



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (06): 1153-1165.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.086
收稿日期:2019-09-20
修回日期:2020-06-15
出版日期:2020-12-22
发布日期:2020-12-22
通讯作者:
胡永兴
作者简介:胡永兴,男,硕士,工程师,1987年出生,环境工程专业,主要从事能源地质调查与研究工作。Email:306762203@qq.com。基金资助:
HU Yan( ), HU Yongxing(
), HU Yongxing( ), ZHANG Xiang, YANG Tao, OU Yangjian
), ZHANG Xiang, YANG Tao, OU Yangjian
Received:2019-09-20
Revised:2020-06-15
Online:2020-12-22
Published:2020-12-22
Contact:
HU Yongxing
摘要:
通过分析鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘镇原地区下白垩统洛河组含铀砂岩的主、微量元素特征,初步探讨了该区砂岩型铀成矿条件及成矿规律。研究结果表明,研究区下白垩统洛河组铀矿石主要为沥青铀矿(UO2),含铀砂岩可能来自古老沉积地体或克拉通/再旋回造山带的石英岩沉积物源区。含铀砂岩富集轻稀土(LREE),亏损重稀土(HREE),且具明显的Eu负异常,一致的稀土元素特征表明该区成矿围岩具有统一的物源、沉积环境和构造背景。含铀砂岩的V/Cr、Ni/Co、U/Th、V/(V+Ni)比值特征说明,该区铀矿化主要发育于弱氧化—弱还原的过渡环境;其δEu和δCe值均随U含量的增加而增大,反映U元素的富集成矿经历了由氧化向还原环境转化的过程,砂体颜色由浅红色褪色蚀变为灰白色。含铀砂岩中Th、Sc、Co、Mo含量与U含量呈正相关关系,认为Th、Sc、Co、Mo可作为研究区洛河组砂岩型铀矿富集的指示元素。研究区砂岩型铀矿的形成与深部向上逸散的还原性油气流体作用关系密切,油气流体的侵入增加了砂体的还原容量,有利于含铀含氧水中铀离子在氧化—还原过渡带发生沉积富集,形成洛河组大面积的铀异常。
中图分类号:
胡妍, 胡永兴, 张翔, 杨涛, 欧扬剑. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘镇原地区砂岩型铀矿元素地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1153-1165.
HU Yan, HU Yongxing, ZHANG Xiang, YANG Tao, OU Yangjian. Geochemical Features and Geological Significance of Sandstone-type Uranium Deposit in Zhenyuan Area, Southwestern Ordos Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(06): 1153-1165.
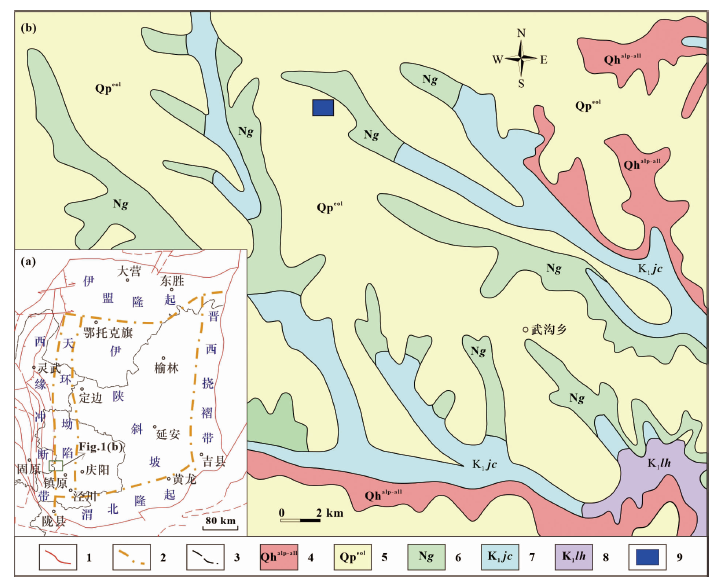
图1 研究区地质简图(修改自1∶25万平凉幅地质图) 1.断层;2.构造单元界线;3.省界;4.全新统;5.更新统;6.干河沟组;7.泾川组;8.罗汉洞组;9.研究区
Fig.1 Geological map of the study area (modified from the Pingliang 1∶250k geological map sheet)
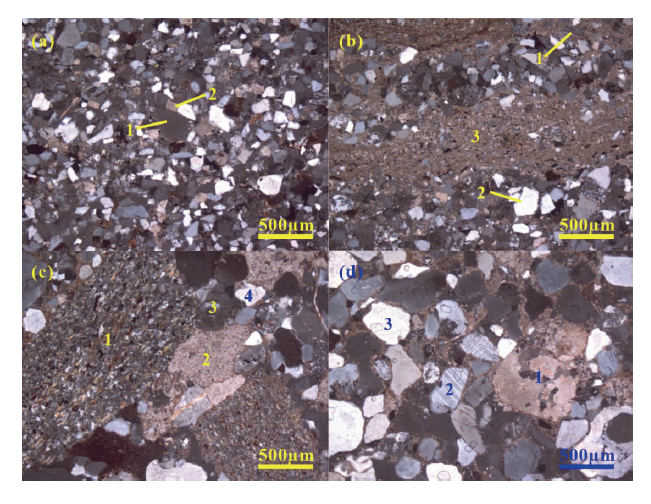
图3 长石石英砂岩((a)、(b))及含砾长石石英砂岩((c)、(d))显微照片 (a)中1.石英,2.碳酸岩;(b)中1.斜长石,2.石英,3.方解石;(c)中1.岩屑,2.方解石,3.长石,4.石英;(d)中1.方解石,2.长石,3.石英
Fig.3 Photomicrographs of the feldspar-quartz sandstone ((a)、(b)) and pebbly feldspar-quartz sandstone ((c)、(d))
| 样品 | 岩性 | 取样深度 /m | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | MnO | TiO2 | 烧失量 | FeO | Fe2O3 | Fe3+/ Fe2+ | CIA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 青灰色细砂岩 | 783.48 | 40.36 | 8.93 | 3.97 | 8.48 | 11.52 | 0.45 | 4.28 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.44 | 18.45 | 1.70 | 2.08 | 26.19 | 59.32 |
| H2 | 青灰色泥质粉砂岩 | 783.69 | 34.57 | 8.24 | 3.91 | 8.96 | 13.56 | 0.29 | 4.26 | 0.61 | 0.13 | 0.36 | 20.75 | 1.90 | 1.80 | 900.00 | 59.64 |
| H3 | 青灰色细砂岩 | 783.79 | 57.23 | 7.54 | 3.31 | 5.84 | 8.22 | 0.73 | 3.41 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.36 | 12.89 | 1.58 | 1.55 | 12.24 | 55.27 |
| H4 | 浅灰色-浅灰褐色中粗粒砂岩 | 910.09 | 40.55 | 2.34 | 1.02 | 7.56 | 22.97 | <0.02 | 0.96 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 25.12 | 0.56 | 0.40 | 22.32 | - |
| H5 | 浅灰色-浅灰褐色砾岩 | 910.29 | 33.64 | 2.10 | 1.05 | 7.05 | 27.76 | <0.02 | 0.75 | 0.57 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 27.74 | 0.44 | 0.56 | 60.66 | - |
| H6 | 浅灰色-浅灰褐色砾岩 | 910.79 | 48.97 | 2.89 | 1.14 | 7.04 | 18.09 | 0.16 | 1.09 | 1.30 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 19.55 | 0.38 | 0.72 | 146.25 | 62.84 |
| H7 | 浅灰色-浅灰褐色中砂岩 | 911.24 | 34.00 | 2.15 | 1.06 | 8.13 | 26.41 | <0.02 | 0.74 | 0.38 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 27.67 | 0.44 | 0.57 | 36.27 | - |
| H8 | 灰白色含砾粗砂岩 | 917.46 | 50.43 | 3.08 | 1.16 | 5.08 | 19.36 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 19.15 | 0.38 | 0.74 | 100.80 | 66.11 |
| H9 | 浅灰褐色-浅砖红色含砾粗砂岩 | 917.76 | 56.69 | 3.09 | 1.17 | 4.75 | 15.87 | 0.30 | 1.20 | 1.70 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 15.09 | 0.32 | 0.81 | 279.00 | 57.44 |
| H10 | 浅灰褐色-浅砖红色含砾粗砂岩 | 918.86 | 45.77 | 3.67 | 1.99 | 5.80 | 19.83 | 0.17 | 1.50 | 1.07 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 20.27 | 0.82 | 1.08 | 360.00 | 62.66 |
| H11 | 浅灰褐色-浅砖红色含砾粗砂岩 | 919.86 | 58.41 | 3.07 | 1.12 | 3.88 | 16.06 | 0.23 | 1.18 | 0.54 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 15.64 | 0.41 | 0.66 | 72.00 | 60.11 |
| H12 | 灰白色砾岩 | 920.16 | 36.99 | 2.29 | 1.09 | 8.16 | 24.89 | <0.02 | 0.78 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 26.34 | 0.26 | 0.80 | 36.99 | - |
| H13 | 灰白色砾岩 | 921.02 | 42.01 | 2.62 | 1.28 | 6.05 | 23.64 | 0.04 | 0.99 | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 23.47 | 0.34 | 0.90 | 43.56 | 68.48 |
