



现代地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (01): 127-137.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2022.066
王圣宜1( ), 邹长春1(
), 邹长春1( ), 彭诚1, 王红才2, 陆敬安3, 康冬菊3, 伍操为1, 蓝茜茜1, 谢莹峰3
), 彭诚1, 王红才2, 陆敬安3, 康冬菊3, 伍操为1, 蓝茜茜1, 谢莹峰3
收稿日期:2022-04-20
修回日期:2022-07-22
出版日期:2023-02-10
发布日期:2023-03-20
通讯作者:
邹长春,男,博士生导师,1969年出生,地球探测与信息技术专业,主要从事岩石物理、测井与井中物探、油气勘察和科学钻探领域的教学和科研工作。Email: zoucc@cugb.edu.cn。
作者简介:王圣宜,女,硕士研究生,1998年出生,地球探测与信息技术专业,主要从事岩石物理建模与反演方面的研究。Email: edhhwu@163.com。
基金资助:
WANG Shengyi1( ), ZOU Changchun1(
), ZOU Changchun1( ), PENG Cheng1, WANG Hongcai2, LU Jingan3, KANG Dongju3, WU Caowei1, LAN Xixi1, XIE Yingfeng3
), PENG Cheng1, WANG Hongcai2, LU Jingan3, KANG Dongju3, WU Caowei1, LAN Xixi1, XIE Yingfeng3
Received:2022-04-20
Revised:2022-07-22
Online:2023-02-10
Published:2023-03-20
摘要:
海域孔隙型天然气水合物储层中,水合物主要以颗粒胶结、包裹胶结、骨架支撑、孔隙悬浮4种赋存模式充填沉积物孔隙,水合物饱和度与赋存模式的不同导致了储层弹性和电性的差异,利用声波和电阻率测井资料联合处理可以进行水合物赋存模式的定量表征。首先利用Simandoux公式计算水合物饱和度,然后通过有效介质模型构建的岩石物理模板识别水合物赋存模式,最后计算储层中不同赋存模式水合物的相对占比。以全球范围内三个典型区域(中国南海神狐海域、北美Blake海台、新西兰Hikurangi边缘)为例,利用水合物储层的实际钻探资料,对水合物赋存模式进行定量分析:(1)中国南海神狐海域SH2站位储层中,水合物主要以骨架支撑模式产出,约占水合物总量的64%;(2)Blake海台994C站位储层中,水合物主要为颗粒胶结和包裹胶结模式,分别占总量的27%和51%;(3)Hikurangi边缘U1518B站位的水合物储层中,水合物主要为包裹胶结和骨架支撑模式,分别占总量的32%和47%。前人针对水合物形成和赋存模式的实验研究显示,水合物更易以颗粒胶结、包裹胶结和骨架支撑模式赋存,从侧面验证了上述分析结果的可靠性。本研究使用的声波和电阻率测井资料联合处理方法可实现海域孔隙型储层水合物赋存模式定量化评价。
中图分类号:
王圣宜, 邹长春, 彭诚, 王红才, 陆敬安, 康冬菊, 伍操为, 蓝茜茜, 谢莹峰. 海域孔隙型储层天然气水合物赋存模式定量化表征:声波和电阻率测井的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(01): 127-137.
WANG Shengyi, ZOU Changchun, PENG Cheng, WANG Hongcai, LU Jingan, KANG Dongju, WU Caowei, LAN Xixi, XIE Yingfeng. Quantitative Characterization of Hydrate Occurrence Mode in Marine Pore-filling Gas Hydrate Reservoirs: Constraints from Acoustic and Resistivity Log Data[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(01): 127-137.
