



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (03): 483-493.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.009
张海华( ), 李永飞, 张健, 苏飞, 郑月娟, 卞雄飞, 张德军
), 李永飞, 张健, 苏飞, 郑月娟, 卞雄飞, 张德军
收稿日期:2018-05-05
修回日期:2019-12-11
出版日期:2020-07-04
发布日期:2020-07-05
作者简介:张海华,男,硕士研究生,1986年出生,构造地质专业,主要从事岩石学、大地构造学研究。Email: zhanghaihua311@163.com。
基金资助:
ZHANG Haihua( ), LI Yongfei, ZHANG Jian, SU Fei, ZHENG Yuejuan, BIAN Xiongfei, ZHANG Dejun
), LI Yongfei, ZHANG Jian, SU Fei, ZHENG Yuejuan, BIAN Xiongfei, ZHANG Dejun
Received:2018-05-05
Revised:2019-12-11
Online:2020-07-04
Published:2020-07-05
摘要:
对内蒙古乌兰浩特地区出露的花岗岩侵入体进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年和岩石地球化学研究,以探讨该区花岗岩形成时代、成因类型和区域构造演化。结果显示,其锆石206Pb/238U年龄的加权平均值为(214.4±2.6) Ma,反映岩体的结晶年龄为晚三叠世。岩石主量元素具高硅、高碱、富钾,贫钙、贫镁及低钛的特征;稀土元素配分曲线呈“海鸥式”较弱的右倾分布特征,具有强烈的Eu负异常;微量元素Rb、Th、Zr、Y和Yb含量较高,Ba、Sr含量较低,岩石具有高的Rb/Sr 、Rb/Nb 值,显示为低 Sr、高 Yb 型花岗岩的特征。综合分析显示花岗岩形成的压力较低,应为减薄地壳物质熔融的产物。综合区域构造演化和K2O-Na2O、(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-(Na2O+K2O)/CaO、SiO2-TFeO/MgO、(Y+Nb)-Rb、(Yb+Ta)-Rb、Nb-Y-Ce图解分析,认为该岩体形成于造山后伸展构造背景,研究区由中三叠世的碰撞造山构造体制向晚三叠世造山后伸展构造体制转变,同时西伯利亚板块和华北板块的碰撞时限持续到中三叠世。
中图分类号:
张海华, 李永飞, 张健, 苏飞, 郑月娟, 卞雄飞, 张德军. 大兴安岭中部乌兰浩特地区花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 483-493.
ZHANG Haihua, LI Yongfei, ZHANG Jian, SU Fei, ZHENG Yuejuan, BIAN Xiongfei, ZHANG Dejun. Zircon U-Pb Age, Geochemical Characteristics and Tectonic Implications of Granites in the Wulanhaote Area, Central Daxing’an Mountains[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(03): 483-493.

图2 二长花岗岩露头(a)及镜下特征(正交偏光)照片(b) Kfs.钾长石; PlI 斜长石; QIz. 石英; Bt.黑云母薄片样品D1125b镜下特征:岩石矿物成分主要为钾长石、斜长石、石英和黑云母等。斜长石半自形板状,大小一般为1~2 mm,部分2~5 mm,少部分0.5~1.0 mm,杂乱分布,被绢云母及铁质交代,含量30%~35%;钾长石半自形板状,大小一般为2~5 mm,部分1~2 mm,少部分0.5~1.0 mm,杂乱分布,含量40%~45%;石英它形粒状,大小一般为2~5 mm,部分1~2 mm,少部分0.5~1.0 mm,填隙状分布,含量25%~30%;黑云母呈片状,片直径一般为0.5~1.0 mm,少部分0.2~0.5 mm,呈星散状分布,多被绢云母、绿泥石及铁质交代。岩石可见少量显微裂隙,沿裂隙有不透明矿物充填交代(图2(b))。
Fig.2 Field (a) and microscopic (b) photos of the monzogranite
| 测 试点 | 元素含量/(mg/g) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 同位素年龄/Ma | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 232Th | 238U | 206Pb | 207Pb/ 206Pb±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U±1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U±1σ | |||
| 1 | 1 578.95 | 4 397.73 | 190.61 | 0.36 | 0.051 96±0.002 35 | 0.244 03±0.009 83 | 0.034 06±0.000 70 | 284±106 | 222±8 | 216±4 | |
| 2 | 1 333.41 | 3 592.65 | 161.13 | 0.37 | 0.061 01±0.002 88 | 0.280 35±0.011 86 | 0.033 33±0.000 70 | 639±104 | 251±9 | 211±4 | |
