



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (02): 378-387.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.002
雷涵1,2,3( ), 黄文辉1,2,3(
), 黄文辉1,2,3( ), 孙启隆1,2,3, 车青松1,2,3
), 孙启隆1,2,3, 车青松1,2,3
收稿日期:2020-09-10
修回日期:2020-11-20
出版日期:2021-04-25
发布日期:2021-05-25
通讯作者:
黄文辉
作者简介:黄文辉,男,教授、博士生导师,1961年出生,沉积学专业,主要从事油气储集层地质学,环境地球化学与煤中金属元素研究。Email: 1999011250@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
LEI Han1,2,3( ), HUANG Wenhui1,2,3(
), HUANG Wenhui1,2,3( ), SUN Qilong1,2,3, CHE Qingsong1,2,3
), SUN Qilong1,2,3, CHE Qingsong1,2,3
Received:2020-09-10
Revised:2020-11-20
Online:2021-04-25
Published:2021-05-25
Contact:
HUANG Wenhui
摘要:
通过研究马五段去白云石化作用的成因及发生模式,可进一步了解鄂尔多斯盆地南部奥陶系碳酸盐岩储集层成岩和物性的演化。通过岩心与薄片的观察,结合地球化学方法,和对白云岩的碳、氧同位素与微量元素的测定,分析了去白云石化作用成因及成岩演化过程,并结合物性资料分析去白云石化作用对储集层的影响,建立了研究区去白云石化的作用模式。结合样品的碳氧同位素和微量元素特征显示:M51+2含石膏结核的白云岩层段普遍受淡水淋滤作用影响,但只有部分层段发生淡水淋滤成因的去白云石化作用,Th/U、Th/Cr、Cr/Zr与Y/Ho特征表明由于淡水淋滤作用,大气淡水溶解陆源花岗岩类物质并携带陆源泥质灌入岩层。淡水淋滤去白云石化作用流体Ca2+源来自溶解蒸发岩(膏盐层)和石膏结核,
中图分类号:
雷涵, 黄文辉, 孙启隆, 车青松. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部奥陶系马五段去白云石化成因及模式[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 378-387.
LEI Han, HUANG Wenhui, SUN Qilong, CHE Qingsong. Dedolomitization Origin and Model for the Ordovician Majiagou Formation (5th Member) in the Southern Ordos Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(02): 378-387.
| 井号 | 深度/m | 岩性 | δ13CPDB/‰ | δ18OVPDB/‰ | Mn/Sr | Y/Ho | Cr/Zr | Th/Cr | Th/U |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1725 | 2 301.43 | 微晶白云岩 | -0.30 | -6.30 | 1.302 | 45.081 | 4.094 | 0.108 | 0.230 |
| Y1757 | 2 906.43 | -0.40 | -6.30 | 0.862 | 44.168 | 1.447 | 0.108 | 0.277 | |
| Y1758 | 3 060.91 | 0.20 | -6.17 | 0.490 | 54.487 | 1.255 | 0.075 | 0.634 | |
| Y1758 | 3 599.74 | 0.40 | -5.40 | 1.042 | 43.234 | 2.407 | 0.053 | 0.761 | |
| Y430 | 2 385.41 | 0.60 | -5.05 | 0.710 | 50.584 | 1.757 | 0.057 | 0.231 | |
| Y391 | 2 903.74 | 0.20 | -5.17 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Y628 | 2 810.72 | 0.50 | -5.55 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Y391 | 2 790.89 | 含膏模孔微 晶云岩 | -0.30 | -5.97 | 2.724 | - | - | - | - |
| Y391 | 2 889.75 | -0.30 | -5.45 | 2.143 | - | - | - | - | |
| Y391 | 2 810.63 | -0.80 | -6.18 | 1.313 | - | - | - | - | |
| Y391 | 3 313.2 | 1.02 | -7.88 | 1.727 | - | - | - | - | |
| Y391 | 3 114.7 | 0.38 | -7.82 | 2.157 | - | - | - | - | |
| Y1725 | 3 275.1 | -1.24 | -7.16 | 1.313 | 44.168 | 1.447 | 0.236 | 0.826 | |
| Y431 | 2 720.6 | -0.89 | -7.45 | 1.205 | 42.995 | 1.193 | 0.158 | 1.083 | |
| Y1757 | 3 320.3 | -0.26 | -7.28 | 2.564 | 39.779 | 0.573 | 0.148 | 0.963 | |
| Y1758 | 3 108.4 | -1.01 | -6.86 | 2.042 | 34.530 | 0.618 | 0.053 | 2.199 | |
