



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (04): 1026-1042.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.087
焦建刚1,2,3( ), 谭福1, 李林娜1, 刘健1, 杨兴科1, 高栋4
), 谭福1, 李林娜1, 刘健1, 杨兴科1, 高栋4
出版日期:2024-08-10
发布日期:2024-10-16
作者简介:焦建刚,男,教授,1976年出生,主要从事矿床学研究与教学。Email: jiangang@chd.edu.cn。
基金资助:
JIAO Jiangang1,2,3( ), TAN Fu1, LI Linna1, LIU Jian1, YANG Xingke1, GAO Dong4
), TAN Fu1, LI Linna1, LIU Jian1, YANG Xingke1, GAO Dong4
Published:2024-08-10
Online:2024-10-16
摘要:
甘肃金川超大型铜镍硫化物矿床形成于新元古代,从其母岩浆侵位到后期构造叠加改造,该矿床经历了复杂的地质演化过程。尽管前人开展了相关研究,但是关于该矿床的矿区构造研究仍然存在较大争议。此外,厘清矿区控岩控矿构造对探讨岩浆侵入与就位过程、矿床深部找矿等具有重要意义。本次研究根据矿区构造分类、配套、交切关系与成岩成矿时序组合等,划分出成矿前、成矿期和成矿后构造系统,借助断裂、共轭节理产状统计分析了矿区构造应力场,确定主压应力方向分别为N-S向、NE-SW向和NNE-SSW向。最后将矿区构造与区域大地构造演化相结合,总结归纳出成矿前、成矿期与成矿后构造演化过程:成矿前经历吕梁运动阶段,该区发生强烈褶皱和变质作用。成矿期晋宁运动阶段,金川赋矿岩体的母岩浆沿着吕梁期形成的褶皱构造虚脱空间侵入就位。成矿后,加里东运动阶段,龙首山地区发生陆内造山,大量基性岩脉侵入;海西运动阶段,推覆造山运动强烈,形成泥盆纪地层,发育一系列同斜紧闭褶皱;燕山运动阶段,挤压-走滑作用占主导形成东西向展布的山前拉分盆地和北东向展布的断陷盆地;喜马拉雅运动阶段,急剧隆升和剥蚀,金川矿床从深部被抬升到了地表。研究成果为金川矿床深、边部找矿提供了新思路。
中图分类号:
焦建刚, 谭福, 李林娜, 刘健, 杨兴科, 高栋. 甘肃金川铜镍硫化物矿床成岩成矿构造观测及解析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 1026-1042.
JIAO Jiangang, TAN Fu, LI Linna, LIU Jian, YANG Xingke, GAO Dong. Observation and Analysis of Diagenesis and Mineralization Structures of the Jinchuan Cu-Ni Sulfide Deposit in Gansu[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(04): 1026-1042.

图2 金川铜镍硫化物矿床地质图(a)与矿区纵投影图(b)(据文献[29])
Fig.2 Maps of the geological plane (a) and vertical projection (b) of the Jinchuan Cu-Ni sulfide deposit (modified after ref.[29])
| 测点号、 剖面走向 及岩性 | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEE | NNE | NE | NNW | NE | NNW | NNE | NWW | ||||
| 白家嘴子组大理岩 | 塔马子沟组变质灰岩 | ||||||||||
| 产状 | 154°∠76° | 102°∠74°* | 150°∠68° | 76°∠52° | 150°∠58° | 72°∠60° | 108°∠74° | 12°∠55° | |||
| 164°∠89° | 108°∠73°* | 146°∠55° | 65°∠45° | 135°∠80° | 65°∠52° | 104°∠49° | 5°∠46° | ||||
| 153°∠85° | 125°∠62°* | 160°∠47° | 80°∠55° | 142°∠77° | 72°∠35° | 98°∠58° | 10°∠54° | ||||
| 153°∠77° | 120°∠37°* | 165°∠55° | 73°∠52° | 130°∠74° | 72°∠45° | 110°∠65° | 25°∠55° | ||||
| 168°∠88° | 106°∠69°* | 156°∠55° | 75°∠50° | 147°∠84° | 69°∠52° | 112°∠65° | 7°∠52° | ||||
| 172°∠74° | 110°∠62°* | 150°∠47° | 70°∠55° | 134°∠72° | 78°∠66° | 116°∠74° | 3°∠50° | ||||
| 170°∠85° | 102°∠60°* | 144°∠71° | 79°∠56° | 143°∠64° | 55°∠71° | 102°∠71° | 10°∠30° | ||||
| 160°∠70° | 122°∠68°* | 152°∠52° | 75°∠43° | 122°∠77° | 74°∠60°* | 125°∠50° | 15°∠45°* | ||||
| 169°∠45° | 98°∠83°* | 154°∠54° | 76°∠40° | 142°∠61° | 69°∠52°* | 100°∠67° | 8°∠46°* | ||||
| 160°∠78° | 100°∠58°* | 158°∠50° | 80°∠56° | 135°∠86° | 76°∠39°* | 112°∠55° | 11°∠56°* | ||||
| 155°∠59°* | 102°∠76°* | 155°∠57°* | 79°∠54°* | 147°∠84° | 79°∠45°* | 101°∠76° | 22°∠52°* | ||||
| 158°∠68°* | 115°∠75°* | 165°∠55°* | 65°∠48°* | 134°∠72° | 68°∠52°* | 115°∠80° | 17°∠48°* | ||||
| 162°∠62°* | 120°∠62°* | 156°∠56°* | 78°∠56°* | 141°∠83° | 59°∠61°* | 114°∠76° | 13°∠40°* | ||||
