



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (05): 1380-1396.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.21
收稿日期:2020-05-20
修回日期:2021-06-30
出版日期:2021-10-10
发布日期:2021-11-04
通讯作者:
肖荣阁
作者简介:肖荣阁,男,教授,博士生导师,1949年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事矿床地球化学研究。Email: rgxiao@163.com。基金资助:
ZHAO Baoju1,2( ), ZHANG Yanfei3, YAN Kai4, XIAO Rongge1(
), ZHANG Yanfei3, YAN Kai4, XIAO Rongge1( )
)
Received:2020-05-20
Revised:2021-06-30
Online:2021-10-10
Published:2021-11-04
Contact:
XIAO Rongge
摘要:
大兴安岭中段是我国重要的铅锌银等有色金属成矿区,探讨其成矿物质来源对区内成矿预测及找矿工作具有重要意义。经广泛地质调查、典型矿床采样、岩矿鉴定、全岩地球化学分析,并在此基础上进行元素聚类分析,结果显示海西期成矿岩浆岩稀土总量偏低,负铕异常不明显,轻重稀土比值较大,与稀土总量呈正相关关系,与δEu值呈负相关关系,表明成岩物质以幔源为主。燕山期成矿岩浆岩则相反,显示壳源物质特征。铅锌银多金属矿以锌为主,铅锌矿石与幔源分异岩浆岩的稀土配分模式基本一致;聚类分析显示TFeO-Cu-Zn为独立群组,表明铁铜锌物质是从岩浆结晶晚期的岩浆中分异出来;TFeO-Cu-Zn独立群组显示区域内闪锌矿均为高温铁闪锌矿。研究认为,大兴安岭中段铅锌银矿成矿物质来自闪长岩,后期热液改造对铅银富集有一定作用,中基性岩浆岩形成铅锌银成矿系统,而酸性岩浆岩形成铜钼及铜锡成矿系统。
中图分类号:
赵保具, 张艳飞, 颜开, 肖荣阁. 大兴安岭中段有色金属矿床成矿物质来源探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1380-1396.
ZHAO Baoju, ZHANG Yanfei, YAN Kai, XIAO Rongge. Ore-forming Material Source of Non-ferrous Metal Deposits in the Central Great Xing’an Range[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(05): 1380-1396.

图1 研究区区域地质图((a)据Xiao等[16], 2003)和大兴安岭中段多金属矿床分布图((b)据欧阳荷根[26],2013) 1.华北前寒武纪克拉通;2.华北早古生代大陆边缘;3.索伦缝合带晚古生代增生杂岩;4.内蒙古古生代增生杂岩;5.内蒙古古生代大陆边缘;6.蛇绿岩。
Fig.1 Regional geological map of the study area ((a)after Xiao et al. [16],2003) and distribution of polymetallic deposits in the central Great Xing’an Range((b)据Ouyang et al.[26],2013)
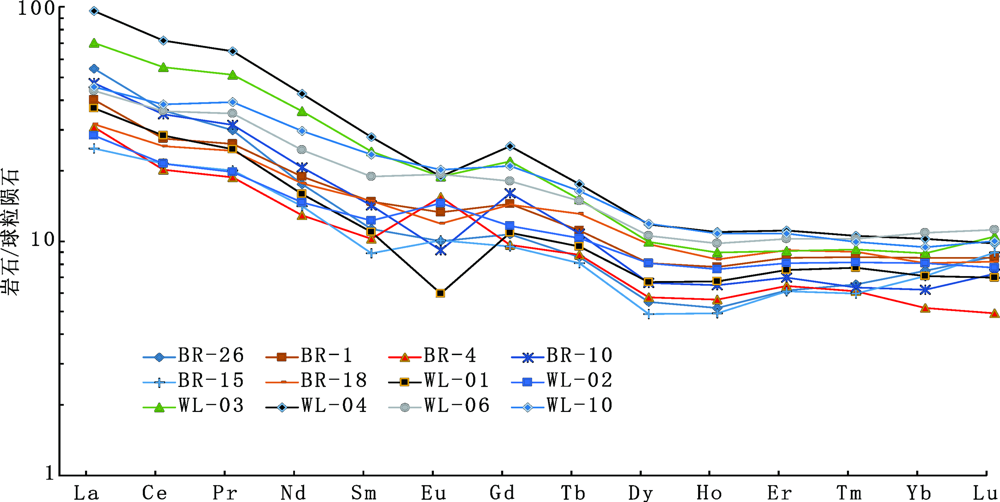
图2 拜仁达坝闪长岩稀土配分曲线(球粒陨石标准化数据据Belousova等[42],2002)
Fig.2 Distribution curves of REEs in Bairendaba dioritoids(chondrite normalizing values after Belousova et al.[42],2002)
| 岩性 | 样号 | 年龄/Ma | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 霏细岩 | DJM1 | 170.7 | 76.39 | 0.09 | 13.73 | 0.27 | 2.00 | 0.07 | 0.30 | 0.19 | |||||||
| DJM3 | 72.25 | 0.08 | 13.13 | 0.74 | 4.60 | 0.08 | 0.42 | 0.14 | |||||||||
| 黑云二长花岗岩 | DJR4 | 279.7 | 72.65 | 0.20 | 13.05 | 1.45 | 1.65 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 1.29 | |||||||
| DJR5 | 73.02 | 0.21 | 13.17 | 1.58 | 1.15 | 0.06 | 0.17 | 1.12 | |||||||||
| 似斑状二长花岗岩 | DJR6 | 242.8 | 71.06 | 0.42 | 14.10 | 0.61 | 1.95 | 0.04 | 0.86 | 2.05 | |||||||
| DJR7 | 70.85 | 0.44 | 14.17 | 0.62 | 2.00 | 0.05 | 0.90 | 2.20 | |||||||||
| 闪长玢岩 | DJA8 | 252.0 | 59.62 | 0.80 | 14.44 | 3.73 | 2.25 | 0.10 | 5.90 | 3.15 | |||||||
| DJA9 | 60.50 | 0.78 | 14.26 | 3.46 | 2.40 | 0.10 | 5.18 | 3.48 | |||||||||
| 钾长花岗岩 | KHG1 | 136.8 | 77.39 | 0.09 | 11.33 | 0.45 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.83 | |||||||
| KHG2 | 76.62 | 0.06 | 11.75 | 0.78 | 0.20 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.92 | |||||||||
| KHG3 | 71.90 | 0.02 | 14.54 | 0.51 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 2.25 | |||||||||
| 花岗斑岩 | BHG4 | 136.7 | 74.62 | 0.06 | 11.50 | 1.34 | 0.90 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.53 | |||||||
| BHG5 | 66.81 | 0.12 | 13.88 | 0.61 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 4.41 | |||||||||
| BHG6 | 74.71 | 0.05 | 12.25 | 1.95 | 1.25 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 2.01 | |||||||||
| 平均 | 71.31 | 0.24 | 13.24 | 1.29 | 1.49 | 0.05 | 1.03 | 1.76 | |||||||||
| 岩性 | 样号 | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总计 | Na2O+K2O | K2O/Na2O | A/CNK | ||||||||
| 霏细岩 | DJM1 | 0.15 | 3.43 | 0.02 | 3.25 | 99.89 | 3.58 | 22.87 | 3.18 | ||||||||
| DJM3 | 0.15 | 3.52 | 0.02 | 4.74 | 99.87 | 3.67 | 23.47 | 3.04 | |||||||||
| 黑云二长花岗岩 | DJR4 | 4.44 | 3.83 | 0.05 | 1.03 | 99.84 | 8.27 | 0.86 | 0.94 | ||||||||
| DJR5 | 4.48 | 3.85 | 0.05 | 1.01 | 99.87 | 8.33 | 0.86 | 0.97 | |||||||||
| 似斑状二长花岗岩 | DJR6 | 4.07 | 4.20 | 0.12 | 0.46 | 99.94 | 8.27 | 1.03 | 0.94 | ||||||||
| DJR7 | 4.20 | 3.94 | 0.12 | 0.46 | 99.95 | 8.14 | 0.94 | 0.93 | |||||||||
| 闪长玢岩 | DJA8 | 4.07 | 2.60 | 0.19 | 2.86 | 99.71 | 6.67 | 0.64 | 0.95 | ||||||||
| DJA9 | 4.29 | 2.51 | 0.18 | 2.58 | 99.72 | 6.80 | 0.59 | 0.88 | |||||||||
| 钾长花岗岩 | KHG1 | 3.49 | 5.65 | 0.02 | 0.64 | 100.15 | 9.14 | 1.62 | 0.85 | ||||||||
| KHG2 | 4.15 | 5.02 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 100.19 | 9.17 | 1.21 | 0.84 | |||||||||
| KHG3 | 6.79 | 2.17 | 0.03 | 1.64 | 100.15 | 8.96 | 0.32 | 0.83 | |||||||||
| 花岗斑岩 | BHG4 | 4.02 | 4.76 | 0.01 | 3.00 | 100.81 | 8.78 | 1.18 | 0.90 | ||||||||
| BHG5 | 3.78 | 6.89 | 0.03 | 3.30 | 100.06 | 10.67 | 1.82 | 0.64 | |||||||||
| BHG6 | 0.49 | 5.16 | 0.01 | 2.75 | 100.97 | 5.65 | 10.53 | 1.22 | |||||||||
| 平均 | 3.47 | 4.11 | 0.06 | 2.03 | 100.08 | 7.58 | 4.85 | 1.22 | |||||||||
表1 大井子—黄岗梁矿区岩浆岩化学组成(wB/%)
Table 1 Petrochemical compositions of the magmatic rocks from the Dajingzi-Huanggangliang mining area (%)
| 岩性 | 样号 | 年龄/Ma | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 霏细岩 | DJM1 | 170.7 | 76.39 | 0.09 | 13.73 | 0.27 | 2.00 | 0.07 | 0.30 | 0.19 | |||||||
| DJM3 | 72.25 | 0.08 | 13.13 | 0.74 | 4.60 | 0.08 | 0.42 | 0.14 | |||||||||
| 黑云二长花岗岩 | DJR4 | 279.7 | 72.65 | 0.20 | 13.05 | 1.45 | 1.65 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 1.29 | |||||||
| DJR5 | 73.02 | 0.21 | 13.17 | 1.58 | 1.15 | 0.06 | 0.17 | 1.12 | |||||||||
| 似斑状二长花岗岩 | DJR6 | 242.8 | 71.06 | 0.42 | 14.10 | 0.61 | 1.95 | 0.04 | 0.86 | 2.05 | |||||||
| DJR7 | 70.85 | 0.44 | 14.17 | 0.62 | 2.00 | 0.05 | 0.90 | 2.20 | |||||||||
| 闪长玢岩 | DJA8 | 252.0 | 59.62 | 0.80 | 14.44 | 3.73 | 2.25 | 0.10 | 5.90 | 3.15 | |||||||
| DJA9 | 60.50 | 0.78 | 14.26 | 3.46 | 2.40 | 0.10 | 5.18 | 3.48 | |||||||||
| 钾长花岗岩 | KHG1 | 136.8 | 77.39 | 0.09 | 11.33 | 0.45 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.83 | |||||||
| KHG2 | 76.62 | 0.06 | 11.75 | 0.78 | 0.20 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.92 | |||||||||
| KHG3 | 71.90 | 0.02 | 14.54 | 0.51 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 2.25 | |||||||||
| 花岗斑岩 | BHG4 | 136.7 | 74.62 | 0.06 | 11.50 | 1.34 | 0.90 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.53 | |||||||
| BHG5 | 66.81 | 0.12 | 13.88 | 0.61 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 4.41 | |||||||||
| BHG6 | 74.71 | 0.05 | 12.25 | 1.95 | 1.25 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 2.01 | |||||||||
| 平均 | 71.31 | 0.24 | 13.24 | 1.29 | 1.49 | 0.05 | 1.03 | 1.76 | |||||||||
| 岩性 | 样号 | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总计 | Na2O+K2O | K2O/Na2O | A/CNK | ||||||||
| 霏细岩 | DJM1 | 0.15 | 3.43 | 0.02 | 3.25 | 99.89 | 3.58 | 22.87 | 3.18 | ||||||||
| DJM3 | 0.15 | 3.52 | 0.02 | 4.74 | 99.87 | 3.67 | 23.47 | 3.04 | |||||||||
| 黑云二长花岗岩 | DJR4 | 4.44 | 3.83 | 0.05 | 1.03 | 99.84 | 8.27 | 0.86 | 0.94 | ||||||||
| DJR5 | 4.48 | 3.85 | 0.05 | 1.01 | 99.87 | 8.33 | 0.86 | 0.97 | |||||||||
| 似斑状二长花岗岩 | DJR6 | 4.07 | 4.20 | 0.12 | 0.46 | 99.94 | 8.27 | 1.03 | 0.94 | ||||||||