| Y391 | 3 113.7 | -0.65 | -8.03 | 1.938 | 38.982 | 0.963 | 0.197 | 0.634 | |
| Y1725 | 2 265 | 含膏模孔微晶 灰质云岩 | -1.71 | -7.99 | 4.450 | 30.058 | 0.618 | 0.148 | 3.826 |
| Y1725 | 2 269 | -2.95 | -8.32 | 5.337 | 36.271 | 0.571 | 0.220 | 3.423 | |
| Y1758 | 3 063 | -2.56 | -8.02 | 3.724 | 34.530 | 0.380 | 0.307 | 3.138 | |
| Y1758 | 3 067 | -2.14 | -7.23 | 3.776 | 34.858 | 0.368 | 0.341 | 3.002 | |
| Y1757 | 3 317.85 | -1.92 | -7.83 | 4.687 | 29.697 | 0.647 | 0.234 | 4.233 | |
| Y431 | 2 718.8 | -3.77 | -11.04 | 5.787 | - | - | - | - | |
| Y628 | 2 809.7 | -2.89 | -8.68 | 3.173 | - | - | - | - | |
| Y677 | 2 259.82 | -4.23 | -8.76 | 3.776 | - | - | - | - |
表1 鄂尔多斯盆地南部马五段白云岩地化数据
Table 1 Geochemical data of dolomite (M5 member) in the southern Ordos basin
| 井号 | 深度/m | 岩性 | δ13CPDB/‰ | δ18OVPDB/‰ | Mn/Sr | Y/Ho | Cr/Zr | Th/Cr | Th/U |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1725 | 2 301.43 | 微晶白云岩 | -0.30 | -6.30 | 1.302 | 45.081 | 4.094 | 0.108 | 0.230 |
| Y1757 | 2 906.43 | -0.40 | -6.30 | 0.862 | 44.168 | 1.447 | 0.108 | 0.277 | |
| Y1758 | 3 060.91 | 0.20 | -6.17 | 0.490 | 54.487 | 1.255 | 0.075 | 0.634 | |
| Y1758 | 3 599.74 | 0.40 | -5.40 | 1.042 | 43.234 | 2.407 | 0.053 | 0.761 | |
| Y430 | 2 385.41 | 0.60 | -5.05 | 0.710 | 50.584 | 1.757 | 0.057 | 0.231 | |
| Y391 | 2 903.74 | 0.20 | -5.17 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Y628 | 2 810.72 | 0.50 | -5.55 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Y391 | 2 790.89 | 含膏模孔微 晶云岩 | -0.30 | -5.97 | 2.724 | - | - | - | - |
| Y391 | 2 889.75 | -0.30 | -5.45 | 2.143 | - | - | - | - | |
| Y391 | 2 810.63 | -0.80 | -6.18 | 1.313 | - | - | - | - | |
| Y391 | 3 313.2 | 1.02 | -7.88 | 1.727 | - | - | - | - | |
| Y391 | 3 114.7 | 0.38 | -7.82 | 2.157 | - | - | - | - | |
| Y1725 | 3 275.1 | -1.24 | -7.16 | 1.313 | 44.168 | 1.447 | 0.236 | 0.826 | |
| Y431 | 2 720.6 | -0.89 | -7.45 | 1.205 | 42.995 | 1.193 | 0.158 | 1.083 | |
| Y1757 | 3 320.3 | -0.26 | -7.28 | 2.564 | 39.779 | 0.573 | 0.148 | 0.963 | |
| Y1758 | 3 108.4 | -1.01 | -6.86 | 2.042 | 34.530 | 0.618 | 0.053 | 2.199 | |
| Y391 | 3 113.7 | -0.65 | -8.03 | 1.938 | 38.982 | 0.963 | 0.197 | 0.634 | |
| Y1725 | 2 265 | 含膏模孔微晶 灰质云岩 | -1.71 | -7.99 | 4.450 | 30.058 | 0.618 | 0.148 | 3.826 |
| Y1725 | 2 269 | -2.95 | -8.32 | 5.337 | 36.271 | 0.571 | 0.220 | 3.423 | |
| Y1758 | 3 063 | -2.56 | -8.02 | 3.724 | 34.530 | 0.380 | 0.307 | 3.138 | |
| Y1758 | 3 067 | -2.14 | -7.23 | 3.776 | 34.858 | 0.368 | 0.341 | 3.002 | |
| Y1757 | 3 317.85 | -1.92 | -7.83 | 4.687 | 29.697 | 0.647 | 0.234 | 4.233 | |
| Y431 | 2 718.8 | -3.77 | -11.04 | 5.787 | - | - | - | - | |
| Y628 | 2 809.7 | -2.89 | -8.68 | 3.173 | - | - | - | - | |
