



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (03): 787-797.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.055
叶枫1,2( ), 董国臣2(
), 董国臣2( ), 任建勋1, 龚杰立3, 李猛兴1, 王权1, 张兆琪1, 赵三波1
), 任建勋1, 龚杰立3, 李猛兴1, 王权1, 张兆琪1, 赵三波1
收稿日期:2020-04-15
修回日期:2020-07-17
出版日期:2021-06-23
发布日期:2021-06-24
通讯作者:
董国臣
作者简介:董国臣,男,教授,博士生导师,1962年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事岩石学及矿床学研究。Email: donggc@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
YE Feng1,2( ), DONG Guochen2(
), DONG Guochen2( ), REN Jianxun1, GONG Jieli3, LI Mengxing1, WANG Quan1, ZHANG Zhaoqi1, ZHAO Sanbo1
), REN Jianxun1, GONG Jieli3, LI Mengxing1, WANG Quan1, ZHANG Zhaoqi1, ZHAO Sanbo1
Received:2020-04-15
Revised:2020-07-17
Online:2021-06-23
Published:2021-06-24
Contact:
DONG Guochen
摘要:
为深化对华北克拉通破坏机制的认识,选取山西黄榆沟岩体中较新鲜的石英二长斑岩开展年代学和地球化学研究。研究结果表明,黄榆沟岩体由石英二长斑岩组成,LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb谐和年龄为(149.3±0.9)Ma,是晚侏罗世岩浆活动的产物。石英二长斑岩富碱,为钙碱性钾玄岩系列,属于准铝质花岗岩类。相对富集K、Sr、Eu等大离子亲石元素,相对亏损Nb、Ce、Zr、Ti等高场强元素;轻稀土元素相对富集,重稀土元素相对亏损,Eu具弱正异常,为I型花岗岩成因。具高Al2O3、Sr、Ba、高Sr/Y比值和低Yb、MgO等特征,具埃达克岩性质。岩石地球化学特征表明,黄榆沟岩体总体为下地壳物质的部分熔融成因,并有幔源物质成分的加入和遭受岩浆混合作用,推测其形成于碰撞造山后的伸展构造环境。
中图分类号:
叶枫, 董国臣, 任建勋, 龚杰立, 李猛兴, 王权, 张兆琪, 赵三波. 山西黄榆沟岩体锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 787-797.
YE Feng, DONG Guochen, REN Jianxun, GONG Jieli, LI Mengxing, WANG Quan, ZHANG Zhaoqi, ZHAO Sanbo. Zircon U-Pb Geochronology, Geochemical Characteristics and Geological Significance of Huangyugou Intrusion, Shanxi Province[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(03): 787-797.
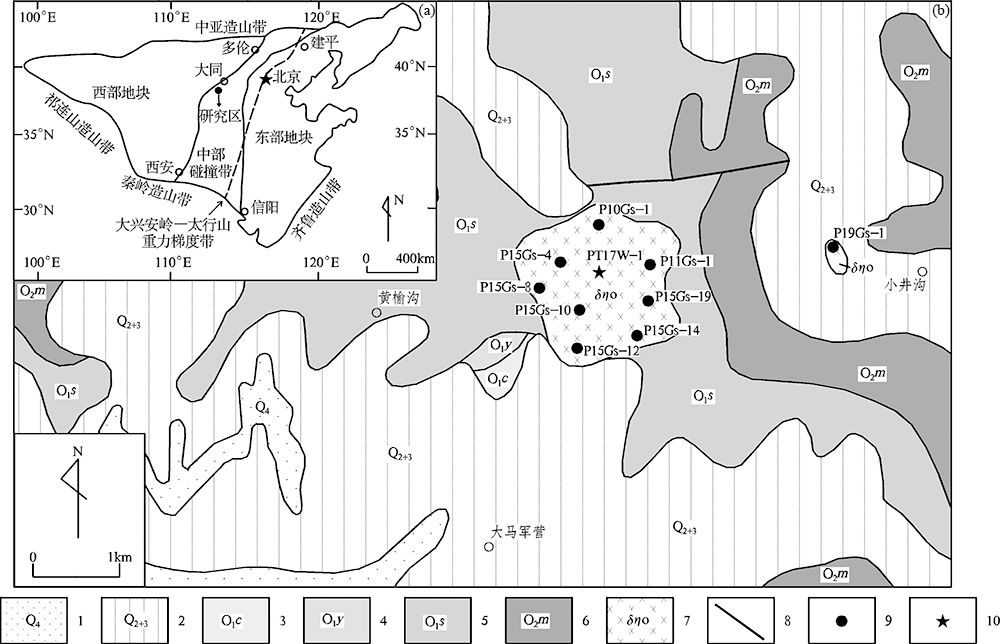
图1 华北克拉通构造简图(a)和山西黄榆沟地区地质简图(b) ((a)据Zhao等[33]修改; (b)据山西省地质调查院①(① 山西省地质调查院. 1:25万偏关县幅区域地质调查报告.2014.)修改) 1.第四系冲洪积物;2.第四系残坡积物;3.奥陶系炒米店组;4.奥陶系冶里组;5.奥陶系三山子组;6.奥陶系马家沟组;7.石英二长斑岩;8.构造断裂;9.地球化学样品采样位置;10.年龄样品采样位置
Fig.1 Simplified tectonic map of North China Craton (a) and geological sketch map of the study area (b)
| 测点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Th | U | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | ||||
| PT17W-1-1 | 9 | 51 | 388 | 0.13 | 0.049 13 | 0.001 03 | 0.160 17 | 0.002 27 | 0.023 63 | 0.000 27 | 153.9 | 48.3 | 150.9 | 2.0 | 150.5 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-2 | 10 | 59 | 399 | 0.15 | 0.049 05 | 0.001 07 | 0.158 10 | 0.002 46 | 0.023 36 | 0.000 27 | 150.3 | 50.6 | 149.0 | 2.2 | 148.8 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-3 | 5 | 32 | 209 | 0.15 | 0.049 11 | 0.001 72 | 0.158 02 | 0.004 88 | 0.023 33 | 0.000 31 | 153.2 | 80.1 | 149.0 | 4.3 | 148.6 | 1.9 | ||
| PT17W-1-4 | 11 | 70 | 447 | 0.16 | 0.049 13 | 0.001 03 | 0.159 06 | 0.002 21 | 0.023 47 | 0.000 27 | 154.1 | 48.2 | 149.9 | 1.9 | 149.6 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-5 | 6 | 39 | 273 | 0.14 | 0.049 12 | 0.001 01 | 0.159 15 | 0.002 12 | 0.023 50 | 0.000 27 | 153.7 | 47.5 | 150.0 | 1.9 | 149.7 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-6 | 11 | 65 | 409 | 0.16 | 0.049 00 | 0.001 11 | 0.157 44 | 0.002 54 | 0.023 30 | 0.000 27 | 147.8 | 52.1 | 148.5 | 2.2 | 148.5 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-7 | 8 | 47 | 346 | 0.14 | 0.049 03 | 0.000 98 | 0.158 74 | 0.001 97 | 0.023 48 | 0.000 27 | 149.5 | 46.2 | 149.6 | 1.7 | 149.6 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-8 | 11 | 74 | 464 | 0.16 | 0.049 05 | 0.001 02 | 0.157 82 | 0.002 14 | 0.023 34 | 0.000 27 | 150.1 | 48.1 | 148.8 | 1.9 | 148.7 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-9 | 9 | 47 | 368 | 0.13 | 0.049 19 | 0.001 94 | 0.158 01 | 0.005 67 | 0.023 30 | 0.000 29 | 156.9 | 89.8 | 149.0 | 5.0 | 148.5 | 1.8 | ||
| PT17W-1-10 | 17 | 118 | 684 | 0.17 | 0.049 13 | 0.001 93 | 0.159 78 | 0.005 67 | 0.023 60 | 0.000 31 | 153.8 | 89.4 | 150.5 | 5.0 | 150.3 | 1.9 | ||