| H14 | 灰白色中粗粒砂岩 | 921.42 | 58.81 | 6.03 | 2.70 | 4.64 | 10.74 | 0.49 | 2.59 | 1.81 | 0.05 | 0.24 | 11.66 | 0.64 | 1.99 | 792.00 | 57.69 |
| H15 | 灰白色中粗粒砂岩 | 921.62 | 77.72 | 3.95 | 0.77 | 1.87 | 6.14 | 0.64 | 1.54 | 2.20 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 4.64 | 0.17 | 0.58 | 288.00 | 51.12 |
| H16 | 灰白色中粗粒砂岩 | 921.92 | 58.74 | 3.09 | 1.07 | 4.31 | 15.15 | 0.28 | 1.22 | 1.28 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 14.91 | 0.42 | 0.60 | 158.40 | 57.92 |
| H17 | 灰白色砾岩 | 922.17 | 44.08 | 2.61 | 1.33 | 8.14 | 19.98 | <0.02 | 0.95 | 0.79 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 22.57 | 0.43 | 0.85 | 144.00 | - |
| H18 | 灰白色中粒砂岩 | 927.44 | 61.49 | 4.74 | 1.58 | 4.91 | 10.68 | 0.58 | 2.12 | 1.81 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 11.75 | 0.58 | 0.94 | 110.70 | 52.97 |
| H19 | 灰白色砾岩 | 928.54 | 60.27 | 5.63 | 1.98 | 4.56 | 10.80 | 0.47 | 2.41 | 1.16 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 12.28 | 0.76 | 1.14 | 140.40 | 57.50 |
| H20 | 灰白色砾岩 | 929.04 | 57.89 | 3.25 | 1.41 | 4.54 | 15.05 | 0.27 | 1.27 | 1.04 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 15.30 | 0.63 | 0.71 | 79.47 | 58.91 |
| H21 | 灰白色砾岩 | 929.64 | 37.90 | 2.97 | 1.46 | 6.29 | 24.88 | 0.03 | 1.16 | 0.84 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 24.68 | 0.68 | 0.70 | 405.00 | 68.63 |
| H22 | 浅灰白色中粗粒砂岩 | 958.57 | 81.99 | 5.08 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 4.28 | 0.94 | 2.01 | 1.28 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 2.78 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 107.55 | 49.06 |
| H23 | 浅灰白色中粗粒砂岩 | 958.97 | 62.15 | 7.84 | 3.05 | 3.74 | 7.07 | 0.74 | 3.30 | 0.77 | 0.06 | 0.29 | 8.90 | 1.33 | 1.57 | 549.00 | 56.58 |
| H24 | 浅灰白色中粗粒砂岩 | 959.15 | 79.21 | 4.89 | 1.07 | 1.79 | 4.23 | 0.91 | 2.00 | 0.77 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 4.69 | 0.62 | 0.38 | 64.53 | 48.64 |
表1 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘镇原地区砂岩型铀矿含铀砂岩主量元素分析结果表(%)
Table 1 Major element data of the uranium-bearing sandstone in the Zhenyuan sandstone-type uranium deposit,southwestern Ordos Basin (%)
| 样品 | 岩性 | 取样深度 /m | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | MnO | TiO2 | 烧失量 | FeO | Fe2O3 | Fe3+/ Fe2+ | CIA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 青灰色细砂岩 | 783.48 | 40.36 | 8.93 | 3.97 | 8.48 | 11.52 | 0.45 | 4.28 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.44 | 18.45 | 1.70 | 2.08 | 26.19 | 59.32 |
| H2 | 青灰色泥质粉砂岩 | 783.69 | 34.57 | 8.24 | 3.91 | 8.96 | 13.56 | 0.29 | 4.26 | 0.61 | 0.13 | 0.36 | 20.75 | 1.90 | 1.80 | 900.00 | 59.64 |
| H3 | 青灰色细砂岩 | 783.79 | 57.23 | 7.54 | 3.31 | 5.84 | 8.22 | 0.73 | 3.41 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.36 | 12.89 | 1.58 | 1.55 | 12.24 | 55.27 |
| H4 | 浅灰色-浅灰褐色中粗粒砂岩 | 910.09 | 40.55 | 2.34 | 1.02 | 7.56 | 22.97 | <0.02 | 0.96 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 25.12 | 0.56 | 0.40 | 22.32 | - |
| H5 | 浅灰色-浅灰褐色砾岩 | 910.29 | 33.64 | 2.10 | 1.05 | 7.05 | 27.76 | <0.02 | 0.75 | 0.57 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 27.74 | 0.44 | 0.56 | 60.66 | - |
| H6 | 浅灰色-浅灰褐色砾岩 | 910.79 | 48.97 | 2.89 | 1.14 | 7.04 | 18.09 | 0.16 | 1.09 | 1.30 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 19.55 | 0.38 | 0.72 | 146.25 | 62.84 |
| H7 | 浅灰色-浅灰褐色中砂岩 | 911.24 | 34.00 | 2.15 | 1.06 | 8.13 | 26.41 | <0.02 | 0.74 | 0.38 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 27.67 | 0.44 | 0.57 | 36.27 | - |
| H8 | 灰白色含砾粗砂岩 | 917.46 | 50.43 | 3.08 | 1.16 | 5.08 | 19.36 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 19.15 | 0.38 | 0.74 | 100.80 | 66.11 |
| H9 | 浅灰褐色-浅砖红色含砾粗砂岩 | 917.76 | 56.69 | 3.09 | 1.17 | 4.75 | 15.87 | 0.30 | 1.20 | 1.70 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 15.09 | 0.32 | 0.81 | 279.00 | 57.44 |
| H10 | 浅灰褐色-浅砖红色含砾粗砂岩 | 918.86 | 45.77 | 3.67 | 1.99 | 5.80 | 19.83 | 0.17 | 1.50 | 1.07 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 20.27 | 0.82 | 1.08 | 360.00 | 62.66 |
| H11 | 浅灰褐色-浅砖红色含砾粗砂岩 | 919.86 | 58.41 | 3.07 | 1.12 | 3.88 | 16.06 | 0.23 | 1.18 | 0.54 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 15.64 | 0.41 | 0.66 | 72.00 | 60.11 |
| H12 | 灰白色砾岩 | 920.16 | 36.99 | 2.29 | 1.09 | 8.16 | 24.89 | <0.02 | 0.78 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 26.34 | 0.26 | 0.80 | 36.99 | - |