| Y677 | 2 259.82 | -4.23 | -8.76 | 3.776 | - | - | - | - |

图2 鄂尔多斯盆地南部奥陶系马五段碳酸盐岩岩石学特征 (a)Y1725,2 260.82 m,微晶白云岩,铸体薄片;(b)Y1757,3 275.1 m,含膏模孔微晶云岩,膏模孔发育;(c) Y391,3 113.2 m,含膏模孔微晶云岩,膏模孔发育为示底构造;(d)Y1758,3 067 m,含膏模孔微晶灰质云岩,茜素红染色,膏模孔发育为示底构造; (e)Y1758,3 063 m,微晶灰质云岩,铸体薄片,茜素红染色;(f)Y628,2 810.7 m,溶蚀缝将晶粒灰岩破裂成角砾状,溶蚀缝内充填大量泥质(Arg)
Fig.2 Thin-section microscopic features of Ordovician carbonate rocks (M5 member) in the southern Ordos basin

图5 鄂尔多斯盆地南部马五段碳酸盐岩Z值与Y/Ho、Cr/Zr、Th/Cr、Th/U交汇图
Fig.5 Plots of Z vs. Y/Ho, Cr/Zr, Th/Cr, and Th/U of Ordovician carbonate rock samples (M5 member) in the southern Ordos basin
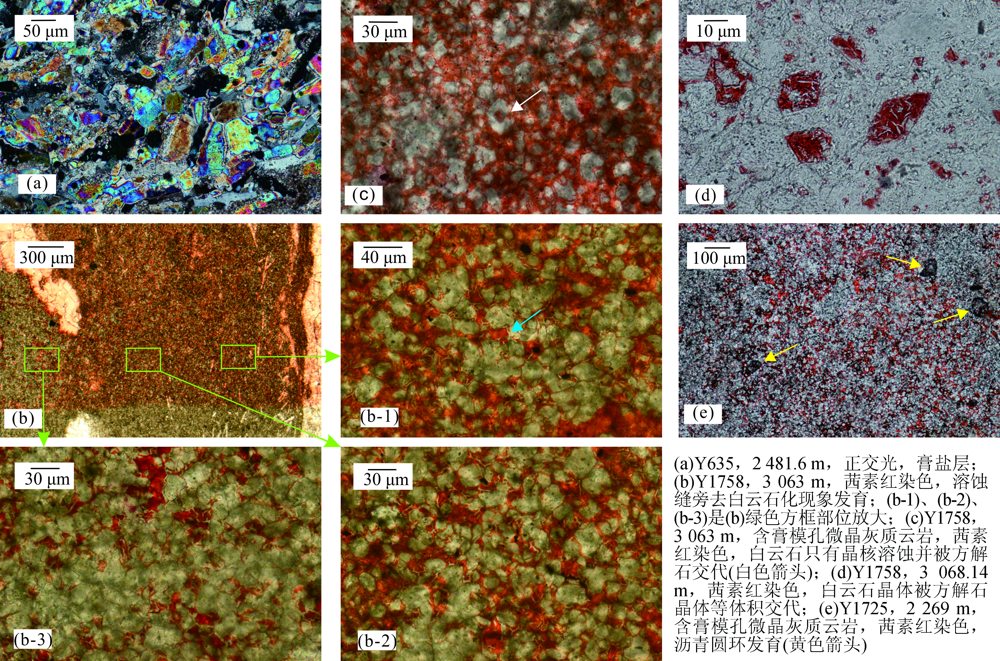
图6 鄂尔多斯盆地南部奥陶系马五段碳酸盐岩—膏盐层岩石学特征
Fig.6 Thin-Section microscopic features of Ordovician carbonate rocks and gypsum layer(M5 member) in the southern Ordos basin
| [1] | EVAMY B. Dedolomitization and the development of rhombohedral pores in limestones[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1967,37(4):1204-1215. |
| [2] | FAIRBRIDGE R W, BOURGEOIS J. The Encyclopedia of sedimentology[M]. Stroudsburg, Pennsylvania: Dowden, 1978: 233-235. |
| [3] | 张杰, 寿建峰, 文应初, 等. 去白云石化作用机理及其对储集层的改造[J]. 古地理学报, 2012,14(1):69-84. |
| [4] | 郭彦如, 付金华, 魏新善, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系碳酸盐岩成藏特征与模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014,41(4):393-403. |
| [5] | 李凤杰, 杜凌春, 赵俊兴, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地苏东地区马家沟组五段5亚段白云岩成因[J]. 石油学报, 2016,37(3):328-338. |
| [6] | 李国欣, 赵太平, 石玉江, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地马家沟组碳酸盐岩储集层成岩相测井识别评价[J]. 石油学报, 2018,39(10):1141-1154. |
| [7] |
RONCHI P, JADOUL F, SAVINO R. Quaternary dedolomitization along fracture systems in a late Triassic Dolomitized platform (western southern Alps, Italy)[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 2004,19(1):51-66.
DOI URL |
| [8] | JØRGENSEN N. Dolomite and dedolomitization in Danian bryozoan limestone from Fakse, Denmark[J]. Bull Geol Soc Denmark, 1988,19(1):51-66. |
| [9] |
KYSER T K, JAMES N P, BONE Y. Shallow burial dolomitization and dedolomitization of Cenozoic cool-water limestones, southern Australia: geochemistry and origin[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2002,72(1) : 146-157.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
RAMEIL N. Early diagenetic dolomitization and dedolomitization of late Jurassic and earliest Cretaceous platform carbonates: a case study from the Jura Mountains (NW Switzerland, E France)[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2008,212(1/4):70-85.
DOI URL |
| [11] | FAUST G T. Dedolomitization, and its relation to a possible derivation of a magnesium-rich hydrothermal solution[J]. American Mineralogist, 1949,34(11):789-823. |
