



现代地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (03): 588-597.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2025.039
牛花朋1,2( ), 刘姗1,2, 焦小芹3, 张关龙4, 王千军4, 周健4, 赵贤1,2, 于洪洲4, 熊峥嵘4, 何晓1,2
), 刘姗1,2, 焦小芹3, 张关龙4, 王千军4, 周健4, 赵贤1,2, 于洪洲4, 熊峥嵘4, 何晓1,2
出版日期:2025-06-10
发布日期:2025-07-03
作者简介:牛花朋,女,博士,教授,1979年出生,主要从事矿物岩石学与储层地质学相关研究工作。Email:niuhuapeng@126.com。
基金资助:
NIU Huapeng1,2( ), LIU Shan1,2, JIAO Xiaoqin3, ZHANG Guanlong4, WANG Qianjun4, ZHOU Jian4, ZHAO Xian1,2, YU Hongzhou4, XIONG Zhengrong4, HE Xiao1,2
), LIU Shan1,2, JIAO Xiaoqin3, ZHANG Guanlong4, WANG Qianjun4, ZHOU Jian4, ZHAO Xian1,2, YU Hongzhou4, XIONG Zhengrong4, HE Xiao1,2
Published:2025-06-10
Online:2025-07-03
摘要:
本文选取准噶尔盆地西北缘哈拉阿拉特山(哈山)地区石炭系火山熔岩(玄武岩、玄武安山岩、安山岩)来说明其成因机制及构造背景。研究结果表明,三类岩石的MgO含量中等(3.21%~6.82%),Al2O3含量中等偏高(11.30%~17.78%),全碱K2O+Na2O含量较高(4.24%~7.24%)。其中,玄武岩样品整体K2O含量较低,体现 Na 相对于K 富集的特点,判断其为低钾拉斑系列玄武岩;玄武安山岩、安山岩的钙碱元素含量高,具有弧火山岩特征。三类火山岩整体呈现87Sr/86Sr值中等偏低(0.702877~0.706620)、εNd(t)同位素值(+4.59~+9.85)高的特征,表明岩浆在深部岩浆房经历了壳-幔混合作用。玄武安山岩、安山岩的稀土元素含量与玄武岩相比,大离子亲石元素Ba富集,高场强元素U、Pb相对富集、Nb亏损,表现出与俯冲消减带相关的岛弧岩浆作用的特点。通过与稀土、微量元素相关的构造环境分析,玄武岩含有源自亏损地幔的组分,低钾拉斑系列产于洋盆俯冲消减的构造背景,中性火山岩则刻度了大洋板块向大陆板块俯冲消减的过程,具体表现为亏损地幔楔受俯冲板块脱水释放的沉积物或洋壳熔体交代后,部分熔融形成玄武安山岩和安山岩。结合区域地质资料分析,准噶尔洋盆的俯冲消减可持续至晚石炭世。
中图分类号:
牛花朋, 刘姗, 焦小芹, 张关龙, 王千军, 周健, 赵贤, 于洪洲, 熊峥嵘, 何晓. 准噶尔盆地西北缘石炭系火山岩地球化学特征及其成因机制[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(03): 588-597.
NIU Huapeng, LIU Shan, JIAO Xiaoqin, ZHANG Guanlong, WANG Qianjun, ZHOU Jian, ZHAO Xian, YU Hongzhou, XIONG Zhengrong, HE Xiao. Geochemical Characteristics and Petrogenesis of Carboniferous Volcanic Rocks in the Northwestern Margin of the Junggar Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2025, 39(03): 588-597.

