



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (05): 1058-1066.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.031
侯江龙1( ), 李建康1(
), 李建康1( ), 王登红1, 代鸿章1, 刘丽君1,2
), 王登红1, 代鸿章1, 刘丽君1,2
收稿日期:2018-01-25
修回日期:2020-04-13
出版日期:2020-10-28
发布日期:2020-10-29
通讯作者:
李建康
作者简介:李建康,男,研究员,1976年出生,矿床学专业,主要从事矿床学研究。Email: Li9968@126.com。基金资助:
HOU Jianglong1( ), LI Jiankang1(
), LI Jiankang1( ), WANG Denghong1, DAI Hongzhang1, LIU Lijun1,2
), WANG Denghong1, DAI Hongzhang1, LIU Lijun1,2
Received:2018-01-25
Revised:2020-04-13
Online:2020-10-28
Published:2020-10-29
Contact:
LI Jiankang
摘要:
四川甲基卡锂矿床为超大型锂矿床,矿区南部呈岩株状产出的二云母花岗岩与稀有金属伟晶岩在时间、空间及成因上具有密切关系。通过对该岩体元素地球化学特征和氢氧同位素组成的研究,探讨了其在稀有金属成矿过程中的作用。研究结果表明,甲基卡二云母花岗岩为富硅、高钾、钙碱性、强过铝质S型花岗岩,其稀土总量较低,岩浆来源为三叠系西康群砂泥岩为代表的地壳物质的部分熔融,流体来源可能是岩浆水和变质水的混合水。岩体微量元素R型聚类分析显示,与稀有金属成矿最密切的元素为Li、Rb、Ti、W、Mn,而岩体稀有元素含量的变化规律指示岩体北侧成矿效率高于南侧,是下一步找矿工作的重点。综合地球化学、氢氧同位素及前人研究,认为花岗岩浆在底辟侵入过程中可能发生了不混溶作用,由此分离出的伟晶岩浆在运移过程中稀有金属得到不断富集,最终形成伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床。
中图分类号:
侯江龙, 李建康, 王登红, 代鸿章, 刘丽君. 四川甲基卡锂矿区二长花岗岩的地球化学、氢氧同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 1058-1066.
HOU Jianglong, LI Jiankang, WANG Denghong, DAI Hongzhang, LIU Lijun. Geochemistry and Hydrogen-Oxygen Isotope Compositions of Jiajik Two-mica Granite, Sichuan Province, and Their Geological Significance[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(05): 1058-1066.

图1 四川甲基卡矿区地质简图(改编自文献[6,12]) SPGZ.松潘—甘孜褶皱带;EKL.东昆仑构造带;STM.柴达木地块;YZ.扬子地块;JT.羌塘地块;GDS.冈底斯地块;QL.祁连构造带;①柴北缘蛇绿杂岩带;②昆中蛇绿杂岩带;③昆南—阿尼玛卿蛇绿杂岩带;④可可西里—金沙江缝合线;⑤班公湖—怒江蛇绿杂岩带;⑥龙门山断裂;⑦理塘蛇绿杂岩带;⑧若尔盖地块;TX.三叠系西康群;Ⅰ.微斜长石伟晶岩带;Ⅱ.微斜长石-钠长石带;Ⅲ.钠长石带;Ⅳ.锂辉石带;Ⅴ.锂(白)云母带;1.二云母花岗岩;2.微斜长石型伟晶岩;3.微斜长石钠长石型伟晶岩;4.钠长石型伟晶岩;5.钠长石锂辉石型伟晶岩;6.钠长石锂云母型伟晶岩;7.伟晶岩脉编号;8.类型分带线及编号;9.样品采集位置
Fig.1 Geological sketch map of the Jiajika ore deposit, Sichuan (modified after references [6,12])

图2 四川甲基卡二云母花岗岩手标本(a)及显微镜下照片(b) (a)手标本照片;(b)显微镜照片;Qtz.石英;Ms.白云母;Bt.黑云母;Ab.钠长石
Fig.2 Hand-specimen photo (a) and micrograph (b) of the Jiajika two-mica granite, Sichuan
| 样号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | Fe2O3 | FeO | K2O | MgO | MnO | Na2O | P2O5 | TiO2 | CO2 | H2O+ | 总和 | A/NK | A/CNK | DI | SI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J5 | 74.38 | 14.99 | 0.69 | 0.11 | 0.62 | 4.94 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 3.55 | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.17 | 0.73 | 100.60 | 1.34 | 1.21 | 92.62 | 1.99 |
| J6 | 73.99 | 14.98 | 0.61 | 0.19 | 0.70 | 4.75 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 3.49 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.88 | 100.22 | 1.38 | 1.25 | 92.26 | 1.99 |