| 3 | 43.12 | 147.30 | 7.50 | 0.29 | 0.051 16±0.002 82 | 0.295 30±0.016 10 | 0.041 87±0.000 97 | 248±83 | 263±13 | 264±6 | |
| 4 | 13.11 | 44.26 | 2.23 | 0.30 | 0.050 85±0.004 05 | 0.287 38±0.022 59 | 0.040 99±0.001 05 | 234±131 | 256±18 | 259±7 | |
| 5* | 671.63 | 1 085.02 | 48.25 | 0.62 | 0.078 75±0.001 74 | 0.363 58±0.008 30 | 0.033 48±0.000 68 | 1 166±20 | 315±6 | 212±4 | |
| 6 | 220.82 | 510.71 | 22.88 | 0.43 | 0.058 18±0.003 22 | 0.267 41±0.013 65 | 0.033 33±0.000 72 | 537±125 | 241±11 | 211±4 | |
| 7 | 254.17 | 543.10 | 23.58 | 0.47 | 0.050 90±0.001 35 | 0.238 81±0.006 47 | 0.034 03±0.000 70 | 236±29 | 217±5 | 216±4 | |
| 8 | 90.26 | 251.17 | 10.90 | 0.36 | 0.051 29±0.001 75 | 0.245 84±0.008 44 | 0.034 76±0.000 73 | 254±42 | 223±7 | 220±5 | |
| 9* | 345.74 | 563.04 | 34.14 | 0.61 | 0.078 65±0.005 19 | 0.394 26±0.024 40 | 0.036 36±0.000 83 | 1 163±134 | 337±18 | 230±5 | |
| 10 | 43.84 | 106.50 | 4.71 | 0.41 | 0.051 03±0.002 82 | 0.243 31±0.013 30 | 0.034 58±0.000 80 | 242±83 | 221±11 | 219±5 | |
| 11 | 179.54 | 310.83 | 14.37 | 0.58 | 0.051 59±0.001 50 | 0.250 61±0.007 38 | 0.035 22±0.000 73 | 267±33 | 227±6 | 223±5 | |
| 12 | 34.23 | 91.16 | 3.80 | 0.38 | 0.052 21±0.003 52 | 0.240 15±0.015 92 | 0.033 35±0.000 82 | 295±106 | 219±13 | 211±5 | |
| 13 | 55.57 | 153.71 | 6.51 | 0.36 | 0.051 95±0.002 76 | 0.241 48±0.012 67 | 0.033 70±0.007 70 | 283±78 | 220±10 | 214±5 | |
| 14 | 71.53 | 154.84 | 7.11 | 0.46 | 0.050 22±0.002 82 | 0.248 92±0.013 84 | 0.035 94±0.000 82 | 205±87 | 226±11 | 228±5 | |
| 15 | 24.84 | 78.57 | 4.02 | 0.32 | 0.052 57±0.002 42 | 0.295 96±0.013 52 | 0.040 82±0.000 90 | 310±64 | 263±11 | 258±6 | |
| 16* | 118.47 | 139.99 | 7.02 | 0.85 | 0.105 45±0.006 07 | 0.479 84±0.025 20 | 0.033 00±0.000 78 | 1 722±109 | 398±17 | 209±5 | |
| 17 | 40.10 | 99.36 | 4.59 | 0.40 | 0.064 50±0.004 69 | 0.294 32±0.020 25 | 0.033 09±0.000 77 | 758±158 | 262±16 | 210±5 | |
| 18 | 52.40 | 75.46 | 3.98 | 0.69 | 0.051 59±0.003 57 | 0.282 68±0.019 28 | 0.039 72±0.000 98 | 267±111 | 253±15 | 251±6 | |
| 19 | 75.44 | 217.32 | 9.36 | 0.35 | 0.057 30±0.003 23 | 0.266 00±0.013 86 | 0.033 67±0.000 73 | 503±128 | 239±11 | 213±5 | |
| 20 | 82.69 | 162.11 | 7.02 | 0.51 | 0.049 73±0.001 75 | 0.227 71±0.008 01 | 0.033 19±0.000 70 | 182±44 | 208±7 | 210±4 | |
| 21* | 120.45 | 252.94 | 10.39 | 0.48 | 0.053 82±0.003 21 | 0.226 12±0.012 58 | 0.030 47±0.000 66 | 364±138 | 207±10 | 193±4 | |
| 22 | 102.66 | 210.93 | 9.08 | 0.49 | 0.051 52±0.001 50 | 0.236 49±0.006 97 | 0.033 28±0.000 68 | 264±33 | 216±6 | 211±4 | |
| 23 | 58.65 | 115.65 | 5.01 | 0.51 | 0.050 01±0.002 05 | 0.230 07±0.009 37 | 0.033 35±0.000 71 | 195±56 | 210±8 | 211±4 | |