| PT17W-1-11 | 12 | 91 | 471 | 0.19 | 0.049 05 | 0.001 03 | 0.157 92 | 0.002 16 | 0.023 36 | 0.000 27 | 150.4 | 48.5 | 148.9 | 1.9 | 148.8 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-12 | 14 | 120 | 584 | 0.21 | 0.049 04 | 0.001 11 | 0.158 19 | 0.002 51 | 0.023 40 | 0.000 28 | 149.7 | 52.3 | 149.1 | 2.2 | 149.1 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-13 | 13 | 84 | 526 | 0.16 | 0.049 09 | 0.001 04 | 0.158 65 | 0.002 18 | 0.023 45 | 0.000 27 | 151.9 | 48.9 | 149.5 | 1.9 | 149.4 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-14 | 13 | 83 | 518 | 0.16 | 0.049 05 | 0.001 39 | 0.159 13 | 0.003 68 | 0.023 53 | 0.000 29 | 150.2 | 65.3 | 149.9 | 3.2 | 149.9 | 1.8 | ||
| PT17W-1-15 | 26 | 368 | 999 | 0.37 | 0.049 12 | 0.001 33 | 0.157 89 | 0.003 38 | 0.023 31 | 0.000 28 | 153.7 | 62.3 | 148.9 | 3.0 | 148.6 | 1.8 | ||
| PT17W-1-16 | 12 | 72 | 497 | 0.15 | 0.049 12 | 0.002 46 | 0.159 27 | 0.007 42 | 0.023 51 | 0.000 35 | 153.6 | 113.3 | 150.1 | 6.5 | 149.8 | 2.2 | ||
表1 黄榆沟岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results of the Huangyugou intrusion
| 测点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Th | U | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | ||||
| PT17W-1-1 | 9 | 51 | 388 | 0.13 | 0.049 13 | 0.001 03 | 0.160 17 | 0.002 27 | 0.023 63 | 0.000 27 | 153.9 | 48.3 | 150.9 | 2.0 | 150.5 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-2 | 10 | 59 | 399 | 0.15 | 0.049 05 | 0.001 07 | 0.158 10 | 0.002 46 | 0.023 36 | 0.000 27 | 150.3 | 50.6 | 149.0 | 2.2 | 148.8 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-3 | 5 | 32 | 209 | 0.15 | 0.049 11 | 0.001 72 | 0.158 02 | 0.004 88 | 0.023 33 | 0.000 31 | 153.2 | 80.1 | 149.0 | 4.3 | 148.6 | 1.9 | ||
| PT17W-1-4 | 11 | 70 | 447 | 0.16 | 0.049 13 | 0.001 03 | 0.159 06 | 0.002 21 | 0.023 47 | 0.000 27 | 154.1 | 48.2 | 149.9 | 1.9 | 149.6 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-5 | 6 | 39 | 273 | 0.14 | 0.049 12 | 0.001 01 | 0.159 15 | 0.002 12 | 0.023 50 | 0.000 27 | 153.7 | 47.5 | 150.0 | 1.9 | 149.7 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-6 | 11 | 65 | 409 | 0.16 | 0.049 00 | 0.001 11 | 0.157 44 | 0.002 54 | 0.023 30 | 0.000 27 | 147.8 | 52.1 | 148.5 | 2.2 | 148.5 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-7 | 8 | 47 | 346 | 0.14 | 0.049 03 | 0.000 98 | 0.158 74 | 0.001 97 | 0.023 48 | 0.000 27 | 149.5 | 46.2 | 149.6 | 1.7 | 149.6 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-8 | 11 | 74 | 464 | 0.16 | 0.049 05 | 0.001 02 | 0.157 82 | 0.002 14 | 0.023 34 | 0.000 27 | 150.1 | 48.1 | 148.8 | 1.9 | 148.7 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-9 | 9 | 47 | 368 | 0.13 | 0.049 19 | 0.001 94 | 0.158 01 | 0.005 67 | 0.023 30 | 0.000 29 | 156.9 | 89.8 | 149.0 | 5.0 | 148.5 | 1.8 | ||
| PT17W-1-10 | 17 | 118 | 684 | 0.17 | 0.049 13 | 0.001 93 | 0.159 78 | 0.005 67 | 0.023 60 | 0.000 31 | 153.8 | 89.4 | 150.5 | 5.0 | 150.3 | 1.9 | ||
| PT17W-1-11 | 12 | 91 | 471 | 0.19 | 0.049 05 | 0.001 03 | 0.157 92 | 0.002 16 | 0.023 36 | 0.000 27 | 150.4 | 48.5 | 148.9 | 1.9 | 148.8 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-12 | 14 | 120 | 584 | 0.21 | 0.049 04 | 0.001 11 | 0.158 19 | 0.002 51 | 0.023 40 | 0.000 28 | 149.7 | 52.3 | 149.1 | 2.2 | 149.1 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-13 | 13 | 84 | 526 | 0.16 | 0.049 09 | 0.001 04 | 0.158 65 | 0.002 18 | 0.023 45 | 0.000 27 | 151.9 | 48.9 | 149.5 | 1.9 | 149.4 | 1.7 | ||
| PT17W-1-14 | 13 | 83 | 518 | 0.16 | 0.049 05 | 0.001 39 | 0.159 13 | 0.003 68 | 0.023 53 | 0.000 29 | 150.2 | 65.3 | 149.9 | 3.2 | 149.9 | 1.8 | ||
| PT17W-1-15 | 26 | 368 | 999 | 0.37 | 0.049 12 | 0.001 33 | 0.157 89 | 0.003 38 | 0.023 31 | 0.000 28 | 153.7 | 62.3 | 148.9 | 3.0 | 148.6 | 1.8 | ||
| PT17W-1-16 | 12 | 72 | 497 | 0.15 | 0.049 12 | 0.002 46 | 0.159 27 | 0.007 42 | 0.023 51 | 0.000 35 | 153.6 | 113.3 | 150.1 | 6.5 | 149.8 | 2.2 | ||
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | P2O5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P19Gs-1 | 62.88 | 16.15 | 4.20 | 1.14 | 0.06 | 3.85 | 1.88 | 3.94 | 4.06 | 0.33 |
