



现代地质 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (03): 460-473.
李江涛1,2( ), 何学锋1(
), 何学锋1( ), 刘亮1,2, 杨鹏涛1, 梁斌1,2, 苏画1, 杨宇东1, 韩洪明1, 刘应忠3, 戴智慧4
), 刘亮1,2, 杨鹏涛1, 梁斌1,2, 苏画1, 杨宇东1, 韩洪明1, 刘应忠3, 戴智慧4
收稿日期:2016-05-12
修回日期:2017-01-29
出版日期:2017-06-10
发布日期:2017-06-27
通讯作者:
何学锋,男,高级工程师,1966年出生,地质矿产勘查专业,主要从事区域地质调查研究。Email:hxf66@sohu.com。
作者简介:李江涛,男,助理工程师,1989年出生,地质矿产勘查专业,主要从事区域地质调查研究。Email:lijiangtao_cool@163.com。
基金资助:
LI Jiangtao1,2( ), HE Xuefeng1(
), HE Xuefeng1( ), LIU Liang1,2, YANG Pengtao1, LIANG Bin1,2, SU Hua1, YANG Yudong1, HAN Hongming1, LIU Yingzhong3, DAI Zhihui4
), LIU Liang1,2, YANG Pengtao1, LIANG Bin1,2, SU Hua1, YANG Yudong1, HAN Hongming1, LIU Yingzhong3, DAI Zhihui4
Received:2016-05-12
Revised:2017-01-29
Online:2017-06-10
Published:2017-06-27
摘要:
新疆东天山哈尔里克造山带火山岩为一套酸性—基性岩(流纹岩、英安岩、安山岩、玄武岩)夹火山碎屑岩(凝灰岩)的岩石组合。流纹岩样品的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果显示,时代为中奥陶世大坪期((468.8±9.1) Ma),代表了该套火山岩的形成年龄。岩石地球化学分析结果显示,该套火山岩SiO2含量介于49.12%~78.24%,TiO2介于0.12%~1.00%,Al2O3介于11.31%~20.86%;铝饱和指数A/CNK值为0.80~1.31(均值为0.99),里特曼指数σ值为0.19~3.86(均值为1.29),Mg#值为8.87~49.29(均值为31.20);富集大离子亲石元素(LILE)Ba、Rb以及轻稀土元素(∑LREE)La、Ce,亏损高场强元素(HFSE)Nb、Ta、Ti等。微量元素和稀土元素的相关图解与比值以及发育的捕获锆石反映了俯冲带岛弧钙碱性火山岩特征,且存在大陆地壳混染作用。综合区域地质资料分析,在早古生代期间(中奥陶世—早志留世),哈尔里克造山带存在大面积的与岛弧演化有关的加里东期岩浆活动,此期间哈尔里克造山带的构造背景为洋壳俯冲有关的岛弧环境,其形成可能与东准噶尔南部克拉麦里洋向南俯冲作用有关。
中图分类号:
李江涛, 何学锋, 刘亮, 杨鹏涛, 梁斌, 苏画, 杨宇东, 韩洪明, 刘应忠, 戴智慧. 新疆东天山哈尔里克奥陶纪的构造属性:来自火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学与地球化学的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(03): 460-473.
LI Jiangtao, HE Xuefeng, LIU Liang, YANG Pengtao, LIANG Bin, SU Hua, YANG Yudong, HAN Hongming, LIU Yingzhong, DAI Zhihui. Ordovician Tectonic Evolution of Harlik in Eastern Tianshan of Xinjiang:Constraints from LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Geochemistry of Volcanic Rocks[J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(03): 460-473.

图1 哈尔里克山地区火山岩分布略图(据新疆地质矿产勘查开发局第一区域地质调查大队①(① 新疆地质矿产勘查开发局第一区域地质调查大队.1:5万哈密市口门子南一带区域地质调查报告.2006.)修改) 1.早—中奥陶世;2.中—晚奥陶世;3.中—晚志留世;4.早泥盆世;5.中泥盆世;6.早石炭世;7.晚石炭世;8.早二叠世;9.中—晚侏罗世;10.U-Pb年龄样品
Fig.1 Distribution map of volcanic rocks in Harlik area①
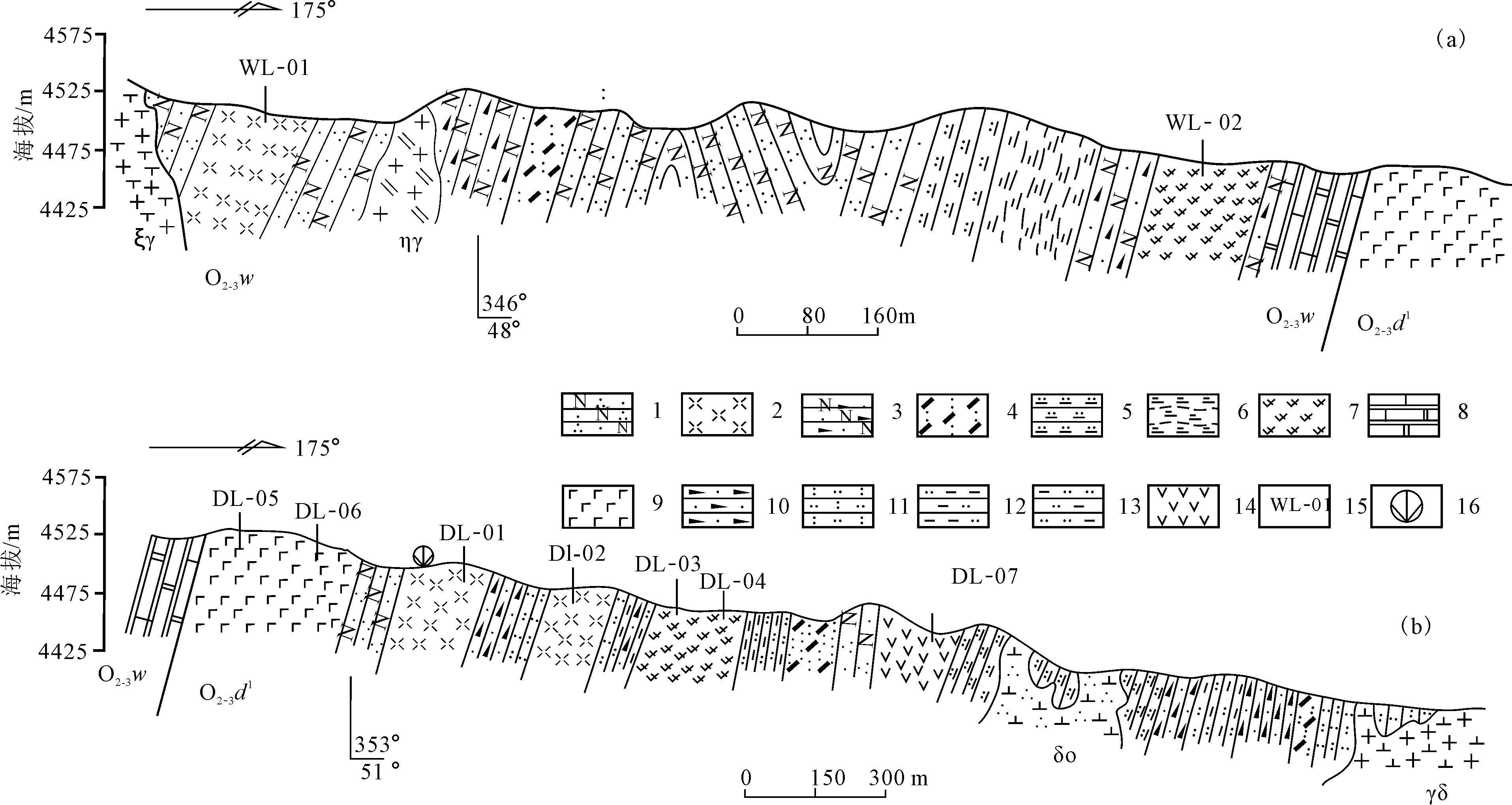
图2 奥陶纪火山岩剖面及采样位置((a)乌列盖组;(b)大柳沟组) 1.长石石英砂岩;2.流纹岩;3.长石岩屑砂岩;4.晶屑凝灰岩;5.硅质岩;6.绢云母千枚岩;7.英安岩;8.大理岩化粉晶灰岩;9.玄武岩;10.岩屑砂岩;11.凝灰质砂岩;12.粉砂质泥岩;13.泥质粉砂岩;14.安山岩;15.化学分析样品;16.同位素测年样品
Fig.2 Geological section and sampling sites of Ordovician volcanic rocks
| 地层 | 岩性 | 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 总量 | Mg# | Σ | A/CNK | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乌列 盖组 | 流纹岩 | WL-01 | 78.24 | 0.13 | 11.50 | 0.66 | 1.03 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.83 | 2.14 | 5.26 | 0.01 | 100.00 | 15.12 | 1.55 | 1.07 | ||||||||||
| 英安岩 | WL-02 | 71.75 | 0.71 | 13.22 | 4.33 | 1.25 | 0.11 | 2.05 | 1.93 | 3.03 | 1.48 | 0.13 | 100.00 | 41.52 | 0.71 | 1.31 | |||||||||||
| 大柳 沟组 | 流纹岩 | DL-01 | 77.88 | 0.12 | 11.31 | 0.54 | 2.10 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 3.22 | 4.50 | 0.01 | 100.00 | 8.87 | 1.71 | 1.09 | ||||||||||