| J7 | 74.12 | 14.85 | 0.70 | 0.12 | 0.80 | 5.04 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 3.18 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.99 | 100.45 | 1.39 | 1.24 | 91.68 | 2.35 |
| J8 | 74.02 | 14.70 | 0.59 | 0.07 | 0.82 | 4.83 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 3.30 | 0.20 | 0.06 | 0.27 | 1.11 | 100.14 | 1.38 | 1.25 | 92.31 | 1.96 |
| J9 | 73.60 | 14.74 | 0.69 | 0.12 | 0.71 | 4.83 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 3.26 | 0.23 | 0.07 | 0.23 | 1.02 | 99.72 | 1.39 | 1.24 | 92.00 | 2.41 |
| J10 | 73.65 | 14.76 | 0.63 | 0.13 | 0.69 | 4.88 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 3.22 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.26 | 0.74 | 99.44 | 1.39 | 1.26 | 92.09 | 2.52 |
表1 甲基卡二云母花岗岩主量分析数据(wB/%)
Table 1 Major element composition of the Jiajika two-mica granite(%)
| 样号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | Fe2O3 | FeO | K2O | MgO | MnO | Na2O | P2O5 | TiO2 | CO2 | H2O+ | 总和 | A/NK | A/CNK | DI | SI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J5 | 74.38 | 14.99 | 0.69 | 0.11 | 0.62 | 4.94 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 3.55 | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.17 | 0.73 | 100.60 | 1.34 | 1.21 | 92.62 | 1.99 |
| J6 | 73.99 | 14.98 | 0.61 | 0.19 | 0.70 | 4.75 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 3.49 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.88 | 100.22 | 1.38 | 1.25 | 92.26 | 1.99 |
| J7 | 74.12 | 14.85 | 0.70 | 0.12 | 0.80 | 5.04 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 3.18 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.99 | 100.45 | 1.39 | 1.24 | 91.68 | 2.35 |
| J8 | 74.02 | 14.70 | 0.59 | 0.07 | 0.82 | 4.83 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 3.30 | 0.20 | 0.06 | 0.27 | 1.11 | 100.14 | 1.38 | 1.25 | 92.31 | 1.96 |
| J9 | 73.60 | 14.74 | 0.69 | 0.12 | 0.71 | 4.83 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 3.26 | 0.23 | 0.07 | 0.23 | 1.02 | 99.72 | 1.39 | 1.24 | 92.00 | 2.41 |
| J10 | 73.65 | 14.76 | 0.63 | 0.13 | 0.69 | 4.88 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 3.22 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.26 | 0.74 | 99.44 | 1.39 | 1.26 | 92.09 | 2.52 |

图3 甲基卡二云母花岗岩微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图((a),原始地幔数据据文献[14])和稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线图((b),球粒陨石数据据文献[15])
Fig.3 Primitive mantle-normalized trace element spidergram ((a),primitive mantle normalizing values after reference [14]) and chondrite-normalized REE patterns of the Jiajika two-mica granite ((b),chondrite normalizing values after reference [15])
