



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (05): 1067-1076.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.038
任永健1( ), 程烁1(
), 程烁1( ), 张明明1, 曹光远2, 于汪1, 赵寒1, 梁恒1, 王富强1, 祁才吉1
), 张明明1, 曹光远2, 于汪1, 赵寒1, 梁恒1, 王富强1, 祁才吉1
收稿日期:2018-10-18
修回日期:2020-05-06
出版日期:2020-10-28
发布日期:2020-10-29
通讯作者:
程烁
作者简介:程 烁,女,工程师,1988年出生,机电与维修专业,主要从事地质图件编制、期刊编辑工作。Email: 641318804@qq.com。基金资助:
REN Yongjian1( ), CHENG Shuo1(
), CHENG Shuo1( ), ZHANG Mingming1, CAO Guangyuan2, YU Wang1, ZHAO Han1, LIANG Heng1, WANG Fuqiang1, QI Caiji1
), ZHANG Mingming1, CAO Guangyuan2, YU Wang1, ZHAO Han1, LIANG Heng1, WANG Fuqiang1, QI Caiji1
Received:2018-10-18
Revised:2020-05-06
Online:2020-10-28
Published:2020-10-29
Contact:
CHENG Shuo
摘要:
通过对黑龙江张家湾地区中侏罗世正长花岗岩和碱长花岗岩进行岩石地球化学分析,探讨该区域花岗质岩浆作用、成因类型及其构造环境。研究结果表明,正长花岗岩和碱长花岗岩具有高SiO2(73.12%~77.82%)、富碱(K2O+Na2O=6.36%~8.56%)、富铁贫镁(TFeO/MgO=6.67~25.43)的特点,铝饱和指数A/CNK值大多大于1.1,Eu负异常明显(δEu=0.01~0.74),富集Th、U、K和Rb,亏损Ba、Sr、P和Ti;锆石饱和温度变化范围为757~900 ℃,平均为816 ℃,具有A型花岗岩的特征;岩石由高分异花岗岩向过铝质A型花岗岩演化。稀土元素特征指示,岩浆物源由幔源和下地壳物质混合而成,中侏罗世正长花岗岩和碱长花岗岩构造类型为A2型花岗岩,形成于造山后岩石圈伸展环境作用阶段。上述岩石地球化学特征表明,受古太平洋板块向西俯冲-碰撞后造山作用的影响,中侏罗世张家湾地区处于造山后伸展拉张的环境,岩石圈由挤压向伸展构造背景转变,地幔物质上涌并伴随岩浆的底侵作用,引发地壳物质的熔融,最终形成了该区域的正长花岗岩和碱长花岗岩。
中图分类号:
任永健, 程烁, 张明明, 曹光远, 于汪, 赵寒, 梁恒, 王富强, 祁才吉. 黑龙江张家湾地区中侏罗世A型花岗岩地球化学特征及构造环境分析[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 1067-1076.
REN Yongjian, CHENG Shuo, ZHANG Mingming, CAO Guangyuan, YU Wang, ZHAO Han, LIANG Heng, WANG Fuqiang, QI Caiji. Geochemistry Characteristics and Tectonic Environment Analysis of Middle Jurassic A-type Granites in Zhangjiawan Area, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(05): 1067-1076.

图1 研究区地质简图[9] 1.第四系;2.下侏罗统二浪河组;3.上二叠统红山组;4.下二叠统杨木岗组;5.早侏罗世石英闪长岩;6.早侏罗世似斑状花岗闪长岩;7.早侏罗世花岗闪长岩;8.早侏罗世二长花岗岩;9.早侏罗世黑云英云闪长岩;10.中侏罗世正长花岗岩;11.中侏罗世碱长花岗岩;12.样品采集位置、测试方法及年龄(Ma)
Fig.1 Geological sketch map of the study area[9]
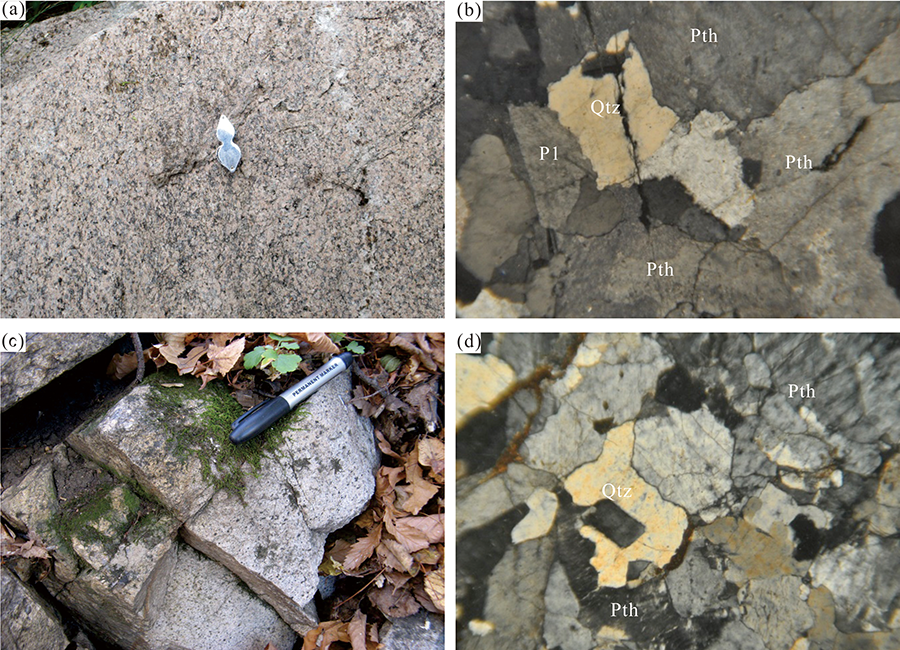

图2 研究区中侏罗世花岗岩野外地质特征及镜下照片 (a)中细粒正长花岗岩野外特征;(b)中细粒正长花岗岩镜下特征;(c)细粒碱长花岗岩野外特征;(d)细粒碱长花岗岩镜下特征;Pl.斜长石;Pth.条纹长石;Qtz.石英
Fig.2 Field geological characteristics and microscopic photos of the Middle Jurassic granite in the study area
| 样号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | TZr/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM005-YH1 | 正长花岗岩 | 77.56 | 0.16 | 12.52 | 0.52 | 1.2 | 0.058 | 0.250 | 0.86 | 3.02 | 3.73 | 0.035 | 809.19 |
| PM005-YH2 | 正长花岗岩 | 77.09 | 0.92 | 12.24 | 0.77 | 0.96 | 0.049 | 0.065 | 0.79 | 2.85 | 3.51 | 0.032 | 815.80 |
| PM005-YH3 | 正长花岗岩 | 73.61 | 0.15 | 16.42 | 0.17 | 0.42 | 0.033 | 0.067 | 0.43 | 3.35 | 4.71 | 0.022 | 898.77 |
| PM005-YH4 | 正长花岗岩 | 74.76 | 0.13 | 13.87 | 0.59 | 1.14 | 0.056 | 0.110 | 0.78 | 3.45 | 4.36 | 0.031 | 846.15 |
| PM005-YH5 | 正长花岗岩 | 77.16 | 0.08 | 12.84 | 0.78 | 0.72 | 0.038 | 0.200 | 0.53 | 2.78 | 3.79 | 0.025 | 798.97 |
| PM006-YH3 | 正长花岗岩 | 77.05 | 0.15 | 13.29 | 0.89 | 0.64 | 0.05 | 0.120 | 0.70 | 2.58 | 4.28 | 0.05 | 705.77 |