| DJR7 | 4.20 | 3.94 | 0.12 | 0.46 | 99.95 | 8.14 | 0.94 | 0.93 | |||||||||
| 闪长玢岩 | DJA8 | 4.07 | 2.60 | 0.19 | 2.86 | 99.71 | 6.67 | 0.64 | 0.95 | ||||||||
| DJA9 | 4.29 | 2.51 | 0.18 | 2.58 | 99.72 | 6.80 | 0.59 | 0.88 | |||||||||
| 钾长花岗岩 | KHG1 | 3.49 | 5.65 | 0.02 | 0.64 | 100.15 | 9.14 | 1.62 | 0.85 | ||||||||
| KHG2 | 4.15 | 5.02 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 100.19 | 9.17 | 1.21 | 0.84 | |||||||||
| KHG3 | 6.79 | 2.17 | 0.03 | 1.64 | 100.15 | 8.96 | 0.32 | 0.83 | |||||||||
| 花岗斑岩 | BHG4 | 4.02 | 4.76 | 0.01 | 3.00 | 100.81 | 8.78 | 1.18 | 0.90 | ||||||||
| BHG5 | 3.78 | 6.89 | 0.03 | 3.30 | 100.06 | 10.67 | 1.82 | 0.64 | |||||||||
| BHG6 | 0.49 | 5.16 | 0.01 | 2.75 | 100.97 | 5.65 | 10.53 | 1.22 | |||||||||
| 平均 | 3.47 | 4.11 | 0.06 | 2.03 | 100.08 | 7.58 | 4.85 | 1.22 | |||||||||
| 岩性 | 样号 | 年龄/Ma | Rb | Sr | Ba | Zr | Hf | Th | U | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 霏细岩 | DJM1 | 170.7 | 212 | 34.3 | 327 | 101 | 3.5 | 11.1 | 5.46 | 12.5 |
| DJM3 | 251 | 14.2 | 225 | 79.2 | 3.36 | 12.0 | 5.67 | 10.6 | ||
| 黑云二长花岗岩 | DJR4 | 279.7 | 92.1 | 105 | 1 040 | 138 | 4.96 | 9.11 | 1.21 | 41.9 |
| DJR5 | 98.3 | 111 | 1 166 | 173 | 5.8 | 10.9 | 4.39 | 45.5 | ||
| 似斑状二长花岗岩 | DJR6 | 242.8 | 65.2 | 168 | 540 | 150 | 4.38 | 8.72 | 0.94 | 9.64 |
| DJR7 | 123 | 281 | 552 | 150 | 4 | 14.1 | 1.75 | 10 | ||
| 闪长玢岩 | DJA8 | 252.0 | 72.7 | 590 | 618 | 204 | 5.24 | 6.16 | 1.8 | 16.1 |
| DJA9 | 70.8 | 636 | 629 | 224 | 5.65 | 6.36 | 1.76 | 17.1 | ||
| 钾长花岗岩 | KHG1 | 136.8 | 263 | 26.2 | 142 | 196 | 7.06 | 33.8 | 5.48 | 30 |
| KHG2 | 232 | 10.8 | 44.1 | 324 | 10.6 | 38.4 | 8.63 | 62.9 | ||
| KHG3 | 227 | 30.3 | 109 | 316 | 12.6 | 18.3 | 4.2 | 48.2 | ||
| 花岗斑岩 | BHG4 | 136.7 | 654 | 19.3 | 40 | 243 | 11.9 | 75.6 | 34.6 | 105 |
| BHG5 | 600 | 47.2 | 281 | 266 | 9.81 | 49 | 4.88 | 40.8 | ||
| BHG6 | 793 | 20.1 | 155 | 270 | 11.9 | 91.1 | 35.7 | 63.3 | ||
| 平均 | 268.15 | 149.53 | 419.15 | 202.44 | 7.2 | 27.48 | 8.32 | 36.68 | ||
| 岩性 | 样号 | Nb | Ta | Rb/Sr | Sr/Ba | Th/U | Zr/Y | Nb/Ta | ||
| 霏细岩 | DJM1 | 8.39 | 0.98 | 6.18 | 0.10 | 2.03 | 8.08 | 8.56 | ||
| DJM3 | 8.11 | 1.01 | 17.68 | 0.06 | 2.12 | 7.47 | 8.03 | |||
| 黑云二长花岗岩 | DJR4 | 9.69 | 0.63 | 0.88 | 0.10 | 7.53 | 3.29 | 15.38 | ||
| DJR5 | 10.9 | 0.74 | 0.89 | 0.10 | 2.48 | 3.8 | 14.73 | |||
| 似斑状二长花岗岩 | DJR6 | 6.56 | 1.01 | 0.39 | 0.31 | 9.28 | 15.56 | 6.50 | ||
| DJR7 | 5.79 | 0.63 | 0.44 | 0.51 | 8.06 | 15 | 9.19 | |||
| 闪长玢岩 | DJA8 | 4.81 | 0.37 | 0.12 | 0.95 | 3.42 | 12.67 | 13.0 | ||
| DJA9 | 5.12 | 0.35 | 0.11 | 1.01 | 3.61 | 13.1 | 14.63 | |||
| 钾长花岗岩 | KHG1 | 20.8 | 2.28 | 10.04 | 0.18 | 6.17 | 6.53 | 9.12 | ||
| KHG2 | 31.5 | 3.33 | 21.48 | 0.24 | 4.45 | 5.15 | 9.46 | |||
| KHG3 | 11.3 | 1.45 | 7.49 | 0.28 | 4.36 | 6.56 | 7.79 | |||
| 花岗斑岩 | BHG4 | 51.8 | 11.3 | 33.89 | 0.48 | 2.18 | 2.31 | 4.58 | ||
| BHG5 | 20.8 | 3.19 | 12.71 | 0.17 | 10.04 | 6.52 | 6.52 | |||
| BHG6 | 28.4 | 4.84 | 39.45 | 0.13 | 2.55 | 4.27 | 5.87 | |||
| 平均 | 16.0 | 2.29 | 10.84 | 0.33 | 4.88 | 7.88 | 9.53 |
表2 大井子—黄岗梁矿区岩浆微量元素含量(wB/10-6)
Table 2 Trace element contents of the magmatic rocks in the Dajingzi-Huanggangliang mining area (10-6)
| 岩性 | 样号 | 年龄/Ma | Rb | Sr | Ba | Zr | Hf | Th | U | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 霏细岩 | DJM1 | 170.7 | 212 | 34.3 | 327 | 101 | 3.5 | 11.1 | 5.46 | 12.5 |
| DJM3 | 251 | 14.2 | 225 | 79.2 | 3.36 | 12.0 | 5.67 | 10.6 | ||
| 黑云二长花岗岩 | DJR4 | 279.7 | 92.1 | 105 | 1 040 | 138 | 4.96 | 9.11 | 1.21 | 41.9 |
| DJR5 | 98.3 | 111 | 1 166 | 173 | 5.8 | 10.9 | 4.39 | 45.5 | ||
| 似斑状二长花岗岩 | DJR6 | 242.8 | 65.2 | 168 | 540 | 150 | 4.38 | 8.72 | 0.94 | 9.64 |
| DJR7 | 123 | 281 | 552 | 150 | 4 | 14.1 | 1.75 | 10 | ||
| 闪长玢岩 | DJA8 | 252.0 | 72.7 | 590 | 618 | 204 | 5.24 | 6.16 | 1.8 | 16.1 |
| DJA9 | 70.8 | 636 | 629 | 224 | 5.65 | 6.36 | 1.76 | 17.1 | ||
| 钾长花岗岩 | KHG1 | 136.8 | 263 | 26.2 | 142 | 196 | 7.06 | 33.8 | 5.48 | 30 |
| KHG2 | 232 | 10.8 | 44.1 | 324 | 10.6 | 38.4 | 8.63 | 62.9 | ||
| KHG3 | 227 | 30.3 | 109 | 316 | 12.6 | 18.3 | 4.2 | 48.2 | ||
| 花岗斑岩 | BHG4 | 136.7 | 654 | 19.3 | 40 | 243 | 11.9 | 75.6 | 34.6 | 105 |
| BHG5 | 600 | 47.2 | 281 | 266 | 9.81 | 49 | 4.88 | 40.8 | ||
| BHG6 | 793 | 20.1 | 155 | 270 | 11.9 | 91.1 | 35.7 | 63.3 | ||
| 平均 | 268.15 | 149.53 | 419.15 | 202.44 | 7.2 | 27.48 | 8.32 | 36.68 | ||
| 岩性 | 样号 | Nb | Ta | Rb/Sr | Sr/Ba | Th/U | Zr/Y | Nb/Ta | ||
| 霏细岩 | DJM1 | 8.39 | 0.98 | 6.18 | 0.10 | 2.03 | 8.08 | 8.56 | ||
| DJM3 | 8.11 | 1.01 | 17.68 | 0.06 | 2.12 | 7.47 | 8.03 | |||
| 黑云二长花岗岩 | DJR4 | 9.69 | 0.63 | 0.88 | 0.10 | 7.53 | 3.29 | 15.38 | ||
| DJR5 | 10.9 | 0.74 | 0.89 | 0.10 | 2.48 | 3.8 | 14.73 | |||
| 似斑状二长花岗岩 | DJR6 | 6.56 | 1.01 | 0.39 | 0.31 | 9.28 | 15.56 | 6.50 | ||
| DJR7 | 5.79 | 0.63 | 0.44 | 0.51 | 8.06 | 15 | 9.19 | |||
| 闪长玢岩 | DJA8 | 4.81 | 0.37 | 0.12 | 0.95 | 3.42 | 12.67 | 13.0 | ||
| DJA9 | 5.12 | 0.35 | 0.11 | 1.01 | 3.61 | 13.1 | 14.63 | |||
| 钾长花岗岩 | KHG1 | 20.8 | 2.28 | 10.04 | 0.18 | 6.17 | 6.53 | 9.12 | ||
| KHG2 | 31.5 | 3.33 | 21.48 | 0.24 | 4.45 | 5.15 | 9.46 | |||
| KHG3 | 11.3 | 1.45 | 7.49 | 0.28 | 4.36 | 6.56 | 7.79 | |||
| 花岗斑岩 | BHG4 | 51.8 | 11.3 | 33.89 | 0.48 | 2.18 | 2.31 | 4.58 | ||
| BHG5 | 20.8 | 3.19 | 12.71 | 0.17 | 10.04 | 6.52 | 6.52 | |||
| BHG6 | 28.4 | 4.84 | 39.45 | 0.13 | 2.55 | 4.27 | 5.87 | |||
| 平均 | 16.0 | 2.29 | 10.84 | 0.33 | 4.88 | 7.88 | 9.53 |
| 岩性 | 样号 | 年龄/Ma | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 霏细岩 | DJM1 | 170.7 | 27.8 | 50.1 | 5.34 | 18.1 | 2.96 | 0.62 | 2.20 | 0.38 | 2.27 |
| DJM3 | 20.2 | 38.2 | 4.06 | 14.4 | 2.38 | 0.35 | 1.88 | 0.34 | 1.92 | ||
| 黑云母二长花岗岩 | DJM4 | 279.7 | 32.8 | 63.8 | 7.88 | 31.2 | 6.63 | 1.28 | 6.67 | 1.28 | 7.50 |
| DJM5 | 41.2 | 79.5 | 9.61 | 37.2 | 7.61 | 1.28 | 7.07 | 1.39 | 8.56 | ||
| 似斑状二长花岗岩 | DJR6 | 242.8 | 14.8 | 35.1 | 3.42 | 13.3 | 2.52 | 0.62 | 2.30 | 0.37 | 1.85 |
| DJR7 | 22.7 | 43.9 | 4.78 | 17.3 | 2.90 | 0.79 | 2.50 | 0.39 | 2.00 | ||
| 闪长玢岩 | DJA8 | 252.0 | 18.7 | 39.5 | 4.9 | 20.6 | 4.11 | 1.21 | 3.56 | 0.59 | 3.30 |
| DJA9 | 20.3 | 41.4 | 5.34 | 22.3 | 3.96 | 1.27 | 3.65 | 0.60 | 3.30 | ||
| 钾长花岗岩 | KHG1 | 136.8 | 49.6 | 100 | 11.6 | 41.2 | 7.35 | 0.21 | 6.14 | 1.01 | 5.28 |
| KHG2 | 165.0 | 305 | 33.9 | 107.0 | 17.40 | 0.13 | 14.10 | 2.10 | 11.50 | ||
| KHG3 | 197.0 | 362 | 39.3 | 121.0 | 17.30 | 0.21 | 12.90 | 1.76 | 8.86 | ||
| 花岗斑岩 | BHG4 | 136.7 | 56.50 | 131.0 | 15.90 | 55.2 | 12.80 | 0.13 | 11.60 | 2.52 | 16.6 |
| BHG5 | 31.10 | 61.4 | 7.15 | 25.7 | 5.17 | 0.33 | 4.78 | 0.97 | 6.15 | ||
| BHG6 | 24.50 | 54.5 | 6.76 | 26.2 | 6.03 | 0.18 | 5.62 | 1.20 | 8.01 | ||
| 平均 | 51.59 | 100.39 | 11.42 | 39.34 | 7.08 | 0.62 | 6.07 | 1.06 | 6.22 | ||
| 岩性 | 样号 | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | REE | LREE/HREE | δCe | δEu | |
| 霏细岩 | DJM1 | 0.42 | 1.19 | 0.21 | 1.43 | 0.23 | 113.25 | 12.60 | 0.99 | 0.74 | |
| DJM3 | 0.37 | 1.13 | 0.18 | 1.33 | 0.20 | 86.94 | 10.83 | 1.02 | 0.51 | ||