| 24 | 86.26 | 190.25 | 8.47 | 0.45 | 0.048 62±0.001 87 | 0.232 39±0.008 88 | 0.034 65±0.000 74 | 130±51 | 212±7 | 220±5 | |
| 25 | 72.16 | 160.08 | 7.92 | 0.45 | 0.057 51±0.004 04 | 0.261 24±0.017 42 | 0.032 95±0.000 74 | 511±159 | 236±14 | 209±5 | |
表1 三叠纪二长花岗岩样品锆石U-Pb定年数据
Table 1 Zircon U-Pb dating results of the Triassic monzogranite sample D1125TWS
| 测 试点 | 元素含量/(mg/g) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 同位素年龄/Ma | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 232Th | 238U | 206Pb | 207Pb/ 206Pb±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U±1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U±1σ | |||
| 1 | 1 578.95 | 4 397.73 | 190.61 | 0.36 | 0.051 96±0.002 35 | 0.244 03±0.009 83 | 0.034 06±0.000 70 | 284±106 | 222±8 | 216±4 | |
| 2 | 1 333.41 | 3 592.65 | 161.13 | 0.37 | 0.061 01±0.002 88 | 0.280 35±0.011 86 | 0.033 33±0.000 70 | 639±104 | 251±9 | 211±4 | |
| 3 | 43.12 | 147.30 | 7.50 | 0.29 | 0.051 16±0.002 82 | 0.295 30±0.016 10 | 0.041 87±0.000 97 | 248±83 | 263±13 | 264±6 | |
| 4 | 13.11 | 44.26 | 2.23 | 0.30 | 0.050 85±0.004 05 | 0.287 38±0.022 59 | 0.040 99±0.001 05 | 234±131 | 256±18 | 259±7 | |
| 5* | 671.63 | 1 085.02 | 48.25 | 0.62 | 0.078 75±0.001 74 | 0.363 58±0.008 30 | 0.033 48±0.000 68 | 1 166±20 | 315±6 | 212±4 | |
| 6 | 220.82 | 510.71 | 22.88 | 0.43 | 0.058 18±0.003 22 | 0.267 41±0.013 65 | 0.033 33±0.000 72 | 537±125 | 241±11 | 211±4 | |
| 7 | 254.17 | 543.10 | 23.58 | 0.47 | 0.050 90±0.001 35 | 0.238 81±0.006 47 | 0.034 03±0.000 70 | 236±29 | 217±5 | 216±4 | |
| 8 | 90.26 | 251.17 | 10.90 | 0.36 | 0.051 29±0.001 75 | 0.245 84±0.008 44 | 0.034 76±0.000 73 | 254±42 | 223±7 | 220±5 | |
| 9* | 345.74 | 563.04 | 34.14 | 0.61 | 0.078 65±0.005 19 | 0.394 26±0.024 40 | 0.036 36±0.000 83 | 1 163±134 | 337±18 | 230±5 | |
| 10 | 43.84 | 106.50 | 4.71 | 0.41 | 0.051 03±0.002 82 | 0.243 31±0.013 30 | 0.034 58±0.000 80 | 242±83 | 221±11 | 219±5 | |
| 11 | 179.54 | 310.83 | 14.37 | 0.58 | 0.051 59±0.001 50 | 0.250 61±0.007 38 | 0.035 22±0.000 73 | 267±33 | 227±6 | 223±5 | |
| 12 | 34.23 | 91.16 | 3.80 | 0.38 | 0.052 21±0.003 52 | 0.240 15±0.015 92 | 0.033 35±0.000 82 | 295±106 | 219±13 | 211±5 | |
| 13 | 55.57 | 153.71 | 6.51 | 0.36 | 0.051 95±0.002 76 | 0.241 48±0.012 67 | 0.033 70±0.007 70 | 283±78 | 220±10 | 214±5 | |
| 14 | 71.53 | 154.84 | 7.11 | 0.46 | 0.050 22±0.002 82 | 0.248 92±0.013 84 | 0.035 94±0.000 82 | 205±87 | 226±11 | 228±5 | |
| 15 | 24.84 | 78.57 | 4.02 | 0.32 | 0.052 57±0.002 42 | 0.295 96±0.013 52 | 0.040 82±0.000 90 | 310±64 | 263±11 | 258±6 | |