| 161°∠51°* | 118°∠50°* | 160°∠52°* | 66°∠48°* | 125°∠62°* | 55°∠69°* | 112°∠68°* | 10°∠32°* | ||||
| 154°∠69°* | 106°∠70°* | 157°∠45°* | 75°∠47°* | 165°∠72°* | 73°∠46°* | 105°∠56°* | 12°∠56°* | ||||
| 155°∠62°* | 110°∠59°* | 161°∠59°* | 68°∠59°* | 132°∠75°* | 65°∠47°* | 100°∠58°* | 5°∠48°* | ||||
| 149°∠66°* | 102°∠71°* | 148°∠70°* | 63°∠49°* | 143°∠80°* | 72°∠43°* | 125°∠56°* | 10°∠50°* | ||||
| 152°∠67°* | 114°∠68°* | 155°∠58°* | 75°∠43°* | 139°∠75°* | 69°∠46°* | 107°∠72°* | 21°∠52°* | ||||
| 158°∠83°* | 102°∠81°* | 153°∠50°* | 72°∠41°* | 128°∠79°* | 68°∠52°* | 113°∠60°* | 7°∠42°* | ||||
| 160°∠59°* | 112°∠62°* | 159°∠56°* | 78°∠56°* | 138°∠81°* | 79°∠45°* | 101°∠70°* | 3°∠40°* | ||||
表1 地层中节理产状
Table 1 Record of joint occurrences in the strata
| 测点号、 剖面走向 及岩性 | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEE | NNE | NE | NNW | NE | NNW | NNE | NWW | ||||
| 白家嘴子组大理岩 | 塔马子沟组变质灰岩 | ||||||||||
| 产状 | 154°∠76° | 102°∠74°* | 150°∠68° | 76°∠52° | 150°∠58° | 72°∠60° | 108°∠74° | 12°∠55° | |||
| 164°∠89° | 108°∠73°* | 146°∠55° | 65°∠45° | 135°∠80° | 65°∠52° | 104°∠49° | 5°∠46° | ||||
| 153°∠85° | 125°∠62°* | 160°∠47° | 80°∠55° | 142°∠77° | 72°∠35° | 98°∠58° | 10°∠54° | ||||
| 153°∠77° | 120°∠37°* | 165°∠55° | 73°∠52° | 130°∠74° | 72°∠45° | 110°∠65° | 25°∠55° | ||||
| 168°∠88° | 106°∠69°* | 156°∠55° | 75°∠50° | 147°∠84° | 69°∠52° | 112°∠65° | 7°∠52° | ||||
| 172°∠74° | 110°∠62°* | 150°∠47° | 70°∠55° | 134°∠72° | 78°∠66° | 116°∠74° | 3°∠50° | ||||
| 170°∠85° | 102°∠60°* | 144°∠71° | 79°∠56° | 143°∠64° | 55°∠71° | 102°∠71° | 10°∠30° | ||||
| 160°∠70° | 122°∠68°* | 152°∠52° | 75°∠43° | 122°∠77° | 74°∠60°* | 125°∠50° | 15°∠45°* | ||||
| 169°∠45° | 98°∠83°* | 154°∠54° | 76°∠40° | 142°∠61° | 69°∠52°* | 100°∠67° | 8°∠46°* | ||||
| 160°∠78° | 100°∠58°* | 158°∠50° | 80°∠56° | 135°∠86° | 76°∠39°* | 112°∠55° | 11°∠56°* | ||||
| 155°∠59°* | 102°∠76°* | 155°∠57°* | 79°∠54°* | 147°∠84° | 79°∠45°* | 101°∠76° | 22°∠52°* | ||||
| 158°∠68°* | 115°∠75°* | 165°∠55°* | 65°∠48°* | 134°∠72° | 68°∠52°* | 115°∠80° | 17°∠48°* | ||||
| 162°∠62°* | 120°∠62°* | 156°∠56°* | 78°∠56°* | 141°∠83° | 59°∠61°* | 114°∠76° | 13°∠40°* | ||||
| 161°∠51°* | 118°∠50°* | 160°∠52°* | 66°∠48°* | 125°∠62°* | 55°∠69°* | 112°∠68°* | 10°∠32°* | ||||
| 154°∠69°* | 106°∠70°* | 157°∠45°* | 75°∠47°* | 165°∠72°* | 73°∠46°* | 105°∠56°* | 12°∠56°* | ||||
| 155°∠62°* | 110°∠59°* | 161°∠59°* | 68°∠59°* | 132°∠75°* | 65°∠47°* | 100°∠58°* | 5°∠48°* | ||||
| 149°∠66°* | 102°∠71°* | 148°∠70°* | 63°∠49°* | 143°∠80°* | 72°∠43°* | 125°∠56°* | 10°∠50°* | ||||
| 152°∠67°* | 114°∠68°* | 155°∠58°* | 75°∠43°* | 139°∠75°* | 69°∠46°* | 107°∠72°* | 21°∠52°* | ||||
| 158°∠83°* | 102°∠81°* | 153°∠50°* | 72°∠41°* | 128°∠79°* | 68°∠52°* | 113°∠60°* | 7°∠42°* | ||||
| 160°∠59°* | 112°∠62°* | 159°∠56°* | 78°∠56°* | 138°∠81°* | 79°∠45°* | 101°∠70°* | 3°∠40°* | ||||
| 测点号、 剖面走向 及岩性 | G5 | G6 | G7 | G8 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NWW | NNW | NW | NNE | NW | NNE | NEE | NNW | ||||
