



现代地质 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (05): 990-1005.
刘刚1,2( ), 刘家军1,2(
), 刘家军1,2( ), 袁峰1,2, 张帅1,2, 沙亚洲3, 张宏远1,2, 王功文1,2
), 袁峰1,2, 张帅1,2, 沙亚洲3, 张宏远1,2, 王功文1,2
收稿日期:2017-04-13
修回日期:2017-06-18
出版日期:2017-10-10
发布日期:2017-11-06
通讯作者:
刘家军,男,教授,博士生导师,1963年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事矿床地球化学方面的教学与研究工作。Email: liujiajun@cugb.edu.cn。
作者简介:刘刚,男,硕士,1991年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事矿床地球化学方面的研究。Email:18782959317@163.com。
基金资助:
LIU Gang1,2( ), LIU Jiajun1,2(
), LIU Jiajun1,2( ), YUAN Feng1,2, ZHANG Shuai1,2, SHA Yazhou3, ZHANG Hongyuan1,2, WANG Gongwen1,2
), YUAN Feng1,2, ZHANG Shuai1,2, SHA Yazhou3, ZHANG Hongyuan1,2, WANG Gongwen1,2
Received:2017-04-13
Revised:2017-06-18
Online:2017-10-10
Published:2017-11-06
摘要:
陕西小花岔铀矿床位于北秦岭造山带的东北部,矿体产于黑云母花岗伟晶岩和黑云斜长片麻岩的接触带同化混染区。为了厘定研究区花岗质岩浆演化与铀矿化作用的关系,对矿区内出露的花岗岩、花岗伟晶岩开展了详细的年代学和岩石地球化学研究。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果表明:灰池子花岗岩体的形成年龄为(444±4.0) Ma;高山沟花岗岩株的形成年龄为(422±0.82) Ma;产铀黑云母花岗伟晶岩的形成年龄为(417±2.6) Ma;非含矿黑云母花岗伟晶岩的形成年龄为(413±1.8) Ma。地球化学数据表明:矿区花岗质岩石富集大离子亲石元素Rb、Ba、K,亏损高场强元素Nb、Ta。含矿黑云母花岗伟晶岩由于同化混染作用及与围岩的元素交换等原因,其基性组分Fe、Mg和挥发分F-含量较高,同一条黑云母花岗伟晶岩脉元素组成的差异是由于伟晶岩浆的同化分离结晶所致,在伟晶岩-黑云斜长片麻岩的接触带发生化学组分的元素交换,使得伟晶岩浆中U-F络合物发生分解,并且在良好的成矿条件下(围岩的铀含量较高、较好的构造环境)使得铀饱和沉淀形成铀矿物,如晶质铀矿等。小花岔铀矿床的形成主要受到了伟晶岩浆、围岩成分、岩浆热液中挥发分共同的作用,最终导致了铀矿床的形成。
中图分类号:
刘刚, 刘家军, 袁峰, 张帅, 沙亚洲, 张宏远, 王功文. 陕西小花岔铀矿床岩浆演化及其对铀成矿作用的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(05): 990-1005.
LIU Gang, LIU Jiajun, YUAN Feng, ZHANG Shuai, SHA Yazhou, ZHANG Hongyuan, WANG Gongwen. The Magmatic Evolution and Its Constraints on Uranium Mineralization in the Xiaohuacha Uranium Deposit, Shaanxi Province[J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(05): 990-1005.

图1 北秦岭造山带地质简图(a)(据杨力等[16],2010修改)和北秦岭丹凤三角地区铀矿地质简图(b)(据冯张生等[6],2011修改) QL.祁连造山带;KL.昆仑造山带;WQ.西秦岭造山带;EQ.东秦岭造山带;DB.大别造山带;SPGZ.松潘-甘孜褶皱带
Fig.1 Simplified geologic map of North Qinling orogenic belt(a) (modified after Yang et al.[16], 2010) and simplified geologic map of the Danfeng triangular zone (b) (modified after Feng et al.[6], 2011)

图4 小花岔铀矿床花岗岩、花岗伟晶岩野外照片 a.高山沟岩株侵入到灰池子岩体中(高山沟岩株东南侧);b.高山沟岩株中的花岗伟晶岩脉(高山沟岩株南侧小河家岔旁);c.伟晶岩脉、高山沟岩株以及灰池子岩体的接触带(庙沟沟口北侧);d.高山沟岩株中残留的花岗伟晶岩(高山沟岩株东南侧);e.高山沟岩株中的伟晶岩(15号勘探线ZK1501旁);f.高山沟岩体与灰池子岩体呈侵入接触(0号勘探线ZK005南侧)
Fig.4 Representative field photographs of the granites and granitic pegmatites from the Xiaohuacha uranium deposit

图5 晶质铀矿在铀矿石(KT 2-1)中的产出形态 a.晶质铀矿产于黑云母中伴随有黄铁矿和锆石的生成;b.晶质铀矿产于黑云母包晶中,周围有钛铁矿、金红石和辉钼矿等硫化物的产生;c.晶质铀矿在背散射图像中产于黑云母包晶中,金红石和钛铁矿呈环带围绕晶质铀矿分布;d.晶质铀矿产于石英中,周围分布有少量黄铁矿。Bi.黑云母;Ilm.钛铁矿;Ur.晶质铀矿;Py.黄铁矿;Rt.金红石;Mo.辉钼矿 Q.石英
Fig.5 The occurrence state of uraninite in the ores(KT 2-1)
 |
表2 花岗岩、花岗伟晶岩的主量元素(%)和微量元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 2 Analytic results of major elements (%) and teace elements (10-6) of granite and granitic pegmatite in the Xiaohuacha uranium deposit
 |

图8 小花岔铀矿区花岗质岩石的地球化学图解 a.SiO2-K2O图解;b.A/NK-A/CNK图解;c.花岗岩分类图解;d.花岗岩类型判别图解。1.灰池子岩体;2.高山沟岩株;3.含矿黑云母花岗伟晶岩;4.非含矿黑云母花岗伟晶岩
Fig.8 The geochemical diagrams of granitic rocks in the Xiaohuacha uranium deposit

图9 小花岔铀矿区岩浆岩的SiO2与Al2O3、FeOt、MgO、CaO、K2O及P2O5的协变关系图(图例同图8)
Fig.9 SiO2 vs.Al2O3,FeOt,MgO,CaO,K2O and P2O5 diagram of granites in the Xiaohuacha uranium deposit (symbols as Fig.8)
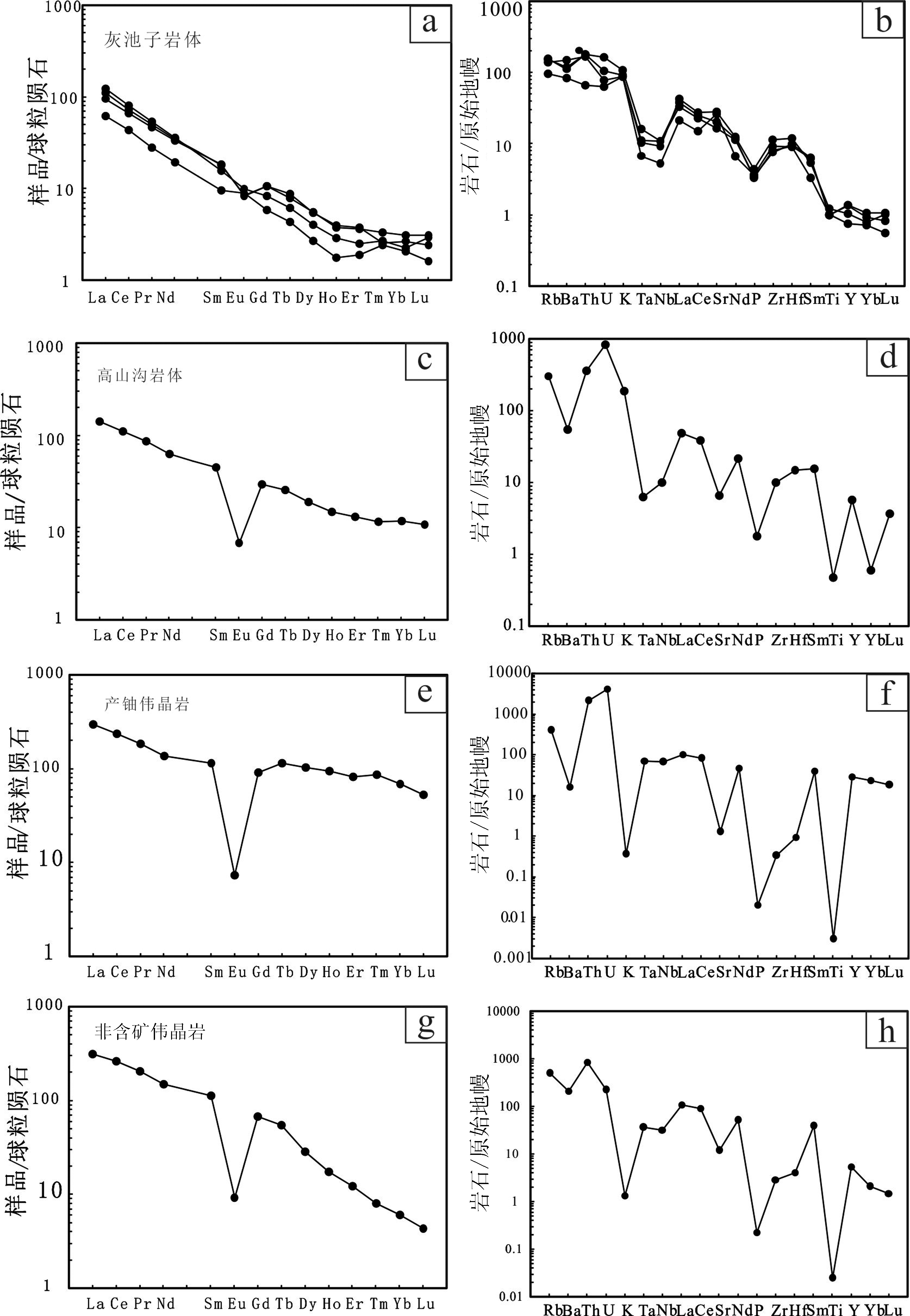
图10 小花岔铀矿区花岗质岩石稀土元素配分图和微量元素蛛网图 (球粒陨石标准化数值据Taylor et al.[34], 1985);原始地幔标准化数值据Sun et al.[35], 1989)
Fig.10 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle-normalized spider diagrams of granitic rocks in the Xiaohuacha uranium deposit
| 测点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | ||||
| XHC-17-01 | 543 | 20 292 | 0.03 | 0.056 15 | 0.001 49 | 0.512 47 | 0.014 27 | 0.065 85 | 0.000 91 | 457 | 59 | 420 | 10 | 411 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-02 | 284 | 12 487 | 0.02 | 0.055 19 | 0.001 53 | 0.509 18 | 0.014 57 | 0.066 16 | 0.000 87 | 420 | 56 | 418 | 10 | 413 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-03 | 438 | 17 164 | 0.03 | 0.053 85 | 0.001 59 | 0.497 62 | 0.014 92 | 0.066 13 | 0.000 89 | 365 | 67 | 410 | 10 | 413 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-04 | 296 | 13 906 | 0.02 | 0.052 09 | 0.001 52 | 0.480 97 | 0.014 20 | 0.066 03 | 0.000 89 | 300 | 67 | 399 | 10 | 412 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-05 | 405 | 16 198 | 0.03 | 0.051 74 | 0.001 35 | 0.479 76 | 0.012 97 | 0.066 30 | 0.000 86 | 272 | 59 | 398 | 9 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-06 | 156 | 9 215 | 0.02 | 0.052 11 | 0.001 28 | 0.481 14 | 0.012 42 | 0.066 21 | 0.000 90 | 300 | 57 | 399 | 9 | 413 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-07 | 403 | 16 470 | 0.02 | 0.052 03 | 0.001 34 | 0.481 08 | 0.012 42 | 0.066 30 | 0.000 78 | 287 | 56 | 399 | 9 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-08 | 644 | 22 925 | 0.03 | 0.055 88 | 0.001 75 | 0.516 41 | 0.016 04 | 0.066 39 | 0.000 89 | 456 | 70 | 423 | 11 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-09 | 661 | 23 506 | 0.03 | 0.051 58 | 0.001 32 | 0.475 50 | 0.012 44 | 0.066 30 | 0.000 98 | 333 | 59 | 395 | 9 | 414 | 6 | ||
