



现代地质 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (01): 20-32.
袁建国1,2( ), 顾玉超1,3(
), 顾玉超1,3( ), 肖荣阁1, 屈云燕2, 段凯波2, 韩玥4
), 肖荣阁1, 屈云燕2, 段凯波2, 韩玥4
收稿日期:2016-02-24
修回日期:2016-10-26
出版日期:2017-02-10
发布日期:2017-03-16
通讯作者:
顾玉超,男,工程师,1986年出生,区域成矿学专业,主要从事矿床学和岩石学方面的研究。Email:guyi1224@126.com。
作者简介:袁建国,男,博士研究生,1988年出生,区域成矿学专业,主要从事矿床学和岩石学方面的研究。Email:yuanjg0112@163.com。
基金资助:
YUAN Jianguo1,2( ), GU Yuchao1,3(
), GU Yuchao1,3( ), XIAO Rongge1, QU Yunyan2, DUAN Kaibo2, HAN Yue4
), XIAO Rongge1, QU Yunyan2, DUAN Kaibo2, HAN Yue4
Received:2016-02-24
Revised:2016-10-26
Online:2017-02-10
Published:2017-03-16
摘要:
通过对锡林浩特东部地区早白垩世花岗岩体进行SHRIMP锆石U-Pb测年、地球化学测试,讨论其形成构造环境。花岗岩测年结果为:正长花岗岩(DS214)(139.1±1.7) Ma,花岗岩(DS220)(134.7±1.7) Ma,表明研究区花岗岩形成于早白垩世早期。花岗岩地球化学具有高硅、富碱、相对低铝的特征,A/CNK平均值1.06,为弱过铝质花岗岩。微量元素相对富集大离子亲石元素(Th、U、K),明显亏损Nb、Ba、Sr、P、Ti等高场强元素;稀土总量高,为122.90×10-6~368.77×10-6,LREE/HREE值为5.71~14.36,呈右倾模式,负Eu异常显著(0.10~0.50),表现为A型花岗岩特征。K2O-Na2O构造环境判别图表明样品为A型花岗岩,Y/Nb-Ce/Nb图解显示花岗岩为A2型。主量元素、微量元素特征指示花岗岩形成于造山后岩石圈伸展作用阶段,在壳源岩浆演化过程中存在幔源物质混染作用。花岗岩成因可能是晚古生代末—中生代初期间古亚洲洋闭合引起的一系列板块碰撞作用(包括蒙古—鄂霍次克洋闭合),使造山后期地壳逐渐增厚并发生重力垮塌,导致构造环境由挤压转变为伸展,同时受古太平洋板块西向俯冲的影响。
中图分类号:
袁建国, 顾玉超, 肖荣阁, 屈云燕, 段凯波, 韩玥. 内蒙古锡林浩特东部地区早白垩世花岗岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(01): 20-32.
YUAN Jianguo, GU Yuchao, XIAO Rongge, QU Yunyan, DUAN Kaibo, HAN Yue. Geochemistry and Zircon U-Pb Dating of Granites in Early Cretaceous in Eastern Xilin Hot, Inner Mongolia and Its Geological Implications[J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(01): 20-32.

图1 内蒙古锡林浩特地区地质简图((a)据参考文献[12]修改;(b)据参考文献[18]修改) 1.新近系;2.白垩系;3.侏罗系—白垩系;4.二叠系;5.石炭系—二叠系;6.泥盆系;7.温都尔庙群;8.古元古界宝音图群(Pt1B);9.侏罗纪—白垩纪花岗岩(γJ-K);10.二叠纪花岗岩(γP); 11. 二叠纪闪长岩(δP);12. 超基性岩
Fig.1 Sketch geological map of Xilin Hot area in Inner Mongolia

图3 锡林浩特东部地区花岗岩锆石阴极发光(CL)图像及测试位置
Fig.3 Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of representative zircons and measuring position of the granites in eastern Xilin Hot
| 测点号 | 206Pbc/ 10-6 | U/ 10-6 | Th/ 10-6 | 206Pb*/ 10-6 | 232Th/ 238U | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb*/ 235U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS214-1-1.1 | 1.60 | 360 | 138 | 7.03 | 0.40 | 0.022 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.153 0 | 0.001 8 | 0.062 4 | 0.000 3 | 142.7 | 2.7 | 180 | 420 |
| DS214-1-2.1 | 2.29 | 303 | 115 | 5.55 | 0.39 | 0.020 8 | 0.000 3 | 0.143 0 | 0.003 1 | 0.068 2 | 0.001 3 | 132.5 | 3.4 | 194 | 710 |
| DS214-1-3.1 | 2.82 | 148 | 53 | 2.87 | 0.37 | 0.021 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.164 0 | 0.003 3 | 0.076 7 | 0.000 9 | 138.9 | 3.6 | 387 | 730 |
| DS214-1-4.1 | 3.24 | 384 | 179 | 7.50 | 0.48 | 0.022 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.112 0 | 0.003 0 | 0.063 2 | 0.000 3 | 142.4 | 3.0 | -554 | 810 |
| DS214-1-5.1 | 1.76 | 375 | 159 | 6.95 | 0.44 | 0.021 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.137 0 | 0.001 8 | 0.060 9 | 0.000 8 | 135.5 | 2.7 | 42 | 420 |
| DS214-1-6.1 | 1.89 | 162 | 81 | 3.05 | 0.51 | 0.021 5 | 0.000 3 | 0.195 0 | 0.002 5 | 0.080 3 | 0.000 5 | 134.5 | 3.1 | 794 | 530 |
| DS214-1-7.1 | 3.24 | 126 | 42 | 2.41 | 0.34 | 0.021 5 | 0.000 3 | 0.181 0 | 0.002 3 | 0.086 6 | 0.000 7 | 134.9 | 3.2 | 646 | 480 |
| DS214-1-8.1 | 0.58 | 242 | 131 | 4.65 | 0.56 | 0.022 3 | 0.000 2 | 0.190 0 | 0.001 7 | 0.066 5 | 0.000 4 | 139.6 | 2.8 | 670 | 370 |
| DS214-1-9.1 | 2.13 | 159 | 51 | 3.16 | 0.33 | 0.022 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.178 0 | 0.001 8 | 0.073 7 | 0.000 7 | 142.9 | 3.2 | 488 | 390 |
| DS214-1-10.1 | 3.05 | 302 | 148 | 5.75 | 0.50 | 0.021 5 | 0.000 3 | 0.127 0 | 0.002 9 | 0.067 2 | 0.000 8 | 137.9 | 3.1 | -182 | 710 |
| DS214-1-11.1 | 1.80 | 492 | 190 | 9.51 | 0.40 | 0.022 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.132 0 | 0.002 0 | 0.057 7 | 0.000 3 | 141.7 | 2.6 | -154 | 490 |