| 黑云母二长花岗岩 | DJM4 | 1.54 | 4.75 | 0.77 | 5.07 | 0.81 | 171.98 | 5.06 | 0.96 | 0.59 | |
| DJM5 | 1.69 | 5.03 | 0.87 | 5.75 | 0.90 | 207.66 | 5.64 | 0.96 | 0.53 | ||
| 似斑状二长花岗岩 | DJR6 | 0.35 | 1.06 | 0.17 | 1.07 | 0.17 | 77.10 | 9.50 | 1.19 | 0.79 | |
| DJR7 | 0.36 | 1.02 | 0.16 | 0.91 | 0.13 | 99.84 | 12.37 | 1.01 | 0.90 | ||
| 闪长玢岩 | DJA8 | 0.59 | 1.72 | 0.26 | 1.60 | 0.26 | 100.90 | 7.49 | 0.99 | 0.97 | |
| DJA9 | 0.63 | 1.75 | 0.25 | 1.65 | 0.26 | 106.66 | 7.82 | 0.96 | 1.02 | ||
| 钾长花岗岩 | KHG1 | 0.94 | 2.86 | 0.44 | 2.68 | 0.43 | 229.74 | 10.61 | 1.00 | 0.10 | |
| KHG2 | 2.07 | 6.10 | 0.96 | 6.09 | 0.93 | 672.28 | 14.33 | 0.98 | 0.03 | ||
| KHG3 | 1.53 | 4.95 | 0.82 | 5.26 | 0.94 | 773.83 | 19.9 | 0.99 | 0.04 | ||
| 花岗斑岩 | BHG4 | 3.41 | 11.80 | 2.09 | 14.60 | 2.29 | 336.44 | 4.18 | 1.05 | 0.03 | |
| BHG5 | 1.27 | 4.25 | 0.77 | 5.16 | 0.82 | 155.02 | 5.41 | 0.99 | 0.20 | ||
| BHG6 | 1.67 | 5.48 | 1.00 | 6.77 | 1.13 | 149.05 | 3.83 | 1.02 | 0.09 | ||
| 平均 | 1.20 | 3.79 | 0.64 | 4.24 | 0.68 | 234.34 | 9.26 | 1.01 | 0.47 |
表3 大井子—黄岗梁矿区岩浆岩稀土元素含量(wB/10-6)
Table 3 REE contents of the magmatic rocks in the Dajingzi-Huanggangliang mining area (10-6)
| 岩性 | 样号 | 年龄/Ma | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 霏细岩 | DJM1 | 170.7 | 27.8 | 50.1 | 5.34 | 18.1 | 2.96 | 0.62 | 2.20 | 0.38 | 2.27 |
| DJM3 | 20.2 | 38.2 | 4.06 | 14.4 | 2.38 | 0.35 | 1.88 | 0.34 | 1.92 | ||
| 黑云母二长花岗岩 | DJM4 | 279.7 | 32.8 | 63.8 | 7.88 | 31.2 | 6.63 | 1.28 | 6.67 | 1.28 | 7.50 |
| DJM5 | 41.2 | 79.5 | 9.61 | 37.2 | 7.61 | 1.28 | 7.07 | 1.39 | 8.56 | ||
| 似斑状二长花岗岩 | DJR6 | 242.8 | 14.8 | 35.1 | 3.42 | 13.3 | 2.52 | 0.62 | 2.30 | 0.37 | 1.85 |
| DJR7 | 22.7 | 43.9 | 4.78 | 17.3 | 2.90 | 0.79 | 2.50 | 0.39 | 2.00 | ||
| 闪长玢岩 | DJA8 | 252.0 | 18.7 | 39.5 | 4.9 | 20.6 | 4.11 | 1.21 | 3.56 | 0.59 | 3.30 |
| DJA9 | 20.3 | 41.4 | 5.34 | 22.3 | 3.96 | 1.27 | 3.65 | 0.60 | 3.30 | ||
| 钾长花岗岩 | KHG1 | 136.8 | 49.6 | 100 | 11.6 | 41.2 | 7.35 | 0.21 | 6.14 | 1.01 | 5.28 |
| KHG2 | 165.0 | 305 | 33.9 | 107.0 | 17.40 | 0.13 | 14.10 | 2.10 | 11.50 | ||
| KHG3 | 197.0 | 362 | 39.3 | 121.0 | 17.30 | 0.21 | 12.90 | 1.76 | 8.86 | ||
| 花岗斑岩 | BHG4 | 136.7 | 56.50 | 131.0 | 15.90 | 55.2 | 12.80 | 0.13 | 11.60 | 2.52 | 16.6 |
| BHG5 | 31.10 | 61.4 | 7.15 | 25.7 | 5.17 | 0.33 | 4.78 | 0.97 | 6.15 | ||
| BHG6 | 24.50 | 54.5 | 6.76 | 26.2 | 6.03 | 0.18 | 5.62 | 1.20 | 8.01 | ||
| 平均 | 51.59 | 100.39 | 11.42 | 39.34 | 7.08 | 0.62 | 6.07 | 1.06 | 6.22 | ||
| 岩性 | 样号 | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | REE | LREE/HREE | δCe | δEu | |
| 霏细岩 | DJM1 | 0.42 | 1.19 | 0.21 | 1.43 | 0.23 | 113.25 | 12.60 | 0.99 | 0.74 | |
| DJM3 | 0.37 | 1.13 | 0.18 | 1.33 | 0.20 | 86.94 | 10.83 | 1.02 | 0.51 | ||
| 黑云母二长花岗岩 | DJM4 | 1.54 | 4.75 | 0.77 | 5.07 | 0.81 | 171.98 | 5.06 | 0.96 | 0.59 | |
| DJM5 | 1.69 | 5.03 | 0.87 | 5.75 | 0.90 | 207.66 | 5.64 | 0.96 | 0.53 | ||
| 似斑状二长花岗岩 | DJR6 | 0.35 | 1.06 | 0.17 | 1.07 | 0.17 | 77.10 | 9.50 | 1.19 | 0.79 | |
| DJR7 | 0.36 | 1.02 | 0.16 | 0.91 | 0.13 | 99.84 | 12.37 | 1.01 | 0.90 | ||
| 闪长玢岩 | DJA8 | 0.59 | 1.72 | 0.26 | 1.60 | 0.26 | 100.90 | 7.49 | 0.99 | 0.97 | |
| DJA9 | 0.63 | 1.75 | 0.25 | 1.65 | 0.26 | 106.66 | 7.82 | 0.96 | 1.02 | ||
| 钾长花岗岩 | KHG1 | 0.94 | 2.86 | 0.44 | 2.68 | 0.43 | 229.74 | 10.61 | 1.00 | 0.10 | |
| KHG2 | 2.07 | 6.10 | 0.96 | 6.09 | 0.93 | 672.28 | 14.33 | 0.98 | 0.03 | ||
| KHG3 | 1.53 | 4.95 | 0.82 | 5.26 | 0.94 | 773.83 | 19.9 | 0.99 | 0.04 | ||
| 花岗斑岩 | BHG4 | 3.41 | 11.80 | 2.09 | 14.60 | 2.29 | 336.44 | 4.18 | 1.05 | 0.03 | |
| BHG5 | 1.27 | 4.25 | 0.77 | 5.16 | 0.82 | 155.02 | 5.41 | 0.99 | 0.20 | ||
| BHG6 | 1.67 | 5.48 | 1.00 | 6.77 | 1.13 | 149.05 | 3.83 | 1.02 | 0.09 | ||
| 平均 | 1.20 | 3.79 | 0.64 | 4.24 | 0.68 | 234.34 | 9.26 | 1.01 | 0.47 |

图4 大井子岩浆岩稀土配分曲线(球粒陨石标准化数据据Belousova等[42],2002)
Fig.4 Distribution curves of REE in the Dajingzi magmatic rocks (chondrite normalizing values after Belousova et al.[42],2002)
| 序号 | 矿床 | 位置 | 规模 | 矿床成因类型 | 矿化特征 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 白音查干 | 西乌珠穆沁旗巴拉嘎尔高勒镇西90 km | 大型锡银锌铅矿 | 爆破角砾岩 夕卡岩型 | 矿床属于爆破角砾岩夕卡岩型矿床,以石英斑岩为核心分为爆破角砾岩带,北部矿化带属于震裂角砾岩矿化带,爆破角砾及震裂角砾之间的空间裂隙是热液充填结晶的有效空间。成矿岩体为石英斑岩,成岩年龄140 Ma左右 |
| 2 | 道伦达坝 | 西乌珠穆沁旗道伦达坝苏木 | 大型铜钨锡矿床 | 岩浆热液脉 型 | 矿体呈脉状产出于上二叠统林西组和华力西期黑云母花岗岩体内的构造破碎带中。矿体多数呈北东走向,倾向南东,倾角10°~60°。其成矿作用与隐伏的早白垩世花岗岩有密切联系,属于与早白垩世花岗岩有关的岩浆热液型矿床 |
| 3 | 花敖包特 | 西乌珠穆沁旗宝日格斯台苏木北东约25 km | 大型银铅锌矿床 | 热液脉型、夕卡岩型 | 矿床矿化主要产在蛇纹岩和泥灰岩之间及闪长玢岩中,蛇纹岩与泥灰岩之间主要为块状闪锌矿矿化,闪锌矿-方铅矿-黄铁矿经常呈现互层条带状分布,属于不同阶段热液结晶的矿物,以闪锌矿条带为主,其次是方铅矿,黄铁矿条带呈薄脉状,一些地段见方铅矿细脉穿切闪锌矿,或呈团块状分布于闪锌矿中。闪长玢岩中以细脉状闪锌矿、方铅矿为主,表层氧化呈黄褐色,新鲜面为灰白色,见星点状黄铁矿。矿床属于蛇纹石夕卡岩矿床,成矿岩体为闪长玢岩,岩体内以浸染状黄铁矿化和脉状方铅矿、闪锌矿为特征 |
| 4 | 双尖山 | 巴林左旗富河镇海力吐村 | 超大型银铅锌矿 | 玢岩型、中低温热液脉 | 矿床矿化主要分布在闪长玢岩岩体中及其边部韧性剪切带中,矿带宽40~50 m,矿石构造主要为细脉状、浸染状,矿带边缘1号富矿脉和2号富矿脉为强破碎糜棱岩带,呈大脉状矿化。矿石矿物主要为闪锌矿、方铅矿、自然银等,在石英方解石细脉中分布,局部集中成大脉,浅部岩石断面方铅矿氧化形成铅黄,呈浅黄色。闪长玢岩中以细脉状闪锌矿为主,表层氧化呈红褐色,新鲜面为黑褐色,见星点状黄铁矿。侏罗系不整合覆盖在二叠系矿化粉砂质板岩上,其间具有薄层风化壳矿化,侏罗系砂岩未见明显矿化。矿床类型为玢岩型银铅锌矿,成矿岩体为闪长玢岩,细脉状、浸染状矿化为主,主矿体边缘强韧性剪切带中有脉状富矿 |
| 5 | 富河东山湾 | 巴林左旗富河镇东山湾村 | 中型钼矿 床 | 云英岩型 | 矿区地层为二叠系泥灰岩、粉砂质板岩,岩体为黄褐色细粒花岗斑岩及霏细斑岩。花岗岩硅化强,硅化花岗岩呈灰白色细粒状致密岩石,硅化蚀变与黄褐色花岗岩呈不规则锯齿状、蚕食状接触。围岩为灰黑色石英细砂岩、粉砂岩,其中未见矿化。辉钼矿产于花岗岩中,新鲜花岗斑岩中有辉钼矿硫化物石英细脉,强硅化花岗斑岩呈灰白色颗粒状,规模较大,矿石的后期石英细脉中有粗晶辉钼矿。矿石品位高,辉钼矿晶片大,矿石中有少量黄铜矿,偶见黑钨矿板状晶体 |
| 6 | 小北沟 | 巴林左旗富河镇小北沟村 | 小型铅锌矿床 | 热液脉型 | 矿区出露侏罗系火山碎屑岩及闪长岩脉,侏罗系角砾状碎屑岩裂隙及构造节理面有铅锌矿化,构造糜棱岩中矿化较好,裂隙中形成闪锌矿脉 |
| 7 | 榆树林 | 巴林左旗三山 乡 | 小型银铜铅锌矿床 | 热液脉型 | 矿体赋存于大石寨组上段变质粉砂岩、粉砂质板岩地层中,受地层内部构造裂隙控制,北西向构造裂隙成矿较好 |
| 8 | 红岭 | 巴林左旗乌兰达坝苏木 | 大型铅锌矿床 | 夕卡岩型 | 矿床产于乌兰坝岩体与二叠系大石寨组接触带上,矿带沿大石寨组大理岩层分布,呈北东方向展布,倾向北西,倾角较陡。矿体呈层状、似层状产出,沿大理岩层分布,夕卡岩化为区内最重要的蚀变类型,该矿床主要工业矿体均产在夕卡岩中 |
| 9 | 哈布特盖 | 阿鲁科尔沁旗坤都镇 | 小型铅锌银矿 | 热液脉型 | 矿区分布地层岩石为二叠系钙泥质板岩、花岗闪长岩、红色钾长斑岩、霏细斑岩、石英闪长岩,地表大面积出露花岗闪长岩。沿着侏罗系凝灰岩构造破碎带发生硅化、铅锌银矿化,银可以达到200 g/t,见少量黄铜矿,见有硫化物块状矿石。矿化带内节理面及破碎带附近绿帘石化、绿泥石化、硅化、青磐岩化蚀变强,蚀变岩石分布较多,区域找矿潜力较大 |
| 10 | 敖包吐 | 阿鲁科尔沁旗坤都镇 | 中型铅锌银矿床 | 热液脉型 | 矿体赋存于中侏罗统新民组上段的凝灰质细砂岩、粉砂岩中,黄铜矿化与方铅矿化仅见于燕山期花岗闪长斑岩内及周围的断裂破碎带中,矿体形态简单,以大脉状为主,矿石多为半自形-它形粒状结构,浸染状构造 |
| 11 | 半拉山 | 阿鲁科尔沁旗半拉山村 | 中型钼矿 | 爆破角砾岩型、斑岩型 | 矿床属于爆破角砾岩型钼矿床,侏罗系火山碎屑岩和细晶花岗斑岩的接触带含有爆破角砾岩矿化。成矿细晶花岗斑岩为黄褐色霏细结构,斑状构造,斑晶为石英、长石。矿化角砾岩以震裂角砾岩为主,角砾成分有细晶花岗斑岩角砾及火山碎屑岩角砾,角砾互相镶嵌,大的角砾中发育较多的震裂纹,震裂纹及角砾间为辉钼矿石英脉充填胶结,大型角砾之间被细碎角砾及含辉钼矿的硅化脉充填胶结 |
| 12 | 好力宝 | 阿鲁科尔沁旗东20 km | 中型铜钼矿床 | 斑岩型 | 矿体主要赋存于斜长花岗斑岩中,是海西晚期岩浆活动形成的中高温斑岩型铜钼矿床 |
| 13 | 敖仑花 | 阿鲁科尔沁旗敖仑花 | 中型钼铜矿床 | 斑岩型 | 成矿岩体为灰白色中粒斜长花岗岩,细脉状矿化为主,局部见有浸染状矿化,有平行细脉和不规则网脉,网脉中充填辉钼矿,见有黄铜矿伴生。岩体中混染暗色岩石团块,为部分熔融残余含铁镁质岩石残留体 |
表4 研究区典型矿床矿化特征
Table 4 Mineralization characteristics of typical ore deposits in the study area
| 序号 | 矿床 | 位置 | 规模 | 矿床成因类型 | 矿化特征 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 白音查干 | 西乌珠穆沁旗巴拉嘎尔高勒镇西90 km | 大型锡银锌铅矿 | 爆破角砾岩 夕卡岩型 | 矿床属于爆破角砾岩夕卡岩型矿床,以石英斑岩为核心分为爆破角砾岩带,北部矿化带属于震裂角砾岩矿化带,爆破角砾及震裂角砾之间的空间裂隙是热液充填结晶的有效空间。成矿岩体为石英斑岩,成岩年龄140 Ma左右 |
| 2 | 道伦达坝 | 西乌珠穆沁旗道伦达坝苏木 | 大型铜钨锡矿床 | 岩浆热液脉 型 | 矿体呈脉状产出于上二叠统林西组和华力西期黑云母花岗岩体内的构造破碎带中。矿体多数呈北东走向,倾向南东,倾角10°~60°。其成矿作用与隐伏的早白垩世花岗岩有密切联系,属于与早白垩世花岗岩有关的岩浆热液型矿床 |
