



现代地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (04): 1180-1192.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2025.029
• 能源地质与工程 • 上一篇
潘磊1( ), 全力2,*(
), 全力2,*( ), 杨浩1, 徐芮2, 王广伟2,3
), 杨浩1, 徐芮2, 王广伟2,3
出版日期:2025-08-10
发布日期:2025-08-27
通信作者:
*全力,女,博士研究生,1996年出生,主要从事碳酸盐岩储层沉积学研究工作。Email:quanli1996@outlook.com。作者简介:潘磊,男,高级工程师,1984年出生,主要从事石油地质综合研究工作。Email:panl.ktnf@sinopec.com。
基金资助:
PAN Lei1( ), QUAN Li2,*(
), QUAN Li2,*( ), YANG Hao1, XU Rui2, WANG Guangwei2,3
), YANG Hao1, XU Rui2, WANG Guangwei2,3
Published:2025-08-10
Online:2025-08-27
摘要:
四川盆地二叠系茅口组发育多种类型的碳酸盐岩储层,勘探潜力大,前期研究多关注白云岩和岩溶灰岩储层,针对滩相孔隙型灰岩储层成因的研究较少,对孔隙形成机理及储集作用了解薄弱。基于川东野外露头、薄片、物性和岩石地球化学等资料,识别了茅口组滩相灰岩储层的孔隙类型和成岩作用,分析了孔隙的形成与演化过程,建立了滩相灰岩储层的孔隙演化曲线。研究结果表明:茅口组滩相灰岩储层岩性主要为亮晶生屑灰岩,局部发生白云石化的含云生屑灰岩、云斑生屑灰岩。含云生屑灰岩内白云石以自形、零散状分布,成簇状选择性交代生物碎屑和沿微缝合线分布。滩相灰岩储层的孔隙类型主要为铸模孔﹑晶模孔和粒内溶孔,孔隙内壁普遍可见沥青衬边充填,生屑灰岩中的斑状白云岩发育少量晶间孔。岩石经历的主要成岩作用包括压实作用、白云石化作用、压溶作用﹑埋藏溶蚀作用和埋藏胶结作用。生屑灰岩储层孔隙的形成与准同生期大气淡水溶蚀作用与选择性的白云石埋藏溶蚀作用紧密有关。准同生期大气淡水暴露溶蚀形成了少量零散分布的生物铸模孔。埋藏溶蚀孔隙主要沿缝合线或者裂缝分布,指示原油运移过程中的有机酸对输导通道周缘白云石选择性溶蚀的结果。相关成果认识为四川盆地茅口组灰岩储层的勘探提供理论借鉴。
中图分类号:
潘磊, 全力, 杨浩, 徐芮, 王广伟. 川东南茅口组滩相灰岩储层特征及形成机理——以南川双河场剖面为例[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(04): 1180-1192.
PAN Lei, QUAN Li, YANG Hao, XU Rui, WANG Guangwei. Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Limestone Reservoir of Shoals in the Middle Permian Maokou Formation: A Case Study of Shuanghechang Outcrop in Southeastern Sichuan[J]. Geoscience, 2025, 39(04): 1180-1192.