| [12] |
LAND L, PREZBINDOWSKI D. The origin and evolution of saline formation water, lower Cretaceous carbonates, south-central Texas, U.S.A[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1981,54(1/3):51-74.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
WOO K S, MOORE C H. Burial dolomitization and dedolomitization of the late Cambrian Wagok Formation, Yeongweol, Korea[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 1996,11(1):104-112.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 崔欢, 关平, 简星. 塔北西部岩浆热液-地层水流体系统及碳酸盐岩储集层的成岩作用响应[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2012,48(3):433-443. |
| [15] | 覃建雄, 杨作升. 鄂尔多斯碳酸盐岩去白云石化及其与储集性的关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1997(4):61-67. |
| [16] | 李婧娟, 史云鹤, 魏柳斌, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南部奥陶系马五段去白云石化过程的地球化学示踪[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019,38(3):336-343. |
| [17] |
RAINES M A, DEWERS T A. Dedolomitization as a driving mechanism for karst generation in Permian Blaine formation, southwestern Oklahoma, USA[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 1997,12(1):24-31.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
BACK W, HANSHAW B B, PLUMMER L N, et al. Process and rate of dedolomitization: mass transfer and 14C dating in a regional carbonate aquifer[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1983,94(12):1415-1429.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 苏中堂, 陈洪德, 朱平, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部马家沟组孔隙类型及其演化[J]. 海相油气地质, 2010,15(4):6-13. |
| [20] | 何明倩, 黄文辉, 久博. 鄂尔多斯盆地膏质白云岩有利储集层的成因及演化[J/OL]. 地学前缘:1-13[2020-09-13]. https://doi.org/10.13745/j.esf.sf.2020.5.6. |
| [21] | 杨华, 包洪平. 鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系中组合成藏特征及勘探启示[J]. 天然气工业, 2011,31(12):11-20+124. |
| [22] | LI R, LI Y. Tectonic evolution of the western margin of the Ordos Basin (central China)[J]. Russian Geology & Geophysics, 2008,49(1):23-27. |
| [23] | MEYERS W J, LU F H, ZACHARIAH J K. Dolomitization by mixed evaporative brines and freshwater, upper Miocene carbonates, Nijar, Spain[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1997,67(5):898-912. |
| [24] | 王坤, 李伟, 陆进, 等. 川东地区石炭系碳酸盐岩碳、氧、锶同位素特征及其成因分析[J]. 地球化学, 2011,40(4):351-362. |
| [25] | GAT J R. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the hydrologic cycle annual[J]. Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1996,24(1):225-262. |
| [26] | 贺训云, 寿建峰, 沈安江, 等. 白云岩地球化学特征及成因:以鄂尔多斯盆地靖西马五段中组合为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014,41(3) : 375-384. |
| [27] | 李秋芬, 苗顺德, 李永新, 等. 四川盆地川中地区盐亭—潼南海槽台缘带二叠系长兴组储集层特征及成因探讨[J]. 地球科学, 2018,43(10):3553-3567. |