图2 哈山地区中-基性火山岩类矿物组成特征 (a)玄武岩, 哈浅6井, 141.7 m (-); (b) 玄武岩, 哈浅6井, 141.7 m (+); (c) 玄武安山岩, 哈山101井, 900~904 m (-); (d) 玄武安山岩, 哈山101井, 900~904 m (+); (e) 安山岩, 哈山2井, 151.9 m (-); (f) 安山岩, 哈山2井, 151.9 m (+). Pl.斜长石;Aug.辉石;Hbl.角闪石;Mag.磁铁矿
Fig.2 Mineral composition characteristics of andesitic-basaltic volcanic rocks in Hashan area
| 样品号 | HS-2 | HS-7 | HS-1 | HS-3 | HS-4 | HS-5 | HS-6 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 岩性 | 安山岩 | 玄武安山岩 | 玄武岩 | ||||||
| SiO2 | 60.59 | 60.35 | 56.54 | 54.80 | 47.24 | 47.60 | 45.61 | ||
| Al2O3 | 11.30 | 14.55 | 17.49 | 17.35 | 17.55 | 17.78 | 16.74 | ||
| Fe2O3 | 4.73 | 7.99 | 9.25 | 7.33 | 13.00 | 12.53 | 12.42 | ||
| CaO | 12.31 | 5.76 | 6.05 | 6.35 | 9.17 | 6.30 | 11.97 | ||
| MgO | 3.23 | 3.21 | 4.57 | 5.57 | 6.07 | 6.82 | 5.81 | ||
| K2O | 2.72 | 1.28 | 1.07 | 1.02 | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.27 | ||
| Na2O | 4.32 | 5.26 | 3.58 | 6.22 | 3.98 | 6.38 | 5.24 | ||
| TiO2 | 0.57 | 1.23 | 1.02 | 0.96 | 2.24 | 1.93 | 1.54 | ||
| P2O5 | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.35 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.20 | ||
| MnO | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.19 | ||
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Cu | 35.40 | 30.40 | 51.00 | 73.20 | 401.00 | 50.10 | 24.80 | ||
| Pb | 9.94 | 5.89 | 7.41 | 4.60 | 1.55 | 1.76 | 1.08 | ||
| Cr | 39.30 | 43.20 | 82.10 | 127.00 | 37.20 | 12.60 | 17.50 | ||
| Ni | 39.80 | 27.50 | 49.50 | 63.70 | 74.00 | 70.00 | 66.80 | ||
| Co | 12.80 | 19.70 | 26.50 | 21.90 | 41.6 | 43.30 | 36.80 | ||
| Rb | 61.00 | 35.50 | 29.90 | 14.00 | 1.69 | 2.68 | 11.50 | ||
| Sr | 596.00 | 377.00 | 210.00 | 460.00 | 433.00 | 364.00 | 380.00 | ||
| Ba | 485.00 | 494.00 | 164.00 | 1040.00 | 75.20 | 168.00 | 182.00 | ||
| V | 99.10 | 108.00 | 137.00 | 131.00 | 250.00 | 195.00 | 187.00 | ||
| Nb | 6.28 | 5.11 | 6.07 | 5.26 | 4.81 | 3.52 | 2.74 | ||
| Ta | 0.78 | 0.60 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.93 | 0.72 | 0.65 | ||
| Zr | 113.00 | 200.00 | 123.00 | 83.20 | 165.00 | 140.00 | 105.00 | ||
| Hf | 2.75 | 4.80 | 2.68 | 1.73 | 3.24 | 2.79 | 2.14 | ||
| Ga | 12.50 | 17.40 | 18.30 | 19.00 | 17.70 | 16.60 | 14.20 | ||
| U | 1.89 | 0.47 | 0.71 | 0.53 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.13 | ||
| Th | 3.97 | 3.96 | 2.69 | 1.62 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.22 | ||