图1 研究区地质概况 (a)四川盆地构造分区及剖面位置,南川双河场剖面位于四川盆地东南部,构造上隶属于川东高陡褶皱带;(b)南川双河场剖面航拍图,左下为剖面底部,右上为剖面顶部;(c)川东南茅口组综合柱状图(以泰来601井为例),剖面位置应大致对应于茅三段底部白云岩发育段
Fig.1 Geological overview of the study area

图2 双河场剖面综合柱状图 (a)第1层,灰色厚层泥晶生屑灰岩,红色箭头所指位置为SHC-2取样位置; (b)第2层,浅灰色厚层含云亮晶生屑灰岩,红色箭头所指位置为SHC-3取样位置;(c)第3层,灰色薄层含云亮晶生屑灰岩,红色箭头所指位置为SHC-4取样位置;(d)第4层,浅灰色薄层云斑生屑灰岩,粒间孔、粒内孔很发育,红色箭头所指位置为SHC-9取样位置;(e)第5层,灰色厚层含云亮晶生屑灰岩,孔隙发育,红色箭头所指位置为SHC-10取样位置;(f)第6层,浅灰色薄层状含云亮晶生屑灰岩,大量铸模孔发育,箭头所指位置为SHC-11取样位置;(g)第7层,浅灰色厚层状云斑生屑灰岩,铸模孔发育,箭头所指位置为斑状白云石发育位置;(h)第8层,灰色厚层状生屑灰岩,硅质条带发育,箭头所指位置从左至右依次为SHC-18,SHC-19,SHC-20取样位置; M、W、P、G分别为泥灰岩、粒泥灰岩、泥粒灰岩、颗粒灰岩的简写
Fig.2 Composite columnar section of the Shuanghechang outcrop

图3 不同类型灰岩的岩石学特征 (a)SHC-2,第一层,泥晶生屑灰岩,手标本,几乎不发育孔隙;(b)SHC-2,与图(a)为同一块样品,镜下孔隙不发育,单偏光;(c)SHC-9,第四层,含云生屑灰岩,零散状自形-半自形白云石发育,白云石被不同程度溶蚀形成粒内溶孔(还未完全溶蚀),溶孔内壁见沥青衬边充填;(d)SHC-11,第六层,含云生屑灰岩手标本中发育大量铸模孔、粒内溶孔(白色箭头指示);(e)SHC-11,与图(d)为同一块样品,含白亮晶生屑灰岩,可见绿藻等生物碎屑被选择性白云石化(大部分为Mizzia sp.,为二叠系特有),白云石在早期形成的铸模孔、粒内溶孔基础上被选择性溶蚀,使孔隙进一步溶蚀扩大,单偏光;(f)图(b)的局部放大照片,可见铸模孔中溶蚀残余的白云石;(g)SHC-14,第7层,发育在亮晶生屑灰岩中的斑状白云石,手标本上略呈土黄色,与周围灰岩界线明显;(h)SHC-14,与图(g)为同一块样品,可见斑状白云石发育晶间(溶)孔和晶间(溶)缝,与周围亮晶颗粒灰岩的岩性接触面的溶蚀孔(缝)更发育;(i)图(h)的局部放大照片,斑块状白云石由半自形-他形中-细晶白云石组成,发育晶间(溶)孔和晶间(溶)缝
Fig.3 Petrological characteristics of different limestone types
| 样号 | 岩性 | 层数 | Mn | Sr | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHC-9 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 第四层 | 13.652 | 891.172 | 0.704 | 0.093 | 0.166 | 0.021 | 0.092 | 0.021 | 0.008 | 0.024 | 0.005 |
| SHC-14-1 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 第七层 | 8.573 | 1433.916 | 0.428 | 0.149 | 0.252 | 0.026 | 0.119 | 0.025 | 0.010 | 0.026 | 0.006 |
| SHC-14-2 | 斑状白云石 | 第七层 | 16.857 | 764.049 | 0.352 | 0.091 | 0.178 | 0.021 | 0.081 | 0.020 | 0.005 | 0.021 | 0.004 |
| SHC-15-1 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 第七层 | 6.363 | 1509.878 | 0.363 | 0.106 | 0.204 | 0.023 | 0.091 | 0.021 | 0.007 | 0.021 | 0.004 |
| SHC-15-2 | 斑状白云石 | 第七层 | 20.182 | 850.299 | 0.321 | 0.141 | 0.268 | 0.031 | 0.126 | 0.022 | 0.006 | 0.030 | 0.004 |
| SHC-23 | 斑状白云石 | 第七层 | 27.083 | 1844.276 | 0.607 | 0.243 | 0.444 | 0.050 | 0.203 | 0.046 | 0.021 | 0.052 | 0.010 |
| 样号 | 岩性 | 层数 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Mn/Sr | ∑REE | LaN/YbN | Y/Ho | δCeN |