| XHC-17-10 | 298 | 12 999 | 0.02 | 0.053 55 | 0.001 38 | 0.494 81 | 0.013 45 | 0.066 28 | 0.000 76 | 354 | 55 | 408 | 9 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-11 | 467 | 19 020 | 0.02 | 0.053 42 | 0.001 30 | 0.491 58 | 0.011 98 | 0.066 28 | 0.000 78 | 346 | 83 | 406 | 8 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-12 | 233 | 10 192 | 0.02 | 0.057 21 | 0.001 68 | 0.527 17 | 0.015 52 | 0.066 26 | 0.000 79 | 498 | 63 | 430 | 10 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-13 | 198 | 9 098 | 0.02 | 0.054 33 | 0.001 79 | 0.503 71 | 0.015 74 | 0.066 16 | 0.000 78 | 383 | 74 | 414 | 11 | 413 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-14 | 216 | 10 043 | 0.02 | 0.055 24 | 0.001 59 | 0.511 73 | 0.015 15 | 0.066 19 | 0.001 05 | 420 | 58 | 420 | 10 | 413 | 6 | ||
| XHC-17-15 | 356 | 14 540 | 0.02 | 0.056 68 | 0.001 54 | 0.525 36 | 0.014 17 | 0.066 27 | 0.000 83 | 480 | 61 | 429 | 9 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-16 | 399 | 16 239 | 0.02 | 0.055 98 | 0.001 63 | 0.519 13 | 0.014 88 | 0.066 31 | 0.000 91 | 450 | 65 | 425 | 10 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-17 | 323 | 14 146 | 0.02 | 0.054 97 | 0.001 81 | 0.512 55 | 0.016 18 | 0.066 37 | 0.000 86 | 409 | 69 | 420 | 11 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-18 | 435 | 15 669 | 0.03 | 0.057 13 | 0.001 64 | 0.532 83 | 0.014 75 | 0.066 39 | 0.000 80 | 498 | 68 | 434 | 10 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-01 | 296 | 9 861 | 0.03 | 0.055 09 | 0.001 66 | 0.524 07 | 0.015 88 | 0.067 73 | 0.000 88 | 417 | 69 | 428 | 11 | 422 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-02 | 257 | 7 577 | 0.03 | 0.057 10 | 0.001 82 | 0.541 42 | 0.017 15 | 0.067 78 | 0.000 89 | 494 | 66 | 439 | 11 | 423 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-03 | 217 | 8 051 | 0.03 | 0.057 82 | 0.001 68 | 0.546 48 | 0.015 90 | 0.067 56 | 0.000 88 | 524 | 65 | 443 | 10 | 421 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-04 | 358 | 8 666 | 0.04 | 0.055 56 | 0.001 70 | 0.527 88 | 0.016 60 | 0.067 84 | 0.000 90 | 435 | 69 | 430 | 11 | 423 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-05 | 318 | 9 017 | 0.04 | 0.056 64 | 0.001 86 | 0.536 80 | 0.017 63 | 0.067 79 | 0.000 89 | 476 | 42 | 436 | 12 | 423 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-06 | 272 | 7 621 | 0.04 | 0.055 94 | 0.001 84 | 0.524 97 | 0.017 00 | 0.067 51 | 0.001 10 | 450 | 72 | 428 | 11 | 421 | 7 | ||
| XHC-28-07 | 250 | 8 994 | 0.03 | 0.055 16 | 0.001 51 | 0.520 50 | 0.014 38 | 0.067 58 | 0.000 76 | 420 | 56 | 425 | 10 | 422 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-08 | 297 | 8 644 | 0.03 | 0.058 71 | 0.001 80 | 0.552 40 | 0.017 26 | 0.067 32 | 0.000 84 | 567 | 67 | 447 | 11 | 420 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-09 | 158 | 8 906 | 0.02 | 0.054 28 | 0.001 48 | 0.511 77 | 0.014 41 | 0.067 50 | 0.000 84 | 383 | 61 | 420 | 10 | 421 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-10 | 551 | 9 895 | 0.06 | 0.058 28 | 0.001 94 | 0.550 28 | 0.018 65 | 0.067 58 | 0.000 92 | 539 | 74 | 445 | 12 | 422 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-11 | 277 | 8 679 | 0.03 | 0.053 79 | 0.001 91 | 0.505 89 | 0.017 99 | 0.067 36 | 0.000 92 | 361 | 80 | 416 | 12 | 420 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-12 | 425 | 8 983 | 0.05 | 0.056 60 | 0.001 84 | 0.532 30 | 0.017 39 | 0.067 35 | 0.000 94 | 476 | 40 | 433 | 12 | 420 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-13 | 183 | 9 014 | 0.02 | 0.055 13 | 0.001 58 | 0.523 98 | 0.015 79 | 0.068 05 | 0.000 96 | 417 | 63 | 428 | 11 | 424 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-14 | 208 | 8 913 | 0.02 | 0.057 40 | 0.001 67 | 0.541 18 | 0.016 52 | 0.067 47 | 0.000 96 | 506 | 63 | 439 | 11 | 421 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-15 | 196 | 7 524 | 0.03 | 0.053 68 | 0.002 27 | 0.506 25 | 0.022 31 | 0.067 33 | 0.001 01 | 367 | 94 | 416 | 15 | 420 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-16 | 223 | 10 873 | 0.02 | 0.058 35 | 0.002 08 | 0.548 56 | 0.019 77 | 0.067 41 | 0.000 97 | 543 | 78 | 444 | 13 | 421 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-17 | 207 | 6 552 | 0.03 | 0.054 75 | 0.001 94 | 0.514 46 | 0.018 71 | 0.067 58 | 0.000 98 | 467 | 80 | 421 | 13 | 422 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-18 | 114 | 7 212 | 0.02 | 0.054 14 | 0.002 09 | 0.509 98 | 0.020 52 | 0.067 72 | 0.001 00 | 376 | 87 | 418 | 14 | 422 | 7 | ||
| XHC-28-19 | 330 | 10 725 | 0.03 | 0.055 80 | 0.002 13 | 0.525 84 | 0.021 84 | 0.067 63 | 0.001 13 | 443 | 81 | 429 | 15 | 422 | 7 | ||
| XHC-28-20 | 170 | 8 204 | 0.02 | 0.059 22 | 0.002 35 | 0.557 66 | 0.023 79 | 0.067 70 | 0.001 11 | 576 | 86 | 450 | 16 | 422 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-21 | 228 | 7 736 | 0.03 | 0.056 83 | 0.001 88 | 0.533 86 | 0.018 30 | 0.067 68 | 0.000 93 | 483 | 79 | 434 | 12 | 422 | 8 | ||