| 区域 | 石英 含量/% | 黏土 含量/% | 方解石 含量/% | 长石 含量/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国南海神狐海域 | 60 | 25 | 15 | - |
| 北美Blake海台 | 18 | 75 | 7 | - |
| 新西兰Hikurangi边缘 | 25 | 45 | 17 | 13 |
表1 含水合物松散沉积物矿物组分含量[45??-48]
Table 1 Mineral fraction and content of hydrate reservoirs[45??-48]
| 区域 | 石英 含量/% | 黏土 含量/% | 方解石 含量/% | 长石 含量/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国南海神狐海域 | 60 | 25 | 15 | - |
| 北美Blake海台 | 18 | 75 | 7 | - |
| 新西兰Hikurangi边缘 | 25 | 45 | 17 | 13 |
| 区域 | 站位 | 储层范 围/mbsf | 电阻率/ (Ω·m) | 纵波速度 /(m/s) | 饱和度/% | 赋存模式相对含量/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 | 最大值 | ① | ② | ③ | ④ | ||||||
| 神狐海域 | SH2 | 192~224 | 1.4~3.3 | 1770~2480 | 27.6 | 48.3 | 2 | 15 | 64 | 19 | |
| Blake海台 | 994C | 212~429 | 0.6~1.2 | 1580~1980 | 8.4 | 21.1 | 27 | 51 | 6 | 16 | |
| Hikurangi边缘 | U1518B | 33~317 | 1.4~4.9 | 1710~2300 | 18.7 | 37.2 | 9 | 32 | 47 | 12 | |
表2 水合物储层赋存模式定量计算结果
Table 2 Calculation results of hydrate occurrence model in hydrate reservoirs
| 区域 | 站位 | 储层范 围/mbsf | 电阻率/ (Ω·m) | 纵波速度 /(m/s) | 饱和度/% | 赋存模式相对含量/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 | 最大值 | ① | ② | ③ | ④ | ||||||
| 神狐海域 | SH2 | 192~224 | 1.4~3.3 | 1770~2480 | 27.6 | 48.3 | 2 | 15 | 64 | 19 | |
| Blake海台 | 994C | 212~429 | 0.6~1.2 | 1580~1980 | 8.4 | 21.1 | 27 | 51 | 6 | 16 | |
| Hikurangi边缘 | U1518B | 33~317 | 1.4~4.9 | 1710~2300 | 18.7 | 37.2 | 9 | 32 | 47 | 12 | |

图3 神狐海域SH2站位电阻率曲线(a)和电阻率、氯离子浓度计算的水合物饱和度(b)(1 mbsf示海底面以下深度1 m,下同)
Fig.3 Resistivity logging data (a) and hydrate saturation from resistivity calculation and chlorine ion concentration analysis (b) for site SH2 in Shenhu area
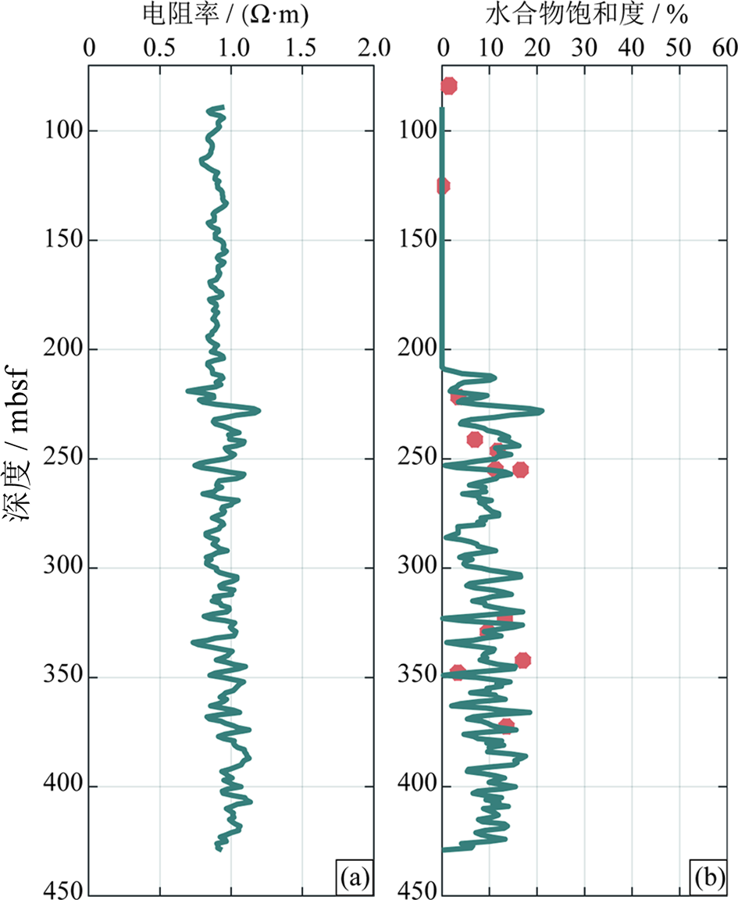
图5 Blake海台994C站位电阻率曲线(a)和电阻率、氯离子浓度计算的水合物饱和度(b)
Fig.5 Resistivity logging data (a) and hydrate saturation from resistivity calculation and chlorine ion concentration analysis (b) for site 994C in Blake ridge

图6 Blake海台994C站位测井数据及各赋存模式水合物含量(5点平滑结果)
Fig.6 Well-log data from site 994C in Blake ridge and saturation for each hydrate occurrence model (5-point smoothing results)

图7 Hikurangi边缘U1518B站位电阻率曲线(a)和电阻率、氯离子浓度计算的水合物饱和度(b)
Fig.7 Resistivity logging data (a) and hydrate saturation from resistivity calculation and chlorine ion concentration analysis (b) for site U1518B in Hikurange margin

图8 Hikurangi边缘D1815B井测井数据及各赋存模式水合物含量(3点平滑结果)
Fig.8 Well-log data from site U1518B in Hikurange margin and saturation for each hydrate occurrence model (3-point smoothing results)
| [1] |
LEE M W, COLLETT T S. In-situ gas hydrate hydrate saturation estimated from various well logs at the Mount Elbert Gas Hydrate Stratigraphic Test Well, Alaska North Slope[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(2): 439-449.
DOI URL |
| [2] | GHOSH R, SAIN K, OJHA M. Effective medium modeling of gas hydrate-filled fractures using the sonic log in the Krishna-Godavari basin, offshore eastern India[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth), 2010, 115(6): 3659-3667. |
| [3] |