| SHC-9 | 斑状白云石 | 第四层 | 0.028 | 0.009 | 0.031 | 0.004 | 0.031 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.539 | 0.219 | 80.800 | 1.781 |
| SHC-14-1 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 第七层 | 0.021 | 0.006 | 0.020 | 0.003 | 0.020 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.686 | 0.562 | 76.333 | 1.812 |
| SHC-14-2 | 斑状白云石 | 第七层 | 0.021 | 0.005 | 0.017 | 0.003 | 0.015 | 0.003 | 0.022 | 0.484 | 0.435 | 68.500 | 2.039 |
| SHC-15-1 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 第七层 | 0.020 | 0.005 | 0.016 | 0.002 | 0.017 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.538 | 0.469 | 73.600 | 2.016 |
| SHC-15-2 | 斑状白云石 | 第七层 | 0.023 | 0.004 | 0.015 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 0.003 | 0.024 | 0.690 | 0.773 | 71.400 | 1.969 |
| SHC-23 | 斑状白云石 | 第七层 | 0.040 | 0.009 | 0.030 | 0.004 | 0.031 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 1.191 | 0.571 | 64.333 | 1.933 |
表1 双河场剖面不同类型岩石微量元素特征
Table 1 Trace element characteristics of different rock types in the Shuanghechang outcrop
| 样号 | 岩性 | 层数 | Mn | Sr | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHC-9 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 第四层 | 13.652 | 891.172 | 0.704 | 0.093 | 0.166 | 0.021 | 0.092 | 0.021 | 0.008 | 0.024 | 0.005 |
| SHC-14-1 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 第七层 | 8.573 | 1433.916 | 0.428 | 0.149 | 0.252 | 0.026 | 0.119 | 0.025 | 0.010 | 0.026 | 0.006 |
| SHC-14-2 | 斑状白云石 | 第七层 | 16.857 | 764.049 | 0.352 | 0.091 | 0.178 | 0.021 | 0.081 | 0.020 | 0.005 | 0.021 | 0.004 |
| SHC-15-1 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 第七层 | 6.363 | 1509.878 | 0.363 | 0.106 | 0.204 | 0.023 | 0.091 | 0.021 | 0.007 | 0.021 | 0.004 |
| SHC-15-2 | 斑状白云石 | 第七层 | 20.182 | 850.299 | 0.321 | 0.141 | 0.268 | 0.031 | 0.126 | 0.022 | 0.006 | 0.030 | 0.004 |
| SHC-23 | 斑状白云石 | 第七层 | 27.083 | 1844.276 | 0.607 | 0.243 | 0.444 | 0.050 | 0.203 | 0.046 | 0.021 | 0.052 | 0.010 |
| 样号 | 岩性 | 层数 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Mn/Sr | ∑REE | LaN/YbN | Y/Ho | δCeN |
| SHC-9 | 斑状白云石 | 第四层 | 0.028 | 0.009 | 0.031 | 0.004 | 0.031 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.539 | 0.219 | 80.800 | 1.781 |