| 角闪岩 | 含矿超基性岩 | 石英正长岩 | |||||||||
| 产状 | 25°∠74° | 72°∠27° | 56°∠69° | 298°∠80° | 30°∠75° | 112°∠65° | 165°∠81° | 74°∠52°* | |||
| 25°∠77° | 77°∠42° | 55°∠73° | 296°∠86° | 40°∠89° | 110°∠70° | 163°∠66°* | 74°∠43°* | ||||
| 21°∠72° | 72°∠36° | 45°∠80° | 310°∠75° | 58°∠62° | 118°∠80° | 160°∠59°* | 75°∠45°* | ||||
| 36°∠59° | 84°∠39° | 64°∠84° | 274°∠89° | 35°∠88° | 110°∠70° | 153°∠79° | 73°∠34°* | ||||
| 30°∠52° | 70°∠37° | 53°∠75° | 309°∠80° | 30°∠73° | 114°∠62° | 163°∠71° | 70°∠48°* | ||||
| 22°∠79° | 85°∠43° | 53°∠80° | 312°∠78° | 35°∠62° | 130°∠70° | 163°∠72° | 67°∠46° | ||||
| 25°∠54° | 75°∠26° | 40°∠83° | 265°∠82° | 32°∠90° | 110°∠74° | 168°∠68° | 75°∠60° | ||||
| 28°∠56° | 68°∠43° | 44°∠81° | 296°∠80° | 64°∠80° | 125°∠75° | 162°∠69° | 67°∠54°* | ||||
| 30°∠52° | 76°∠25°* | 55°∠80° | 296°∠86° | 56°∠72° | 140°∠76° | 160°∠77° | 73°∠44°* | ||||
| 20°∠79° | 78°∠32°* | 56°∠77° | 310°∠80° | 33°∠64° | 112°∠68°* | 160°∠72° | 70°∠48°* | ||||
| 25°∠76° | 69°∠36°* | 48°∠79° | 284°∠89°* | 40°∠75° | 109°∠72°* | 158°∠73°* | 67°∠46°* | ||||
| 30°∠66°* | 82°∠40°* | 49°∠78° | 307°∠82°* | 44°∠84°* | 108°∠80°* | 158°∠70° | 74°∠43°* | ||||
| 22°∠60°* | 70°∠36°* | 56°∠72° | 310°∠76°* | 42°∠70°* | 112°∠70°* | 160°∠75° | 75°∠35°* | ||||
| 30°∠62°* | 83°∠43°* | 55°∠80°* | 265°∠81°* | 38°∠80°* | 114°∠72°* | 155°∠72°* | 73°∠54°* | ||||
| 22°∠56°* | 75°∠28°* | 56°∠86°* | 309°∠87°* | 43°∠78°* | 130°∠78°* | 154°∠73°* | 70°∠48°* | ||||
| 34°∠59°* | 69°∠33°* | 52°∠75°* | 297°∠80°* | 44°∠62°* | 115°∠74°* | 155°∠75°* | 67°∠46°* | ||||
| 20°∠67°* | 68°∠43°* | 54°∠89°* | 298°∠82°* | 48°∠76°* | 125°∠78°* | 153°∠64°* | 75°∠60°* | ||||
| 25°∠73°* | 70°∠36°* | 58°∠80°* | 296°∠79°* | 52°∠84°* | 130°∠76°* | 160°∠68°* | 73°∠34°* | ||||
| 28°∠76°* | 85°∠43°* | 60°∠78°* | 296°∠85°* | 46°∠75°* | 110°∠76°* | 157°∠76°* | 70°∠47°* | ||||
| 28°∠63°* | 70°∠37°* | 55°∠82°* | 298°∠80°* | 45°∠84°* | 114°∠75°* | 161°∠60°* | 67°∠46°* | ||||
表2 金川矿区岩浆岩中节理产状
Table 2 Record of joint occurrences in the magmatic rock
| 测点号、 剖面走向 及岩性 | G5 | G6 | G7 | G8 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NWW | NNW | NW | NNE | NW | NNE | NEE | NNW | ||||
| 角闪岩 | 含矿超基性岩 | 石英正长岩 | |||||||||
| 产状 | 25°∠74° | 72°∠27° | 56°∠69° | 298°∠80° | 30°∠75° | 112°∠65° | 165°∠81° | 74°∠52°* | |||
| 25°∠77° | 77°∠42° | 55°∠73° | 296°∠86° | 40°∠89° | 110°∠70° | 163°∠66°* | 74°∠43°* | ||||
| 21°∠72° | 72°∠36° | 45°∠80° | 310°∠75° | 58°∠62° | 118°∠80° | 160°∠59°* | 75°∠45°* | ||||
| 36°∠59° | 84°∠39° | 64°∠84° | 274°∠89° | 35°∠88° | 110°∠70° | 153°∠79° | 73°∠34°* | ||||
| 30°∠52° | 70°∠37° | 53°∠75° | 309°∠80° | 30°∠73° | 114°∠62° | 163°∠71° | 70°∠48°* | ||||
| 22°∠79° | 85°∠43° | 53°∠80° | 312°∠78° | 35°∠62° | 130°∠70° | 163°∠72° | 67°∠46° | ||||
| 25°∠54° | 75°∠26° | 40°∠83° | 265°∠82° | 32°∠90° | 110°∠74° | 168°∠68° | 75°∠60° | ||||
| 28°∠56° | 68°∠43° | 44°∠81° | 296°∠80° | 64°∠80° | 125°∠75° | 162°∠69° | 67°∠54°* | ||||