| DS214-1-12.1 | 2.61 | 341 | 133 | 6.63 | 0.40 | 0.022 0 | 0.000 2 | 0.122 0 | 0.002 6 | 0.061 1 | 0.000 3 | 141.9 | 2.7 | -341 | 660 |
| DS214-1-13.1 | 2.83 | 321 | 135 | 6.15 | 0.43 | 0.021 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.102 0 | 0.003 1 | 0.057 2 | 0.000 9 | 140.5 | 2.9 | -772 | 860 |
| DS214-1-14.1 | 1.83 | 434 | 167 | 8.02 | 0.40 | 0.021 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.122 0 | 0.002 0 | 0.056 5 | 0.000 4 | 135.9 | 2.6 | -234 | 500 |
| DS214-1-15.1 | 1.70 | 522 | 172 | 10.2 | 0.34 | 0.022 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.139 0 | 0.001 4 | 0.058 6 | 0.000 3 | 143.8 | 2.6 | -53 | 330 |
| DS220-1-3.1 | 0.08 | 2035 | 530 | 38.1 | 0.27 | 0.021 8 | 0.000 2 | 0.152 6 | 0.000 3 | 0.051 5 | 0.000 2 | 138.4 | 2.3 | 235 | 47 |
| DS220-1-5.1 | 0.53 | 442 | 173 | 8.09 | 0.40 | 0.021 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.168 0 | 0.000 8 | 0.061 5 | 0.000 6 | 133.8 | 2.5 | 506 | 170 |
| DS220-1-6.1 | - | 544 | 194 | 9.90 | 0.37 | 0.021 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.162 7 | 0.000 6 | 0.054 2 | 0.000 6 | 134.2 | 2.5 | 438 | 130 |
| DS220-1-8.1 | 2.03 | 364 | 104 | 6.62 | 0.29 | 0.020 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.136 0 | 0.001 3 | 0.063 9 | 0.000 3 | 132.5 | 2.5 | 86 | 300 |
| DS220-1-9.1 | 1.56 | 475 | 146 | 8.76 | 0.32 | 0.021 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.132 0 | 0.001 4 | 0.057 8 | 0.000 3 | 135.4 | 2.5 | -40 | 330 |
| DS220-1-13.1 | 1.49 | 487 | 124 | 8.96 | 0.26 | 0.021 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.138 0 | 0.001 3 | 0.059 4 | 0.000 4 | 134.9 | 2.5 | 75 | 310 |
| DS220-1-14.1 | 1.53 | 533 | 116 | 9.69 | 0.22 | 0.020 8 | 0.000 2 | 0.122 0 | 0.001 3 | 0.054 6 | 0.000 3 | 134.0 | 2.4 | -203 | 320 |
| DS220-1-15.1 | 2.56 | 804 | 346 | 14.8 | 0.45 | 0.020 9 | 0.000 2 | 0.167 0 | 0.001 5 | 0.078 3 | 0.000 8 | 131.5 | 2.5 | 534 | 320 |
| DS220-1-16.1 | 2.47 | 600 | 222 | 11.1 | 0.38 | 0.021 0 | 0.000 2 | 0.139 0 | 0.001 3 | 0.067 5 | 0.000 3 | 134.3 | 2.4 | 89 | 310 |
表1 锡林浩特东部地区花岗岩锆石U-Pb测年数据
Table 1 SHRIMP U-Pb dating of zircons in the granites in eastern Xilin Hot
| 测点号 | 206Pbc/ 10-6 | U/ 10-6 | Th/ 10-6 | 206Pb*/ 10-6 | 232Th/ 238U | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb*/ 235U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS214-1-1.1 | 1.60 | 360 | 138 | 7.03 | 0.40 | 0.022 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.153 0 | 0.001 8 | 0.062 4 | 0.000 3 | 142.7 | 2.7 | 180 | 420 |
| DS214-1-2.1 | 2.29 | 303 | 115 | 5.55 | 0.39 | 0.020 8 | 0.000 3 | 0.143 0 | 0.003 1 | 0.068 2 | 0.001 3 | 132.5 | 3.4 | 194 | 710 |
| DS214-1-3.1 | 2.82 | 148 | 53 | 2.87 | 0.37 | 0.021 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.164 0 | 0.003 3 | 0.076 7 | 0.000 9 | 138.9 | 3.6 | 387 | 730 |
| DS214-1-4.1 | 3.24 | 384 | 179 | 7.50 | 0.48 | 0.022 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.112 0 | 0.003 0 | 0.063 2 | 0.000 3 | 142.4 | 3.0 | -554 | 810 |
| DS214-1-5.1 | 1.76 | 375 | 159 | 6.95 | 0.44 | 0.021 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.137 0 | 0.001 8 | 0.060 9 | 0.000 8 | 135.5 | 2.7 | 42 | 420 |
| DS214-1-6.1 | 1.89 | 162 | 81 | 3.05 | 0.51 | 0.021 5 | 0.000 3 | 0.195 0 | 0.002 5 | 0.080 3 | 0.000 5 | 134.5 | 3.1 | 794 | 530 |
| DS214-1-7.1 | 3.24 | 126 | 42 | 2.41 | 0.34 | 0.021 5 | 0.000 3 | 0.181 0 | 0.002 3 | 0.086 6 | 0.000 7 | 134.9 | 3.2 | 646 | 480 |
| DS214-1-8.1 | 0.58 | 242 | 131 | 4.65 | 0.56 | 0.022 3 | 0.000 2 | 0.190 0 | 0.001 7 | 0.066 5 | 0.000 4 | 139.6 | 2.8 | 670 | 370 |
| DS214-1-9.1 | 2.13 | 159 | 51 | 3.16 | 0.33 | 0.022 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.178 0 | 0.001 8 | 0.073 7 | 0.000 7 | 142.9 | 3.2 | 488 | 390 |
| DS214-1-10.1 | 3.05 | 302 | 148 | 5.75 | 0.50 | 0.021 5 | 0.000 3 | 0.127 0 | 0.002 9 | 0.067 2 | 0.000 8 | 137.9 | 3.1 | -182 | 710 |