表1 哈山地区石炭系火山岩的常量(%)元素分析结果
Table 1 Major (%) element (ppm) data for the Carboniferous volcanic rocks of the Hashan area
| 样品号 | HS-2 | HS-7 | HS-1 | HS-3 | HS-4 | HS-5 | HS-6 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 岩性 | 安山岩 | 玄武安山岩 | 玄武岩 | ||||||
| SiO2 | 60.59 | 60.35 | 56.54 | 54.80 | 47.24 | 47.60 | 45.61 | ||
| Al2O3 | 11.30 | 14.55 | 17.49 | 17.35 | 17.55 | 17.78 | 16.74 | ||
| Fe2O3 | 4.73 | 7.99 | 9.25 | 7.33 | 13.00 | 12.53 | 12.42 | ||
| CaO | 12.31 | 5.76 | 6.05 | 6.35 | 9.17 | 6.30 | 11.97 | ||
| MgO | 3.23 | 3.21 | 4.57 | 5.57 | 6.07 | 6.82 | 5.81 | ||
| K2O | 2.72 | 1.28 | 1.07 | 1.02 | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.27 | ||
| Na2O | 4.32 | 5.26 | 3.58 | 6.22 | 3.98 | 6.38 | 5.24 | ||
| TiO2 | 0.57 | 1.23 | 1.02 | 0.96 | 2.24 | 1.93 | 1.54 | ||
| P2O5 | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.35 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.20 | ||
| MnO | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.19 | ||
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Cu | 35.40 | 30.40 | 51.00 | 73.20 | 401.00 | 50.10 | 24.80 | ||
| Pb | 9.94 | 5.89 | 7.41 | 4.60 | 1.55 | 1.76 | 1.08 | ||
| Cr | 39.30 | 43.20 | 82.10 | 127.00 | 37.20 | 12.60 | 17.50 | ||
| Ni | 39.80 | 27.50 | 49.50 | 63.70 | 74.00 | 70.00 | 66.80 | ||
| Co | 12.80 | 19.70 | 26.50 | 21.90 | 41.6 | 43.30 | 36.80 | ||
| Rb | 61.00 | 35.50 | 29.90 | 14.00 | 1.69 | 2.68 | 11.50 | ||
| Sr | 596.00 | 377.00 | 210.00 | 460.00 | 433.00 | 364.00 | 380.00 | ||
| Ba | 485.00 | 494.00 | 164.00 | 1040.00 | 75.20 | 168.00 | 182.00 | ||
| V | 99.10 | 108.00 | 137.00 | 131.00 | 250.00 | 195.00 | 187.00 | ||
| Nb | 6.28 | 5.11 | 6.07 | 5.26 | 4.81 | 3.52 | 2.74 | ||
| Ta | 0.78 | 0.60 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.93 | 0.72 | 0.65 | ||
| Zr | 113.00 | 200.00 | 123.00 | 83.20 | 165.00 | 140.00 | 105.00 | ||
| Hf | 2.75 | 4.80 | 2.68 | 1.73 | 3.24 | 2.79 | 2.14 | ||
| Ga | 12.50 | 17.40 | 18.30 | 19.00 | 17.70 | 16.60 | 14.20 | ||
| U | 1.89 | 0.47 | 0.71 | 0.53 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.13 | ||
| Th | 3.97 | 3.96 | 2.69 | 1.62 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.22 | ||

图3 哈山地区石炭系火山岩地球化学特征 (a) TAS火山岩岩性判别图(边界据文献[19]); (b) K2O-SiO2关系图 (边界据文献[20])
Fig.3 Geochemical characteristics of the Carboniferous volcanic rocks in Hashan area
