



现代地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (01): 194-208.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2025.007
田冉婷( ), 白峰(
), 白峰( ), 许玲玲, 李净净, 车延东, 杜季明
), 许玲玲, 李净净, 车延东, 杜季明
出版日期:2025-02-10
发布日期:2025-02-20
通信作者:
白 峰,男,博士,教授,1971年出生,主要从事宝石教学与科研工作。Email: baifeng@cugb.edu.cn。作者简介:田冉婷,女,硕士研究生,2000年出生,材料与化工专业,主要从事宝石矿物学方向的研究。Email:2109220001@email.cugb.edu.cn。
基金资助:
TIAN Ranting( ), BAI Feng(
), BAI Feng( ), XU Lingling, LI Jingjing, CHE Yandong, DU Jiming
), XU Lingling, LI Jingjing, CHE Yandong, DU Jiming
Published:2025-02-10
Online:2025-02-20
摘要:
软玉作为重要的矿物资源,其地球化学特征对于理解矿床成因与评估资源潜力具有关键作用。本文选择贵州罗甸、广西大化和广西巴马地区的基性岩交代型软玉为研究对象,通过电子探针技术和激光剥蚀-电感耦合等离子体质谱法(LA-ICP-MS),对代表性软玉样品进行了系统的主微量及稀土元素含量分析。研究结果显示,黔桂地区基性岩交代型软玉的主要成分以SiO2、CaO和MgO为主,其平均含量低于透闪石矿物的理论值,而SiO2的整体含量高于超基性岩矿床,呈现出与围岩及后期热液硅供给密切相关的成矿特征。微量元素分析中,U、La、Sm表现出显著的正异常,而Nb则为负异常,缺乏Ba负异常的特征进一步强化了其与其他成因软玉的区别。稀土元素的配分模式具有较高一致性,轻重稀土元素分异明显,轻稀土元素的富集以及Ce和Eu的负异常使其在成因上可与其他软玉类型有效区分。此外,贵州和广西的辉绿岩与峨眉山玄武岩在稀土元素配分特征上呈现出较高的相似性。综上所述,通过分析不同产地软玉的δCe、δEu及∑REE值,构建的树状图有效实现了对其的分类与区分。本研究为深入理解华南地区软玉的成矿机制及资源开发提供了基础性地球化学依据。
中图分类号:
田冉婷, 白峰, 许玲玲, 李净净, 车延东, 杜季明. 中国黔桂地区基性岩交代型软玉地球化学特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(01): 194-208.
TIAN Ranting, BAI Feng, XU Lingling, LI Jingjing, CHE Yandong, DU Jiming. Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis of Basaltic Metasomatic Nephrite in the Qiangui Region, China[J]. Geoscience, 2025, 39(01): 194-208.

图1 中国黔桂地区软玉矿床地理位置、成矿年代及各矿区地质简图 (a)黔桂软玉地理位置和成矿年代;(b)罗甸软玉矿区地质简图(据文献[6]修改);(c)大化软玉矿区地质简图(据文献[7]修改);(d)巴马软玉矿区地质简图(据文献[8]修改)
Fig.1 Geographic location, ore-forming age and simplified geological maps of nephrite deposits in the Qiangui region, China
| 产地 | 样品编号 | Na2O | Al2O3 | MgO | K2O | CaO | SiO2 | MnO | FeO | Cr2O3 | TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贵州 罗甸 | LD1-2-2 | 0.23 | 0.14 | 24.64 | 0.08 | 11.96 | 58.28 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.05 |
| LD1-2-8 | 0.25 | 0.16 | 22.77 | 0.14 | 10.28 | 55.27 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.01 | |
| LD1-4-1 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 25.21 | 0.04 | 12.71 | 57.36 | - | - | 0.01 | - | |
| LD1-4-4 | 0.21 | 0.30 | 20.59 | 0.07 | 17.90 | 58.22 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.21 | 0.04 | |
| LD2-1-3 | 0.17 | 0.32 | 22.66 | 0.06 | 12.15 | 57.72 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.02 | |
| LD2-1-5 | 0.13 | 0.22 | 21.77 | 0.16 | 10.06 | 57.08 | 0.02 | 0.17 | - | - | |
| LD2-1-6 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 22.53 | 0.09 | 11.12 | 58.28 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| LD2-2-2 | 0.19 | 0.75 | 16.87 | 0.05 | 18.78 | 53.83 | 0.07 | 0.70 | - | 0.04 | |
| LD2-2-3 | 0.16 | 0.23 | 24.79 | 0.15 | 8.81 | 58.49 | - | 0.15 | - | - | |
| LD2-2-7 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 24.00 | 0.03 | 11.04 | 58.76 | - | 0.19 | 0.04 | - | |
| LD3-1-6 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 25.10 | 0.13 | 12.91 | 57.43 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.12 | - | |
| LD3-2-1 | 0.17 | 0.34 | 24.26 | 1.33 | 11.40 | 57.64 | 0.13 | 0.11 | - | 0.05 | |
| LD3-2-2 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 23.45 | 0.46 | 10.55 | 58.65 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.01 | - | |
| LD3-2-3 | 0.13 | 0.29 | 23.82 | 0.37 | 11.35 | 57.39 | 0.04 | 0.10 | - | 0.03 | |
| LD3-2-6 | 0.12 | 0.28 | 24.05 | 0.08 | 11.44 | 58.92 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.03 | |
| LD3-2-8 | 0.20 | 0.45 | 23.63 | 0.13 | 11.13 | 58.21 | 0.08 | 0.15 | - | - | |
| 广西 大化 | DH1-1-1 | 0.08 | 0.46 | 22.70 | 0.08 | 12.40 | 56.47 | 0.13 | 2.11 | 0.02 | 0.07 |
| DH1-1-2 | 0.04 | 0.64 | 22.69 | 0.14 | 11.70 | 57.09 | 0.16 | 2.31 | 0.01 | 0.04 | |
| DH1-1-5 | 0.09 | 0.48 | 22.24 | 0.07 | 12.56 | 57.47 | 0.19 | 2.13 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| DH1-1-6 | 0.14 | 0.40 | 22.79 | 0.09 | 12.02 | 58.47 | 0.19 | 1.92 | 0.07 | 0.06 | |
| DH1-2-3 | 0.07 | 0.36 | 23.51 | 0.02 | 12.03 | 60.14 | 0.12 | 1.83 | - | 0.06 | |
| DH1-2-6 | 0.06 | 0.40 | 23.41 | 0.04 | 12.22 | 59.58 | 0.16 | 1.52 | 0.01 | 0.05 | |
| DH1-2-7 | 0.03 | 0.33 | 23.49 | 0.04 | 12.27 | 59.93 | 0.17 | 1.69 | 0.01 | 0.09 | |
| DH1-3-1 | 0.08 | 0.33 | 21.29 | 0.04 | 11.33 | 57.93 | 0.19 | 5.30 | 0.06 | 0.02 | |
| DH1-3-3 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 20.81 | 0.05 | 11.33 | 58.11 | 0.18 | 4.89 | 0.05 | - | |
| DH1-3-7 | 0.08 | 0.32 | 21.25 | 0.05 | 11.19 | 57.32 | 0.17 | 5.27 | 0.03 | 0.07 | |
| DH1-3-9 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 20.62 | 0.03 | 11.27 | 57.22 | 0.11 | 5.28 | - | 0.09 | |
| DH1-4-1 | 0.09 | 0.26 | 23.82 | 0.07 | 12.17 | 58.92 | 0.24 | 1.69 | 0.10 | 0.06 | |
| DH1-4-3 | 0.12 | 0.53 | 23.65 | 0.23 | 11.90 | 59.22 | 0.27 | 1.59 | - | 0.05 | |
| DH1-4-4 | 0.11 | 0.55 | 22.78 | 0.11 | 11.88 | 58.14 | 0.20 | 2.29 | 0.01 | - | |
| DH1-4-5 | 0.11 | 0.31 | 24.31 | 0.08 | 12.46 | 60.49 | 0.26 | 1.46 | - | 0.04 | |
| DH2-1-2 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 23.43 | 0.04 | 12.04 | 59.53 | 0.11 | 1.74 | 0.01 | 0.08 | |
| DH2-1-5 | 0.14 | 0.47 | 23.09 | 0.07 | 11.66 | 58.81 | 0.13 | 2.31 | - | 0.06 | |
| DH2-2-3 | 0.18 | 0.34 | 22.09 | 0.12 | 12.08 | 57.10 | 0.11 | 2.06 | 0.03 | 0.07 | |
| DH2-2-4 | 0.18 | 0.40 | 23.18 | 0.08 | 12.16 | 59.11 | 0.04 | 2.15 | 0.02 | - | |
| DH2-2-5 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 22.25 | 0.11 | 12.12 | 57.02 | 0.06 | 1.87 | - | 0.07 | |
| DH2-2-6 | 0.14 | 0.30 | 22.25 | 0.10 | 12.33 | 58.64 | 0.07 | 1.89 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| DH2-3-1 | 0.09 | 0.38 | 23.12 | 0.08 | 12.25 | 58.93 | 0.15 | 1.86 | 0.10 | - | |
| DH2-3-7 | 0.08 | 0.47 | 23.54 | 0.10 | 12.07 | 58.53 | 0.15 | 1.59 | 0.02 | 0.03 | |
| DH2-4-2 | 0.14 | 0.40 | 22.73 | 0.07 | 11.90 | 57.53 | 0.11 | 2.54 | 0.06 | - | |
| DH3-2-2 | 0.22 | 0.56 | 23.56 | 0.07 | 11.57 | 57.80 | 0.15 | 1.74 | 0.12 | 0.03 | |
| DH3-2-3 | 0.17 | 0.41 | 22.82 | 0.06 | 11.99 | 56.26 | 0.11 | 1.54 | - | 0.03 | |
| DH3-2-4 | 0.18 | 0.48 | 22.67 | 0.05 | 11.90 | 56.80 | 0.19 | 1.90 | 1.26 | 0.01 | |
| 广西 巴马 | 巴-1 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 23.89 | - | 11.16 | 58.60 | 0.42 | 1.86 | - | 0.01 |
| 巴-3 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 23.82 | - | 11.05 | 58.82 | 0.31 | 2.48 | - | 0.01 | |
| 巴-9 | 0.01 | 0.27 | 24.43 | - | 11.76 | 58.24 | 0.50 | 0.82 | - | 0.03 | |
| 巴-10 | 0.02 | 0.46 | 22.19 | - | 9.82 | 57.58 | 0.33 | 5.82 | - | 0.01 | |
| 巴-13 | 0.02 | 0.55 | 24.43 | - | 11.14 | 58.60 | 0.64 | 1.04 | - | 0.01 |
表1 中国黔桂基性岩型软玉主量元素测试结果(%)
Table 1 Major element results of basaltic metasomatic nephrite in the Qiangui region, China (%)
| 产地 | 样品编号 | Na2O | Al2O3 | MgO | K2O | CaO | SiO2 | MnO | FeO | Cr2O3 | TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贵州 罗甸 | LD1-2-2 | 0.23 | 0.14 | 24.64 | 0.08 | 11.96 | 58.28 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.05 |
| LD1-2-8 | 0.25 | 0.16 | 22.77 | 0.14 | 10.28 | 55.27 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.01 | |
| LD1-4-1 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 25.21 | 0.04 | 12.71 | 57.36 | - | - | 0.01 | - | |
| LD1-4-4 | 0.21 | 0.30 | 20.59 | 0.07 | 17.90 | 58.22 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.21 | 0.04 | |
| LD2-1-3 | 0.17 | 0.32 | 22.66 | 0.06 | 12.15 | 57.72 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.02 | |
| LD2-1-5 | 0.13 | 0.22 | 21.77 | 0.16 | 10.06 | 57.08 | 0.02 | 0.17 | - | - | |