| 流纹岩 | DL-02 | 73.29 | 0.97 | 12.19 | 2.03 | 2.28 | 0.14 | 0.95 | 3.41 | 4.24 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 100.00 | 29.20 | 0.66 | 0.91 | |||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-03 | 63.12 | 0.62 | 17.07 | 1.62 | 3.88 | 0.13 | 2.19 | 2.43 | 6.35 | 2.46 | 0.13 | 100.00 | 42.27 | 3.86 | 0.97 | |||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-04 | 68.97 | 1.00 | 14.04 | 1.70 | 3.71 | 0.18 | 1.20 | 4.07 | 4.57 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 100.00 | 28.95 | 0.91 | 0.92 | |||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-05 | 49.12 | 0.93 | 20.86 | 5.36 | 6.95 | 0.35 | 3.38 | 10.68 | 1.06 | 1.15 | 0.15 | 100.00 | 33.88 | 0.80 | 0.93 | |||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-06 | 49.94 | 0.86 | 19.56 | 5.94 | 6.49 | 0.38 | 3.09 | 12.45 | 0.83 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 100.00 | 31.72 | 0.19 | 0.80 | |||||||||||
| 安山岩 | DL-07 | 60.94 | 0.88 | 16.36 | 2.92 | 3.82 | 0.15 | 3.51 | 6.53 | 2.75 | 1.95 | 0.19 | 100.00 | 49.29 | 1.23 | 0.88 | |||||||||||
| 地层 | 岩性 | 样品号 | Cr | Ni | Co | Rb | Cs | Sr | Ba | V | Sc | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | U | Th | ||||||||||
| 乌列 盖组 | 流纹岩 | WL-01 | 6.43 | 2.60 | 1.41 | 134.34 | 8.95 | 113.69 | 389.62 | 4.18 | 2.19 | 19.40 | 1.94 | 163.61 | 5.27 | 7.34 | 30.02 | ||||||||||
| 英安岩 | WL-02 | 17.98 | 6.46 | 11.13 | 31.59 | 5.37 | 248.28 | 411.88 | 58.59 | 15.38 | 9.13 | 0.78 | 138.03 | 3.92 | 0.74 | 4.01 | |||||||||||
| 大柳 沟组 | 流纹岩 | DL-01 | 12.81 | 3.84 | 1.66 | 137.60 | 2.27 | 54.68 | 113.85 | 4.39 | 1.67 | 22.17 | 1.79 | 564.04 | 13.97 | 5.66 | 21.41 | ||||||||||
| 流纹岩 | DL-02 | 16.02 | 2.78 | 13.86 | 5.66 | 0.70 | 147.18 | 50.98 | 108.97 | 26.49 | 2.42 | 0.17 | 106.85 | 9.27 | 0.83 | 1.72 | |||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-03 | 35.35 | 9.00 | 16.51 | 55.68 | 3.91 | 164.98 | 401.47 | 104.04 | 18.01 | 5.60 | 0.46 | 179.66 | 5.08 | 2.37 | 8.06 | |||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-04 | 14.58 | 1.33 | 18.26 | 6.11 | 0.73 | 177.22 | 55.86 | 133.44 | 27.28 | 2.57 | 0.19 | 113.14 | 12.15 | 0.88 | 1.77 | |||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-05 | 122.23 | 52.95 | 29.04 | 28.27 | 3.02 | 289.83 | 601.59 | 220.87 | 37.11 | 2.41 | 0.19 | 67.96 | 2.59 | 0.56 | 0.94 | |||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-06 | 114.37 | 49.11 | 25.46 | 8.33 | 0.85 | 322.56 | 172.00 | 194.88 | 38.58 | 1.99 | 0.15 | 63.78 | 2.08 | 0.66 | 0.83 | |||||||||||
| 安山岩 | DL-07 | 22.80 | 10.80 | 20.60 | 36.60 | 2.43 | 710.00 | 1450.00 | 151.00 | 23.00 | 6.18 | 0.53 | 160.00 | 4.57 | 1.86 | 6.41 | |||||||||||
| 地层 | 岩性 | 样品号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ∑REE | δEu | |||||||||
| 乌列 盖组 | 流纹岩 | WL-01 | 48.67 | 100.84 | 10.70 | 39.94 | 7.30 | 0.48 | 7.92 | 1.35 | 7.49 | 1.67 | 5.93 | 0.84 | 5.79 | 0.95 | 239.87 | 0.19 | |||||||||
