



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (02): 345-355.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.02.13
黎霆( ), 诸丹诚, 李海平, 杨明磊, 李涛, 李平平, 邹华耀(
), 诸丹诚, 李海平, 杨明磊, 李涛, 李平平, 邹华耀( )
)
收稿日期:2019-05-20
修回日期:2019-09-07
出版日期:2020-05-25
发布日期:2020-05-25
通讯作者:
邹华耀
作者简介:邹华耀,男,教授,博士生导师;1963年出生,石油地质学专业,主要从事油气成藏机理与富集规律的教学与科研工作。Email: huayaozou@cup.edu.cn。基金资助:
LI Ting( ), ZHU Dancheng, LI Haiping, YANG Minglei, LI Tao, LI Pingping, ZOU Huayao(
), ZHU Dancheng, LI Haiping, YANG Minglei, LI Tao, LI Pingping, ZOU Huayao( )
)
Received:2019-05-20
Revised:2019-09-07
Online:2020-05-25
Published:2020-05-25
Contact:
ZOU Huayao
摘要:
白云岩储层是茅口组一种重要的储层类型,其成因是研究重点。为此,以川中-川东地区茅口组白云岩为例,通过露头观测、岩心观察、岩石薄片鉴定及岩石地球化学分析的方法,分析了茅口组白云岩(石)的成因。结果表明:茅口组白云岩(石)可划分为层状粉晶白云岩、层状细-中晶白云岩、灰岩中零散分布的白云石、透镜状中-粗晶白云岩和鞍形白云石胶结物5种类型。其中,层状粉晶白云岩原始结构保存较好,地球化学特征与原始灰岩相似,是早期埋藏环境下形成的产物;层状细-中晶白云岩与层状粉晶白云岩相伴生,δ18O值较灰岩偏负,包裹体均一温度大于正常地层埋藏温度,部分样品可见Eu正异常,是由层状粉晶白云岩在热液作用下重结晶形成;灰岩中零散分布的白云石则与矿物的稳定化有关;透镜状中-粗晶白云岩和鞍形白云石胶结物镜下可见白云石晶面弯曲和波状消光,其δ18O值可达-10‰,包裹体均一温度高于正常地层埋藏温度,Eu正异常明显,是典型的热液白云岩(石)。
中图分类号:
黎霆, 诸丹诚, 李海平, 杨明磊, 李涛, 李平平, 邹华耀. 中二叠统茅口组白云岩发育机理:以川中-川东地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(02): 345-355.
LI Ting, ZHU Dancheng, LI Haiping, YANG Minglei, LI Tao, LI Pingping, ZOU Huayao. Genetic Mechanism of Dolomite in Middle Permian Maokou Formation:Case Study of Central and Eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(02): 345-355.

图2 茅口组白云岩宏观特征 A.层状白云岩,华蓥二崖剖面,茅二段;B.A中红框放大,见明显的晶粒结构;C.透镜状白云岩,与围岩突变接触,华蓥二崖剖面,茅二段;D.层状白云岩,发育条带状硅质岩和条带状方解石,白云岩中可见残余生屑,丰都放牛坝,茅三段;E.破碎的硅质团块被白云石胶结,丰都放牛坝剖面,茅三段;F.鞍形白云石沿缝洞壁充填,基岩为粉-细白云岩,泰来6井,茅三段;G.粉-细晶白云岩,发育热碎裂作用形成的裂缝和角砾,裂缝中充填白云石、方解石和石英(红圈处);H.透镜状白云岩,溶洞中充填方解石和沥青,丰都放牛坝剖面,茅三段;I.斑马状构造,丰都放牛坝剖面,茅三段;Dol.白云岩(石);Cal.方解石;Lim.灰岩;Bre.角砾;Si.硅质岩;SD.鞍形白云石;Bit.沥青
Fig.2 Macroscopic characteristics of dolomite in Moukou Formation
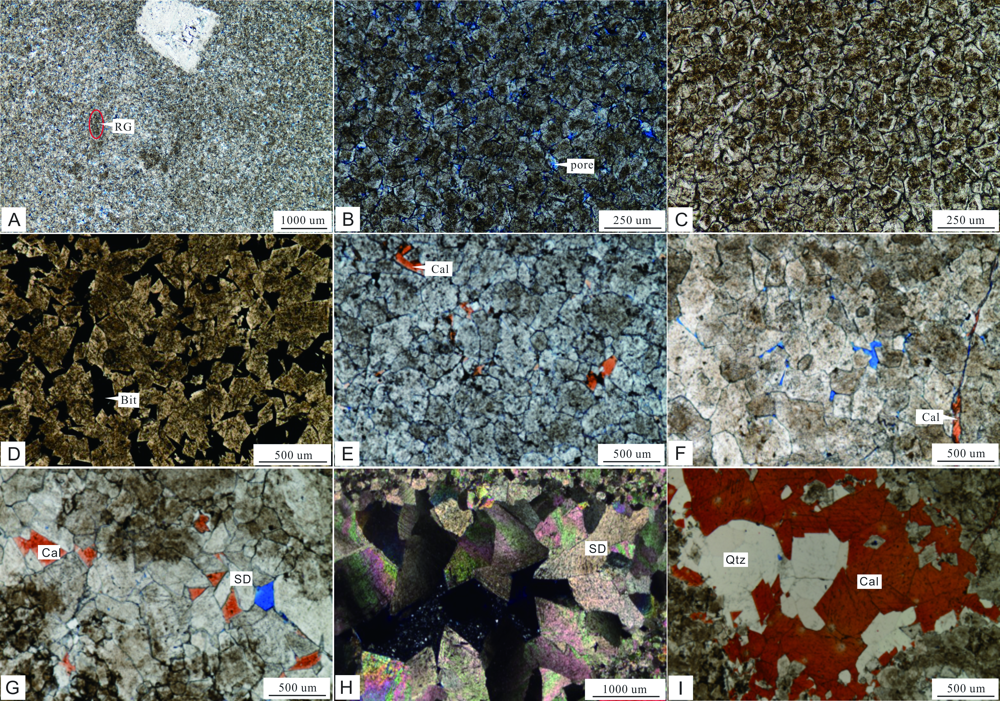