| 30°∠52° | 76°∠25°* | 55°∠80° | 296°∠86° | 56°∠72° | 140°∠76° | 160°∠77° | 73°∠44°* | ||||
| 20°∠79° | 78°∠32°* | 56°∠77° | 310°∠80° | 33°∠64° | 112°∠68°* | 160°∠72° | 70°∠48°* | ||||
| 25°∠76° | 69°∠36°* | 48°∠79° | 284°∠89°* | 40°∠75° | 109°∠72°* | 158°∠73°* | 67°∠46°* | ||||
| 30°∠66°* | 82°∠40°* | 49°∠78° | 307°∠82°* | 44°∠84°* | 108°∠80°* | 158°∠70° | 74°∠43°* | ||||
| 22°∠60°* | 70°∠36°* | 56°∠72° | 310°∠76°* | 42°∠70°* | 112°∠70°* | 160°∠75° | 75°∠35°* | ||||
| 30°∠62°* | 83°∠43°* | 55°∠80°* | 265°∠81°* | 38°∠80°* | 114°∠72°* | 155°∠72°* | 73°∠54°* | ||||
| 22°∠56°* | 75°∠28°* | 56°∠86°* | 309°∠87°* | 43°∠78°* | 130°∠78°* | 154°∠73°* | 70°∠48°* | ||||
| 34°∠59°* | 69°∠33°* | 52°∠75°* | 297°∠80°* | 44°∠62°* | 115°∠74°* | 155°∠75°* | 67°∠46°* | ||||
| 20°∠67°* | 68°∠43°* | 54°∠89°* | 298°∠82°* | 48°∠76°* | 125°∠78°* | 153°∠64°* | 75°∠60°* | ||||
| 25°∠73°* | 70°∠36°* | 58°∠80°* | 296°∠79°* | 52°∠84°* | 130°∠76°* | 160°∠68°* | 73°∠34°* | ||||
| 28°∠76°* | 85°∠43°* | 60°∠78°* | 296°∠85°* | 46°∠75°* | 110°∠76°* | 157°∠76°* | 70°∠47°* | ||||
| 28°∠63°* | 70°∠37°* | 55°∠82°* | 298°∠80°* | 45°∠84°* | 114°∠75°* | 161°∠60°* | 67°∠46°* | ||||

图3 早元古代白家嘴子组褶皱-岩体侵入示意图 (a)白家嘴子组大理岩受左行剪切作用;(b)白家嘴子组大理岩中揉皱变形;(c)白家嘴子组混合花岗岩中发生柔流褶皱作用;(d)白家嘴子组斜长片麻岩中发生剪切褶皱作用
Fig.3 Schematic diagrams showing the Early Proterozoic Baijiazuizi Formation folds and intrusions

图5 金川铜镍硫化物矿床剩余化极磁异常图(红色为高磁区,黄色为中磁区,蓝色为低磁区)(a)与断裂构造纲要图(b)(据文献[19]修改)
Fig.5 Map of the remaining chemical polar magnetic anomalies of the Jinchuan Cu-Ni-sulfide deposit (a), with an outline of the fracture tectonics (b) (modified after ref.[19])
| 断裂 组别 | 断裂 编号 | 位置 | 产状及规模 | 特征 | 影响 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一组: 北西— 南东向 断层 | F1 | 位于矿区北部山麓边缘 | 走向300°,倾向205°,倾角60°左右,延长数百千米 | 呈上陡下缓的产状构造向下延伸,前震旦系逆冲于第四系砾石层之上。地表见断层破碎带、断层泥等;断层带自下而上见透镜-碎粉-碎裂结构;断层面见大量近水平展布的擦痕和阶步 | 对含矿岩体有控制作用 |
| F2 | 龙首山南侧 | 倾向SW,倾角60°~75°,长约2 km,宁远堡以东则转为东西向,直达红崖山南沿一带,在白家嘴子地层和较新的白垩系地层之间以断裂为界,为不整合接触关系 | 地表可见断层破碎带,沿断层断续可见角闪岩、花岗岩出露 | 对超基性岩体的控制作用较弱 | |
| F3 | Ⅲ矿区南西侧 | 与矿体产状基本一致,出露长度1000多米,走向320°,倾向SW,倾角约60°,断层性质为逆断层,东端隐没于第四系覆盖物下 | 地表可见断层破碎带,带内可见因挤压形成的破裂面;断层两侧可见揉皱现象 | 对矿体破坏作用小 | |
| F16 | Ⅰ矿区含矿超基性岩体下盘 | 倾向195°,倾角75°左右,延长4 km以上 | 断层两侧岩层产状相交,上盘大理岩常形成紧闭褶曲,呈挤压特征,下盘断层面中见仰冲阶梯 | 对岩体下盘围岩有破坏作用 | |
| F18 | 位于Ⅱ矿区南西方向采石场附近 | 倾向SW,倾角70°左右,长600 m,断层破碎带宽1~5 m,该断层位于Ⅱ矿区南侧300 m处 | 断裂下盘为花岗岩,上盘为第四系,断裂带内可见角砾糜棱化带,角砾主要为花岗岩和大理岩;角砾明显受到挤压、揉搓和破碎 | 对岩体下盘围岩有破坏作用 | |
| 第二组: 北东东— 南西西 向层 | F16-1 | Ⅰ矿区3行以西,大致紧贴Ⅰ矿区延伸 | 倾向SSE,倾角75°~85°,长约700 m,向下延伸小于50 m | 断层上盘为老变质岩系,下盘为含矿超基性岩,受断层影响,含矿超基性岩被拖拽成弯曲状,断层破碎带宽2~3 m | 对Ⅰ、Ⅱ矿区金川岩体有错断作用 |
| F8 | 位于Ⅰ矿区和Ⅲ矿区之间 | 倾向SE,倾角75°~80°,长约5.3 km,斜穿于Ⅰ矿区和Ⅲ矿区之间 | 截切F1与F3断裂,断层具多期活动的特征,早期为正断层,晚期为逆冲走滑断层。断层破碎带宽15~32 m | 对Ⅰ、Ⅲ矿区金川岩体有错断作用 | |
| F23 | Ⅳ矿区56行附近 | 倾向SE,倾角大于70°,延长约1.2 km | 将Ⅱ矿含矿岩体南东段错开,使其位移至现在Ⅳ矿含矿岩体位置 | 构成Ⅱ矿与Ⅳ矿的分界 | |
| 第三组: 北东— 南西向层 | F17 | 位于Ⅱ矿区38行附近 | 倾向140°,倾角73°左右,延长约1.8 km | 横切岩体及围岩地层,断层带宽2~6 m,断层面附近见岩石破碎物、断层泥及角砾。该断层上下盘中节理发育,岩石比较破碎。使2号矿体在40行左右断开,水平断距130~260 m,垂直断距90~150 m | 破坏含矿超基性岩体 |