| XHC-41-01 | 218 | 11 518 | 0.02 | 0.053 73 | 0.001 40 | 0.501 18 | 0.013 47 | 0.066 73 | 0.000 92 | 367 | 59 | 413 | 9 | 416 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-02 | 69 | 4 354 | 0.02 | 0.053 77 | 0.001 49 | 0.503 22 | 0.014 35 | 0.066 89 | 0.000 79 | 361 | 68 | 414 | 10 | 417 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-03 | 71 | 4 640 | 0.02 | 0.053 93 | 0.001 61 | 0.501 61 | 0.015 63 | 0.066 66 | 0.000 94 | 369 | 69 | 413 | 11 | 416 | 8 | ||
| XHC-41-04 | 24 | 3 584 | 0.01 | 0.053 65 | 0.001 82 | 0.500 35 | 0.016 85 | 0.067 03 | 0.001 25 | 367 | 78 | 412 | 11 | 418 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-05 | 124 | 7 175 | 0.02 | 0.054 71 | 0.001 68 | 0.510 78 | 0.016 42 | 0.066 81 | 0.000 95 | 467 | 73 | 419 | 11 | 417 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-06 | 46 | 3 672 | 0.01 | 0.056 00 | 0.001 57 | 0.521 27 | 0.014 75 | 0.066 80 | 0.000 80 | 454 | 68 | 426 | 10 | 417 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-07 | 94 | 6 287 | 0.01 | 0.056 38 | 0.001 62 | 0.524 11 | 0.014 84 | 0.066 80 | 0.000 84 | 478 | 32 | 428 | 10 | 417 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-08 | 89 | 4 756 | 0.02 | 0.056 19 | 0.001 64 | 0.522 28 | 0.015 28 | 0.066 81 | 0.000 82 | 461 | 65 | 427 | 10 | 417 | 8 | ||
| XHC-41-09 | 93 | 5 765 | 0.02 | 0.056 14 | 0.001 54 | 0.520 83 | 0.015 16 | 0.066 95 | 0.001 26 | 457 | 61 | 426 | 10 | 418 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-10 | 105 | 6 487 | 0.02 | 0.055 63 | 0.001 59 | 0.517 95 | 0.015 09 | 0.067 07 | 0.001 02 | 439 | 65 | 424 | 10 | 418 | 7 | ||
| XHC-41-11 | 75 | 4 463 | 0.02 | 0.05511 | 0.001 69 | 0.512 85 | 0.017 68 | 0.066 90 | 0.001 19 | 417 | 69 | 420 | 12 | 417 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-12 | 58 | 4 675 | 0.01 | 0.054 76 | 0.001 55 | 0.508 72 | 0.015 58 | 0.066 90 | 0.001 06 | 467 | 63 | 418 | 10 | 417 | 4 | ||
| XHC-41-13 | 112 | 7 576 | 0.01 | 0.054 55 | 0.001 32 | 0.504 83 | 0.012 42 | 0.066 64 | 0.000 72 | 394 | 58 | 415 | 8 | 416 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-14 | 82 | 5 525 | 0.01 | 0.053 35 | 0.001 35 | 0.497 23 | 0.013 90 | 0.067 05 | 0.000 98 | 343 | 92 | 410 | 9 | 418 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-15 | 62 | 4 172 | 0.01 | 0.054 17 | 0.001 57 | 0.500 21 | 0.014 88 | 0.066 55 | 0.000 86 | 389 | 60 | 412 | 10 | 415 | 7 | ||
| XHC-41-16 | 196 | 10 657 | 0.02 | 0.054 28 | 0.001 63 | 0.504 86 | 0.016 27 | 0.066 95 | 0.001 09 | 383 | 64 | 415 | 11 | 418 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-17 | 103 | 6 902 | 0.01 | 0.055 24 | 0.001 70 | 0.512 89 | 0.016 15 | 0.066 79 | 0.000 93 | 420 | 73 | 420 | 11 | 417 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-18 | 79 | 5 579 | 0.01 | 0.054 76 | 0.001 55 | 0.510 06 | 0.015 11 | 0.066 86 | 0.000 87 | 467 | 60 | 418 | 10 | 417 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-19 | 79 | 4 763 | 0.02 | 0.054 69 | 0.001 57 | 0.508 58 | 0.014 64 | 0.066 89 | 0.000 96 | 398 | 58 | 417 | 10 | 417 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-20 | 94 | 5 638 | 0.02 | 0.053 22 | 0.001 57 | 0.497 18 | 0.014 67 | 0.066 92 | 0.000 86 | 339 | 67 | 410 | 10 | 418 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-21 | 148 | 8 071 | 0.02 | 0.054 60 | 0.001 76 | 0.514 19 | 0.016 60 | 0.067 50 | 0.001 07 | 394 | 79 | 421 | 11 | 421 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-22 | 112 | 6 911 | 0.02 | 0.053 22 | 0.001 95 | 0.496 44 | 0.017 67 | 0.066 72 | 0.000 97 | 339 | 83 | 409 | 12 | 416 | 7 | ||
| XHC-41-23 | 86 | 4 261 | 0.02 | 0.052 92 | 0.002 11 | 0.492 99 | 0.019 14 | 0.066 71 | 0.001 14 | 324 | 91 | 407 | 13 | 416 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-24 | 32 | 4 395 | 0.01 | 0.052 67 | 0.001 75 | 0.490 14 | 0.016 11 | 0.066 69 | 0.001 05 | 322 | 76 | 405 | 11 | 416 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-25 | 118 | 7 315 | 0.02 | 0.053 37 | 0.001 56 | 0.497 42 | 0.014 29 | 0.066 66 | 0.000 82 | 343 | 67 | 410 | 10 | 416 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-26 | 144 | 8 101 | 0.02 | 0.053 69 | 0.001 47 | 0.499 34 | 0.013 73 | 0.066 54 | 0.000 84 | 367 | 63 | 411 | 9 | 415 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-27 | 86 | 4 693 | 0.02 | 0.054 61 | 0.001 64 | 0.507 56 | 0.015 18 | 0.066 48 | 0.000 81 | 394 | 67 | 417 | 10 | 415 | 9 | ||
| XHC-41-28 | 22 | 3 796 | 0.01 | 0.054 17 | 0.001 62 | 0.505 91 | 0.017 74 | 0.066 79 | 0.001 42 | 389 | 67 | 416 | 12 | 417 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-29 | 100 | 6 147 | 0.02 | 0.053 38 | 0.001 76 | 0.497 78 | 0.016 67 | 0.066 78 | 0.001 04 | 346 | 42 | 410 | 11 | 417 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-30 | 40 | 3 175 | 0.01 | 0.054 67 | 0.001 46 | 0.510 59 | 0.014 85 | 0.066 72 | 0.000 96 | 398 | 56 | 419 | 10 | 416 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-31 | 112 | 7 115 | 0.02 | 0.052 68 | 0.001 31 | 0.492 01 | 0.012 37 | 0.066 84 | 0.000 80 | 322 | 56 | 406 | 8 | 417 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-32 | 50 | 3 877 | 0.01 | 0.053 90 | 0.001 47 | 0.504 21 | 0.014 28 | 0.067 05 | 0.001 03 | 369 | 61 | 415 | 10 | 418 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-33 | 89 | 5 328 | 0.02 | 0.052 63 | 0.001 39 | 0.489 44 | 0.013 23 | 0.066 52 | 0.000 82 | 322 | 61 | 405 | 9 | 415 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-34 | 71 | 4 581 | 0.02 | 0.054 54 | 0.001 56 | 0.509 48 | 0.014 84 | 0.066 82 | 0.000 91 | 394 | 65 | 418 | 10 | 417 | 7 | ||