| 样号 | Li | Be | Mn | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | Mo | Cs | Ba | Pb | Th | U | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J5 | 322.67 | 16.77 | 188.67 | 109.87 | 16.17 | 2.43 | 41.47 | 17.07 | 369.67 | 29.37 | 0.24 | 55.93 | 50.43 | 40.90 | 3.20 | 3.15 | ||
| J6 | 429.00 | 9.29 | 278.50 | 54.02 | 7.70 | 2.13 | 43.25 | 16.75 | 408.00 | 21.30 | 1.59 | 105.45 | 38.30 | 37.70 | 2.90 | 2.51 | ||
| J7 | 297.00 | 7.84 | 358.00 | 57.64 | 9.34 | 25.39 | 49.55 | 16.80 | 311.50 | 33.00 | 2.12 | 45.55 | 63.70 | 45.90 | 4.09 | 3.42 | ||
| J8 | 339.50 | 29.75 | 295.50 | 62.64 | 11.83 | 2.81 | 39.90 | 17.50 | 388.00 | 28.90 | 3.19 | 70.15 | 48.30 | 40.30 | 3.04 | 2.99 | ||
| J9 | 283.50 | 9.88 | 225.50 | 118.50 | 14.60 | 2.17 | 44.20 | 16.70 | 327.00 | 29.80 | 0.17 | 58.65 | 50.30 | 42.60 | 3.71 | 3.06 | ||
| J10 | 192.00 | 5.63 | 164.50 | 63.57 | 10.31 | 2.71 | 34.65 | 15.95 | 298.50 | 33.75 | 2.72 | 32.65 | 62.80 | 45.15 | 3.34 | 4.01 | ||
| 样号 | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | Ti | W | Y | Cr | Sn | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | ||
| J5 | 17.10 | 3.93 | 28.13 | 1.45 | 267.00 | 388.33 | 3.39 | 2.01 | 23.50 | 5.86 | 12.07 | 1.31 | 4.50 | 1.40 | 0.25 | 1.38 | ||
| J6 | 21.75 | 7.66 | 27.05 | 1.51 | 245.50 | 190.24 | 3.89 | 41.08 | 33.75 | 4.93 | 11.08 | 1.08 | 3.73 | 1.19 | 0.19 | 1.17 | ||
| J7 | 16.55 | 3.31 | 33.60 | 1.66 | 333.50 | 219.70 | 4.37 | 56.40 | 24.40 | 7.91 | 15.80 | 1.73 | 6.02 | 1.77 | 0.32 | 1.75 | ||
| J8 | 19.55 | 6.11 | 28.00 | 1.47 | 270.00 | 196.32 | 4.11 | 88.00 | 30.35 | 5.70 | 11.25 | 1.25 | 4.33 | 1.34 | 0.23 | 1.33 | ||
| J9 | 16.15 | 3.59 | 31.70 | 1.64 | 304.00 | 395.00 | 3.25 | 1.85 | 22.35 | 6.52 | 14.00 | 1.47 | 5.19 | 1.58 | 0.29 | 1.51 | ||
| J10 | 7.76 | 1.65 | 29.60 | 1.44 | 229.00 | 219.22 | 4.44 | 73.02 | 14.95 | 6.62 | 13.35 | 1.50 | 5.18 | 1.62 | 0.30 | 1.62 | ||
| 样号 | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ∑REE | LREE | HREE | (La/Yb)N | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Yb)N | δEu | δCe | |||
| J5 | 0.24 | 1.03 | 0.12 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 28.60 | 25.39 | 3.21 | 25.61 | 2.63 | 7.11 | 0.55 | 1.01 | |||
| J6 | 0.22 | 1.06 | 0.14 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 25.31 | 22.20 | 3.11 | 17.04 | 2.61 | 4.84 | 0.47 | 1.10 | |||
| J7 | 0.30 | 1.36 | 0.16 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 37.65 | 33.53 | 4.12 | 25.53 | 2.82 | 6.71 | 0.55 | 0.99 | |||