| Fa | 位于Ⅰ矿区12行附近 | 倾向SW,倾角60°~70°,纵向延伸650 m | 断层在1300水平横切含矿超基性岩体,且在井下可见断层破碎带 | 破坏含矿超基性岩体 | |
| Fc | 位于Ⅱ矿区23行附近 | 倾向SW,倾角40°~50° | 井下可见断层横切含矿超基性岩体,断距8~10 m | 破坏含矿超基性岩体 |
表3 金川矿区主要断裂构造特征(据文献[18,35,41-42]修改)
Table 3 Main fractures in the Jinchuan mining area (modified after refs.[18], [35], [41] and [42])
| 断裂 组别 | 断裂 编号 | 位置 | 产状及规模 | 特征 | 影响 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一组: 北西— 南东向 断层 | F1 | 位于矿区北部山麓边缘 | 走向300°,倾向205°,倾角60°左右,延长数百千米 | 呈上陡下缓的产状构造向下延伸,前震旦系逆冲于第四系砾石层之上。地表见断层破碎带、断层泥等;断层带自下而上见透镜-碎粉-碎裂结构;断层面见大量近水平展布的擦痕和阶步 | 对含矿岩体有控制作用 |
| F2 | 龙首山南侧 | 倾向SW,倾角60°~75°,长约2 km,宁远堡以东则转为东西向,直达红崖山南沿一带,在白家嘴子地层和较新的白垩系地层之间以断裂为界,为不整合接触关系 | 地表可见断层破碎带,沿断层断续可见角闪岩、花岗岩出露 | 对超基性岩体的控制作用较弱 | |
| F3 | Ⅲ矿区南西侧 | 与矿体产状基本一致,出露长度1000多米,走向320°,倾向SW,倾角约60°,断层性质为逆断层,东端隐没于第四系覆盖物下 | 地表可见断层破碎带,带内可见因挤压形成的破裂面;断层两侧可见揉皱现象 | 对矿体破坏作用小 | |
| F16 | Ⅰ矿区含矿超基性岩体下盘 | 倾向195°,倾角75°左右,延长4 km以上 | 断层两侧岩层产状相交,上盘大理岩常形成紧闭褶曲,呈挤压特征,下盘断层面中见仰冲阶梯 | 对岩体下盘围岩有破坏作用 | |
| F18 | 位于Ⅱ矿区南西方向采石场附近 | 倾向SW,倾角70°左右,长600 m,断层破碎带宽1~5 m,该断层位于Ⅱ矿区南侧300 m处 | 断裂下盘为花岗岩,上盘为第四系,断裂带内可见角砾糜棱化带,角砾主要为花岗岩和大理岩;角砾明显受到挤压、揉搓和破碎 | 对岩体下盘围岩有破坏作用 | |
| 第二组: 北东东— 南西西 向层 | F16-1 | Ⅰ矿区3行以西,大致紧贴Ⅰ矿区延伸 | 倾向SSE,倾角75°~85°,长约700 m,向下延伸小于50 m | 断层上盘为老变质岩系,下盘为含矿超基性岩,受断层影响,含矿超基性岩被拖拽成弯曲状,断层破碎带宽2~3 m | 对Ⅰ、Ⅱ矿区金川岩体有错断作用 |
| F8 | 位于Ⅰ矿区和Ⅲ矿区之间 | 倾向SE,倾角75°~80°,长约5.3 km,斜穿于Ⅰ矿区和Ⅲ矿区之间 | 截切F1与F3断裂,断层具多期活动的特征,早期为正断层,晚期为逆冲走滑断层。断层破碎带宽15~32 m | 对Ⅰ、Ⅲ矿区金川岩体有错断作用 | |
| F23 | Ⅳ矿区56行附近 | 倾向SE,倾角大于70°,延长约1.2 km | 将Ⅱ矿含矿岩体南东段错开,使其位移至现在Ⅳ矿含矿岩体位置 | 构成Ⅱ矿与Ⅳ矿的分界 | |
| 第三组: 北东— 南西向层 | F17 | 位于Ⅱ矿区38行附近 | 倾向140°,倾角73°左右,延长约1.8 km | 横切岩体及围岩地层,断层带宽2~6 m,断层面附近见岩石破碎物、断层泥及角砾。该断层上下盘中节理发育,岩石比较破碎。使2号矿体在40行左右断开,水平断距130~260 m,垂直断距90~150 m | 破坏含矿超基性岩体 |
| Fa | 位于Ⅰ矿区12行附近 | 倾向SW,倾角60°~70°,纵向延伸650 m | 断层在1300水平横切含矿超基性岩体,且在井下可见断层破碎带 | 破坏含矿超基性岩体 | |
| Fc | 位于Ⅱ矿区23行附近 | 倾向SW,倾角40°~50° | 井下可见断层横切含矿超基性岩体,断距8~10 m | 破坏含矿超基性岩体 |
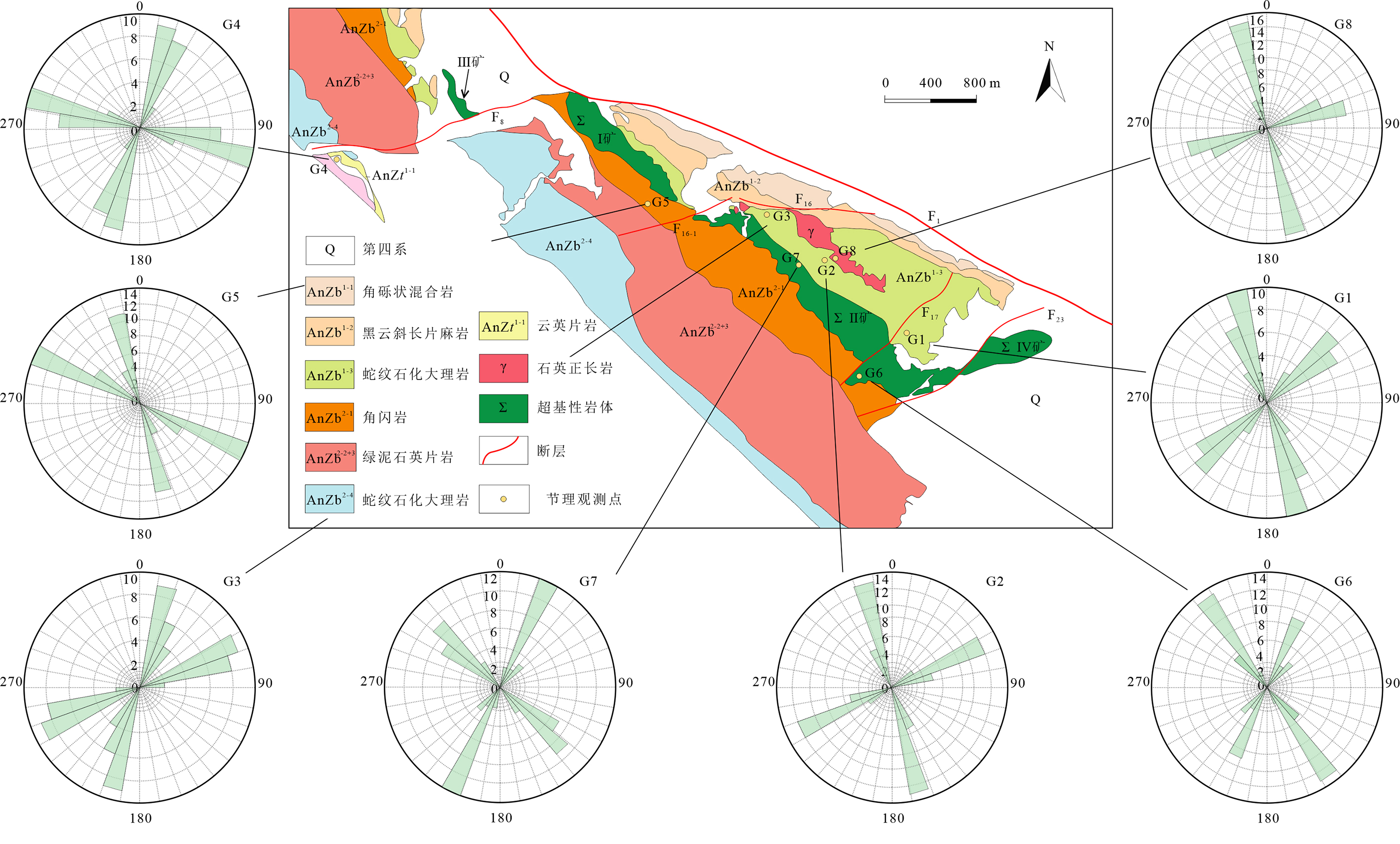
图6 金川矿区各个节理观测点走向玫瑰花图 G1-G3.白家嘴子组大理岩;G4.塔马子沟组变质灰岩;G5.角闪岩;G6-G7.超基性岩;G8.石英正长岩
Fig.6 Strike rosette for each joint observation point in the Jinchuan deposit area
| 测点 | 岩性 | 共轭剪节理产状 | 主应力方向 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | σ1 | σ2 | σ3 | ||||||||
| G1 | 白家嘴子组大理岩 | 155°∠57° | 76°∠52° | 203.34°∠3.92° | 109.12°∠46.99° | 296.97°∠42.74° | ||||||
| G2 | 白家嘴子组大理岩 | 139°∠75° | 79°∠45° | 184°∠27.37° | 64°∠44.01° | 294.1°∠33.58° | ||||||
| G4 | 塔马子沟组灰岩 | 116°∠74° | 12°∠56° | 249.4°∠37.02° | 46.51°∠50.7° | 150.7°∠11.35° | ||||||
| G6 | 超基性岩 | 296°∠86° | 55°∠80° | 174.87°∠13.6° | 9.78°∠75.95° | 265.72°∠3.48° | ||||||
| G7 | 超基性岩 | 110°∠76° | 44°∠76° | 348.09°∠7.31° | 109.07°∠76° | 256.54°∠11.87° | ||||||
| G8 | 石英正长岩 | 160°∠75° | 70°∠48° | 197.57°∠18.61° | 86.57°∠46.79° | 302.43°∠37.29° | ||||||
表4 共轭剪节理及其主应力方向统计
Table 4 Statistics of conjugate shear joints and their principal stresses
| 测点 | 岩性 | 共轭剪节理产状 | 主应力方向 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | σ1 | σ2 | σ3 | ||||||||
| G1 | 白家嘴子组大理岩 | 155°∠57° | 76°∠52° | 203.34°∠3.92° | 109.12°∠46.99° | 296.97°∠42.74° | ||||||
