川铜镍硫化物矿床成岩成矿构造观测及解析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 1026-1042. |
| [3] | 陈志友, 曾广乾, 柏道远, 姚泽钰, 王灵珏, 文春华, 陈旭, 王勇, 李彬, 黄乐清, 陈剑锋, 梁恩云, 许若潮, 马慧英, 向轲. 湘南大义山地区中—新生代变形序列及其动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 1092-1108. |
| [4] | 张宝林, 吕古贤, 沈晓丽, 张壮, 曹明坚, 黄新硕, 苏艳平, 贾文臣. 基于构造变形岩相带的覆盖区化探资料解释与找矿应用:以广西金秀镍钴多金属矿田为例[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 934-946. |
| [5] | 谢昭涵, 冯昌, 仇永峰, 李鹤永, 张建波, 唐海氢. 苏北盆地盐城凹陷盐③断裂带构造演化及其控圈作用[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(02): 300-311. |
| [6] | 汪锴, 王根厚, 贾庆军, 张笑. 琼东南盆地深水区松南—宝岛凹陷的构造演化及其与油气成藏关系[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 245-258. |
| [7] | 李波, 金胜, 叶高峰, 魏文博. 中亚造山带东段岩石圈电性结构特征及其构造涵义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(01): 15-30. |
| [8] | 吕古贤, 张宝林, 吕承训, 胡宝群, 曾勇, 郭涛, 申玉科, 王红才, 马立成, 焦建刚, 毕珉烽. 长江中下游地区新华夏构造体系的“米字型”结构特征[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1240-1250. |
| [9] | 吕承训, 霍庆龙, 唐占信, 范潇, 汤磊, 许亚青, 袁月蕾. 胶西北断裂构造蚀变分带及其铲式分布特征[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1274-1281. |
| [10] | 刘爱荣, 徐永婧, 刘成林, 庞尔成. 大同盆地地质特征及构造演化研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1296-1310. |
| [11] | 孙自明, 张荣强, 孙炜, 郝运轻, 卞昌蓉. 四川盆地东部海相下组合油气勘探领域与有利勘探方向[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 798-806. |
| [12] | 余海波, 程秀申, 徐田武, 谈玉明, 漆家福. 东濮凹陷古近纪盆地结构控烃控藏特征[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1119-1131. |
| [13] | 余尚江, 李玮. 洛南、山阳盆地沉积充填特征及其对东秦岭中—新生代陆内演化的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 687-699. |
| [14] | 杨旺东, 高福磊, 王功文, 庞振山, 沈和明, 龚灵明, 申红涛, 张智强, 刘晓宁. 四川红泥坡铜矿床三维地质建模及控矿构造演化的新认识[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 598-608. |
| [15] | 罗晓华, 杨明慧, 贾春阳, 李占元, 雷志斌, 张少华. 晋北地区口泉断裂带晚中生代分段构造特征[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(03): 551-560. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||