| 16* | 118.47 | 139.99 | 7.02 | 0.85 | 0.105 45±0.006 07 | 0.479 84±0.025 20 | 0.033 00±0.000 78 | 1 722±109 | 398±17 | 209±5 | |
| 17 | 40.10 | 99.36 | 4.59 | 0.40 | 0.064 50±0.004 69 | 0.294 32±0.020 25 | 0.033 09±0.000 77 | 758±158 | 262±16 | 210±5 | |
| 18 | 52.40 | 75.46 | 3.98 | 0.69 | 0.051 59±0.003 57 | 0.282 68±0.019 28 | 0.039 72±0.000 98 | 267±111 | 253±15 | 251±6 | |
| 19 | 75.44 | 217.32 | 9.36 | 0.35 | 0.057 30±0.003 23 | 0.266 00±0.013 86 | 0.033 67±0.000 73 | 503±128 | 239±11 | 213±5 | |
| 20 | 82.69 | 162.11 | 7.02 | 0.51 | 0.049 73±0.001 75 | 0.227 71±0.008 01 | 0.033 19±0.000 70 | 182±44 | 208±7 | 210±4 | |
| 21* | 120.45 | 252.94 | 10.39 | 0.48 | 0.053 82±0.003 21 | 0.226 12±0.012 58 | 0.030 47±0.000 66 | 364±138 | 207±10 | 193±4 | |
| 22 | 102.66 | 210.93 | 9.08 | 0.49 | 0.051 52±0.001 50 | 0.236 49±0.006 97 | 0.033 28±0.000 68 | 264±33 | 216±6 | 211±4 | |
| 23 | 58.65 | 115.65 | 5.01 | 0.51 | 0.050 01±0.002 05 | 0.230 07±0.009 37 | 0.033 35±0.000 71 | 195±56 | 210±8 | 211±4 | |
| 24 | 86.26 | 190.25 | 8.47 | 0.45 | 0.048 62±0.001 87 | 0.232 39±0.008 88 | 0.034 65±0.000 74 | 130±51 | 212±7 | 220±5 | |
| 25 | 72.16 | 160.08 | 7.92 | 0.45 | 0.057 51±0.004 04 | 0.261 24±0.017 42 | 0.032 95±0.000 74 | 511±159 | 236±14 | 209±5 | |
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | A/CNK | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1125HX-1 | 77.14 | 0.074 | 12.12 | 1.01 | 0.49 | 0.039 | 0.051 | 0.16 | 3.84 | 4.67 | 0.006 0 | 0.73 | 99.605 1 | 1.038 9 | ||||
| D1125HX-2 | 76.22 | 0.081 | 12.84 | 0.26 | 0.45 | 0.024 | 0.089 | 0.23 | 4.08 | 4.90 | 0.009 0 | 0.75 | 99.178 1 | 1.033 3 | ||||
| D1125HX-3 | 75.59 | 0.090 | 12.86 | 0.57 | 0.63 | 0.033 | 0.140 | 0.29 | 3.89 | 4.68 | 0.008 0 | 0.82 | 98.771 1 | 1.072 8 | ||||
| D1125HX-4 | 76.93 | 0.081 | 12.80 | 0.37 | 0.49 | 0.025 | 0.080 | 0.25 | 3.90 | 4.76 | 0.008 5 | 0.88 | 99.690 1 | 1.064 3 | ||||
| 样品编号 | Ba | Rb | Sr | Zr | Nb | Th | U | Pb | Ga | Cu | Ni | Cr | Cs | Sc | ||||
| D1125HX-1 | 76.4 | 188 | 25.3 | 131 | 23.3 | 19.6 | 2.63 | 40.6 | 26.7 | 3.37 | 2.24 | 4.48 | 3.26 | 4.15 | ||||
| D1125HX-2 | 61.1 | 215 | 20.8 | 135 | 18.0 | 19.1 | 2.59 | 37.2 | 29.2 | 2.83 | 1.94 | 4.02 | 6.11 | 3.70 | ||||
| D1125HX-3 | 68.8 | 215 | 23.3 | 139 | 21.5 | 19.4 | 3.25 | 42.3 | 28.2 | 4.02 | 3.02 | 3.86 | 6.76 | 4.66 | ||||
| D1125HX-4 | 59.3 | 213 | 21.1 | 129 | 18.1 | 20.8 | 2.80 | 37.5 | 29.0 | 3.91 | 2.48 | 3.63 | 6.46 | 4.22 | ||||
| 样品编号 | Hf | Ta | Li | Co | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | ||||
| D1125HX-1 | 5.98 | 1.26 | 6.07 | 2.64 | 69.3 | 7.37 | 53.1 | 3.51 | 15.3 | 6.52 | 0.086 | 6.64 | 1.64 | 13.3 | ||||