| P10Gs-1 | 61.72 | 16.54 | 3.97 | 2.06 | 0.14 | 3.40 | 2.12 | 4.33 | 3.51 | 0.11 |
| P11Gs-1 | 63.54 | 16.15 | 3.78 | 2.01 | 0.12 | 2.78 | 1.71 | 4.48 | 3.40 | 0.15 |
| P15Gs-4 | 64.24 | 16.11 | 3.41 | 1.09 | 0.11 | 4.13 | 1.82 | 3.99 | 3.18 | 0.18 |
| P15Gs-8 | 62.80 | 16.11 | 3.72 | 1.40 | 0.09 | 4.58 | 1.56 | 4.10 | 3.55 | 0.14 |
| P15Gs-10 | 63.60 | 16.40 | 3.96 | 1.25 | 0.09 | 3.52 | 1.50 | 4.35 | 3.23 | 0.17 |
| P15Gs-12 | 62.02 | 16.38 | 3.93 | 1.47 | 0.10 | 3.93 | 1.79 | 4.06 | 3.42 | 0.16 |
| P15Gs-14 | 62.26 | 16.38 | 3.59 | 2.08 | 0.11 | 4.26 | 1.76 | 4.13 | 3.62 | 0.22 |
| P15Gs-19 | 62.94 | 15.49 | 4.21 | 1.96 | 0.11 | 3.36 | 1.71 | 5.21 | 2.35 | 0.43 |
| 样品编号 | TiO2 | CO2 | H2O+ | H2O- | 总量 | σ | AR | K2O/Na2O | A/NK | A/CNK |
| P19Gs-1 | 0.55 | 0.37 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 99.56 | 3.18 | 2.33 | 0.97 | 1.47 | 0.90 |
| P10Gs-1 | 0.46 | 0.07 | 0.34 | 0.68 | 98.77 | 3.22 | 2.30 | 1.23 | 1.58 | 0.99 |
| P11Gs-1 | 0.47 | 0.22 | 0.80 | 0.56 | 99.61 | 2.98 | 2.43 | 1.32 | 1.54 | 1.04 |
| P15Gs-4 | 0.46 | 0 | 0.26 | 0.55 | 98.98 | 2.39 | 2.10 | 1.25 | 1.68 | 0.94 |
| P15Gs-8 | 0.45 | 0.44 | 0.16 | 0.36 | 99.10 | 2.91 | 2.17 | 1.15 | 1.57 | 0.86 |
| P15Gs-10 | 0.43 | 0.22 | 0.09 | 0.27 | 98.81 | 2.75 | 2.23 | 1.35 | 1.63 | 1.00 |
| P15Gs-12 | 0.45 | 0.07 | 2.72 | 0.26 | 100.50 | 2.86 | 2.17 | 1.19 | 1.63 | 0.95 |
| P15Gs-14 | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.12 | 99.49 | 3.08 | 2.20 | 1.14 | 1.57 | 0.90 |
| P15Gs-19 | 0.49 | 0 | 0.45 | 0.27 | 98.71 | 2.81 | 2.34 | 2.22 | 1.63 | 0.99 |
表2 黄榆沟岩体主量元素分析结果(%)
Table 2 Whole-rock major element oxide contents (%) of the Huangyugou intrusion
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | P2O5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P19Gs-1 | 62.88 | 16.15 | 4.20 | 1.14 | 0.06 | 3.85 | 1.88 | 3.94 | 4.06 | 0.33 |
| P10Gs-1 | 61.72 | 16.54 | 3.97 | 2.06 | 0.14 | 3.40 | 2.12 | 4.33 | 3.51 | 0.11 |
| P11Gs-1 | 63.54 | 16.15 | 3.78 | 2.01 | 0.12 | 2.78 | 1.71 | 4.48 | 3.40 | 0.15 |
| P15Gs-4 | 64.24 | 16.11 | 3.41 | 1.09 | 0.11 | 4.13 | 1.82 | 3.99 | 3.18 | 0.18 |
| P15Gs-8 | 62.80 | 16.11 | 3.72 | 1.40 | 0.09 | 4.58 | 1.56 | 4.10 | 3.55 | 0.14 |
| P15Gs-10 | 63.60 | 16.40 | 3.96 | 1.25 | 0.09 | 3.52 | 1.50 | 4.35 | 3.23 | 0.17 |
| P15Gs-12 | 62.02 | 16.38 | 3.93 | 1.47 | 0.10 | 3.93 | 1.79 | 4.06 | 3.42 | 0.16 |
| P15Gs-14 | 62.26 | 16.38 | 3.59 | 2.08 | 0.11 | 4.26 | 1.76 | 4.13 | 3.62 | 0.22 |
| P15Gs-19 | 62.94 | 15.49 | 4.21 | 1.96 | 0.11 | 3.36 | 1.71 | 5.21 | 2.35 | 0.43 |
| 样品编号 | TiO2 | CO2 | H2O+ | H2O- | 总量 | σ | AR | K2O/Na2O | A/NK | A/CNK |
| P19Gs-1 | 0.55 | 0.37 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 99.56 | 3.18 | 2.33 | 0.97 | 1.47 | 0.90 |
| P10Gs-1 | 0.46 | 0.07 | 0.34 | 0.68 | 98.77 | 3.22 | 2.30 | 1.23 | 1.58 | 0.99 |
| P11Gs-1 | 0.47 | 0.22 | 0.80 | 0.56 | 99.61 | 2.98 | 2.43 | 1.32 | 1.54 | 1.04 |
| P15Gs-4 | 0.46 | 0 | 0.26 | 0.55 | 98.98 | 2.39 | 2.10 | 1.25 | 1.68 | 0.94 |
| P15Gs-8 | 0.45 | 0.44 | 0.16 | 0.36 | 99.10 | 2.91 | 2.17 | 1.15 | 1.57 | 0.86 |
| P15Gs-10 | 0.43 | 0.22 | 0.09 | 0.27 | 98.81 | 2.75 | 2.23 | 1.35 | 1.63 | 1.00 |
| P15Gs-12 | 0.45 | 0.07 | 2.72 | 0.26 | 100.50 | 2.86 | 2.17 | 1.19 | 1.63 | 0.95 |
| P15Gs-14 | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.12 | 99.49 | 3.08 | 2.20 | 1.14 | 1.57 | 0.90 |
| P15Gs-19 | 0.49 | 0 | 0.45 | 0.27 | 98.71 | 2.81 | 2.34 | 2.22 | 1.63 | 0.99 |
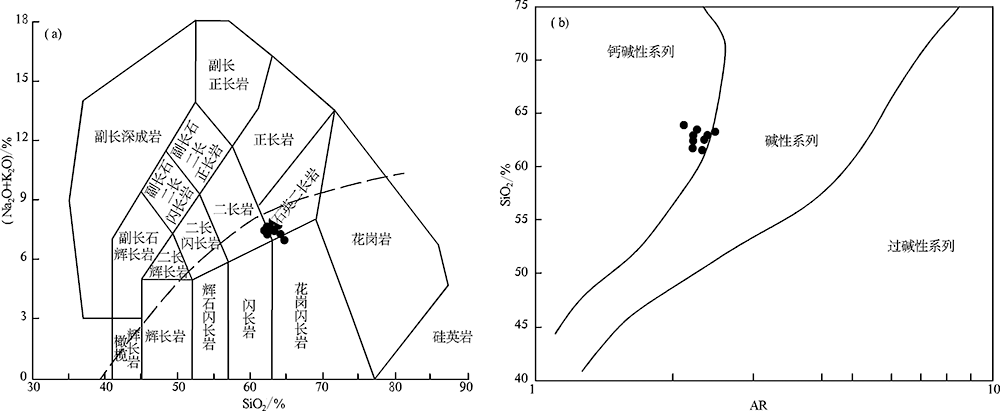
图5 黄榆沟岩体岩石类型((a), 底图据Lemaitre等[37])和SiO2-AR((b), 底图据Wright[38])图解
Fig.5 TAS (a) and SiO2 vs. AR (b) diagrams for the Huangyugou intrusion((a) after Lemaitre et al. [37], and (b) after Wright[38]])
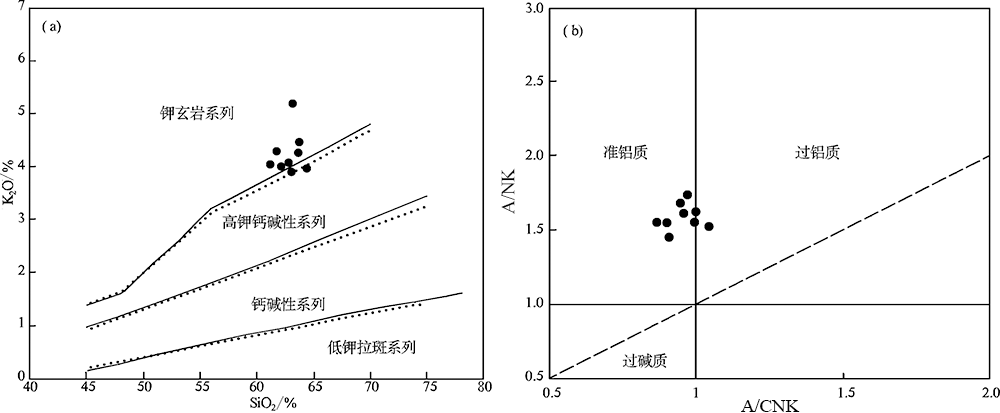
图6 黄榆沟岩体K2O-SiO2图解((a), 底图据Rollinson等[39])和A/NK-A/CNK图解((b), 底图据Maniar等[40])
Fig.6 K2O vs. SiO2 ((a), after Rollinson et al. [39]) and A/NK vs. A/CNK ((b), after Maniar et al. [40]) plots for the Huangyugou intrusion