图3 茅口组白云岩微观特征 A.粉晶白云岩,见残余颗粒结构,发育晶间孔隙,丰都放牛坝,茅三段,层状;B.粉晶白云岩,丰都放牛坝剖面,茅三段,层状;C.粉晶白云岩,见雾心亮边结构,丰都放牛坝剖面,茅三段,层状;D.细晶白云岩,泰来6井,茅三段,层状;E.中晶白云岩,晶体晶面弯曲,丰都放牛坝,茅三段,层状;F.粗晶白云岩,华蓥二崖剖面,茅二段,透镜状;G.鞍形白云岩沿洞壁发育,见波状消光,与黄铁矿伴生,泰来6井,5 505.2 m; H.溶洞被方解石和石英全充填,丰都放牛坝,茅三段;I.粗晶白云岩,发育鞍形白云石,丰都放牛坝,茅三段,透镜状;RG.残余颗粒结构;Bit.沥青;Cal.方解石;Dol.白云石;SD.鞍形白云石;Py.黄铁矿;Qtz.石英
Fig.3 Microscopic characteristics of dolomite in Moukou Formation
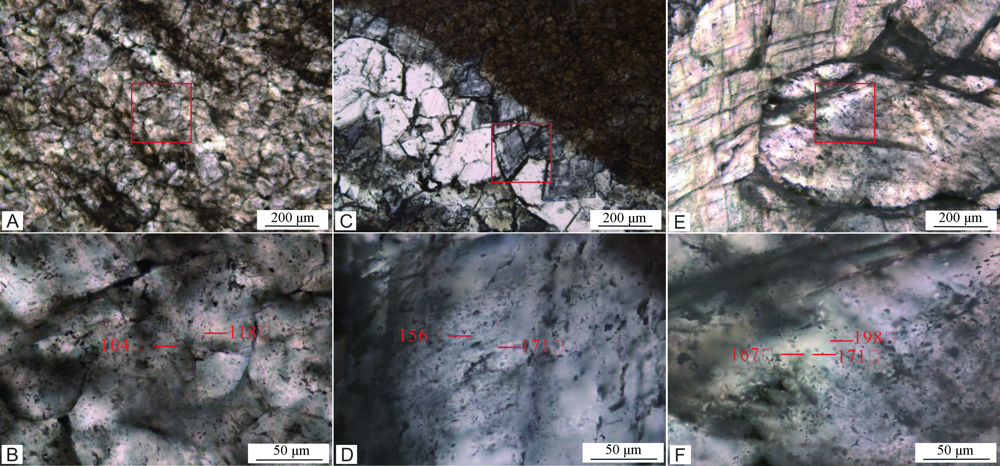

图8 茅口组不同类型白云岩流体包裹体特征 A.细晶白云岩,华蓥二崖,茅二段,层状;B.A中红框放大照片;C.粉晶白云岩,发育鞍形白云石胶结物,泰来6井,茅三段,5 505.1 m;D.C中红框处放大照片;E.粗晶白云岩,华蓥二崖,茅二段,透镜状;F.E中红框放大
Fig.8 Fluid inclusion from different types of dolomite in Maokou Formation
| 样品来源 | 岩石类型 | 包裹体类型 | 气液比/% | 包裹体均一 温度范围/℃ | 包裹体均一 温度平均值/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丰都放牛坝剖面 泰来6井 | 层状粉晶白云岩 | 液态包裹体 | / | / | / |
| 丰都放牛坝剖面 华蓥二崖剖面 | 层状细-中晶白云岩 | 气液两相包裹体 | 5~10 | 108.3~134.4 | 116.9 |
| 华蓥二崖剖面 | 透镜状中粗晶白云岩 | 气液两相包裹体 | 5~10 | 92.7~185.6 | 114.8 |
| 丰都放牛坝剖面、 泰来6井、华蓥二崖剖面 | 鞍形白云岩胶结物 | 气液两相包裹体 | 5~10 | 93.7~198.4 | 126.4 |
表1 茅口组不同类型白云岩包裹体均一温度统计表
Table 1 Homogenization temperature of inclusions from different types of dolomite in Maokou Formation
| 样品来源 | 岩石类型 | 包裹体类型 | 气液比/% | 包裹体均一 温度范围/℃ | 包裹体均一 温度平均值/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丰都放牛坝剖面 泰来6井 | 层状粉晶白云岩 | 液态包裹体 | / | / | / |
| 丰都放牛坝剖面 华蓥二崖剖面 | 层状细-中晶白云岩 | 气液两相包裹体 | 5~10 | 108.3~134.4 | 116.9 |
| 华蓥二崖剖面 | 透镜状中粗晶白云岩 | 气液两相包裹体 | 5~10 | 92.7~185.6 | 114.8 |
| 丰都放牛坝剖面、 泰来6井、华蓥二崖剖面 | 鞍形白云岩胶结物 | 气液两相包裹体 | 5~10 | 93.7~198.4 | 126.4 |

图9 茅口组不同类型白云岩阴极发光特征 A.粉晶白云岩,见完整的生物颗粒,丰都放牛坝剖面,茅三段,层状;B.A对应的阴极发光照片,方解石胶结物不放光,白云石发暗红色光;C.细-中晶白云岩;见生物幻影,丰都放牛坝剖面,茅三段,层状;D.C对应的阴极发光照片,整体发暗红色光,局部发亮红色光;E.中-粗晶白云岩,见方解石胶结物,华蓥二崖剖面,茅二段,透镜状;F.E对应的阴极发光照片,方解石胶结物发暗色光,白云石发亮红色光;G.粉-细晶白云岩,见鞍形白云石胶结物,泰来6井,茅三段,5 491.9 m;H.G对应的阴极发光照片,粉-细晶白云石发暗红色光,鞍形白云石发亮红色光
Fig.9 Cathodoluminescence characteristics of different types of dolomite in Maokou Formation
| [1] | 胡安平, 潘立银, 郝毅, 等. 四川盆地二叠系栖霞组、茅口组白云岩储层特征、成因和分布[J]. 海相油气地质, 2018,23(2):39-51. |
| [2] | 王良军, 杨诚, 王庆波, 等. 四川盆地涪陵地区茅口组热液白云岩储层预测[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2018,40(3):298-305. |
| [3] | 宋晓波, 隆轲, 王琼仙, 等. 四川盆地西部中二叠统茅口组油气地质条件及勘探潜力[J]. 海相油气地质, 2016,21(1):1-6. |