| XHC-41-35 | 89 | 6 578 | 0.01 | 0.053 93 | 0.001 57 | 0.503 94 | 0.015 63 | 0.066 78 | 0.001 18 | 369 | 65 | 414 | 11 | 417 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-36 | 76 | 5 270 | 0.01 | 0.053 72 | 0.001 49 | 0.503 15 | 0.013 88 | 0.066 94 | 0.000 93 | 367 | 63 | 414 | 9 | 418 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-37 | 78 | 4 338 | 0.02 | 0.054 34 | 0.001 43 | 0.508 64 | 0.013 27 | 0.066 66 | 0.000 79 | 383 | 59 | 418 | 9 | 416 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-38 | 31 | 4 930 | 0.01 | 0.055 85 | 0.001 44 | 0.525 94 | 0.014 12 | 0.067 01 | 0.001 03 | 456 | 57 | 429 | 9 | 418 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-39 | 109 | 6 530 | 0.02 | 0.052 53 | 0.001 29 | 0.495 85 | 0.011 67 | 0.066 95 | 0.000 75 | 309 | 57 | 409 | 8 | 418 | 10 | ||
| XHC-41-40 | 56 | 4 578 | 0.01 | 0.056 41 | 0.001 74 | 0.529 79 | 0.021 14 | 0.066 78 | 0.001 68 | 478 | 101 | 432 | 14 | 417 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-01 | 335 | 3 694 | 0.09 | 0.059 38 | 0.001 00 | 0.593 96 | 0.010 65 | 0.072 53 | 0.000 96 | 581 | 19 | 473 | 7 | 451 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-02 | 915 | 4 892 | 0.19 | 0.055 94 | 0.000 95 | 0.549 24 | 0.009 93 | 0.071 20 | 0.000 95 | 450 | 19 | 444 | 7 | 443 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-03 | 158 | 3 954 | 0.04 | 0.054 69 | 0.000 93 | 0.534 63 | 0.009 72 | 0.070 89 | 0.000 94 | 400 | 20 | 435 | 6 | 442 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-04 | 867 | 4 048 | 0.21 | 0.056 27 | 0.000 97 | 0.555 56 | 0.010 17 | 0.071 59 | 0.000 96 | 463 | 19 | 449 | 7 | 446 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-05 | 403 | 6 697 | 0.06 | 0.058 80 | 0.000 99 | 0.586 41 | 0.010 56 | 0.072 32 | 0.000 96 | 560 | 19 | 469 | 7 | 450 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-06 | 275 | 4 148 | 0.07 | 0.056 10 | 0.000 97 | 0.555 42 | 0.010 19 | 0.071 79 | 0.000 96 | 456 | 20 | 449 | 7 | 447 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-07 | 1 611 | 4 981 | 0.32 | 0.056 93 | 0.001 00 | 0.566 40 | 0.010 54 | 0.072 14 | 0.000 97 | 489 | 20 | 456 | 7 | 449 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-08 | 352 | 2 341 | 0.15 | 0.056 44 | 0.001 01 | 0.560 18 | 0.010 61 | 0.071 97 | 0.000 97 | 470 | 20 | 452 | 7 | 448 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-09 | 2 040 | 4 728 | 0.43 | 0.055 56 | 0.000 94 | 0.541 64 | 0.009 76 | 0.070 69 | 0.000 94 | 435 | 19 | 440 | 6 | 440 | 6 | ||
表1 小花岔铀矿区花岗岩和花岗伟晶岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb分析数据
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of zircons for granite and granitic pegmatite in the Xiaohuacha uranium deposit
| 测点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | ||||
| XHC-17-01 | 543 | 20 292 | 0.03 | 0.056 15 | 0.001 49 | 0.512 47 | 0.014 27 | 0.065 85 | 0.000 91 | 457 | 59 | 420 | 10 | 411 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-02 | 284 | 12 487 | 0.02 | 0.055 19 | 0.001 53 | 0.509 18 | 0.014 57 | 0.066 16 | 0.000 87 | 420 | 56 | 418 | 10 | 413 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-03 | 438 | 17 164 | 0.03 | 0.053 85 | 0.001 59 | 0.497 62 | 0.014 92 | 0.066 13 | 0.000 89 | 365 | 67 | 410 | 10 | 413 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-04 | 296 | 13 906 | 0.02 | 0.052 09 | 0.001 52 | 0.480 97 | 0.014 20 | 0.066 03 | 0.000 89 | 300 | 67 | 399 | 10 | 412 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-05 | 405 | 16 198 | 0.03 | 0.051 74 | 0.001 35 | 0.479 76 | 0.012 97 | 0.066 30 | 0.000 86 | 272 | 59 | 398 | 9 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-06 | 156 | 9 215 | 0.02 | 0.052 11 | 0.001 28 | 0.481 14 | 0.012 42 | 0.066 21 | 0.000 90 | 300 | 57 | 399 | 9 | 413 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-07 | 403 | 16 470 | 0.02 | 0.052 03 | 0.001 34 | 0.481 08 | 0.012 42 | 0.066 30 | 0.000 78 | 287 | 56 | 399 | 9 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-08 | 644 | 22 925 | 0.03 | 0.055 88 | 0.001 75 | 0.516 41 | 0.016 04 | 0.066 39 | 0.000 89 | 456 | 70 | 423 | 11 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-09 | 661 | 23 506 | 0.03 | 0.051 58 | 0.001 32 | 0.475 50 | 0.012 44 | 0.066 30 | 0.000 98 | 333 | 59 | 395 | 9 | 414 | 6 | ||
| XHC-17-10 | 298 | 12 999 | 0.02 | 0.053 55 | 0.001 38 | 0.494 81 | 0.013 45 | 0.066 28 | 0.000 76 | 354 | 55 | 408 | 9 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-11 | 467 | 19 020 | 0.02 | 0.053 42 | 0.001 30 | 0.491 58 | 0.011 98 | 0.066 28 | 0.000 78 | 346 | 83 | 406 | 8 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-12 | 233 | 10 192 | 0.02 | 0.057 21 | 0.001 68 | 0.527 17 | 0.015 52 | 0.066 26 | 0.000 79 | 498 | 63 | 430 | 10 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-13 | 198 | 9 098 | 0.02 | 0.054 33 | 0.001 79 | 0.503 71 | 0.015 74 | 0.066 16 | 0.000 78 | 383 | 74 | 414 | 11 | 413 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-14 | 216 | 10 043 | 0.02 | 0.055 24 | 0.001 59 | 0.511 73 | 0.015 15 | 0.066 19 | 0.001 05 | 420 | 58 | 420 | 10 | 413 | 6 | ||