| J8 | 0.25 | 1.13 | 0.14 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 27.45 | 24.09 | 3.37 | 19.91 | 2.69 | 5.50 | 0.52 | 0.97 | |||
| J9 | 0.25 | 1.04 | 0.12 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 32.37 | 29.03 | 3.34 | 29.98 | 2.61 | 8.10 | 0.56 | 1.05 | |||
| J10 | 0.30 | 1.31 | 0.16 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 32.51 | 28.56 | 3.96 | 21.25 | 2.58 | 6.23 | 0.56 | 0.98 | |||
表2 甲基卡二云母花岗岩微量和稀土元素分析数据(wB/10-6)
Table 2 Trace element and REE compositions of the Jiajika two-mica granite(10-6)
| 样号 | Li | Be | Mn | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | Mo | Cs | Ba | Pb | Th | U | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J5 | 322.67 | 16.77 | 188.67 | 109.87 | 16.17 | 2.43 | 41.47 | 17.07 | 369.67 | 29.37 | 0.24 | 55.93 | 50.43 | 40.90 | 3.20 | 3.15 | ||
| J6 | 429.00 | 9.29 | 278.50 | 54.02 | 7.70 | 2.13 | 43.25 | 16.75 | 408.00 | 21.30 | 1.59 | 105.45 | 38.30 | 37.70 | 2.90 | 2.51 | ||
| J7 | 297.00 | 7.84 | 358.00 | 57.64 | 9.34 | 25.39 | 49.55 | 16.80 | 311.50 | 33.00 | 2.12 | 45.55 | 63.70 | 45.90 | 4.09 | 3.42 | ||
| J8 | 339.50 | 29.75 | 295.50 | 62.64 | 11.83 | 2.81 | 39.90 | 17.50 | 388.00 | 28.90 | 3.19 | 70.15 | 48.30 | 40.30 | 3.04 | 2.99 | ||
| J9 | 283.50 | 9.88 | 225.50 | 118.50 | 14.60 | 2.17 | 44.20 | 16.70 | 327.00 | 29.80 | 0.17 | 58.65 | 50.30 | 42.60 | 3.71 | 3.06 | ||
| J10 | 192.00 | 5.63 | 164.50 | 63.57 | 10.31 | 2.71 | 34.65 | 15.95 | 298.50 | 33.75 | 2.72 | 32.65 | 62.80 | 45.15 | 3.34 | 4.01 | ||
| 样号 | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | Ti | W | Y | Cr | Sn | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | ||
| J5 | 17.10 | 3.93 | 28.13 | 1.45 | 267.00 | 388.33 | 3.39 | 2.01 | 23.50 | 5.86 | 12.07 | 1.31 | 4.50 | 1.40 | 0.25 | 1.38 | ||
| J6 | 21.75 | 7.66 | 27.05 | 1.51 | 245.50 | 190.24 | 3.89 | 41.08 | 33.75 | 4.93 | 11.08 | 1.08 | 3.73 | 1.19 | 0.19 | 1.17 | ||
| J7 | 16.55 | 3.31 | 33.60 | 1.66 | 333.50 | 219.70 | 4.37 | 56.40 | 24.40 | 7.91 | 15.80 | 1.73 | 6.02 | 1.77 | 0.32 | 1.75 | ||
| J8 | 19.55 | 6.11 | 28.00 | 1.47 | 270.00 | 196.32 | 4.11 | 88.00 | 30.35 | 5.70 | 11.25 | 1.25 | 4.33 | 1.34 | 0.23 | 1.33 | ||
| J9 | 16.15 | 3.59 | 31.70 | 1.64 | 304.00 | 395.00 | 3.25 | 1.85 | 22.35 | 6.52 | 14.00 | 1.47 | 5.19 | 1.58 | 0.29 | 1.51 | ||
| J10 | 7.76 | 1.65 | 29.60 | 1.44 | 229.00 | 219.22 | 4.44 | 73.02 | 14.95 | 6.62 | 13.35 | 1.50 | 5.18 | 1.62 | 0.30 | 1.62 | ||
| 样号 | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ∑REE | LREE | HREE | (La/Yb)N | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Yb)N | δEu | δCe | |||