| DS214-1-11.1 | 1.80 | 492 | 190 | 9.51 | 0.40 | 0.022 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.132 0 | 0.002 0 | 0.057 7 | 0.000 3 | 141.7 | 2.6 | -154 | 490 |
| DS214-1-12.1 | 2.61 | 341 | 133 | 6.63 | 0.40 | 0.022 0 | 0.000 2 | 0.122 0 | 0.002 6 | 0.061 1 | 0.000 3 | 141.9 | 2.7 | -341 | 660 |
| DS214-1-13.1 | 2.83 | 321 | 135 | 6.15 | 0.43 | 0.021 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.102 0 | 0.003 1 | 0.057 2 | 0.000 9 | 140.5 | 2.9 | -772 | 860 |
| DS214-1-14.1 | 1.83 | 434 | 167 | 8.02 | 0.40 | 0.021 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.122 0 | 0.002 0 | 0.056 5 | 0.000 4 | 135.9 | 2.6 | -234 | 500 |
| DS214-1-15.1 | 1.70 | 522 | 172 | 10.2 | 0.34 | 0.022 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.139 0 | 0.001 4 | 0.058 6 | 0.000 3 | 143.8 | 2.6 | -53 | 330 |
| DS220-1-3.1 | 0.08 | 2035 | 530 | 38.1 | 0.27 | 0.021 8 | 0.000 2 | 0.152 6 | 0.000 3 | 0.051 5 | 0.000 2 | 138.4 | 2.3 | 235 | 47 |
| DS220-1-5.1 | 0.53 | 442 | 173 | 8.09 | 0.40 | 0.021 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.168 0 | 0.000 8 | 0.061 5 | 0.000 6 | 133.8 | 2.5 | 506 | 170 |
| DS220-1-6.1 | - | 544 | 194 | 9.90 | 0.37 | 0.021 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.162 7 | 0.000 6 | 0.054 2 | 0.000 6 | 134.2 | 2.5 | 438 | 130 |
| DS220-1-8.1 | 2.03 | 364 | 104 | 6.62 | 0.29 | 0.020 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.136 0 | 0.001 3 | 0.063 9 | 0.000 3 | 132.5 | 2.5 | 86 | 300 |
| DS220-1-9.1 | 1.56 | 475 | 146 | 8.76 | 0.32 | 0.021 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.132 0 | 0.001 4 | 0.057 8 | 0.000 3 | 135.4 | 2.5 | -40 | 330 |
| DS220-1-13.1 | 1.49 | 487 | 124 | 8.96 | 0.26 | 0.021 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.138 0 | 0.001 3 | 0.059 4 | 0.000 4 | 134.9 | 2.5 | 75 | 310 |
| DS220-1-14.1 | 1.53 | 533 | 116 | 9.69 | 0.22 | 0.020 8 | 0.000 2 | 0.122 0 | 0.001 3 | 0.054 6 | 0.000 3 | 134.0 | 2.4 | -203 | 320 |
| DS220-1-15.1 | 2.56 | 804 | 346 | 14.8 | 0.45 | 0.020 9 | 0.000 2 | 0.167 0 | 0.001 5 | 0.078 3 | 0.000 8 | 131.5 | 2.5 | 534 | 320 |
| DS220-1-16.1 | 2.47 | 600 | 222 | 11.1 | 0.38 | 0.021 0 | 0.000 2 | 0.139 0 | 0.001 3 | 0.067 5 | 0.000 3 | 134.3 | 2.4 | 89 | 310 |
| 岩性 | 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | K2O | Na2O | P2O5 | 烧失 量 | 总 量 | A/ CNK | KN/ A | K2O/ Na2O | K2O+ Na2O | AR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正长花岗岩 | DS214-1-1 | 71.83 | 0.29 | 14.08 | 2.80 | 0.72 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.23 | 5.29 | 3.81 | 0.08 | 1.07 | 100.480 | 1.12 | 0.86 | 1.39 | 9.11 | 3.28 |
| 正长花岗岩 | DS214-1-2 | 71.16 | 0.31 | 13.91 | 3.69 | 1.08 | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.36 | 5.15 | 3.87 | 0.09 | 1.05 | 100.930 | 1.10 | 0.87 | 1.33 | 9.03 | 3.37 |
| 花岗岩 | DS220-1-1 | 70.78 | 0.26 | 14.35 | 2.96 | 2.02 | 0.05 | 0.32 | 1.34 | 4.69 | 4.31 | 0.07 | 0.72 | 101.870 | 0.98 | 0.86 | 1.09 | 9.00 | 3.43 |
| 花岗岩 | DS220-1-2 | 70.89 | 0.28 | 14.49 | 2.95 | 2.20 | 0.05 | 0.35 | 1.19 | 4.59 | 4.14 | 0.07 | 0.69 | 101.890 | 1.03 | 0.82 | 1.11 | 8.74 | 3.24 |
| 花岗斑岩 | P4YQ01 | 72.32 | 0.45 | 13.00 | 2.07 | 1.41 | 0.063 | 0.46 | 1.17 | 4.78 | 2.83 | 0.14 | 1.03 | 99.723 | 1.08 | 0.76 | 1.69 | 7.61 | 2.33 |
| 花岗斑岩 | P4YQ12 | 70.69 | 0.46 | 13.58 | 2.16 | 1.46 | 0.069 | 0.64 | 1.75 | 4.13 | 3.41 | 0.36 | 1.21 | 99.919 | 1.02 | 0.75 | 1.21 | 7.54 | 2.60 |
| 花岗斑岩 | P5YQ06 | 69.96 | 0.52 | 12.73 | 2.01 | 1.77 | 0.11 | 0.59 | 1.85 | 4.28 | 2.72 | 0.61 | 2.37 | 99.520 | 1.02 | 0.72 | 1.57 | 7.00 | 2.19 |
| 花岗斑岩 | P5YQ07 | 71.21 | 0.39 | 13.52 | 2.08 | 1.29 | 0.062 | 0.35 | 1.18 | 5.20 | 2.97 | 0.23 | 1.23 | 99.712 | 1.06 | 0.78 | 1.75 | 8.17 | 2.36 |