| XHC-17-15 | 356 | 14 540 | 0.02 | 0.056 68 | 0.001 54 | 0.525 36 | 0.014 17 | 0.066 27 | 0.000 83 | 480 | 61 | 429 | 9 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-16 | 399 | 16 239 | 0.02 | 0.055 98 | 0.001 63 | 0.519 13 | 0.014 88 | 0.066 31 | 0.000 91 | 450 | 65 | 425 | 10 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-17 | 323 | 14 146 | 0.02 | 0.054 97 | 0.001 81 | 0.512 55 | 0.016 18 | 0.066 37 | 0.000 86 | 409 | 69 | 420 | 11 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-17-18 | 435 | 15 669 | 0.03 | 0.057 13 | 0.001 64 | 0.532 83 | 0.014 75 | 0.066 39 | 0.000 80 | 498 | 68 | 434 | 10 | 414 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-01 | 296 | 9 861 | 0.03 | 0.055 09 | 0.001 66 | 0.524 07 | 0.015 88 | 0.067 73 | 0.000 88 | 417 | 69 | 428 | 11 | 422 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-02 | 257 | 7 577 | 0.03 | 0.057 10 | 0.001 82 | 0.541 42 | 0.017 15 | 0.067 78 | 0.000 89 | 494 | 66 | 439 | 11 | 423 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-03 | 217 | 8 051 | 0.03 | 0.057 82 | 0.001 68 | 0.546 48 | 0.015 90 | 0.067 56 | 0.000 88 | 524 | 65 | 443 | 10 | 421 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-04 | 358 | 8 666 | 0.04 | 0.055 56 | 0.001 70 | 0.527 88 | 0.016 60 | 0.067 84 | 0.000 90 | 435 | 69 | 430 | 11 | 423 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-05 | 318 | 9 017 | 0.04 | 0.056 64 | 0.001 86 | 0.536 80 | 0.017 63 | 0.067 79 | 0.000 89 | 476 | 42 | 436 | 12 | 423 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-06 | 272 | 7 621 | 0.04 | 0.055 94 | 0.001 84 | 0.524 97 | 0.017 00 | 0.067 51 | 0.001 10 | 450 | 72 | 428 | 11 | 421 | 7 | ||
| XHC-28-07 | 250 | 8 994 | 0.03 | 0.055 16 | 0.001 51 | 0.520 50 | 0.014 38 | 0.067 58 | 0.000 76 | 420 | 56 | 425 | 10 | 422 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-08 | 297 | 8 644 | 0.03 | 0.058 71 | 0.001 80 | 0.552 40 | 0.017 26 | 0.067 32 | 0.000 84 | 567 | 67 | 447 | 11 | 420 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-09 | 158 | 8 906 | 0.02 | 0.054 28 | 0.001 48 | 0.511 77 | 0.014 41 | 0.067 50 | 0.000 84 | 383 | 61 | 420 | 10 | 421 | 5 | ||
| XHC-28-10 | 551 | 9 895 | 0.06 | 0.058 28 | 0.001 94 | 0.550 28 | 0.018 65 | 0.067 58 | 0.000 92 | 539 | 74 | 445 | 12 | 422 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-11 | 277 | 8 679 | 0.03 | 0.053 79 | 0.001 91 | 0.505 89 | 0.017 99 | 0.067 36 | 0.000 92 | 361 | 80 | 416 | 12 | 420 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-12 | 425 | 8 983 | 0.05 | 0.056 60 | 0.001 84 | 0.532 30 | 0.017 39 | 0.067 35 | 0.000 94 | 476 | 40 | 433 | 12 | 420 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-13 | 183 | 9 014 | 0.02 | 0.055 13 | 0.001 58 | 0.523 98 | 0.015 79 | 0.068 05 | 0.000 96 | 417 | 63 | 428 | 11 | 424 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-14 | 208 | 8 913 | 0.02 | 0.057 40 | 0.001 67 | 0.541 18 | 0.016 52 | 0.067 47 | 0.000 96 | 506 | 63 | 439 | 11 | 421 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-15 | 196 | 7 524 | 0.03 | 0.053 68 | 0.002 27 | 0.506 25 | 0.022 31 | 0.067 33 | 0.001 01 | 367 | 94 | 416 | 15 | 420 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-16 | 223 | 10 873 | 0.02 | 0.058 35 | 0.002 08 | 0.548 56 | 0.019 77 | 0.067 41 | 0.000 97 | 543 | 78 | 444 | 13 | 421 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-17 | 207 | 6 552 | 0.03 | 0.054 75 | 0.001 94 | 0.514 46 | 0.018 71 | 0.067 58 | 0.000 98 | 467 | 80 | 421 | 13 | 422 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-18 | 114 | 7 212 | 0.02 | 0.054 14 | 0.002 09 | 0.509 98 | 0.020 52 | 0.067 72 | 0.001 00 | 376 | 87 | 418 | 14 | 422 | 7 | ||
| XHC-28-19 | 330 | 10 725 | 0.03 | 0.055 80 | 0.002 13 | 0.525 84 | 0.021 84 | 0.067 63 | 0.001 13 | 443 | 81 | 429 | 15 | 422 | 7 | ||
| XHC-28-20 | 170 | 8 204 | 0.02 | 0.059 22 | 0.002 35 | 0.557 66 | 0.023 79 | 0.067 70 | 0.001 11 | 576 | 86 | 450 | 16 | 422 | 6 | ||
| XHC-28-21 | 228 | 7 736 | 0.03 | 0.056 83 | 0.001 88 | 0.533 86 | 0.018 30 | 0.067 68 | 0.000 93 | 483 | 79 | 434 | 12 | 422 | 8 | ||
| XHC-41-01 | 218 | 11 518 | 0.02 | 0.053 73 | 0.001 40 | 0.501 18 | 0.013 47 | 0.066 73 | 0.000 92 | 367 | 59 | 413 | 9 | 416 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-02 | 69 | 4 354 | 0.02 | 0.053 77 | 0.001 49 | 0.503 22 | 0.014 35 | 0.066 89 | 0.000 79 | 361 | 68 | 414 | 10 | 417 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-03 | 71 | 4 640 | 0.02 | 0.053 93 | 0.001 61 | 0.501 61 | 0.015 63 | 0.066 66 | 0.000 94 | 369 | 69 | 413 | 11 | 416 | 8 | ||