| 样品号 | HS-2 | HS-7 | HS-1 | HS-3 | HS-4 | HS-5 | HS-6 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 岩性 | 安山岩 | 玄武安山岩 | 玄武岩 | ||||||
| La | 17.60 | 24.90 | 16.60 | 12.80 | 8.84 | 7.38 | 5.67 | ||
| Ce | 39.00 | 62.4 | 35.90 | 29.60 | 26.90 | 22.80 | 16.80 | ||
| Pr | 4.68 | 8.45 | 5.12 | 3.60 | 4.02 | 3.48 | 2.85 | ||
| Nd | 19.10 | 37.40 | 21.90 | 15.20 | 19.70 | 17.40 | 14.90 | ||
| Sm | 4.01 | 8.05 | 4.52 | 3.09 | 5.31 | 4.60 | 4.21 | ||
| Eu | 0.90 | 2.04 | 1.25 | 1.31 | 1.67 | 1.51 | 1.40 | ||
| Gd | 3.72 | 7.59 | 3.83 | 2.99 | 4.86 | 4.44 | 3.99 | ||
| Tb | 0.57 | 1.31 | 0.58 | 0.41 | 0.92 | 0.82 | 0.75 | ||
| Dy | 3.49 | 8.02 | 3.40 | 2.41 | 5.79 | 5.18 | 4.93 | ||
| Ho | 0.68 | 1.60 | 0.63 | 0.46 | 1.12 | 1.03 | 1.01 | ||
| Er | 1.94 | 4.60 | 1.68 | 1.24 | 3.08 | 2.84 | 2.75 | ||
| Tm | 0.29 | 0.71 | 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.44 | 0.40 | 0.38 | ||
| Yb | 1.93 | 4.73 | 1.52 | 1.07 | 2.86 | 2.62 | 2.57 | ||
| Lu | 0.27 | 0.71 | 0.20 | 0.14 | 0.39 | 0.36 | 0.36 | ||
| Y | 18.20 | 40.90 | 16.10 | 11.50 | 28.40 | 25.80 | 24.80 | ||
| LREE | 85.29 | 143.24 | 85.29 | 65.60 | 66.44 | 57.17 | 45.83 | ||
| HREE | 31.09 | 70.17 | 28.18 | 20.38 | 47.86 | 43.49 | 41.54 | ||
| LREE/ HREE | 2.74 | 2.04 | 3.03 | 3.22 | 1.39 | 1.31 | 1.10 | ||
表2 哈山地区石炭系火山岩的微量元素分析结果 (10-6)
Table 2 Trace element data for the Carboniferous volcanic rocks of the Hashan area (10-6)
| 样品号 | HS-2 | HS-7 | HS-1 | HS-3 | HS-4 | HS-5 | HS-6 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 岩性 | 安山岩 | 玄武安山岩 | 玄武岩 | ||||||
| La | 17.60 | 24.90 | 16.60 | 12.80 | 8.84 | 7.38 | 5.67 | ||
| Ce | 39.00 | 62.4 | 35.90 | 29.60 | 26.90 | 22.80 | 16.80 | ||
| Pr | 4.68 | 8.45 | 5.12 | 3.60 | 4.02 | 3.48 | 2.85 | ||
| Nd | 19.10 | 37.40 | 21.90 | 15.20 | 19.70 | 17.40 | 14.90 | ||
| Sm | 4.01 | 8.05 | 4.52 | 3.09 | 5.31 | 4.60 | 4.21 | ||
| Eu | 0.90 | 2.04 | 1.25 | 1.31 | 1.67 | 1.51 | 1.40 | ||
| Gd | 3.72 | 7.59 | 3.83 | 2.99 | 4.86 | 4.44 | 3.99 | ||
| Tb | 0.57 | 1.31 | 0.58 | 0.41 | 0.92 | 0.82 | 0.75 | ||
| Dy | 3.49 | 8.02 | 3.40 | 2.41 | 5.79 | 5.18 | 4.93 | ||
| Ho | 0.68 | 1.60 | 0.63 | 0.46 | 1.12 | 1.03 | 1.01 | ||
| Er | 1.94 | 4.60 | 1.68 | 1.24 | 3.08 | 2.84 | 2.75 | ||
| Tm | 0.29 | 0.71 | 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.44 | 0.40 | 0.38 | ||
| Yb | 1.93 | 4.73 | 1.52 | 1.07 | 2.86 | 2.62 | 2.57 | ||
| Lu | 0.27 | 0.71 | 0.20 | 0.14 | 0.39 | 0.36 | 0.36 | ||