| 英安岩 | WL-02 | 29.39 | 61.62 | 6.49 | 29.95 | 6.10 | 1.62 | 5.74 | 0.91 | 4.91 | 1.03 | 2.98 | 0.42 | 2.89 | 0.47 | 154.54 | 0.84 | ||||||||||
| 大柳 沟组 | 流纹岩 | DL-01 | 62.39 | 119.27 | 14.98 | 67.03 | 14.98 | 0.59 | 13.61 | 2.31 | 12.92 | 2.76 | 8.07 | 1.23 | 8.05 | 1.27 | 329.45 | 0.13 | |||||||||
| 流纹岩 | DL-02 | 13.83 | 29.63 | 4.22 | 22.40 | 5.60 | 1.34 | 5.59 | 0.98 | 5.63 | 1.19 | 3.46 | 0.51 | 3.28 | 0.52 | 98.17 | 0.73 | ||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-03 | 17.94 | 38.00 | 4.67 | 20.81 | 4.16 | 1.25 | 3.94 | 0.65 | 3.68 | 0.80 | 2.42 | 0.37 | 2.55 | 0.41 | 101.64 | 0.95 | ||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-04 | 15.54 | 27.92 | 4.06 | 21.77 | 5.55 | 1.48 | 5.73 | 1.04 | 5.87 | 1.29 | 3.66 | 0.54 | 3.62 | 0.60 | 98.66 | 0.80 | ||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-05 | 8.91 | 16.16 | 2.67 | 13.85 | 3.63 | 1.52 | 4.13 | 0.73 | 4.47 | 0.98 | 2.80 | 0.41 | 2.86 | 0.46 | 68.59 | 1.20 | ||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-06 | 8.21 | 18.01 | 2.39 | 12.90 | 3.48 | 1.40 | 4.01 | 0.77 | 4.70 | 1.02 | 2.97 | 0.44 | 2.92 | 0.47 | 63.68 | 1.15 | ||||||||||
| 安山岩 | DL-07 | 17.20 | 37.20 | 4.89 | 19.70 | 4.52 | 1.43 | 4.58 | 0.86 | 6.06 | 1.24 | 3.65 | 0.58 | 3.60 | 0.56 | 106.07 | 0.96 | ||||||||||
表1 哈尔里克山奥陶纪火山岩主量元素(wB/%)、微量元素及稀土元素(wB/10-6)分析结果
Table 1 Major (%),rare earth and trace(10-6) element compositions of the Ordovician volcanic rocks in Harlik Mountain
| 地层 | 岩性 | 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 总量 | Mg# | Σ | A/CNK | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乌列 盖组 | 流纹岩 | WL-01 | 78.24 | 0.13 | 11.50 | 0.66 | 1.03 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.83 | 2.14 | 5.26 | 0.01 | 100.00 | 15.12 | 1.55 | 1.07 | ||||||||||
| 英安岩 | WL-02 | 71.75 | 0.71 | 13.22 | 4.33 | 1.25 | 0.11 | 2.05 | 1.93 | 3.03 | 1.48 | 0.13 | 100.00 | 41.52 | 0.71 | 1.31 | |||||||||||
| 大柳 沟组 | 流纹岩 | DL-01 | 77.88 | 0.12 | 11.31 | 0.54 | 2.10 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 3.22 | 4.50 | 0.01 | 100.00 | 8.87 | 1.71 | 1.09 | ||||||||||
| 流纹岩 | DL-02 | 73.29 | 0.97 | 12.19 | 2.03 | 2.28 | 0.14 | 0.95 | 3.41 | 4.24 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 100.00 | 29.20 | 0.66 | 0.91 | |||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-03 | 63.12 | 0.62 | 17.07 | 1.62 | 3.88 | 0.13 | 2.19 | 2.43 | 6.35 | 2.46 | 0.13 | 100.00 | 42.27 | 3.86 | 0.97 | |||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-04 | 68.97 | 1.00 | 14.04 | 1.70 | 3.71 | 0.18 | 1.20 | 4.07 | 4.57 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 100.00 | 28.95 | 0.91 | 0.92 | |||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-05 | 49.12 | 0.93 | 20.86 | 5.36 | 6.95 | 0.35 | 3.38 | 10.68 | 1.06 | 1.15 | 0.15 | 100.00 | 33.88 | 0.80 | 0.93 | |||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-06 | 49.94 | 0.86 | 19.56 | 5.94 | 6.49 | 0.38 | 3.09 | 12.45 | 0.83 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 100.00 | 31.72 | 0.19 | 0.80 | |||||||||||