| H13 | 灰白色砾岩 | 921.02 | 42.01 | 2.62 | 1.28 | 6.05 | 23.64 | 0.04 | 0.99 | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 23.47 | 0.34 | 0.90 | 43.56 | 68.48 |
| H14 | 灰白色中粗粒砂岩 | 921.42 | 58.81 | 6.03 | 2.70 | 4.64 | 10.74 | 0.49 | 2.59 | 1.81 | 0.05 | 0.24 | 11.66 | 0.64 | 1.99 | 792.00 | 57.69 |
| H15 | 灰白色中粗粒砂岩 | 921.62 | 77.72 | 3.95 | 0.77 | 1.87 | 6.14 | 0.64 | 1.54 | 2.20 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 4.64 | 0.17 | 0.58 | 288.00 | 51.12 |
| H16 | 灰白色中粗粒砂岩 | 921.92 | 58.74 | 3.09 | 1.07 | 4.31 | 15.15 | 0.28 | 1.22 | 1.28 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 14.91 | 0.42 | 0.60 | 158.40 | 57.92 |
| H17 | 灰白色砾岩 | 922.17 | 44.08 | 2.61 | 1.33 | 8.14 | 19.98 | <0.02 | 0.95 | 0.79 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 22.57 | 0.43 | 0.85 | 144.00 | - |
| H18 | 灰白色中粒砂岩 | 927.44 | 61.49 | 4.74 | 1.58 | 4.91 | 10.68 | 0.58 | 2.12 | 1.81 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 11.75 | 0.58 | 0.94 | 110.70 | 52.97 |
| H19 | 灰白色砾岩 | 928.54 | 60.27 | 5.63 | 1.98 | 4.56 | 10.80 | 0.47 | 2.41 | 1.16 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 12.28 | 0.76 | 1.14 | 140.40 | 57.50 |
| H20 | 灰白色砾岩 | 929.04 | 57.89 | 3.25 | 1.41 | 4.54 | 15.05 | 0.27 | 1.27 | 1.04 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 15.30 | 0.63 | 0.71 | 79.47 | 58.91 |
| H21 | 灰白色砾岩 | 929.64 | 37.90 | 2.97 | 1.46 | 6.29 | 24.88 | 0.03 | 1.16 | 0.84 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 24.68 | 0.68 | 0.70 | 405.00 | 68.63 |
| H22 | 浅灰白色中粗粒砂岩 | 958.57 | 81.99 | 5.08 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 4.28 | 0.94 | 2.01 | 1.28 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 2.78 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 107.55 | 49.06 |
| H23 | 浅灰白色中粗粒砂岩 | 958.97 | 62.15 | 7.84 | 3.05 | 3.74 | 7.07 | 0.74 | 3.30 | 0.77 | 0.06 | 0.29 | 8.90 | 1.33 | 1.57 | 549.00 | 56.58 |
| H24 | 浅灰白色中粗粒砂岩 | 959.15 | 79.21 | 4.89 | 1.07 | 1.79 | 4.23 | 0.91 | 2.00 | 0.77 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 4.69 | 0.62 | 0.38 | 64.53 | 48.64 |
| 样号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/ HREE | δEu | δCe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 26.9 | 47.9 | 6.11 | 21.5 | 3.83 | 0.89 | 3.52 | 0.55 | 2.77 | 0.56 | 1.56 | 0.25 | 1.58 | 0.25 | 14.8 | 133.00 | 107.17 | 25.82 | 4.15 | 0.74 | 0.92 |
| H2 | 35.5 | 65.7 | 7.98 | 29.4 | 5.40 | 1.13 | 4.94 | 0.85 | 4.92 | 1.08 | 3.21 | 0.52 | 2.93 | 0.45 | 31.3 | 195.29 | 145.11 | 50.18 | 2.89 | 0.67 | 0.96 |
| H3 | 23.6 | 42.3 | 5.08 | 17.4 | 3.12 | 0.72 | 2.91 | 0.45 | 2.23 | 0.43 | 1.24 | 0.22 | 1.34 | 0.22 | 11.2 | 112.49 | 92.26 | 20.23 | 4.56 | 0.73 | 0.95 |
| H4 | 9.73 | 17.6 | 2.06 | 7.64 | 1.38 | 0.43 | 1.28 | 0.21 | 1.10 | 0.23 | 0.63 | 0.12 | 0.69 | 0.12 | 6.55 | 49.80 | 38.87 | 10.92 | 3.56 | 0.98 | 0.97 |
| H5 | 7.98 | 14.4 | 1.73 | 6.20 | 1.21 | 0.29 | 1.11 | 0.18 | 1.01 | 0.22 | 0.69 | 0.14 | 0.92 | 0.17 | 6.51 | 42.79 | 31.84 | 10.95 | 2.91 | 0.78 | 0.95 |
| H6 | 9.37 | 17.2 | 2.01 | 7.31 | 1.32 | 0.37 | 1.25 | 0.20 | 1.21 | 0.29 | 1.13 | 0.27 | 1.71 | 0.34 | 8.64 | 52.62 | 37.59 | 15.03 | 2.50 | 0.87 | 0.97 |
| H7 | 8.72 | 16.0 | 1.88 | 6.84 | 1.31 | 0.34 | 1.22 | 0.20 | 1.08 | 0.22 | 0.69 | 0.14 | 0.89 | 0.16 | 6.88 | 46.56 | 35.09 | 11.47 | 3.06 | 0.81 | 0.97 |
| H8 | 10.7 | 19.4 | 2.28 | 8.04 | 1.56 | 0.40 | 1.47 | 0.23 | 1.29 | 0.26 | 0.78 | 0.13 | 0.86 | 0.14 | 7.78 | 55.38 | 42.43 | 12.95 | 3.28 | 0.81 | 0.96 |
| H9 | 10.8 | 20.8 | 2.38 | 8.62 | 1.63 | 0.44 | 1.51 | 0.26 | 1.42 | 0.33 | 0.92 | 0.14 | 0.90 | 0.16 | 8.78 | 59.09 | 44.68 | 14.42 | 3.10 | 0.86 | 1.00 |
| H10 | 11.7 | 22.8 | 2.55 | 9.28 | 1.78 | 0.43 | 1.63 | 0.28 | 1.62 | 0.33 | 0.94 | 0.15 | 0.89 | 0.16 | 9.09 | 63.63 | 48.52 | 15.10 | 3.21 | 0.77 | 1.02 |
| H11 | 10.9 | 19.9 | 2.34 | 8.24 | 1.55 | 0.41 | 1.40 | 0.22 | 1.13 | 0.23 | 0.63 | 0.11 | 0.69 | 0.11 | 6.36 | 54.18 | 43.30 | 10.87 | 3.98 | 0.85 | 0.97 |
| H12 | 10.1 | 18.6 | 2.12 | 7.48 | 1.36 | 0.35 | 1.33 | 0.21 | 1.10 | 0.22 | 0.58 | 0.09 | 0.60 | 0.10 | 6.15 | 50.44 | 40.06 | 10.38 | 3.86 | 0.79 | 0.99 |
| H13 | 10.7 | 18.8 | 2.23 | 7.80 | 1.45 | 0.40 | 1.40 | 0.22 | 1.20 | 0.25 | 0.68 | 0.11 | 0.68 | 0.12 | 6.90 | 52.94 | 41.39 | 11.55 | 3.58 | 0.87 | 0.94 |