| G2 | 白家嘴子组大理岩 | 139°∠75° | 79°∠45° | 184°∠27.37° | 64°∠44.01° | 294.1°∠33.58° | ||||||
| G4 | 塔马子沟组灰岩 | 116°∠74° | 12°∠56° | 249.4°∠37.02° | 46.51°∠50.7° | 150.7°∠11.35° | ||||||
| G6 | 超基性岩 | 296°∠86° | 55°∠80° | 174.87°∠13.6° | 9.78°∠75.95° | 265.72°∠3.48° | ||||||
| G7 | 超基性岩 | 110°∠76° | 44°∠76° | 348.09°∠7.31° | 109.07°∠76° | 256.54°∠11.87° | ||||||
| G8 | 石英正长岩 | 160°∠75° | 70°∠48° | 197.57°∠18.61° | 86.57°∠46.79° | 302.43°∠37.29° | ||||||
| 构造活动序列 | 构造环境 | 构造应力场 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 时期 | 构造阶段 | 构造事件 | 最大压应 力方向 | 应变椭球体 | |||||
| 成矿后 | 新生代 | 喜山阶段 | 印度板块与青藏板块碰撞,太平洋板块向欧亚大陆俯冲 | 挤压 | 南北 | 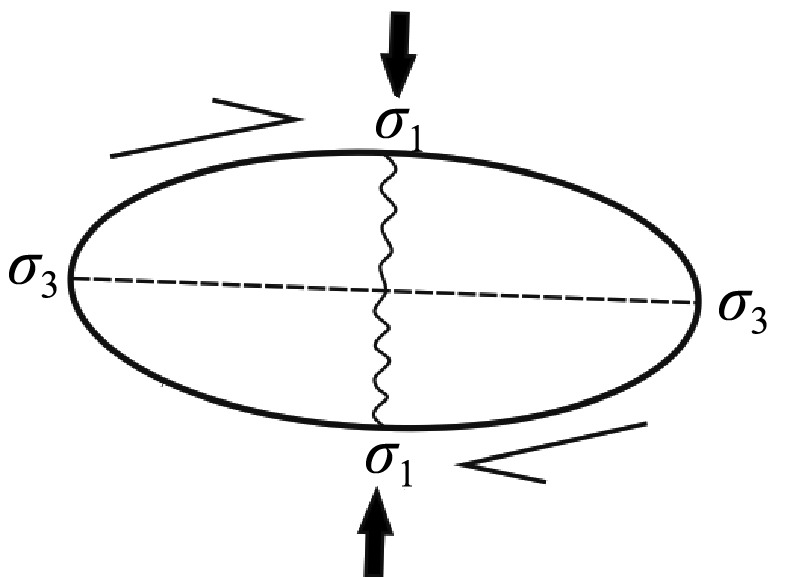 | |||
| 中生代 | 燕山阶段 | 燕山运动与潮水盆地形成 | 北东— 南西 | 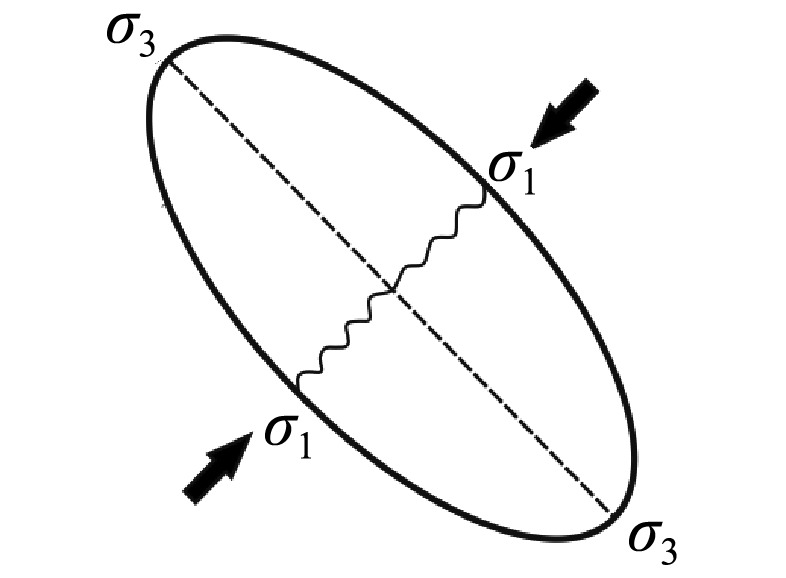 | |||||
| 晚古 生代 | 海西阶段 | 海陆交互相堆积结束,发生陆内推覆造山和陆壳隆起 | 近南北 | 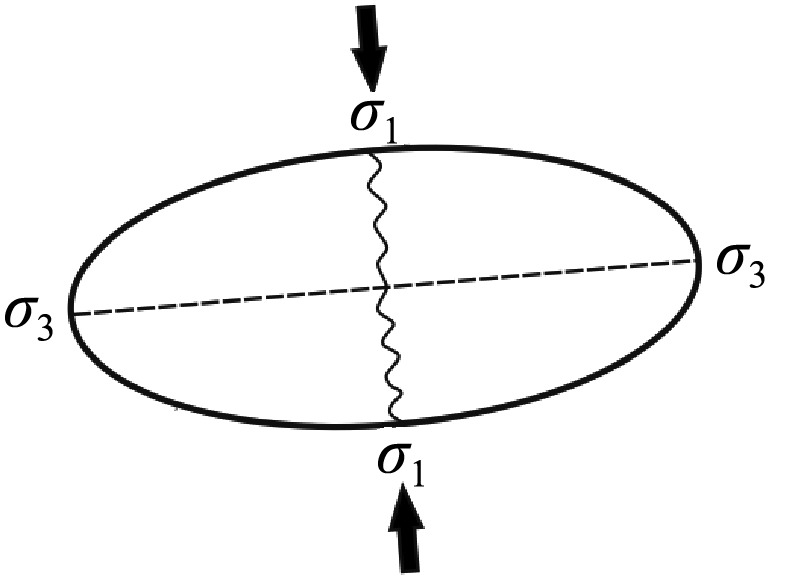 | |||||
| 早古 生代 | 加里东 阶段 | 阿拉善地块与祁连—柴达木地块经历了祁连洋闭合与板块拼合,龙首山地区发生陆内造山 | 北北东— 南南西 | 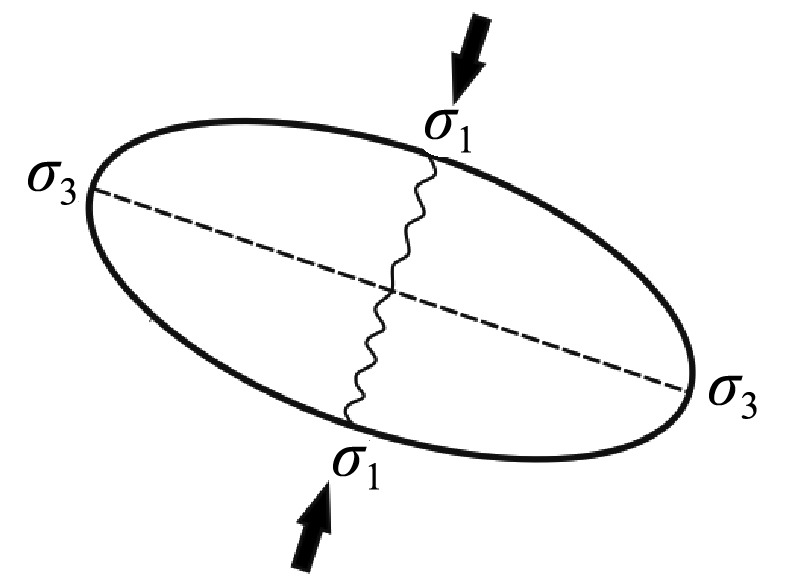 | |||||
| 成矿期 | 新元 古代 | 晋宁阶段 | Rodinia超大陆裂解,幔源岩浆侵入 | 拉伸 | 北东— 南西 | 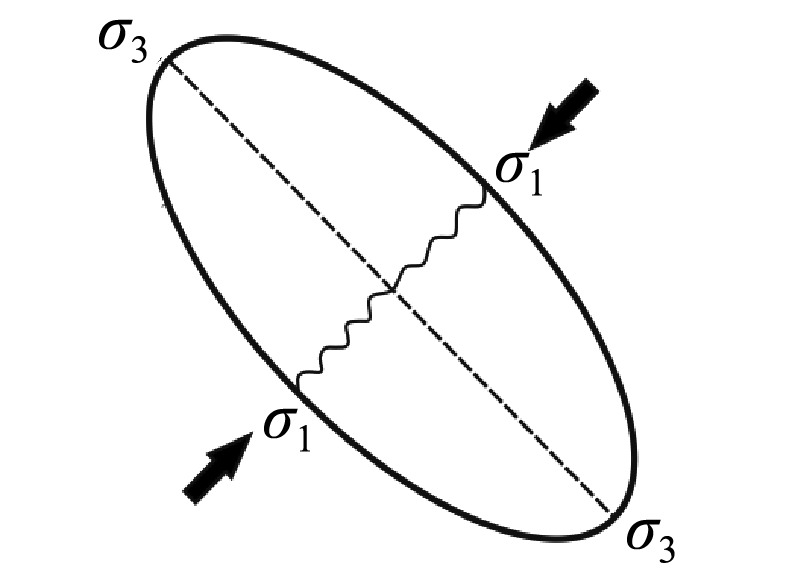 | |||
| 成矿前 | 古元 古代 | 吕梁阶段 | 吕梁造山运动,即华北克拉通最终稳定固结的造山运动 | 挤压 | 近南北 | 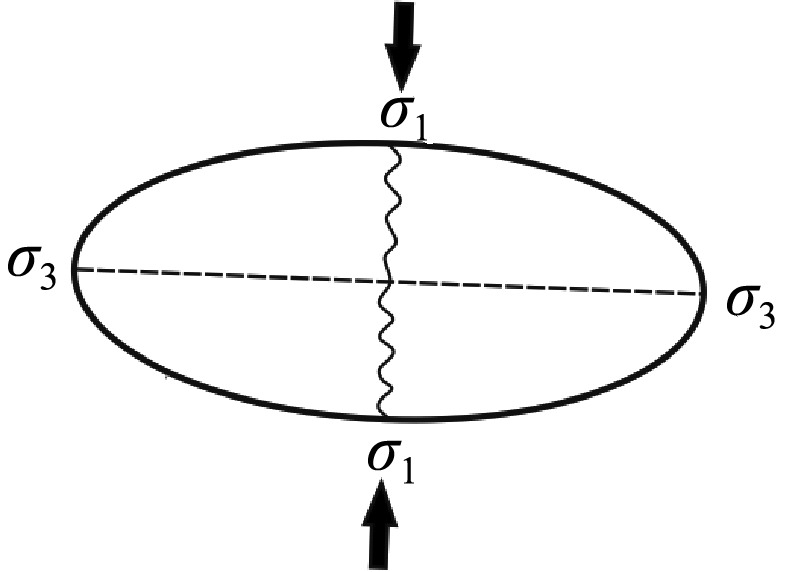 | |||
表5 金川矿区构造活动时序阶段和构造应力场演化
Table 5 Evolution of the tectonic stress field in the Jinchuan deposit area
| 构造活动序列 | 构造环境 | 构造应力场 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 时期 | 构造阶段 | 构造事件 | 最大压应 力方向 | 应变椭球体 | |||||
| 成矿后 | 新生代 | 喜山阶段 | 印度板块与青藏板块碰撞,太平洋板块向欧亚大陆俯冲 | 挤压 | 南北 |  | |||
| 中生代 | 燕山阶段 | 燕山运动与潮水盆地形成 | 北东— 南西 |  | |||||
| 晚古 生代 | 海西阶段 | 海陆交互相堆积结束,发生陆内推覆造山和陆壳隆起 | 近南北 |  | |||||
| 早古 生代 | 加里东 阶段 | 阿拉善地块与祁连—柴达木地块经历了祁连洋闭合与板块拼合,龙首山地区发生陆内造山 | 北北东— 南南西 |  | |||||
| 成矿期 | 新元 古代 | 晋宁阶段 | Rodinia超大陆裂解,幔源岩浆侵入 | 拉伸 | 北东— 南西 |  | |||
| 成矿前 | 古元 古代 | 吕梁阶段 | 吕梁造山运动,即华北克拉通最终稳定固结的造山运动 | 挤压 | 近南北 |  | |||
| [1] | 董耀松, 范继璋, 杨言辰, 等. 吉林红旗岭铜镍矿床的地质特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2004, 18(2): 197-202. |
| [2] | 李士彬, 宋谢炎, 胡瑞忠, 等. 甘肃金川Ⅱ号岩浆硫化物含矿岩体岩浆演化过程探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(4): 703-711. |
| [3] | 宋谢炎, 康健, 隆廷茂, 等. 甘肃金川超大型Ni-Cu-PGE硫化物矿床岩浆通道分枝构造及其深部找矿意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2023, 45(5): 1049-1062. |
| [4] | 宋谢炎. 岩浆通道成矿核心内涵“两深一浅一通道”及其找矿意义[J/OL]. 地质学报, 2024: 1-12.DOI:10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2024111. |
| [5] | LI C S, XU Z H, DE WAAL S A, et al. Compositional variations of olivine from the Jinchuan Ni-Cu sulfide deposit, Western China: Implications for ore genesis[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2004, 39(2): 159-172. |
| [6] | 苏哲, 毛先成, 黎隆交, 等. 金川铜镍硫化物矿床构造控矿定量分析[J]. 矿产勘查, 2023, 14(5): 679-690. |
| [7] | CHEN L M, SONG X Y, KEAYS R, et al. Segregation and fractionation of magmatic Ni-Cu-PGE sulfides in the western Jinchuan intrusion, northwestern China: Insights from platinum group element geochemistry[J]. Economic Geology, 2013, 108: 1793-1811. |