| J5 | 0.24 | 1.03 | 0.12 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 28.60 | 25.39 | 3.21 | 25.61 | 2.63 | 7.11 | 0.55 | 1.01 | |||
| J6 | 0.22 | 1.06 | 0.14 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 25.31 | 22.20 | 3.11 | 17.04 | 2.61 | 4.84 | 0.47 | 1.10 | |||
| J7 | 0.30 | 1.36 | 0.16 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 37.65 | 33.53 | 4.12 | 25.53 | 2.82 | 6.71 | 0.55 | 0.99 | |||
| J8 | 0.25 | 1.13 | 0.14 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 27.45 | 24.09 | 3.37 | 19.91 | 2.69 | 5.50 | 0.52 | 0.97 | |||
| J9 | 0.25 | 1.04 | 0.12 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 32.37 | 29.03 | 3.34 | 29.98 | 2.61 | 8.10 | 0.56 | 1.05 | |||
| J10 | 0.30 | 1.31 | 0.16 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 32.51 | 28.56 | 3.96 | 21.25 | 2.58 | 6.23 | 0.56 | 0.98 | |||
| 样号 | δ18OV-SMOW/‰ | δDV-SMOW/‰ |
|---|---|---|
| J5 | 17.1 | -104 |
| J6 | 17.4 | -102 |
| J7 | 17.5 | -110 |
| J8 | 17.5 | -114 |
| J9 | 17.5 | -114 |
表3 甲基卡二云母花岗岩石英氢氧同位素测试结果
Table 3 Hydrogen-oxygen isotope compositions of quartz from the Jiajika two-mica granite
| 样号 | δ18OV-SMOW/‰ | δDV-SMOW/‰ |
|---|---|---|
| J5 | 17.1 | -104 |
| J6 | 17.4 | -102 |
| J7 | 17.5 | -110 |
| J8 | 17.5 | -114 |
| J9 | 17.5 | -114 |
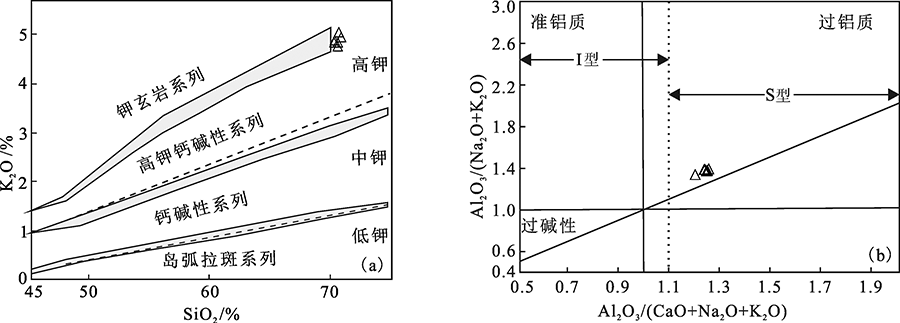
图4 甲基卡二云母花岗岩SiO2-K2O ((a), 底图据文献[16])和A/CNK-A/NK图解((b), 底图据文献[17])
Fig.4 SiO2-K2O ((a),base map modified after reference [16] ) and A/CNK-A/NK diagrams((b),base map modified after reference [17] )of the Jiajika two-mica granite
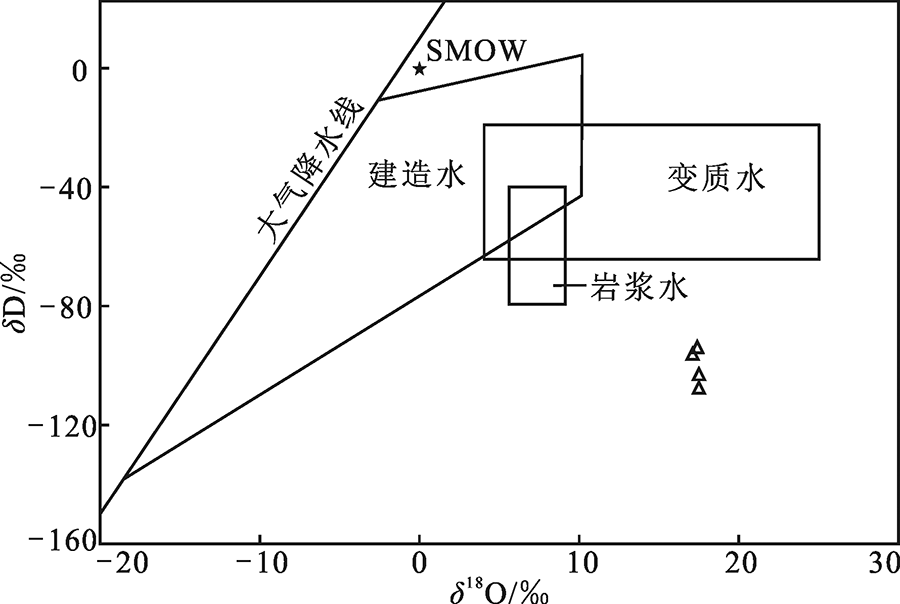
图7 甲基卡二云母花岗岩氢氧同位素组成图解[19]
Fig.7 Hydrogen-oxygen isotope compositions of quartz from the Jiajika two-mica granite(base map modified after reference [19])
| [1] | 王登红, 付小方. 四川甲基卡外围锂矿找矿取得突破[J]. 岩矿测试, 2013,32(6):987. |
| [2] | 付小方, 侯立玮, 王登红, 等. 四川甘孜甲基卡锂辉石矿矿产调查评价成果[J]. 中国地质调查, 2014,1(3):38-43. |
| [3] | 付小方, 袁蔺平, 王登红, 等. 四川甲基卡矿田新三号稀有金属矿脉的成矿特征与勘查模型[J]. 矿床地质, 2015,34(6):1172-1186. |
| [4] | 郝雪峰, 付小方, 梁斌, 等. 川西甲基卡花岗岩和新三号矿脉的形成时代及意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2015,34(6):1199-1208. |
| [5] | 王登红, 李建康, 付小方. 四川甲基卡伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床的成矿时代及其意义[J]. 地球化学, 2005,34(6):542-547. |
| [6] | 唐国凡, 吴盛先. 四川省康定县甲基卡花岗伟晶岩锂矿床地质研究报告[R]. 攀枝花:四川省地质矿产局攀西地质大队, 1984: 1-104. |
| [7] | 张舟, 张廷山, 蓝光志. 川西北二叠系栖霞组小有孔虫动物群[J]. 现代地质, 2011,25(5):988-994. |
| [8] | 白宪洲, 何明友, 王玉婷, 等. 四川若尔盖地区西康群地球化学特征及其物源区和古风化程度分析[J]. 现代地质, 2010,24(1):152-157. |
| [9] | 苏嫒娜, 田世洪, 侯增谦, 等. 锂同位素及其在四川甲基卡伟晶岩型锂多金属矿床研究中的应用[J]. 现代地质, 2011,25(2):237-242. |