| 3 | 花敖包特 | 西乌珠穆沁旗宝日格斯台苏木北东约25 km | 大型银铅锌矿床 | 热液脉型、夕卡岩型 | 矿床矿化主要产在蛇纹岩和泥灰岩之间及闪长玢岩中,蛇纹岩与泥灰岩之间主要为块状闪锌矿矿化,闪锌矿-方铅矿-黄铁矿经常呈现互层条带状分布,属于不同阶段热液结晶的矿物,以闪锌矿条带为主,其次是方铅矿,黄铁矿条带呈薄脉状,一些地段见方铅矿细脉穿切闪锌矿,或呈团块状分布于闪锌矿中。闪长玢岩中以细脉状闪锌矿、方铅矿为主,表层氧化呈黄褐色,新鲜面为灰白色,见星点状黄铁矿。矿床属于蛇纹石夕卡岩矿床,成矿岩体为闪长玢岩,岩体内以浸染状黄铁矿化和脉状方铅矿、闪锌矿为特征 |
| 4 | 双尖山 | 巴林左旗富河镇海力吐村 | 超大型银铅锌矿 | 玢岩型、中低温热液脉 | 矿床矿化主要分布在闪长玢岩岩体中及其边部韧性剪切带中,矿带宽40~50 m,矿石构造主要为细脉状、浸染状,矿带边缘1号富矿脉和2号富矿脉为强破碎糜棱岩带,呈大脉状矿化。矿石矿物主要为闪锌矿、方铅矿、自然银等,在石英方解石细脉中分布,局部集中成大脉,浅部岩石断面方铅矿氧化形成铅黄,呈浅黄色。闪长玢岩中以细脉状闪锌矿为主,表层氧化呈红褐色,新鲜面为黑褐色,见星点状黄铁矿。侏罗系不整合覆盖在二叠系矿化粉砂质板岩上,其间具有薄层风化壳矿化,侏罗系砂岩未见明显矿化。矿床类型为玢岩型银铅锌矿,成矿岩体为闪长玢岩,细脉状、浸染状矿化为主,主矿体边缘强韧性剪切带中有脉状富矿 |
| 5 | 富河东山湾 | 巴林左旗富河镇东山湾村 | 中型钼矿 床 | 云英岩型 | 矿区地层为二叠系泥灰岩、粉砂质板岩,岩体为黄褐色细粒花岗斑岩及霏细斑岩。花岗岩硅化强,硅化花岗岩呈灰白色细粒状致密岩石,硅化蚀变与黄褐色花岗岩呈不规则锯齿状、蚕食状接触。围岩为灰黑色石英细砂岩、粉砂岩,其中未见矿化。辉钼矿产于花岗岩中,新鲜花岗斑岩中有辉钼矿硫化物石英细脉,强硅化花岗斑岩呈灰白色颗粒状,规模较大,矿石的后期石英细脉中有粗晶辉钼矿。矿石品位高,辉钼矿晶片大,矿石中有少量黄铜矿,偶见黑钨矿板状晶体 |
| 6 | 小北沟 | 巴林左旗富河镇小北沟村 | 小型铅锌矿床 | 热液脉型 | 矿区出露侏罗系火山碎屑岩及闪长岩脉,侏罗系角砾状碎屑岩裂隙及构造节理面有铅锌矿化,构造糜棱岩中矿化较好,裂隙中形成闪锌矿脉 |
| 7 | 榆树林 | 巴林左旗三山 乡 | 小型银铜铅锌矿床 | 热液脉型 | 矿体赋存于大石寨组上段变质粉砂岩、粉砂质板岩地层中,受地层内部构造裂隙控制,北西向构造裂隙成矿较好 |
| 8 | 红岭 | 巴林左旗乌兰达坝苏木 | 大型铅锌矿床 | 夕卡岩型 | 矿床产于乌兰坝岩体与二叠系大石寨组接触带上,矿带沿大石寨组大理岩层分布,呈北东方向展布,倾向北西,倾角较陡。矿体呈层状、似层状产出,沿大理岩层分布,夕卡岩化为区内最重要的蚀变类型,该矿床主要工业矿体均产在夕卡岩中 |
| 9 | 哈布特盖 | 阿鲁科尔沁旗坤都镇 | 小型铅锌银矿 | 热液脉型 | 矿区分布地层岩石为二叠系钙泥质板岩、花岗闪长岩、红色钾长斑岩、霏细斑岩、石英闪长岩,地表大面积出露花岗闪长岩。沿着侏罗系凝灰岩构造破碎带发生硅化、铅锌银矿化,银可以达到200 g/t,见少量黄铜矿,见有硫化物块状矿石。矿化带内节理面及破碎带附近绿帘石化、绿泥石化、硅化、青磐岩化蚀变强,蚀变岩石分布较多,区域找矿潜力较大 |
| 10 | 敖包吐 | 阿鲁科尔沁旗坤都镇 | 中型铅锌银矿床 | 热液脉型 | 矿体赋存于中侏罗统新民组上段的凝灰质细砂岩、粉砂岩中,黄铜矿化与方铅矿化仅见于燕山期花岗闪长斑岩内及周围的断裂破碎带中,矿体形态简单,以大脉状为主,矿石多为半自形-它形粒状结构,浸染状构造 |
| 11 | 半拉山 | 阿鲁科尔沁旗半拉山村 | 中型钼矿 | 爆破角砾岩型、斑岩型 | 矿床属于爆破角砾岩型钼矿床,侏罗系火山碎屑岩和细晶花岗斑岩的接触带含有爆破角砾岩矿化。成矿细晶花岗斑岩为黄褐色霏细结构,斑状构造,斑晶为石英、长石。矿化角砾岩以震裂角砾岩为主,角砾成分有细晶花岗斑岩角砾及火山碎屑岩角砾,角砾互相镶嵌,大的角砾中发育较多的震裂纹,震裂纹及角砾间为辉钼矿石英脉充填胶结,大型角砾之间被细碎角砾及含辉钼矿的硅化脉充填胶结 |
| 12 | 好力宝 | 阿鲁科尔沁旗东20 km | 中型铜钼矿床 | 斑岩型 | 矿体主要赋存于斜长花岗斑岩中,是海西晚期岩浆活动形成的中高温斑岩型铜钼矿床 |
| 13 | 敖仑花 | 阿鲁科尔沁旗敖仑花 | 中型钼铜矿床 | 斑岩型 | 成矿岩体为灰白色中粒斜长花岗岩,细脉状矿化为主,局部见有浸染状矿化,有平行细脉和不规则网脉,网脉中充填辉钼矿,见有黄铜矿伴生。岩体中混染暗色岩石团块,为部分熔融残余含铁镁质岩石残留体 |

图6 大兴安岭中段典型有色金属矿床照片 a.拜仁达坝石英闪长岩中浸染状矿化;b.银都闪长岩中条带状矿化;c.银都石英闪长岩中裂隙充填铁闪锌矿细脉;d.拜仁达坝石英闪长岩中石英闪锌矿团块;e.银都闪锌矿脉体及边缘闪锌矿细脉;f.银都闪锌矿胶结石英闪长岩角砾;g.银都石英闪长岩中裂隙充填型闪锌矿细脉;h.拜仁达坝石英闪长岩中闪锌矿及石英闪锌矿细脉;i.银都后期石英胶结早期闪锌矿角砾;j.条带状闪锌矿分布在石英脉边缘;k.闪锌矿磁黄铁矿胶结闪长岩角砾;l.边家大院方铅矿脉与石英脉交切;m.白音诺尔夕卡岩与大理岩规则接触;n.敖仑花斑岩铜钼矿细脉浸染状构造;o.半拉山爆破角砾岩型矿石。
Fig.6 Photographs of typical nonferrous metal deposits in the central Great Xing’an Range
| 矿区 | 样号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拜仁达坝 | BR-12 | 硅质闪长岩 | 59.23 | 0.35 | 11.25 | 3.89 | 10.13 | 0.062 | 1.35 | 2.00 | 0.081 | 3.52 | 0.16 | ||||||||||
| BR-20 | 55.78 | 0.32 | 9.29 | 1.35 | 14.64 | 0.055 | 0.93 | 1.48 | 0.062 | 2.84 | 0.11 | ||||||||||||
| BR-22 | 辉石闪长岩 | 28.09 | 0.13 | 4.42 | 0.80 | 31.17 | 0.08 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.066 | 1.41 | 0.04 | |||||||||||
| BR-24 | 硅质闪长岩 | 62.53 | 0.12 | 7.69 | 1.45 | 11.11 | 0.059 | 0.64 | 0.23 | 0.035 | 2.57 | 0.075 | |||||||||||
| 银都 | YD-03 | 辉石闪长岩 | 32.37 | 0.13 | 3.87 | 12.22 | 3.23 | 1.18 | 0.75 | 2.87 | 0.033 | 0.96 | 1.35 | ||||||||||
| YD-05 | 44.31 | 0.36 | 6.79 | 1.66 | 32.06 | 0.11 | 1.32 | 1.21 | 0.023 | 1.63 | 0.048 | ||||||||||||
| 边家大院 | BJ-05 | 硅质闪长岩 | 59.26 | 0.42 | 10.15 | 5.85 | 1.95 | 0.35 | 0.99 | 1.85 | 0.034 | 3.00 | 0.110 | ||||||||||
| BJ-06 | 48.25 | 0.37 | 8.41 | 10.22 | 1.08 | 0.18 | 1.14 | 0.66 | 0.034 | 2.02 | 0.083 | ||||||||||||
| BJ-09 | 61.42 | 0.29 | 6.9 | 1.45 | 7.05 | 0.16 | 0.94 | 0.67 | 0.09 | 1.45 | 0.071 | ||||||||||||
| 白音诺尔 | BY-07 | 辉石闪长岩 | 41.09 | 0.016 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 7.92 | 0.57 | 0.11 | 2.36 | 0.011 | 0.02 | 0.049 | ||||||||||
| BY-08 | 4.11 | 0.043 | 0.8 | 6.94 | 8.73 | 2.14 | 0.59 | 10.54 | 0.11 | 0.073 | 0.14 | ||||||||||||
| BY-09 | 37.65 | 0.031 | 1.8 | 0.92 | 7.87 | 2.09 | 0.76 | 20.35 | 0.07 | 0.034 | 0.074 | ||||||||||||
| BY-10 | 38.89 | 0.01 | 0.28 | 11.19 | 5.10 | 2.92 | 0.63 | 6.01 | 0.033 | 0.009 | 0.087 | ||||||||||||
| BY-11 | 45.1 | 0.01 | 0.29 | 0.99 | 18.26 | 3.93 | 0.64 | 4.96 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.07 | ||||||||||||
| BY-12 | 42.29 | 0.05 | 0.99 | 3.73 | 14.16 | 3.03 | 0.93 | 3.45 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.15 | ||||||||||||
| BY-13 | 31.51 | 0.015 | 0.39 | 0.62 | 18.78 | 2.93 | 0.7 | 8.00 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.10 | ||||||||||||
| BY-15 | 36.34 | 0.06 | 1.10 | 0.50 | 16.38 | 2.18 | 0.44 | 5.35 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.059 | ||||||||||||
| BY-16 | 33.23 | 0.02 | 0.55 | 0.66 | 13.3 | 2.64 | 0.45 | 14.24 | 0.02 | 0.004 | 0.087 | ||||||||||||
| 矿区 | 样号 | 岩性 | 烧失量 | 总量 | TFeO | Zn | Pb | Ag | Cu | Zn/Pb | Na2O+K2O | K2O/Na2O | A/CNK | ||||||||||
| 拜仁达坝 | BR-12 | 硅质闪长岩 | 0.51 | 92.53 | 13.63 | 3.15 | 0.033 | 9.39 | 774.7 | 94.51 | 3.61 | 43.25 | 1.48 | ||||||||||
| BR-20 | 0.44 | 87.29 | 15.85 | 4.82 | 0.043 | 3.73 | 1 785.0 | 111.80 | 2.90 | 45.63 | 1.58 | ||||||||||||
| BR-22 | 辉石闪长岩 | 0.57 | 67.43 | 31.89 | 20.89 | 0.28 | 7.88 | 5 077.0 | 75.88 | 1.47 | 21.37 | 2.02 | |||||||||||
| BR-24 | 硅质闪长岩 | 0.59 | 87.08 | 12.41 | 6.76 | 0.0088 | 12.98 | 934.2 | 768.02 | 2.60 | 73.75 | 2.36 | |||||||||||
| 银都 | YD-03 | 辉石闪长岩 | 1.59 | 60.56 | 14.23 | 20.23 | 0.26 | 3.62 | 1 410 | 76.66 | 0.99 | 28.64 | 0.61 | ||||||||||
| YD-05 | 0.50 | 90.02 | 33.56 | 0.90 | 1.55 | 6.26 | 2 102 | 0.58 | 1.65 | 71.52 | 1.70 | ||||||||||||
| 边家大院 | BJ-05 | 硅质闪长岩 | 0.52 | 84.47 | 7.21 | 6.17 | 0.82 | 5.17 | 303.4 | 7.51 | 3.04 | 88.04 | 1.52 | ||||||||||
| BJ-06 | 0.63 | 73.07 | 10.28 | 19.29 | 0.95 | 4.08 | 629.6 | 20.40 | 2.06 | 58.81 | 2.44 | ||||||||||||
| BJ-09 | 0.66 | 81.15 | 8.36 | 13.53 | 0.35 | 20.78 | 239.4 | 39.01 | 1.54 | 16.12 | 2.34 | ||||||||||||
| 白音诺尔 | BY-07 | 辉石闪长岩 | 0.51 | 53.16 | 7.99 | 37.44 | 6.84 | 224.00 | 136.20 | 5.47 | 0.03 | 1.86 | 0.10 | ||||||||||
| BY-08 | 4.28 | 38.49 | 14.98 | 8.10 | 8.75 | 79.89 | 132.70 | 0.93 | 0.18 | 0.69 | 0.04 | ||||||||||||
| BY-09 | 11.46 | 83.09 | 8.70 | 0.43 | 8.37 | 97.56 | 3.64 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.48 | 0.05 | ||||||||||||
| BY-10 | 0.24 | 65.40 | 15.17 | 9.50 | 6.54 | 58.10 | 19.68 | 1.45 | 0.04 | 0.27 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||
| BY-11 | 0.25 | 74.60 | 19.15 | 6.01 | 0.054 | 2.95 | 9.56 | 110.56 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||
| BY-12 | 0.31 | 69.19 | 17.52 | 10.80 | 0.26 | 21.10 | 1 193.00 | 42.09 | 0.09 | 0.57 | 0.15 | ||||||||||||
| BY-13 | 0.25 | 63.35 | 19.34 | 8.75 | 0.069 | 9.84 | 16.79 | 126.94 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||
| BY-15 | 0.59 | 63.06 | 16.83 | 17.68 | 3.48 | 40.9 | 118.00 | 5.08 | 0.07 | 0.44 | 0.11 | ||||||||||||
| BY-16 | 5.23 | 70.42 | 13.89 | 9.25 | 8.12 | 125.00 | 66.84 | 1.14 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||
表5 大兴安岭中段典型矿床矿石化学分析表(wB/%)
Table 5 Whole-rock geochemical compositions of the ores from typical deposits in the central Great Xing’an Range(%)