| [4] | 杨光, 汪华, 沈浩, 等. 四川盆地中二叠统储层特征与勘探方向[J]. 天然气工业, 2015,35(7):10-16. |
| [5] | 张荫本. 四川盆地二迭系中的白云岩化[J]. 石油学报, 1982,3(1):33-37. |
| [6] | 宋文海. 四川盆地二叠系白云岩的分布及天然气勘探[J]. 天然气工业, 1985,4(4):32-33. |
| [7] | 何幼斌, 冯增昭. 四川盆地及其周缘下二叠统细-粗晶白云岩成因探讨[J]. 江汉石油学院学报, 1996,18(4):15-20. |
| [8] | 廖小漫, 张本健, 徐后伟, 等. 川西地区中二叠统储集层成岩作用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2012,33(3):312-315. |
| [9] | 金振奎, 冯增昭. 滇东—川西下二叠统白云岩的形成机理——玄武岩淋滤白云化[J]. 沉积学报, 1999,17(3):383-389. |
| [10] | 李毅, 沈浩, 石学文, 等. 川东—川中地区茅口组白云岩成因初探及“热次盆” 概念的提出[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2013,36(4):1-3. |
| [11] | 汪华, 沈浩, 黄东, 等. 四川盆地中二叠统热水白云岩成因及其分布[J]. 天然气工业, 2014,34(9):25-32. |
| [12] | 赵锡奎. 黔中下二叠统碳酸盐岩中的构造-埋藏热液白云化作用[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 1991,8(6):41-47. |
| [13] | 陈轩, 赵文智, 刘银河, 等. 川西南地区中二叠统热液白云岩特征及勘探思路[J]. 石油学报, 2013,34(3):460-466. |
| [14] | 李祖兵, 欧加强, 陈轩, 等. 川中地区下二叠统白云岩储层特征及发育主控因素[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2017,36(4):1-8. |
| [15] | 蒋裕强, 谷一凡, 李开鸿, 等. 四川盆地中部中二叠统热液白云岩储渗空间类型及成因[J]. 天然气工业, 2018,38(2):16-24. |
| [16] | 王珏博, 谷一凡, 陶艳忠, 等. 川中地区茅口组两期流体叠合控制下的白云石化模式[J]. 沉积学报, 2016,34(2):236-249. |
| [17] | 刘建强, 郑浩夫, 刘波, 等. 川中地区中二叠统茅口组白云岩特征及成因机理[J]. 石油学报, 2017,38(4):386-398. |
| [18] | 赵宗举, 周慧, 陈轩, 等. 四川盆地及邻区二叠纪层序岩相古地理及有利勘探区带[J]. 石油学报, 2012,33(增刊2):35-51. |
| [19] | 何斌, 徐义刚, 王雅玫, 等. 东吴运动性质的厘定及其时空演变规律[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2005,30(1):89-96. |
| [20] | 刘成英, 朱日祥. 试论峨眉山玄武岩的地球动力学含义[J]. 地学前缘, 2009(2):52-69. |
| [21] | 何斌, 徐义刚, 肖龙, 等. 峨眉山大火成岩省的形成机制及空间展布:来自沉积地层学的新证据[J]. 地质学报, 2003,77(2):194-202. |
| [22] | 朱传庆, 徐明, 袁玉松, 等. 峨眉山玄武岩喷发在四川盆地的地热学响应[J]. 科学通报, 2010,55(6):474-482. |
| [23] | 解发川. 四川盆地西—北部中二叠统热液作用及对储层影响[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2012. |
| [24] | PRATT B R. Limestone response to stress:Pressure solution and dolomitization—Discussion and examples of compaction in carbonate sediments[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1982,52(1):323-328. |