| Y | 18.20 | 40.90 | 16.10 | 11.50 | 28.40 | 25.80 | 24.80 | ||
| LREE | 85.29 | 143.24 | 85.29 | 65.60 | 66.44 | 57.17 | 45.83 | ||
| HREE | 31.09 | 70.17 | 28.18 | 20.38 | 47.86 | 43.49 | 41.54 | ||
| LREE/ HREE | 2.74 | 2.04 | 3.03 | 3.22 | 1.39 | 1.31 | 1.10 | ||
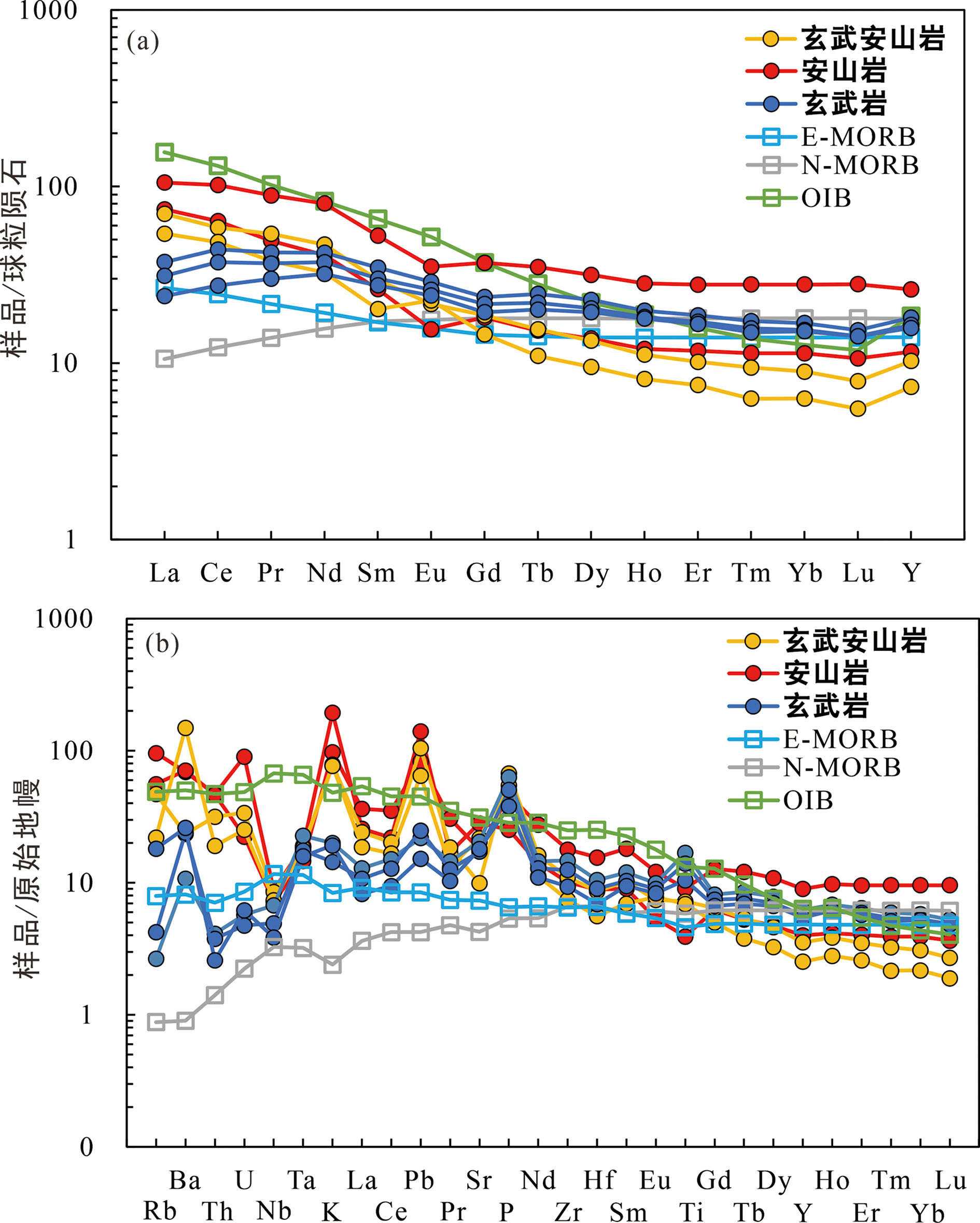
图4 (a)哈山地区石炭系火山岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图 (标准化值据文献[22]) 和 (b) 微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图 (标准化值据文献[22])
Fig.4 (a) Chondrite-normalized REE patterns and (b) primitive mantle-normalized trace element spidergrams for Carboniferous volcanic rocks of the Hashan area
| 岩性 | 样品号 | 87Sr/86Sr | SE | Rb (10-6) | Sr (10-6) | 143Nd/ 144Nd | SE | Sm (ppm) | Nd (ppm) | 87Rb/ 86Sr | 147Sm/ 144Nd | εNd(t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安山岩 | HS2 | 0.70662 | 0.000007 | 61 | 596 | 0.512721 | 0.000005 | 4.01 | 19.1 | 0.296089423 | 0.126928268 | 4.59 |
| HS7 | 0.704834 | 0.000005 | 35.5 | 377 | 0.512937 | 0.000002 | 8.05 | 37.4 | 0.272364453 | 0.130134887 | 8.67 | |
| 玄武 安山岩 | HS1 | 0.705716 | 0.000008 | 29.9 | 210 | 0.512866 | 0.000003 | 4.52 | 21.9 | 0.411863019 | 0.124783313 | 7.51 |
| HS3 | 0.704365 | 0.000004 | 14 | 460 | 0.51286 | 0.000004 | 3.09 | 15.2 | 0.088026553 | 0.122906958 | 7.48 | |
| 玄武岩 | HS4 | 0.702877 | 0.000004 | 1.69 | 433 | 0.513067 | 0.000005 | 5.31 | 19.7 | 0.011287014 | 0.162971275 | 9.81 |
| HS5 | 0.703324 | 0.000007 | 2.68 | 364 | 0.513062 | 0.000004 | 4.6 | 17.4 | 0.021292794 | 0.159841976 | 9.85 | |
| HS6 | 0.703889 | 0.000009 | 11.5 | 380 | 0.513084 | 0.000004 | 4.21 | 14.9 | 0.087526085 | 0.170836371 | 9.81 |
表3 哈山地区石炭系火山岩Sr-Nd同位素组成分析结果
Table 3 Sr-Nd isotope compositions of Carboniferous volcanic rocks from the Hashan area
| 岩性 | 样品号 | 87Sr/86Sr | SE | Rb (10-6) | Sr (10-6) | 143Nd/ 144Nd | SE | Sm (ppm) | Nd (ppm) | 87Rb/ 86Sr | 147Sm/ 144Nd | εNd(t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安山岩 | HS2 | 0.70662 | 0.000007 | 61 | 596 | 0.512721 | 0.000005 | 4.01 | 19.1 | 0.296089423 | 0.126928268 | 4.59 |
| HS7 | 0.704834 | 0.000005 | 35.5 | 377 | 0.512937 | 0.000002 | 8.05 | 37.4 | 0.272364453 | 0.130134887 | 8.67 | |
| 玄武 安山岩 | HS1 | 0.705716 | 0.000008 | 29.9 | 210 | 0.512866 | 0.000003 | 4.52 | 21.9 | 0.411863019 | 0.124783313 | 7.51 |
| HS3 | 0.704365 | 0.000004 | 14 | 460 | 0.51286 | 0.000004 | 3.09 | 15.2 | 0.088026553 | 0.122906958 | 7.48 | |