| 矿区 | 样号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拜仁达坝 | BR-12 | 硅质闪长岩 | 59.23 | 0.35 | 11.25 | 3.89 | 10.13 | 0.062 | 1.35 | 2.00 | 0.081 | 3.52 | 0.16 | ||||||||||
| BR-20 | 55.78 | 0.32 | 9.29 | 1.35 | 14.64 | 0.055 | 0.93 | 1.48 | 0.062 | 2.84 | 0.11 | ||||||||||||
| BR-22 | 辉石闪长岩 | 28.09 | 0.13 | 4.42 | 0.80 | 31.17 | 0.08 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.066 | 1.41 | 0.04 | |||||||||||
| BR-24 | 硅质闪长岩 | 62.53 | 0.12 | 7.69 | 1.45 | 11.11 | 0.059 | 0.64 | 0.23 | 0.035 | 2.57 | 0.075 | |||||||||||
| 银都 | YD-03 | 辉石闪长岩 | 32.37 | 0.13 | 3.87 | 12.22 | 3.23 | 1.18 | 0.75 | 2.87 | 0.033 | 0.96 | 1.35 | ||||||||||
| YD-05 | 44.31 | 0.36 | 6.79 | 1.66 | 32.06 | 0.11 | 1.32 | 1.21 | 0.023 | 1.63 | 0.048 | ||||||||||||
| 边家大院 | BJ-05 | 硅质闪长岩 | 59.26 | 0.42 | 10.15 | 5.85 | 1.95 | 0.35 | 0.99 | 1.85 | 0.034 | 3.00 | 0.110 | ||||||||||
| BJ-06 | 48.25 | 0.37 | 8.41 | 10.22 | 1.08 | 0.18 | 1.14 | 0.66 | 0.034 | 2.02 | 0.083 | ||||||||||||
| BJ-09 | 61.42 | 0.29 | 6.9 | 1.45 | 7.05 | 0.16 | 0.94 | 0.67 | 0.09 | 1.45 | 0.071 | ||||||||||||
| 白音诺尔 | BY-07 | 辉石闪长岩 | 41.09 | 0.016 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 7.92 | 0.57 | 0.11 | 2.36 | 0.011 | 0.02 | 0.049 | ||||||||||
| BY-08 | 4.11 | 0.043 | 0.8 | 6.94 | 8.73 | 2.14 | 0.59 | 10.54 | 0.11 | 0.073 | 0.14 | ||||||||||||
| BY-09 | 37.65 | 0.031 | 1.8 | 0.92 | 7.87 | 2.09 | 0.76 | 20.35 | 0.07 | 0.034 | 0.074 | ||||||||||||
| BY-10 | 38.89 | 0.01 | 0.28 | 11.19 | 5.10 | 2.92 | 0.63 | 6.01 | 0.033 | 0.009 | 0.087 | ||||||||||||
| BY-11 | 45.1 | 0.01 | 0.29 | 0.99 | 18.26 | 3.93 | 0.64 | 4.96 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.07 | ||||||||||||
| BY-12 | 42.29 | 0.05 | 0.99 | 3.73 | 14.16 | 3.03 | 0.93 | 3.45 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.15 | ||||||||||||
| BY-13 | 31.51 | 0.015 | 0.39 | 0.62 | 18.78 | 2.93 | 0.7 | 8.00 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.10 | ||||||||||||
| BY-15 | 36.34 | 0.06 | 1.10 | 0.50 | 16.38 | 2.18 | 0.44 | 5.35 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.059 | ||||||||||||
| BY-16 | 33.23 | 0.02 | 0.55 | 0.66 | 13.3 | 2.64 | 0.45 | 14.24 | 0.02 | 0.004 | 0.087 | ||||||||||||
| 矿区 | 样号 | 岩性 | 烧失量 | 总量 | TFeO | Zn | Pb | Ag | Cu | Zn/Pb | Na2O+K2O | K2O/Na2O | A/CNK | ||||||||||
| 拜仁达坝 | BR-12 | 硅质闪长岩 | 0.51 | 92.53 | 13.63 | 3.15 | 0.033 | 9.39 | 774.7 | 94.51 | 3.61 | 43.25 | 1.48 | ||||||||||
| BR-20 | 0.44 | 87.29 | 15.85 | 4.82 | 0.043 | 3.73 | 1 785.0 | 111.80 | 2.90 | 45.63 | 1.58 | ||||||||||||
| BR-22 | 辉石闪长岩 | 0.57 | 67.43 | 31.89 | 20.89 | 0.28 | 7.88 | 5 077.0 | 75.88 | 1.47 | 21.37 | 2.02 | |||||||||||
| BR-24 | 硅质闪长岩 | 0.59 | 87.08 | 12.41 | 6.76 | 0.0088 | 12.98 | 934.2 | 768.02 | 2.60 | 73.75 | 2.36 | |||||||||||
| 银都 | YD-03 | 辉石闪长岩 | 1.59 | 60.56 | 14.23 | 20.23 | 0.26 | 3.62 | 1 410 | 76.66 | 0.99 | 28.64 | 0.61 | ||||||||||
| YD-05 | 0.50 | 90.02 | 33.56 | 0.90 | 1.55 | 6.26 | 2 102 | 0.58 | 1.65 | 71.52 | 1.70 | ||||||||||||
| 边家大院 | BJ-05 | 硅质闪长岩 | 0.52 | 84.47 | 7.21 | 6.17 | 0.82 | 5.17 | 303.4 | 7.51 | 3.04 | 88.04 | 1.52 | ||||||||||
| BJ-06 | 0.63 | 73.07 | 10.28 | 19.29 | 0.95 | 4.08 | 629.6 | 20.40 | 2.06 | 58.81 | 2.44 | ||||||||||||
| BJ-09 | 0.66 | 81.15 | 8.36 | 13.53 | 0.35 | 20.78 | 239.4 | 39.01 | 1.54 | 16.12 | 2.34 | ||||||||||||
| 白音诺尔 | BY-07 | 辉石闪长岩 | 0.51 | 53.16 | 7.99 | 37.44 | 6.84 | 224.00 | 136.20 | 5.47 | 0.03 | 1.86 | 0.10 | ||||||||||
| BY-08 | 4.28 | 38.49 | 14.98 | 8.10 | 8.75 | 79.89 | 132.70 | 0.93 | 0.18 | 0.69 | 0.04 | ||||||||||||
| BY-09 | 11.46 | 83.09 | 8.70 | 0.43 | 8.37 | 97.56 | 3.64 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.48 | 0.05 | ||||||||||||
| BY-10 | 0.24 | 65.40 | 15.17 | 9.50 | 6.54 | 58.10 | 19.68 | 1.45 | 0.04 | 0.27 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||
| BY-11 | 0.25 | 74.60 | 19.15 | 6.01 | 0.054 | 2.95 | 9.56 | 110.56 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||
| BY-12 | 0.31 | 69.19 | 17.52 | 10.80 | 0.26 | 21.10 | 1 193.00 | 42.09 | 0.09 | 0.57 | 0.15 | ||||||||||||
| BY-13 | 0.25 | 63.35 | 19.34 | 8.75 | 0.069 | 9.84 | 16.79 | 126.94 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||
| BY-15 | 0.59 | 63.06 | 16.83 | 17.68 | 3.48 | 40.9 | 118.00 | 5.08 | 0.07 | 0.44 | 0.11 | ||||||||||||
| BY-16 | 5.23 | 70.42 | 13.89 | 9.25 | 8.12 | 125.00 | 66.84 | 1.14 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||
| 矿区 | 样号 | 岩性 | Rb | Sr | Ba | Zr | Hf | Th | U | Y | Nb | Ta | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拜仁达坝 | BR-12 | 硅质闪长岩 | 339.06 | 39.12 | 483.56 | 133.62 | 1.72 | 14.83 | 3.12 | 20.09 | 12.31 | 0.61 | |
| BR-20 | 300.98 | 65.44 | 258.82 | 123.18 | 1.43 | 10.62 | 1.31 | 11.14 | 10.25 | 0.56 | |||
| BR-22 | 辉石闪长岩 | 130.32 | 6.25 | 155.66 | 57.66 | 0.10 | 4.02 | 0.35 | 4.04 | 8.47 | 0.10 | ||
| BR-24 | 硅质闪长岩 | 251.04 | 62.31 | 215.13 | 133.18 | 2.04 | 14.86 | 1.98 | 12.02 | 10.53 | 0.25 | ||
| 银都 | YD-03 | 辉石闪长岩 | 117.10 | 515.56 | 142.06 | 58.37 | 0.22 | 2.84 | 0.59 | 5.88 | 1.76 | 0.22 | |
| YD-05 | 118.44 | 6.81 | 104.52 | 124.82 | 1.36 | 12.28 | 1.14 | 18.67 | 12.18 | 0.64 | |||
| 边家大院 | BJ-05 | 硅质闪长岩 | 459.28 | 34.95 | 123.23 | 204.95 | 6.28 | 8.10 | 1.80 | 20.34 | 11.47 | 0.68 | |
| BJ-06 | 261.44 | 10.97 | 102.70 | 100.20 | 6.20 | 5.33 | 1.37 | 11.05 | 8.36 | 0.42 | |||
| BJ-09 | 168.45 | 18.18 | 96.37 | 84.67 | 4.02 | 3.75 | 0.82 | 8.13 | 6.39 | 0.28 | |||
| 白音诺尔 | BY-07 | 辉石闪长岩 | 445.45 | 6.10 | 21.53 | 627.49 | 0.1 | 0.39 | 0.07 | 2.77 | 4.84 | 0.32 | |
| BY-08 | 129.66 | 16.60 | 32.62 | 193.57 | 0.35 | 0.65 | 0.26 | 5.26 | 2.66 | 0.11 | |||
| BY-09 | 126.95 | 65.27 | 26.00 | 175.53 | 0.2 | 0.19 | 0.29 | 3.92 | 2.07 | 0.37 | |||
| BY-10 | 74.10 | 3.00 | 12.60 | 118.63 | 0.24 | 0.56 | 0.43 | 2.91 | 2.55 | 0.65 | |||
| BY-11 | 1.05 | 5.90 | 4.72 | 10.96 | 0.33 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 4.13 | 2.08 | 0.12 | |||
| BY-12 | 7.84 | 10.52 | 23.70 | 26.34 | 0.27 | 0.37 | 0.15 | 3.87 | 2.34 | 0.26 | |||
| BY-13 | 1.17 | 5.97 | 15.02 | 12.91 | 0.22 | 0.13 | 0.36 | 4.82 | 1.78 | 0.34 | |||
| BY-15 | 45.40 | 12.82 | 19.38 | 85.41 | 0.31 | 0.54 | 0.11 | 5.73 | 3.45 | 0.33 | |||
| BY-16 | 106.90 | 27.64 | 16.69 | 165.12 | 0.06 | 0.27 | 0.16 | 8.56 | 3.12 | 0.45 | |||
| 矿区 | 样号 | 岩性 | Cr | Ni | Ca | V | Rb/Sr | Sr/Ba | Th/U | V/Cr | Zr/Y | Nb/Ta | |
| 拜仁达坝 | BR-12 | 硅质闪长岩 | 41.27 | 45.88 | 9.21 | 55.6 | 8.67 | 0.08 | 4.76 | 1.35 | 6.65 | 20.03 | |
| BR-20 | 32.47 | 42.56 | 6.91 | 54.48 | 4.60 | 0.25 | 8.12 | 1.68 | 11.06 | 18.46 | |||
| BR-22 | 辉石闪长岩 | 11.93 | 54.17 | 2.43 | 22.79 | 20.83 | 0.04 | 11.42 | 1.91 | 14.27 | 81.11 | ||
| BR-24 | 硅质闪长岩 | 24.14 | 18.2 | 1.79 | 38.25 | 4.03 | 0.29 | 7.49 | 1.58 | 11.08 | 41.51 | ||
| 银都 | YD-03 | 辉石闪长岩 | 41.00 | 55.43 | 4.72 | 37.12 | 0.23 | 3.63 | 4.82 | 0.91 | 9.93 | 7.84 | |