| 安山岩 | DL-07 | 60.94 | 0.88 | 16.36 | 2.92 | 3.82 | 0.15 | 3.51 | 6.53 | 2.75 | 1.95 | 0.19 | 100.00 | 49.29 | 1.23 | 0.88 | |||||||||||
| 地层 | 岩性 | 样品号 | Cr | Ni | Co | Rb | Cs | Sr | Ba | V | Sc | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | U | Th | ||||||||||
| 乌列 盖组 | 流纹岩 | WL-01 | 6.43 | 2.60 | 1.41 | 134.34 | 8.95 | 113.69 | 389.62 | 4.18 | 2.19 | 19.40 | 1.94 | 163.61 | 5.27 | 7.34 | 30.02 | ||||||||||
| 英安岩 | WL-02 | 17.98 | 6.46 | 11.13 | 31.59 | 5.37 | 248.28 | 411.88 | 58.59 | 15.38 | 9.13 | 0.78 | 138.03 | 3.92 | 0.74 | 4.01 | |||||||||||
| 大柳 沟组 | 流纹岩 | DL-01 | 12.81 | 3.84 | 1.66 | 137.60 | 2.27 | 54.68 | 113.85 | 4.39 | 1.67 | 22.17 | 1.79 | 564.04 | 13.97 | 5.66 | 21.41 | ||||||||||
| 流纹岩 | DL-02 | 16.02 | 2.78 | 13.86 | 5.66 | 0.70 | 147.18 | 50.98 | 108.97 | 26.49 | 2.42 | 0.17 | 106.85 | 9.27 | 0.83 | 1.72 | |||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-03 | 35.35 | 9.00 | 16.51 | 55.68 | 3.91 | 164.98 | 401.47 | 104.04 | 18.01 | 5.60 | 0.46 | 179.66 | 5.08 | 2.37 | 8.06 | |||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-04 | 14.58 | 1.33 | 18.26 | 6.11 | 0.73 | 177.22 | 55.86 | 133.44 | 27.28 | 2.57 | 0.19 | 113.14 | 12.15 | 0.88 | 1.77 | |||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-05 | 122.23 | 52.95 | 29.04 | 28.27 | 3.02 | 289.83 | 601.59 | 220.87 | 37.11 | 2.41 | 0.19 | 67.96 | 2.59 | 0.56 | 0.94 | |||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-06 | 114.37 | 49.11 | 25.46 | 8.33 | 0.85 | 322.56 | 172.00 | 194.88 | 38.58 | 1.99 | 0.15 | 63.78 | 2.08 | 0.66 | 0.83 | |||||||||||
| 安山岩 | DL-07 | 22.80 | 10.80 | 20.60 | 36.60 | 2.43 | 710.00 | 1450.00 | 151.00 | 23.00 | 6.18 | 0.53 | 160.00 | 4.57 | 1.86 | 6.41 | |||||||||||
| 地层 | 岩性 | 样品号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ∑REE | δEu | |||||||||
| 乌列 盖组 | 流纹岩 | WL-01 | 48.67 | 100.84 | 10.70 | 39.94 | 7.30 | 0.48 | 7.92 | 1.35 | 7.49 | 1.67 | 5.93 | 0.84 | 5.79 | 0.95 | 239.87 | 0.19 | |||||||||
| 英安岩 | WL-02 | 29.39 | 61.62 | 6.49 | 29.95 | 6.10 | 1.62 | 5.74 | 0.91 | 4.91 | 1.03 | 2.98 | 0.42 | 2.89 | 0.47 | 154.54 | 0.84 | ||||||||||
| 大柳 沟组 | 流纹岩 | DL-01 | 62.39 | 119.27 | 14.98 | 67.03 | 14.98 | 0.59 | 13.61 | 2.31 | 12.92 | 2.76 | 8.07 | 1.23 | 8.05 | 1.27 | 329.45 | 0.13 | |||||||||
| 流纹岩 | DL-02 | 13.83 | 29.63 | 4.22 | 22.40 | 5.60 | 1.34 | 5.59 | 0.98 | 5.63 | 1.19 | 3.46 | 0.51 | 3.28 | 0.52 | 98.17 | 0.73 | ||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-03 | 17.94 | 38.00 | 4.67 | 20.81 | 4.16 | 1.25 | 3.94 | 0.65 | 3.68 | 0.80 | 2.42 | 0.37 | 2.55 | 0.41 | 101.64 | 0.95 | ||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-04 | 15.54 | 27.92 | 4.06 | 21.77 | 5.55 | 1.48 | 5.73 | 1.04 | 5.87 | 1.29 | 3.66 | 0.54 | 3.62 | 0.60 | 98.66 | 0.80 | ||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-05 | 8.91 | 16.16 | 2.67 | 13.85 | 3.63 | 1.52 | 4.13 | 0.73 | 4.47 | 0.98 | 2.80 | 0.41 | 2.86 | 0.46 | 68.59 | 1.20 | ||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-06 | 8.21 | 18.01 | 2.39 | 12.90 | 3.48 | 1.40 | 4.01 | 0.77 | 4.70 | 1.02 | 2.97 | 0.44 | 2.92 | 0.47 | 63.68 | 1.15 | ||||||||||