| 玄武岩 | HS4 | 0.702877 | 0.000004 | 1.69 | 433 | 0.513067 | 0.000005 | 5.31 | 19.7 | 0.011287014 | 0.162971275 | 9.81 |
| HS5 | 0.703324 | 0.000007 | 2.68 | 364 | 0.513062 | 0.000004 | 4.6 | 17.4 | 0.021292794 | 0.159841976 | 9.85 | |
| HS6 | 0.703889 | 0.000009 | 11.5 | 380 | 0.513084 | 0.000004 | 4.21 | 14.9 | 0.087526085 | 0.170836371 | 9.81 |
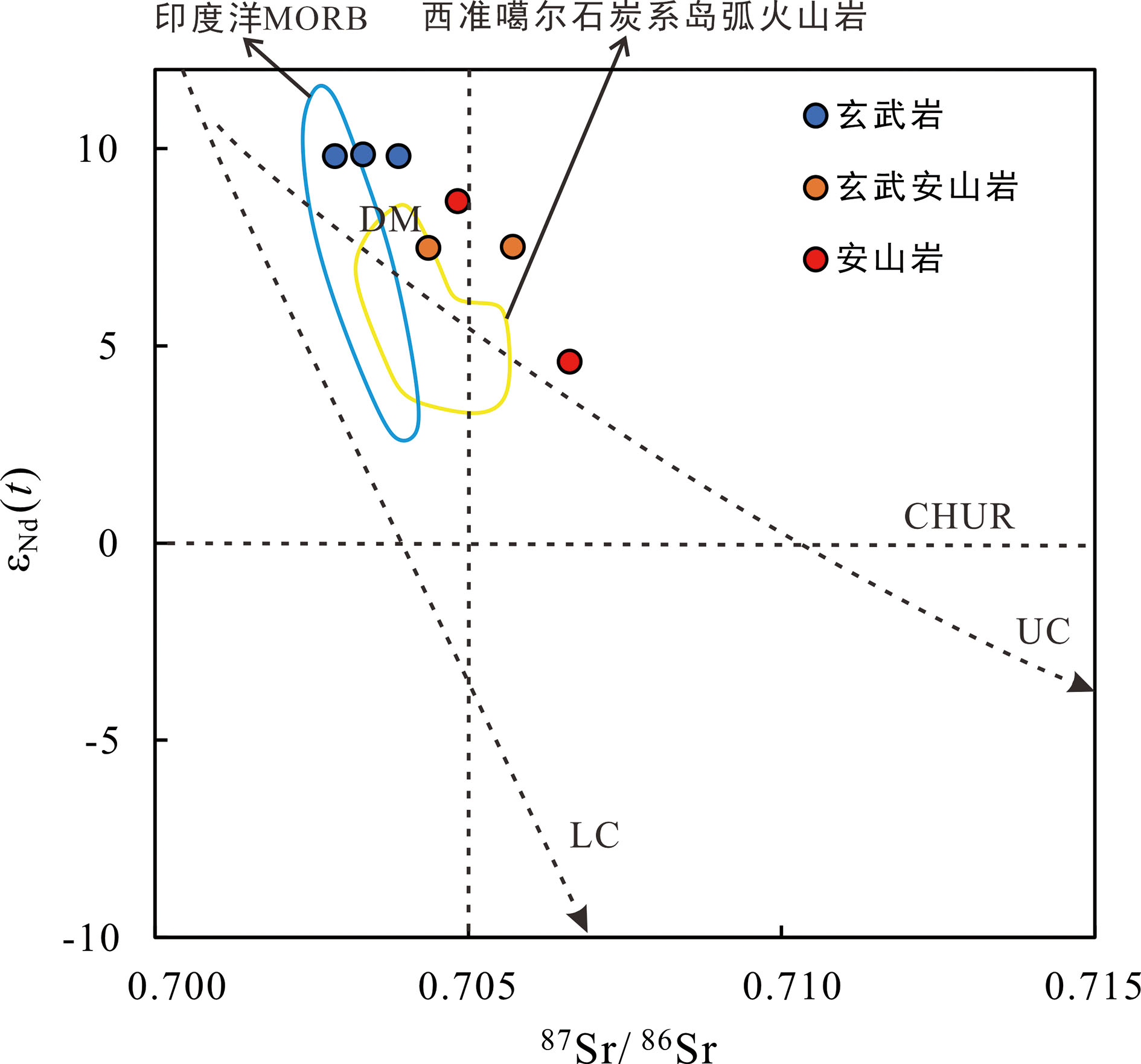
图5 哈山地区石炭系火山岩Sr-Nd同位素图解(边界据文献[27]) LC:下地壳;UC:上地壳;DM:亏损地幔西准噶尔岛弧火山岩数据引自Geng等[28],印度洋MORB数据引自Stracke et al.[29]
Fig.5 εNd(t) versus 87Sr/86Sr plot for Carboniferous volcanic rocks of the Hashan area (modified from ref.[27])

图6 哈山地区石炭系火山岩构造判别图解((a)TiO2-Zr图解,边界据文献[33]; (b) Nb/Th-Nb图解; (c) Th/Yb-Nb/Yb图解, 边界据文献[34]; (d) Nb/Zr-Th/Zr图解,边界据文献[35])
Fig.6 Tectonic identification diagrams for the Carboniferous volcanic rocks in Hashan area ((a) TiO2 versus Zr plot, modified from ref.[33];(b) Nb/Thversus Nb plot;(c) Th/Yb versus Nb/Yb plot, modified from ref.[34];(d) Nb/Zr versus Th/Zr plot, modified from ref.[35])
| [1] | COLEMAN R G. Continental growth of northwest China[J]. Tectonics, 1989, 8(3): 621-635. |
| [2] | 肖序常. 新疆北部及其邻区大地构造[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1992. |
| [3] | JAHN B M, WINDLEY B, NATAL’IN B, et al. Phanerozoic continental growth in central Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23(5): 599-603. |
| [4] | 陈发景, 汪新文, 汪新伟. 准噶尔盆地的原型和构造演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(3): 77-89. |
| [5] | 肖文进, 肖剑, 杜斌, 等. 新疆哈密天宇北金钨矿地质特征及找矿预测[J]. 地质与勘探, 2023, 59(5): 921-931. |
| [6] | 潘杰, 赵留升, 张杰, 等. 新疆哈密大青山金矿床成矿期构造特征及找矿方向[J]. 地质与勘探, 2023, 59(5): 932-945. |
| [7] | FENG Y, COLEMAN R G, TILTON G, et al. Tectonic evolution of the west Junggar Region, Xinjiang, China[J]. Tectonics, 1989, 8(4): 729-752. |
| [8] | 梁云海, 李文铅, 李卫东. 新疆准噶尔造山带多旋回开合构造特征[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(3): 279-285. |
| [9] | CAI Q R, SONG Z H, ZHANG G L, et al. Geochronological and geochemical study of the Late Carboniferous volcanic drilling cores from the Piedmont of the Hala’alate Mountain in West Junggar: Implications for stratigraphic division and tectonic evolution[J]. Lithos, 2023, 456: 107305. |
| [10] | 肖文交, 韩春明, 袁超, 等. 新疆北部石炭纪—二叠纪独特的构造-成矿作用: 对古亚洲洋构造域南部大地构造演化的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(5): 1062-1076. |
| [11] | 毛治国, 邹才能, 朱如凯, 等. 准噶尔盆地石炭纪火山岩岩石地球化学特征及其构造环境意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(1): 207-216. |