| [8] | SONG X Y, DANYUSHEVSKY L V, KEAYS R R, et al. Structural, lithological, and geochemical constraints on the dynamic magma plumbing system of the Jinchuan Ni-Cu sulfide deposit, NW China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2012, 47(3): 277-297. |
| [9] | LEHMANN J, ARNDT N, WINDLEY B, et al. Field relationships and geochemical constraints on the emplacement of the Jinchuan intrusion and its Ni-Cu-PGE sulfide deposit, Gansu, China[J]. Economic Geology, 2007, 102(1): 75-94. |
| [10] | 汤中立, 李文渊. 金川铜镍硫化物(含铂)矿床成矿模式及地质对比[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1995. |
| [11] | CHAI G, NALDRETT A J. The Jinchuan ultramafic intrusion: Cumulate of a high-Mg basaltic magma[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1992, 33(2): 277-303. |
| [12] | CHAI G, NALDRETT A J. Characteristics of Ni-Cu-PGE mineralization and genesis of the Jinchuan Deposit, Northwest China[J]. Economic Geology, 1992, 87(6): 1475-1495. |
| [13] | 王守良, 王荆程, 夏明强, 等. 金川铜镍硫化矿床成岩(矿)断裂构造分析[J]. 青海大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 32(3): 43-50. |
| [14] | 樊步恭. 金川铜镍矿田的构造特征[J]. 西北地质, 1988, 21(1): 1-10. |
| [15] | 孙桂玉. 脆-韧性剪切带控矿的初步探讨: 对金川铜镍矿控岩控矿构造的新见解[J]. 矿床地质, 1990, 9(4): 352-362. |
| [16] | 宋谢炎, 陈列锰, 邓宇峰, 等. 金川两个岩体的识别及其深边部找矿意义[J]. 矿物学报, 2011, 31(增): 389-390. |
| [17] | 和秋姣, 赖健清, 毛先成, 等. 甘肃金川矿区构造应力场与构造演化研究[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2019, 34(2): 265-273. |
| [18] | 廖文建. 金川铜镍矿区构造岩相填图、应力场分析和深部成矿预测[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016. |
| [19] | 赵远方, 施炜, 张宇. 甘肃金川矿区古构造应力场恢复及演化研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2023, 29(6): 770-785. |
| [20] | 焦建刚, 汤中立, 闫海卿, 等. 金川铜镍硫化物矿床的岩浆质量平衡与成矿过程[J]. 矿床地质, 2012, 31(6): 1135-1148. |
| [21] | 李文渊. 中国岩浆铜镍钴硫化物矿床成矿理论创新和找矿突破[J]. 地质力学学报, 2022, 28(5): 793-820. |
| [22] | 汤中立. 中国镍铜铂岩浆硫化物矿床与成矿预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006. |
| [23] | 曾认宇. 金川铜镍硫化物矿床岩浆通道系统及岩浆演化研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2014. |
| [24] | 靳树芳. 甘肃金川铜镍硫化物矿床磁黄铁矿与磁铁矿地球化学特征及成因研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2018. |
| [25] | 王振江. 中国金川Ni-Cu(PGE)硫化物矿床深部成矿过程的实验研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2020. |
| [26] | 李佐. 甘肃金川铜镍硫化物矿床控矿构造研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2009. |
| [27] | 黄满湘. 金川矿床构造体系研究[R]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2013. |
| [28] | 乔富贵. 金川铜镍硫化矿床成因研究及成矿预测[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2005. |
| [29] | JIAO J G, HAN F, ZHAO L D, et al. Magnetite geochemistry of the Jinchuan Ni-Cu-PGE deposit, NW China: Implication for its ore-forming processes[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(10): 593. |
| [30] | 丁瑞颖, 闫海卿, 赵焕强, 等. 金川镍铜铂硫化物矿床成矿期次、阶段划分[J]. 矿物学报, 2011, 31(增): 162-164. |
| [31] | 汤中立, BARNES S J. 岩浆硫化物矿床成矿机制[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998. |
| [32] |
张晓旭, 苏尚国, 刘美玉, 等. 甘肃金川早古生代正长花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学、岩石学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(4): 283-298.