| PM006-YH4 | 正长花岗岩 | 76.89 | 0.10 | 13.40 | 0.95 | 0.55 | 0.042 | 0.170 | 0.81 | 2.58 | 3.9 | 0.046 | 757.26 |
| PM014-1-YH02 | 正长花岗岩 | 73.12 | 0.20 | 13.75 | 0.85 | 1.22 | 0.087 | 0.260 | 0.78 | 4.40 | 4.16 | 0.071 | 819.38 |
| PM012-YH01 | 碱长花岗岩 | 75.75 | 0.18 | 12.58 | 0.55 | 1.36 | 0.073 | 0.300 | 1.04 | 4.01 | 3.47 | 0.077 | 793.11 |
| PM012-YH02 | 碱长花岗岩 | 77.82 | 0.05 | 12.40 | 0.36 | 0.91 | 0.039 | 0.060 | 0.34 | 4.49 | 4.01 | 0.019 | 827.59 |
| DC08-YH01 | 碱长花岗岩 | 76.97 | 0.17 | 13.37 | 0.42 | 1.33 | 0.051 | 0.170 | 1.06 | 3.18 | 3.38 | 0.047 | 791.00 |
| 样号 | 岩性 | C | DI | SI | δ | τ | R1 | R2 | AR | ALK | A/CNK | A/NK | K/Na |
| PM005-YH1 | 正长花岗岩 | 2.59 | 90.98 | 2.87 | 1.32 | 59.38 | 3 165 | 349 | 3.04 | 6.75 | 1.025 | 1.85 | 1.24 |
| PM005-YH2 | 正长花岗岩 | 2.53 | 90.99 | 0.80 | 1.18 | 10.21 | 3 254 | 330 | 2.91 | 6.36 | 1.045 | 1.92 | 1.23 |
| PM005-YH3 | 正长花岗岩 | 5.36 | 91.89 | 0.77 | 2.12 | 87.13 | 2 605 | 373 | 2.83 | 8.06 | 1.174 | 2.04 | 1.41 |
| PM005-YH4 | 正长花岗岩 | 2.40 | 91.39 | 1.14 | 1.92 | 80.15 | 2 701 | 363 | 3.28 | 7.81 | 1.185 | 1.78 | 1.26 |
| PM005-YH5 | 正长花岗岩 | 3.41 | 91.67 | 2.42 | 1.26 | 121.20 | 3 257 | 322 | 2.93 | 6.57 | 1.233 | 1.95 | 1.36 |
| PM006-YH3 | 正长花岗岩 | 3.38 | 91.14 | 1.41 | 1.38 | 71.40 | 3 176 | 342 | 2.92 | 6.86 | 1.309 | 1.94 | 1.66 |
| PM006-YH4 | 正长花岗岩 | 3.71 | 90.16 | 2.09 | 1.24 | 108.20 | 3 269 | 360 | 2.68 | 6.48 | 1.332 | 2.07 | 1.51 |
| PM014-1-YH02 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.93 | 92.08 | 2.39 | 2.42 | 46.75 | 2 298 | 370 | 3.87 | 8.56 | 1.348 | 1.61 | 0.95 |
| PM012-YH01 | 碱长花岗岩 | 1.54 | 91.62 | 3.10 | 1.71 | 47.61 | 2 758 | 374 | 3.44 | 7.48 | 1.030 | 1.68 | 0.87 |
| PM012-YH02 | 碱长花岗岩 | 0.47 | 96.46 | 0.61 | 2.08 | 161.43 | 2 598 | 281 | 5.01 | 8.50 | 1.000 | 1.46 | 0.89 |
| DC08-YH01 | 碱长花岗岩 | 2.71 | 89.06 | 2.00 | 1.27 | 59.94 | 3 149 | 383 | 2.67 | 6.56 | 1.240 | 2.04 | 1.06 |
表1 张家湾地区中侏罗世花岗岩主量元素分析结果(wB/%)和CIPW标准矿物参数
Table 1 Major element oxide (%) contents and CIPW norm of the Middle Jurassic Zhangjiawan granite
| 样号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | TZr/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM005-YH1 | 正长花岗岩 | 77.56 | 0.16 | 12.52 | 0.52 | 1.2 | 0.058 | 0.250 | 0.86 | 3.02 | 3.73 | 0.035 | 809.19 |
| PM005-YH2 | 正长花岗岩 | 77.09 | 0.92 | 12.24 | 0.77 | 0.96 | 0.049 | 0.065 | 0.79 | 2.85 | 3.51 | 0.032 | 815.80 |
| PM005-YH3 | 正长花岗岩 | 73.61 | 0.15 | 16.42 | 0.17 | 0.42 | 0.033 | 0.067 | 0.43 | 3.35 | 4.71 | 0.022 | 898.77 |
| PM005-YH4 | 正长花岗岩 | 74.76 | 0.13 | 13.87 | 0.59 | 1.14 | 0.056 | 0.110 | 0.78 | 3.45 | 4.36 | 0.031 | 846.15 |
| PM005-YH5 | 正长花岗岩 | 77.16 | 0.08 | 12.84 | 0.78 | 0.72 | 0.038 | 0.200 | 0.53 | 2.78 | 3.79 | 0.025 | 798.97 |
| PM006-YH3 | 正长花岗岩 | 77.05 | 0.15 | 13.29 | 0.89 | 0.64 | 0.05 | 0.120 | 0.70 | 2.58 | 4.28 | 0.05 | 705.77 |
| PM006-YH4 | 正长花岗岩 | 76.89 | 0.10 | 13.40 | 0.95 | 0.55 | 0.042 | 0.170 | 0.81 | 2.58 | 3.9 | 0.046 | 757.26 |