| YD-05 | 19.93 | 50.42 | 17.67 | 33.37 | 17.38 | 0.07 | 10.78 | 1.67 | 6.69 | 18.89 | |||
| 边家大院 | BJ-05 | 硅质闪长岩 | 35.33 | 33.95 | 13.37 | 40.87 | 13.14 | 0.28 | 4.50 | 1.16 | 10.07 | 16.90 | |
| BJ-06 | 34.67 | 106.71 | 59.52 | 54.18 | 23.83 | 0.11 | 3.89 | 1.56 | 9.07 | 20.04 | |||
| BJ-09 | 38.59 | 80.71 | 51.23 | 45.94 | 9.27 | 0.19 | 4.57 | 1.19 | 10.42 | 22.90 | |||
| 白音诺尔 | BY-07 | 辉石闪长岩 | 0.65 | 323.37 | 13.31 | 33.29 | 73.03 | 0.28 | 5.80 | 51.05 | 226.76 | 14.93 | |
| BY-08 | 1.02 | 64.40 | 19.14 | 21.65 | 7.81 | 0.51 | 2.50 | 21.16 | 36.81 | 23.77 | |||
| BY-09 | 1.11 | 36.69 | 14.21 | 22.86 | 1.94 | 2.51 | 0.65 | 20.55 | 44.80 | 5.67 | |||
| BY-10 | 0.88 | 41.61 | 20.99 | 18.98 | 24.66 | 0.24 | 1.32 | 21.69 | 40.79 | 3.91 | |||
| BY-11 | 0.68 | 12.53 | 23.59 | 8.03 | 0.18 | 1.25 | 0.54 | 11.82 | 2.65 | 18.06 | |||
| BY-12 | 10.2 | 29.19 | 31.89 | 15.80 | 0.75 | 0.44 | 2.40 | 1.55 | 6.81 | 9.05 | |||
| BY-13 | 0.81 | 15.68 | 33.56 | 7.75 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.35 | 9.60 | 2.68 | 5.24 | |||
| BY-15 | 0.56 | 49.29 | 37.50 | 15.80 | 3.54 | 0.66 | 5.06 | 28.41 | 14.89 | 10.53 | |||
| BY-16 | 0.62 | 51.10 | 21.97 | 19.50 | 3.87 | 1.66 | 1.69 | 31.26 | 19.30 | 6.91 | |||
表6 大兴安岭中段典型矿床矿石微量元素成分(wB/10-6)
Table 6 Trace element contents of the ores from typical deposits in the central Great Xing’an Range(10-6)
| 矿区 | 样号 | 岩性 | Rb | Sr | Ba | Zr | Hf | Th | U | Y | Nb | Ta | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拜仁达坝 | BR-12 | 硅质闪长岩 | 339.06 | 39.12 | 483.56 | 133.62 | 1.72 | 14.83 | 3.12 | 20.09 | 12.31 | 0.61 | |
| BR-20 | 300.98 | 65.44 | 258.82 | 123.18 | 1.43 | 10.62 | 1.31 | 11.14 | 10.25 | 0.56 | |||
| BR-22 | 辉石闪长岩 | 130.32 | 6.25 | 155.66 | 57.66 | 0.10 | 4.02 | 0.35 | 4.04 | 8.47 | 0.10 | ||
| BR-24 | 硅质闪长岩 | 251.04 | 62.31 | 215.13 | 133.18 | 2.04 | 14.86 | 1.98 | 12.02 | 10.53 | 0.25 | ||
| 银都 | YD-03 | 辉石闪长岩 | 117.10 | 515.56 | 142.06 | 58.37 | 0.22 | 2.84 | 0.59 | 5.88 | 1.76 | 0.22 | |
| YD-05 | 118.44 | 6.81 | 104.52 | 124.82 | 1.36 | 12.28 | 1.14 | 18.67 | 12.18 | 0.64 | |||
| 边家大院 | BJ-05 | 硅质闪长岩 | 459.28 | 34.95 | 123.23 | 204.95 | 6.28 | 8.10 | 1.80 | 20.34 | 11.47 | 0.68 | |
| BJ-06 | 261.44 | 10.97 | 102.70 | 100.20 | 6.20 | 5.33 | 1.37 | 11.05 | 8.36 | 0.42 | |||
| BJ-09 | 168.45 | 18.18 | 96.37 | 84.67 | 4.02 | 3.75 | 0.82 | 8.13 | 6.39 | 0.28 | |||
| 白音诺尔 | BY-07 | 辉石闪长岩 | 445.45 | 6.10 | 21.53 | 627.49 | 0.1 | 0.39 | 0.07 | 2.77 | 4.84 | 0.32 | |
| BY-08 | 129.66 | 16.60 | 32.62 | 193.57 | 0.35 | 0.65 | 0.26 | 5.26 | 2.66 | 0.11 | |||
| BY-09 | 126.95 | 65.27 | 26.00 | 175.53 | 0.2 | 0.19 | 0.29 | 3.92 | 2.07 | 0.37 | |||
| BY-10 | 74.10 | 3.00 | 12.60 | 118.63 | 0.24 | 0.56 | 0.43 | 2.91 | 2.55 | 0.65 | |||
| BY-11 | 1.05 | 5.90 | 4.72 | 10.96 | 0.33 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 4.13 | 2.08 | 0.12 | |||
| BY-12 | 7.84 | 10.52 | 23.70 | 26.34 | 0.27 | 0.37 | 0.15 | 3.87 | 2.34 | 0.26 | |||
| BY-13 | 1.17 | 5.97 | 15.02 | 12.91 | 0.22 | 0.13 | 0.36 | 4.82 | 1.78 | 0.34 | |||
| BY-15 | 45.40 | 12.82 | 19.38 | 85.41 | 0.31 | 0.54 | 0.11 | 5.73 | 3.45 | 0.33 | |||
| BY-16 | 106.90 | 27.64 | 16.69 | 165.12 | 0.06 | 0.27 | 0.16 | 8.56 | 3.12 | 0.45 | |||
| 矿区 | 样号 | 岩性 | Cr | Ni | Ca | V | Rb/Sr | Sr/Ba | Th/U | V/Cr | Zr/Y | Nb/Ta | |
| 拜仁达坝 | BR-12 | 硅质闪长岩 | 41.27 | 45.88 | 9.21 | 55.6 | 8.67 | 0.08 | 4.76 | 1.35 | 6.65 | 20.03 | |
| BR-20 | 32.47 | 42.56 | 6.91 | 54.48 | 4.60 | 0.25 | 8.12 | 1.68 | 11.06 | 18.46 | |||
| BR-22 | 辉石闪长岩 | 11.93 | 54.17 | 2.43 | 22.79 | 20.83 | 0.04 | 11.42 | 1.91 | 14.27 | 81.11 | ||
| BR-24 | 硅质闪长岩 | 24.14 | 18.2 | 1.79 | 38.25 | 4.03 | 0.29 | 7.49 | 1.58 | 11.08 | 41.51 | ||
| 银都 | YD-03 | 辉石闪长岩 | 41.00 | 55.43 | 4.72 | 37.12 | 0.23 | 3.63 | 4.82 | 0.91 | 9.93 | 7.84 | |
| YD-05 | 19.93 | 50.42 | 17.67 | 33.37 | 17.38 | 0.07 | 10.78 | 1.67 | 6.69 | 18.89 | |||
| 边家大院 | BJ-05 | 硅质闪长岩 | 35.33 | 33.95 | 13.37 | 40.87 | 13.14 | 0.28 | 4.50 | 1.16 | 10.07 | 16.90 | |
| BJ-06 | 34.67 | 106.71 | 59.52 | 54.18 | 23.83 | 0.11 | 3.89 | 1.56 | 9.07 | 20.04 | |||
| BJ-09 | 38.59 | 80.71 | 51.23 | 45.94 | 9.27 | 0.19 | 4.57 | 1.19 | 10.42 | 22.90 | |||
| 白音诺尔 | BY-07 | 辉石闪长岩 | 0.65 | 323.37 | 13.31 | 33.29 | 73.03 | 0.28 | 5.80 | 51.05 | 226.76 | 14.93 | |
| BY-08 | 1.02 | 64.40 | 19.14 | 21.65 | 7.81 | 0.51 | 2.50 | 21.16 | 36.81 | 23.77 | |||
| BY-09 | 1.11 | 36.69 | 14.21 | 22.86 | 1.94 | 2.51 | 0.65 | 20.55 | 44.80 | 5.67 | |||
| BY-10 | 0.88 | 41.61 | 20.99 | 18.98 | 24.66 | 0.24 | 1.32 | 21.69 | 40.79 | 3.91 | |||
| BY-11 | 0.68 | 12.53 | 23.59 | 8.03 | 0.18 | 1.25 | 0.54 | 11.82 | 2.65 | 18.06 | |||
| BY-12 | 10.2 | 29.19 | 31.89 | 15.80 | 0.75 | 0.44 | 2.40 | 1.55 | 6.81 | 9.05 | |||
| BY-13 | 0.81 | 15.68 | 33.56 | 7.75 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.35 | 9.60 | 2.68 | 5.24 | |||
| BY-15 | 0.56 | 49.29 | 37.50 | 15.80 | 3.54 | 0.66 | 5.06 | 28.41 | 14.89 | 10.53 | |||
| BY-16 | 0.62 | 51.10 | 21.97 | 19.50 | 3.87 | 1.66 | 1.69 | 31.26 | 19.30 | 6.91 | |||
| 矿区 | 样号 | 岩性 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拜仁达坝 | BR-12 | 硅质闪长岩 | 31.04 | 57.14 | 7.00 | 21.70 | 4.75 | 0.92 | 6.59 | 0.80 | 3.75 | ||
| BR-20 | 8.04 | 15.59 | 2.03 | 6.28 | 1.43 | 0.33 | 2.23 | 0.36 | 1.76 | ||||
| BR-22 | 辉石闪长岩 | 11.79 | 25.59 | 3.07 | 9.50 | 2.00 | 0.27 | 2.44 | 0.31 | 0.99 | |||
| BR-24 | 硅质闪长岩 | 5.24 | 10.14 | 1.33 | 4.20 | 1.04 | 0.24 | 1.74 | 0.37 | 2.13 | |||
| 银都 | YD-03 | 辉石闪长岩 | 6.44 | 12.37 | 1.80 | 5.92 | 1.19 | 0.26 | 1.62 | 0.27 | 1.03 | ||
| YD-05 | 35.46 | 67.29 | 8.41 | 26.57 | 5.75 | 1.70 | 7.86 | 0.91 | 3.97 | ||||
| 边家大院 | BJ-05 | 硅质闪长岩 | 26.22 | 48.74 | 6.73 | 20.70 | 4.40 | 0.82 | 5.73 | 0.73 | 3.64 | ||
| BJ-06 | 15.25 | 30.10 | 4.02 | 12.72 | 2.68 | 0.37 | 3.37 | 0.45 | 1.89 | ||||
| BJ-09 | 9.98 | 19.79 | 2.74 | 8.63 | 1.79 | 0.31 | 2.52 | 0.34 | 1.42 | ||||
| 白音诺尔 | BY-07 | 辉石闪长岩 | 0.68 | 1.17 | 0.26 | 1.18 | 0.26 | 0.08 | 0.42 | 0.13 | 0.30 | ||
| BY-08 | 7.75 | 4.40 | 1.46 | 4.85 | 0.98 | 0.11 | 1.33 | 0.20 | 0.62 | ||||
| BY-09 | 1.09 | 1.87 | 0.46 | 2.23 | 0.64 | 0.17 | 0.62 | 0.16 | 0.37 | ||||
| BY-10 | 5.28 | 2.53 | 0.81 | 2.56 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 0.63 | 0.15 | 0.27 | ||||
| BY-11 | 5.30 | 2.62 | 0.81 | 2.50 | 0.37 | 0.05 | 0.66 | 0.16 | 0.31 | ||||
| BY-12 | 5.86 | 3.67 | 0.90 | 2.71 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 0.74 | 0.16 | 0.34 | ||||
| BY-13 | 6.43 | 3.16 | 0.91 | 3.17 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 0.76 | 0.16 | 0.42 | ||||
| BY-15 | 7.78 | 3.88 | 1.31 | 4.31 | 0.80 | 0.09 | 1.22 | 0.20 | 0.54 | ||||
| BY-16 | 6.86 | 4.47 | 1.53 | 5.56 | 1.09 | 0.24 | 1.45 | 0.26 | 0.78 | ||||
| 矿区 | 样号 | 岩性 | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | REE | LREE/HREE | δCe | δEu | ||
| 拜仁达坝 | BR-12 | 硅质闪长岩 | 0.76 | 2.22 | 0.32 | 2.13 | 0.34 | 139.46 | 7.24 | 0.93 | 0.50 | ||