| XHC-41-04 | 24 | 3 584 | 0.01 | 0.053 65 | 0.001 82 | 0.500 35 | 0.016 85 | 0.067 03 | 0.001 25 | 367 | 78 | 412 | 11 | 418 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-05 | 124 | 7 175 | 0.02 | 0.054 71 | 0.001 68 | 0.510 78 | 0.016 42 | 0.066 81 | 0.000 95 | 467 | 73 | 419 | 11 | 417 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-06 | 46 | 3 672 | 0.01 | 0.056 00 | 0.001 57 | 0.521 27 | 0.014 75 | 0.066 80 | 0.000 80 | 454 | 68 | 426 | 10 | 417 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-07 | 94 | 6 287 | 0.01 | 0.056 38 | 0.001 62 | 0.524 11 | 0.014 84 | 0.066 80 | 0.000 84 | 478 | 32 | 428 | 10 | 417 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-08 | 89 | 4 756 | 0.02 | 0.056 19 | 0.001 64 | 0.522 28 | 0.015 28 | 0.066 81 | 0.000 82 | 461 | 65 | 427 | 10 | 417 | 8 | ||
| XHC-41-09 | 93 | 5 765 | 0.02 | 0.056 14 | 0.001 54 | 0.520 83 | 0.015 16 | 0.066 95 | 0.001 26 | 457 | 61 | 426 | 10 | 418 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-10 | 105 | 6 487 | 0.02 | 0.055 63 | 0.001 59 | 0.517 95 | 0.015 09 | 0.067 07 | 0.001 02 | 439 | 65 | 424 | 10 | 418 | 7 | ||
| XHC-41-11 | 75 | 4 463 | 0.02 | 0.05511 | 0.001 69 | 0.512 85 | 0.017 68 | 0.066 90 | 0.001 19 | 417 | 69 | 420 | 12 | 417 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-12 | 58 | 4 675 | 0.01 | 0.054 76 | 0.001 55 | 0.508 72 | 0.015 58 | 0.066 90 | 0.001 06 | 467 | 63 | 418 | 10 | 417 | 4 | ||
| XHC-41-13 | 112 | 7 576 | 0.01 | 0.054 55 | 0.001 32 | 0.504 83 | 0.012 42 | 0.066 64 | 0.000 72 | 394 | 58 | 415 | 8 | 416 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-14 | 82 | 5 525 | 0.01 | 0.053 35 | 0.001 35 | 0.497 23 | 0.013 90 | 0.067 05 | 0.000 98 | 343 | 92 | 410 | 9 | 418 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-15 | 62 | 4 172 | 0.01 | 0.054 17 | 0.001 57 | 0.500 21 | 0.014 88 | 0.066 55 | 0.000 86 | 389 | 60 | 412 | 10 | 415 | 7 | ||
| XHC-41-16 | 196 | 10 657 | 0.02 | 0.054 28 | 0.001 63 | 0.504 86 | 0.016 27 | 0.066 95 | 0.001 09 | 383 | 64 | 415 | 11 | 418 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-17 | 103 | 6 902 | 0.01 | 0.055 24 | 0.001 70 | 0.512 89 | 0.016 15 | 0.066 79 | 0.000 93 | 420 | 73 | 420 | 11 | 417 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-18 | 79 | 5 579 | 0.01 | 0.054 76 | 0.001 55 | 0.510 06 | 0.015 11 | 0.066 86 | 0.000 87 | 467 | 60 | 418 | 10 | 417 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-19 | 79 | 4 763 | 0.02 | 0.054 69 | 0.001 57 | 0.508 58 | 0.014 64 | 0.066 89 | 0.000 96 | 398 | 58 | 417 | 10 | 417 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-20 | 94 | 5 638 | 0.02 | 0.053 22 | 0.001 57 | 0.497 18 | 0.014 67 | 0.066 92 | 0.000 86 | 339 | 67 | 410 | 10 | 418 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-21 | 148 | 8 071 | 0.02 | 0.054 60 | 0.001 76 | 0.514 19 | 0.016 60 | 0.067 50 | 0.001 07 | 394 | 79 | 421 | 11 | 421 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-22 | 112 | 6 911 | 0.02 | 0.053 22 | 0.001 95 | 0.496 44 | 0.017 67 | 0.066 72 | 0.000 97 | 339 | 83 | 409 | 12 | 416 | 7 | ||
| XHC-41-23 | 86 | 4 261 | 0.02 | 0.052 92 | 0.002 11 | 0.492 99 | 0.019 14 | 0.066 71 | 0.001 14 | 324 | 91 | 407 | 13 | 416 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-24 | 32 | 4 395 | 0.01 | 0.052 67 | 0.001 75 | 0.490 14 | 0.016 11 | 0.066 69 | 0.001 05 | 322 | 76 | 405 | 11 | 416 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-25 | 118 | 7 315 | 0.02 | 0.053 37 | 0.001 56 | 0.497 42 | 0.014 29 | 0.066 66 | 0.000 82 | 343 | 67 | 410 | 10 | 416 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-26 | 144 | 8 101 | 0.02 | 0.053 69 | 0.001 47 | 0.499 34 | 0.013 73 | 0.066 54 | 0.000 84 | 367 | 63 | 411 | 9 | 415 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-27 | 86 | 4 693 | 0.02 | 0.054 61 | 0.001 64 | 0.507 56 | 0.015 18 | 0.066 48 | 0.000 81 | 394 | 67 | 417 | 10 | 415 | 9 | ||
| XHC-41-28 | 22 | 3 796 | 0.01 | 0.054 17 | 0.001 62 | 0.505 91 | 0.017 74 | 0.066 79 | 0.001 42 | 389 | 67 | 416 | 12 | 417 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-29 | 100 | 6 147 | 0.02 | 0.053 38 | 0.001 76 | 0.497 78 | 0.016 67 | 0.066 78 | 0.001 04 | 346 | 42 | 410 | 11 | 417 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-30 | 40 | 3 175 | 0.01 | 0.054 67 | 0.001 46 | 0.510 59 | 0.014 85 | 0.066 72 | 0.000 96 | 398 | 56 | 419 | 10 | 416 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-31 | 112 | 7 115 | 0.02 | 0.052 68 | 0.001 31 | 0.492 01 | 0.012 37 | 0.066 84 | 0.000 80 | 322 | 56 | 406 | 8 | 417 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-32 | 50 | 3 877 | 0.01 | 0.053 90 | 0.001 47 | 0.504 21 | 0.014 28 | 0.067 05 | 0.001 03 | 369 | 61 | 415 | 10 | 418 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-33 | 89 | 5 328 | 0.02 | 0.052 63 | 0.001 39 | 0.489 44 | 0.013 23 | 0.066 52 | 0.000 82 | 322 | 61 | 405 | 9 | 415 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-34 | 71 | 4 581 | 0.02 | 0.054 54 | 0.001 56 | 0.509 48 | 0.014 84 | 0.066 82 | 0.000 91 | 394 | 65 | 418 | 10 | 417 | 7 | ||
| XHC-41-35 | 89 | 6 578 | 0.01 | 0.053 93 | 0.001 57 | 0.503 94 | 0.015 63 | 0.066 78 | 0.001 18 | 369 | 65 | 414 | 11 | 417 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-36 | 76 | 5 270 | 0.01 | 0.053 72 | 0.001 49 | 0.503 15 | 0.013 88 | 0.066 94 | 0.000 93 | 367 | 63 | 414 | 9 | 418 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-37 | 78 | 4 338 | 0.02 | 0.054 34 | 0.001 43 | 0.508 64 | 0.013 27 | 0.066 66 | 0.000 79 | 383 | 59 | 418 | 9 | 416 | 6 | ||