| [28] | 金民东, 谭秀成, 李毕松, 等. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组白云岩成因[J]. 沉积学报, 2019,37(3):443-454. |
| [29] | 王保全, 强子同, 张帆, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系马家沟组马五段白云岩的同位素地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, 2009,38(5):472-479. |
| [30] |
KEITH M L, WEBER J N. Carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of selected limestones and fossils[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1964,28(10/11):1787-1816.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
URMANTSEVA L, TURKINA O M, KAPITONOV I N. Protoliths of paleoproterozoic calciphyres from the Irkut block (Sharyzhalgai uplift of the Siberian Craton): Composition and origin[J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 2012,53(12):1291-1303.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
MORADI A, SARI A, AKKAYA P. Geochemistry of the Miocene oil shale (Hançili Formation) in the Çankırı-Çorum Basin, central Turkey: implications for paleoclimate conditions, source-area weathering, provenance and tectonic setting[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2016,341:289-303.
DOI URL |
| [33] | 冯轲, 徐胜林, 陈洪德, 等. 四川盆地西南部中二叠统白云岩成因分析——来自锶同位素、稀土元素证据[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018,37(5):659-670. |
| [34] |
WRONKIEWICZ D, CONDIE K. Geochemistry and provenance of sediments from the Pongola Supergroup, South Africa: evidence for a 3.0-Ga-old continental craton[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989,53(7):1537-1549.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
CULLERS R. Implications of elemental concentrations for provenance, redox conditions, and metamorphic studies of shales and limestones near Pueblo, CO, USA[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002,191(4):305-327.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 黄思静, QING HaiRuo, 胡作维, 等. 封闭系统中的白云石化作用及其石油地质学和矿床学意义——以四川盆地东北部三叠系飞仙关组碳酸盐岩为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(11):2955-2962. |
| [37] | 包洪平, 杨帆, 白海峰, 等. 细分小层岩相古地理编图的沉积学研究及油气勘探意义——以鄂尔多斯地区中东部奥陶系马家沟组马五段为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2017,33(4):1094-1106. |
| [38] | 卢蜀秀, 邓军, 白海峰. 鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系盐下二氧化碳气藏成因分析[J]. 石油化工应用, 2013,32(5):77-81. |
| [39] | 伊硕, 黄文辉, 王一刚, 等. 延安以南地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩储层中流体包裹体及烃类物质的油气指示意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2018,25(6):38-44. |
| [40] |
FU Q L, QING H R, KATHERINE M B, et al. Dedolomitization and calcite cementation in the middle Devonian Winnipegosis Formation in central Saskatchewan,Canada[J]. Sedimentology, 2008,55(6):1623-1642.