| PM014-1-YH02 | 正长花岗岩 | 73.12 | 0.20 | 13.75 | 0.85 | 1.22 | 0.087 | 0.260 | 0.78 | 4.40 | 4.16 | 0.071 | 819.38 |
| PM012-YH01 | 碱长花岗岩 | 75.75 | 0.18 | 12.58 | 0.55 | 1.36 | 0.073 | 0.300 | 1.04 | 4.01 | 3.47 | 0.077 | 793.11 |
| PM012-YH02 | 碱长花岗岩 | 77.82 | 0.05 | 12.40 | 0.36 | 0.91 | 0.039 | 0.060 | 0.34 | 4.49 | 4.01 | 0.019 | 827.59 |
| DC08-YH01 | 碱长花岗岩 | 76.97 | 0.17 | 13.37 | 0.42 | 1.33 | 0.051 | 0.170 | 1.06 | 3.18 | 3.38 | 0.047 | 791.00 |
| 样号 | 岩性 | C | DI | SI | δ | τ | R1 | R2 | AR | ALK | A/CNK | A/NK | K/Na |
| PM005-YH1 | 正长花岗岩 | 2.59 | 90.98 | 2.87 | 1.32 | 59.38 | 3 165 | 349 | 3.04 | 6.75 | 1.025 | 1.85 | 1.24 |
| PM005-YH2 | 正长花岗岩 | 2.53 | 90.99 | 0.80 | 1.18 | 10.21 | 3 254 | 330 | 2.91 | 6.36 | 1.045 | 1.92 | 1.23 |
| PM005-YH3 | 正长花岗岩 | 5.36 | 91.89 | 0.77 | 2.12 | 87.13 | 2 605 | 373 | 2.83 | 8.06 | 1.174 | 2.04 | 1.41 |
| PM005-YH4 | 正长花岗岩 | 2.40 | 91.39 | 1.14 | 1.92 | 80.15 | 2 701 | 363 | 3.28 | 7.81 | 1.185 | 1.78 | 1.26 |
| PM005-YH5 | 正长花岗岩 | 3.41 | 91.67 | 2.42 | 1.26 | 121.20 | 3 257 | 322 | 2.93 | 6.57 | 1.233 | 1.95 | 1.36 |
| PM006-YH3 | 正长花岗岩 | 3.38 | 91.14 | 1.41 | 1.38 | 71.40 | 3 176 | 342 | 2.92 | 6.86 | 1.309 | 1.94 | 1.66 |
| PM006-YH4 | 正长花岗岩 | 3.71 | 90.16 | 2.09 | 1.24 | 108.20 | 3 269 | 360 | 2.68 | 6.48 | 1.332 | 2.07 | 1.51 |
| PM014-1-YH02 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.93 | 92.08 | 2.39 | 2.42 | 46.75 | 2 298 | 370 | 3.87 | 8.56 | 1.348 | 1.61 | 0.95 |
| PM012-YH01 | 碱长花岗岩 | 1.54 | 91.62 | 3.10 | 1.71 | 47.61 | 2 758 | 374 | 3.44 | 7.48 | 1.030 | 1.68 | 0.87 |
| PM012-YH02 | 碱长花岗岩 | 0.47 | 96.46 | 0.61 | 2.08 | 161.43 | 2 598 | 281 | 5.01 | 8.50 | 1.000 | 1.46 | 0.89 |
| DC08-YH01 | 碱长花岗岩 | 2.71 | 89.06 | 2.00 | 1.27 | 59.94 | 3 149 | 383 | 2.67 | 6.56 | 1.240 | 2.04 | 1.06 |
| 样号 | 岩性 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | L/H | (La/Yb)N | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM005-YH1 | 正长花岗岩 | 47.7 | 115.0 | 9.10 | 34.2 | 4.95 | 0.56 | 4.19 | 0.60 | 3.31 | 0.64 | 1.84 | 0.29 | 2.14 | 0.40 | 16.9 | 224.92 | 15.77 | 15.99 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH2 | 正长花岗岩 | 46.0 | 94.3 | 8.88 | 32.8 | 4.81 | 0.46 | 3.93 | 0.60 | 3.43 | 0.64 | 1.86 | 0.30 | 2.03 | 0.41 | 16.6 | 200.45 | 14.19 | 16.25 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH3 | 正长花岗岩 | 103.0 | 129.0 | 17.40 | 60.0 | 6.90 | 1.20 | 6.15 | 0.77 | 4.05 | 0.79 | 2.43 | 0.40 | 2.82 | 0.55 | 21.1 | 335.46 | 17.68 | 26.20 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH4 | 正长花岗岩 | 77.9 | 134.0 | 12.60 | 44.3 | 5.40 | 0.91 | 4.66 | 0.61 | 3.28 | 0.62 | 1.82 | 0.28 | 2.09 | 0.40 | 16.5 | 288.87 | 19.99 | 26.74 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH5 | 正长花岗岩 | 13.8 | 31.5 | 4.43 | 18.9 | 4.42 | 0.40 | 3.86 | 0.81 | 5.17 | 1.01 | 2.84 | 0.45 | 3.07 | 0.53 | 25.7 | 91.19 | 4.14 | 3.22 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM006-YH3 | 正长花岗岩 | 27.2 | 69.2 | 5.84 | 21.1 | 3.48 | 0.60 | 