| D1125HX-2 | 7.11 | 0.75 | 11.00 | 2.43 | 61.9 | 12.10 | 43.9 | 5.27 | 22.6 | 7.63 | 0.099 | 6.72 | 1.50 | 11.5 | ||||
| D1125HX-3 | 6.57 | 1.22 | 10.40 | 2.41 | 70.1 | 9.90 | 56.4 | 4.39 | 19.0 | 6.96 | 0.120 | 6.78 | 1.62 | 12.9 | ||||
| D1125HX-4 | 6.67 | 1.00 | 10.20 | 2.51 | 60.7 | 9.87 | 47.4 | 3.97 | 17.5 | 5.85 | 0.099 | 5.81 | 1.32 | 10.4 | ||||
| 样品编号 | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | δEu | δCe | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | ||||||
| D1125HX-1 | 2.52 | 7.58 | 1.09 | 7.85 | 0.88 | 0.039 5 | 2.549 1 | 2.070 4 | 0.673 4 | 127.296 4 | 85.836 9 | 41.459 5 | ||||||
| D1125HX-2 | 2.14 | 6.54 | 0.95 | 6.92 | 0.78 | 0.041 2 | 1.349 6 | 2.471 2 | 1.250 0 | 128.606 8 | 91.557 6 | 37.049 2 | ||||||
| D1125HX-3 | 2.46 | 7.44 | 1.08 | 7.63 | 0.85 | 0.053 4 | 2.094 6 | 2.374 5 | 0.930 4 | 137.539 2 | 96.780 6 | 40.758 7 | ||||||
| D1125HX-4 | 2.07 | 6.34 | 0.91 | 7.44 | 0.82 | 0.051 5 | 1.855 4 | 2.409 2 | 0.951 3 | 119.753 4 | 84.626 5 | 35.126 9 | ||||||
表2 二长花岗岩样品主量元素(%)、稀土元素(10-6)和微量元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 2 Analysis results of major elements (%), REE (10-6) and trace elements (10-6) of the monzogranite sample
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | A/CNK | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1125HX-1 | 77.14 | 0.074 | 12.12 | 1.01 | 0.49 | 0.039 | 0.051 | 0.16 | 3.84 | 4.67 | 0.006 0 | 0.73 | 99.605 1 | 1.038 9 | ||||
| D1125HX-2 | 76.22 | 0.081 | 12.84 | 0.26 | 0.45 | 0.024 | 0.089 | 0.23 | 4.08 | 4.90 | 0.009 0 | 0.75 | 99.178 1 | 1.033 3 | ||||
| D1125HX-3 | 75.59 | 0.090 | 12.86 | 0.57 | 0.63 | 0.033 | 0.140 | 0.29 | 3.89 | 4.68 | 0.008 0 | 0.82 | 98.771 1 | 1.072 8 | ||||
| D1125HX-4 | 76.93 | 0.081 | 12.80 | 0.37 | 0.49 | 0.025 | 0.080 | 0.25 | 3.90 | 4.76 | 0.008 5 | 0.88 | 99.690 1 | 1.064 3 | ||||
| 样品编号 | Ba | Rb | Sr | Zr | Nb | Th | U | Pb | Ga | Cu | Ni | Cr | Cs | Sc | ||||
| D1125HX-1 | 76.4 | 188 | 25.3 | 131 | 23.3 | 19.6 | 2.63 | 40.6 | 26.7 | 3.37 | 2.24 | 4.48 | 3.26 | 4.15 | ||||
| D1125HX-2 | 61.1 | 215 | 20.8 | 135 | 18.0 | 19.1 | 2.59 | 37.2 | 29.2 | 2.83 | 1.94 | 4.02 | 6.11 | 3.70 | ||||
| D1125HX-3 | 68.8 | 215 | 23.3 | 139 | 21.5 | 19.4 | 3.25 | 42.3 | 28.2 | 4.02 | 3.02 | 3.86 | 6.76 | 4.66 | ||||
| D1125HX-4 | 59.3 | 213 | 21.1 | 129 | 18.1 | 20.8 | 2.80 | 37.5 | 29.0 | 3.91 | 2.48 | 3.63 | 6.46 | 4.22 | ||||
| 样品编号 | Hf | Ta | Li | Co | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | ||||
| D1125HX-1 | 5.98 | 1.26 | 6.07 | 2.64 | 69.3 | 7.37 | 53.1 | 3.51 | 15.3 | 6.52 | 0.086 | 6.64 | 1.64 | 13.3 | ||||