DOI URL |
| [41] | JONES B, PLEYDELL S M, NG K-C, et al. Formation of poikilotopic calcite-dolomite fabrics in the Oligocene-Miocene Bluff Formation of Grand Cayman, British West Indies[J]. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 1989,37(3):255-265. |
| [42] |
GUO B, SANDERS J E, FRIEDMAN G M. Timing and origin of dedolomite in upper Wappinger Group (Lower Ordovician) strata, southeastern New York[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 1996,11(1):113-133.
DOI URL |
| [43] | 朱光有, 张水昌, 梁英波, 等. TSR对深部碳酸盐岩储层的溶蚀改造——四川盆地深部碳酸盐岩优质储层形成的重要方式[J]. 岩石学报, 2006,22(8):2182-2194. |
| [1] | 师良, 范柏江, 王霞, 李亚婷, 黄飞飞, 戴欣洋. 鄂尔多斯盆地长9页岩烃源岩的元素组成及其古沉积环境[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1254-1263. |
| [2] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [3] | 邵威猛, 牛永斌, 程梦园, 韩科龙, 孙凤余, 程怡高, 荆楚涵. 豫西北奥陶系马家沟组碳酸盐岩中裂缝-溶洞的发育特征及成因机制[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1306-1320. |
| [4] | 柳晨, 李江海, 王志琛. 南中国海形成演化的动力学模式分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 259-269. |
| [5] | 崔树辉, 吴鹏, 赵霏, 牛艳伟, 蔡文浙, 王波. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘临兴区块页岩气成藏因素分析及富集区预测[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1271-1280. |
| [6] | 郑庆华, 刘行军, 张小龙, 王洪君, 廖永乐, 安二亮, 刘涛, 张建娜, 左琴. 再论鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长73砂层组与烃源岩相关的高伽马砂岩[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1087-1094. |
| [7] | 朱必清, 陈世加, 白艳军, 雷俊杰, 尹相东. 鄂尔多斯盆地甘泉地区延长组长8段原油地球化学特征及来源[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 742-754. |
| [8] | 杨峰田, 石宇佳, 李文庆. 基于水文地球化学特征的辽宁丹东地区地热水成因模式研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 474-483. |
| [9] | 师良, 赵彤彤, 查辉, 王妍妍, 霍萍萍, 范柏江. 延安周边地区页岩地球化学特征及页岩油潜力评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 1043-1053. |
| [10] | 崔改霞, 魏钦廉, 肖玲, 王松, 胡榕, 王翀峘. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区二叠系盒8下段致密砂岩储层特征[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 1088-1097. |
| [11] | 李海学, 程旭学, 马岳昆, 刘伟坡, 周斌. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部马莲河流域地下水中锶富集特征及成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 682-692. |
| [12] | 卢丽, 陈余道, 代俊鸽, 王喆, 邹胜章, 樊连杰, 林永生, 周长松. 四川昭觉竹核温泉水文地球化学特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 703-710. |
| [13] | 张卢明, 杨东, 周勇, 刘鹏. 震后深切拉槽型泥石流成因模式、暴发特点与防治:以四川九寨沟牙扎沟为例[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 744-752. |
| [14] | 张春潮, 李向全, 马剑飞, 付昌昌, 白占学. 基于水化学及稳定同位素的西藏察雅地下热水成因研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 199-208. |
| [15] | 胡妍, 胡永兴, 张翔, 杨涛, 欧扬剑. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘镇原地区砂岩型铀矿元素地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1153-1165. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||