| 花岗斑岩 | P3YQ1 | 75.87 | 0.1 | 11.89 | 1.41 | 1.47 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.32 | 4.73 | 3.4 | 0.04 | 0.60 | 99.960 | 1.04 | 0.91 | 1.39 | 8.13 | 3.51 |
| 花岗斑岩 | P3YQ2 | 75.49 | 0.12 | 12.21 | 1.53 | 1.06 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.28 | 4.60 | 3.7 | 0.04 | 0.75 | 99.930 | 1.05 | 0.91 | 1.24 | 8.30 | 3.91 |
| 花岗斑岩 | P3YQ3 | 75.96 | 0.08 | 12.00 | 1.37 | 0.84 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.29 | 4.68 | 3.4 | 0.04 | 1.18 | 100.030 | 1.06 | 0.90 | 1.38 | 8.08 | 3.48 |
| 花岗斑岩 | P10YQ1 | 75.48 | 0.02 | 12.38 | 1.77 | 0.57 | 0.02 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 4.70 | 2.83 | 0.07 | 1.38 | 99.810 | 1.19 | 0.79 | 1.66 | 7.53 | 2.60 |
| 平均值 | 72.34 | 0.29 | 13.30 | 2.31 | 1.31 | 0.05 | 0.34 | 0.91 | 4.74 | 3.45 | 0.16 | 1.15 | 100.34 | 1.06 | 0.82 | 1.40 | 8.19 | 1.22 | |
表2 锡林浩特东部地区花岗岩主量元素化学分析结果(wB/%)
Table 2 Petrochemical analysis and characteristic parameters of granites in eastern Xilin Hot(%)
| 岩性 | 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | K2O | Na2O | P2O5 | 烧失 量 | 总 量 | A/ CNK | KN/ A | K2O/ Na2O | K2O+ Na2O | AR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正长花岗岩 | DS214-1-1 | 71.83 | 0.29 | 14.08 | 2.80 | 0.72 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.23 | 5.29 | 3.81 | 0.08 | 1.07 | 100.480 | 1.12 | 0.86 | 1.39 | 9.11 | 3.28 |
| 正长花岗岩 | DS214-1-2 | 71.16 | 0.31 | 13.91 | 3.69 | 1.08 | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.36 | 5.15 | 3.87 | 0.09 | 1.05 | 100.930 | 1.10 | 0.87 | 1.33 | 9.03 | 3.37 |
| 花岗岩 | DS220-1-1 | 70.78 | 0.26 | 14.35 | 2.96 | 2.02 | 0.05 | 0.32 | 1.34 | 4.69 | 4.31 | 0.07 | 0.72 | 101.870 | 0.98 | 0.86 | 1.09 | 9.00 | 3.43 |
| 花岗岩 | DS220-1-2 | 70.89 | 0.28 | 14.49 | 2.95 | 2.20 | 0.05 | 0.35 | 1.19 | 4.59 | 4.14 | 0.07 | 0.69 | 101.890 | 1.03 | 0.82 | 1.11 | 8.74 | 3.24 |
| 花岗斑岩 | P4YQ01 | 72.32 | 0.45 | 13.00 | 2.07 | 1.41 | 0.063 | 0.46 | 1.17 | 4.78 | 2.83 | 0.14 | 1.03 | 99.723 | 1.08 | 0.76 | 1.69 | 7.61 | 2.33 |
| 花岗斑岩 | P4YQ12 | 70.69 | 0.46 | 13.58 | 2.16 | 1.46 | 0.069 | 0.64 | 1.75 | 4.13 | 3.41 | 0.36 | 1.21 | 99.919 | 1.02 | 0.75 | 1.21 | 7.54 | 2.60 |
| 花岗斑岩 | P5YQ06 | 69.96 | 0.52 | 12.73 | 2.01 | 1.77 | 0.11 | 0.59 | 1.85 | 4.28 | 2.72 | 0.61 | 2.37 | 99.520 | 1.02 | 0.72 | 1.57 | 7.00 | 2.19 |
| 花岗斑岩 | P5YQ07 | 71.21 | 0.39 | 13.52 | 2.08 | 1.29 | 0.062 | 0.35 | 1.18 | 5.20 | 2.97 | 0.23 | 1.23 | 99.712 | 1.06 | 0.78 | 1.75 | 8.17 | 2.36 |
| 花岗斑岩 | P3YQ1 | 75.87 | 0.1 | 11.89 | 1.41 | 1.47 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.32 | 4.73 | 3.4 | 0.04 | 0.60 | 99.960 | 1.04 | 0.91 | 1.39 | 8.13 | 3.51 |
| 花岗斑岩 | P3YQ2 | 75.49 | 0.12 | 12.21 | 1.53 | 1.06 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.28 | 4.60 | 3.7 | 0.04 | 0.75 | 99.930 | 1.05 | 0.91 | 1.24 | 8.30 | 3.91 |
| 花岗斑岩 | P3YQ3 | 75.96 | 0.08 | 12.00 | 1.37 | 0.84 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.29 | 4.68 | 3.4 | 0.04 | 1.18 | 100.030 | 1.06 | 0.90 | 1.38 | 8.08 | 3.48 |
| 花岗斑岩 | P10YQ1 | 75.48 | 0.02 | 12.38 | 1.77 | 0.57 | 0.02 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 4.70 | 2.83 | 0.07 | 1.38 | 99.810 | 1.19 | 0.79 | 1.66 | 7.53 | 2.60 |
| 平均值 | 72.34 | 0.29 | 13.30 | 2.31 | 1.31 | 0.05 | 0.34 | 0.91 | 4.74 | 3.45 | 0.16 | 1.15 | 100.34 | 1.06 | 0.82 | 1.40 | 8.19 | 1.22 | |

图5 岩浆岩-火山岩系统全碱-硅(TAS)(a)、A/CNK-KN/A(b)和K2O-SiO2图解(c)
Fig.5 TAS classification of igneous or volcanic rock system(a), A/CNK-KN/A(b) and K2O-SiO2 (c)diagrams
| 样号 | 岩性 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS214-1-1 | 正长花岗岩 | 22.45 | 92.93 | 5.74 | 22.50 | 4.96 | 0.82 | 4.84 | 0.87 | 5.56 | 1.22 | 3.37 |
| DS214-1-2 | 正长花岗岩 | 51.57 | 125.80 | 13.21 | 51.82 | 10.84 | 1.17 | 9.56 | 1.54 | 8.78 | 1.83 | 4.79 |
| DS220-1-1 | 花岗岩 | 54.55 | 110.70 | 11.41 | 40.95 | 6.89 | 1.05 | 6.13 | 0.80 | 4.23 | 0.85 | 2.35 |