| SHC-14-1 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 第七层 | 0.021 | 0.006 | 0.020 | 0.003 | 0.020 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.686 | 0.562 | 76.333 | 1.812 |
| SHC-14-2 | 斑状白云石 | 第七层 | 0.021 | 0.005 | 0.017 | 0.003 | 0.015 | 0.003 | 0.022 | 0.484 | 0.435 | 68.500 | 2.039 |
| SHC-15-1 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 第七层 | 0.020 | 0.005 | 0.016 | 0.002 | 0.017 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.538 | 0.469 | 73.600 | 2.016 |
| SHC-15-2 | 斑状白云石 | 第七层 | 0.023 | 0.004 | 0.015 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 0.003 | 0.024 | 0.690 | 0.773 | 71.400 | 1.969 |
| SHC-23 | 斑状白云石 | 第七层 | 0.040 | 0.009 | 0.030 | 0.004 | 0.031 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 1.191 | 0.571 | 64.333 | 1.933 |
| 序号 | 样号 | 层数 | 岩性 | δ13C (‰VPDB) | δ18O (‰VPDB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SHC-2 | 第一层 | 泥晶生屑灰岩 | 2.61 | -10.17 |
| 2 | SHC-3 | 第二层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 3.90 | -9.03 |
| 3 | SHC-4 | 第三层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 4.04 | -9.89 |
| 4 | SHC-6 | 第四层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 4.10 | -9.01 |
| 5 | SHC-7 | 第四层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 1.74 | -9.67 |
| 6 | SHC-9 | 第四层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 5.01 | -7.16 |
| 7 | SHC-10 | 第五层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 4.30 | -9.76 |
| 8 | SHC-11 | 第六层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 2.39 | -8.49 |
| 9 | SHC-12 | 第六层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 3.58 | -8.69 |
| 10 | SHC-14-1 | 第七层 | 斑状白云石 | 5.45 | -6.08 |
| 11 | SHC-14-2 | 第七层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 3.93 | -7.92 |
| 12 | SHC-15-1 | 第七层 | 斑状白云石 | 5.12 | -7.14 |
| 13 | SHC-23 | 第七层 | 斑状白云石 | 3.67 | -7.90 |
| 14 | SHC-15-2 | 第七层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 3.60 | -7.87 |
| 15 | SHC-16 | 第七层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 2.78 | -8.69 |
| 16 | SHC-17 | 第七层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 2.83 | -7.90 |
| 17 | SHC-18 | 第八层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 3.56 | -7.59 |
| 18 | SHC-20 | 第八层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 2.93 | -7.24 |