| 安山岩 | DL-07 | 17.20 | 37.20 | 4.89 | 19.70 | 4.52 | 1.43 | 4.58 | 0.86 | 6.06 | 1.24 | 3.65 | 0.58 | 3.60 | 0.56 | 106.07 | 0.96 | ||||||||||
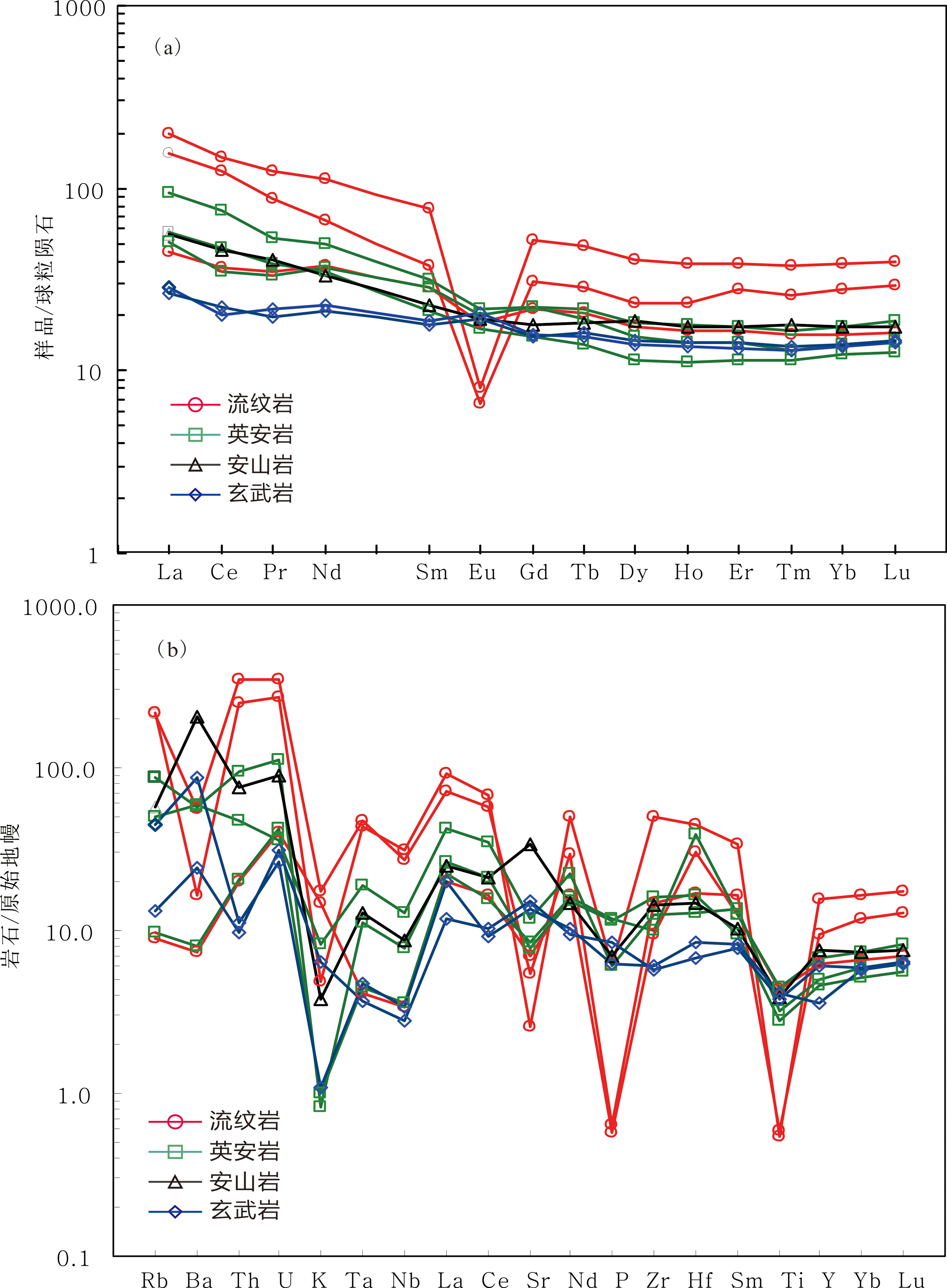
图7 哈尔里克山奥陶纪火山岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图[25]和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图[26]
Fig.7 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle-normalized trace element abundance spider diagram of the Ordovician volcanic rocks in Harlik Mountain
| 测点 编号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/ U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | ||
| 01(C) | 297 | 1 077 | 0.28 | 0.056 8 | 0.001 6 | 0.528 0 | 0.015 9 | 0.065 9 | 0.001 0 | 483.4 | 56.5 | 430.5 | 10.6 | 411.2 | 5.9 |
| 02(C) | 369 | 410 | 0.90 | 0.056 5 | 0.001 7 | 0.535 4 | 0.016 2 | 0.067 7 | 0.001 1 | 472.3 | 97.2 | 435.4 | 10.7 | 422.6 | 6.7 |
| 03 | 446 | 585 | 0.76 | 0.055 8 | 0.001 7 | 0.569 4 | 0.017 2 | 0.072 8 | 0.001 1 | 455.6 | 73.1 | 457.6 | 11.1 | 452.8 | 6.7 |
| 04(C) | 467 | 960 | 0.49 | 0.058 1 | 0.001 2 | 0.571 8 | 0.011 3 | 0.070 3 | 0.000 8 | 600.0 | 50.9 | 459.2 | 7.3 | 437.9 | 4.6 |
| 05 | 140 | 231 | 0.61 | 0.056 5 | 0.001 8 | 0.574 7 | 0.016 7 | 0.073 4 | 0.001 0 | 472.3 | 70.4 | 461.1 | 10.8 | 456.8 | 5.9 |
| 06 | 316 | 1 044 | 0.30 | 0.055 5 | 0.001 1 | 0.580 4 | 0.011 5 | 0.074 6 | 0.000 9 | 431.5 | 44.4 | 464.7 | 7.4 | 463.7 | 5.1 |
| 07 | 182 | 497 | 0.37 | 0.057 4 | 0.001 4 | 0.583 0 | 0.014 1 | 0.072 5 | 0.001 0 | 509.3 | 53.7 | 466.4 | 9.1 | 451.3 | 5.8 |
| 08 | 727 | 1 019 | 0.71 | 0.057 3 | 0.001 5 | 0.585 8 | 0.015 8 | 0.072 7 | 0.001 0 | 501.9 | 55.6 | 468.2 | 10.1 | 452.4 | 5.9 |
| 09 | 369 | 739 | 0.50 | 0.056 5 | 0.001 4 | 0.596 5 | 0.014 8 | 0.075 3 | 0.001 0 | 477.8 | 53.7 | 475.0 | 9.4 | 467.8 | 6.0 |
| 10 | 149 | 362 | 0.41 | 0.056 8 | 0.001 8 | 0.601 7 | 0.017 5 | 0.076 3 | 0.001 0 | 483.4 | 72.2 | 478.3 | 11.1 | 473.7 | 6.2 |
| 11 | 225 | 619 | 0.36 | 0.057 9 | 0.001 7 | 0.607 5 | 0.017 5 | 0.075 0 | 0.001 2 | 524.1 | 66.7 | 482.0 | 11.0 | 466.4 | 7.2 |
| 12(C) | 966 | 1 409 | 0.69 | 0.065 0 | 0.001 8 | 0.614 9 | 0.017 8 | 0.067 3 | 0.001 1 | 772.2 | 53.5 | 486.7 | 11.2 | 420.0 | 6.7 |
| 13 | 422 | 1 342 | 0.31 | 0.056 8 | 0.001 2 | 0.616 1 | 0.013 1 | 0.077 3 | 0.000 9 | 483.4 | 48.1 | 487.4 | 8.2 | 480.1 | 5.6 |
| 14 | 274 | 751 | 0.36 | 0.057 1 | 0.002 1 | 0.620 0 | 0.022 4 | 0.077 3 | 0.001 3 | 498.2 | 81.5 | 489.9 | 14.0 | 480.0 | 7.8 |
| 15 | 128 | 192 | 0.67 | 0.058 4 | 0.001 9 | 0.637 3 | 0.019 9 | 0.078 8 | 0.001 2 | 546.3 | 71.1 | 500.6 | 12.3 | 488.9 | 7.1 |
| 16 | 142 | 267 | 0.53 | 0.057 7 | 0.001 7 | 0.648 0 | 0.018 9 | 0.080 5 | 0.001 1 | 516.7 | 66.7 | 507.2 | 11.6 | 499.1 | 6.8 |
| 17 | 229 | 279 | 0.82 | 0.059 7 | 0.002 7 | 0.655 9 | 0.028 4 | 0.079 1 | 0.001 6 | 590.8 | 93.5 | 512.1 | 17.4 | 490.9 | 9.5 |
| 18(C) | 184 | 359 | 0.51 | 0.063 0 | 0.001 4 | 1.092 5 | 0.023 7 | 0.123 8 | 0.001 5 | 709.3 | 47.1 | 749.7 | 11.5 | 752.5 | 8.6 |