2.67 | 0.38 | 2.14 | 0.43 | 1.27 | 0.22 | 1.64 | 0.33 | 12.0 | 136.50 | 14.03 | 11.90 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM006-YH4 | 正长花岗岩 | 15.2 | 38.4 | 3.00 | 10.1 | 1.93 | 0.43 | 1.50 | 0.23 | 1.43 | 0.31 | 1.01 | 0.20 | 1.66 | 0.35 | 8.9 | 75.75 | 10.32 | 6.57 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM014-1-YH02 | 正长花岗岩 | 40.6 | 84.2 | 8.65 | 30.2 | 5.52 | 0.61 | 4.87 | 0.81 | 4.96 | 0.98 | 2.97 | 0.47 | 3.09 | 0.54 | 27.8 | 188.47 | 9.08 | 9.42 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM012-YH01 | 碱长花岗岩 | 19.5 | 53.4 | 4.08 | 14.2 | 2.87 | 0.60 | 2.80 | 0.47 | 3.02 | 0.63 | 1.97 | 0.34 | 2.17 | 0.39 | 17.7 | 106.44 | 8.03 | 6.45 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM012-YH02 | 碱长花岗岩 | 15.3 | 44.5 | 6.30 | 25.3 | 9.00 | 0.04 | 9.17 | 2.31 | 18.20 | 3.85 | 12.50 | 2.26 | 14.90 | 2.46 | 134.0 | 166.09 | 1.53 | 0.74 | ||||||||||||||||
| DC08-YH01 | 碱长花岗岩 | 34.7 | 81.5 | 8.96 | 35.7 | 7.67 | 0.51 | 6.90 | 1.21 | 7.18 | 1.43 | 4.10 | 0.66 | 4.29 | 0.70 | 37.5 | 195.51 | 6.39 | 5.80 | ||||||||||||||||
| 样号 | 岩性 | δEu | Ba | Be | Co | Cr | Hf | Li | Nb | Ni | Rb | Sc | Sr | Th | U | V | Zr | Rb/Sr | Ba/Sr | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH1 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.37 | 422.0 | 1.55 | 1.75 | 4.01 | 3.05 | 10.10 | 009.41 | 1.69 | 78.8 | 3.92 | 83.6 | 007.89 | 01.00 | 10.30 | 168.0 | 0.94 | 5.05 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH2 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.31 | 415.0 | 1.44 | 0.91 | 4.82 | 3.27 | 6.88 | 8.72 | 1.58 | 79.2 | 3.41 | 29.5 | 7.13 | 0.80 | 2.42 | 172.0 | 2.68 | 14.07 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH3 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.55 | 913.0 | 1.16 | 0.62 | 3.40 | 5.90 | 4.42 | 11.00 | 1.62 | 119.0 | 6.04 | 77.2 | 9.48 | 0.78 | 2.38 | 369.0 | 1.54 | 11.83 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH4 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.54 | 1 078.0 | 1.63 | 0.63 | 4.35 | 4.84 | 6.60 | 8.41 | 1.47 | 90.1 | 4.76 | 43.2 | 7.33 | 0.62 | 1.82 | 261.0 | 2.09 | 24.95 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH5 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.29 | 353.0 | 2.16 | 1.36 | 4.42 | 2.02 | 3.16 | 9.85 | 1.92 | 111.0 | 7.45 | 62.5 | 10.70 | 1.75 | 1.91 | 134.0 | 1.78 | 5.65 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM006-YH3 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.58 | 438.0 | 2.36 | 1.30 | 6.32 | 0.62 | 13.50 | 11.10 | 1.71 | 152.0 | 2.74 | 99.9 | 12.30 | 2.06 | 3.86 | 43.6 | 1.52 | 4.38 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM006-YH4 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.74 | 280.0 | 3.17 | 1.24 | 3.38 | 1.09 | 8.83 | 11.30 | 2.17 | 162.0 | 1.64 | 141.0 | 35.40 | 3.72 | 3.78 | 82.0 | 1.15 | 1.99 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM014-1-YH02 