| 19 | SHC-21 | 第十层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 2.68 | -7.21 |
| 20 | SHC-22 | 第十层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 2.67 | -8.04 |
表2 双河场剖面不同类型岩石碳氧同位素特征
Table 2 Carbon and oxygen isotopic characteristics of different rock types in the Shuanghechang outcrop
| 序号 | 样号 | 层数 | 岩性 | δ13C (‰VPDB) | δ18O (‰VPDB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SHC-2 | 第一层 | 泥晶生屑灰岩 | 2.61 | -10.17 |
| 2 | SHC-3 | 第二层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 3.90 | -9.03 |
| 3 | SHC-4 | 第三层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 4.04 | -9.89 |
| 4 | SHC-6 | 第四层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 4.10 | -9.01 |
| 5 | SHC-7 | 第四层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 1.74 | -9.67 |
| 6 | SHC-9 | 第四层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 5.01 | -7.16 |
| 7 | SHC-10 | 第五层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 4.30 | -9.76 |
| 8 | SHC-11 | 第六层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 2.39 | -8.49 |
| 9 | SHC-12 | 第六层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 3.58 | -8.69 |
| 10 | SHC-14-1 | 第七层 | 斑状白云石 | 5.45 | -6.08 |
| 11 | SHC-14-2 | 第七层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 3.93 | -7.92 |
| 12 | SHC-15-1 | 第七层 | 斑状白云石 | 5.12 | -7.14 |
| 13 | SHC-23 | 第七层 | 斑状白云石 | 3.67 | -7.90 |
| 14 | SHC-15-2 | 第七层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 3.60 | -7.87 |
| 15 | SHC-16 | 第七层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 2.78 | -8.69 |
| 16 | SHC-17 | 第七层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 2.83 | -7.90 |
| 17 | SHC-18 | 第八层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 3.56 | -7.59 |
| 18 | SHC-20 | 第八层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 2.93 | -7.24 |
| 19 | SHC-21 | 第十层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 2.68 | -7.21 |
| 20 | SHC-22 | 第十层 | 含云生屑灰岩 | 2.67 | -8.04 |

图4 斑状白云石岩石学及阴极发光特征 (a)第四层,SHC-9,斑状白云石,白云石呈半自形-他形细晶结构,白云石晶粒间残留有尚未被云化的生屑颗粒,单偏光;(b)与图4(a)为同一视域,白云石晶粒呈暗红色阴极光;(c)第七层,SHC-14,斑状白云石,白云石呈半自形-他形中-细晶镶嵌状发育,晶体具有“雾心亮边”结构;(d)与图4(c)为同一视域,白云石晶粒“雾心”发暗红色阴极光,“亮边”发红色阴极光,周围基质灰岩颗粒间的亮晶方解石胶结物也发红色阴极光
Fig.4 Petrology and cathodoluminescence characteristics of patchy dolomite