表2 哈尔里克山流纹岩(DL-01)锆石的LA-ICP-MS U-Pb分析结果
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb analyses of zircon for the rhyolite (DL-01) from the Harlik Mountain
| 测点 编号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/ U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | ||
| 01(C) | 297 | 1 077 | 0.28 | 0.056 8 | 0.001 6 | 0.528 0 | 0.015 9 | 0.065 9 | 0.001 0 | 483.4 | 56.5 | 430.5 | 10.6 | 411.2 | 5.9 |
| 02(C) | 369 | 410 | 0.90 | 0.056 5 | 0.001 7 | 0.535 4 | 0.016 2 | 0.067 7 | 0.001 1 | 472.3 | 97.2 | 435.4 | 10.7 | 422.6 | 6.7 |
| 03 | 446 | 585 | 0.76 | 0.055 8 | 0.001 7 | 0.569 4 | 0.017 2 | 0.072 8 | 0.001 1 | 455.6 | 73.1 | 457.6 | 11.1 | 452.8 | 6.7 |
| 04(C) | 467 | 960 | 0.49 | 0.058 1 | 0.001 2 | 0.571 8 | 0.011 3 | 0.070 3 | 0.000 8 | 600.0 | 50.9 | 459.2 | 7.3 | 437.9 | 4.6 |
| 05 | 140 | 231 | 0.61 | 0.056 5 | 0.001 8 | 0.574 7 | 0.016 7 | 0.073 4 | 0.001 0 | 472.3 | 70.4 | 461.1 | 10.8 | 456.8 | 5.9 |
| 06 | 316 | 1 044 | 0.30 | 0.055 5 | 0.001 1 | 0.580 4 | 0.011 5 | 0.074 6 | 0.000 9 | 431.5 | 44.4 | 464.7 | 7.4 | 463.7 | 5.1 |
| 07 | 182 | 497 | 0.37 | 0.057 4 | 0.001 4 | 0.583 0 | 0.014 1 | 0.072 5 | 0.001 0 | 509.3 | 53.7 | 466.4 | 9.1 | 451.3 | 5.8 |
| 08 | 727 | 1 019 | 0.71 | 0.057 3 | 0.001 5 | 0.585 8 | 0.015 8 | 0.072 7 | 0.001 0 | 501.9 | 55.6 | 468.2 | 10.1 | 452.4 | 5.9 |
| 09 | 369 | 739 | 0.50 | 0.056 5 | 0.001 4 | 0.596 5 | 0.014 8 | 0.075 3 | 0.001 0 | 477.8 | 53.7 | 475.0 | 9.4 | 467.8 | 6.0 |
| 10 | 149 | 362 | 0.41 | 0.056 8 | 0.001 8 | 0.601 7 | 0.017 5 | 0.076 3 | 0.001 0 | 483.4 | 72.2 | 478.3 | 11.1 | 473.7 | 6.2 |
| 11 | 225 | 619 | 0.36 | 0.057 9 | 0.001 7 | 0.607 5 | 0.017 5 | 0.075 0 | 0.001 2 | 524.1 | 66.7 | 482.0 | 11.0 | 466.4 | 7.2 |
| 12(C) | 966 | 1 409 | 0.69 | 0.065 0 | 0.001 8 | 0.614 9 | 0.017 8 | 0.067 3 | 0.001 1 | 772.2 | 53.5 | 486.7 | 11.2 | 420.0 | 6.7 |
| 13 | 422 | 1 342 | 0.31 | 0.056 8 | 0.001 2 | 0.616 1 | 0.013 1 | 0.077 3 | 0.000 9 | 483.4 | 48.1 | 487.4 | 8.2 | 480.1 | 5.6 |
| 14 | 274 | 751 | 0.36 | 0.057 1 | 0.002 1 | 0.620 0 | 0.022 4 | 0.077 3 | 0.001 3 | 498.2 | 81.5 | 489.9 | 14.0 | 480.0 | 7.8 |
| 15 | 128 | 192 | 0.67 | 0.058 4 | 0.001 9 | 0.637 3 | 0.019 9 | 0.078 8 | 0.001 2 | 546.3 | 71.1 | 500.6 | 12.3 | 488.9 | 7.1 |
| 16 | 142 | 267 | 0.53 | 0.057 7 | 0.001 7 | 0.648 0 | 0.018 9 | 0.080 5 | 0.001 1 | 516.7 | 66.7 | 507.2 | 11.6 | 499.1 | 6.8 |
| 17 | 229 | 279 | 0.82 | 0.059 7 | 0.002 7 | 0.655 9 | 0.028 4 | 0.079 1 | 0.001 6 | 590.8 | 93.5 | 512.1 | 17.4 | 490.9 | 9.5 |
| 18(C) | 184 | 359 | 0.51 | 0.063 0 | 0.001 4 | 1.092 5 | 0.023 7 | 0.123 8 | 0.001 5 | 709.3 | 47.1 | 749.7 | 11.5 | 752.5 | 8.6 |
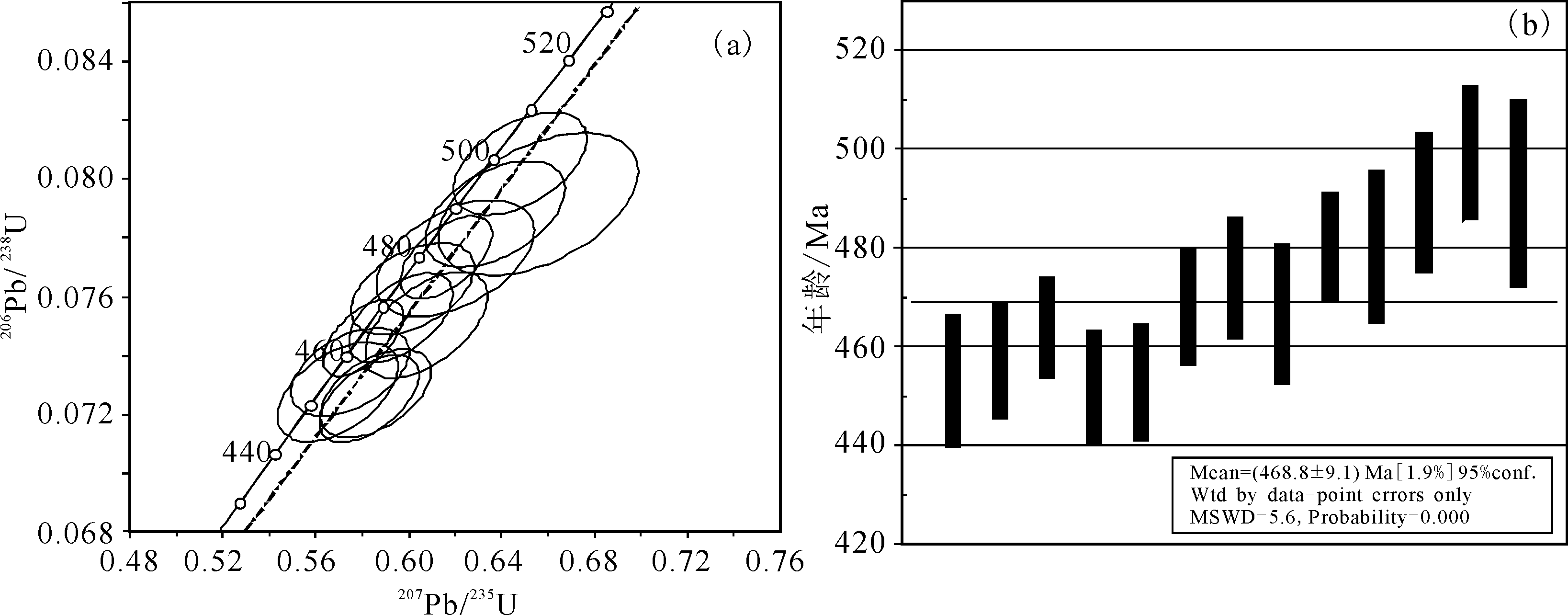
图9 样品DL-01流纹岩锆石207Pb/235U-206Pb/238U谐和曲线和加权平均年龄图
Fig.9 207Pb/235U-206Pb/238U concordia diagram and averaged age of zircon from the sample DL-01 of rhyolite
| [1] |