| LD2-1-6 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 22.53 | 0.09 | 11.12 | 58.28 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| LD2-2-2 | 0.19 | 0.75 | 16.87 | 0.05 | 18.78 | 53.83 | 0.07 | 0.70 | - | 0.04 | |
| LD2-2-3 | 0.16 | 0.23 | 24.79 | 0.15 | 8.81 | 58.49 | - | 0.15 | - | - | |
| LD2-2-7 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 24.00 | 0.03 | 11.04 | 58.76 | - | 0.19 | 0.04 | - | |
| LD3-1-6 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 25.10 | 0.13 | 12.91 | 57.43 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.12 | - | |
| LD3-2-1 | 0.17 | 0.34 | 24.26 | 1.33 | 11.40 | 57.64 | 0.13 | 0.11 | - | 0.05 | |
| LD3-2-2 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 23.45 | 0.46 | 10.55 | 58.65 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.01 | - | |
| LD3-2-3 | 0.13 | 0.29 | 23.82 | 0.37 | 11.35 | 57.39 | 0.04 | 0.10 | - | 0.03 | |
| LD3-2-6 | 0.12 | 0.28 | 24.05 | 0.08 | 11.44 | 58.92 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.03 | |
| LD3-2-8 | 0.20 | 0.45 | 23.63 | 0.13 | 11.13 | 58.21 | 0.08 | 0.15 | - | - | |
| 广西 大化 | DH1-1-1 | 0.08 | 0.46 | 22.70 | 0.08 | 12.40 | 56.47 | 0.13 | 2.11 | 0.02 | 0.07 |
| DH1-1-2 | 0.04 | 0.64 | 22.69 | 0.14 | 11.70 | 57.09 | 0.16 | 2.31 | 0.01 | 0.04 | |
| DH1-1-5 | 0.09 | 0.48 | 22.24 | 0.07 | 12.56 | 57.47 | 0.19 | 2.13 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| DH1-1-6 | 0.14 | 0.40 | 22.79 | 0.09 | 12.02 | 58.47 | 0.19 | 1.92 | 0.07 | 0.06 | |
| DH1-2-3 | 0.07 | 0.36 | 23.51 | 0.02 | 12.03 | 60.14 | 0.12 | 1.83 | - | 0.06 | |
| DH1-2-6 | 0.06 | 0.40 | 23.41 | 0.04 | 12.22 | 59.58 | 0.16 | 1.52 | 0.01 | 0.05 | |
| DH1-2-7 | 0.03 | 0.33 | 23.49 | 0.04 | 12.27 | 59.93 | 0.17 | 1.69 | 0.01 | 0.09 | |
| DH1-3-1 | 0.08 | 0.33 | 21.29 | 0.04 | 11.33 | 57.93 | 0.19 | 5.30 | 0.06 | 0.02 | |
| DH1-3-3 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 20.81 | 0.05 | 11.33 | 58.11 | 0.18 | 4.89 | 0.05 | - | |
| DH1-3-7 | 0.08 | 0.32 | 21.25 | 0.05 | 11.19 | 57.32 | 0.17 | 5.27 | 0.03 | 0.07 | |
| DH1-3-9 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 20.62 | 0.03 | 11.27 | 57.22 | 0.11 | 5.28 | - | 0.09 | |
| DH1-4-1 | 0.09 | 0.26 | 23.82 | 0.07 | 12.17 | 58.92 | 0.24 | 1.69 | 0.10 | 0.06 | |
| DH1-4-3 | 0.12 | 0.53 | 23.65 | 0.23 | 11.90 | 59.22 | 0.27 | 1.59 | - | 0.05 | |
| DH1-4-4 | 0.11 | 0.55 | 22.78 | 0.11 | 11.88 | 58.14 | 0.20 | 2.29 | 0.01 | - | |
| DH1-4-5 | 0.11 | 0.31 | 24.31 | 0.08 | 12.46 | 60.49 | 0.26 | 1.46 | - | 0.04 | |
| DH2-1-2 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 23.43 | 0.04 | 12.04 | 59.53 | 0.11 | 1.74 | 0.01 | 0.08 | |
| DH2-1-5 | 0.14 | 0.47 | 23.09 | 0.07 | 11.66 | 58.81 | 0.13 | 2.31 | - | 0.06 | |
| DH2-2-3 | 0.18 | 0.34 | 22.09 | 0.12 | 12.08 | 57.10 | 0.11 | 2.06 | 0.03 | 0.07 | |
| DH2-2-4 | 0.18 | 0.40 | 23.18 | 0.08 | 12.16 | 59.11 | 0.04 | 2.15 | 0.02 | - | |
| DH2-2-5 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 22.25 | 0.11 | 12.12 | 57.02 | 0.06 | 1.87 | - | 0.07 | |
| DH2-2-6 | 0.14 | 0.30 | 22.25 | 0.10 | 12.33 | 58.64 | 0.07 | 1.89 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| DH2-3-1 | 0.09 | 0.38 | 23.12 | 0.08 | 12.25 | 58.93 | 0.15 | 1.86 | 0.10 | - | |
| DH2-3-7 | 0.08 | 0.47 | 23.54 | 0.10 | 12.07 | 58.53 | 0.15 | 1.59 | 0.02 | 0.03 | |
| DH2-4-2 | 0.14 | 0.40 | 22.73 | 0.07 | 11.90 | 57.53 | 0.11 | 2.54 | 0.06 | - | |
| DH3-2-2 | 0.22 | 0.56 | 23.56 | 0.07 | 11.57 | 57.80 | 0.15 | 1.74 | 0.12 | 0.03 | |
| DH3-2-3 | 0.17 | 0.41 | 22.82 | 0.06 | 11.99 | 56.26 | 0.11 | 1.54 | - | 0.03 | |
| DH3-2-4 | 0.18 | 0.48 | 22.67 | 0.05 | 11.90 | 56.80 | 0.19 | 1.90 | 1.26 | 0.01 | |
| 广西 巴马 | 巴-1 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 23.89 | - | 11.16 | 58.60 | 0.42 | 1.86 | - | 0.01 |
| 巴-3 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 23.82 | - | 11.05 | 58.82 | 0.31 | 2.48 | - | 0.01 | |
| 巴-9 | 0.01 | 0.27 | 24.43 | - | 11.76 | 58.24 | 0.50 | 0.82 | - | 0.03 | |
| 巴-10 | 0.02 | 0.46 | 22.19 | - | 9.82 | 57.58 | 0.33 | 5.82 | - | 0.01 | |
| 巴-13 | 0.02 | 0.55 | 24.43 | - | 11.14 | 58.60 | 0.64 | 1.04 | - | 0.01 |
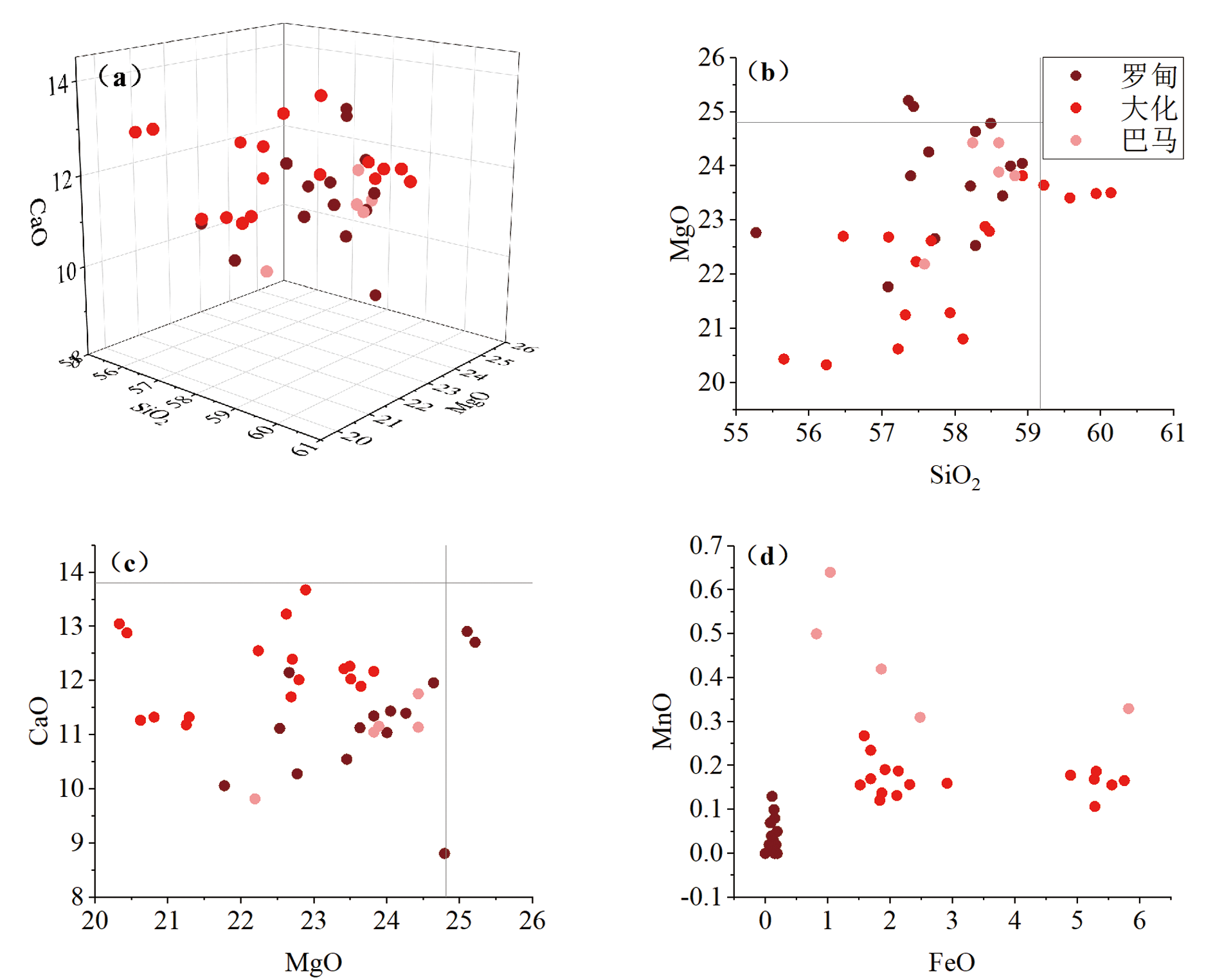
图4 中国黔桂基性岩型软玉各产地主量元素含量投点图(%)
Fig.4 Projections of the content of major elementsin basaltic metasomatic nephrite in the Qiangui region, China(%) (a)SiO2-MgO-CaO;(b)SiO2-MgO;(c)MgO-CaO;(d)FeO-MnO
| 产地 | 样品编号 | Na2O | Al2O3 | MgO | K2O | CaO | SiO2 | MnO | FeO | Cr2O3 | TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贵州 罗甸 | LD01 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 24.60 | 0.10 | 11.69 | 56.58 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.04 |
| LD02 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 25.65 | 0.11 | 11.99 | 57.01 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.03 | |
| LD04 | 0.04 | 0.20 | 25.86 | 0.10 | 12.09 | 57.13 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.02 | |
| LD05 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 24.51 | 0.13 | 13.48 | 54.29 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.02 | |
| LD001 | 0.48 | 0.35 | 22.25 | 0.12 | 14.81 | 54.75 | 0.02 | - | - | 0.05 | |
| PL950 | 0.24 | 0.52 | 24.41 | 0.11 | 11.87 | 59.12 | 0.03 | - | - | 0.02 | |
| W1 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 24.39 | 0.10 | 11.90 | 58.99 | 0.03 | 0.06 | - | 0.02 | |
| W2 | 0.14 | 0.58 | 24.05 | 0.06 | 12.00 | 57.86 | 0.04 | 0.28 | - | 0.03 | |
| W3 | 0.17 | 0.57 | 27.47 | 0.07 | 11.20 | 56.35 | 0.02 | 0.23 | - | 0.03 | |
| W4 | 0.21 | 0.48 | 24.72 | 0.07 | 14.43 | 53.59 | 0.01 | 0.19 | - | 0.02 | |
| W5 | 0.26 | 0.55 | 26.79 | 0.08 | 12.22 | 56.28 | 0.01 | 0.29 | - | 0.02 | |
| W6 | 0.20 | 0.41 | 26.77 | 0.09 | 11.99 | 56.60 | 0.02 | 0.45 | - | 0.01 | |
| W7 | 0.11 | 0.29 | 26.70 | 0.08 | 12.23 | 56.38 | 0.01 | 0.38 | - | 0.01 | |
| B1 | 0.27 | 1.38 | 21.15 | 0.24 | 14.68 | 54.28 | - | 0.76 | - | 0.18 | |
| G1 | 0.60 | 0.32 | 16.93 | 0.07 | 14.61 | 57.25 | 0.01 | 0.89 | - | 0.01 | |
| G2 | 0.51 | 0.20 | 17.17 | 0.02 | 17.29 | 54.82 | 0.02 | 0.65 | - | 0.01 | |
| G3 | 0.56 | 0.45 | 17.07 | 0.06 | 12.84 | 58.32 | 0.01 | 0.68 | - | 0.02 | |
| G4 | 0.48 | 0.27 | 21.60 | 0.11 | 14.92 | 54.48 | 0.02 | 0.41 | - | 0.06 | |
| G5 | 0.13 | 0.38 | 23.93 | 0.10 | 14.22 | 56.74 | 0.04 | 0.26 | - | 0.06 | |
| G6 | 0.57 | 0.19 | 18.04 | 0.03 | 15.66 | 55.84 | 0.01 | 0.77 | - | 0.02 | |
| G7 | 0.22 | 0.28 | 23.43 | 0.09 | 14.65 | 56.69 | 0.01 | 0.32 | - | 0.04 | |
| T-1 | 0.09 | 0.23 | 24.4 | 0.05 | 12.45 | 59.42 | 0.12 | 0.47 | 0.02 | 0.03 | |
| T-2 | 0.08 | 0.27 | 24.03 | 0.03 | 12.71 | 59.15 | 0.13 | - | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| T-3 | 0.09 | 0.32 | 23.73 | 0.04 | 12.32 | 59.41 | 0.17 | 1.1 | 0.17 | 0.02 | |
| 1-1-1 | 0.28 | 0.04 | 24.93 | 0.16 | 12.26 | 59.69 | 0.02 | 0.24 | - | - | |
| 2-1-1 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 25.39 | 0.13 | 11.89 | 59.79 | - | 0.17 | - | 0.01 | |
| 2-2-1 | 0.37 | 0.16 | 25.94 | 0.12 | 11.17 | 58.80 | - | 0.39 | - | 0.09 | |
| 2-2-2 | 0.37 | 0.10 | 25.86 | 0.12 | 11.84 | 58.63 | - | 0.37 | - | 0.05 | |
| 2-3-1 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 25.43 | 0.07 | 11.96 | 59.46 | 0.14 | 0.05 | - | 0.07 | |
| 3-1-1 | 0.40 | 0.12 | 26.42 | 0.04 | 11.04 | 59.23 | 0.20 | 0.04 | - | 0.01 | |
| 3-1-2 | 0.35 | 0.18 | 26.56 | 0.09 | 10.93 | 59.55 | 0.04 | 0.18 | - | - | |
| 广西 大化 | 1-2-1 | 0.05 | 0.32 | 23.26 | 0.02 | 13.87 | 58.30 | 0.16 | 0.76 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| 1-3-1 | 0.05 | 0.36 | 23.53 | 0.04 | 14.08 | 58.57 | 0.15 | 0.79 | 0.01 | - | |