| DS220-1-2 | 花岗岩 | 59.81 | 125.10 | 12.27 | 43.56 | 6.99 | 1.08 | 6.39 | 0.79 | 3.96 | 0.81 | 2.20 |
| P4XT02 | 花岗斑岩 | 81.20 | 147.00 | 17.90 | 65.80 | 11.20 | 1.28 | 9.46 | 1.34 | 6.48 | 1.19 | 3.2 |
| P4XT11 | 花岗斑岩 | 71.00 | 152.00 | 17.10 | 63.40 | 10.90 | 1.17 | 9.18 | 1.39 | 6.98 | 1.32 | 3.61 |
| P4XT12 | 花岗斑岩 | 83.10 | 158.00 | 18.40 | 68.20 | 11.60 | 1.12 | 9.82 | 1.46 | 7.40 | 1.40 | 3.81 |
| P3YQ1 | 花岗斑岩 | 40.20 | 77.80 | 10.60 | 47.90 | 10.20 | 0.31 | 7.26 | 1.17 | 6.71 | 1.19 | 3.47 |
| P3YQ2 | 花岗斑岩 | 43.80 | 99.68 | 11.00 | 47.70 | 9.80 | 0.41 | 7.42 | 1.25 | 7.64 | 1.42 | 4.21 |
| P10YQ1 | 花岗斑岩 | 27.70 | 42.00 | 6.39 | 23.70 | 3.92 | 0.88 | 2.84 | 0.86 | 4.94 | 1.47 | 2.99 |
| 样号 | 岩性 | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | δEu | δCe |
| DS214-1-1 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.65 | 3.78 | 0.52 | 32.05 | 170.21 | 149.39 | 20.82 | 7.17 | 4.26 | 0.50 | 1.96 |
| DS214-1-2 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.87 | 4.96 | 0.69 | 49.28 | 287.42 | 254.41 | 33.01 | 7.71 | 7.46 | 0.34 | 1.15 |
| DS220-1-1 | 花岗岩 | 0.44 | 2.61 | 0.37 | 23.87 | 243.32 | 225.54 | 17.78 | 12.69 | 14.97 | 0.48 | 1.03 |
| DS220-1-2 | 花岗岩 | 0.41 | 2.44 | 0.34 | 22.17 | 266.12 | 248.80 | 17.33 | 14.36 | 17.59 | 0.49 | 1.07 |
| P4XT02 | 花岗斑岩 | 0.44 | 2.74 | 0.47 | 30.40 | 349.70 | 324.38 | 25.32 | 12.81 | 21.26 | 0.37 | 0.90 |
| P4XT11 | 花岗斑岩 | 0.52 | 3.13 | 0.54 | 33.20 | 342.24 | 315.57 | 26.67 | 11.83 | 16.27 | 0.35 | 1.04 |
| P4XT12 | 花岗斑岩 | 0.55 | 3.34 | 0.57 | 37.90 | 368.77 | 340.42 | 28.35 | 12.01 | 17.85 | 0.31 | 0.95 |
| P3YQ1 | 花岗斑岩 | 1.08 | 3.78 | 0.87 | 25.90 | 212.54 | 187.01 | 25.53 | 7.33 | 7.63 | 0.10 | 0.90 |
| P3YQ2 | 花岗斑岩 | 1.16 | 4.73 | 1.05 | 32.90 | 241.27 | 212.39 | 28.88 | 7.35 | 6.64 | 0.14 | 1.08 |
| P10YQ1 | 花岗斑岩 | 0.82 | 3.67 | 0.72 | 20.50 | 122.90 | 104.59 | 18.31 | 5.71 | 5.41 | 0.77 | 0.75 |
表3 锡林浩特东部地区花岗岩稀土元素含量及参数(wB/10-6)
Table 3 Rare earth element abundance and characteristic parameters of granites in eastern Xilin Hot(10-6)
| 样号 | 岩性 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS214-1-1 | 正长花岗岩 | 22.45 | 92.93 | 5.74 | 22.50 | 4.96 | 0.82 | 4.84 | 0.87 | 5.56 | 1.22 | 3.37 |
| DS214-1-2 | 正长花岗岩 | 51.57 | 125.80 | 13.21 | 51.82 | 10.84 | 1.17 | 9.56 | 1.54 | 8.78 | 1.83 | 4.79 |
| DS220-1-1 | 花岗岩 | 54.55 | 110.70 | 11.41 | 40.95 | 6.89 | 1.05 | 6.13 | 0.80 | 4.23 | 0.85 | 2.35 |
| DS220-1-2 | 花岗岩 | 59.81 | 125.10 | 12.27 | 43.56 | 6.99 | 1.08 | 6.39 | 0.79 | 3.96 | 0.81 | 2.20 |
| P4XT02 | 花岗斑岩 | 81.20 | 147.00 | 17.90 | 65.80 | 11.20 | 1.28 | 9.46 | 1.34 | 6.48 | 1.19 | 3.2 |
| P4XT11 | 花岗斑岩 | 71.00 | 152.00 | 17.10 | 63.40 | 10.90 | 1.17 | 9.18 | 1.39 | 6.98 | 1.32 | 3.61 |
| P4XT12 | 花岗斑岩 | 83.10 | 158.00 | 18.40 | 68.20 | 11.60 | 1.12 | 9.82 | 1.46 | 7.40 | 1.40 | 3.81 |
| P3YQ1 | 花岗斑岩 | 40.20 | 77.80 | 10.60 | 47.90 | 10.20 | 0.31 | 7.26 | 1.17 | 6.71 | 1.19 | 3.47 |
| P3YQ2 | 花岗斑岩 | 43.80 | 99.68 | 11.00 | 47.70 | 9.80 | 0.41 | 7.42 | 1.25 | 7.64 | 1.42 | 4.21 |
| P10YQ1 | 花岗斑岩 | 27.70 | 42.00 | 6.39 | 23.70 | 3.92 | 0.88 | 2.84 | 0.86 | 4.94 | 1.47 | 2.99 |
| 样号 | 岩性 | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | δEu | δCe |
| DS214-1-1 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.65 | 3.78 | 0.52 | 32.05 | 170.21 | 149.39 | 20.82 | 7.17 | 4.26 | 0.50 | 1.96 |
| DS214-1-2 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.87 | 4.96 | 0.69 | 49.28 | 287.42 | 254.41 | 33.01 | 7.71 | 7.46 | 0.34 | 1.15 |
| DS220-1-1 | 花岗岩 | 0.44 | 2.61 | 0.37 | 23.87 | 243.32 | 225.54 | 17.78 | 12.69 | 14.97 | 0.48 | 1.03 |
| DS220-1-2 | 花岗岩 | 0.41 | 2.44 | 0.34 | 22.17 | 266.12 | 248.80 | 17.33 | 14.36 | 17.59 | 0.49 | 1.07 |
| P4XT02 | 花岗斑岩 | 0.44 | 2.74 | 0.47 | 30.40 | 349.70 | 324.38 | 25.32 | 12.81 | 21.26 | 0.37 | 0.90 |
| P4XT11 | 花岗斑岩 | 0.52 | 3.13 | 0.54 | 33.20 | 342.24 | 315.57 | 26.67 | 11.83 | 16.27 | 0.35 | 1.04 |