BADARCH G, CUNNINGHAM W D, WINDLEY B F. A new terrane subdivision for Mongolia:Implications for the Phanerozoic crustal growth of Central Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2002, 21(1):87-110.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
XIAO W J, ZHANG L C, QIN K Z, et al. Paleozoic accretionary and collisional tectonics of the eastern Tianshan (China):Implications for the continental growth of central Asia[J]. American Journal of Science, 2004, 304(4):370-395.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 刘亮, 何学锋, 李江涛, 等. 新疆东部哈尔里克沁城天生圈岩体岩石成因及其构造意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(2):86-96. |
| [4] | 马星华, 陈斌, 王超, 等. 早古生代古亚洲洋俯冲作用:来自新疆哈尔里克侵入岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学和Sr-Nd同位素证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(1):89-104. |
| [5] | 王赐银, 舒良树, 赵明, 等. 东天山北部哈尔里克晚古生代推覆构造与岩浆作用研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 1996, 2(2):198-206. |
| [6] | 李锦轶. 新疆东部新元古代晚期和古生代构造格局及其演变[J]. 地质论评, 2004, 50(3):304-322. |
| [7] | 张传恒, 刘典波, 张传林, 等. 新疆博格达山初始隆升时间的地层学标定[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(1):294-302. |
| [8] | 马瑞士, 王赐银, 叶尚夫. 东天山构造格架及地壳演化[M]. 南京: 南京大学出版社, 1993:1-225. |
| [9] | 赵明, 舒良树, 王赐银. 东疆哈尔里克变质带变质作用特征及形成构造环境研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 1997, 3(1):40-50. |
| [10] | 成守德, 张湘江. 新疆大地构造基本格架[J]. 新疆地质, 2000, 18(4):293-296. |
| [11] | 靳刘圆, 张济, 朱志新, 等. 哈尔里克山古生代火山岩地质特征及构造意义[J]. 新疆地质, 2013, 31(3):173-179. |
| [12] | 刘德权, 唐延龄, 周汝洪. 新疆北部古生代地壳演化及成矿系列[J]. 矿床地质, 1992, 11(4):307-314. |
| [13] | 王宗秀, 周高志, 李涛. 对新疆北部蛇绿岩及相关问题的思考和认识[J]. 岩石学报, 2003, 19(4):683-691. |
| [14] | 李文明, 任秉琛, 杨兴科, 等. 东天山中酸性侵入岩浆作用及其地球动力学意义[J]. 西北地质, 2002, 35(4):41-64. |
| [15] | 李锦轶, 何国琦, 徐新, 等. 新疆北部及邻区地壳构造格架及其形成过程的初步探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(1):148-168. |
| [16] | 孙桂华, 李锦轶, 朱志新, 等. 新疆东部哈尔里克山片麻状黑云母花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 新疆地质, 2007, 25(1):4-10. |
| [17] | 李锦轶, 王克卓, 孙桂华, 等. 东天山吐哈盆地南缘古生代活动陆缘残片:中亚地区古亚洲洋板块俯冲的地质记录[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(5):1087-1102. |
| [18] |
LE BAS M J, LE MAITRE R W, STRECKEISEN A. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali-silica diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1986, 27:745-750.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
WINCHESTER J A, FLOYD P A. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using im-mobile elements[J]. Chemical Geology, 1977, 20:325-343.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
BINNS R A, DUGGAN M B, WILKINSON J F G. High pressure megacrysts in alkaline lavas from Northeastern New South Wales[J]. American Journal of Science, 1970, 269:132-168.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
EWART A, COLLERSON K D, REGELOUS M, et al. Geochemical evolution within the Tonga-Kermadec-Lau arc-back-arcsystems:The role of varying mantle wedge composition in space and time[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1998, 39(3):331-368.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
IRVINE T N, BARAGAR W R A. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Science, 1971, 8:523-548.