| 样品编号 | Rb | Ba | Th | Ta | Nb | Zr | Hf | Sm | Yb | Ni | Sr | Cr | Sc | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P19Gs-1 | 167.00 | 1 209.00 | 4.96 | 0.46 | 56.60 | 4.95 | 11.80 | 3.07 | 1.31 | 2.06 | 1 130.00 | 11.90 | 20.40 | |||||||||||
| P10Gs-1 | 115.00 | 1 062.00 | 4.43 | 0.44 | 51.90 | 5.69 | 11.80 | 2.86 | 1.24 | 1.89 | 984.00 | 11.60 | 13.20 | |||||||||||
| P11Gs-1 | 103.00 | 863.00 | 4.18 | 0.64 | 51.00 | 6.08 | 9.16 | 2.71 | 1.33 | 1.87 | 810.00 | 9.35 | 10.10 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-4 | 112.00 | 822.00 | 3.45 | 0.67 | 67.80 | 6.28 | 10.80 | 2.82 | 1.24 | 2.41 | 1 293.00 | 10.30 | 15.80 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-8 | 90.50 | 833.00 | 3.59 | 0.72 | 65.90 | 7.39 | 8.96 | 3.05 | 1.31 | 2.41 | 1 279.00 | 10.20 | 15.30 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-10 | 90.40 | 1 082.00 | 3.50 | 0.54 | 58.30 | 6.96 | 9.11 | 2.90 | 1.24 | 2.13 | 1 271.00 | 9.19 | 19.40 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-12 | 93.60 | 886.00 | 3.34 | 0.27 | 53.10 | 4.56 | 8.79 | 3.06 | 1.32 | 1.91 | 1 397.00 | 9.89 | 12.50 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-14 | 105.00 | 1 276.00 | 3.56 | 0.44 | 60.20 | 5.28 | 10.30 | 2.79 | 1.11 | 2.18 | 1 574.00 | 10.00 | 13.50 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-19 | 167.00 | 1 209.00 | 4.96 | 0.46 | 56.60 | 4.95 | 11.80 | 3.07 | 1.31 | 2.06 | 1 130.00 | 11.90 | 20.40 | |||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Co | V | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | |||||||||||
| P19Gs-1 | 3.90 | 159.00 | 18.50 | 34.40 | 4.21 | 16.30 | 3.10 | 1.07 | 3.12 | 0.41 | 2.38 | 0.44 | 1.42 | |||||||||||
| P10Gs-1 | 4.40 | 118.00 | 14.70 | 30.20 | 3.50 | 13.70 | 2.86 | 0.99 | 2.69 | 0.38 | 2.23 | 0.44 | 1.24 | |||||||||||
| P11Gs-1 | 7.50 | 114.00 | 13.40 | 30.40 | 3.31 | 13.20 | 2.71 | 0.94 | 2.79 | 0.40 | 2.35 | 0.46 | 1.23 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-4 | 2.13 | 121.00 | 15.00 | 28.00 | 3.49 | 14.10 | 2.82 | 0.99 | 2.64 | 0.38 | 2.22 | 0.43 | 1.24 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-8 | 4.31 | 114.00 | 16.30 | 30.50 | 3.94 | 15.20 | 3.05 | 1.08 | 2.89 | 0.39 | 2.33 | 0.44 | 1.28 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-10 | 10.50 | 127.00 | 15.50 | 29.90 | 3.76 | 14.40 | 2.90 | 1.01 | 2.65 | 0.38 | 2.15 | 0.43 | 1.22 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-12 | 3.41 | 119.00 | 16.80 | 28.60 | 4.06 | 15.20 | 3.06 | 1.05 | 2.85 | 0.42 | 2.36 | 0.46 | 1.29 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-14 | 2.02 | 123.00 | 15.10 | 25.30 | 3.42 | 13.40 | 2.79 | 1.02 | 2.58 | 0.36 | 2.10 | 0.41 | 1.16 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-19 | 3.90 | 159.00 | 16.20 | 29.70 | 3.81 | 14.90 | 3.07 | 1.11 | 2.93 | 0.41 | 2.39 | 0.48 | 1.27 | |||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | ΣLREE | ΣHREE | ΣLREE/ ΣHREE | (La/Yb)N | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Lu)N | δEu | δCe | |||||||||||
| P19Gs-1 | 0.18 | 1.24 | 0.18 | 20.20 | 86.94 | 77.58 | 9.36 | 8.29 | 10.06 | 3.75 | 2.27 | 1.04 | 0.90 | |||||||||||
| P10Gs-1 | 0.19 | 1.24 | 0.19 | 11.90 | 74.54 | 65.95 | 8.59 | 7.68 | 7.99 | 3.23 | 1.81 | 1.08 | 0.98 | |||||||||||
| P11Gs-1 | 0.19 | 1.33 | 0.19 | 12.40 | 72.89 | 63.96 | 8.93 | 7.16 | 6.79 | 3.11 | 1.90 | 1.04 | 1.07 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-4 | 0.17 | 1.24 | 0.19 | 12.10 | 72.91 | 64.40 | 8.51 | 7.57 | 8.16 | 3.35 | 1.81 | 1.09 | 0.90 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-8 | 0.18 | 1.31 | 0.19 | 12.50 | 79.08 | 70.07 | 9.01 | 7.78 | 8.39 | 3.36 | 1.91 | 1.10 | 0.89 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-10 | 0.17 | 1.24 | 0.18 | 12.10 | 75.90 | 67.47 | 8.43 | 8.00 | 8.43 | 3.36 | 1.87 | 1.09 | 0.92 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-12 | 0.19 | 1.32 | 0.20 | 12.70 | 77.86 | 68.77 | 9.09 | 7.57 | 8.58 | 3.45 | 1.86 | 1.07 | 0.81 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-14 | 0.16 | 1.11 | 0.17 | 11.40 | 69.09 | 61.03 | 8.06 | 7.57 | 9.17 | 3.40 | 1.95 | 1.14 | 0.82 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-19 | 0.19 | 1.31 | 0.20 | 12.80 | 77.96 | 68.79 | 9.17 | 7.50 | 8.34 | 3.32 | 1.88 | 1.12 | 0.88 | |||||||||||