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.35 | 485.0 | 3.19 | 1.71 | 4.96 | 8.66 | 21.00 | 15.70 | 2.17 | 113.0 | 4.43 | 298.0 | 17.90 | 2.46 | 5.07 | 230.0 | 0.38 | 1.63 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM012-YH01 | 碱长花岗岩 | 0.64 | 386.0 | 2.95 | 1.70 | 7.28 | 7.32 | 29.80 | 16.30 | 2.88 | 121.0 | 3.60 | 290.0 | 17.50 | 2.16 | 6.09 | 168.0 | 0.42 | 1.33 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM012-YH02 | 碱长花岗岩 | 0.01 | 12.5 | 3.73 | 0.59 | 5.75 | 15.90 | 84.20 | 53.70 | 1.97 | 134.0 | 1.71 | 15.4 | 49.80 | 5.00 | 1.10 | 249.0 | 8.70 | 0.81 | ||||||||||||||||
| DC08-YH01 | 碱长花岗岩 | 0.21 | 236.0 | 2.65 | 1.55 | 6.01 | 5.94 | 37.20 | 15.40 | 3.64 | 119.0 | 7.98 | 63.2 | 12.40 | 1.45 | 7.78 | 133.0 | 1.88 | 3.73 | ||||||||||||||||
表2 张家湾中侏罗世花岗岩稀土元素(10-6)和微量元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 2 REE (10-6) and trace element (10-6) compositions of the Middle Jurassic Zhangjiawan granite
| 样号 | 岩性 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | L/H | (La/Yb)N | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM005-YH1 | 正长花岗岩 | 47.7 | 115.0 | 9.10 | 34.2 | 4.95 | 0.56 | 4.19 | 0.60 | 3.31 | 0.64 | 1.84 | 0.29 | 2.14 | 0.40 | 16.9 | 224.92 | 15.77 | 15.99 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH2 | 正长花岗岩 | 46.0 | 94.3 | 8.88 | 32.8 | 4.81 | 0.46 | 3.93 | 0.60 | 3.43 | 0.64 | 1.86 | 0.30 | 2.03 | 0.41 | 16.6 | 200.45 | 14.19 | 16.25 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH3 | 正长花岗岩 | 103.0 | 129.0 | 17.40 | 60.0 | 6.90 | 1.20 | 6.15 | 0.77 | 4.05 | 0.79 | 2.43 | 0.40 | 2.82 | 0.55 | 21.1 | 335.46 | 17.68 | 26.20 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH4 | 正长花岗岩 | 77.9 | 134.0 | 12.60 | 44.3 | 5.40 | 0.91 | 4.66 | 0.61 | 3.28 | 0.62 | 1.82 | 0.28 | 2.09 | 0.40 | 16.5 | 288.87 | 19.99 | 26.74 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH5 | 正长花岗岩 | 13.8 | 31.5 | 4.43 | 18.9 | 4.42 | 0.40 | 3.86 | 0.81 | 5.17 | 1.01 | 2.84 | 0.45 | 3.07 | 0.53 | 25.7 | 91.19 | 4.14 | 3.22 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM006-YH3 | 正长花岗岩 | 27.2 | 69.2 | 5.84 | 21.1 | 3.48 | 0.60 | 2.67 | 0.38 | 2.14 | 0.43 | 1.27 | 0.22 | 1.64 | 0.33 | 12.0 | 136.50 | 14.03 | 11.90 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM006-YH4 | 正长花岗岩 | 15.2 | 38.4 | 3.00 | 10.1 | 1.93 | 0.43 | 1.50 | 0.23 | 1.43 | 0.31 | 1.01 | 0.20 | 1.66 | 0.35 | 8.9 | 75.75 | 10.32 | 6.57 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM014-1-YH02 | 正长花岗岩 | 40.6 | 84.2 | 8.65 | 30.2 | 5.52 | 0.61 | 4.87 | 0.81 | 4.96 | 0.98 | 2.97 | 0.47 | 3.09 | 0.54 | 27.8 | 188.47 | 9.08 | 9.42 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM012-YH01 | 碱长花岗岩 | 19.5 | 53.4 | 4.08 | 14.2 | 2.87 | 0.60 | 2.80 | 0.47 | 3.02 | 0.63 | 1.97 | 0.34 | 2.17 | 0.39 | 17.7 | 106.44 | 8.03 | 6.45 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM012-YH02 | 碱长花岗岩 | 15.3 | 44.5 | 6.30 | 25.3 | 9.00 | 0.04 | 9.17 | 2.31 | 18.20 | 3.85 | 12.50 | 2.26 | 14.90 | 2.46 | 134.0 | 166.09 | 1.53 | 0.74 | ||||||||||||||||