| [10] | 李建康. 川西典型伟晶岩型矿床的形成机理及其大陆动力学背景[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2006: 1-237. |
| [11] | 徐志刚, 陈毓川, 王登红, 等. 中国成矿区带划分方案[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2008: 1-138. |
| [12] | LI J K, WANG D H, CHEN Y C. The ore-forming mechanism of the Jiajika pegmatite-type rare metal deposit in western Sichuan Province: evidence from isotope dating[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013,87(1):91-101. |
| [13] | 黎彤, 哀怀雨, 吴胜普. 中国花岗岩类和世界花岗岩类平均化学成分的对比研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 1998,22(1):29-34. |
| [14] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989,42:313-345.
DOI URL |
| [15] | BOYNTON W V. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies[M] //HENDERSON P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984: 63-114. |
| [16] |
RICKWOOD P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989,22(4):247-263.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989,101:635-643.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 梁斌, 付小方, 唐屹, 等. 川西甲基卡稀有金属矿区花岗岩岩石地球化学特征[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2016,36(1):43-49. |
| [19] |
TAYLOR H P. The application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal alteration and ore deposition[J]. Economic Geology, 1974,69(6):843-883.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 唐屹. 川西甲基卡稀有金属矿区花岗岩特征及找矿意义[D]. 成都: 西南科技大学, 2016: 1-78. |
| [1] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [2] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [3] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [4] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [5] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [6] | 梁鸣, 高文, 罗先熔, 王晓东, 刘秀娟, 陈皓, 刘攀峰, 竹峰, 李伟. 冀北高尖子地区土壤地球化学特征及其找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1567-1579. |
| [7] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [8] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [9] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [10] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [11] | 可行, 赵青芳, 吴飘, 杨传胜, 廖晶, 龚建明. 胶莱盆地东北部白垩系烃源岩特征与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1358-1368. |
| [12] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [13] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [14] | 王向伟, 张保涛, 杨浩强, 韩进国. 青海省海晏县团宝山一带变质岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 586-598. |
| [15] | 徐立明, 刘涛, 郑吉林. 大兴安岭北段阿里河镇早白垩世高分异花岗岩的确定及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 613-626. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||