| H14 | 19.1 | 37.4 | 4.36 | 15.8 | 2.93 | 0.66 | 2.81 | 0.47 | 2.65 | 0.54 | 1.42 | 0.22 | 1.26 | 0.21 | 14.3 | 104.08 | 80.20 | 23.88 | 3.36 | 0.71 | 1.00 |
| H15 | 10.3 | 19.1 | 2.21 | 7.93 | 1.46 | 0.45 | 1.42 | 0.25 | 1.49 | 0.33 | 0.92 | 0.15 | 0.85 | 0.14 | 8.86 | 55.82 | 41.42 | 14.40 | 2.88 | 0.95 | 0.98 |
| H16 | 9.39 | 17.4 | 2.08 | 7.32 | 1.33 | 0.35 | 1.24 | 0.21 | 1.15 | 0.25 | 0.72 | 0.13 | 0.74 | 0.12 | 6.92 | 49.39 | 37.91 | 11.48 | 3.30 | 0.84 | 0.97 |
| H17 | 10.1 | 19.2 | 2.21 | 8.43 | 1.54 | 0.38 | 1.37 | 0.22 | 1.14 | 0.22 | 0.66 | 0.10 | 0.59 | 0.095 | 6.35 | 52.66 | 41.92 | 10.74 | 3.90 | 0.80 | 0.99 |
| H18 | 13.9 | 25.3 | 2.87 | 10.1 | 1.80 | 0.48 | 1.71 | 0.27 | 1.51 | 0.33 | 1.02 | 0.16 | 1.01 | 0.15 | 9.18 | 69.79 | 54.45 | 15.33 | 3.55 | 0.84 | 0.98 |
| H19 | 16.1 | 29.6 | 3.41 | 12.3 | 2.17 | 0.60 | 2.04 | 0.33 | 1.67 | 0.33 | 0.94 | 0.16 | 0.97 | 0.16 | 8.79 | 79.63 | 64.25 | 15.38 | 4.18 | 0.87 | 0.98 |
| H20 | 10.1 | 18.6 | 2.18 | 7.83 | 1.41 | 0.39 | 1.32 | 0.21 | 1.10 | 0.24 | 0.66 | 0.12 | 0.79 | 0.13 | 6.51 | 51.61 | 40.53 | 11.08 | 3.66 | 0.87 | 0.97 |
| H21 | 11.6 | 21.8 | 2.55 | 9.01 | 1.67 | 0.38 | 1.60 | 0.25 | 1.31 | 0.26 | 0.71 | 0.12 | 0.77 | 0.12 | 7.42 | 59.62 | 47.06 | 12.57 | 3.74 | 0.70 | 0.98 |
| H22 | 9.38 | 19.1 | 2.14 | 7.45 | 1.29 | 0.37 | 1.18 | 0.18 | 0.99 | 0.20 | 0.63 | 0.12 | 0.81 | 0.14 | 5.58 | 49.57 | 39.74 | 9.83 | 4.04 | 0.91 | 1.05 |
| H23 | 22.7 | 44.1 | 5.08 | 18.2 | 3.40 | 0.80 | 3.04 | 0.49 | 2.50 | 0.47 | 1.34 | 0.20 | 1.29 | 0.21 | 13.1 | 116.92 | 94.30 | 22.62 | 4.17 | 0.76 | 1.01 |
| H24 | 11.7 | 22.6 | 2.55 | 8.94 | 1.58 | 0.46 | 1.46 | 0.22 | 1.16 | 0.23 | 0.67 | 0.11 | 0.73 | 0.13 | 6.29 | 58.81 | 47.80 | 11.02 | 4.34 | 0.92 | 1.01 |
表2 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘镇原地区砂岩型铀矿含铀砂岩稀土元素分析结果表(10-6)
Table 2 REE data of the uranium-bearing sandstone in the Zhenyuan sandstone-type uranium deposit,southwestern Ordos Basin (10-6)
| 样号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/ HREE | δEu | δCe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 26.9 | 47.9 | 6.11 | 21.5 | 3.83 | 0.89 | 3.52 | 0.55 | 2.77 | 0.56 | 1.56 | 0.25 | 1.58 | 0.25 | 14.8 | 133.00 | 107.17 | 25.82 | 4.15 | 0.74 | 0.92 |
| H2 | 35.5 | 65.7 | 7.98 | 29.4 | 5.40 | 1.13 | 4.94 | 0.85 | 4.92 | 1.08 | 3.21 | 0.52 | 2.93 | 0.45 | 31.3 | 195.29 | 145.11 | 50.18 | 2.89 | 0.67 | 0.96 |
| H3 | 23.6 | 42.3 | 5.08 | 17.4 | 3.12 | 0.72 | 2.91 | 0.45 | 2.23 | 0.43 | 1.24 | 0.22 | 1.34 | 0.22 | 11.2 | 112.49 | 92.26 | 20.23 | 4.56 | 0.73 | 0.95 |
| H4 | 9.73 | 17.6 | 2.06 | 7.64 | 1.38 | 0.43 | 1.28 | 0.21 | 1.10 | 0.23 | 0.63 | 0.12 | 0.69 | 0.12 | 6.55 | 49.80 | 38.87 | 10.92 | 3.56 | 0.98 | 0.97 |
| H5 | 7.98 | 14.4 | 1.73 | 6.20 | 1.21 | 0.29 | 1.11 | 0.18 | 1.01 | 0.22 | 0.69 | 0.14 | 0.92 | 0.17 | 6.51 | 42.79 | 31.84 | 10.95 | 2.91 | 0.78 | 0.95 |
| H6 | 9.37 | 17.2 | 2.01 | 7.31 | 1.32 | 0.37 | 1.25 | 0.20 | 1.21 | 0.29 | 1.13 | 0.27 | 1.71 | 0.34 | 8.64 | 52.62 | 37.59 | 15.03 | 2.50 | 0.87 | 0.97 |
| H7 | 8.72 | 16.0 | 1.88 | 6.84 | 1.31 | 0.34 | 1.22 | 0.20 | 1.08 | 0.22 | 0.69 | 0.14 | 0.89 | 0.16 | 6.88 | 46.56 | 35.09 | 11.47 | 3.06 | 0.81 | 0.97 |
| H8 | 10.7 | 19.4 | 2.28 | 8.04 | 1.56 | 0.40 | 1.47 | 0.23 | 1.29 | 0.26 | 0.78 | 0.13 | 0.86 | 0.14 | 7.78 | 55.38 | 42.43 | 12.95 | 3.28 | 0.81 | 0.96 |
| H9 | 10.8 | 20.8 | 2.38 | 8.62 | 1.63 | 0.44 | 1.51 | 0.26 | 1.42 | 0.33 | 0.92 | 0.14 | 0.90 | 0.16 | 8.78 | 59.09 | 44.68 | 14.42 | 3.10 | 0.86 | 1.00 |
| H10 | 11.7 | 22.8 | 2.55 | 9.28 | 1.78 | 0.43 | 1.63 | 0.28 | 1.62 | 0.33 | 0.94 | 0.15 | 0.89 | 0.16 | 9.09 | 63.63 | 48.52 | 15.10 | 3.21 | 0.77 | 1.02 |
| H11 | 10.9 | 19.9 | 2.34 | 8.24 | 1.55 | 0.41 | 1.40 | 0.22 | 1.13 | 0.23 | 0.63 | 0.11 | 0.69 | 0.11 | 6.36 | 54.18 | 43.30 | 10.87 | 3.98 | 0.85 | 0.97 |
| H12 | 10.1 | 18.6 | 2.12 | 7.48 | 1.36 | 0.35 | 1.33 | 0.21 | 1.10 | 0.22 | 0.58 | 0.09 | 0.60 | 0.10 | 6.15 | 50.44 | 40.06 | 10.38 | 3.86 | 0.79 | 0.99 |
| H13 | 10.7 | 18.8 | 2.23 | 7.80 | 1.45 | 0.40 | 1.40 | 0.22 | 1.20 | 0.25 | 0.68 | 0.11 | 0.68 | 0.12 | 6.90 | 52.94 | 41.39 | 11.55 | 3.58 | 0.87 | 0.94 |
| H14 | 19.1 | 37.4 | 4.36 | 15.8 | 2.93 | 0.66 | 2.81 | 0.47 | 2.65 | 0.54 | 1.42 | 0.22 | 1.26 | 0.21 | 14.3 | 104.08 | 80.20 | 23.88 | 3.36 | 0.71 | 1.00 |