| DC08-YH01 | 碱长花岗岩 | 34.7 | 81.5 | 8.96 | 35.7 | 7.67 | 0.51 | 6.90 | 1.21 | 7.18 | 1.43 | 4.10 | 0.66 | 4.29 | 0.70 | 37.5 | 195.51 | 6.39 | 5.80 | ||||||||||||||||
| 样号 | 岩性 | δEu | Ba | Be | Co | Cr | Hf | Li | Nb | Ni | Rb | Sc | Sr | Th | U | V | Zr | Rb/Sr | Ba/Sr | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH1 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.37 | 422.0 | 1.55 | 1.75 | 4.01 | 3.05 | 10.10 | 009.41 | 1.69 | 78.8 | 3.92 | 83.6 | 007.89 | 01.00 | 10.30 | 168.0 | 0.94 | 5.05 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH2 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.31 | 415.0 | 1.44 | 0.91 | 4.82 | 3.27 | 6.88 | 8.72 | 1.58 | 79.2 | 3.41 | 29.5 | 7.13 | 0.80 | 2.42 | 172.0 | 2.68 | 14.07 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH3 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.55 | 913.0 | 1.16 | 0.62 | 3.40 | 5.90 | 4.42 | 11.00 | 1.62 | 119.0 | 6.04 | 77.2 | 9.48 | 0.78 | 2.38 | 369.0 | 1.54 | 11.83 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH4 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.54 | 1 078.0 | 1.63 | 0.63 | 4.35 | 4.84 | 6.60 | 8.41 | 1.47 | 90.1 | 4.76 | 43.2 | 7.33 | 0.62 | 1.82 | 261.0 | 2.09 | 24.95 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM005-YH5 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.29 | 353.0 | 2.16 | 1.36 | 4.42 | 2.02 | 3.16 | 9.85 | 1.92 | 111.0 | 7.45 | 62.5 | 10.70 | 1.75 | 1.91 | 134.0 | 1.78 | 5.65 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM006-YH3 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.58 | 438.0 | 2.36 | 1.30 | 6.32 | 0.62 | 13.50 | 11.10 | 1.71 | 152.0 | 2.74 | 99.9 | 12.30 | 2.06 | 3.86 | 43.6 | 1.52 | 4.38 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM006-YH4 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.74 | 280.0 | 3.17 | 1.24 | 3.38 | 1.09 | 8.83 | 11.30 | 2.17 | 162.0 | 1.64 | 141.0 | 35.40 | 3.72 | 3.78 | 82.0 | 1.15 | 1.99 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM014-1-YH02 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.35 | 485.0 | 3.19 | 1.71 | 4.96 | 8.66 | 21.00 | 15.70 | 2.17 | 113.0 | 4.43 | 298.0 | 17.90 | 2.46 | 5.07 | 230.0 | 0.38 | 1.63 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM012-YH01 | 碱长花岗岩 | 0.64 | 386.0 | 2.95 | 1.70 | 7.28 | 7.32 | 29.80 | 16.30 | 2.88 | 121.0 | 3.60 | 290.0 | 17.50 | 2.16 | 6.09 | 168.0 | 0.42 | 1.33 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM012-YH02 | 碱长花岗岩 | 0.01 | 12.5 | 3.73 | 0.59 | 5.75 | 15.90 | 84.20 | 53.70 | 1.97 | 134.0 | 1.71 | 15.4 | 49.80 | 5.00 | 1.10 | 249.0 | 8.70 | 0.81 | ||||||||||||||||
| DC08-YH01 | 碱长花岗岩 | 0.21 | 236.0 | 2.65 | 1.55 | 6.01 | 5.94 | 37.20 | 15.40 | 3.64 | 119.0 | 7.98 | 63.2 | 12.40 | 1.45 | 7.78 | 133.0 | 1.88 | 3.73 | ||||||||||||||||
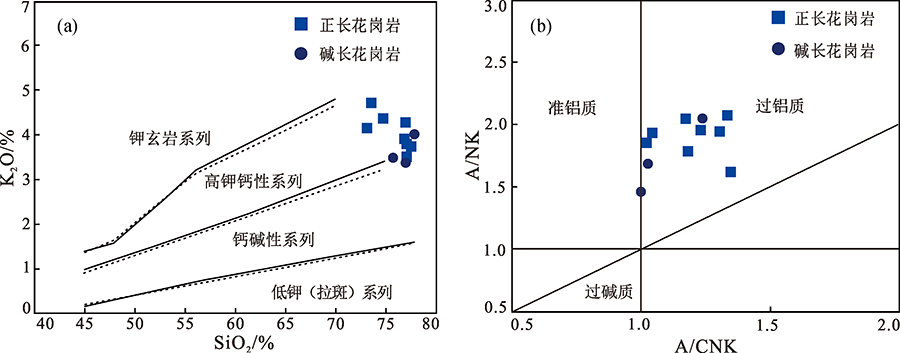