DOI URL |
| [23] | 潘桂堂, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 等. 大地构造相的定义、划分、特征及其鉴别标志[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(10):1613-1637. |
| [24] | CULLERS R L, GRAF J L. Rare earth elements in igneous rocks of the continental crust:Intermediate and silicic rocks-ore petro-genesis[M]// HENDERSON P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam:Elsevier, 1984:273-308. |
| [25] | BOYNTON W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements:Meteorite studies[M]// HENDERSON P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam:Elsevier, 1984:63-114. |
| [26] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[M]// SAUNDERS A D, NORRY M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. London: Geological Society of London, 1989:313-345. |
| [27] | GILL J B. Orogenic Andesites and Plate Tectonic[M]. Berlin: Springer Verlag, 1981: 358. |
| [28] | PEARC E. Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries[M]// THORPE R S.Andesite. New York: John and Wiley Sons, 1982:525-548. |
| [29] |
SALTERS V T M, HART S R. The mantle sources of ocean ridges, island arcs:the Hf-isotope connection[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 104:364-380.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
CONDIE K C. Geochemical changes in basalts and andesites across the Archaean-Proterozoic boundary:Identification and significance[J]. Lithos, 1989, 23:1-18.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
ANDERSON T. Correction of Pb in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192:59-79.
DOI URL |
| [32] | LUDWIG K R. User’s Manual for Isoplot 3.00. A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Geochronology Center, 2003:1-10. |
| [33] |
KOSCHEK G. Origin and significance of the SEM cathodoluminescence from zircon[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 1993, 171(3):223-232.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 周济元, 茅燕石, 黄志勋, 等. 东天山古大陆边缘火山地质[M]. 成都: 成都科技大学出版社, 1994:1-90. |
| [35] | 曹福根, 涂其军, 张晓梅, 等. 哈尔里克山早古生代岩浆弧的初步确定——来自塔水河一带花岗质岩体锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年的证据[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(8):923-927. |
| [36] | MESCHEDE M. A method of discriminating between different types of mid-ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites with the Nb-Zr-Y diagram[J]. Chemical Geology, 1986, 56:275-282. |
| [37] |
WOOD D A. The application of a Th-Hf-Ta diagram to problems of tectonomagmatic Tertiary volcanic province[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1980, 50:11-30.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4):956-983.
DOI URL |
| [39] | 李曙光. εNd-La/Nb、Ba/Nb、Nb/Th图对地幔不均一性研究的意义——岛弧火山岩分类及EMII端元的分解[J]. 地球化学, 1994, 23(2):105-114. |
| [40] | 吴根耀, 邝国敦. 滇桂交界处古特提斯的洋岛和岛弧火山岩[J]. 现代地质, 2000, 14(4):393-400. |
| [41] |
KEPEZHINSKA S P, MCDERMOT T F, DEFANT M J. Trace element and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic constraints on a three-component model of Kamchatka arc petrogenesis[J]. Geochimica Cosmochimica, 1997, 61:577-600.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
WOODHEAD J D, HERGT J M, DAVIDISON J P, et al. Hafnium isotope evidence for “conservation” element mobility during subduction zone processes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 192:331-346.
DOI URL |
| [43] | HANYU T, TATSUMI Y, NAKAI S, et al. Contribution of slab melting and slab dehydration to magmatism in the NE Japan arc for the last 25 Myr:Constraints from geochemistry[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70:299. |
| [44] | 黄岗, 牛广智, 王新录, 等. 新疆东准噶尔早志留世弧岩浆岩:来自姜格尔库都克石英二长闪长岩岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素证据[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(6):1219-1233. |
| [45] |
PLANK T. Constraints from thorium/lanthanum on sediment recycling at subduction zones and the evolution of the continents[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2005, 46(5):921-944.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
YOGODZINSKI G M, KEY R W, VOLYNETS O N, et al. Magnesian andesite in the Western Aleutian Komandorsky Region:Implications for slab melting and processes in the mantle wedge[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1995, 107(5):505-519.
DOI URL |
| [47] | 胡霭琴, 章振根, 张积斌. 天山东段中天山隆起带前寒武纪变质岩系时代及演化——据U-Pb年代学研究[J]. 地球化学, 1986, 15(1):23-25. |
| [48] | 孙桂华, 李锦轶, 朱志新, 等. 新疆东部哈尔里克山南麓石炭纪砂岩碎屑锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2007, 34(5):778-789. |
| [49] | 郭华春, 钟莉, 李丽群. 新疆哈尔里克山口门子地区石英闪长岩年代研究及地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(8):928-931. |
| [1] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [2] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [3] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [4] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [5] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [6] | 梁鸣, 高文, 罗先熔, 王晓东, 刘秀娟, 陈皓, 刘攀峰, 竹峰, 李伟. 冀北高尖子地区土壤地球化学特征及其找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1567-1579. |
| [7] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [8] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [9] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [10] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [11] | 可行, 赵青芳, 吴飘, 杨传胜, 廖晶, 龚建明. 胶莱盆地东北部白垩系烃源岩特征与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1358-1368. |
| [12] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [13] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [14] | 王向伟, 张保涛, 杨浩强, 韩进国. 青海省海晏县团宝山一带变质岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 586-598. |
| [15] | 薛仲凯, 范堡程, 黄豪擎, 唐卫东, 葛战林, 李朋伟, 胡建辉, 杨晓奇, 郭永超, 李空. 内蒙古北山地区中基性岩脉年代学和地球化学特征:对塔里木板块北缘构造演化的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 627-644. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||