| [12] |
焦小芹, 张关龙, 牛花朋, 等. 准噶尔盆地东北缘石炭系火山岩形成机制: 对准噶尔洋盆闭合时限的新启示[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(4): 385-402.
DOI |
| [13] | GENG H Y, SUN M, YUAN C, et al. Geochemical, Sr-Nd and zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopic studies of Late Carboniferous magmatism in the West Junggar, Xinjiang: Implications for ridge subduction?[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 266(3/4): 364-389. |
| [14] | YIN J Y, CHEN W, YUAN C, et al. Petrogenesis of Early Carboniferous adakitic dikes, Sawur region, northern West Junggar, NW China: Implications for geodynamic evolution[J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 27(4): 1630-1645. |
| [15] | DING W C, LI T D, CHEN X H, et al. Intra-continental deformation and tectonic evolution of the West Junggar Orogenic Belt, Central Asia: Evidence from remote sensing and structural geological analyses[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2020, 11(2): 651-663. |
| [16] | YIN J Y, YUAN C, SUN M, et al. Late Carboniferous high-Mg dioritic dikes in Western Junggar, NW China: Geochemical features, petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Gondwana Research, 2010, 17(1): 145-152. |
| [17] |
李永军, 徐倩, 杨高学, 等. 陆内“滞后” 弧岩浆岩特征及其地质意义: 来自西准噶尔乌尔禾北早二叠世岩浆作用的证据[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(4): 190-199.
DOI |
| [18] | 张韶琛. 准噶尔盆地西北缘哈山构造样式及对成藏影响作用研究[D]. 东营: 中国石油大学(华东), 2015. |
| [19] | LE BAS M J, LE MAITRE R W, STRECKEISEN A, et al. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali-silica diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1986, 27(3): 745-750. |
| [20] | RICKWOOD P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989, 22(4): 247-263. |
| [21] | PEARCE J A. Trace Element Characteristics of Lavas from Destructive Plate Boundaries[M]// THORPE, R.S. Andesites:Orogenic Andesites and Related Rocks. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1982: 252-548. |
| [22] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. |
| [23] | CULLERS R L, GRAF J L. Chapter 8 rare earth elements in igneous rocks of the continental crust: Intermediate and silicic rocks-ore petrogenesis[J]. Developments in Geochemistry, 1984, 2: 275-316. |
| [24] |
HOFFMAN P F. Did the breakout of laurentia turn Gondwanaland inside-out?[J]. Science, 1991, 252(5011): 1409-1412.