| H15 | 10.3 | 19.1 | 2.21 | 7.93 | 1.46 | 0.45 | 1.42 | 0.25 | 1.49 | 0.33 | 0.92 | 0.15 | 0.85 | 0.14 | 8.86 | 55.82 | 41.42 | 14.40 | 2.88 | 0.95 | 0.98 |
| H16 | 9.39 | 17.4 | 2.08 | 7.32 | 1.33 | 0.35 | 1.24 | 0.21 | 1.15 | 0.25 | 0.72 | 0.13 | 0.74 | 0.12 | 6.92 | 49.39 | 37.91 | 11.48 | 3.30 | 0.84 | 0.97 |
| H17 | 10.1 | 19.2 | 2.21 | 8.43 | 1.54 | 0.38 | 1.37 | 0.22 | 1.14 | 0.22 | 0.66 | 0.10 | 0.59 | 0.095 | 6.35 | 52.66 | 41.92 | 10.74 | 3.90 | 0.80 | 0.99 |
| H18 | 13.9 | 25.3 | 2.87 | 10.1 | 1.80 | 0.48 | 1.71 | 0.27 | 1.51 | 0.33 | 1.02 | 0.16 | 1.01 | 0.15 | 9.18 | 69.79 | 54.45 | 15.33 | 3.55 | 0.84 | 0.98 |
| H19 | 16.1 | 29.6 | 3.41 | 12.3 | 2.17 | 0.60 | 2.04 | 0.33 | 1.67 | 0.33 | 0.94 | 0.16 | 0.97 | 0.16 | 8.79 | 79.63 | 64.25 | 15.38 | 4.18 | 0.87 | 0.98 |
| H20 | 10.1 | 18.6 | 2.18 | 7.83 | 1.41 | 0.39 | 1.32 | 0.21 | 1.10 | 0.24 | 0.66 | 0.12 | 0.79 | 0.13 | 6.51 | 51.61 | 40.53 | 11.08 | 3.66 | 0.87 | 0.97 |
| H21 | 11.6 | 21.8 | 2.55 | 9.01 | 1.67 | 0.38 | 1.60 | 0.25 | 1.31 | 0.26 | 0.71 | 0.12 | 0.77 | 0.12 | 7.42 | 59.62 | 47.06 | 12.57 | 3.74 | 0.70 | 0.98 |
| H22 | 9.38 | 19.1 | 2.14 | 7.45 | 1.29 | 0.37 | 1.18 | 0.18 | 0.99 | 0.20 | 0.63 | 0.12 | 0.81 | 0.14 | 5.58 | 49.57 | 39.74 | 9.83 | 4.04 | 0.91 | 1.05 |
| H23 | 22.7 | 44.1 | 5.08 | 18.2 | 3.40 | 0.80 | 3.04 | 0.49 | 2.50 | 0.47 | 1.34 | 0.20 | 1.29 | 0.21 | 13.1 | 116.92 | 94.30 | 22.62 | 4.17 | 0.76 | 1.01 |
| H24 | 11.7 | 22.6 | 2.55 | 8.94 | 1.58 | 0.46 | 1.46 | 0.22 | 1.16 | 0.23 | 0.67 | 0.11 | 0.73 | 0.13 | 6.29 | 58.81 | 47.80 | 11.02 | 4.34 | 0.92 | 1.01 |
| 样品 | U | Th | Th/U | Rb | Pb | Mo | Nb | Sr | Zr | Ta | V | Sc | Cr | Co | Ni | Zn | S2- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 29.10 | 8.42 | 0.29 | 82.00 | 43.10 | 1.89 | 11.80 | 245.00 | 129.00 | 1.07 | 89.60 | 8.13 | 73.60 | 13.20 | 57.40 | 39.70 | 22.64 |
| H2 | 1000.00 | 11.30 | 0.01 | 78.00 | 34.00 | 2.12 | 8.76 | 377.00 | 112.00 | 0.70 | 98.30 | 7.91 | 60.50 | 15.70 | 44.30 | 283.00 | 16.74 |
| H3 | 13.60 | 5.68 | 0.42 | 77.10 | 25.40 | 0.95 | 8.23 | 197.00 | 159.00 | 0.72 | 72.20 | 5.46 | 47.90 | 7.48 | 28.90 | 50.40 | 5.27 |
| H4 | 24.80 | 4.39 | 0.18 | 23.90 | 15.00 | 0.76 | 4.25 | 239.00 | 64.90 | 0.24 | 56.20 | 1.03 | 27.70 | 3.87 | 19.00 | 22.50 | 0.31 |
| H5 | 67.40 | 5.74 | 0.09 | 20.80 | 10.90 | 0.68 | 3.85 | 326.00 | 65.60 | 0.21 | 52.00 | 0.82 | 28.90 | 3.52 | 19.30 | 18.90 | 3.41 |
| H6 | 162.50 | 8.49 | 0.05 | 33.60 | 20.05 | 0.70 | 3.16 | 413.50 | 76.80 | 0.30 | 41.45 | 0.95 | 21.60 | 3.51 | 14.85 | 21.45 | 3.41 |
| H7 | 40.30 | 2.70 | 0.07 | 21.25 | 20.30 | 0.68 | 3.12 | 283.00 | 60.35 | 0.18 | 51.45 | 0.71 | 16.75 | 3.37 | 17.60 | 11.65 | 0.78 |
| H8 | 112.00 | 3.07 | 0.03 | 30.50 | 15.50 | 0.65 | 7.16 | 267.00 | 77.00 | 0.34 | 45.00 | 1.20 | 24.90 | 4.38 | 16.50 | 8.84 | 0.62 |
| H9 | 310.00 | 3.90 | 0.01 | 34.70 | 17.00 | 0.69 | 6.64 | 353.00 | 79.60 | 0.32 | 39.70 | 1.15 | 4.60 | 4.15 | 14.40 | 25.00 | 5.27 |
| H10 | 400.00 | 4.20 | 0.01 | 40.70 | 19.50 | 0.72 | 5.64 | 317.00 | 82.00 | 0.36 | 54.00 | 1.93 | 15.40 | 5.63 | 17.40 | 37.40 | 2.95 |
| H11 | 80.00 | 2.29 | 0.03 | 37.00 | 15.00 | 0.65 | 4.26 | 228.00 | 85.60 | 0.29 | 38.70 | 1.08 | 2.26 | 3.61 | 13.10 | 9.55 | 1.24 |
| H12 | 41.10 | 2.38 | 0.06 | 24.70 | 45.20 | 0.68 | 3.90 | 242.00 | 58.00 | 0.22 | 54.30 | 1.00 | 4.16 | 4.53 | 16.90 | 10.80 | 2.79 |
| H13 | 48.40 | 2.07 | 0.04 | 30.20 | 11.00 | 0.71 | 3.66 | 235.00 | 84.10 | 0.23 | 52.50 | 1.23 | 24.70 | 4.21 | 16.60 | 8.10 | 3.72 |
| H14 | 880.00 | 8.60 | 0.01 | 69.75 | 28.35 | 0.93 | 4.83 | 322.50 | 120.00 | 0.44 | 52.65 | 3.25 | 39.40 | 5.00 | 16.40 | 31.10 | 3.10 |
| H15 | 320.00 | 4.82 | 0.02 | 44.75 | 19.80 | 0.68 | 3.64 | 299.50 | 88.50 | 0.28 | 29.75 | 0.57 | 20.50 | 3.58 | 10.55 | 15.60 | 6.20 |
| H16 | 176.00 | 3.33 | 0.02 | 34.00 | 17.80 | 0.70 | 4.85 | 263.00 | 73.30 | 0.27 | 36.50 | 0.83 | 25.70 | 4.21 | 13.40 | 17.50 | 4.50 |
| H17 | 160.00 | 2.95 | 0.02 | 26.00 | 27.50 | 0.70 | 4.64 | 209.00 | 64.80 | 0.29 | 48.00 | 0.74 | 18.50 | 3.85 | 17.00 | 17.80 | 6.20 |
| H18 | 123.00 | 4.53 | 0.04 | 52.50 | 12.60 | 0.73 | 4.45 | 273.00 | 79.50 | 0.35 | 42.70 | 1.66 | 26.80 | 3.88 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 5.58 |
| H19 | 156.00 | 4.72 | 0.03 | 59.30 | 17.40 | 0.73 | 5.08 | 214.00 | 97.60 | 0.46 | 43.30 | 2.53 | 4.29 | 4.43 | 17.10 | 25.40 | 3.10 |