图3 张家湾地区中侏罗世花岗岩SiO2-K2O(a)和A/CNK-A/NK图解(b)(底图据参考文献[13])
Fig.3 SiO2-K2O(a) and A/CNK-A/NK(b) diagrams for the Middle Jurassic Zhangjiawan granite(base map after reference [13])
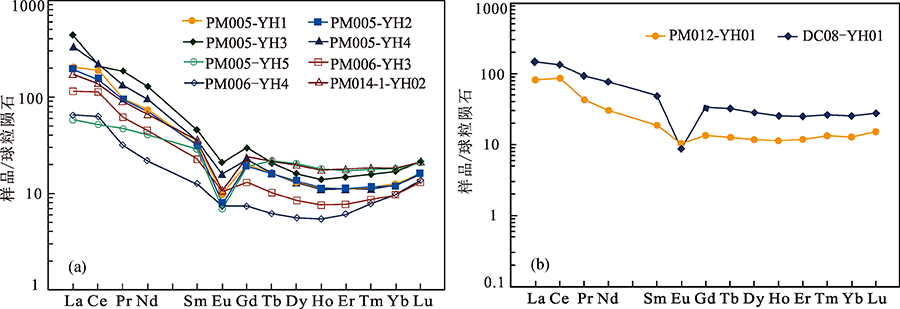
图4 张家湾地区中侏罗世正长花岗岩(a)和碱长花岗岩(b)稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线(底图据参考文献[14])
Fig.4 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns for the Middle Jurassic Zhangjiawan syenogranite(a) and alkali feldspar granite(b) (base map after reference [14])
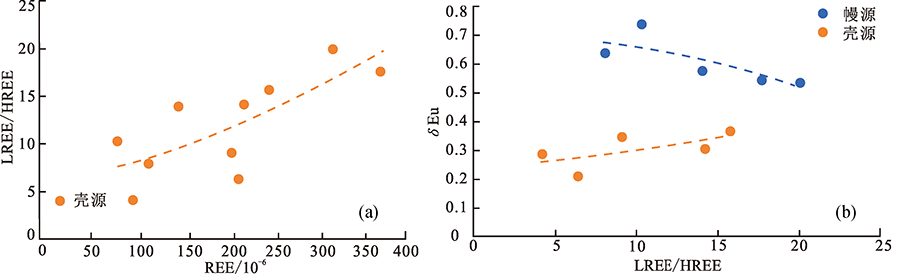
图5 张家湾地区中侏罗世花岗岩REE-LREE/HREE(a)和LREE/HREE-δEu(b)图解(底图据参考文献[14])
Fig.5 REE vs.LREE/HREE (a) and LREE/HREE vs. δEu(b) plots for the Zhangjiawan granite (base map after reference [14])
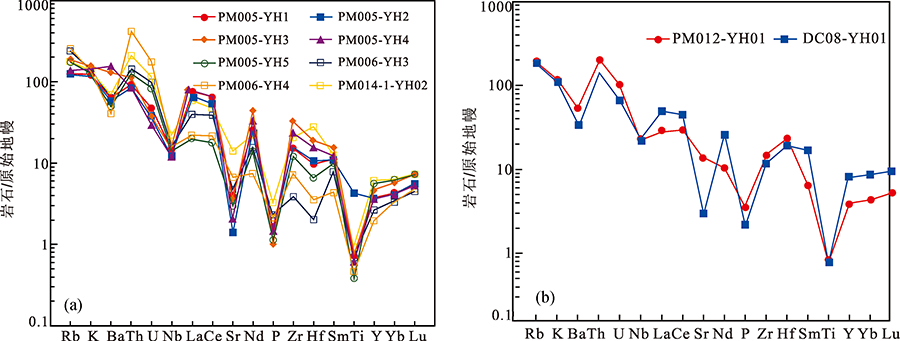
图6 张家湾地区中侏罗世正长花岗岩(a)和碱长花岗岩(b)微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(底图据参考文献[14])
Fig.6 Primitive mantle-normalized multi-element spider diagrams for the Middle Jurassic Zhangjiawan syenogranite(a) and alkali feldspar granite(b) (base map after reference [14])
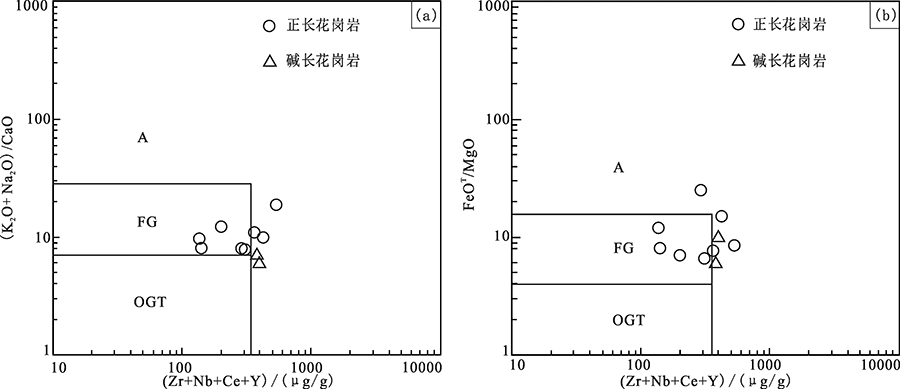
图7 中侏罗世花岗岩判别图解(底图据文献[22]) OGT.未分异的I型和S型花岗岩;FG.高分异花岗岩;A.A型花岗岩
Fig.7 Tectonic discrimination diagrams for the Middle Jurassic Zhangjiawan granites(base map after reference [22])
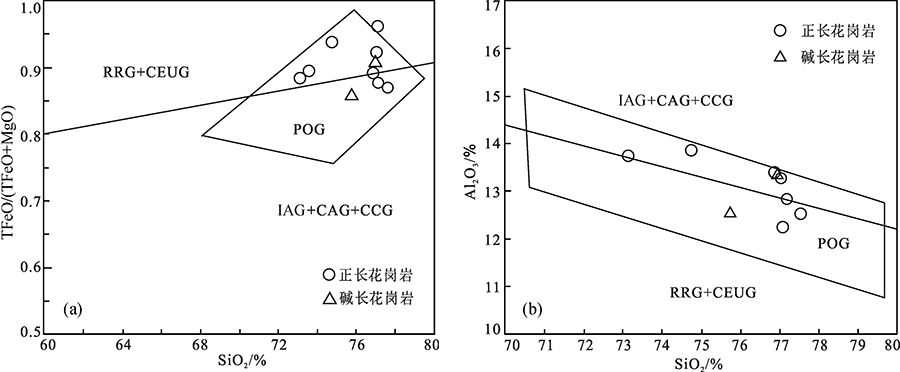
图8 张家湾地区中侏罗世花岗岩TFeO/(TFeO+MgO)-SiO2 (a)和SiO2-Al2O3(b)图解(底图据参考文献[25]) IAG.岛弧花岗岩类;CAG.大陆弧花岗岩类;CCG.大陆碰撞花岗岩类;POG.后造山花岗岩类;RRG.与裂谷有关的花岗岩类;CEUG.与大陆的造陆抬升有关的花岗岩类
Fig.8 TFeO/(TFeO+MgO) vs. SiO2(a) and SiO2-Al2O3 (b) diagrams for the Middle Jurassic Zhangjiawan granite(base map after reference [25])
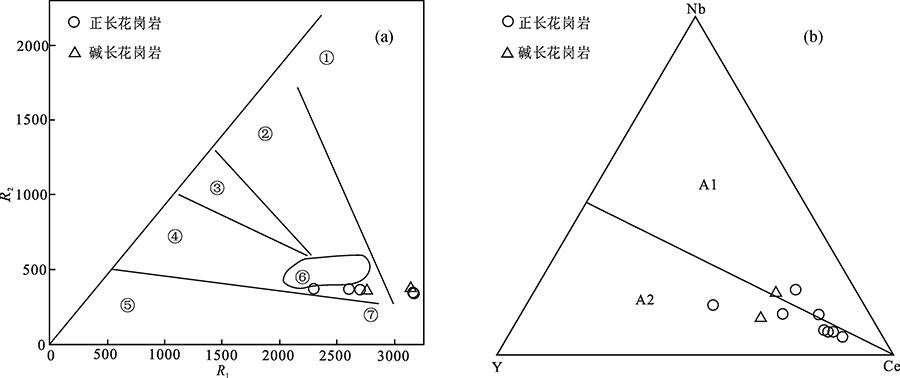
图9 花岗岩类R1-R2 ((a),底图据参考文献[26])和Nb-Y-Ce((b),底图据参考文献[27,28] )构造判别图解 ①地幔分异;②板块碰撞前消减的活动板块边缘;③碰撞后隆起;④造山晚期;⑤非造山;⑥同碰撞;⑦造山后
Fig.9 R1-R2(a) and ternary Nb-Y-Ce(b) tectonic discrimination diagrams for the Zhangjiawan granite
| [1] | 耿雯, 秦江锋, 李永飞, 等. 黑龙江张广才岭一面坡晚三叠世花岗岩地球化学特征和LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 地质通报, 2014,33(9):1333-1341. |
| [2] | 高嵩, 欧阳兆灼, 赵爱林, 等. 东北地区若干重要基础地质问题[J]. 地质与资源, 2013,22(4):337-339. |
| [3] | 孙晓. 张广才岭花岗岩带南段侏罗纪花岗岩的年代学特征及形成环境[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2016. |
| [4] | 耿雯. 张广才岭南段尚志地区花岗岩类成因及其地质意义[D]. 西安:西北大学, 2015. |
| [5] | 敖光. 张广才岭南部侵入岩锆石U-Pb LA-ICP-MS年代[J]. 地质与资源, 2016,25(6):533-538. |
| [6] | 唐杰, 许文良, 王枫, 等. 古太平洋板块在欧亚大陆下的俯冲历史:东北亚陆缘中生代—古近纪岩浆记录[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2018,48(5):549-583. |
| [7] | 潘桂棠, 陆松年, 肖庆辉, 等. 中国大地构造阶段划分和演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2016,23(6):1-23. |
| [8] | 张夺, 刘永江, 李伟民, 等. 佳木斯地块及邻区早古生代—晚中生代构造演化[J]. 世界地质, 2018,37(4):1149-1166. |
| [9] | 朱敬宾, 任永健, 王博, 等. 黑龙江南蛤拉河子1∶5万等四幅区域地质矿产调查报告[R]. 北京:中化地质矿山总局地质研究院, 2016: 69-176. |
| [10] | 任永健. 张广才岭南部早—中侏罗世花岗质岩浆作用及构造演化[J]. 地质学报, 2019,93(11):2813-2831. |
| [11] |
CHEN B, JAHN B M, WILDE S A, et al. Two contrasting Paleozoic magmatic belts in northern Inner Mongolia,China: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000,328(1/2) : 157-182.