| D1125HX-2 | 7.11 | 0.75 | 11.00 | 2.43 | 61.9 | 12.10 | 43.9 | 5.27 | 22.6 | 7.63 | 0.099 | 6.72 | 1.50 | 11.5 | ||||
| D1125HX-3 | 6.57 | 1.22 | 10.40 | 2.41 | 70.1 | 9.90 | 56.4 | 4.39 | 19.0 | 6.96 | 0.120 | 6.78 | 1.62 | 12.9 | ||||
| D1125HX-4 | 6.67 | 1.00 | 10.20 | 2.51 | 60.7 | 9.87 | 47.4 | 3.97 | 17.5 | 5.85 | 0.099 | 5.81 | 1.32 | 10.4 | ||||
| 样品编号 | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | δEu | δCe | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | ||||||
| D1125HX-1 | 2.52 | 7.58 | 1.09 | 7.85 | 0.88 | 0.039 5 | 2.549 1 | 2.070 4 | 0.673 4 | 127.296 4 | 85.836 9 | 41.459 5 | ||||||
| D1125HX-2 | 2.14 | 6.54 | 0.95 | 6.92 | 0.78 | 0.041 2 | 1.349 6 | 2.471 2 | 1.250 0 | 128.606 8 | 91.557 6 | 37.049 2 | ||||||
| D1125HX-3 | 2.46 | 7.44 | 1.08 | 7.63 | 0.85 | 0.053 4 | 2.094 6 | 2.374 5 | 0.930 4 | 137.539 2 | 96.780 6 | 40.758 7 | ||||||
| D1125HX-4 | 2.07 | 6.34 | 0.91 | 7.44 | 0.82 | 0.051 5 | 1.855 4 | 2.409 2 | 0.951 3 | 119.753 4 | 84.626 5 | 35.126 9 | ||||||
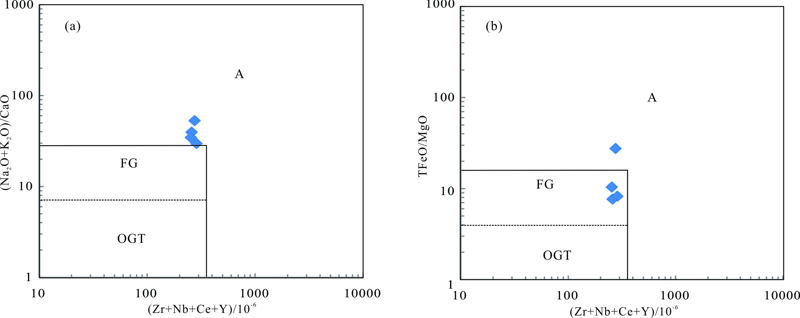
图9 二长花岗岩样品(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-(Na2O+K2O)/CaO(a)和(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-TFeO/MgO图解(b) FG.分异型 I型花岗岩;OGT.I、S、M型花岗岩;A.A型花岗岩
Fig.9 (Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-(Na2O+K2O)/CaO (a) and (Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-TFeO/MgO (b) I-type granite discriminationdiagrams of the monzogranite samples
| [1] | 吴福元, 孙德有, 林强. 东北地区显生宙花岗岩的成因与地壳增生[J]. 岩石学报, 1999,15(2):181-189. |
| [2] | 吴福元, 孙德有, 李惠民, 等. 松辽盆地基底岩石的锆石 U-Pb年龄[J]. 科学通报, 2000,45(6):656-660. |
| [3] | 吴福元, 杨进辉, 张艳斌, 等. 辽西东南部中生代花岗岩时代[J]. 岩石学报, 2006,22(2):315-325. |
| [4] | 葛文春, 吴福元, 周长勇, 等. 大兴安岭北部塔河花岗岩体的时代及对额尔古纳地块构造属性的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2005,50(12):1239-1247. |
| [5] | 葛文春, 吴福元, 周长勇, 等. 大兴安岭中部乌兰浩特地区中生代花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2005,21(3):749-762. |
| [6] | 葛文春, 隋振民, 吴福元, 等. 大兴安岭东北部早古生代花岗岩锆石 U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(2):423-440. |
| [7] | 武广, 陈衍景, 赵振华, 等. 大兴安岭北端洛古河东花岗岩的地球化学、SHRIMP 锆石U-Pb年龄和岩石成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2009,25(2):233-247. |
| [8] | 隋振民, 葛文春, 吴福元, 等. 大兴安岭北部察哈彦岩体的 Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2009,39(5):849-856. |
| [9] | 徐美君, 许文良, 王枫, 等. 小兴安岭中部早侏罗世花岗质岩石的年代学与地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013,29(2):354-368. |
| [10] | 许文良, 王枫, 裴福萍, 等. 中国东北中生代构造体制与区域成矿背景:来自中生代火山岩组合时空变化的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2013,29(2):339-353. |