| H20 | 88.30 | 3.11 | 0.04 | 35.50 | 12.30 | 0.88 | 3.61 | 244.00 | 84.70 | 0.29 | 36.30 | 0.97 | 28.20 | 3.35 | 12.80 | 19.60 | 4.19 |
| H21 | 450.00 | 3.30 | 0.01 | 30.30 | 14.55 | 0.72 | 3.37 | 290.50 | 76.95 | 0.26 | 52.10 | 1.59 | 21.65 | 4.92 | 19.50 | 15.45 | 4.03 |
| H22 | 119.50 | 3.22 | 0.03 | 56.25 | 17.55 | 0.62 | 4.50 | 201.50 | 81.40 | 0.32 | 27.90 | 0.26 | 22.00 | 1.74 | 6.33 | 55.25 | 3.10 |
| H23 | 610.00 | 6.92 | 0.01 | 80.40 | 43.10 | 0.88 | 6.32 | 192.00 | 113.00 | 0.61 | 53.40 | 4.31 | 49.80 | 11.90 | 36.20 | 62.40 | 9.92 |
| H24 | 71.70 | 3.29 | 0.05 | 54.40 | 16.40 | 0.68 | 3.50 | 161.00 | 100.00 | 0.27 | 24.00 | 0.81 | 23.60 | 1.71 | 6.58 | 12.10 | 3.72 |
表3 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘镇原地区砂岩型铀矿含铀砂岩微量元素分析结果表(10-6)
Table 3 Trace element data of the uranium-bearing sandstone in the Zhenyuan sandstone-type uranium deposit,southwestern Ordos Basin (10-6)
| 样品 | U | Th | Th/U | Rb | Pb | Mo | Nb | Sr | Zr | Ta | V | Sc | Cr | Co | Ni | Zn | S2- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 29.10 | 8.42 | 0.29 | 82.00 | 43.10 | 1.89 | 11.80 | 245.00 | 129.00 | 1.07 | 89.60 | 8.13 | 73.60 | 13.20 | 57.40 | 39.70 | 22.64 |
| H2 | 1000.00 | 11.30 | 0.01 | 78.00 | 34.00 | 2.12 | 8.76 | 377.00 | 112.00 | 0.70 | 98.30 | 7.91 | 60.50 | 15.70 | 44.30 | 283.00 | 16.74 |
| H3 | 13.60 | 5.68 | 0.42 | 77.10 | 25.40 | 0.95 | 8.23 | 197.00 | 159.00 | 0.72 | 72.20 | 5.46 | 47.90 | 7.48 | 28.90 | 50.40 | 5.27 |
| H4 | 24.80 | 4.39 | 0.18 | 23.90 | 15.00 | 0.76 | 4.25 | 239.00 | 64.90 | 0.24 | 56.20 | 1.03 | 27.70 | 3.87 | 19.00 | 22.50 | 0.31 |
| H5 | 67.40 | 5.74 | 0.09 | 20.80 | 10.90 | 0.68 | 3.85 | 326.00 | 65.60 | 0.21 | 52.00 | 0.82 | 28.90 | 3.52 | 19.30 | 18.90 | 3.41 |
| H6 | 162.50 | 8.49 | 0.05 | 33.60 | 20.05 | 0.70 | 3.16 | 413.50 | 76.80 | 0.30 | 41.45 | 0.95 | 21.60 | 3.51 | 14.85 | 21.45 | 3.41 |
| H7 | 40.30 | 2.70 | 0.07 | 21.25 | 20.30 | 0.68 | 3.12 | 283.00 | 60.35 | 0.18 | 51.45 | 0.71 | 16.75 | 3.37 | 17.60 | 11.65 | 0.78 |
| H8 | 112.00 | 3.07 | 0.03 | 30.50 | 15.50 | 0.65 | 7.16 | 267.00 | 77.00 | 0.34 | 45.00 | 1.20 | 24.90 | 4.38 | 16.50 | 8.84 | 0.62 |
| H9 | 310.00 | 3.90 | 0.01 | 34.70 | 17.00 | 0.69 | 6.64 | 353.00 | 79.60 | 0.32 | 39.70 | 1.15 | 4.60 | 4.15 | 14.40 | 25.00 | 5.27 |
| H10 | 400.00 | 4.20 | 0.01 | 40.70 | 19.50 | 0.72 | 5.64 | 317.00 | 82.00 | 0.36 | 54.00 | 1.93 | 15.40 | 5.63 | 17.40 | 37.40 | 2.95 |
| H11 | 80.00 | 2.29 | 0.03 | 37.00 | 15.00 | 0.65 | 4.26 | 228.00 | 85.60 | 0.29 | 38.70 | 1.08 | 2.26 | 3.61 | 13.10 | 9.55 | 1.24 |
| H12 | 41.10 | 2.38 | 0.06 | 24.70 | 45.20 | 0.68 | 3.90 | 242.00 | 58.00 | 0.22 | 54.30 | 1.00 | 4.16 | 4.53 | 16.90 | 10.80 | 2.79 |
| H13 | 48.40 | 2.07 | 0.04 | 30.20 | 11.00 | 0.71 | 3.66 | 235.00 | 84.10 | 0.23 | 52.50 | 1.23 | 24.70 | 4.21 | 16.60 | 8.10 | 3.72 |
| H14 | 880.00 | 8.60 | 0.01 | 69.75 | 28.35 | 0.93 | 4.83 | 322.50 | 120.00 | 0.44 | 52.65 | 3.25 | 39.40 | 5.00 | 16.40 | 31.10 | 3.10 |
| H15 | 320.00 | 4.82 | 0.02 | 44.75 | 19.80 | 0.68 | 3.64 | 299.50 | 88.50 | 0.28 | 29.75 | 0.57 | 20.50 | 3.58 | 10.55 | 15.60 | 6.20 |
| H16 | 176.00 | 3.33 | 0.02 | 34.00 | 17.80 | 0.70 | 4.85 | 263.00 | 73.30 | 0.27 | 36.50 | 0.83 | 25.70 | 4.21 | 13.40 | 17.50 | 4.50 |
| H17 | 160.00 | 2.95 | 0.02 | 26.00 | 27.50 | 0.70 | 4.64 | 209.00 | 64.80 | 0.29 | 48.00 | 0.74 | 18.50 | 3.85 | 17.00 | 17.80 | 6.20 |
| H18 | 123.00 | 4.53 | 0.04 | 52.50 | 12.60 | 0.73 | 4.45 | 273.00 | 79.50 | 0.35 | 42.70 | 1.66 | 26.80 | 3.88 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 5.58 |
| H19 | 156.00 | 4.72 | 0.03 | 59.30 | 17.40 | 0.73 | 5.08 | 214.00 | 97.60 | 0.46 | 43.30 | 2.53 | 4.29 | 4.43 | 17.10 | 25.40 | 3.10 |
| H20 | 88.30 | 3.11 | 0.04 | 35.50 | 12.30 | 0.88 | 3.61 | 244.00 | 84.70 | 0.29 | 36.30 | 0.97 | 28.20 | 3.35 | 12.80 | 19.60 | 4.19 |
| H21 | 450.00 | 3.30 | 0.01 | 30.30 | 14.55 | 0.72 | 3.37 | 290.50 | 76.95 | 0.26 | 52.10 | 1.59 | 21.65 | 4.92 | 19.50 | 15.45 | 4.03 |
| H22 | 119.50 | 3.22 | 0.03 | 56.25 | 17.55 | 0.62 | 4.50 | 201.50 | 81.40 | 0.32 | 27.90 | 0.26 | 22.00 | 1.74 | 6.33 | 55.25 | 3.10 |
| H23 | 610.00 | 6.92 | 0.01 | 80.40 | 43.10 | 0.88 | 6.32 | 192.00 | 113.00 | 0.61 | 53.40 | 4.31 | 49.80 | 11.90 | 36.20 | 62.40 | 9.92 |
| H24 | 71.70 | 3.29 | 0.05 | 54.40 | 16.40 | 0.68 | 3.50 | 161.00 | 100.00 | 0.27 | 24.00 | 0.81 | 23.60 | 1.71 | 6.58 | 12.10 | 3.72 |