| XHC-41-38 | 31 | 4 930 | 0.01 | 0.055 85 | 0.001 44 | 0.525 94 | 0.014 12 | 0.067 01 | 0.001 03 | 456 | 57 | 429 | 9 | 418 | 5 | ||
| XHC-41-39 | 109 | 6 530 | 0.02 | 0.052 53 | 0.001 29 | 0.495 85 | 0.011 67 | 0.066 95 | 0.000 75 | 309 | 57 | 409 | 8 | 418 | 10 | ||
| XHC-41-40 | 56 | 4 578 | 0.01 | 0.056 41 | 0.001 74 | 0.529 79 | 0.021 14 | 0.066 78 | 0.001 68 | 478 | 101 | 432 | 14 | 417 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-01 | 335 | 3 694 | 0.09 | 0.059 38 | 0.001 00 | 0.593 96 | 0.010 65 | 0.072 53 | 0.000 96 | 581 | 19 | 473 | 7 | 451 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-02 | 915 | 4 892 | 0.19 | 0.055 94 | 0.000 95 | 0.549 24 | 0.009 93 | 0.071 20 | 0.000 95 | 450 | 19 | 444 | 7 | 443 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-03 | 158 | 3 954 | 0.04 | 0.054 69 | 0.000 93 | 0.534 63 | 0.009 72 | 0.070 89 | 0.000 94 | 400 | 20 | 435 | 6 | 442 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-04 | 867 | 4 048 | 0.21 | 0.056 27 | 0.000 97 | 0.555 56 | 0.010 17 | 0.071 59 | 0.000 96 | 463 | 19 | 449 | 7 | 446 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-05 | 403 | 6 697 | 0.06 | 0.058 80 | 0.000 99 | 0.586 41 | 0.010 56 | 0.072 32 | 0.000 96 | 560 | 19 | 469 | 7 | 450 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-06 | 275 | 4 148 | 0.07 | 0.056 10 | 0.000 97 | 0.555 42 | 0.010 19 | 0.071 79 | 0.000 96 | 456 | 20 | 449 | 7 | 447 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-07 | 1 611 | 4 981 | 0.32 | 0.056 93 | 0.001 00 | 0.566 40 | 0.010 54 | 0.072 14 | 0.000 97 | 489 | 20 | 456 | 7 | 449 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-08 | 352 | 2 341 | 0.15 | 0.056 44 | 0.001 01 | 0.560 18 | 0.010 61 | 0.071 97 | 0.000 97 | 470 | 20 | 452 | 7 | 448 | 6 | ||
| XHC-1-09 | 2 040 | 4 728 | 0.43 | 0.055 56 | 0.000 94 | 0.541 64 | 0.009 76 | 0.070 69 | 0.000 94 | 435 | 19 | 440 | 6 | 440 | 6 | ||
| [1] | 左文乾, 沙亚洲, 陈冰, 等. 丹凤地区光石沟铀矿床大毛沟岩株锆石U-Pb同位素定年及其地质意义[J]. 铀矿地质, 2010, 26(4):222-227. |
| [2] | 郭国林, 张展适, 刘晓东, 等. 光石沟铀矿床晶质铀矿电子探针化学定年研究[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 35(4):309-314. |
| [3] | 沙亚洲, 左文乾, 张展适, 等. 陕西秦岭光石沟铀矿床含矿与非含矿伟晶岩差异性及其研究意义[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 34(3):215-223. |
| [4] | 冯张生. 陕南光石沟伟晶岩型铀矿床中长石矿物化学初步研究[J]. 化工矿产地质, 2012, 34(2):71-76. |
| [5] | 陈佑纬, 毕献武, 胡瑞忠, 等. 陕南光石沟伟晶岩型铀矿床黑云母矿物化学研究及其对铀成矿的启示[J]. 矿物岩石, 2013, 33(4):17-28. |
| [6] | 冯张生, 焦金荣, 张夏涛. 丹凤地区北部加里东期岩浆岩特征及其与铀矿化关系[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2011, 28(4):202-207. |
| [7] | 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 等. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001:1-855. |
| [8] | 王涛, 王晓霞, 田伟, 等. 北秦岭古生代花岗岩组合、岩浆时空演变及其对造山作用的启示[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 2009, 39(7):949-971. |
| [9] |
DONG Y, ZHANG G, NEUBAUER F, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, China: review and synthesis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(3): 213-237.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 张成立, 刘良, 王涛, 等. 北秦岭早古生代大陆碰撞过程中的花岗岩浆作用[J]. 科学通报, 2013, 58(23):2323-2329. |
| [11] | 刘丙祥. 北秦岭地体东段岩浆作用与地壳演化[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2014:1-244. |
| [12] | 张国伟. 华北地块南部早前寒武纪地壳的组成及其演化和秦岭造山带的形成及其演化[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 1988, 18(1):21-23. |
| [13] | 张国伟, 张宗清, 董云鹏. 秦岭造山带主要构造岩石地层单元的构造性质及其大地构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 1995, 11( 2):101-114. |
| [14] | 张国伟, 孟庆任. 秦岭造山带的结构构造[J]. 中国科学: B 辑, 1995, 25(9): 994-1003. |
| [15] | 陆松年, 陈志宏, 相振群, 等. 秦岭岩群副变质岩碎屑锆石年龄谱及其地质意义探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(6):303-310. |
| [16] | 杨力, 陈福坤, 杨一增, 等. 丹凤地区秦岭岩群片麻岩锆石U-Pb年龄:北秦岭地体中-新元古代岩浆作用和早古生代变质作用的记录[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(5):1589-1603. |
| [17] | 时毓, 于津海, 徐夕生, 等. 秦岭造山带东段秦岭岩群的年代学和地球化学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(10):2651-2670. |
| [18] | 张本仁, 骆庭川, 高山, 等. 秦巴岩石圈构造及成矿规律地球化学研究[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1994:1-446. |
| [19] | 张国伟, 孟庆任. 秦岭造山带的造山过程及其动力学特征[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 1996, 26(3):193-200. |
| [20] | 王宗起, 闫全人, 闫臻. 秦岭造山带主要大地构造单元的新划分[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(11):5-24. |
| [21] | 张旗, 张宗清, 孙勇, 等. 陕西商县—丹凤地区丹凤群变质玄武岩的微量元素和同位素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 1995, 11(1):43-54. |
| [22] | 裴先治, 李厚民, 李国光. 东秦岭丹凤岩群的形成时代和构造属性[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2001, 20(2):180-188. |
| [23] | 王凯, 刘少峰, 王平, 等. 扬子板块北缘中段前陆带构造变形特征及意义[J]. 地质科学, 2013, 48(3):609-625. |
| [24] |
RATSCHBACHER L, HACKER B R, CALVERT A, et al. Tectonics of the Qinling(Central China): tectonostratigraphy, geochronology, and deformation history[J]. Tectonophysics, 2003, 366(1): 1-53.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 王江波, 赖绍聪, 李卫红, 等. 北秦岭东段宽坪岩体地质地球化学特征及其与铀成矿关系[J]. 地质与勘探, 2015, 51(1):98-107. |