| [11] | 李之彤, 赵春荆. 东北北部三叠纪 A型花岗岩的初步研究[M]// 沈阳地质矿产研究所.中国地质科学院沈阳地质矿产研究所集刊,第 1号. 北京:地震出版社, 1992: 96-108. |
| [12] | 吴福元, 林强, 葛文春, 等. 张广才岭新华屯岩体的形成时代与成因研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 1998,17(3):226-234. |
| [13] | 苗来成, 范蔚茗, 张福勤, 等. 小兴安岭西北部新开岭一科洛杂岩锆石 SHRIMP年代学研究及其意义[J]. 科学通报, 2003,48(22):2315-2323. |
| [14] | 张艳斌, 吴福元, 翟明国, 等. 和龙地块的构造属性与华北地台北缘东段边界[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2004,34(9):795-806. |
| [15] | 宋彪, 张玉海, 万渝生, 等. 锆石SHRIMP样品靶制作、年龄测定及有关现象讨论[J]. 地质论评, 2002,48(增刊):26-30. |
| [16] | PEARCE N J G, PERKINS W T, WESTGATE J A, et al. A compilation of new and published major and trace element data for NIST SRM 610 and NIST SRM 612 glass reference materials[J]. Geostandards Newsletter, 1997,21(1) : 115-144. |
| [17] | BLACK L P, KAMO S L, ALLEN C M, et al. TEMORA 1:a new zircon standard for Phanerozoic U-Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2003,200:155-170. |
| [18] | 李献华, 唐国强, 龚冰, 等. Qinghu(清湖)锆石: 一个新的U-Pb年龄和O,Hf同位素微区分析工作标样[J]. 科学通报, 2013,58(20):1954-1961. |
| [19] | ANDERSON T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb [J]. Chemical Geology, 2002,192:59-79. |
| [20] | 张旗, 王焰, 李承东, 等. 花岗岩的Sr-Yb分类及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006,22(9):2249-2269. |
| [21] | 张旗, 金惟俊, 李承东, 等. 再论花岗岩按照Sr-Yb的分类:标志[J]. 岩石学报, 2010,26(4):985-1015. |
| [22] | WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type granites:Geochemical characteristics,discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987,95:407-419. |
| [23] | 张旗, 王焰, 熊小林, 等. 埃达克岩和花岗岩:挑战与机遇[M]. 北京: 中国大地出版社, 2008: 1-344. |
| [24] | 杨增海, 王建平, 刘家军, 等. 内蒙古乌日尼图花岗岩的年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2016,30(3):528-540. |
| [25] | 贾小辉, 王强, 唐功建. A型花岗岩的研究进展及意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2009,33(3):465-480. |
| [26] | 宋维民, 陶楠, 庞雪娇, 等. 内蒙古科尔沁右翼中旗敖兰三队侵入体年龄及地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2016,35(6):932-942. |
| [27] | RAPP R P, WATSON E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8-32 kbar:Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995,36:891-931. |
| [28] | TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. London:Blackwell, 1985: 57-72. |
| [29] | 隋振民, 葛文春, 吴福元, 等. 大兴安岭东北部侏罗纪花岗质岩石的锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(2):461-480. |
| [30] | LOISELLE M C, WONES D R. Characteristics and origin of anorogenic granites[J]. Geological Society of America Abstract Progressing, 1979,11:468. |
| [31] | SYLVESTER P J. Post-collisional alkaline granites[J]. Journal of Geology, 1989,97:261-280. |
| [32] | EBY G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992,20:641-644. |