PMID |
| [25] | TAYLOR S.R., MCLENNAN S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[D]. Blackwell: Oxford, 1985. |
| [26] | 张继恩, 肖文交, 韩春明, 等. 西准噶尔石炭纪洋中脊俯冲岩浆活动: 以玛里雅蛇绿岩为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(11): 3272-3282. |
| [27] | DOSSO L, MURTHY V R. A Nd isotopic study of the Kerguelen Islands: Inferences on enriched oceanic mantle sources[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1980, 48(2): 268-276. |
| [28] | GENG H Y, SUN M, YUAN C, et al. Geochemical and geochronological study of early Carboniferous volcanic rocks from the West Junggar: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 42(5): 854-866. |
| [29] | STRACKE A, BIZIMIS M, SALTERS V J M. Recycling oceanic crust: Quantitative constraints[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2003, 4(3): 8003. |
| [30] | TANG G J, WANG Q, WYMAN D A, et al. Ridge subduction and crustal growth in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Evidence from late Carboniferous adakites and high-Mg diorites in the western Junggar Region, northern Xinjiang (west China)[J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 277(3/4): 281-300. |
| [31] | 向坤鹏. 新疆西准噶尔包古图—哈拉阿拉特山一带石炭纪沉积盆地分析及构造意义[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2015. |
| [32] | 王福同. 新疆维吾尔自治区古地理及地质生态图集[M]. 北京: 中国地图出版社, 2006. |
| [33] | PEARCE J A, CANN J R. Tectonic setting of basic volcanic rocks determined using trace element analyses[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1973, 19(2): 290-300. |
| [34] | PEARCE J. Tectonic implications of the composition of volcanic arc magmas[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 23: 251-285. |
| [35] | LI D, HE D F, MA D L, et al. Carboniferous-Permian tectonic framework and its later modifications to the area from eastern Kazakhstan to southern Altai: Insights from the Zaysan-Jimunai Basin evolution[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 113: 16-35. |
| [36] | SHEN P, PAN H D, XIAO W J, et al. Early Carboniferous intra-oceanic arc and back-arc basin system in the West Junggar, NW China[J]. International Geology Review, 2013, 55(16): 1991-2007. |
| [37] | DUAN F H, LI Y J, ZHI Q, et al. Petrogenesis and geodynamic implications of Late Carboniferous sanukitic dikes from the Bieluagaxi area of West Junggar, NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 175: 158-177. |
| [38] | 徐新, 周可法, 王煜. 西准噶尔晚古生代残余洋盆消亡时间与构造背景研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(11): 3206-3214. |
| [39] |
杨高学, 李永军, 佟丽莉, 等. 西准噶尔海山俯冲的地质效应: 来自泥盆纪—石炭纪火山岩地球化学证据[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(6): 60-67.
DOI |
| [1] | 曲彦胜, 潘志强, 何大祥, 钟宁宁, 牛花朋, 杨梅华, 韩立国. 准噶尔盆地莫西庄地区侏罗系三工河组原油芳烃地球化学特征及油源对比[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(03): 814-824. |
| [2] | 魏超凡, 张志杰, 万力, 成大伟, 李顺利, 孙洪伟. 准噶尔盆地东南缘井井子沟组物源分析及构造-沉积学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(02): 327-350. |
| [3] | 马立成, 江万, 施辉, 胡俊杰, 张浩, 陈程, 董敏, 彭博, 方欣欣. 柴达木盆地东部尕海南山地区新生代叠加褶皱与油气运移[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(05): 1209-1220. |
| [4] | 郑英, 韩杰, 张小永, 缑明亮, 王明, 袁博武. 柴达木盆地东北部拉合根地区中生代火山岩的发现及其地质意义:来自地球化学与锆石年代学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 1147-1161. |
| [5] | 王佳新, 焦建刚, 马云飞, 李峰, 高超. 内蒙古中部乌兰陶勒盖铜镍矿床形成时代与岩浆源区[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 991-1012. |
| [6] | 邓毅, 高崇龙, 王剑, 刘明, 孟元林, 任影, 刘可, 王柯. 准噶尔盆地南缘西段齐古组深层储层特征及物性控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(02): 335-349. |
| [7] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [8] | 倪敏婕, 祝贺暄, 何文军, 杨森, 邹阳, 张元元. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组沉积环境与沉积模式分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1194-1207. |
| [9] | 于景维, 丁韦, 张欣, 祁利祺, 黄舒雅, 张智越, 张以勒. 准噶尔盆地AH5井区八道湾组碳酸盐胶结物成因及对储层影响分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1336-1344. |
| [10] | 韩飞, 宋元宝, 张伟, 李道凌, 黄永高, 李应栩, 贾小川, 杨学俊, 杨青松, 宋旭波, 卢柳. 西藏冈底斯南木林地区晚三叠世中酸性岩浆作用及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 547-561. |
| [11] | 田安琦, 陈石, 余一欣, 修金磊, 金峰. 准噶尔盆地莫索湾凸起西缘走滑断裂分层变形特征及形成机理[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 296-306. |
| [12] | 李文霞, 赵志丹, 王晓丽, 严溶, 路远发. 西藏日喀则蛇绿岩镁铁质岩石Re-Os同位素特征及意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1503-1512. |
| [13] | 张韩静, 李素梅, 高永进, 张林, 柯昌炜. 准噶尔盆地东南缘二叠系芦草沟组烃源岩有机地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1538-1550. |
| [14] | 樊丹, 李涤, 何登发, 侯烁钦, 孙天鸽, 杨浩, 甄宇. 东天山博格达地区石炭系构造-地层划分及成盆背景分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1206-1217. |
| [15] | 李二庭, 马万云, 李际, 马新星, 潘长春, 曾立飞, 王明. 准噶尔盆地南缘侏罗系煤生烃热模拟实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1313-1323. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||