| BR-20 | 0.42 | 1.43 | 0.20 | 1.24 | 0.21 | 41.55 | 4.29 | 0.93 | 0.56 | ||||
| BR-22 | 辉石闪长岩 | 0.19 | 0.70 | 0.07 | 0.4 | 0.06 | 57.35 | 10.14 | 1.02 | 0.37 | |||
| BR-24 | 硅质闪长岩 | 0.45 | 1.51 | 0.22 | 1.26 | 0.21 | 30.09 | 2.81 | 0.92 | 0.54 | |||
| 银都 | YD-03 | 辉石闪长岩 | 0.22 | 0.84 | 0.13 | 0.94 | 0.17 | 33.21 | 5.36 | 0.87 | 0.58 | ||
| YD-05 | 0.76 | 2.21 | 0.32 | 1.88 | 0.28 | 163.36 | 7.98 | 0.94 | 0.77 | ||||
| 边家大院 | BJ-05 | 硅质闪长岩 | 0.75 | 2.33 | 0.35 | 2.29 | 0.37 | 123.83 | 6.64 | 0.88 | 0.50 | ||
| BJ-06 | 0.42 | 1.48 | 0.23 | 1.38 | 0.24 | 74.61 | 6.89 | 0.93 | 0.38 | ||||
| BJ-09 | 0.33 | 1.19 | 0.16 | 1.15 | 0.17 | 50.53 | 5.94 | 0.91 | 0.45 | ||||
| 白音诺尔 | BY-07 | 辉石闪长岩 | 0.07 | 0.46 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 5.22 | 2.31 | 0.67 | 0.75 | ||
| BY-08 | 0.12 | 0.57 | 0.05 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 22.77 | 6.08 | 0.31 | 0.29 | ||||
| BY-09 | 0.09 | 0.55 | 0.04 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 8.63 | 2.96 | 0.64 | 0.82 | ||||
| BY-10 | 0.06 | 0.47 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 13.48 | 6.35 | 0.29 | 0.31 | ||||
| BY-11 | 0.07 | 0.49 | 0.04 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 13.71 | 5.67 | 0.30 | 0.31 | ||||
| BY-12 | 0.08 | 0.51 | 0.04 | 0.32 | 0.06 | 15.94 | 6.10 | 0.39 | 0.38 | ||||
| BY-13 | 0.10 | 0.52 | 0.04 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 16.57 | 6.13 | 0.31 | 0.35 | ||||
| BY-15 | 0.13 | 0.59 | 0.06 | 0.39 | 0.08 | 21.37 | 5.66 | 0.29 | 0.27 | ||||
| BY-16 | 0.16 | 0.79 | 0.06 | 0.39 | 0.06 | 23.68 | 5.01 | 0.33 | 0.58 | ||||
表7 大兴安岭中段典型矿床矿石稀土元素含量(wB/10-6)
Table 7 REE contents of the ores from typical deposits in the central Great Xing’an Range(10-6)
| 矿区 | 样号 | 岩性 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拜仁达坝 | BR-12 | 硅质闪长岩 | 31.04 | 57.14 | 7.00 | 21.70 | 4.75 | 0.92 | 6.59 | 0.80 | 3.75 | ||
| BR-20 | 8.04 | 15.59 | 2.03 | 6.28 | 1.43 | 0.33 | 2.23 | 0.36 | 1.76 | ||||
| BR-22 | 辉石闪长岩 | 11.79 | 25.59 | 3.07 | 9.50 | 2.00 | 0.27 | 2.44 | 0.31 | 0.99 | |||
| BR-24 | 硅质闪长岩 | 5.24 | 10.14 | 1.33 | 4.20 | 1.04 | 0.24 | 1.74 | 0.37 | 2.13 | |||
| 银都 | YD-03 | 辉石闪长岩 | 6.44 | 12.37 | 1.80 | 5.92 | 1.19 | 0.26 | 1.62 | 0.27 | 1.03 | ||
| YD-05 | 35.46 | 67.29 | 8.41 | 26.57 | 5.75 | 1.70 | 7.86 | 0.91 | 3.97 | ||||
| 边家大院 | BJ-05 | 硅质闪长岩 | 26.22 | 48.74 | 6.73 | 20.70 | 4.40 | 0.82 | 5.73 | 0.73 | 3.64 | ||
| BJ-06 | 15.25 | 30.10 | 4.02 | 12.72 | 2.68 | 0.37 | 3.37 | 0.45 | 1.89 | ||||
| BJ-09 | 9.98 | 19.79 | 2.74 | 8.63 | 1.79 | 0.31 | 2.52 | 0.34 | 1.42 | ||||
| 白音诺尔 | BY-07 | 辉石闪长岩 | 0.68 | 1.17 | 0.26 | 1.18 | 0.26 | 0.08 | 0.42 | 0.13 | 0.30 | ||
| BY-08 | 7.75 | 4.40 | 1.46 | 4.85 | 0.98 | 0.11 | 1.33 | 0.20 | 0.62 | ||||
| BY-09 | 1.09 | 1.87 | 0.46 | 2.23 | 0.64 | 0.17 | 0.62 | 0.16 | 0.37 | ||||
| BY-10 | 5.28 | 2.53 | 0.81 | 2.56 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 0.63 | 0.15 | 0.27 | ||||
| BY-11 | 5.30 | 2.62 | 0.81 | 2.50 | 0.37 | 0.05 | 0.66 | 0.16 | 0.31 | ||||
| BY-12 | 5.86 | 3.67 | 0.90 | 2.71 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 0.74 | 0.16 | 0.34 | ||||
| BY-13 | 6.43 | 3.16 | 0.91 | 3.17 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 0.76 | 0.16 | 0.42 | ||||
| BY-15 | 7.78 | 3.88 | 1.31 | 4.31 | 0.80 | 0.09 | 1.22 | 0.20 | 0.54 | ||||
| BY-16 | 6.86 | 4.47 | 1.53 | 5.56 | 1.09 | 0.24 | 1.45 | 0.26 | 0.78 | ||||
| 矿区 | 样号 | 岩性 | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | REE | LREE/HREE | δCe | δEu | ||
| 拜仁达坝 | BR-12 | 硅质闪长岩 | 0.76 | 2.22 | 0.32 | 2.13 | 0.34 | 139.46 | 7.24 | 0.93 | 0.50 | ||
| BR-20 | 0.42 | 1.43 | 0.20 | 1.24 | 0.21 | 41.55 | 4.29 | 0.93 | 0.56 | ||||
| BR-22 | 辉石闪长岩 | 0.19 | 0.70 | 0.07 | 0.4 | 0.06 | 57.35 | 10.14 | 1.02 | 0.37 | |||
| BR-24 | 硅质闪长岩 | 0.45 | 1.51 | 0.22 | 1.26 | 0.21 | 30.09 | 2.81 | 0.92 | 0.54 | |||
| 银都 | YD-03 | 辉石闪长岩 | 0.22 | 0.84 | 0.13 | 0.94 | 0.17 | 33.21 | 5.36 | 0.87 | 0.58 | ||
| YD-05 | 0.76 | 2.21 | 0.32 | 1.88 | 0.28 | 163.36 | 7.98 | 0.94 | 0.77 | ||||
| 边家大院 | BJ-05 | 硅质闪长岩 | 0.75 | 2.33 | 0.35 | 2.29 | 0.37 | 123.83 | 6.64 | 0.88 | 0.50 | ||
| BJ-06 | 0.42 | 1.48 | 0.23 | 1.38 | 0.24 | 74.61 | 6.89 | 0.93 | 0.38 | ||||
| BJ-09 | 0.33 | 1.19 | 0.16 | 1.15 | 0.17 | 50.53 | 5.94 | 0.91 | 0.45 | ||||
| 白音诺尔 | BY-07 | 辉石闪长岩 | 0.07 | 0.46 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 5.22 | 2.31 | 0.67 | 0.75 | ||
| BY-08 | 0.12 | 0.57 | 0.05 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 22.77 | 6.08 | 0.31 | 0.29 | ||||
| BY-09 | 0.09 | 0.55 | 0.04 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 8.63 | 2.96 | 0.64 | 0.82 | ||||
| BY-10 | 0.06 | 0.47 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 13.48 | 6.35 | 0.29 | 0.31 | ||||
| BY-11 | 0.07 | 0.49 | 0.04 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 13.71 | 5.67 | 0.30 | 0.31 | ||||
| BY-12 | 0.08 | 0.51 | 0.04 | 0.32 | 0.06 | 15.94 | 6.10 | 0.39 | 0.38 | ||||
| BY-13 | 0.10 | 0.52 | 0.04 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 16.57 | 6.13 | 0.31 | 0.35 | ||||
| BY-15 | 0.13 | 0.59 | 0.06 | 0.39 | 0.08 | 21.37 | 5.66 | 0.29 | 0.27 | ||||
| BY-16 | 0.16 | 0.79 | 0.06 | 0.39 | 0.06 | 23.68 | 5.01 | 0.33 | 0.58 | ||||
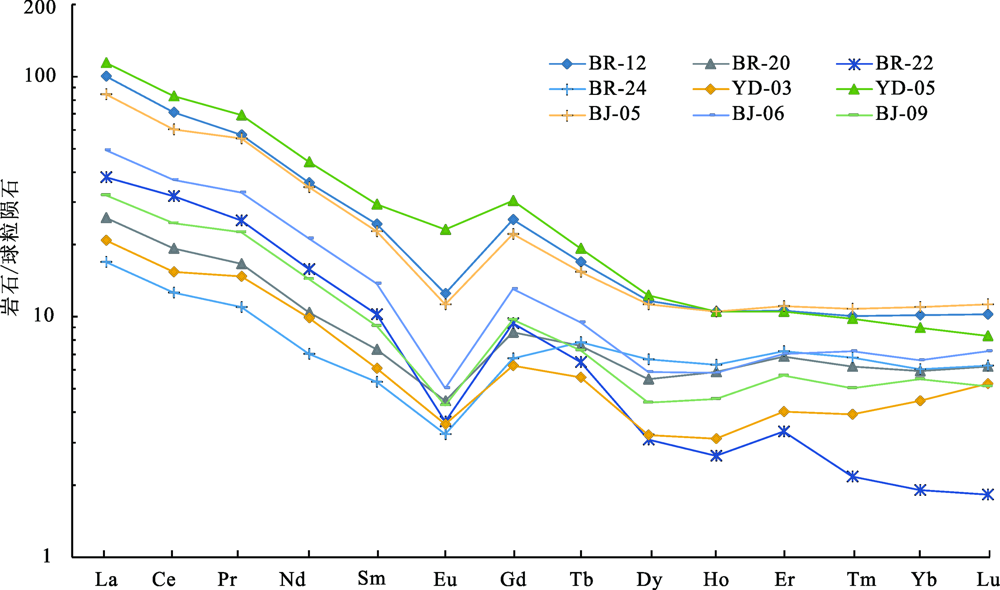
图7 拜仁达坝矿区矿石稀土配分曲线(球粒陨石标准数据Belousova等[42],2002)
Fig.7 REE distribution curves of ores in Bairendaba mining area (chondrite normalizing values after Belousova et al. [42],2002)
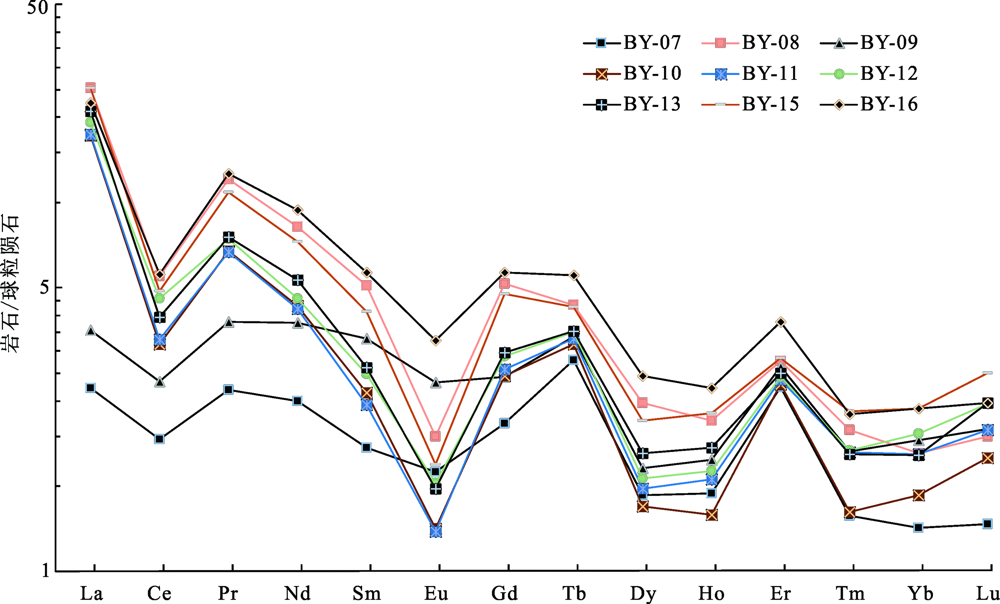
图8 白音诺尔矿床矿石稀土配分曲线(球粒陨石标准数据Belousova等[42],2002)
Fig.8 REE distribution curves of ores in Baiyinnuo’er deposit (chondrite normalizing values after Belousova et al. [42],2002)
| [1] | 何鹏, 郭硕, 张天福, 等. 大兴安岭中南段扎木钦铅锌银多金属矿床成矿物质来源及矿床成因:来自S、Pb同位素的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(12):3597-3610. |
| [2] | 沈存利, 杨发亭, 王金娃, 等. 内蒙古大兴安岭地区银铅锌多金属矿找矿新进展及勘查前景分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2019, 55(4):899-912. |
| [3] | 王莹, 谢玉玲, 陈伟, 等. 内蒙古拜仁达坝银多金属矿床成矿机理研究[J]. 合肥工业大学学报, 2019, 42(3):315-320. |
| [4] | 武广, 刘瑞麟, 陈公正, 等. 内蒙古维拉斯托稀有金属-锡多金属矿床的成矿作用:来自花岗质岩浆结晶分异的启示[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(3):637-664. |
| [5] | 陈永清, 周顶, 郭令芬. 内蒙古花敖包特铅锌银多金属矿床成因探讨:流体包裹体及硫、铅、氢、氧同位素证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(5):1478-1491. |
| [6] | 王喜龙, 刘家军, 翟德高, 等. 内蒙古林西边家大院银多金属矿床同位素地球化学特征及成矿物质来源探讨[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(4):1288-1303. |
| [7] | 王喜龙, 刘家军, 翟德高, 等. 内蒙古边家大院铅锌银多金属矿床的矿物组成及其成因意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(1):73-86. |
| [8] | 王喜龙, 刘家军, 翟德高, 等. 内蒙古边家大院矿区石英斑岩U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2014, 33(5):654-665. |
| [9] | 王喜龙, 刘家军, 翟德高, 等. 内蒙古边家大院铅锌银矿区侵入岩LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2013, 37(4):730-742. |
| [10] | 吴晓琳, 赵骏峰, 刘文元, 等. 内蒙古双尖子山银多金属矿床锡矿化的发现及其意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2021, 40(3):631-635. |