| P4XT12 | 花岗斑岩 | 0.55 | 3.34 | 0.57 | 37.90 | 368.77 | 340.42 | 28.35 | 12.01 | 17.85 | 0.31 | 0.95 |
| P3YQ1 | 花岗斑岩 | 1.08 | 3.78 | 0.87 | 25.90 | 212.54 | 187.01 | 25.53 | 7.33 | 7.63 | 0.10 | 0.90 |
| P3YQ2 | 花岗斑岩 | 1.16 | 4.73 | 1.05 | 32.90 | 241.27 | 212.39 | 28.88 | 7.35 | 6.64 | 0.14 | 1.08 |
| P10YQ1 | 花岗斑岩 | 0.82 | 3.67 | 0.72 | 20.50 | 122.90 | 104.59 | 18.31 | 5.71 | 5.41 | 0.77 | 0.75 |
| 样号 | 岩性 | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Ta | Nb | Sr | Nd | Zr | Hf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS214-1-1 | 正长花岗岩 | 23.19 | 104.39 | 13.56 | 3.11 | 26.045 | 5.64 | 178.53 | 22.50 | 17.00 | 0.68 |
| DS214-1-2 | 正长花岗岩 | 23.84 | 105.19 | 16.08 | 4.49 | 32.290 | 6.42 | 177.11 | 51.82 | 18.32 | 0.35 |
| DS220-1-1 | 花岗岩 | 20.12 | 216.81 | 14.39 | 3.99 | 36.460 | 6.50 | 175.67 | 40.95 | 9.84 | 0.90 |
| DS220-1-2 | 花岗岩 | 20.34 | 225.70 | 13.41 | 3.83 | 34.930 | 6.51 | 170.50 | 43.56 | 9.43 | 0.55 |
| P3YQ1 | 花岗斑岩 | 340.00 | 183.00 | 27.20 | 2.33 | 2.310 | 25.20 | 55.50 | 47.90 | 187.00 | 6.50 |
| P3YQ2 | 花岗斑岩 | 299.00 | 164.00 | 24.50 | 2.26 | 1.760 | 20.70 | 37.40 | 47.70 | 167.00 | 6.20 |
| P10YQ1 | 花岗斑岩 | 227.00 | 253.00 | 20.46 | 0.36 | 1.550 | 10.70 | 51.60 | 23.70 | 191.00 | 6.30 |
表4 锡林浩特东部地区花岗岩微量元素分析结果(wB/10-6)
Table 4 Trace elements abundance of granites in eastern Xilin Hot(10-6)
| 样号 | 岩性 | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Ta | Nb | Sr | Nd | Zr | Hf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS214-1-1 | 正长花岗岩 | 23.19 | 104.39 | 13.56 | 3.11 | 26.045 | 5.64 | 178.53 | 22.50 | 17.00 | 0.68 |
| DS214-1-2 | 正长花岗岩 | 23.84 | 105.19 | 16.08 | 4.49 | 32.290 | 6.42 | 177.11 | 51.82 | 18.32 | 0.35 |
| DS220-1-1 | 花岗岩 | 20.12 | 216.81 | 14.39 | 3.99 | 36.460 | 6.50 | 175.67 | 40.95 | 9.84 | 0.90 |
| DS220-1-2 | 花岗岩 | 20.34 | 225.70 | 13.41 | 3.83 | 34.930 | 6.51 | 170.50 | 43.56 | 9.43 | 0.55 |
| P3YQ1 | 花岗斑岩 | 340.00 | 183.00 | 27.20 | 2.33 | 2.310 | 25.20 | 55.50 | 47.90 | 187.00 | 6.50 |
| P3YQ2 | 花岗斑岩 | 299.00 | 164.00 | 24.50 | 2.26 | 1.760 | 20.70 | 37.40 | 47.70 | 167.00 | 6.20 |
| P10YQ1 | 花岗斑岩 | 227.00 | 253.00 | 20.46 | 0.36 | 1.550 | 10.70 | 51.60 | 23.70 | 191.00 | 6.30 |
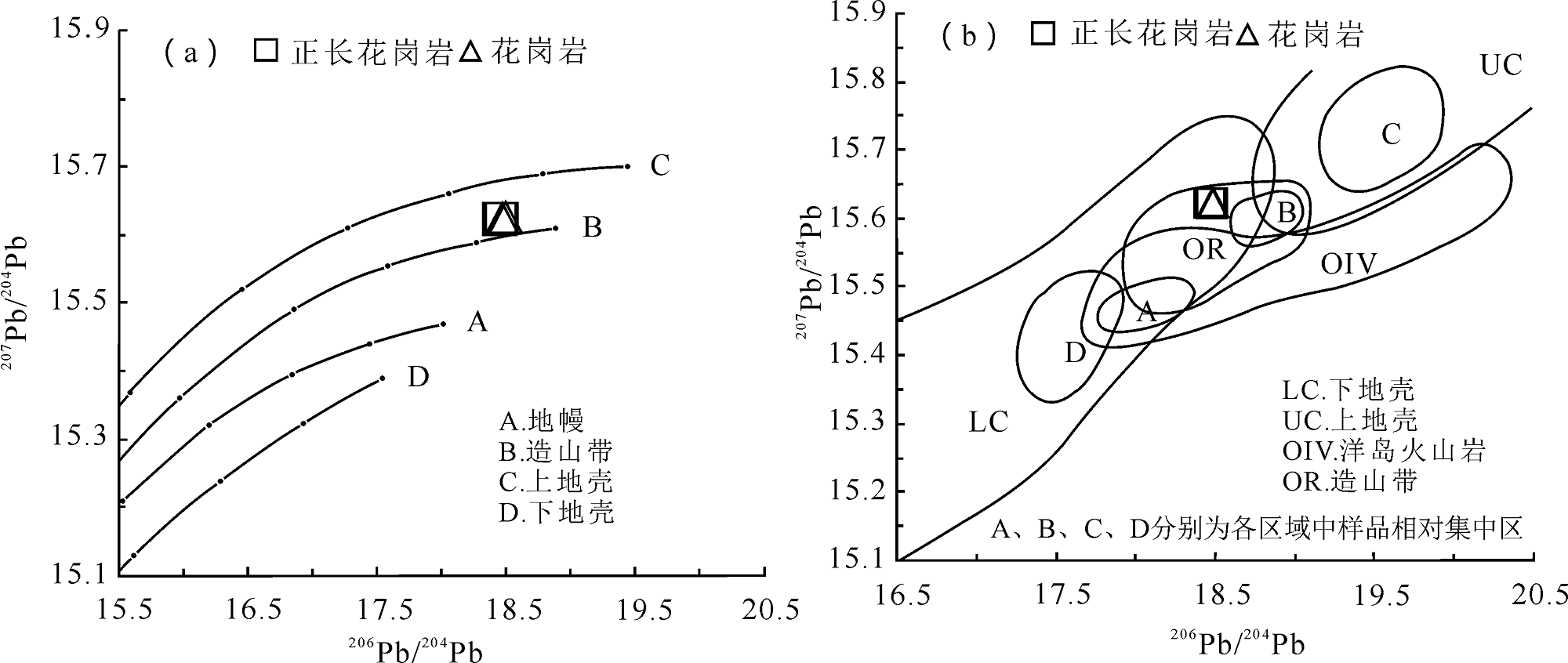
图8 铅同位素模式(a)和构造判别图(b)(底图据Zartman R E和Doe B R,1981)
Fig.8 Diagrams for lead isotope pattern(a) and tectonic environments(b) (base map after Zartman R E and Doe B R, 1981)

图9 锡林浩特东部地区花岗岩岩浆来源及构造环境判别图 (a) 岩石系列K2O-Na2O构造环境判别图解;(b)不同构造环境中A型花岗岩的Y/Nb-Ce/Nb图;(c)花岗岩Nb-Y-Ce构造环境判别图;(d)SiO2-Al2O3构造环境判别图解;(e) Y-Nb构造环境判别图;(f)R1-R2花岗岩成因分类图解
Fig.9 Discrimination diagrams for the source and tectonic environments of granites in eastern Xilin Hot
| [1] | 施光海, 苗来成, 张福勤, 等. 内蒙古锡林浩特A型花岗岩的时代及区域构造意义[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(4): 384-389. |
| [2] | 刘建峰, 迟效国, 张兴洲, 等. 内蒙古西乌旗南部石炭纪石英闪长岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(3): 365-376. |
| [3] | 陈斌, 马星华, 刘安坤, 等. 锡林浩特杂岩和蓝片岩的锆石U-Pb年代学及其对索仑缝合带演化的意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(12): 3123-3129. |
| [4] | 王新宇, 侯青叶, 王瑾, 等. 内蒙古维拉斯托矿床花岗岩类SHRIMP年代学及Hf同位素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(1): 67-78. |
| [5] | 刘翠, 邓晋福, 许立权, 等. 大兴安岭-小兴安岭地区中生代岩浆-构造-钼成矿地质事件序列的初步框架[J]. 地学前缘, 2011, 18(3): 166-178. |
| [6] | 罗飞, 罗照华, 李达靖, 等. 内蒙古中部白垩纪碱性花岗岩的发现及意义[J]. 现代地质, 1995, 9(2): 203-211. |
| [7] | 罗照华, 邓晋福, 罗飞, 等. 内蒙古中部深成侵入岩谱系单位及构造岩浆活动初探──以苏尼特左旗等8幅1∶5万区域地质调查为例[J]. 现代地质, 1995, 9(2): 189-202. |
| [8] | 李可, 张志诚, 李建锋, 等. 内蒙古西乌珠穆沁旗地区中生代中酸性火山岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(5): 671-685. |
| [9] | 周振华, 吕林素, 杨永军, 等. 内蒙古黄岗锡铁矿区早白垩世A型花岗岩成因:锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(12): 3521-3537. |
| [10] | 毛景文, 谢桂青, 张作衡, 等. 中国北方中生代大规模成矿作用的期次及其地球动力学背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(1): 171-190. |