| 1-3-4 | 0.08 | 0.65 | 23.28 | 0.13 | 13.46 | 58.10 | 0.17 | 0.80 | 0.05 | - | |
| 1-4-2 | 0.05 | 0.46 | 23.26 | 0.08 | 13.17 | 58.14 | 0.13 | 0.88 | 0.04 | - | |
| 2-2-1 | 0.13 | 0.36 | 22.83 | 0.07 | 14.07 | 57.35 | 0.13 | 0.95 | - | 0.02 | |
| 2-3-1 | 0.05 | 0.36 | 22.87 | 0.07 | 14.11 | 58.92 | 0.19 | 0.82 | - | - | |
| 2-3-2 | 0.05 | 0.31 | 24.08 | 0.07 | 13.67 | 58.26 | 0.18 | 0.53 | - | - | |
| 2-4-1 | 0.12 | 0.33 | 23.56 | 0.04 | 13.94 | 57.47 | 0.07 | 0.90 | - | - | |
| 2-4-2 | 0.11 | 0.41 | 25.15 | 0.06 | 13.67 | 57.89 | 0.09 | 0.91 | - | - | |
| 3-2-1 | 0.12 | 0.40 | 23.86 | 0.05 | 14.15 | 58.27 | 0.11 | 0.63 | 0.03 | 0.02 | |
| 3-4-1 | 0.16 | 0.28 | 23.96 | 0.08 | 13.63 | 57.33 | 0.09 | 0.36 | 0.01 | 0.04 | |
| D2 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 23.44 | 0.17 | 12.51 | 58.40 | 0.05 | 0.15 | - | - | |
| D3 | 0.29 | 0.16 | 23.60 | 0.20 | 12.47 | 59.14 | - | 0.09 | - | - | |
| D4 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 23.33 | 0.09 | 12.31 | 58.45 | 0.03 | 0.09 | - | - | |
| D5 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 22.45 | 0.10 | 14.37 | 58.49 | 0.03 | 0.27 | - | - | |
| D6 | 0.38 | 0.22 | 24.01 | 0.27 | 11.02 | 59.71 | 0.03 | 0.04 | - | - | |
| D8 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 21.53 | 0.09 | 16.52 | 57.39 | 0.03 | 0.28 | - | - | |
| E1 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 24.00 | 0.14 | 12.60 | 57.97 | 0.02 | 0.03 | - | - | |
| E5 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 24.10 | 0.16 | 12.93 | 57.81 | 0 | 0.01 | - | - | |
| E6 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 24.01 | 0.09 | 13.50 | 57.56 | 0.03 | 0.05 | - | - | |
| E10 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 23.92 | 0.16 | 12.93 | 58.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | - | - | |
| Dh-1 | 0.06 | 0.76 | 25.70 | 0.06 | 14.20 | 58.70 | 0.13 | 0.28 | - | 0.01 | |
| Dh-2 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 26.60 | 0.14 | 13.60 | 59.10 | 0.01 | 0.02 | - | - | |
| Dh-3 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 25.50 | 0.14 | 13.90 | 59.70 | 0.04 | 0.06 | - | - | |
| Dh-4 | 0.05 | 0.57 | 26.50 | 0.05 | 13.30 | 58.60 | 0.06 | 0.67 | - | - | |
| Dh-5 | 0.09 | 0.42 | 26.00 | 0.08 | 13.50 | 58.70 | 0.03 | 1.01 | - | 0.01 | |
| Dh-6 | 0.12 | 0.59 | 23.90 | 0.12 | 13.60 | 58.10 | 0.15 | 3.22 | - | - | |
| Dh-7 | 0.09 | 0.60 | 25.80 | 0.07 | 14.20 | 58.60 | 0.04 | 0.41 | - | 0.01 |
表2 中国黔桂基性岩型软玉主量元素样品数据(%)
Table 2 Major element compositions of basaltic metasomatic nephrite in the Qiangui region, China(%)
| 产地 | 样品编号 | Na2O | Al2O3 | MgO | K2O | CaO | SiO2 | MnO | FeO | Cr2O3 | TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贵州 罗甸 | LD01 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 24.60 | 0.10 | 11.69 | 56.58 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.04 |
| LD02 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 25.65 | 0.11 | 11.99 | 57.01 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.03 | |
| LD04 | 0.04 | 0.20 | 25.86 | 0.10 | 12.09 | 57.13 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.02 | |
| LD05 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 24.51 | 0.13 | 13.48 | 54.29 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.02 | |
| LD001 | 0.48 | 0.35 | 22.25 | 0.12 | 14.81 | 54.75 | 0.02 | - | - | 0.05 | |
| PL950 | 0.24 | 0.52 | 24.41 | 0.11 | 11.87 | 59.12 | 0.03 | - | - | 0.02 | |
| W1 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 24.39 | 0.10 | 11.90 | 58.99 | 0.03 | 0.06 | - | 0.02 | |
| W2 | 0.14 | 0.58 | 24.05 | 0.06 | 12.00 | 57.86 | 0.04 | 0.28 | - | 0.03 | |
| W3 | 0.17 | 0.57 | 27.47 | 0.07 | 11.20 | 56.35 | 0.02 | 0.23 | - | 0.03 | |
| W4 | 0.21 | 0.48 | 24.72 | 0.07 | 14.43 | 53.59 | 0.01 | 0.19 | - | 0.02 | |
| W5 | 0.26 | 0.55 | 26.79 | 0.08 | 12.22 | 56.28 | 0.01 | 0.29 | - | 0.02 | |
| W6 | 0.20 | 0.41 | 26.77 | 0.09 | 11.99 | 56.60 | 0.02 | 0.45 | - | 0.01 | |
| W7 | 0.11 | 0.29 | 26.70 | 0.08 | 12.23 | 56.38 | 0.01 | 0.38 | - | 0.01 | |
| B1 | 0.27 | 1.38 | 21.15 | 0.24 | 14.68 | 54.28 | - | 0.76 | - | 0.18 | |
| G1 | 0.60 | 0.32 | 16.93 | 0.07 | 14.61 | 57.25 | 0.01 | 0.89 | - | 0.01 | |
| G2 | 0.51 | 0.20 | 17.17 | 0.02 | 17.29 | 54.82 | 0.02 | 0.65 | - | 0.01 | |
| G3 | 0.56 | 0.45 | 17.07 | 0.06 | 12.84 | 58.32 | 0.01 | 0.68 | - | 0.02 | |
| G4 | 0.48 | 0.27 | 21.60 | 0.11 | 14.92 | 54.48 | 0.02 | 0.41 | - | 0.06 | |
| G5 | 0.13 | 0.38 | 23.93 | 0.10 | 14.22 | 56.74 | 0.04 | 0.26 | - | 0.06 | |
| G6 | 0.57 | 0.19 | 18.04 | 0.03 | 15.66 | 55.84 | 0.01 | 0.77 | - | 0.02 | |
| G7 | 0.22 | 0.28 | 23.43 | 0.09 | 14.65 | 56.69 | 0.01 | 0.32 | - | 0.04 | |
| T-1 | 0.09 | 0.23 | 24.4 | 0.05 | 12.45 | 59.42 | 0.12 | 0.47 | 0.02 | 0.03 | |
| T-2 | 0.08 | 0.27 | 24.03 | 0.03 | 12.71 | 59.15 | 0.13 | - | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| T-3 | 0.09 | 0.32 | 23.73 | 0.04 | 12.32 | 59.41 | 0.17 | 1.1 | 0.17 | 0.02 | |
| 1-1-1 | 0.28 | 0.04 | 24.93 | 0.16 | 12.26 | 59.69 | 0.02 | 0.24 | - | - | |
| 2-1-1 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 25.39 | 0.13 | 11.89 | 59.79 | - | 0.17 | - | 0.01 | |
| 2-2-1 | 0.37 | 0.16 | 25.94 | 0.12 | 11.17 | 58.80 | - | 0.39 | - | 0.09 | |
| 2-2-2 | 0.37 | 0.10 | 25.86 | 0.12 | 11.84 | 58.63 | - | 0.37 | - | 0.05 | |
| 2-3-1 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 25.43 | 0.07 | 11.96 | 59.46 | 0.14 | 0.05 | - | 0.07 | |
| 3-1-1 | 0.40 | 0.12 | 26.42 | 0.04 | 11.04 | 59.23 | 0.20 | 0.04 | - | 0.01 | |
| 3-1-2 | 0.35 | 0.18 | 26.56 | 0.09 | 10.93 | 59.55 | 0.04 | 0.18 | - | - | |
| 广西 大化 | 1-2-1 | 0.05 | 0.32 | 23.26 | 0.02 | 13.87 | 58.30 | 0.16 | 0.76 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| 1-3-1 | 0.05 | 0.36 | 23.53 | 0.04 | 14.08 | 58.57 | 0.15 | 0.79 | 0.01 | - | |
| 1-3-4 | 0.08 | 0.65 | 23.28 | 0.13 | 13.46 | 58.10 | 0.17 | 0.80 | 0.05 | - | |
| 1-4-2 | 0.05 | 0.46 | 23.26 | 0.08 | 13.17 | 58.14 | 0.13 | 0.88 | 0.04 | - | |
| 2-2-1 | 0.13 | 0.36 | 22.83 | 0.07 | 14.07 | 57.35 | 0.13 | 0.95 | - | 0.02 | |
| 2-3-1 | 0.05 | 0.36 | 22.87 | 0.07 | 14.11 | 58.92 | 0.19 | 0.82 | - | - | |
| 2-3-2 | 0.05 | 0.31 | 24.08 | 0.07 | 13.67 | 58.26 | 0.18 | 0.53 | - | - | |
| 2-4-1 | 0.12 | 0.33 | 23.56 | 0.04 | 13.94 | 57.47 | 0.07 | 0.90 | - | - | |
| 2-4-2 | 0.11 | 0.41 | 25.15 | 0.06 | 13.67 | 57.89 | 0.09 | 0.91 | - | - | |
| 3-2-1 | 0.12 | 0.40 | 23.86 | 0.05 | 14.15 | 58.27 | 0.11 | 0.63 | 0.03 | 0.02 | |
| 3-4-1 | 0.16 | 0.28 | 23.96 | 0.08 | 13.63 | 57.33 | 0.09 | 0.36 | 0.01 | 0.04 | |
| D2 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 23.44 | 0.17 | 12.51 | 58.40 | 0.05 | 0.15 | - | - | |
| D3 | 0.29 | 0.16 | 23.60 | 0.20 | 12.47 | 59.14 | - | 0.09 | - | - | |
| D4 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 23.33 | 0.09 | 12.31 | 58.45 | 0.03 | 0.09 | - | - | |
| D5 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 22.45 | 0.10 | 14.37 | 58.49 | 0.03 | 0.27 | - | - | |
| D6 | 0.38 | 0.22 | 24.01 | 0.27 | 11.02 | 59.71 | 0.03 | 0.04 | - | - | |
| D8 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 21.53 | 0.09 | 16.52 | 57.39 | 0.03 | 0.28 | - | - | |
| E1 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 24.00 | 0.14 | 12.60 | 57.97 | 0.02 | 0.03 | - | - | |
| E5 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 24.10 | 0.16 | 12.93 | 57.81 | 0 | 0.01 | - | - | |
| E6 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 24.01 | 0.09 | 13.50 | 57.56 | 0.03 | 0.05 | - | - | |
| E10 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 23.92 | 0.16 | 12.93 | 58.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | - | - | |
| Dh-1 | 0.06 | 0.76 | 25.70 | 0.06 | 14.20 | 58.70 | 0.13 | 0.28 | - | 0.01 | |
| Dh-2 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 26.60 | 0.14 | 13.60 | 59.10 | 0.01 | 0.02 | - | - | |
| Dh-3 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 25.50 | 0.14 | 13.90 | 59.70 | 0.04 | 0.06 | - | - | |
| Dh-4 | 0.05 | 0.57 | 26.50 | 0.05 | 13.30 | 58.60 | 0.06 | 0.67 | - | - | |
| Dh-5 | 0.09 | 0.42 | 26.00 | 0.08 | 13.50 | 58.70 | 0.03 | 1.01 | - | 0.01 | |
| Dh-6 | 0.12 | 0.59 | 23.90 | 0.12 | 13.60 | 58.10 | 0.15 | 3.22 | - | - | |
| Dh-7 | 0.09 | 0.60 | 25.80 | 0.07 | 14.20 | 58.60 | 0.04 | 0.41 | - | 0.01 |
| 产地 | 样品编号 | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | La | Ce | Sr | Zr | Hf | Sm | Yb | Lu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 罗甸 | LD1-1-1 | 0.10 | 3.44 | 0.50 | 0.21 | 0.62 | 0.06 | 5.91 | 3.97 | 39.53 | 4.88 | 0.17 | 0.84 | 0.53 | 0.08 |
| LD1-1-2 | 0.11 | 3.03 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.51 | 0.06 | 4.11 | 2.94 | 38.53 | 3.69 | 0.18 | 0.58 | 0.37 | - | |
| LD1-1-3 | 0.12 | 2.32 | 0.29 | 0.18 | 0.67 | 0.05 | 4.12 | 2.83 | 37.34 | 2.68 | 0.16 | 0.54 | 0.20 | - | |
| LD1-1-4 | 0.16 | 3.14 | 0.63 | 0.27 | 0.68 | 0.07 | 6.82 | 4.31 | 48.79 | 3.59 | 0.25 | 1.02 | 0.32 | - | |
| LD1-1-5 | 0.19 | 3.79 | 0.48 | 0.26 | 0.77 | 0.09 | 6.43 | 4.28 | 51.19 | 3.45 | 0.22 | 1.35 | - | - | |
| LD2-1-1 | 0.52 | 36.91 | 5.42 | 0.59 | 2.06 | 0.30 | 41.46 | 19.55 | 167.24 | 23.24 | 0.99 | 5.76 | 1.48 | 0.24 | |
| LD2-1-2 | 0.69 | 33.94 | 2.05 | 0.49 | 2.11 | 0.28 | 23.32 | 12.08 | 143.99 | 18.26 | 0.87 | 3.38 | - | - | |
| LD2-1-3 | 0.86 | 34.20 | 1.95 | 0.53 | 2.08 | 0.27 | 23.57 | 13.33 | 154.02 | 26.70 | 0.86 | 3.81 | - | - | |
| LD2-1-4 | 0.73 | 34.57 | 3.70 | 0.50 | 1.57 | 0.26 | 35.40 | 18.87 | 157.08 | 20.71 | 1.09 | 6.13 | 1.18 | - | |
| LD2-1-5 | 0.52 | 36.07 | 4.38 | 0.48 | 2.10 | 0.25 | 38.19 | 19.53 | 160.29 | 18.11 | 0.93 | 4.78 | 1.85 | - | |
| LD2-3-1 | 0.19 | 11.57 | 0.23 | 2.15 | 1.23 | 0.08 | 12.50 | 6.55 | 51.40 | 2.91 | 0.24 | 2.03 | 0.35 | - | |
| LD2-3-2 | 0.17 | 10.03 | 0.27 | 2.28 | 1.13 | 0.09 | 11.84 | 6.16 | 53.61 | 2.72 | 0.20 | 1.69 | 0.34 | - | |
| LD2-3-3 | 0.06 | 5.68 | 0.05 | 0.35 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 9.14 | 3.00 | 158.39 | 0.99 | 0.10 | 0.80 | - | - | |
| LD2-4-1 | 0.16 | 8.86 | 0.46 | 0.13 | 0.48 | 0.08 | 6.85 | 3.51 | 38.00 | 3.62 | 0.23 | 1.10 | - | - | |
| LD2-4-2 | 0.19 | 8.02 | 2.43 | 0.20 | 0.51 | 0.06 | 13.58 | 6.88 | 46.71 | 4.40 | 0.21 | 2.05 | 0.38 | 0.06 | |
| LD2-4-3 | 0.30 | 7.82 | 0.60 | 0.11 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 6.48 | 3.39 | 36.84 | 2.47 | 0.20 | 1.05 | - | - | |
| LD3-1-1 | 0.17 | 7.53 | 0.07 | 0.80 | 0.68 | 0.07 | 6.17 | 4.69 | 19.71 | 0.45 | 0.24 | 0.92 | - | - | |
| LD3-1-2 | 0.14 | 7.63 | 0.10 | 0.77 | 0.73 | 0.07 | 5.93 | 4.98 | 19.24 | 0.59 | 0.25 | 1.05 | - | 0.06 | |
| 大化 | 1-1 | 2.03 | 147.41 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 8.59 | 0.22 | 8.02 | 26.36 | 167.32 | 40.78 | 0.44 | 5.43 | 2.13 | 0.28 |
| 1-2 | 1.99 | 113.17 | 3.13 | 0.59 | 9.17 | 0.41 | 45.45 | 87.03 | 201.43 | 126.08 | 3.70 | 8.96 | 1.78 | 0.24 | |
| 1-3 | 1.06 | 111.25 | 0.29 | - | 5.52 | 0.24 | 8.75 | 22.73 | 164.32 | 63.43 | 1.06 | 3.17 | 1.25 | 0.21 | |
| 1-4 | 1.10 | 16.68 | 0.88 | 0.11 | 2.75 | 0.22 | 10.21 | 23.43 | 79.85 | 81.71 | 2.00 | 2.17 | 1.13 | 0.20 | |
| 2-1 | 1.98 | 31.16 | 2.47 | 0.39 | 3.50 | 0.24 | 27.85 | 54.12 | 99.72 | 155.37 | 4.99 | 6.04 | 1.85 | 0.27 | |
| 巴马 | 巴-1 | 0.24 | 2.51 | 0.36 | 0.14 | 0.53 | 0.02 | 2.56 | 1.27 | 16.10 | 2.57 | 0.09 | 0.48 | 0.24 | 0.04 |
| 巴-3 | 0.37 | 8.14 | 0.44 | 0.34 | 0.55 | 0.10 | 3.13 | 1.15 | 24.00 | 4.41 | 0.14 | 0.45 | 0.35 | 0.06 | |
| 巴-9 | 0.24 | 7.03 | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.66 | - | 2.11 | 1.14 | 32.30 | 7.25 | 0.23 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.07 | |
| 巴-10 | 0.23 | 24.10 | 0.49 | 0.28 | 0.68 | 0.13 | 5.07 | 1.95 | 22.80 | 5.01 | 0.17 | 0.70 | 0.32 | 0.04 | |
| 巴-13 | 0.16 | 14.00 | 0.33 | 0.06 | 0.48 | 0.05 | 16.80 | 7.36 | 27.90 | 3.32 | 0.10 | 1.50 | 0.29 | 0.04 |
表3 中国黔桂基性岩型软玉微量元素测试结果(10-6)
Table 3 Trace element results of basaltic metasomatic nephrite in the Qiangui region, China(10-6)
| 产地 | 样品编号 | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | La | Ce | Sr | Zr | Hf | Sm | Yb | Lu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 罗甸 | LD1-1-1 | 0.10 | 3.44 | 0.50 | 0.21 | 0.62 | 0.06 | 5.91 | 3.97 | 39.53 | 4.88 | 0.17 | 0.84 | 0.53 | 0.08 |
| LD1-1-2 | 0.11 | 3.03 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.51 | 0.06 | 4.11 | 2.94 | 38.53 | 3.69 | 0.18 | 0.58 | 0.37 | - | |
| LD1-1-3 | 0.12 | 2.32 | 0.29 | 0.18 | 0.67 | 0.05 | 4.12 | 2.83 | 37.34 | 2.68 | 0.16 | 0.54 | 0.20 | - | |
| LD1-1-4 | 0.16 | 3.14 | 0.63 | 0.27 | 0.68 | 0.07 | 6.82 | 4.31 | 48.79 | 3.59 | 0.25 | 1.02 | 0.32 | - | |
| LD1-1-5 | 0.19 | 3.79 | 0.48 | 0.26 | 0.77 | 0.09 | 6.43 | 4.28 | 51.19 | 3.45 | 0.22 | 1.35 | - | - | |
| LD2-1-1 | 0.52 | 36.91 | 5.42 | 0.59 | 2.06 | 0.30 | 41.46 | 19.55 | 167.24 | 23.24 | 0.99 | 5.76 | 1.48 | 0.24 | |
| LD2-1-2 | 0.69 | 33.94 | 2.05 | 0.49 | 2.11 | 0.28 | 23.32 | 12.08 | 143.99 | 18.26 | 0.87 | 3.38 | - | - | |
| LD2-1-3 | 0.86 | 34.20 | 1.95 | 0.53 | 2.08 | 0.27 | 23.57 | 13.33 | 154.02 | 26.70 | 0.86 | 3.81 | - | - | |
| LD2-1-4 | 0.73 | 34.57 | 3.70 | 0.50 | 1.57 | 0.26 | 35.40 | 18.87 | 157.08 | 20.71 | 1.09 | 6.13 | 1.18 | - | |
| LD2-1-5 | 0.52 | 36.07 | 4.38 | 0.48 | 2.10 | 0.25 | 38.19 | 19.53 | 160.29 | 18.11 | 0.93 | 4.78 | 1.85 | - | |
| LD2-3-1 | 0.19 | 11.57 | 0.23 | 2.15 | 1.23 | 0.08 | 12.50 | 6.55 | 51.40 | 2.91 | 0.24 | 2.03 | 0.35 | - | |
| LD2-3-2 | 0.17 | 10.03 | 0.27 | 2.28 | 1.13 | 0.09 | 11.84 | 6.16 | 53.61 | 2.72 | 0.20 | 1.69 | 0.34 | - | |
| LD2-3-3 | 0.06 | 5.68 | 0.05 | 0.35 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 9.14 | 3.00 | 158.39 | 0.99 | 0.10 | 0.80 | - | - | |
| LD2-4-1 | 0.16 | 8.86 | 0.46 | 0.13 | 0.48 | 0.08 | 6.85 | 3.51 | 38.00 | 3.62 | 0.23 | 1.10 | - | - | |
| LD2-4-2 | 0.19 | 8.02 | 2.43 | 0.20 | 0.51 | 0.06 | 13.58 | 6.88 | 46.71 | 4.40 | 0.21 | 2.05 | 0.38 | 0.06 | |
| LD2-4-3 | 0.30 | 7.82 | 0.60 | 0.11 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 6.48 | 3.39 | 36.84 | 2.47 | 0.20 | 1.05 | - | - | |
| LD3-1-1 | 0.17 | 7.53 | 0.07 | 0.80 | 0.68 | 0.07 | 6.17 | 4.69 | 19.71 | 0.45 | 0.24 | 0.92 | - | - | |
| LD3-1-2 | 0.14 | 7.63 | 0.10 | 0.77 | 0.73 | 0.07 | 5.93 | 4.98 | 19.24 | 0.59 | 0.25 | 1.05 | - | 0.06 | |
| 大化 | 1-1 | 2.03 | 147.41 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 8.59 | 0.22 | 8.02 | 26.36 | 167.32 | 40.78 | 0.44 | 5.43 | 2.13 | 0.28 |
| 1-2 | 1.99 | 113.17 | 3.13 | 0.59 | 9.17 | 0.41 | 45.45 | 87.03 | 201.43 | 126.08 | 3.70 | 8.96 | 1.78 | 0.24 | |
| 1-3 | 1.06 | 111.25 | 0.29 | - | 5.52 | 0.24 | 8.75 | 22.73 | 164.32 | 63.43 | 1.06 | 3.17 | 1.25 | 0.21 | |
| 1-4 | 1.10 | 16.68 | 0.88 | 0.11 | 2.75 | 0.22 | 10.21 | 23.43 | 79.85 | 81.71 | 2.00 | 2.17 | 1.13 | 0.20 | |
| 2-1 | 1.98 | 31.16 | 2.47 | 0.39 | 3.50 | 0.24 | 27.85 | 54.12 | 99.72 | 155.37 | 4.99 | 6.04 | 1.85 | 0.27 | |
| 巴马 | 巴-1 | 0.24 | 2.51 | 0.36 | 0.14 | 0.53 | 0.02 | 2.56 | 1.27 | 16.10 | 2.57 | 0.09 | 0.48 | 0.24 | 0.04 |
| 巴-3 | 0.37 | 8.14 | 0.44 | 0.34 | 0.55 | 0.10 | 3.13 | 1.15 | 24.00 | 4.41 | 0.14 | 0.45 | 0.35 | 0.06 | |
| 巴-9 | 0.24 | 7.03 | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.66 | - | 2.11 | 1.14 | 32.30 | 7.25 | 0.23 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.07 | |