| [11] | 张玉生, 侯涛, 张萌萌, 等. 原生热液新生热液探究——以内蒙古白音查干东山矿区锌多金属矿热液为例[J]. 资源信息与工程, 2018, 33(3):21-23. |
| [12] | 孙爱群, 牛树银, 王宝德, 等. 大兴安岭拜仁达坝银铅锌矿的成矿构造特征[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2010, 32(增刊):71-72,78. |
| [13] | 阮班晓, 吕新彪, 刘申态, 等. 内蒙古边家大院铅锌银矿床成因——来自锆石U-Pb年龄和多元同位素的制约[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(3):501-514. |
| [14] | 翟德高, 刘家军, 李俊明, 等. 内蒙古维拉斯托斑岩型锡矿床成岩、成矿时代及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2016, 35(5):1011-1022. |
| [15] | 任宏, 欧阳荷根. 内蒙古拜仁达坝银多金属矿床二氧化碳不混溶成矿作用研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(2):151-158. |
| [16] | XIAO W J, WINDLEY B F, HAO J, et al. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China: termination of the central Asian orogenic belt[J]. Tecto-nics, 2003, 22:1484-1505. |
| [17] | 要梅娟, 曹烨, 刘家军, 等. 内蒙古黄岗梁铁锡矿床辉钼矿Re-Os年龄及其成因意义[J]. 矿产勘查, 2016, 7(3):399-403. |
| [18] | 要梅娟, 刘家军, 翟德高, 等. 内蒙古道伦达坝铜多金属矿床微量元素地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2013, 35(1):24-33. |
| [19] | 陈贤, 刘家军, 周志广, 等. 内蒙古大石寨地区二叠系碎屑锆石年龄及其构造意义[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(4):1143-1158. |
| [20] | 翟德高, 刘家军, 杨永强, 等. 内蒙古黄岗梁铁锡矿床成岩、成矿时代与构造背景[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 31(4):513-523. |
| [21] |
ZHAI D G, WILLIAMS-JONES A E, LIU J J, et al. The genesis of the giant Shuangjianzishan epithermal Ag-Pb-Zn deposit, Inner Mongolia, northeastern China[J]. Economic Geology, 2020, 115(1):101-128.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHAI D G, LIU J J, ZHANG A L, et al. U-Pb, Re-Os, and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of porphyry Sn±Cu±Mo and polymeta-llic (Ag-Pb-Zn-Cu) vein mineralization at Bianjiadayuan, Inner Mongolia, NE China: Implications for discrete mineralization events[J]. Economic Geology, 2017, 112(8):2041-2059.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHAI D G, LIU J J, COOK N J, et al. Mineralogical, textural, sulfur and lead isotope constraints on the origin of Ag-Pb-Zn mine-ralization at Bianjiadayuan, Inner Mongolia, NE China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2019, 54(1):47-66.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZHAI D G, LIU J J, ZHANG H Y, et al. A magmatic-hydrothermal origin for Ag-Pb-Zn vein formation at the Bianjiadayuan deposit, Inner Mongolia, NE China: Evidences from fluid inclusion, stable (C-H-O) and noble gas isotope studies[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 101:1-16.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZHAI D G, LIU J J, ZHANG H Y, et al. S-Pb isotopic geoche-mistry, U-Pb and Re-Os geochronology of the Huanggangliang Fe-Sn deposit, Inner Mongolia, NE China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 59:109-122.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 欧阳荷根. 大兴安岭南段拜仁达坝—维拉斯托银多金属矿床成矿作用及动力学背景[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013: 1-98. |
| [27] |
LIU Y F, JIANG S H, BAGAS L, et al. The genesis of metal zonation in the Weilasituo and Bairendaba Ag-Zn-Pb-Cu-(Sn-W) deposits in the shallow part of a porphyry Sn-W-Rb system, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 75:150-173.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 石玉若, 刘敦一, 简平, 等. 内蒙古中部苏尼特左旗富钾花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄[J]. 地质通报, 2005, 24(5):424-428. |
| [29] | 刘建峰, 迟效国, 张兴洲, 等. 内蒙古西乌旗南部石炭纪石英闪长岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(3):365-376. |
| [30] | 鲍庆中, 张长捷, 吴之理, 等. 内蒙古白音高勒地区石炭纪石英闪长岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学及其意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2007(1):15-23. |
| [31] | 施光海, 苗来成, 张福勤, 等. 内蒙古锡林浩特A型花岗岩的时代及区域构造意义[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(4):384-389. |
| [32] | 张玉清. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗巴音乌拉二叠纪埃达克质花岗闪长岩类地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2009, 28(4):329-338. |
| [33] | 陈斌, 赵国春, WILDE S. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗南两类花岗岩同位素年代学及其构造意义[J]. 地质论评, 2001, 47(4):361-367. |
| [34] | 张维, 简平, 刘敦一, 等. 内蒙古中部达茂旗地区三叠纪花岗岩和钾玄岩的地球化学、年代学和Hf同位素特征[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(6):821-832. |
| [35] | 李锦轶, 高立明, 孙桂华, 等. 内蒙古东部双井子中三叠世同碰撞壳源花岗岩的确定及其对西伯利亚与中朝古板块碰撞时限的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(3):565-582. |
| [36] | 内蒙古自治区地质矿产局. 内蒙古自治区区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1991: 1-725. |
| [37] | 张万益, 聂凤军, 刘树文, 等. 大兴安岭南段西坡金属矿床特征及成矿规律[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40(5):1583-1599. |
| [38] | 张万益, 聂凤军, 高延光, 等. 内蒙古查干敖包三叠纪碱性石英闪长岩的地球化学特征及成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(2):525-534. |
| [39] | 赵一鸣, 吴良士. 中国主要金属矿床成矿规律[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004: 123-164. |
| [40] | 解洪晶, 王玉往, 蒋炜, 等. 内蒙古硐子铅锌矿床S、Pb同位素特征及成矿物质来源[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(S1):175-176. |
| [41] | 赵宝具. 一种稀土参数图解新方法:以内蒙古拜仁达坝—维拉斯托闪长岩成因研究为例[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(3):608-624. |
| [42] |
BELOUSOVA E A, GRIFFIN W L, O’REILLY SY, et al. Igneous zircon: trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143:602-622.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 张舒, 张赞赞, 胡召齐, 施立胜, 周涛发, 吴明安, 杜建国. 长江中下游成矿带庐枞矿集区花岗岩型铀矿床成矿作用研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1435-1448. |
| [2] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [3] | 王启博, 张寿庭, 唐利, 李军军, 盛渊明. 豫西杨山萤石矿床成因:萤石稀土元素组成和流体包裹体热力学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1524-1537. |
| [4] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [5] | 杜贯新, 闫百泉, 孙雨, 钱程, 秦涛, 臧延庆. 松嫩平原黑土区西北部阿荣旗地下黑土稀土元素特征及环境指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 813-820. |
| [6] | 曹林杰, 张运周, 李四龙, 王志红, 张瑶, 张寒. 北大巴山平利县大坪—金岭重晶石矿床地球化学特征与成矿物源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1497-1502. |
| [7] | 杜保峰, 张荣臻, 杨长青, 李山坡, 谭和勇, 朱红运. 西藏则不吓铅锌矿床硫、铅同位素组成及对成矿物质来源的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1138-1145. |
| [8] | 刘茂涵, 刘海燕, 张卫民, 王振, 吴通航, 王玉罡. 鄱阳湖流域赣江北支水体和沉积物中稀土元素的含量和分异特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 389-405. |
| [9] | 王艺璇, 周训, 陈梦颖, 马静茹, 海阔, 肖萌, 尚子琦, 张颖, 余鸣潇. 河北北部四处温泉的水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 494-506. |
| [10] | 吴小雷, 常晋阳, 曾南石, 徐文杰, 陶明荣, 赵刚, 韩建. 辽宁红透山铜锌矿床含矿岩系地球化学特征及找矿指示[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 362-377. |
| [11] | 远继东, 姜正龙, 代友旭, 郝连成, 张健康, 张德程, 郑立龙. 湛江湾海域表层沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 77-87. |
| [12] | 程天赦, 杨文静, 张学斌, 吴荣泽, 周长红. 内蒙古乌兰乌台花岗闪长岩U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1231-1239. |
| [13] | 王珍珍, 李进孝, 张珂, 郭文牧, 张绍韡, 肖林. 山西西铭煤矿煤中稀土元素地球化学特征及指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 1009-1017. |
| [14] | 赵保具, 颜开, 肖荣阁. 一种稀土参数图解新方法:以内蒙古拜仁达坝-维拉斯托闪长岩成因研究为例[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 608-624. |
| [15] | 寇少磊, 魏立勇, 张振, 李国英, 郑鑫, 路宗悦, 杨瀚文, 孟五一. 西秦岭中段日多玛岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1245-1260. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||