表3 黄榆沟岩体微量、稀土元素分析结果(wB/10-6)
Table 3 Trace and rare-earth elements (10-6) contents of the Huangyugou intrusion
| 样品编号 | Rb | Ba | Th | Ta | Nb | Zr | Hf | Sm | Yb | Ni | Sr | Cr | Sc | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P19Gs-1 | 167.00 | 1 209.00 | 4.96 | 0.46 | 56.60 | 4.95 | 11.80 | 3.07 | 1.31 | 2.06 | 1 130.00 | 11.90 | 20.40 | |||||||||||
| P10Gs-1 | 115.00 | 1 062.00 | 4.43 | 0.44 | 51.90 | 5.69 | 11.80 | 2.86 | 1.24 | 1.89 | 984.00 | 11.60 | 13.20 | |||||||||||
| P11Gs-1 | 103.00 | 863.00 | 4.18 | 0.64 | 51.00 | 6.08 | 9.16 | 2.71 | 1.33 | 1.87 | 810.00 | 9.35 | 10.10 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-4 | 112.00 | 822.00 | 3.45 | 0.67 | 67.80 | 6.28 | 10.80 | 2.82 | 1.24 | 2.41 | 1 293.00 | 10.30 | 15.80 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-8 | 90.50 | 833.00 | 3.59 | 0.72 | 65.90 | 7.39 | 8.96 | 3.05 | 1.31 | 2.41 | 1 279.00 | 10.20 | 15.30 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-10 | 90.40 | 1 082.00 | 3.50 | 0.54 | 58.30 | 6.96 | 9.11 | 2.90 | 1.24 | 2.13 | 1 271.00 | 9.19 | 19.40 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-12 | 93.60 | 886.00 | 3.34 | 0.27 | 53.10 | 4.56 | 8.79 | 3.06 | 1.32 | 1.91 | 1 397.00 | 9.89 | 12.50 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-14 | 105.00 | 1 276.00 | 3.56 | 0.44 | 60.20 | 5.28 | 10.30 | 2.79 | 1.11 | 2.18 | 1 574.00 | 10.00 | 13.50 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-19 | 167.00 | 1 209.00 | 4.96 | 0.46 | 56.60 | 4.95 | 11.80 | 3.07 | 1.31 | 2.06 | 1 130.00 | 11.90 | 20.40 | |||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Co | V | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | |||||||||||
| P19Gs-1 | 3.90 | 159.00 | 18.50 | 34.40 | 4.21 | 16.30 | 3.10 | 1.07 | 3.12 | 0.41 | 2.38 | 0.44 | 1.42 | |||||||||||
| P10Gs-1 | 4.40 | 118.00 | 14.70 | 30.20 | 3.50 | 13.70 | 2.86 | 0.99 | 2.69 | 0.38 | 2.23 | 0.44 | 1.24 | |||||||||||
| P11Gs-1 | 7.50 | 114.00 | 13.40 | 30.40 | 3.31 | 13.20 | 2.71 | 0.94 | 2.79 | 0.40 | 2.35 | 0.46 | 1.23 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-4 | 2.13 | 121.00 | 15.00 | 28.00 | 3.49 | 14.10 | 2.82 | 0.99 | 2.64 | 0.38 | 2.22 | 0.43 | 1.24 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-8 | 4.31 | 114.00 | 16.30 | 30.50 | 3.94 | 15.20 | 3.05 | 1.08 | 2.89 | 0.39 | 2.33 | 0.44 | 1.28 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-10 | 10.50 | 127.00 | 15.50 | 29.90 | 3.76 | 14.40 | 2.90 | 1.01 | 2.65 | 0.38 | 2.15 | 0.43 | 1.22 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-12 | 3.41 | 119.00 | 16.80 | 28.60 | 4.06 | 15.20 | 3.06 | 1.05 | 2.85 | 0.42 | 2.36 | 0.46 | 1.29 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-14 | 2.02 | 123.00 | 15.10 | 25.30 | 3.42 | 13.40 | 2.79 | 1.02 | 2.58 | 0.36 | 2.10 | 0.41 | 1.16 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-19 | 3.90 | 159.00 | 16.20 | 29.70 | 3.81 | 14.90 | 3.07 | 1.11 | 2.93 | 0.41 | 2.39 | 0.48 | 1.27 | |||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | ΣLREE | ΣHREE | ΣLREE/ ΣHREE | (La/Yb)N | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Lu)N | δEu | δCe | |||||||||||
| P19Gs-1 | 0.18 | 1.24 | 0.18 | 20.20 | 86.94 | 77.58 | 9.36 | 8.29 | 10.06 | 3.75 | 2.27 | 1.04 | 0.90 | |||||||||||
| P10Gs-1 | 0.19 | 1.24 | 0.19 | 11.90 | 74.54 | 65.95 | 8.59 | 7.68 | 7.99 | 3.23 | 1.81 | 1.08 | 0.98 | |||||||||||