| [26] | LUDWIG K R. User’s Manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronolo-gical Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003:4-70. |
| [27] |
GAO S, RUDNICK R L, XU W L, et al. Recycling deep cratonic lithosphere and generation of intraplate magmatism in the North China Craton[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 270(1): 41-53.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 赵振华, 增田彰正, 夏巴尼M B. 稀有金属花岗岩的稀土元素四分组效应[J]. 地球化学, 1992, 21(3):221-233. |
| [29] | 赵振华, 熊小林, 韩小东. 花岗岩稀土元素四分组效应形成机理探讨——以千里山和巴尔哲花岗岩为例[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 1999, 29(4):331-338. |
| [30] | 张辉, 刘丛强. 新疆阿尔泰可可托海3号伟晶岩脉磷灰石矿物中稀土元素“四分组效应”及其意义[J]. 地球化学, 2001, 30(4):323-334. |
| [31] | 刘良, 廖小莹, 张成立, 等. 北秦岭高压-超高压岩石的多期变质时代及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(5): 1634-1656. |
| [32] | 秦拯纬, 吴元保. 富钠岛弧花岗岩的成因:以北秦岭灰池子花岗岩为例[M]// 《年刊》编委会.2014 年中国地球科学联合学术年会——专题 31:俯冲带壳幔相互作用论文集. 北京: 中国和平音像电子出版社, 2014:1748. |
| [33] | 王晓霞, 王涛, 齐秋菊, 等. 秦岭晚中生代花岗岩时空分布、成因演变及构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(6):1573-1593. |
| [34] |
TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The continental crust: its composition and evolution[J]. Journal of Geology, 1985, 94(4):632-633.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 鄢明才, 迟清华, 顾铁新, 等. 中国东部上地壳化学组成[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 1997, 27(3):193-199. |
| [37] |
TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1995, 33(2): 241-265.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
BELOUSOVA E, GRIFFIN W L, O’REILLY S Y, et al. Igneous zircon: trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(5): 602-622.
DOI URL |
| [39] | 薛传东, 骆少勇, 宋玉财, 等. 滇西北中甸陆家村石英二长斑岩的锆石SHRIMP定年及其意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010(6):1845-1855. |
| [40] |
CLARKE D B. Assimilation of xenocrysts in granitic magmas: principles, processes, proxies, and problems[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2007, 45(1): 5-30.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
DOUCE A E P, BEARD J S. Effects of P, f(O2) and Mg/Fe ratio on dehydration melting of model metagreywackes[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1996, 37(5): 999-1024.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
BEARD J S, RAGLAND P C, CRAWFORD M L. Reactive bulk assimilation: A model for crust-mantle mixing in silicic magmas[J]. Geology, 2005, 33(8): 681-684.
DOI URL |
| [43] | 冯明月. 商丹地区产铀伟晶岩成因讨论[J]. 铀矿地质, 1996, 12(1):30-36. |
| [44] | 曾令交, 金景福. 某花岗伟晶岩型铀矿床铀迁移沉淀机制探讨[J]. 华东地质学院学报, 1994, 17(3):264-269. |
| [45] |
GRENTHE I, FUGER J, KONINGS R J M, et al. Chemical thermodynamics of uranium[J]. Chemistry International, 1992, 35(10):1-28.
DOI URL |
| [46] | 曾令交, 金景福, 赖生华. 光石沟含铀花岗伟晶岩成因探讨[J]. 矿物岩石, 1998, 18(2):13-18. |
| [47] |
PEIFFERT C, CUNEY M. Uranium in granitic magmas: Part 2.Experimental determination of uranium solubility and fluid-melt partition coefficients in the uranium oxide-haplogranite-H2O-NaX(X=Cl, F) system at 770 ℃, 2 kbar[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(9): 1515-1529.
DOI URL |
| [48] | 凌洪飞. 论花岗岩型铀矿床热液来源——来自氧逸度条件的制约[J]. 地质论评, 2011, 57(2):193-206. |
| [49] | 邵飞, 许健俊, 邵上, 等. 华南花岗岩型铀矿地质特征及成矿作用[J]. 资源调查与环境, 2014, 35(3):211-217. |
| [1] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [2] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [3] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [4] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [5] | 梁东, 华北, 赵德怀, 吴浩, 万生楠, 谭朝欣, 赵晓健, 杨志鹏. 喀喇昆仑麦拉山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征与找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 708-721. |
| [6] | 娄元林, 成明, 唐侥, 张潮明, 蓝景周, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征、构造环境分析及成矿响应[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| [7] | 邓科, 王金贵, 董玉杰, 何林武, 袁仁华, 张泽国, 陈守关, 辛堂. 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世中性侵入岩的成因及对新特提斯板块北向俯冲的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 375-389. |
| [8] | 杨文鹏, 李成禄, 杨元江, 符安宗, 郑博, 周腾飞, 赵瑞君. 黑龙江塔溪地区中侏罗世侵入岩地球化学特征、成因及构造环境[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 390-403. |
| [9] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 吴子杰, 冯玥, 何云龙, 陈兴凯. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋早侏罗世构造演化:来自大兴安岭北段新立屯地区花岗岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| [10] | 夏锦胜, 孙莉, 张鹏, 陈昌阔, 汪君珠, 司江福. 四川坪河晶质石墨矿床地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1486-1496. |
| [11] | 陈世明, 杨镇熙, 雷自强, 康维良, 张晶, 赵青虎. 甘肃北山前红泉地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1513-1524. |
| [12] | 刘同, 刘传朋, 康鹏宇, 赵秀芳, 邓俊, 王凯凯. 山东省沂南县东部土壤重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1173-1182. |
| [13] | 刘洋, 李贤庆, 赵光杰, 刘满仓, 董才源, 李谨, 肖中尧. 库车坳陷东部吐格尔明地区天然气地球化学特征及油气充注史[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 988-997. |
| [14] | 郭云成, 段留安, 韩小梦, 王建田, 王利鹏, 赵鹏飞. 胶东前垂柳金矿区花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 876-897. |
| [15] | 王斌, 任涛, 宋伊圩, 杨可, 王占彬, 孙亚柯. 西秦岭常家山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 911-922. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||