| 巴-10 | 0.23 | 24.10 | 0.49 | 0.28 | 0.68 | 0.13 | 5.07 | 1.95 | 22.80 | 5.01 | 0.17 | 0.70 | 0.32 | 0.04 | |
| 巴-13 | 0.16 | 14.00 | 0.33 | 0.06 | 0.48 | 0.05 | 16.80 | 7.36 | 27.90 | 3.32 | 0.10 | 1.50 | 0.29 | 0.04 |

图5 中国黔桂基性岩型软玉原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(a)和球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图(b)
Fig.5 Primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram(a) and chondrite-normalized rare earth element distribution pattern diagram (b) of basaltic metasomatic nephrite in the Qiangui region, China
| 产地 | 样品编号 | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | La | Ce | Sr | Zr | Hf | Sm | Y | Yb | Lu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贵州 罗甸 | LD01 | 0.42 | 21.40 | 0.29 | 0.79 | 1.04 | 0.11 | 11.80 | 5.79 | 26.70 | 3.35 | 0.09 | 1.64 | 7.92 | 0.25 | 0.03 |
| LD02 | 0.51 | 19.30 | 0.29 | 0.57 | 0.86 | 0.08 | 6.58 | 4.53 | 25.90 | 2.76 | 0.09 | 1.33 | 6.42 | 0.19 | 0.03 | |
| LD04 | 0.38 | 12.60 | 0.44 | 1.04 | 0.71 | 0.07 | 8.65 | 3.89 | 30.10 | 3.71 | 0.10 | 1.43 | 13.80 | 0.43 | 0.06 | |
| LD05 | 0.26 | 8.92 | 0.57 | 0.84 | 0.89 | 0.09 | 11.30 | 4.21 | 39.50 | 5.67 | 0.17 | 1.10 | 7.40 | 0.44 | 0.06 | |
| LD001 | 0.27 | 9.80 | 0.67 | 0.74 | 0.94 | 0.31 | 9.47 | 5.01 | 29.80 | 8.18 | 0.25 | 1.46 | 8.63 | 0.39 | 0.05 | |
| PL950 | 0.45 | 6.21 | 0.18 | 1.25 | 0.60 | 0.38 | 4.78 | 2.59 | 22.30 | 1.68 | 0.03 | 0.93 | 7.03 | 0.23 | 0.03 | |
| LK-7 | 0.90 | 7.00 | 0.21 | - | 0.20 | 0.50 | 3.40 | 2.70 | 195.00 | 2.80 | - | 0.55 | 7.20 | 0.40 | - | |
| BY-6 | 0.40 | 24.90 | 1.84 | - | 1.30 | 0.30 | 13.60 | 10.10 | 45.50 | 25.70 | - | 1.75 | 8.50 | 0.53 | - | |
| BY-9 | 0.40 | 15.40 | 1.14 | - | 1.00 | 0.10 | 18.60 | 10.40 | 43.10 | 10.60 | - | 2.16 | 9.60 | 0.46 | - | |
| LM-3 | 1.00 | 16.00 | 0.64 | - | 0.80 | 0.20 | 14.60 | 2.50 | 160.00 | 8.90 | - | 1.15 | 8.50 | 0.66 | - | |
| LM-4 | 0.40 | 8.10 | 0.16 | - | 0.40 | 0.10 | 4.90 | 2.30 | 47.40 | 2.20 | - | 0.71 | 8.10 | 0.29 | - | |
| LM-5 | 0.30 | 7.70 | 0.11 | - | 0.50 | 0.10 | 4.30 | 1.90 | 41.30 | 2.10 | - | 0.57 | 10.30 | 0.33 | - | |
| Gga | 0.50 | 7.40 | 0.24 | - | 0.60 | 0.10 | 11.20 | 3.70 | 23.30 | 2.10 | - | 0.84 | 5.60 | 0.27 | - | |
| Ggc | 0.50 | 8.90 | 0.44 | - | 0.80 | 0.10 | 9.00 | 4.20 | 21.60 | 3.70 | - | 1.26 | 8.20 | 0.37 | - | |
| Ggd | 0.30 | 14.40 | 0.23 | - | 1.00 | 0.10 | 10.50 | 4.80 | 27.30 | 3.00 | - | 1.17 | 8.30 | 0.24 | - | |
| 广西 大化 | H-2 | 3.50 | 8.30 | 0.12 | 0.95 | 0.78 | - | 0.73 | 0.97 | 4.49 | 1.30 | 0.05 | 0.28 | 6.05 | 0.38 | 0.06 |
| H-12 | 40.27 | 126.79 | 0.17 | 0.62 | 0.25 | 0.02 | 1.53 | 1.91 | 29.11 | 2.35 | 0.10 | 0.39 | 2.87 | 0.19 | 0.03 |
表4 中国黔桂基性岩型软玉微量元素样品数据(10-6)
Table 4 Trace element compositions of basaltic metasomatic nephrite in the Qiangui region, China(10-6)
| 产地 | 样品编号 | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | La | Ce | Sr | Zr | Hf | Sm | Y | Yb | Lu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贵州 罗甸 | LD01 | 0.42 | 21.40 | 0.29 | 0.79 | 1.04 | 0.11 | 11.80 | 5.79 | 26.70 | 3.35 | 0.09 | 1.64 | 7.92 | 0.25 | 0.03 |
| LD02 | 0.51 | 19.30 | 0.29 | 0.57 | 0.86 | 0.08 | 6.58 | 4.53 | 25.90 | 2.76 | 0.09 | 1.33 | 6.42 | 0.19 | 0.03 | |
| LD04 | 0.38 | 12.60 | 0.44 | 1.04 | 0.71 | 0.07 | 8.65 | 3.89 | 30.10 | 3.71 | 0.10 | 1.43 | 13.80 | 0.43 | 0.06 | |
| LD05 | 0.26 | 8.92 | 0.57 | 0.84 | 0.89 | 0.09 | 11.30 | 4.21 | 39.50 | 5.67 | 0.17 | 1.10 | 7.40 | 0.44 | 0.06 | |
| LD001 | 0.27 | 9.80 | 0.67 | 0.74 | 0.94 | 0.31 | 9.47 | 5.01 | 29.80 | 8.18 | 0.25 | 1.46 | 8.63 | 0.39 | 0.05 | |
| PL950 | 0.45 | 6.21 | 0.18 | 1.25 | 0.60 | 0.38 | 4.78 | 2.59 | 22.30 | 1.68 | 0.03 | 0.93 | 7.03 | 0.23 | 0.03 | |
| LK-7 | 0.90 | 7.00 | 0.21 | - | 0.20 | 0.50 | 3.40 | 2.70 | 195.00 | 2.80 | - | 0.55 | 7.20 | 0.40 | - | |
| BY-6 | 0.40 | 24.90 | 1.84 | - | 1.30 | 0.30 | 13.60 | 10.10 | 45.50 | 25.70 | - | 1.75 | 8.50 | 0.53 | - | |
| BY-9 | 0.40 | 15.40 | 1.14 | - | 1.00 | 0.10 | 18.60 | 10.40 | 43.10 | 10.60 | - | 2.16 | 9.60 | 0.46 | - | |
| LM-3 | 1.00 | 16.00 | 0.64 | - | 0.80 | 0.20 | 14.60 | 2.50 | 160.00 | 8.90 | - | 1.15 | 8.50 | 0.66 | - | |
| LM-4 | 0.40 | 8.10 | 0.16 | - | 0.40 | 0.10 | 4.90 | 2.30 | 47.40 | 2.20 | - | 0.71 | 8.10 | 0.29 | - | |
| LM-5 | 0.30 | 7.70 | 0.11 | - | 0.50 | 0.10 | 4.30 | 1.90 | 41.30 | 2.10 | - | 0.57 | 10.30 | 0.33 | - | |
| Gga | 0.50 | 7.40 | 0.24 | - | 0.60 | 0.10 | 11.20 | 3.70 | 23.30 | 2.10 | - | 0.84 | 5.60 | 0.27 | - | |
| Ggc | 0.50 | 8.90 | 0.44 | - | 0.80 | 0.10 | 9.00 | 4.20 | 21.60 | 3.70 | - | 1.26 | 8.20 | 0.37 | - | |
| Ggd | 0.30 | 14.40 | 0.23 | - | 1.00 | 0.10 | 10.50 | 4.80 | 27.30 | 3.00 | - | 1.17 | 8.30 | 0.24 | - | |
| 广西 大化 | H-2 | 3.50 | 8.30 | 0.12 | 0.95 | 0.78 | - | 0.73 | 0.97 | 4.49 | 1.30 | 0.05 | 0.28 | 6.05 | 0.38 | 0.06 |
| H-12 | 40.27 | 126.79 | 0.17 | 0.62 | 0.25 | 0.02 | 1.53 | 1.91 | 29.11 | 2.35 | 0.10 | 0.39 | 2.87 | 0.19 | 0.03 |
| 产地 | 样品编号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 罗甸 | LD1-1-1 | 5.91 | 3.97 | 1.14 | 5.08 | 0.84 | 0.21 | 1.07 | 0.16 | 0.66 | 0.19 |
| LD1-1-2 | 4.11 | 2.94 | 0.77 | 3.20 | 0.58 | 0.12 | 0.70 | 0.09 | 0.78 | 0.18 | |
| LD1-1-3 | 4.12 | 2.83 | 0.77 | 3.33 | 0.54 | 0.16 | 0.58 | 0.10 | 0.68 | 0.17 | |
| LD1-1-4 | 6.82 | 4.31 | 1.32 | 5.38 | 1.02 | 0.18 | 1.44 | 0.10 | 1.05 | 0.17 | |
| LD1-1-5 | 6.43 | 4.28 | 1.22 | 5.42 | 1.35 | 0.16 | 1.32 | 0.15 | 0.82 | 0.24 | |
| LD2-1-1 | 41.46 | 19.55 | 6.72 | 25.90 | 5.76 | 0.81 | 4.42 | 0.51 | 4.20 | 1.06 | |
| LD2-1-2 | 23.32 | 12.08 | 4.00 | 15.60 | 3.38 | 0.48 | 4.47 | 0.65 | 3.93 | 0.75 | |
| LD2-1-3 | 23.57 | 13.33 | 4.31 | 16.90 | 3.81 | 0.59 | 3.56 | 0.55 | 3.84 | 0.86 | |
| LD2-1-4 | 35.40 | 18.87 | 6.38 | 26.88 | 6.13 | 0.72 | 6.05 | 0.73 | 4.24 | 0.72 | |
| LD2-1-5 | 38.19 | 19.53 | 7.01 | 28.50 | 4.78 | 0.77 | 5.89 | 0.54 | 3.90 | 0.79 | |
| LD2-3-1 | 12.50 | 6.55 | 2.38 | 10.30 | 2.03 | 0.39 | 1.75 | 0.26 | 1.24 | 0.33 | |
| LD2-3-2 | 11.84 | 6.16 | 2.26 | 9.94 | 1.69 | 0.42 | 1.71 | 0.25 | 1.59 | 0.28 | |
| LD2-3-3 | 9.14 | 3.00 | 1.51 | 6.29 | 0.80 | 0.14 | 0.70 | 0.05 | 0.33 | 0.08 | |
| LD2-4-1 | 6.85 | 3.51 | 1.14 | 5.15 | 1.10 | - | 1.29 | 0.10 | 0.84 | 0.16 | |
| LD2-4-2 | 13.58 | 6.88 | 2.26 | 10.08 | 2.05 | 0.25 | 1.74 | 0.19 | 1.39 | 0.24 | |
| LD2-4-3 | 6.48 | 3.39 | 1.12 | 4.85 | 1.05 | 0.16 | - | 0.16 | 0.85 | 0.16 | |
| LD3-1-1 | 6.17 | 4.69 | 1.17 | 4.85 | 0.92 | 0.27 | 0.91 | 0.13 | 0.65 | 0.12 | |
| LD3-1-2 | 5.93 | 4.98 | 1.20 | 4.71 | 1.05 | 0.27 | 0.84 | 0.08 | 0.70 | - | |
| 大化 | 1-1 | 8.02 | 26.36 | 4.43 | 22.99 | 5.43 | 2.36 | 4.80 | 0.65 | 3.59 | 0.85 |
| 1-2 | 45.45 | 87.03 | 10.95 | 48.28 | 8.96 | 2.93 | 7.02 | 0.96 | 5.72 | 1.05 | |
| 1-3 | 8.75 | 22.73 | 3.04 | 15.66 | 3.17 | 2.37 | 2.91 | 0.41 | 1.94 | 0.46 | |
| 1-4 | 10.21 | 23.43 | 3.40 | 14.16 | 2.17 | 1.60 | 1.99 | 0.33 | 1.86 | 0.38 | |
| 2-1 | 27.85 | 54.12 | 7.24 | 33.41 | 6.04 | 1.90 | 5.23 | 0.75 | 3.99 | 0.72 | |
| 巴马 | 巴-1 | 2.56 | 1.27 | 0.54 | 1.86 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 0.37 | 0.08 |
| 巴-3 | 3.13 | 1.15 | 0.43 | 1.68 | 0.45 | 0.06 | 0.43 | 0.07 | 0.43 | 0.10 | |
| 巴-9 | 2.11 | 1.14 | 0.35 | 1.59 | 0.50 | 0.14 | 0.63 | 0.11 | 0.78 | 0.18 | |
| 巴-10 | 5.07 | 1.95 | 0.78 | 2.81 | 0.70 | 0.08 | 0.60 | 0.09 | 0.60 | 0.13 | |
| 巴-13 | 16.80 | 7.36 | 2.25 | 7.65 | 1.50 | 0.17 | 1.01 | 0.13 | 0.72 | 0.13 | |
| 产地 | 样品编号 | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ΣREE | LREE/HREE | LaN/YbN | δCe | δEu | |
| 罗甸 | LD1-1-1 | 0.43 | 0.09 | 0.53 | 0.08 | 20.37 | 5.34 | 7.94 | 0.68 | 0.38 | |