| P11Gs-1 | 0.19 | 1.33 | 0.19 | 12.40 | 72.89 | 63.96 | 8.93 | 7.16 | 6.79 | 3.11 | 1.90 | 1.04 | 1.07 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-4 | 0.17 | 1.24 | 0.19 | 12.10 | 72.91 | 64.40 | 8.51 | 7.57 | 8.16 | 3.35 | 1.81 | 1.09 | 0.90 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-8 | 0.18 | 1.31 | 0.19 | 12.50 | 79.08 | 70.07 | 9.01 | 7.78 | 8.39 | 3.36 | 1.91 | 1.10 | 0.89 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-10 | 0.17 | 1.24 | 0.18 | 12.10 | 75.90 | 67.47 | 8.43 | 8.00 | 8.43 | 3.36 | 1.87 | 1.09 | 0.92 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-12 | 0.19 | 1.32 | 0.20 | 12.70 | 77.86 | 68.77 | 9.09 | 7.57 | 8.58 | 3.45 | 1.86 | 1.07 | 0.81 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-14 | 0.16 | 1.11 | 0.17 | 11.40 | 69.09 | 61.03 | 8.06 | 7.57 | 9.17 | 3.40 | 1.95 | 1.14 | 0.82 | |||||||||||
| P15Gs-19 | 0.19 | 1.31 | 0.20 | 12.80 | 77.96 | 68.79 | 9.17 | 7.50 | 8.34 | 3.32 | 1.88 | 1.12 | 0.88 | |||||||||||
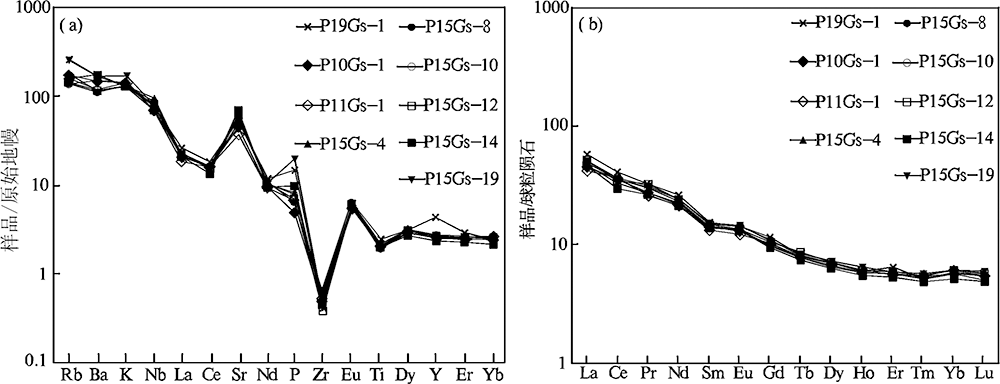
图7 黄榆沟岩体微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(a)和稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式图(b)(原始地幔数据据Sun等[41], 球粒陨石数据据Boynton等[42])
Fig.7 Primitive-mantle-normalized multi-element plot (a) and chondrite-normalized REE patterns (b) for theHuangyugou intrusion
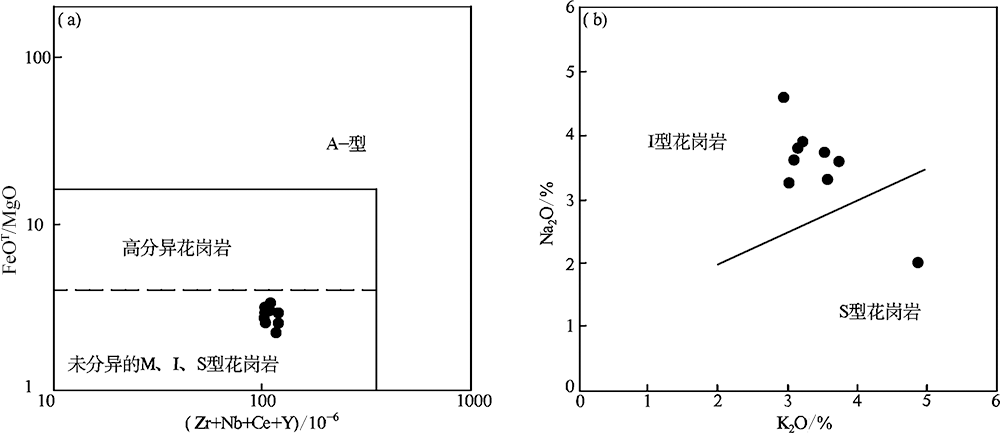
图8 黄榆沟岩体成因类型判别图解((a),底图据Whalen等[47];(b),底图据Chappell等[48])
Fig.8 Petrogenetic discrimination diagrams for the Huangyugou intrusion (a) FeOT/MgO vs. (Zr+Nb+Ce+Y) plot ((a),base map after Whalen et al. [47]) and Na2O vs. K2O plot ((b),base map after Chappell et al.[48])
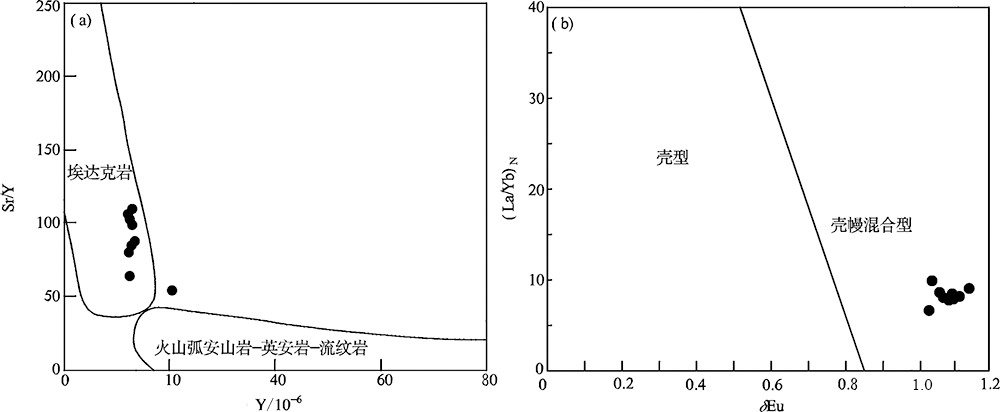
图9 黄榆沟岩体Y-Sr/Y((a),底图据Altherr等[49])和δEu-(La/Yb)N ((b),底图据董毅等[50])图解
Fig.9 Y vs. Sr/Y (a) and δEu vs. (La/Yb)N (b) plots for the Huangyugou intrusion((a) after Altherr et al. [49], and (b) after Dong et al. [50])
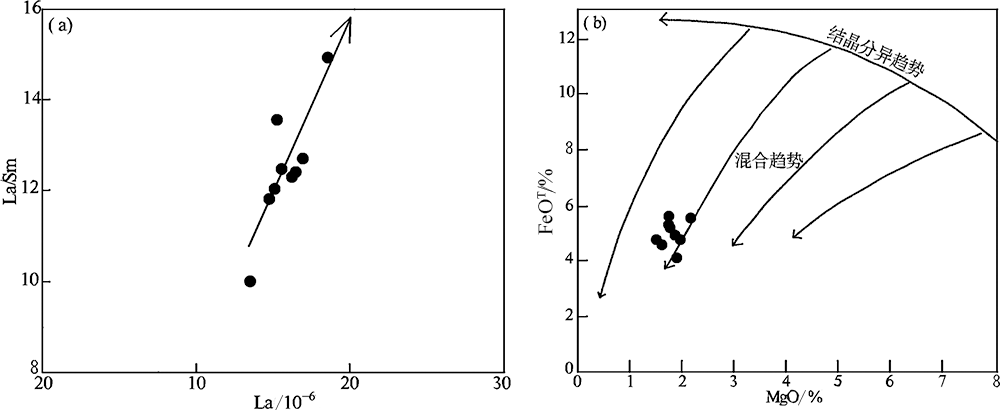
图10 黄榆沟岩体La-La/Sm (a)和MgO-FeOT (b)(底图据Zorpi等[51])图解
Fig.10 La vs. La/Sm (a) and MgO vs. FeOT (b) plots for the Huangyugou intrusion (base map after Zorpi et al. [51])
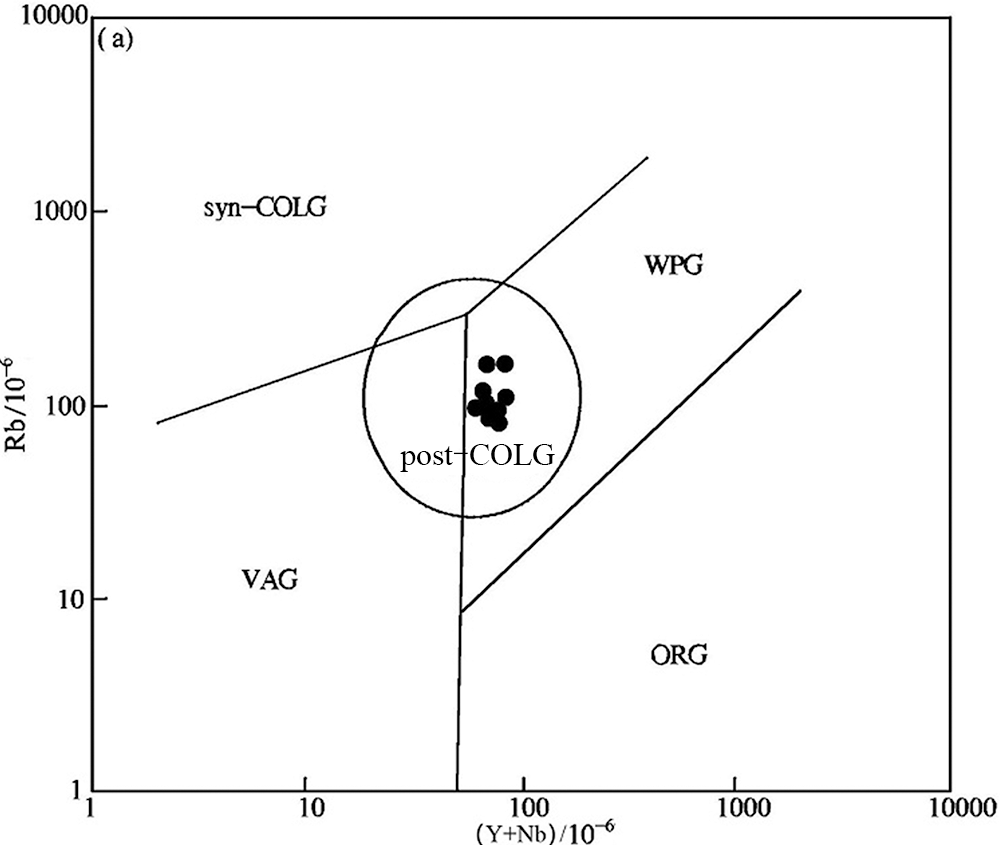
图11 黄榆沟岩体构造环境判别图解(底图据Pearce等[60]) syn-COLG.同碰撞花岗岩;WPG.板内花岗岩;VAG.火山弧花岗岩;ORG.洋脊花岗岩;post-COLG.后碰撞花岗岩
Fig.11 Tectonic discrimination diagrams for the Huangyugou intrusion (base map after Pearce et al. [60])
| [1] | 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 邓晋福, 等. 印度—亚洲大陆主碰撞过程的火山作用响应[J]. 地学前缘, 2003, 10(3): 135-148. |
| [2] | 朱日祥, 徐义刚, 朱光, 等. 华北克拉通破坏[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2012, 42(8): 1135-1159. |
| [3] | 华仁民, 毛景文. 试论中国东部中生代成矿大爆发[J]. 矿床地质, 1999, 18(4): 300-307. |
| [4] |
FAN W M, ZHANG H F, BAKER J, et al. On and off the North China Craton: where is the Archean Keel?[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2000, 41:933-950.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 路凤香, 郑建平, 李伍平, 等. 中国东部显生宙地幔演化的主要样式:“蘑菇云”模型[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(1): 97-107. |
| [6] |
XU Y G. Thermo-tectonic destruction of the Archean lithospheric keel beneath the Sino-Korean craton in China: Evidence, timing and mechanism[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part A: Solid Earth and Geodesy, 2001, 26(9/10): 747-757.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
GAO S, RUDNICK R L, CARLSON R W, et al. Re-Os evidence for replacement of ancient mantle lithosphere beneath the North China Craton[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 198(3/4): 307-322.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
WU F Y, WALKER R J, REN X W, et al. Osmium isotopic constraints on the age of lithospheric mantle beneath northeastern China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 196(1/2/3/4): 107-129.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
DENG J F, MO X X, ZHAO H L, et al. A new model for the dynamic evolution of Chinese lithosphere: “Continental roots-plumetectonics”[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2004, 65(3/4): 223-275.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