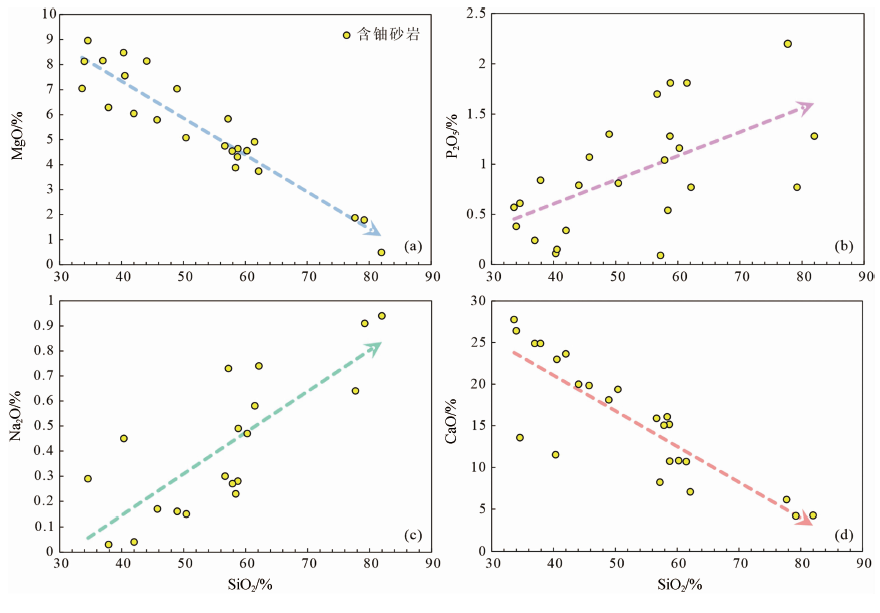
图4 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘镇原地区砂岩型铀矿含铀砂岩SiO2变化图解 (a)SiO2-MgO图解;(b)SiO2-P2O5图解;(c)SiO2-Na2O图解;(d)SiO2-CaO图解
Fig.4 SiO2 variation diagrams of the uranium-bearing sandstone in the Zhenyuan sandstone-type uranium deposit, southwestern Ordos Basin
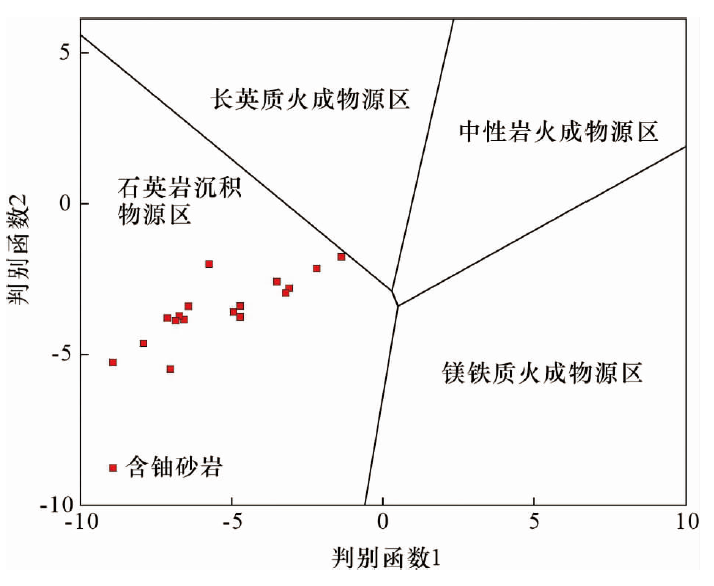
图5 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘镇原地区砂岩型铀矿含铀砂岩物源判别函数图解(据文献[25])
Fig.5 Provenance discrimination diagrams for the uranium-bearing sandstone in the Zhenyuan sandstone-type uranium deposit,southwestern Ordos Basin (modified from reference[25])
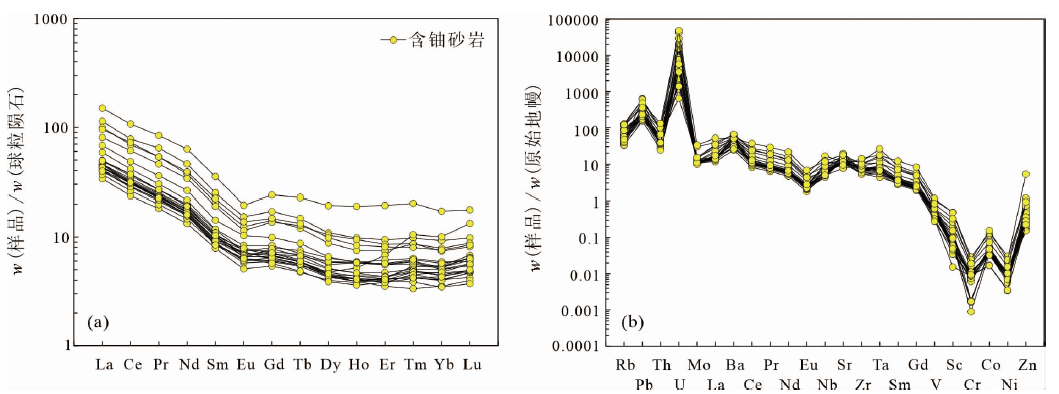
图6 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘镇原地区砂岩型铀矿含铀砂岩稀土元素(a)、微量元素(b)蛛网图(标准化数据自文献[27])
Fig.6 Normalized rare earth element (REE) (a) and multi-element (b) diagrams of the uranium-bearing sandstone in the Zhenyuan sandstone-type uranium deposit,southwestern Ordos Basin (normalizing values from reference[27])
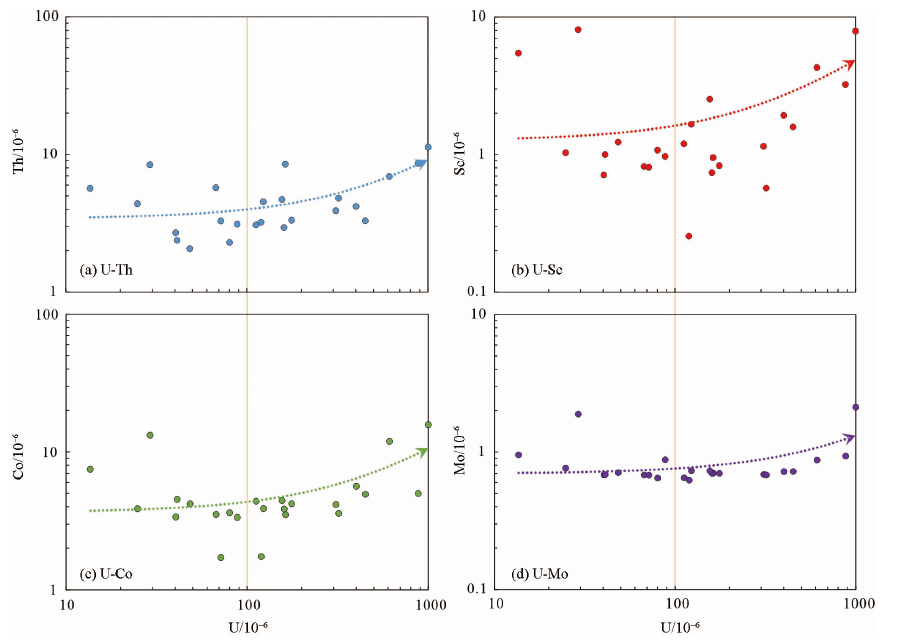
图7 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘镇原地区砂岩型铀矿含铀砂岩U-Th、U-Sc、U-Co、U-Mo关系图解
Fig.7 U-Th, U-Sc, U-Co, and U-Mo diagrams of the uranium-bearing sandstone in the Zhenyuan sandstone-type uraniumdeposit,southwestern Ordos Basin
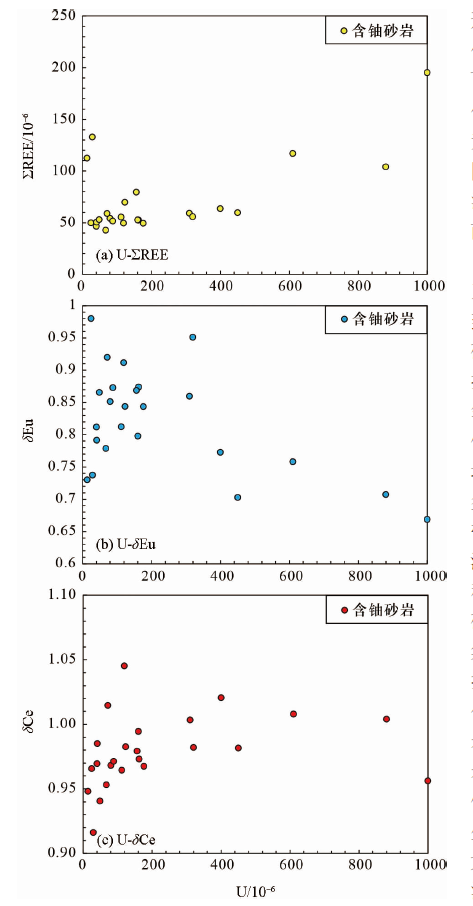
图8 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘镇原地区砂岩型铀矿含铀砂岩U-ΣREE、U-δEu、U-δCe图解
Fig.8 U-ΣREE, U-δEu, and U-δCe diagrams of the uranium-bearing sandstone in the Zhenyuan sandstone-type uranium deposit,southwestern Ordos Basin
| [1] | 邓军. 鄂尔多斯盆地演化与多种能源矿产分布[J]. 现代地质, 2005,19(4):538-545. |
| [2] | 刘晓雪, 汤超, 司马献章, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北部砂岩型铀矿常量元素地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2016,39(3):169-176. |
| [3] | 陈路路, 冯晓曦, 司马献章, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地纳岭沟地区铀矿物赋存形式研究及其地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2017,53(4):632-642. |
| [4] | 陈宏斌, 徐高中, 王金平, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘店头铀矿床矿化特征及其与东胜铀矿床对比[J]. 地质学报, 2006,80(5):724-732. |
| [5] | 樊爱萍, 柳益群, 杨仁超, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜地区砂岩型铀矿成岩作用研究[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 2007,37(增刊):166-172. |
| [6] | 刘汉彬, 李子颖, 秦明宽, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部砂岩型铀矿地球化学研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2012,19(3):139-146. |
| [7] | 陈友良, 朱西养, 张成江, 等. 层间氧化带砂岩型铀矿稀土元素变化规律初探——以伊犁和吐鲁番—哈密盆地为例[J]. 地质论评, 2007,53(4):473-485. |
| [8] | 韩效忠, 张字龙, 姚春玲, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北部砂岩型铀成矿模式研究[J]. 矿床地质, 2008,27(3):415-422. |
| [9] | 吴柏林, 刘池洋, 王建强. 层间氧化带砂岩型铀矿流体地质作用的基本特点[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 2007,37(增刊):157-165. |
| [10] | 黄净白, 李胜祥. 试论我国古层间氧化带砂岩型铀矿床成矿特点、成矿模式及找矿前景[J]. 铀矿地质, 2007,23(1):7-16. |
| [11] | 肖新建, 李子颖, 陈安平. 东胜地区砂岩型铀矿床后生蚀变矿物分带特征初步研究[J]. 铀矿地质, 2004,20(3):136-140. |
| [12] | 肖新建, 李子颖, 方锡珩, 等. 东胜砂岩型铀矿床低温热液流体的证据及意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2004,23(4):301-304. |
| [13] | JIN R S, YU R A, YNAG J, et al. Paleo-environmental constraints on uranium mineralization in the Ordos Basin: Evidence from the color zoning of U-bearing rock series[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019,104:175-189. |
| [14] | PEISEN M. The first discovery of a large sandstone-type uranium deposit in aeolian depositional environment[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020,94(2):583-584. |
| [15] | 胡永兴, 张翔, 胡妍, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘白垩系洛河组砂岩型铀成矿条件及铀赋存特征浅析[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2020, 35(6):待刊. |
| [16] | 张卫民. 元素活动态测量技术在勘查层间氧化带砂岩型铀矿中的应用——以新疆准噶尔盆地北部顶山地区为例[J]. 地质与勘探, 2002,38(6):59-62. |
| [17] | 朱西养, 汪云亮, 王志畅, 等. 东胜砂岩型铀矿微量元素地球化学特征初探[J]. 地质地球化学, 2003,31(2):39-45. |
| [18] | 陈祖伊, 郭庆银. 砂岩型铀矿床层间氧化带前锋区稀有元素富集机制[J]. 铀矿地质, 2010,26(1):1-8. |
| [19] | LIU S F. The coupling mechanism of basin and orogen in the western Ordos Basin and adjacent regions of China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 1998,16(4):369-383. |
| [20] | AKHTAR S, SAHIR N, YANG X Y. Genesis of tuff interval and its uranium enrichment in Upper Triassic of Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Acta Geochimica, 2017,37(1):32-46. |