图5 双河场剖面不同类型岩石地球化学特征 (a)斑状白云石和含云生屑灰岩的稀土元素配分模式图。灰色背景区间代表海水的稀土元素范围[23];斑状白云石和含云生屑灰岩具有相似的REE配分模式,且与海水的稀土元素范围相似;(b)不同类型岩石的碳氧同位素交汇图。数据显示斑状白云石相对灰岩具有偏重的δ13C值和δ18O值
Fig.5 Geochemical characteristics of different rock types in the Shuanghechang outcrop

图6 不同类型白云石岩石学及阴极发光特征 (a)SHC-6,第4层,零散分布的白云石,白云石发育在颗粒之间,为半自形细晶结构,可见白云石晶粒边缘发育缝合线;(b)与图6(a)为同一视域,白云石几乎不发阴极光;(c)SHC-9,第4层,选择性交代绿藻的白云石,白云石为他形-细晶结构,绿藻结构依然较为清晰可见;(d)与图6(c)为同一视域,选择性交代生物颗粒的白云石发暗红色阴极光;(e)SHC-16,第7层,沿缝合线发育的白云石,白云石大多为自形细晶结构,部分白云石晶粒沉淀在颗粒边缘附近,对颗粒具有小面积占位;(f)与图6(e)为同一视域,沿缝合线发育的白云石发红色阴极光
Fig.6 Petrology and cathodoluminescence characteristics of different dolomite types

图7 不同类型成岩作用典型镜下照片 (a)SHC-10,第五层,颗粒的明显形变和破碎,且沿破碎边缘发育微缝合线(黄色箭头指示位置),单偏光;(b)SHC-17,第七层,沿缝合线发育的白云石被溶蚀形成似晶模孔,孔隙内壁有沥青衬边充填,缝合线自身也发生了溶蚀扩大,形成溶蚀缝,单偏光;(c)SHC-10,第五层,可见网状缝合线溶蚀形成网状溶蚀缝,缝内有大量沥青附着,单偏光;(d)SHC-13,第七层,颗粒间先胶结块状方解石胶结物,再胶结鞍形白云石,正交光
Fig.7 Typical microscopic photographs of different diagenetic processes
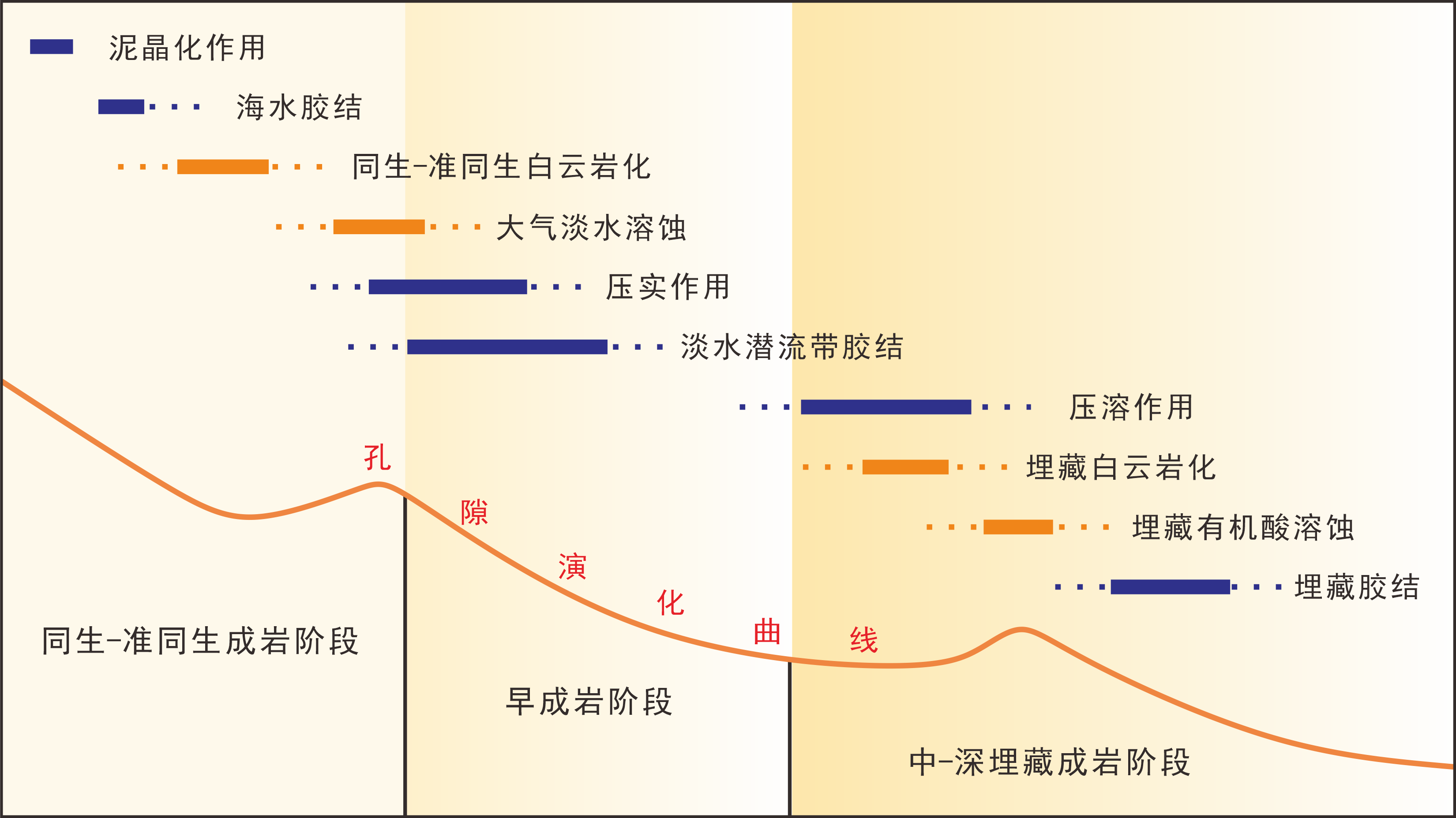
图8 茅口组滩相灰岩储层成岩序列(各成岩作用不确定的起止时间用虚线表示)
Fig.8 Diagenetic sequence of shoal limestone reservoirs in the Maokou Formation(the uncertain starting and ending time of each diagenesis is expressed by dotted line)

图9 川东南茅口组滩相灰岩储层孔隙演化示意图 路径Ⅰ. 生物碎屑被大气淡水选择性溶蚀形成铸膜孔、粒内孔;路径Ⅱ. 斑状白云石在白云石化过程中形成的晶间孔及后期的溶蚀扩大;路径Ⅲ. 自形、零散状白云石在埋藏有机酸溶蚀作用下形成晶模孔;路径Ⅳ. 沿缝合线形成的白云石在埋藏有机酸溶蚀作用下形成晶模孔
Fig.9 Schematic diagram of pore evolution in shoal limestone reservoirs of the Maokou Formation, southeastern Sichuan
| [1] | 胡东风. 四川盆地元坝地区茅口组台缘浅滩天然气勘探的突破与启示[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(3): 1-10. |
| [2] |
曾德铭, 谢晓斌, 黄董, 等. 四川盆地北部二叠系茅口组沉积特征及油气意义[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 45(1):1-12.
DOI |
| [3] | 李素华. 川中资阳地区茅口组岩溶储层识别模式及分布预测[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(4):648-655. |
| [4] | 黎霆, 诸丹诚, 李海平, 等. 中二叠统茅口组白云岩发育机理: 以川中-川东地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(2): 345-355. |
| [5] | 胡东风, 王良军, 张汉荣, 等. 碳酸盐岩烃源岩气藏的发现及其油气地质意义——以四川盆地涪陵地区中二叠统茅口组一段气藏为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(7): 23-33. |
| [6] | 易海永, 张本健, 谷明峰, 等. 四川盆地东部地区二叠系茅口组孤立浅滩的发现及天然气勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业, 2024, 44(6): 1-11. |
| [7] |
匡明志, 张小兵, 袁海锋, 等. 川中地区茅口组碳酸盐岩层序地层及沉积相特征[J]. 古地理学报, 2024: 26(5):1201-1202.