| LD1-1-2 | 0.44 | 0.06 | 0.37 | - | 14.34 | 4.47 | 7.93 | 0.59 | 0.41 | ||
| LD1-1-3 | 0.38 | 0.06 | 0.20 | - | 13.92 | 5.41 | 14.49 | 0.89 | 0.39 | ||
| LD1-1-4 | 0.53 | - | 0.32 | - | 22.65 | 5.26 | 15.01 | 0.45 | 0.35 | ||
| LD1-1-5 | 0.63 | 0.07 | - | - | 22.09 | 5.83 | 1.99 | 0.37 | 0.38 | ||
| LD2-1-1 | 1.99 | - | 1.48 | 0.24 | 114.10 | 7.21 | 20.10 | 0.49 | 0.29 | ||
| LD2-1-2 | 2.06 | - | - | - | 70.72 | 4.96 | - | 0.38 | 0.31 | ||
| LD2-1-3 | 1.59 | 0.31 | - | - | 73.22 | 5.84 | - | 0.49 | 0.32 | ||
| LD2-1-4 | 1.74 | 0.29 | 1.18 | - | 109.33 | 6.31 | 21.52 | 0.36 | 0.31 | ||
| LD2-1-5 | 1.79 | 0.34 | 1.85 | - | 113.88 | 6.54 | 14.81 | 0.44 | 0.29 | ||
| LD2-3-1 | 0.58 | - | 0.35 | - | 38.67 | 7.56 | 25.62 | 0.64 | 0.29 | ||
| LD2-3-2 | 0.68 | 0.08 | 0.34 | - | 37.23 | 6.57 | 24.98 | 0.76 | 0.29 | ||
| LD2-3-3 | 0.16 | - | - | - | 22.19 | 15.90 | - | 0.58 | 0.20 | ||
| LD2-4-1 | 0.34 | - | - | - | 20.49 | 6.49 | - | 1.00 | 0.31 | ||
| LD2-4-2 | 0.57 | - | 0.38 | 0.06 | 39.67 | 7.68 | 25.64 | 0.40 | 0.31 | ||
| LD2-4-3 | 0.35 | - | - | - | 18.56 | 11.28 | - | 0.57 | 0.31 | ||
| LD3-1-1 | 0.24 | - | - | - | 20.11 | 8.82 | - | 0.90 | 0.43 | ||
| LD3-1-2 | 0.26 | - | - | 0.06 | 20.07 | 9.39 | - | 0.88 | 0.46 | ||
| 大化 | 1-1 | 1.83 | 0.33 | 2.13 | 0.28 | 84.05 | 4.81 | 2.71 | 1.38 | 1.07 | |
| 1-2 | 2.39 | 0.36 | 1.78 | 0.24 | 223.12 | 10.43 | 18.32 | 1.09 | 0.93 | ||
| 1-3 | 1.26 | 0.15 | 1.25 | 0.21 | 64.31 | 6.49 | 5.02 | 2.34 | 1.08 | ||
| 1-4 | 1.04 | 0.12 | 1.13 | 0.20 | 62.01 | 7.81 | 6.48 | 2.31 | 0.97 | ||
| 2-1 | 1.93 | 0.28 | 1.85 | 0.27 | 145.58 | 8.69 | 10.80 | 1.01 | 0.91 | ||
| 巴马 | 巴-1 | 0.23 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 8.23 | 4.64 | 7.65 | 0.47 | 0.24 | |
| 巴-3 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.35 | 0.06 | 8.69 | 3.85 | 6.41 | 0.40 | 0.21 | ||
| 巴-9 | 0.52 | 0.08 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 8.72 | 2.03 | 3.03 | 0.77 | 0.29 | ||
| 巴-10 | 0.36 | 0.05 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 13.59 | 5.18 | 11.36 | 0.38 | 0.21 | ||
| 巴-13 | 0.36 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 0.04 | 38.45 | 13.14 | 41.55 | 0.39 | 0.25 | ||
表5 中国黔桂基性岩型软玉稀土元素测试结果(10-6)
Table 5 Rare earth element results of basaltic metasomatic nephrite in the Qiangui region, China (10-6)
| 产地 | 样品编号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 罗甸 | LD1-1-1 | 5.91 | 3.97 | 1.14 | 5.08 | 0.84 | 0.21 | 1.07 | 0.16 | 0.66 | 0.19 |
| LD1-1-2 | 4.11 | 2.94 | 0.77 | 3.20 | 0.58 | 0.12 | 0.70 | 0.09 | 0.78 | 0.18 | |
| LD1-1-3 | 4.12 | 2.83 | 0.77 | 3.33 | 0.54 | 0.16 | 0.58 | 0.10 | 0.68 | 0.17 | |
| LD1-1-4 | 6.82 | 4.31 | 1.32 | 5.38 | 1.02 | 0.18 | 1.44 | 0.10 | 1.05 | 0.17 | |
| LD1-1-5 | 6.43 | 4.28 | 1.22 | 5.42 | 1.35 | 0.16 | 1.32 | 0.15 | 0.82 | 0.24 | |
| LD2-1-1 | 41.46 | 19.55 | 6.72 | 25.90 | 5.76 | 0.81 | 4.42 | 0.51 | 4.20 | 1.06 | |
| LD2-1-2 | 23.32 | 12.08 | 4.00 | 15.60 | 3.38 | 0.48 | 4.47 | 0.65 | 3.93 | 0.75 | |
| LD2-1-3 | 23.57 | 13.33 | 4.31 | 16.90 | 3.81 | 0.59 | 3.56 | 0.55 | 3.84 | 0.86 | |
| LD2-1-4 | 35.40 | 18.87 | 6.38 | 26.88 | 6.13 | 0.72 | 6.05 | 0.73 | 4.24 | 0.72 | |
| LD2-1-5 | 38.19 | 19.53 | 7.01 | 28.50 | 4.78 | 0.77 | 5.89 | 0.54 | 3.90 | 0.79 | |
| LD2-3-1 | 12.50 | 6.55 | 2.38 | 10.30 | 2.03 | 0.39 | 1.75 | 0.26 | 1.24 | 0.33 | |
| LD2-3-2 | 11.84 | 6.16 | 2.26 | 9.94 | 1.69 | 0.42 | 1.71 | 0.25 | 1.59 | 0.28 | |
| LD2-3-3 | 9.14 | 3.00 | 1.51 | 6.29 | 0.80 | 0.14 | 0.70 | 0.05 | 0.33 | 0.08 | |
| LD2-4-1 | 6.85 | 3.51 | 1.14 | 5.15 | 1.10 | - | 1.29 | 0.10 | 0.84 | 0.16 | |
| LD2-4-2 | 13.58 | 6.88 | 2.26 | 10.08 | 2.05 | 0.25 | 1.74 | 0.19 | 1.39 | 0.24 | |
| LD2-4-3 | 6.48 | 3.39 | 1.12 | 4.85 | 1.05 | 0.16 | - | 0.16 | 0.85 | 0.16 | |
| LD3-1-1 | 6.17 | 4.69 | 1.17 | 4.85 | 0.92 | 0.27 | 0.91 | 0.13 | 0.65 | 0.12 | |
| LD3-1-2 | 5.93 | 4.98 | 1.20 | 4.71 | 1.05 | 0.27 | 0.84 | 0.08 | 0.70 | - | |
| 大化 | 1-1 | 8.02 | 26.36 | 4.43 | 22.99 | 5.43 | 2.36 | 4.80 | 0.65 | 3.59 | 0.85 |
| 1-2 | 45.45 | 87.03 | 10.95 | 48.28 | 8.96 | 2.93 | 7.02 | 0.96 | 5.72 | 1.05 | |
| 1-3 | 8.75 | 22.73 | 3.04 | 15.66 | 3.17 | 2.37 | 2.91 | 0.41 | 1.94 | 0.46 | |
| 1-4 | 10.21 | 23.43 | 3.40 | 14.16 | 2.17 | 1.60 | 1.99 | 0.33 | 1.86 | 0.38 | |
| 2-1 | 27.85 | 54.12 | 7.24 | 33.41 | 6.04 | 1.90 | 5.23 | 0.75 | 3.99 | 0.72 | |
| 巴马 | 巴-1 | 2.56 | 1.27 | 0.54 | 1.86 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 0.37 | 0.08 |
| 巴-3 | 3.13 | 1.15 | 0.43 | 1.68 | 0.45 | 0.06 | 0.43 | 0.07 | 0.43 | 0.10 | |
| 巴-9 | 2.11 | 1.14 | 0.35 | 1.59 | 0.50 | 0.14 | 0.63 | 0.11 | 0.78 | 0.18 | |
| 巴-10 | 5.07 | 1.95 | 0.78 | 2.81 | 0.70 | 0.08 | 0.60 | 0.09 | 0.60 | 0.13 | |
| 巴-13 | 16.80 | 7.36 | 2.25 | 7.65 | 1.50 | 0.17 | 1.01 | 0.13 | 0.72 | 0.13 | |
| 产地 | 样品编号 | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ΣREE | LREE/HREE | LaN/YbN | δCe | δEu | |
| 罗甸 | LD1-1-1 | 0.43 | 0.09 | 0.53 | 0.08 | 20.37 | 5.34 | 7.94 | 0.68 | 0.38 | |
| LD1-1-2 | 0.44 | 0.06 | 0.37 | - | 14.34 | 4.47 | 7.93 | 0.59 | 0.41 | ||
| LD1-1-3 | 0.38 | 0.06 | 0.20 | - | 13.92 | 5.41 | 14.49 | 0.89 | 0.39 | ||
| LD1-1-4 | 0.53 | - | 0.32 | - | 22.65 | 5.26 | 15.01 | 0.45 | 0.35 | ||
| LD1-1-5 | 0.63 | 0.07 | - | - | 22.09 | 5.83 | 1.99 | 0.37 | 0.38 | ||
| LD2-1-1 | 1.99 | - | 1.48 | 0.24 | 114.10 | 7.21 | 20.10 | 0.49 | 0.29 | ||
| LD2-1-2 | 2.06 | - | - | - | 70.72 | 4.96 | - | 0.38 | 0.31 | ||
| LD2-1-3 | 1.59 | 0.31 | - | - | 73.22 | 5.84 | - | 0.49 | 0.32 | ||
| LD2-1-4 | 1.74 | 0.29 | 1.18 | - | 109.33 | 6.31 | 21.52 | 0.36 | 0.31 | ||
| LD2-1-5 | 1.79 | 0.34 | 1.85 | - | 113.88 | 6.54 | 14.81 | 0.44 | 0.29 | ||
| LD2-3-1 | 0.58 | - | 0.35 | - | 38.67 | 7.56 | 25.62 | 0.64 | 0.29 | ||
| LD2-3-2 | 0.68 | 0.08 | 0.34 | - | 37.23 | 6.57 | 24.98 | 0.76 | 0.29 | ||
| LD2-3-3 | 0.16 | - | - | - | 22.19 | 15.90 | - | 0.58 | 0.20 | ||
| LD2-4-1 | 0.34 | - | - | - | 20.49 | 6.49 | - | 1.00 | 0.31 | ||
| LD2-4-2 | 0.57 | - | 0.38 | 0.06 | 39.67 | 7.68 | 25.64 | 0.40 | 0.31 | ||
| LD2-4-3 | 0.35 | - | - | - | 18.56 | 11.28 | - | 0.57 | 0.31 | ||
| LD3-1-1 | 0.24 | - | - | - | 20.11 | 8.82 | - | 0.90 | 0.43 | ||
| LD3-1-2 | 0.26 | - | - | 0.06 | 20.07 | 9.39 | - | 0.88 | 0.46 | ||
| 大化 | 1-1 | 1.83 | 0.33 | 2.13 | 0.28 | 84.05 | 4.81 | 2.71 | 1.38 | 1.07 | |
| 1-2 | 2.39 | 0.36 | 1.78 | 0.24 | 223.12 | 10.43 | 18.32 | 1.09 | 0.93 | ||
| 1-3 | 1.26 | 0.15 | 1.25 | 0.21 | 64.31 | 6.49 | 5.02 | 2.34 | 1.08 | ||
| 1-4 | 1.04 | 0.12 | 1.13 | 0.20 | 62.01 | 7.81 | 6.48 | 2.31 | 0.97 | ||
| 2-1 | 1.93 | 0.28 | 1.85 | 0.27 | 145.58 | 8.69 | 10.80 | 1.01 | 0.91 | ||
| 巴马 | 巴-1 | 0.23 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 8.23 | 4.64 | 7.65 | 0.47 | 0.24 | |
| 巴-3 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.35 | 0.06 | 8.69 | 3.85 | 6.41 | 0.40 | 0.21 | ||
| 巴-9 | 0.52 | 0.08 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 8.72 | 2.03 | 3.03 | 0.77 | 0.29 | ||
| 巴-10 | 0.36 | 0.05 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 13.59 | 5.18 | 11.36 | 0.38 | 0.21 | ||
| 巴-13 | 0.36 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 0.04 | 38.45 | 13.14 | 41.55 | 0.39 | 0.25 | ||
| 产地 | 样品编号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贵州 罗甸 | LK-7 | 3.40 | 2.70 | 0.71 | 2.80 | 0.55 | 0.13 | 0.62 | 0.10 | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.57 | 0.08 | 0.40 | 0.06 |
| BY-6 | 13.60 | 10.10 | 2.75 | 10.10 | 1.75 | 0.35 | 1.48 | 0.24 | 1.27 | 0.26 | 0.68 | 0.10 | 0.53 | 0.08 | |
| BY-9 | 18.60 | 10.40 | 3.55 | 13.20 | 2.16 | 0.37 | 1.82 | 0.25 | 1.21 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.13 | 0.46 | 0.08 | |