| [11] | 李忠, 刘少峰, 张金芳, 等. 燕山典型盆地充填序列及迁移特征:对中生代构造转折的响应[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2003, 33(10): 931-940. |
| [12] | 张克信, 潘桂棠, 何卫红, 等. 中国构造-地层大区划分新方案[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(2):206-233. |
| [13] | 潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 等. 中国大地构造单元划分[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(1): 1-28. |
| [14] | 徐备, 刘树文, 王长秋, 等. 内蒙古西北部宝音图群Sm-Nd和Rb-Sr地质年代学研究[J]. 地质论评, 2000, 46(1): 86-90. |
| [15] | 杜理科, 葛梦春. 内蒙古锡林浩特宝音图群斜长角闪岩原岩恢复的地球化学示踪[J]. 新疆地质, 2010, 28(2): 200-203. |
| [16] | 孙立新, 赵凤清, 王惠初, 等. 内蒙古狼山地区宝音图地块变质基底的锆石U-Pb年龄及构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(2): 197-207. |
| [17] | 李承东, 冉皞, 赵利刚, 等. 温都尔庙群锆石的LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb年龄及构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(11): 3706-3714. |
| [18] | 孙立新, 任邦方, 赵凤清, 等. 内蒙古锡林浩特地块中元古代花岗片麻岩的锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素特征[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(2/3): 327-340. |
| [19] | 宋彪. 用SHRIMP测定锆石U-Pb年龄的工作方法[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(10): 1777-1788. |
| [20] | 蔡剑辉, 阎国翰, 许保良, 等. 太行山-大兴安岭东麓晚中生代碱性侵入岩岩石地球化学特征及其意义[J]. 地球学报, 2006, 27(5): 447-459. |
| [21] | CHAPPELLl B W, WHITEA J R. I-and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt[J]. Earth & Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 1992, 83: 1-26. |
| [22] | 刘伟, 潘小菲, 谢烈文, 等. 大兴安岭南段林西地区花岗岩类的源岩:地壳生长的时代和方式[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(2): 441-460. |
| [23] | 杨增海, 王建平, 刘家军, 等. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗乌日尼图钨钼矿床同位素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(1): 13-23. |
| [24] | 肖荣阁, 费红彩, 王安建, 等. 白云鄂博含矿碱性火山岩建造及其地球化学[J]. 地质学报, 2012, 86(5): 735-752. |
| [25] | 杨德彬, 许文良, 裴福萍, 等. 蚌埠隆起区古元古代钾长花岗岩的成因:岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学与Hf同位素的制约[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2009, 34(1): 148-164. |
| [26] | 张旗, 冉皞, 李承东. A型花岗岩的实质是什么?[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 31(4): 621-626. |
| [27] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6): 1217-1238. |
| [28] | 覃锋, 刘建明, 曾庆栋, 等. 内蒙古小东沟斑岩型钼矿床的成矿时代及成矿物质来源[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(2): 173-180. |
| [29] | 朱伟. 内蒙古克什克腾旗晚中生代花岗岩地质特征及其构造意义[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2011: 1-84. |
| [30] | 杨帆, 肖荣阁, 李娜, 等. 内蒙古宝音图钼矿床花岗岩稀土元素地球化学特征及花岗岩成因[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(4): 831-840. |
| [31] | 赵云, 王建平, 杨增海, 等. 内蒙古白乃庙铜矿床稳定同位素地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(6): 1103-1111. |
| [32] | 张晓静, 张连昌, 靳新娣, 等. 内蒙古半砬山钼矿含矿斑岩U-Pb年龄和地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(5): 1411-1422. |
| [33] | 葛文春, 林强, 孙德有, 等. 大兴安岭中生代两类流纹岩成因的地球化学研究[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2000, 25(2): 172-178. |
| [34] | 邵济安, 刘福田, 陈辉, 等. 大兴安岭-燕山晚中生代岩浆活动与俯冲作用关系[J]. 地质学报, 2001, 75(1): 56-63. |
| [35] | 张连昌, 吴华英, 相鹏, 等. 中生代复杂构造体系的成矿过程与成矿作用——以华北大陆北缘西拉木伦钼铜多金属成矿带为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(5): 1351-1362. |
| [36] | 孔维琼, 刘翠, 邓晋福, 等. 内蒙古二连浩特地区乌花敖包钼矿区石英斑岩的锆石U-Pb年代学特征及对钼成矿时代的约束[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 19(5): 123-135. |
| [37] | 孙成杰. 内蒙古巴林右旗查干沐沦花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄经济学院, 2012:1-49. |
| [38] | 张学斌, 周长红, 来林, 等. 锡林浩特东部早白垩世白音高老组岩石地球化学特征、LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2015, 51(2): 290-302. |
| [39] | 程天赦, 杨文静, 王登红, 等. 内蒙古锡林浩特毛登牧场大石寨组细碧-角斑岩系地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(3): 525-536. |
| [40] | 张旗, 王焰, 潘国强, 等. 花岗岩源岩问题——关于花岗岩研究的思考之四[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(6): 1193-1204. |
| [41] | 陈志广, 张连昌, 吴华英, 等. 内蒙古西拉木伦成矿带碾子沟钼矿区A型花岗岩地球化学和构造背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(4): 879-889. |
| [42] |
GREEN T H. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(s 3/4): 347-359.