| [33] | WHALEN J B, JENNER G A, LONGSTAFFE F J, et al. Geochemical and isotopic (O,Nd,Pb and Sr) constraints on A-type granite:Petrogenesis based on the Topsails igneous suite,Newfoundland Appalachians[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1996,37:1463-1489. |
| [34] | PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984,25:956-983. |
| [35] | 石玉若, 刘敦一, 张旗, 等. 内蒙古中部苏尼特左旗地区三叠纪A型花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其区域构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2007,26(2):183-189. |
| [36] | 孙德有, 吴福元, 高山. 小兴安岭东部清水岩体的锆石激光探针U-Pb年龄测定[J]. 地球学报, 2004,25(2):213-218. |
| [37] | 李研, 王建, 孙德有, 等. 内蒙古海拉尔北部八大关地区花岗岩的成岩时代、地球化学特征与成因[J]. 现代地质, 2017,31(2):234-245. |
| [38] | 李锦轶, 高立明, 孙桂华, 等. 内蒙古东部双井子中三叠世同碰撞壳源花岗岩的确定及其对西伯利亚与中朝古板块碰撞时限的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(3):565-582. |
| [39] | 李益龙, 周汉文, 钟增球, 等. 华北与西伯利亚板块的对接过程:来自西拉木伦缝合带变形花岗岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄证据[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2009,34(6):931-938. |
| [40] | 张海华, 郑月娟, 陈树旺, 等. 内蒙古科尔沁右翼中旗三叠纪花岗质岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015,45(2):417-428. |
| [41] | 吕长禄, 肖庆辉, 冯俊岭, 等. 黑龙江松嫩地块北缘晚三叠世—早侏罗世火山岩的发现及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2015,29(4):855-865. |
| [42] | 李世超, 李永飞, 王兴安, 等. 大兴安岭中段晚三叠世四分组效应花岗岩的厘定及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2016,32(9):2793-2806. |
| [1] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [2] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [3] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [4] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [5] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [6] | 梁鸣, 高文, 罗先熔, 王晓东, 刘秀娟, 陈皓, 刘攀峰, 竹峰, 李伟. 冀北高尖子地区土壤地球化学特征及其找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1567-1579. |
| [7] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [8] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [9] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [10] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [11] | 可行, 赵青芳, 吴飘, 杨传胜, 廖晶, 龚建明. 胶莱盆地东北部白垩系烃源岩特征与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1358-1368. |
| [12] | 韩飞, 宋元宝, 张伟, 李道凌, 黄永高, 李应栩, 贾小川, 杨学俊, 杨青松, 宋旭波, 卢柳. 西藏冈底斯南木林地区晚三叠世中酸性岩浆作用及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 547-561. |
| [13] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [14] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [15] | 王向伟, 张保涛, 杨浩强, 韩进国. 青海省海晏县团宝山一带变质岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 586-598. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||