| LM-3 | 14.60 | 2.50 | 1.87 | 7.30 | 1.15 | 0.19 | 0.96 | 0.16 | 0.79 | 0.19 | 0.67 | 0.11 | 0.66 | 0.12 | |
| LM-4 | 4.90 | 2.30 | 0.89 | 3.60 | 0.71 | 0.13 | 0.71 | 0.12 | 0.67 | 0.16 | 0.48 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 0.06 | |
| LM-5 | 4.30 | 1.90 | 0.72 | 2.80 | 0.57 | 0.10 | 0.73 | 0.14 | 0.79 | 0.20 | 0.55 | 0.07 | 0.33 | 0.05 | |
| Gga | 11.20 | 3.70 | 1.47 | 5.30 | 0.84 | 0.23 | 0.81 | 0.11 | 0.56 | 0.14 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.27 | 0.04 | |
| Ggc | 9.00 | 4.20 | 1.88 | 7.00 | 1.26 | 0.34 | 1.13 | 0.17 | 0.92 | 0.20 | 0.59 | 0.10 | 0.37 | 0.07 | |
| Ggd | 10.50 | 4.80 | 1.97 | 7.70 | 1.17 | 0.27 | 1.29 | 0.18 | 0.98 | 0.18 | 0.49 | 0.08 | 0.24 | 0.04 | |
| LD01 | 11.80 | 5.79 | 2.28 | 9.05 | 1.64 | 0.33 | 1.47 | 0.24 | 1.06 | 0.18 | 0.47 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.03 | |
| LD02 | 6.58 | 4.53 | 1.52 | 6.36 | 1.33 | 0.33 | 1.01 | 0.17 | 0.78 | 0.16 | 0.34 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.03 | |
| LD04 | 8.65 | 3.89 | 1.87 | 7.56 | 1.43 | 0.36 | 1.54 | 0.25 | 1.45 | 0.30 | 0.83 | 0.09 | 0.43 | 0.06 | |
| LD05 | 11.30 | 4.21 | 1.67 | 6.64 | 1.10 | 0.24 | 1.03 | 0.17 | 0.87 | 0.19 | 0.52 | 0.08 | 0.44 | 0.06 | |
| LD001 | 9.47 | 5.01 | 1.97 | 7.61 | 1.46 | 0.33 | 1.37 | 0.21 | 1.02 | 0.20 | 0.54 | 0.06 | 0.39 | 0.05 | |
| PL950 | 4.78 | 2.59 | 1.11 | 4.45 | 0.93 | 0.25 | 0.92 | 0.14 | 0.74 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.03 | |
| 广西 大化 | H-2 | 0.73 | 0.97 | 0.23 | 1.15 | 0.28 | 0.06 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 0.58 | 0.14 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.38 | 0.06 |
| H-12 | 1.53 | 1.91 | 0.42 | 2.13 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 0.34 | 0.07 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.03 | |
| Dh-1 | 0.62 | 1.20 | 0.16 | 0.57 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.03 | - | |
| Dh-2 | 3.52 | 1.18 | 0.53 | 2.49 | 0.43 | 0.13 | 0.51 | 0.07 | 0.43 | 0.11 | 0.25 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.03 | |
| Dh-3 | 3.70 | 1.19 | 0.54 | 2.27 | 0.57 | 0.11 | 0.34 | 0.08 | 0.53 | 0.08 | 0.30 | 0.03 | 0.27 | 0.04 | |
| Dh-4 | 0.48 | 0.86 | 0.12 | 0.47 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.35 | 0.12 | 0.33 | 0.05 | 0.33 | 0.05 | |
| Dh-5 | 0.86 | 0.43 | 0.18 | 1.33 | 0.34 | 0.06 | 0.58 | 0.12 | 0.48 | 0.15 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 0.20 | - | |
| Dh-6 | 0.38 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.39 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 0.13 | 0.46 | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.03 | |
| Dh-7 | 0.28 | 0.40 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.11 | - | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.06 | - |
表6 中国黔桂基性岩型软玉稀土元素样品数据(10-6)
Table 6 Rare earth element compositions of basaltic metasomatic nephrite in the Qiangui region, China(10-6)
| 产地 | 样品编号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贵州 罗甸 | LK-7 | 3.40 | 2.70 | 0.71 | 2.80 | 0.55 | 0.13 | 0.62 | 0.10 | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.57 | 0.08 | 0.40 | 0.06 |
| BY-6 | 13.60 | 10.10 | 2.75 | 10.10 | 1.75 | 0.35 | 1.48 | 0.24 | 1.27 | 0.26 | 0.68 | 0.10 | 0.53 | 0.08 | |
| BY-9 | 18.60 | 10.40 | 3.55 | 13.20 | 2.16 | 0.37 | 1.82 | 0.25 | 1.21 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.13 | 0.46 | 0.08 | |
| LM-3 | 14.60 | 2.50 | 1.87 | 7.30 | 1.15 | 0.19 | 0.96 | 0.16 | 0.79 | 0.19 | 0.67 | 0.11 | 0.66 | 0.12 | |
| LM-4 | 4.90 | 2.30 | 0.89 | 3.60 | 0.71 | 0.13 | 0.71 | 0.12 | 0.67 | 0.16 | 0.48 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 0.06 | |
| LM-5 | 4.30 | 1.90 | 0.72 | 2.80 | 0.57 | 0.10 | 0.73 | 0.14 | 0.79 | 0.20 | 0.55 | 0.07 | 0.33 | 0.05 | |
| Gga | 11.20 | 3.70 | 1.47 | 5.30 | 0.84 | 0.23 | 0.81 | 0.11 | 0.56 | 0.14 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.27 | 0.04 | |
| Ggc | 9.00 | 4.20 | 1.88 | 7.00 | 1.26 | 0.34 | 1.13 | 0.17 | 0.92 | 0.20 | 0.59 | 0.10 | 0.37 | 0.07 | |
| Ggd | 10.50 | 4.80 | 1.97 | 7.70 | 1.17 | 0.27 | 1.29 | 0.18 | 0.98 | 0.18 | 0.49 | 0.08 | 0.24 | 0.04 | |
| LD01 | 11.80 | 5.79 | 2.28 | 9.05 | 1.64 | 0.33 | 1.47 | 0.24 | 1.06 | 0.18 | 0.47 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.03 | |
| LD02 | 6.58 | 4.53 | 1.52 | 6.36 | 1.33 | 0.33 | 1.01 | 0.17 | 0.78 | 0.16 | 0.34 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.03 | |
| LD04 | 8.65 | 3.89 | 1.87 | 7.56 | 1.43 | 0.36 | 1.54 | 0.25 | 1.45 | 0.30 | 0.83 | 0.09 | 0.43 | 0.06 | |
| LD05 | 11.30 | 4.21 | 1.67 | 6.64 | 1.10 | 0.24 | 1.03 | 0.17 | 0.87 | 0.19 | 0.52 | 0.08 | 0.44 | 0.06 | |
| LD001 | 9.47 | 5.01 | 1.97 | 7.61 | 1.46 | 0.33 | 1.37 | 0.21 | 1.02 | 0.20 | 0.54 | 0.06 | 0.39 | 0.05 | |
| PL950 | 4.78 | 2.59 | 1.11 | 4.45 | 0.93 | 0.25 | 0.92 | 0.14 | 0.74 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.03 | |
| 广西 大化 | H-2 | 0.73 | 0.97 | 0.23 | 1.15 | 0.28 | 0.06 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 0.58 | 0.14 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.38 | 0.06 |
| H-12 | 1.53 | 1.91 | 0.42 | 2.13 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 0.34 | 0.07 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.03 | |
| Dh-1 | 0.62 | 1.20 | 0.16 | 0.57 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.03 | - | |
| Dh-2 | 3.52 | 1.18 | 0.53 | 2.49 | 0.43 | 0.13 | 0.51 | 0.07 | 0.43 | 0.11 | 0.25 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.03 | |
| Dh-3 | 3.70 | 1.19 | 0.54 | 2.27 | 0.57 | 0.11 | 0.34 | 0.08 | 0.53 | 0.08 | 0.30 | 0.03 | 0.27 | 0.04 | |
| Dh-4 | 0.48 | 0.86 | 0.12 | 0.47 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.35 | 0.12 | 0.33 | 0.05 | 0.33 | 0.05 | |
| Dh-5 | 0.86 | 0.43 | 0.18 | 1.33 | 0.34 | 0.06 | 0.58 | 0.12 | 0.48 | 0.15 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 0.20 | - | |
| Dh-6 | 0.38 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.39 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 0.13 | 0.46 | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.03 | |
| Dh-7 | 0.28 | 0.40 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.11 | - | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.06 | - |
| 产地 | SiO2 | MgO | CaO | Al2O3 | Na2O | K2O | FeO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贵州 罗甸 | 58.36 | 23.90 | 12.46 | 0.28 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.16 |
| 56.48 | 24.55 | 12.66 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.11 | - | |
| 56.44 | 22.79 | 13.58 | 0.39 | 0.31 | 0.07 | 0.42 | |
| 59.31 | 25.79 | 11.58 | 0.12 | 0.33 | 0.10 | 0.21 | |
| 59.32 | 24.05 | 12.49 | 0.27 | 0.09 | 0.04 | - | |
| 广西 大化 | 58.01 | 23.62 | 13.82 | 0.39 | 0.09 | 0.06 | - |
| 58.30 | 23.44 | 13.12 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.11 | |
| 59.89 | 24.14 | 13.76 | 0.48 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.81 | |
| 59.31 | 23.63 | 12.99 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 1.18 | |
| 58.25 | 22.74 | 11.96 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 3.15 | |
| 广西 巴马 | 58.37 | 23.75 | 10.99 | 0.36 | 0.02 | - | 4.02 |
| 青海 格尔 木 | 59.31 | 23.87 | 13.69 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.16 |
| 56.44 | 22.86 | 12.59 | 0.67 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 2.21 | |
| 57.39 | 22.33 | 13.47 | 1.13 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 3.44 | |
| 57.46 | 24.33 | 13.28 | 0.15 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0.45 | |