DOI |
| [8] | 肖笛, 黄天海, 张本健, 等. 四川盆地南部向斜区二叠系岩溶孔隙型石灰岩储层成因与天然气勘探新领域[J]. 天然气工业, 2024, 44(2): 52-67. |
| [9] | 江青春, 胡素云, 姜华, 等. 四川盆地中二叠统茅口组地层缺失量计算及成因探讨[J]. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(1): 21-29. |
| [10] | LI G J, CHEN J, CHEN Y. Primary and secondary carbonate in Chinese loess discriminated by trace element composition[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2013, 103: 26-35. |
| [11] | DUNHAM R J. Classification of carbonate rocks according to depositional texture[M]// HAM W E. Classification of Carbonate Rocks: AAPG Memoir 1,1962. |
| [12] |
冯增昭. 碳酸盐岩分类[J]. 石油学报, 1982, 3(1): 11-18,96-98.
DOI |
| [13] | SCHOLLE P A, ULMER-SCHOLLE D S. A color guide to the petrography of carbonate rocks:grains, textures, porosity, diagenesis[M]. Tulas: Americcan Association of Petroleum Geologists, 2003. |
| [14] | DUNCAN F, SIBLEY JAY M, GREG G. Classification of dolomite rock textures[J]. SEPM Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1987,57: 967-975. |
| [15] | SHIELDS G, STILLE P. Diagenetic constraints on the use of cerium anomalies as palaeoseawater redox proxies: An isotopic and REE study of Cambrian phosphorites[J]. Chemical Geology, 2001, 175(1/2): 29-48. |
| [16] | MCLENNAN S M. Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2001, 2(4): 1021. |
| [17] | 黄思静. 碳酸盐岩的成岩作用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2010. |
| [18] | KAUFMAN A J, KNOLL A H. Neoproterozoic variations in the C-isotopic composition of seawater: Stratigraphic and biogeochemical implications[J]. Precambrian Research, 1995, 73: 27-49. |
| [19] | BAU M, KOSCHINSKY A, DULSKI P, et al. Comparison of the partitioning behaviours of yttrium, rare earth elements, and titanium between hydrogenetic marine ferromanganese crusts and seawater[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(10): 1709-1725. |
| [20] | MCKENZIE J A, KENNETH J H S, SCHNEIDER J F. Movement of subsurface waters under the sabkha, Abu Dhabi, UAE, and its relation to evaporative dolomite genesis[M]// Concepts Models of Dolomitization. Talsa: SEPM Society for Sedimenta Geolog,1980. |
| [21] | CORLETT H J, JONES B. Petrographic and geochemical contrasts between calcite- and dolomite-filled burrows in the middle Devonian lonely bay formation, northwest territories, Canada: Implications for dolomite formation in Paleozoic burrows[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2012, 82(9): 648-663. |
| [22] | MACHEL H G. Concepts and models of dolomitization: A critical reappraisal[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2004, 235(1): 7-63. |
| [23] | ALIBO D S, NOZAKI Y. Dissolved rare earth elements in the South China Sea: Geochemical characterization of the water masses[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2000, 105(C12): 28771-28783. |
| [24] | 黄思静, 成欣怡, 赵杰, 等. 近地表温压条件下白云岩溶解过程的实验研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2012, 31(4): 349-359. |
| [25] | LONGMAN M W. Carbonate diagenetic textures from nearsurface diagenetic environments[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1980, 64(4): 461-487. |
| [26] | 威尔逊(J. L. Wilson). 地质历史中的碳酸盐相[M]. 冯增昭等,译. 北京: 地质出版社, 1981. |
| [27] | 李峰峰, 郭睿, 宋世琦. 中东M油田白垩系Mishrif组碳酸盐岩储层特征及主控因素[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(6): 12-24. |