| [21] | 狄永强. 试论鄂尔多斯北部中新生代盆地砂岩型铀矿找矿前景[J]. 铀矿地质, 2002,18(6):340-347. |
| [22] | AKHTAR S, YANG X Y, PIRAJNO F. Sandstone type uranium deposits in the Ordos Basin, Northwest China: A case study and an overview[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017,146:367-382. |
| [23] | 白云来, 王新民, 刘化清, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西部边界的确定及其地球动力学背景[J]. 地质学报, 2006,80(6):792-813. |
| [24] | 王双明. 鄂尔多斯盆地构造演化和构造控煤作用[J]. 地质通报, 2011,31(4):544-552. |
| [25] | ROSER B P, KORSCH R J. Provenance signatures of sandstone-mudstone suites determined using discriminant function analysis of major-element data[J]. Chemical Geology, 1988,67(1/2):119-139. |
| [26] | 朱西养, 汪云亮, 王志畅, 等. REE地球化学在砂岩型铀成矿研究中的应用——以川北砂岩型铀矿床为例[J]. 地质论评, 2005,51(4):401-408. |
| [27] | SUNS S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989,42(1):313-345. |
| [28] | XUE C J, CHI G X, XUE W. Interaction of two fluid systems in the formation of sandstone-hosted uranium deposits in the Ordos Basin: Geochemical evidence and hydrodynamic modeling[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2010,106:226-235. |
| [29] | JONES B, MANNING D A. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994,111:111-129. |
| [30] | 张天福, 孙立新, 张云, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地北缘侏罗纪延安组, 直罗组泥岩微量, 稀土元素地球化学特征及其古沉积环境意义[J]. 地质学报, 2016,90(12):3454-3472. |
| [31] | HATCH J, LEVENTHAL J. Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the Upper Pennsylvanian (Missourian) Stark Shale Member of the Dennis Limestone, Wabaunsee County, Kansas, USA[J]. Chemical Geology, 1992,99(1/3):65-82. |
| [32] | 王金平, 彭新建, 贾恒. 层间氧化带中稀土元素的赋存特征初步研究[J]. 西北铀矿地质, 2006,32(1):1-6. |
| [33] | BAO Z W, ZHAO Z H. Rare-earth element mobility during ore-forming hydrothermal alteration: A case study of Dongping gold deposit, Hebei Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 2003,22(1):45-57. |
| [34] | PRICER C, GRAY C M, WILSON R E, et al. The effects of weathering on rare-earth element, Y and Ba abundances in Tertiary basalts from southeastern Australia[J]. Chemical Geology, 1991,93(3):245-265. |
| [35] | BRAUNJ J, PAGEL M, HERBILLON A, et al. Mobilization and redistribution of REEs and thorium in a syenitic lateritic profile; a mass balance study[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993,57(18):4419-4434. |
| [36] | 邢秀娟, 柳益群, 樊爱萍. 鄂尔多斯盆地店头地区砂岩型铀矿成因初步探讨[J]. 中国地质, 2006,33(3):591-597. |
| [37] | 杨晓勇, 凌明星, 赖小东. 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜地区地浸砂岩型铀矿成矿模型[J]. 地学前缘, 2009,16(2):239-249. |
| [38] | 刘波, 杨建新, 乔宝成, 等. 腾格尔坳陷砂岩型铀矿控矿成因相特征及远景预测[J]. 地质与勘探, 2015,51(5):870-878. |
| [39] | 彭云彪, 刘波, 秦彦伟, 等. 二连盆地川井坳陷构造演化对砂岩型铀矿成矿作用的约束[J]. 地质与勘探, 2018,54(5):917-928. |
| [40] | 赵兴齐, 李西得, 史清平, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜区直罗组砂岩中烃类流体特征与铀成矿关系[J]. 地质学报, 2016,90(12):3381-3392. |
| [41] | 赵兴齐, 秦明宽, 范洪海, 等. 内蒙古二连盆地中部古河道型铀矿床中烃类流体特征与铀成矿关系[J]. 地球学报, 2019,40(3):405-416. |
| [1] | 黄清华, 席党鹏, 王辉, 张文婧, 王建伟, 曹维福, 贾卧, 王丽静. 松辽盆地北部中二叠统碳酸盐岩元素和稳定同位素地球化学特征与古环境[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1282-1295. |
| [2] | 孙岳, 潘家永, 陈正乐, 韩凤彬, 刘文恒, 肖伟峰. 乌兹别克中卡兹库姆地貌特征对砂岩型铀矿赋存的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(05): 1070-1078. |
| [3] | 马奂奂, 刘池洋, 张龙, 张东东, 王文青, 赵岩, 高明, 全晓园. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长7段沉积岩元素地球化学特征及沉积环境分析[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(04): 872-882. |
| [4] | 邱余波, 陈虹, 杨军锋, 张占峰, 蒋宏, 杜默, 李刚. 伊犁盆地阔斯加尔铀成矿区西山窑组古地下水动力系统[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(02): 431-439. |
| [5] | 封志兵,聂逢君,江丽,曾建刚,严兆彬,李红星. 重力场特征与砂岩型铀矿的关系及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(4): 841-849. |
| [6] | 苗爱生, 陆琦, 刘惠芳, 肖平. 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜砂岩型铀矿中铀矿物的电子显微镜研究[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(4): 785-792. |
| [7] | 薛伟, 薛春纪, 池国祥, 彭云彪, 王凯. 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜砂岩型铀矿微量和稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(4): 776-784. |
| [8] | 薛春纪,薛伟,康明,涂其军,杨友运. 鄂尔多斯盆地流体动力学过程及其砂岩型铀矿化 [J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(1): 1-8. |
| [9] | 王连岱,钟延秋,汪在君,于世泉. 航空放射性测量资料在海拉尔盆地可地浸砂岩型铀矿成矿条件分析中的应用[J]. 现代地质, 2005, 19(Suppl): 286-290. |
| [10] | 焦养泉. 吕新彪. 杨生科. 王正海. 杨琴. 吴立群.. 吐哈盆地西南缘铀成矿的层位标定[J]. 现代地质, 2004, 18(3): 346-352. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||