WU F Y, WALKER R J, YANG Y H, et al. The chemical-temporal evolution of lithospheric mantle underlying the North China Craton[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(19): 5013-5034.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
DENG J F, SU S G, NIU Y L, et al. A possible model for the lithospheric thinning of North China Craton: Evidence from the Yanshanian (Jura-Cretaceous) magmatism and tectonism[J]. Lithos, 2007, 96(1/2): 22-35.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 嵇少丞, 王茜, 许志琴. 华北克拉通破坏与岩石圈减薄[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(2): 174-193. |
| [13] | 吴福元, 徐义刚, 高山, 等. 华北岩石圈减薄与克拉通破坏研究的主要学术争论[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(6): 1145-1174. |
| [14] |
XU Y G, BLUSZTAJN J, MA J L, et al. Late Archean to Early Proterozoic lithospheric mantle beneath the western North China Craton: Sr-Nd-Os isotopes of peridotite xenoliths from Yangyuan and Fansi[J]. Lithos, 2008, 102(1/2): 25-42.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 高山, 章军锋, 许文良, 等. 拆沉作用与华北克拉通破坏[J]. 科学通报, 2009, 54(14): 1962-1973. |
| [16] | 朱日祥, 陈凌, 吴福元, 等. 华北克拉通破坏的时间、范围与机制[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 41(5): 583-592. |
| [17] | 高健翁, 林逸, 张长厚, 等. 基于断层滑动数据反演的燕山中西段晚中生代古构造应力场: 对华北克拉通破坏峰期应力状态的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(5): 919-936. |
| [18] | 董国臣. 论燕山地区燕山运动[J]. 河北地质学院学报, 1996, 19(6): 660-667. |
| [19] | 邓晋福, 莫宣学, 赵海玲, 等. 中国东部燕山期岩石圈-软流圈系统大灾变与成矿环境[J]. 矿床地质, 1999, 18(4): 309-315. |
| [20] | 翟明国, 朱日祥, 刘建明, 等. 华北东部中生代构造体制转折的关键时限[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2003, 33(10): 913-920. |
| [21] | 张旗, 王焰, 钱青, 等. 中国东部燕山期埃达克岩的特征及其构造-成矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2001, 17(2): 236-244. |
| [22] | XIAO W J, WINDLEY B F, HAO J, et al. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China: Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt[J]. Tecto-nics, 2003, 22(6): 1069. |
| [23] | 赵越, 张拴宏, 徐刚, 等. 燕山板内变形带侏罗纪主要构造事件[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(Z2): 854-863. |
| [24] | 陈斌, 田伟, 翟明国, 等. 太行山和华北其它地区中生代岩浆作用的锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学特征及其岩浆成因和地球动力学意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(1): 13-24. |
| [25] | 张旗, 金惟俊, 李承东, 等. 中国东部燕山期大规模岩浆活动与岩石圈减薄:与大火成岩省的关系[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(2): 21-51. |
| [26] | 任荣, 牟保磊, 韩宝福, 等. 河北矾山钾质碱性超镁铁岩-正长岩杂岩体的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(3): 588-594. |
| [27] | 陈斌, 牛晓露, 王志强, 等. 华北克拉通北缘姚家庄过钾质超镁铁岩-正长岩杂岩体的锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石学和地球化学特征[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2013, 43(7): 1073-1087. |
| [28] | 陈春良, 江思宏, 梁清玲, 等. 河北雾灵山杂岩体锆石Hf同位素特征及其区域对比研究[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(4): 663-673. |
| [29] | 刘源, 江思宏, 陈春良, 等. 河北承德甲山正长岩成因的Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf同位素制约[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2015, 24(1): 14-34. |
| [30] | 董朋生, 董国臣, 孙转荣, 等. 冀北五凤楼煌斑岩年代学、地球化学特征及其成因[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(2): 305-315. |
| [31] | 康丛轩, 杨献忠, 蔡逸涛, 等. 华北克拉通东南缘蚌埠隆起带荆山—涂山岩体地质地球化学特征再认识[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(6): 1242-1253. |
| [32] | 董朋生, 董国臣, 孙转荣, 等. 燕山地区寿王坟杂岩体锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(6): 264-276. |
| [33] |
ZHAO G C, SUN M, WILDE S A, et al. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton: Key issues revisited[J]. Precambrian Research, 2005, 136(2) :177-202.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 程裕淇, 沈永和, 张良臣, 等. 中国大陆的地质构造演化[J]. 中国区域地质, 1995, 14(4): 289-294. |
| [35] |
LIU Y S, HU Z C, GAO S, et al. In suit analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1/2) :34-43.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
DULSKI P. Interferences of oxide, hydroxide and chlorideanalyte species in the determination of rare earth elements in geological samples by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Fresenius’ Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 1994, 350(4/5) :194-203.