DOI URL |
| [12] | XIAO W J, WINDLEY B F, HAO J, et al. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture,Inner Mongolia,China: Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt[J]. Tectonics, 2003,22:268-288. |
| [13] | SARVOTHAMAN H. The molar Al2O3/(CaO + Na2O + K2O) ratios as discriminant constraint for oceanic plagiogranites and continental transitions[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 1993,42:513-522. |
| [14] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publications, 1989,42:313-345.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 郭春丽, 曾令森, 高利娥, 等. 福建河田高分异花岗岩的矿物和全岩地球化学找矿标志研究[J]. 地质学报, 2017,91(8):1796-1817. |
| [16] | 吴福元, 刘小驰, 纪伟强, 等. 高分异花岗岩的识别与研究[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2017,47(7):745-765. |
| [17] | WU Fuyuan, LI Xianhua, YANG Jinhui, et al. Discussions on the petrogenesis of granites[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007,23(6):1217-1238. |
| [18] |
YANG J H, WU F Y, CHUNG S L, et al. A hybrid origin for the Qianshan A-type granite, northeast China: Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence[J]. Lithos, 2006,89:89-106.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(6):1217-1238. |
| [20] | 林涛, 邓宇峰, 陈斌, 等. 新疆西天山阿拉套山东部孔吾萨依A型花岗岩成岩年代、地球化学特征及成因[J]. 地质学报, 2019,93(5):1020-1036. |
| [21] | 曾帅, 何莹, 李孟洋, 等. A型花岗岩研究综述[J].内蒙古科技与经济, 2018(18):49-51. |
| [22] | WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 1987,95:407-419. |
| [23] |
WATSON E B, HARRISON T M. Zircon saturation revisited:Temperature and composition effect in a variety of crustal magmas types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983,64:295-304.
DOI URL |
| [24] | WATSON E B, HARRISON T M. Zircon thermometer reveals minimum melting conditions on earliest[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983,308:841-844. |
| [25] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of grani-toids[J]. Geological society of America Bulletin, 1989,101(5):635-643.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
BATCHELOR R A, BOWDEN P. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters[J]. Chemical Geology, 1985,48:43-55
DOI URL |
| [27] |
EDY G N. The A-type granitoids: A review of their occurrence and chemical characteristics and speculations on their petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 1990,26:115-134.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
EDY G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: petrogenesis and implications[J]. Geology, 1992,20:641-644.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 孙德有, 吴福元, 高山, 等. 吉林中部晚三叠世和早侏罗世两期铝质A 型花岗岩的厘定及对吉黑东部构造格局的制约[J]. 地学前缘, 2005,12(2):263-275. |
| [30] | 张海华, 李永飞, 张健, 等. 大兴安岭中部乌兰浩特地区花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020,34(3):483-493. |
| [31] | 莫宣学, 罗照华, 邓晋福, 等. 东昆仑造山带花岗岩及地壳生长[N]. 高校地质学报, 2007,13(3):403-414. |
| [32] | 吕长禄, 徐东海, 李新鹏, 等. 黑龙江太平岭早侏罗世花岗岩成因及壳幔混合作用[J]. 现代地质, 2012,26(4):635-646. |
| [33] | 潘桂棠, 陆松年, 肖庆辉, 等. 中国大地构造阶段划分和演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2016,23(6):1-23. |
| [34] | 张夺, 刘永江, 李伟民, 等. 佳木斯地块及邻区早古生代—晚中生代构造演化[J]. 世界地质, 2018,37(4):1149-1166. |
| [35] | 李良林, 周汉文, 陈植华, 等. 福建太姥山地区和鼓山地区A型花岗岩对比及其地球动力学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2013,27(3):509-524. |
| [36] | 邱啸飞, 杨红梅, 卢山松, 等. 扬子陆核古元古代A型花岗岩的年代学与地球化学研究及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2015,29(4):884-895. |
| [37] | 李良林, 周汉文, 陈植华, 等. 福建太姥山地区和鼓山地区A型花岗岩对比及其地球动力学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2013,27(3):509-524. |
| [1] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [2] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [3] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [4] | 张舒, 张赞赞, 胡召齐, 施立胜, 周涛发, 吴明安, 杜建国. 长江中下游成矿带庐枞矿集区花岗岩型铀矿床成矿作用研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1435-1448. |
| [5] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [6] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [7] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [8] | 梁鸣, 高文, 罗先熔, 王晓东, 刘秀娟, 陈皓, 刘攀峰, 竹峰, 李伟. 冀北高尖子地区土壤地球化学特征及其找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1567-1579. |
| [9] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [10] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [11] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [12] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [13] | 可行, 赵青芳, 吴飘, 杨传胜, 廖晶, 龚建明. 胶莱盆地东北部白垩系烃源岩特征与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1358-1368. |
| [14] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [15] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||