| [28] | DAVIES G R, SMITH L B Jr. Structurally controlled hydrothermal dolomite reservoir facies: An overview[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2006, 90(11): 1641-1690. |
| [29] | 胡力文, 邹华耀, 杨伟强, 等. 川北寒武系碳酸盐岩压溶作用的影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(5): 1221-1231. |
| [30] | WIERZBICKI R, DRAVIS J J, AL-AASM I, et al. Burial dolomitization and dissolution of Upper Jurassic Abenaki platform carbonates, Deep Panuke Reservoir, Nova Scotia, Canada[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2006, 90(11): 1843-1861. |
| [31] | 韩睿, 张尚锋, 罗顺社, 等. 碎屑岩与碳酸盐岩混合沉积模式——以新疆塔西南地区上石炭统卡拉乌依组为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(2):269-276. |
| [32] | 佘敏, 寿建峰, 沈安江, 等. 埋藏有机酸性流体对白云岩储层溶蚀作用的模拟实验[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 38(3): 10-17. |
| [33] | 谢淑云, 雷蕾, 焦存礼, 等. 鲕粒白云岩内部溶蚀及孔隙非均质性演化研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(6): 1174-1187. |
| [34] | 王炳森, 袁海锋, 王涛, 等. 川中蓬莱地区震旦系灯影组四段储层成岩作用、孔隙演化及油气充注[J/OL]. 沉积学报,1-24[2024-06-13]. https://doi.org/10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2024.012. |
| [35] | 孟宪武, 尤东华, 李蓉, 等. 四川盆地茅口组一段缝洞充填物特征及成因——以A1井为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(3):483-490. |
| [36] | 丁梦, 樊太亮, 吴俊, 等. 塔里木盆地塔河油田T738井区一间房组高精度层序地层格架内沉积微相特征[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(5):1270-1290. |
| [37] | 孙自明, 卞昌蓉, 刘光祥. 峨眉山地幔柱主要研究进展及四川盆地二叠纪成盆动力学机制[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(5): 1089-1099. |
| [38] | 邵威猛, 牛永斌, 程梦园, 等. 豫西北奥陶系马家沟组碳酸盐岩中裂缝-溶洞的发育特征及成因机制[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(5): 1306-1320. |
| [1] | 张宏辉, 吴亮, 李鸿, 余杨忠, 袁永盛, 张沥元, 李仕忠, 赵见波, 潘江涛, 詹华思, 石海涛, 陈贵仁. 滇东北乌蒙山地区峨眉地幔柱活动与火山-沉积盆地的响应关系[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 225-243. |
| [2] | 雷涵, 黄文辉, 孙启隆, 车青松. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部奥陶系马五段去白云石化成因及模式[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 378-387. |
| [3] | 王爱, 钟大康, 刘忠群, 王威, 杜红权, 周志恒, 唐自成. 川东北元坝西地区须三段钙屑致密砂岩储层成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1193-1204. |
| [4] | 杨明磊, 诸丹诚, 李涛, 李海平, 黎霆, 邹华耀. 川南地区中二叠统茅口组颗粒滩对早成岩期岩溶储层的控制[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(02): 356-369. |
| [5] | 黎霆, 诸丹诚, 李海平, 杨明磊, 李涛, 李平平, 邹华耀. 中二叠统茅口组白云岩发育机理:以川中-川东地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(02): 345-355. |
| [6] | 伊硕, 黄文辉, 金振奎, 高白水, 朱小二. 哈萨克斯坦Zanazor油田石炭系KT-Ⅱ碳酸盐岩层成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(04): 791-801. |
| [7] | 王晓晨, 罗静兰, 李文厚, 王若谷, 唐启银. 鄂尔多斯盆地苏77、召51区块山23段储层成岩作用与孔隙演化定量分析[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(03): 565-573. |
| [8] | 赵新伟,许红,孙志鹏. 西沙海域新生代生物礁序列的沉积构成:以西科1井为例[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(4): 852-862. |
| [9] | 李锟,于炳松,王黎栋,潘莹露. 塔里木盆地东南地区侏罗系低孔渗砂岩储层成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(2): 388-395. |
| [10] | 董果果,黄文辉,万欢,王华军. 东营凹陷北部陡坡带沙四上亚段砂砾岩储层固体-流体相互作用研究[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(4): 941-948. |
| [11] | 王东, 王国芝. 四川南江地区灯影组白云岩优质储层的形成与演化[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(4): 660-667. |
| [12] | 张丽丽. 张宁. 夏文臣.. 鄂西恩施猫儿山二叠纪茅口组的牙形石[J]. 现代地质, 2004, 18(3): 297-304. |
| [13] | 梅冥相. 李浩. 邓军. 汪新文. 郑宽兵.. 贵阳乌当二叠系茅口组白云岩型古油藏的初步观察与研究[J]. 现代地质, 2004, 18(3): 353-359. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||