DOI URL |
| [37] | LEMAITRE R W, BATERMAN P, DUDEK A, et al. A Classification of Igneous Rocks and Glossary of Terms[M]. Oxford: Blackwell, 1989: 1-200. |
| [38] |
WRIGHT J B. A simple alkalinity ratio and its application to questions of non-orogenic granite genesis[J]. Geological Magazine, 1969, 106(4): 370-384.
DOI URL |
| [39] | ROLLINSON H. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, and Interpretation[M]. Harlow: Longman Scientific & Technical, 1993: 352. |
| [40] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of grani-toids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5): 635-643.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systema-tics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
DOI URL |
| [42] | BOYNTON W V. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies[M]//HENDERSON P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984: 63-114. |
| [43] | RUDNICK R L, GAO S. Composition of the continental crust[J]. Treatise in Geochemistry, 2014, 4:1-51. |
| [44] | 李振宏, 渠洪杰, 杨永恒, 等. 云岗盆地晚中生代沉积-火山充填序列及其构造意义[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(5): 1481-1494. |
| [45] | 李猛兴. 晋蒙地区西施沟复式岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及岩石成因[J]. 地质与勘探, 2019, 55(3): 765-778. |
| [46] | 葛良胜, 王治华, 杨贵才, 等. 晋东北燕山期岩浆活动与金多金属成矿作用动力学[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(2): 619-636. |
| [47] |
WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type gra-nites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-419.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
CHAPPELL B W. Aluminium saturation in I- and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3): 535-551.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
ALTHERR R, HOLL A, HEGNER R, et al. High-potassium, calc-alkaline I-type plutonism in the European Variscides: Northern Vosges(France) and Northern Schwarzwald (Germany)[J]. Lithos, 2000, 50(1/2/3): 51-73.
DOI URL |
| [50] | 董毅, 刘显凡, 邓江红, 等. 中甸弧西斑岩带印支期中酸性侵入岩成因与成矿意义[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(4): 887-899. |
| [51] |
ZORPI M J, COULON C, ORSINI J B. Hybridization between felsic and mafic magmas in calc-alkaline granitoids: A case study in northern Sardinia, Italy[J]. Chemical Geology, 1991, 92(1/2/3/4): 45-86.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
LI X H, LI W X, LI Z X. On the genetic classification and tectonic implications of the Early Yanshanian granitoids in the Nanling Range, South China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(14): 1873-1885.
DOI URL |
| [53] | 王中刚, 于学元, 赵振华. 稀土元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989:222-246. |
| [54] | 刘振声, 王洁民. 青藏高原南部花岗岩地质地球化学[M]. 成都: 四川科学技术出版社, 1994:1-133. |
| [55] |
DEFANT M J, DRUMMOND M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347:662-665.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
MARTIN H, SMITHIES R H, RAPP R, et al. An overview of adakite, tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite(TTG), and sanukitoid: relationships and some implications for crustal evolution[J]. Lithos, 2005, 79(1/2): 1-24.
DOI URL |
| [57] | 张旗, 王焰, 刘伟, 等. 埃达克岩的特征及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(7): 431-435. |
| [58] | 张旗, 钱青, 王二七, 等. 燕山中晚期的中国东部高原:埃达克岩的启示[J]. 地质科学, 2001, 36(2): 248-255. |
| [59] |
SCHIANO P, MONZIER M, EISSEN J P, et al. Simple mixing as the major control of the evolution of volcanic suites in the Ecuadorian Andes[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2010, 160(2): 297-312.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
PEARCE J A, MEI H J. Volcanic rocks of the 1985 Tibet Geotraverse: Lhasa to Golmud[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series A: Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1988, 327:169-201.
DOI URL |
| [61] | 郝彬, 杨欣德, 张明洋, 等. 内蒙古赤峰北部晚侏罗世中酸性火山岩地球化学特征[J]. 地质力学学报, 2011, 17(3): 274-285. |
| [62] | 曲凯, 董国臣, 李胜荣, 等. 太行山木吉村斑岩铜(钼)矿床岩石地球化学、Sr-Nd-Pb同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(3): 449-460. |
| [63] | 申志超, 侯增谦, 陈志宽, 等. 河北木吉村斑岩铜矿辉钼矿Re-Os定年、成矿斑岩锆石U-Pb定年和Hf同位素组成研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2015, 34(4): 526-538. |
| [64] | 鲁艳明, 专少鹏, 所承逊, 等. 内蒙古阿鲁科尔沁地区晚侏罗世侵入岩年代学、地球化学特征及成矿潜力[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 981-993. |
| [65] | 张书义. 内蒙古新巴尔虎右旗塔木兰沟组火山岩年代学与地球化学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(1): 129-138. |
| [66] | 柳长峰, 赵守恒, 张浩然, 等. 内蒙古赤峰大西营子金矿区赋矿火山岩年代学与岩石地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(1): 27-39. |
| [67] | 唐杰, 许文良, 王枫, 等. 古太平洋板块在欧亚大陆下的俯冲历史: 东北亚陆缘中生代-古近纪岩浆记录[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 48(5): 549-583. |
| [1] | 王亿, 李立兴, 李厚民, 李小赛, 马兰晶, 邢玉亮, 孙欣宇, 戴阳, 王小慧. 冀北招兵沟铁磷矿床成矿时代及成因研究[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 46-55. |
| [2] | 张保涛, 梅贞华, 李秀章, 姜晓平, 胡兆国, 王小玉, 赵晓博, 胡加斌, 柳森. 华北克拉通矽卡岩型富铁矿成矿关键控制因素:来自地层学的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 98-116. |
| [3] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [4] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [5] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [6] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [7] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [8] | 梁鸣, 高文, 罗先熔, 王晓东, 刘秀娟, 陈皓, 刘攀峰, 竹峰, 李伟. 冀北高尖子地区土壤地球化学特征及其找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1567-1579. |
| [9] | 苏惠, 曾认宇, 甘德斌, 严杰. 阿拉善北大山地区花岗斑岩岩石成因及构造启示:元素地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1580-1596. |
| [10] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [11] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [12] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [13] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [14] | 可行, 赵青芳, 吴飘, 杨传胜, 廖晶, 龚建明. 胶莱盆地东北部白垩系烃源岩特征与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1358-1368. |
| [15] | 贾冰玲, 张碧云, 汤彬, 郑德顺. 豫西寒武系辛集组含磷层沉积环境及磷酸盐富集机制[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 858-869. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||