DOI URL |
| [43] | 张旗, 潘国强, 李承东, 等. 花岗岩结晶分离作用问题——关于花岗岩研究的思考之二[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6): 1239-1251. |
| [44] |
PEARCE J A, HARRISN B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
EBY G N. The A-type granitoids: A review of their occurrence and chemical characteristics and speculations on their petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 1990, 26(1/2): 115-134.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
EBY G N. Chemical subdivision of A-type granitoids: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(7): 641.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
FROST C D, FROST B R. Reduced rapakivi-type granites: The tholeiite connection[J]. Geology, 1997, 25(7): 647.
DOI URL |
| [48] | WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPLLE B W. A-type granites: geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-419. |
| [49] |
CREASER R A, PRICE R C, WORMLD R J. A-type granites revisited: Assessment of a residual-source model[J]. Geology, 1991, 19(2): 163.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
LITVINOVSKY B A, JAHN Bor-ming, ZANVILEVICH A W, et al. Petrogenesis of syenite-granite suites from the Bryansky Complex (Transbaikalia, Russia): implications for the origin of A-type granitoid magmas[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 189(s 1/2): 105-133.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
YANG J H, WU F Y, CHUNG S L, et al. A hybrid origin for the Qianshan A -type granite, northeast China: Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence[J]. Lithos, 2006, 89: 89-106.
DOI URL |
| [52] | LOISELLE M C, WONES D R. Characteristics and origin of anorogenic granites[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin (Abstracts with Program), 1979, 11: 468. |
| [53] | 张旗, 王焰, 李承东, 等. 花岗岩的Sr-Yb分类及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(9): 2249-2269. |
| [54] | 黄丁伶, 朱洛婷, 侯青叶, 等. 内蒙古维拉斯托矿区花岗岩类地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(6): 1122-1137. |
| [55] | 王涛, 郑亚东, 张进江, 等. 华北克拉通中生代伸展构造研究的几个问题及其在岩石圈减薄研究中的意义[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(9): 1154-1166. |
| [56] | 李锦轶, 杨天南, 陈文, 等. 中国东部东海地区超高压变质岩构造变形事件的40Ar/39Ar定年与超高压变质岩折返过程的重建[J]. 地质学报, 2004, 78(1): 97-108. |
| [57] | 张旗. 中国东部中生代岩浆活动与太平洋板块向西俯冲有关吗?[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2013, 32(1): 113-128. |
| [58] |
JAHN B M, LITVINOVSKY B A, ZANVILEVICH A N, et al. Peralkaline granitoid magmatism in the Mongolian-Transbaikalian Belt: Evolution, petrogenesis and tectonic significance[J]. Lithos, 2009, 113: 521-539.
DOI URL |
| [59] | 徐备, 陈斌. 内蒙古北部华北板块与西伯利亚板块之间中古生代造山带的结构及演化[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 1997, 27(6): 227-232. |
| [60] | 徐备, 赵盼, 鲍庆中, 等. 兴蒙造山带前中生代构造单元划分初探[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(7): 1841-1857. |
| [61] | 王荃, 刘雪亚, 李锦轶. 中国内蒙古中部的古板块构造[J]. 中国地质科学院院报, 1991(1): 1-15. |
| [62] | XIAO Wenjiao, HUANG Baochun. A review of the western part of the Altaids: A key to understanding the architecture of accretionary orogens[J]. Gondwana Research, 2010, 12(1): 253-273. |
| [63] | 邓晋福, 冯艳芳, 狄永军, 等. 古亚洲构造域侵入岩时-空演化框架[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(11): 1211-1224. |
| [1] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [2] | 张舒, 张赞赞, 胡召齐, 施立胜, 周涛发, 吴明安, 杜建国. 长江中下游成矿带庐枞矿集区花岗岩型铀矿床成矿作用研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1435-1448. |
| [3] | 谢亘, 喻光明, 路英川, 冯欣, 田光昊, 王然, 王建. 华北克拉通南缘小秦岭地区花岗质片麻岩年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1702-1712. |
| [4] | 孙晓东, 陈海云, 于光宁. 内蒙古海拉斯图乌拉A型花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1218-1230. |
| [5] | 袁亚平, 刘向东, 张振凯, 曾忠诚, 何元方. 南阿尔金晚泥盆世构造体制转换:来自索尔库里二长花岗岩年代学和地球化学的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 940-954. |
| [6] | 任永健, 程烁, 张明明, 曹光远, 于汪, 赵寒, 梁恒, 王富强, 祁才吉. 黑龙江张家湾地区中侏罗世A型花岗岩地球化学特征及构造环境分析[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 1067-1076. |
| [7] | 滕超, 张晓飞, 周毅, 冯俊岭, 李树才. 内蒙古锡林浩特小乌兰沟早白垩世二长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(05): 1003-1014. |
| [8] | 袁建国, 任永健, 姜振宁, 屈云燕, 魏浩. 内蒙古锡林浩特毛登牧场早石炭世花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(06): 1131-1146. |
| [9] | 王继春 ,王银宏 ,张梅 ,刘家军 ,彭润民 ,王建平 ,宋崇宇 ,周路路. 内蒙古高尔旗银铅锌矿区花岗岩的岩石成因:地球化学、锆石UPb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 961-980. |
| [10] | 邱啸飞,杨红梅,卢山松,谭娟娟,蔡应雄. 扬子陆核古元古代A型花岗岩的年代学与地球化学研究及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(4): 884-895. |
| [11] | 陈春良,江思宏,梁清玲,刘源,韩宁. 河北雾灵山杂岩体锆石Hf同位素特征及其区域对比研究[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(4): 663-673. |
| [12] | 李良林,周汉文,陈植华,王锦荣,陈正华,肖依. 福建太姥山地区和鼓山地区A型花岗岩对比及其地球动力学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(3): 509-524. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||