HU G, YE Y, ZHANG J, et al. Acoustic response of gas hydrate formation in sediments from South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 52: 1-8.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LEI L, SEOL Y, CHOI J H, et al. Pore habit of methane hydrate and its evolution in sediment matrix-Laboratory visualization with phase-contrast micro-CT[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 104: 451-467.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 胡高伟, 业渝光, 张剑, 等. 松散沉积物中天然气水合物生成、分解过程与声学特性的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(3): 465-474. |
| [6] | 刘洋, 陈强, 邹长春, 等. 气体水合物生成实验过程动态监测:一种新的ERT方法及其效果分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(1): 193-201. |
| [7] |
PRIEST J A, BEST A I, CLAYTON C R I. Attenuation of seismic waves in methane gas hydrate-bearing sand[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2005, 164(1): 149-159.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 李承峰, 胡高伟, 张巍, 等. 有孔虫对南海神狐海域细粒沉积层中天然气水合物形成及赋存特征的影响[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2016, 46(9): 1223-1230. |
| [9] |
LV J, XUE K, ZHANG Z, et al. Pore-scale investigation of hydrate morphology evolution and seepage characteristics in hydrate bearing microfluidic chip[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2021, 88: 103881.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
DVORKIN J, NUR A. Elasticity of high-porosity sandstones: theory for two North Sea data sets[J]. Geophysics, 1996, 61(5): 1363-1370.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
CHAND S, MINSHULL T A, GEI D, et al. Elastic velocity models for gas-hydrate-bearing sediments:a comparison[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2004, 159(2): 573-590.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ECKER C, DVORKIN J, NUR A. Sediments with gas hydrates: Internal structure from seismic AVO[J]. Geophysics, 1998, 63(5): 1659-1669.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
HELGERUD M B, DVORKIN J, NUR A, et al. Elastic-wave velocity in marine sediments with gas hydrates: effective medium modeling[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1999, 26(13): 2021-2024.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 宁伏龙, 梁金强, 吴能友, 等. 中国天然气水合物赋存特征[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(8): 1-24,203. |
| [15] |
ECKER C, DVORKIN J, NUR A M. Estimating the amount of gas hydrate and free gas from marine seismic data[J]. Geophysics, 2000, 65(2): 565-573.
DOI URL |
| [16] | TALEB F, GARZIGLIA S, SULTAN N. Hydromechanical pro-perties of gas hydrate-bearing fine sediments from in situ testing[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth), 2018, 123(11): 9615-9634. |
| [17] | 王秀娟. 南海北部陆坡天然气水合物储层特征研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2006. |
| [18] |
LEE M W, HUTCHINSON D R, COLLETT T S, et al. Seismic velocities for hydrate-bearing sediments using weighted equation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1996, 101(9): 20347-20358.