| [25] | CAI C, LI K, LI H, et al. Evidence for cross formational hot brine flow from integrated 87Sr/86Sr, REE and fluid inclusion of the Ordovician veins in Central Tarim, China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2008,23(8):2226-2235. |
| [26] | JNES C E, JENKYNS H C. Seawater strontium isotopes,oceanic anoxic events, and seafloor hydrothermal activity in the Jurassic and Cretaceous[J]. American Journal of Science, 2001,302(2):112-149. |
| [27] | BANNER J L, HANSON G N, MEYERS W J. Rare earth element and Nd isotopic variations in regionally extensive dolomites from the Burlington-Keokuk Formation (Mississippian):implications for REE mobility during carbonate diagenesis[J]. J Sed Petrol, 1988,58:415-432. |
| [28] | WEB G E, KAMBER B S. Rare earth elements in Holocene reefal microbialites: a new shallow seawater proxy[J]. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 2000,64:1557-1565. |
| [29] | HECHT L, FREIBERGER R, GILG H A, et al. Rare earth element and isotope(C, O, Sr)characteristics of hydrothermal carbonates:genetic implications for dolomite-hosted talc mineralization at Göpfersgrǜn (Fichtelgebirge, Germany)[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999,155:115-130. |
| [30] | 赵孟军, 宋岩, 秦胜飞, 等. 中国中-西部4种新生代挤压盆地成藏地质条件及成藏期次[J]. 地质科学, 2007,42(2):234-252. |
| [31] | 马永生, 蔡勋育, 赵培荣, 等. 四川盆地大中型天然气田分布特征与勘探方向[J]. 石油学报, 2010,31(3):347-354. |
| [32] | 江青春, 胡素云, 汪泽成, 等. 四川盆地中二叠统中-粗晶白云岩成因[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014,35(4):503-510. |
| [33] | 黄思静. 碳酸盐矿物的阴极发光性与其Fe,Mn含量的关系[J]. 矿物岩石, 1992(4):74-79. |
| [34] | DAVIES G R, SMITH L B. Structurally controlled hydrothermal dolomite reservoir facies: An overview[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2006,90(11):1641-1690. |
| [35] | 杨博, 蔡忠贤, 赵文光. 川东北飞仙关组白云岩岩石结构演化[J]. 现代地质, 2010,24(5):945-950. |
| [36] | 陈轩, 赵文智, 张利萍, 等. 川中地区中二叠统构造热液白云岩的发现及其勘探意义[J]. 石油学报, 2012,33(4):562-569. |
| [37] | KOZUR H W, KORTE C, BRUCKSCHEN P, et al. Strontium isotope evolution of Late Permian and Triassic seawater[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2003,67(1):47-62. |