DOI |
| [33] | 曾认宇, 赖健清, 毛先成, 等. 金川铜镍矿床中断裂系统的形成演化及对矿体的控制[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(9): 2574-2583. |
| [34] | 李忠权, 刘顺. 构造地质学[M]. 3版. 北京: 地质出版社, 2010. |
| [35] | 高亚林. 金川矿区地质特征、时空演化及深边部找矿研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2009. |
| [36] | 高亚林, 乔富贵, 卢健全, 等. 金川铜镍硫化物矿床中特富矿分布特征及成因[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2014, 36(1): 68-79. |
| [37] | 刘健, 于强, 王猛, 等. 金川铜镍硫化物矿床晚中生代以来抬升冷却事件的磷灰石裂变径迹约束[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2023, 47(3): 618-630. |
| [38] | VINCENT S J, ALLEN M B. Evolution of the Minle and Chaoshui Basins, China: Implications for Mesozoic strike-slip basin formation in Central Asia[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1999, 111(5): 725-742. |
| [39] | 李生栋, 杨永春, 艾启兴, 等. 金川铜镍硫化物矿床F1断裂系统演化及其意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2022, 46(1): 63-76. |
| [40] | 曾南石, 汪劲草, 罗先熔, 等. 金川地区构造序列及与铜镍硫化物矿床的关系[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(6): 210-218. |
| [41] | 刘健. 甘肃金川铜镍硫化物矿床构造演化及成矿预测[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2022. |
| [42] | 丁瑞颖. 甘肃金川镍铜铂岩浆硫化物矿床Ⅱ矿区矿物特征研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2012. |
| [43] | 蓝德初. 甘肃龙首山地区基性岩脉的地质特征及研究意义[D]. 抚州: 东华理工大学, 2019. |
| [44] | 宫江华. 西阿拉善地块早前寒武纪变质基底组成、性质、年代格架及归属[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2013. |
| [45] | 黄汲清, 任纪舜. 中国大地构造及其演化: 1∶400万中国大地构造图简要说明[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1980. |
| [46] | 张振法, 李超英, 牛颖智. 阿拉善: 敦煌陆块的性质、范围及其构造作用和意义[J]. 内蒙古地质, 1997(2): 1-14. |
| [47] | 潘桂棠, 陆松年, 肖庆辉, 等. 中国大地构造阶段划分和演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(6): 1-23. |
| [48] | 陆松年, 杨春亮, 李怀坤, 等. 华北古大陆与哥伦比亚超大陆[J]. 地学前缘, 2002, 9(4): 225-233. |
| [49] | 许志琴. 谈谈裂谷[J]. 地质论评, 1980, 26(3): 260-264. |
| [50] | 王剑, 潘桂棠. 中国南方古大陆研究进展与问题评述[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(5): 818-825. |
| [51] | 马佳虹. 金川矿区韧性剪切带特征及其意义[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2012. |
| [52] | 汤中立, 杨杰东, 徐士进, 等. 金川含矿超铁镁岩的Sm-Nd定年[J]. 科学通报, 1992, 37(10): 918-920. |
| [53] | LI X H, SU L, CHUNG S L, et al. Formation of the Jinchuan ultramafic intrusion and the world's third largest Ni-Cu sulfide deposit: Associated with the-825 Ma South China mantle plume?[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2005, 6(11). |
| [54] | 刘琦. 甘肃金川铜镍硫化物矿床中基性岩脉形成时代与岩石成因[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2020. |
| [55] | 张钶. 甘肃金川铜镍矿区古生代岩浆演化过程与叠加成矿作用[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2023. |
| [56] | 宋晨, 苏尚国, 伍月, 等. 甘肃金川铜镍(铂)硫化物矿床中高镁辉绿岩脉的发现及其意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(11): 3375-3382. |
| [1] | 陈志友, 曾广乾, 柏道远, 姚泽钰, 王灵珏, 文春华, 陈旭, 王勇, 李彬, 黄乐清, 陈剑锋, 梁恩云, 许若潮, 马慧英, 向轲. 湘南大义山地区中—新生代变形序列及其动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 1092-1108. |
| [2] | 王佳新, 焦建刚, 马云飞, 李峰, 高超. 内蒙古中部乌兰陶勒盖铜镍矿床形成时代与岩浆源区[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 991-1012. |
| [3] | 谢昭涵, 冯昌, 仇永峰, 李鹤永, 张建波, 唐海氢. 苏北盆地盐城凹陷盐③断裂带构造演化及其控圈作用[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(02): 300-311. |
| [4] | 汪锴, 王根厚, 贾庆军, 张笑. 琼东南盆地深水区松南—宝岛凹陷的构造演化及其与油气成藏关系[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 245-258. |
| [5] | 李波, 金胜, 叶高峰, 魏文博. 中亚造山带东段岩石圈电性结构特征及其构造涵义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(01): 15-30. |
| [6] | 吕古贤, 张宝林, 吕承训, 胡宝群, 曾勇, 郭涛, 申玉科, 王红才, 马立成, 焦建刚, 毕珉烽. 长江中下游地区新华夏构造体系的“米字型”结构特征[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1240-1250. |
| [7] | 刘爱荣, 徐永婧, 刘成林, 庞尔成. 大同盆地地质特征及构造演化研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1296-1310. |
| [8] | 孙自明, 张荣强, 孙炜, 郝运轻, 卞昌蓉. 四川盆地东部海相下组合油气勘探领域与有利勘探方向[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 798-806. |
| [9] | 余海波, 程秀申, 徐田武, 谈玉明, 漆家福. 东濮凹陷古近纪盆地结构控烃控藏特征[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1119-1131. |
| [10] | 杨旺东, 高福磊, 王功文, 庞振山, 沈和明, 龚灵明, 申红涛, 张智强, 刘晓宁. 四川红泥坡铜矿床三维地质建模及控矿构造演化的新认识[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 598-608. |
| [11] | 罗晓华, 杨明慧, 贾春阳, 李占元, 雷志斌, 张少华. 晋北地区口泉断裂带晚中生代分段构造特征[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(03): 551-560. |
| [12] | 赵子贤, 柳长峰, 赫英福, 叶宝莹, 许鑫, 霍东亮. 新疆南阿尔金木纳布拉克构造混杂岩带物质组成及变形特征[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(01): 25-35. |
| [13] | 钟城, 秦启荣, 魏志红, 李虎, 邓毅, 何威. 酒店垭-桑木场构造须家河组节理发育特征与应力场解析[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(02): 279-288. |
| [14] | 武若晨, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 何格, 康继祖, 余福承, 冯李强, 徐劲驰. 东昆仑造山带早古生代—早中生代构造演化的沉积地球化学记录[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(04): 716-733. |
| [15] | 张祥信, 彭宇, 雷世和, 高永丰, 王广. 内蒙古中部苏尼特左旗地区勃勒金韧性剪切带的厘定及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(03): 433-442. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||