DOI URL |
| [19] | COLLETT T S, LADD J. Detection of gas hydrate with downhole logs and assessment of gas hydrate concentrations (saturations) and gas volumes on the Blake Ridge with electrical resistivity log data[M]// Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program,Scientific Results. College Station: Ocean Drilling Program, 2000: 179-191. |
| [20] | SIMANDOUX P. Dielectric measurements of porous media:Application to the measurement of water saturations, study of the behavior of argillaceous formations[J]. Revue de L, Institut Franais du Petrole, 1963, 18(S1): 193-215. |
| [21] |
TIMUR A. Velocity of compressional waves in porous media at permafrost temperatures[J]. Geophysics, 1968, 33(4): 584.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
CARCIONE J M, TINIVELLA U. Bottom-simulating reflectors: Seismic velocities and AVO effects[J]. Geophysics, 2000, 65(1): 54-67.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LEE M W. Elastic velocities of partially gas-saturated unconsolidated sediments[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2004, 21(6): 641-650.
DOI URL |
| [24] | ZIMMERMAN R W, KING M S. Effect of the extent of freezing on seismic velocities in unconsolidated permafrost[J]. Geophy-sics, 1986, 51(6): 1285-1290. |
| [25] |
TERRY D A, KNAPP C C. A unified effective medium model for gas hydrates in sediments[J]. Geophysics, 2018, 83(6): 317-332.
DOI |
| [26] |
NGUYEN SYAB T, TANGC A M, TOD Q D, et al. A model to predict the elastic properties of gas hydrate-bearing sediments[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2019, 169: 154-164.
DOI URL |
| [27] | PAN H, LI H, CHEN J, et al. A unified contact cementation theory for gas hydrate morphology detection and saturation estimation from elastic-wave velocities.[J]. Marine & PetroleumGeology, 2020, 113: 104146. |
| [28] |
DVORKIN J, NUR A, YIN H. Effective properties of cemented granular materials[J]. Mechanics of Materials, 1994, 18(4): 351-366.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
GASSMANN F. Elastic waves through a packing of spheres[J]. Geophysics, 1951, 16(4): 673.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
BERRYMAN J G. Bounds and estimates for transport coefficients of random and porous media with high contrasts[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 97(6): 063504.
DOI URL |
| [31] | 田海涛, 刘乐乐, 夏宇轩, 等. 水合物赋存形式对石英砂电性特征影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2022, 65(4): 1439-1450. |
| [32] | ZHANG H, YANG S, WU N. Successful and surprising results for China’s first gas hydrate drilling expedition[J]. Fire in the Ice, 2007, 7(3): 6-9. |
| [33] | YANG S, ZHANG M, LIANG J. Preliminary results of China’s third gas hydrate drilling expedition: A critical step from discovery to development in the South China Sea[J]. Fire in the Ice, 2015, 15(2): 1-5. |
| [34] | YANG S, LIANG J, LEI Y. GMGS4 gas hydrate drilling expedition in the South China Sea[J]. Fire in the Ice, 2017, 17(1): 7-11. |
| [35] | 王秀娟, 吴时国, 刘学伟, 等. 基于电阻率测井的天然气水合物饱和度估算及估算精度分析[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(5): 993-999. |
| [36] | 梁劲, 王明君, 王宏斌, 等. 南海神狐海域天然气水合物声波测井速度与饱和度关系分析[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(2): 217-223. |
| [37] | 梁劲, 王明君, 陆敬安, 等. 南海神狐海域含水合物地层测井响应特征[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(3): 506-514. |
| [38] | 姚伯初, 杨木壮, 吴时国, 等. 中国海域的天然气水合物资源[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(3): 333-341. |