| [38] | 王东, 王国芝. 四川南江地区灯影组白云岩优质储层的形成与演化[J]. 现代地质, 2011,25(4):660-667. |
| [1] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [2] | 谭聪, 刘策, 王铜山, 李秋芬, 朱玺, 付景龙, 姜华. 局部白云岩化作用研究:以塔里木盆地阿克苏地区蓬莱坝剖面鹰山组为例[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1182-1193. |
| [3] | 张一范, 高远, 陈积权, 黄帅, 海伦, 毋正轩, 杨柳, 董甜. 松辽盆地晚白垩世湖相白云岩碳氧同位素特征及其古环境意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1243-1253. |
| [4] | 于景维, 丁韦, 张欣, 祁利祺, 黄舒雅, 张智越, 张以勒. 准噶尔盆地AH5井区八道湾组碳酸盐胶结物成因及对储层影响分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1336-1344. |
| [5] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [6] | 周洪福, 方甜, 夏晨皓, 冉涛, 徐如阁, 张景华. 工程扰动诱发川西杜米滑坡复活变形特征及机理分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 1044-1053. |
| [7] | 梁东, 华北, 赵德怀, 吴浩, 万生楠, 谭朝欣, 赵晓健, 杨志鹏. 喀喇昆仑麦拉山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征与找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 708-721. |
| [8] | 张改侠, 孙金佳杰, 龚庆杰, 江彪, 严桃桃. 云南潞西上芒岗金矿区白云岩风化的地球化学基因[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 801-812. |
| [9] | 娄元林, 成明, 唐侥, 张潮明, 蓝景周, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征、构造环境分析及成矿响应[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| [10] | 邓科, 王金贵, 董玉杰, 何林武, 袁仁华, 张泽国, 陈守关, 辛堂. 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世中性侵入岩的成因及对新特提斯板块北向俯冲的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 375-389. |
| [11] | 夏锦胜, 孙莉, 张鹏, 陈昌阔, 汪君珠, 司江福. 四川坪河晶质石墨矿床地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1486-1496. |
| [12] | 陈世明, 杨镇熙, 雷自强, 康维良, 张晶, 赵青虎. 甘肃北山前红泉地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1513-1524. |
| [13] | 刘同, 刘传朋, 康鹏宇, 赵秀芳, 邓俊, 王凯凯. 山东省沂南县东部土壤重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1173-1182. |
| [14] | 刘洋, 李贤庆, 赵光杰, 刘满仓, 董才源, 李谨, 肖中尧. 库车坳陷东部吐格尔明地区天然气地球化学特征及油气充注史[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 988-997. |
| [15] | 王斌, 任涛, 宋伊圩, 杨可, 王占彬, 孙亚柯. 西秦岭常家山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 911-922. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||