| [39] | 陈芳, 苏新, 陆红锋, 等. 南海神狐海域有孔虫与高饱和度水合物的储存关系[J]. 地球科学, 2013, 38(5): 907-915. |
| [40] | 龚跃华, 杨胜雄, 王宏斌, 等. 南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物成藏特征[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(2): 210-216. |
| [41] | 张英, 郭依群, 莫午零, 等. 南海北部水合物中天然气成因及形成条件[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(5): 1180-1185. |
| [42] | 陈芳, 周洋, 苏新, 等. 南海神狐海域含水合物层粒度变化及与水合物饱和度的关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(5): 95-100. |
| [43] | 吴能友, 杨胜雄, 王宏斌, 等. 南海北部陆坡神狐海域天然气水合物成藏的流体运移体系[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(6): 1641-1650. |
| [44] | 苏丕波, 梁金强, 张伟, 等. 南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物成藏系统[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(8): 77-89. |
| [45] | 陈芳, 苏新, 周洋, 等. 南海北部陆坡神狐海域晚中新世以来沉积物中生物组分变化及意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(2): 1-8. |
| [46] | PAULL C K, MATSUMOTO R, WALLACE P J. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, 164 initial reports[R]. College Station: Ocean Drilling Program, 1996. |
| [47] | PECHER I A, BARNES P M, LEVAY L J. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, 372A initial reports[R]. College Station: International Ocean Discovery Program, 2019. |
| [48] | WALLACE L M, SAFFER D M, BARNES P M. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, 372B/375 initial reports[R]. College Station: International Ocean Discovery Program, 2019. |
| [1] | 郭子豪, 李灿苹, 陈凤英, 勾丽敏, 汪洪涛, 曾宪军, 刘一林, 田鑫裕. 天然气水合物分解的甲烷对海洋生物的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(01): 138-152. |
| [2] | 卢俊辉, 张小莉, 杨振, 李亚军, 王晓琳, 赵希. 致密砂岩储层变岩电参数法饱和度计算模型:以苏里格气田西区盒8段例[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1131-1137. |
| [3] | 尚卫, 苏新, 白辰阳, 崔鸿鹏. 东太平洋水合物海岭沉积物中黏土矿物与水合物饱和度相关性研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 159-171. |
| [4] | 谢莹峰, 陆敬安, 匡增桂, 康冬菊, 王通, 蔡慧敏. 南海神狐海域水合物三相混合层测井评价方法研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 182-192. |
| [5] | 刘洋, 陈强, 邹长春, 赵金环, 彭诚, 孙建业, 刘昌岭, 伍操为. 气体水合物生成实验过程动态监测:一种新的ERT方法及其效果分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 193-201. |
| [6] | 胡高伟, 吴能友, 李琦, 白辰阳, 万义钊, 黄丽, 王代刚, 李彦龙, 陈强. 海域天然气水合物试采目标优选定量评价方法初探[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 202-211. |
| [7] | 王进寿, 卢振权, 王富春, 陈静, 薛万文, 张志清. 羌塘北缘开心岭—乌丽冻土区水溶烃组分及甲烷碳、氢同位素特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(06): 1306-1313. |
| [8] | 周亚龙, 杨志斌, 张富贵, 张舜尧, 孙忠军, 王惠艳. 祁连山天然气水合物地球化学勘查方法稳定性和异常重现性分析[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(06): 1314-1324. |
| [9] | 范东稳, 卢振权, 肖睿, 牛索安, 祁拉加, 魏毅, 张永安, 费德亮, 党孝锋. 南祁连盆地木里坳陷石炭系—侏罗系天然气水合物潜在气源岩地质特征[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 985-994. |
| [10] | 周亚龙, 孙忠军, 杨志斌, 张富贵, 张舜尧. 祁连山木里冻土区天然气水合物矿区稀有气体氦、氖地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 995-1002. |
| [11] | 张富贵, 唐瑞玲, 杨志斌, 朱敬华, 周亚龙, 孙忠军. 漠河盆地多年冻土区天然气水合物地球化学调查及远景评价[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 1003-1011. |
| [12] | 张富贵, 王成文, 张舜尧, 周亚龙, 唐瑞玲. 热释光:一种冻土区天然气水合物地球化学勘查新技术[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 1080-1088. |
| [13] | 张舜尧, 杨帆, 张富贵, 施泽明, 杨志斌, 周亚龙, 王惠艳. 青藏高原冻土区湿地甲烷排放及同位素特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 1089-1096. |
| [14] | 万丽华, 梁徳青, 李栋梁, 关进安. 祁连山冻土区天然气水合物储层岩石热物性实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(02): 385-391. |
| [15] | 王超群, 丁莹莹, 胡道功, 戚帮申, 张耀玲, 陶涛, 吴环环. 祁连山冻土区DK-9孔温度监测及天然气水合物稳定带厚度[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(01): 158-166. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||