| 江苏 溧阳 | 55.92 | 25.02 | 12.35 | 1.04 | 2.74 | 0.34 | 0.32 |
| 56.67 | 23.30 | 11.58 | - | - | - | - | |
| 59.66 | 24.37 | 12.24 | 0.62 | 0.53 | 0.30 | 0.31 | |
| 新疆 和田 | 58.11 | 24.25 | 12.39 | 0.85 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.70 |
| 58.92 | 24.33 | 12.14 | 0.92 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.81 | |
| 57.95 | 23.50 | 12.91 | 0.49 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.68 | |
| 58.43 | 24.73 | 13.16 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 1.52 | |
| 58.64 | 23.40 | 13.51 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.02 | |
| 吉林磐 石 | 58.56 | 24.47 | 13.79 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.10 |
| 黑龙江 铁力 | 58.03 | 23.41 | 13.90 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.48 |
| 新疆玛 纳斯 | 53.74 | 22.62 | 11.21 | 1.80 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 4.15 |
表7 中国不同成因软玉主量元素数据(%)
Table 7 Major element compositions for nephrite of different genesis of China (%)
| 产地 | SiO2 | MgO | CaO | Al2O3 | Na2O | K2O | FeO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贵州 罗甸 | 58.36 | 23.90 | 12.46 | 0.28 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.16 |
| 56.48 | 24.55 | 12.66 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.11 | - | |
| 56.44 | 22.79 | 13.58 | 0.39 | 0.31 | 0.07 | 0.42 | |
| 59.31 | 25.79 | 11.58 | 0.12 | 0.33 | 0.10 | 0.21 | |
| 59.32 | 24.05 | 12.49 | 0.27 | 0.09 | 0.04 | - | |
| 广西 大化 | 58.01 | 23.62 | 13.82 | 0.39 | 0.09 | 0.06 | - |
| 58.30 | 23.44 | 13.12 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.11 | |
| 59.89 | 24.14 | 13.76 | 0.48 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.81 | |
| 59.31 | 23.63 | 12.99 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 1.18 | |
| 58.25 | 22.74 | 11.96 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 3.15 | |
| 广西 巴马 | 58.37 | 23.75 | 10.99 | 0.36 | 0.02 | - | 4.02 |
| 青海 格尔 木 | 59.31 | 23.87 | 13.69 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.16 |
| 56.44 | 22.86 | 12.59 | 0.67 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 2.21 | |
| 57.39 | 22.33 | 13.47 | 1.13 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 3.44 | |
| 57.46 | 24.33 | 13.28 | 0.15 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0.45 | |
| 江苏 溧阳 | 55.92 | 25.02 | 12.35 | 1.04 | 2.74 | 0.34 | 0.32 |
| 56.67 | 23.30 | 11.58 | - | - | - | - | |
| 59.66 | 24.37 | 12.24 | 0.62 | 0.53 | 0.30 | 0.31 | |
| 新疆 和田 | 58.11 | 24.25 | 12.39 | 0.85 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.70 |
| 58.92 | 24.33 | 12.14 | 0.92 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.81 | |
| 57.95 | 23.50 | 12.91 | 0.49 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.68 | |
| 58.43 | 24.73 | 13.16 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 1.52 | |
| 58.64 | 23.40 | 13.51 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.02 | |
| 吉林磐 石 | 58.56 | 24.47 | 13.79 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.10 |
| 黑龙江 铁力 | 58.03 | 23.41 | 13.90 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.48 |
| 新疆玛 纳斯 | 53.74 | 22.62 | 11.21 | 1.80 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 4.15 |

图6 中国不同成因软玉主量元素投点图(%)
Fig.6 Plots of major element casts for different genesis nephrite of China (%) (a)SiO2-MgO-CaO;(b)MgO-CaO;(c)SiO2-(Na2O+K2O);(d)Al2O3-FeO
| Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | La | Ce | Sr | Zr | Hf | Sm | Y | Yb | Lu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贵州罗甸 | 0.40 | 13.73 | 0.86 | 0.77 | 0.85 | 0.16 | 10.01 | 4.73 | 65.77 | 6.74 | 0.28 | 1.13 | 8.39 | 0.39 | 0.07 |
| 广西大化 | 9.74 | 117.83 | 1.00 | 0.72 | 5.06 | 0.33 | 8.13 | 15.77 | 179.39 | 50.23 | 1.42 | 2.81 | 13.19 | 0.29 | 0.05 |
| 广西巴马 | 0.25 | 11.16 | 0.41 | 0.22 | 0.58 | 0.06 | 5.93 | 2.57 | 24.62 | 4.51 | 0.15 | 0.73 | 5.62 | - | - |
| 青海格尔木 | 1.67 | 9.43 | 0.34 | 0.80 | 0.78 | 0.19 | 0.83 | 1.90 | 9.80 | 12.12 | 0.30 | 0.14 | 1.47 | 0.21 | 0.03 |
| 新疆和田 | 10.40 | 10.72 | 0.45 | 1.31 | 1.50 | 0.19 | 4.17 | 5.39 | 10.48 | 7.77 | 0.23 | 0.46 | 4.94 | 0.43 | 0.09 |
| 黑龙江铁力 | 0.55 | 2.00 | 0.13 | 0.40 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.70 | 1.59 | 63.30 | 0.81 | 0.08 | 0.26 | 1.21 | 0.14 | 0.03 |
| 吉林磐石 | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.04 | 0.33 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.52 | 0.49 | 14.80 | 1.23 | 0.07 | 0.28 | 3.47 | 0.22 | 0.03 |
| 新疆玛纳斯 | 1.72 | 2.25 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.54 | 2.80 | 20.26 | 43.77 | 1.15 | 0.11 | 0.90 | 0.11 | 0.02 |
表8 中国不同成因软玉微量元素分析数据(10-6)
Table 8 Trace element analytical data of nephrite of different genesis of China(10-6)
| Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | La | Ce | Sr | Zr | Hf | Sm | Y | Yb | Lu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贵州罗甸 | 0.40 | 13.73 | 0.86 | 0.77 | 0.85 | 0.16 | 10.01 | 4.73 | 65.77 | 6.74 | 0.28 | 1.13 | 8.39 | 0.39 | 0.07 |
| 广西大化 | 9.74 | 117.83 | 1.00 | 0.72 | 5.06 | 0.33 | 8.13 | 15.77 | 179.39 | 50.23 | 1.42 | 2.81 | 13.19 | 0.29 | 0.05 |
| 广西巴马 | 0.25 | 11.16 | 0.41 | 0.22 | 0.58 | 0.06 | 5.93 | 2.57 | 24.62 | 4.51 | 0.15 | 0.73 | 5.62 | - | - |
| 青海格尔木 | 1.67 | 9.43 | 0.34 | 0.80 | 0.78 | 0.19 | 0.83 | 1.90 | 9.80 | 12.12 | 0.30 | 0.14 | 1.47 | 0.21 | 0.03 |
| 新疆和田 | 10.40 | 10.72 | 0.45 | 1.31 | 1.50 | 0.19 | 4.17 | 5.39 | 10.48 | 7.77 | 0.23 | 0.46 | 4.94 | 0.43 | 0.09 |
| 黑龙江铁力 | 0.55 | 2.00 | 0.13 | 0.40 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.70 | 1.59 | 63.30 | 0.81 | 0.08 | 0.26 | 1.21 | 0.14 | 0.03 |
| 吉林磐石 | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.04 | 0.33 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.52 | 0.49 | 14.80 | 1.23 | 0.07 | 0.28 | 3.47 | 0.22 | 0.03 |
| 新疆玛纳斯 | 1.72 | 2.25 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.54 | 2.80 | 20.26 | 43.77 | 1.15 | 0.11 | 0.90 | 0.11 | 0.02 |

图7 中国不同成因软玉原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(a)和球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图(b)(玛纳斯数据引自文献[31];溧阳数据引自文献[32])
Fig.7 Primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram(a) and chondrite-normalized rare earth element distribution pattern diagram (b) of nephrite from different genesis of China
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贵州罗甸 | 9.99 | 5.43 | 1.90 | 7.32 | 1.33 | 0.30 | 1.31 | 0.21 | 1.22 |
| 广西大化 | 1.31 | 1.00 | 0.29 | 1.25 | 0.28 | 0.07 | 0.33 | 0.07 | 0.38 |
| 广西巴马 | 5.93 | 2.57 | 0.87 | 3.12 | 0.73 | 0.10 | 0.61 | 0.09 | 0.58 |
| 青海格尔木 | 0.83 | 1.90 | 0.16 | 0.55 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.23 |
| 江苏溧阳 | 0.77 | 1.49 | 0.29 | 1.11 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 0.33 | 0.04 | 0.21 |
| 新疆和田 | 2.67 | 4.65 | 0.51 | 1.91 | 0.40 | 0.07 | 0.44 | 0.08 | 0.52 |
| 黑龙江铁力 | 0.69 | 1.59 | 0.19 | 0.78 | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 0.20 |
| 吉林磐石 | 0.52 | 0.49 | 0.15 | 0.76 | 0.28 | 0.06 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.36 |
| 新疆玛纳斯 | 0.54 | 2.80 | 0.19 | 0.67 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.14 |
| Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ΣREE | LREE/HREE | δCe | δEu | |
| 贵州罗甸 | 0.25 | 0.69 | 0.10 | 0.53 | 0.08 | 32.80 | 6.99 | 0.48 | 0.58 |
| 广西大化 | 0.10 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 5.67 | 4.17 | 0.60 | 0.88 |
| 广西巴马 | 0.12 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.34 | 0.05 | 15.54 | 5.77 | 0.24 | 0.48 |
| 青海格尔木 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 4.50 | 3.76 | 1.26 | 1.00 |
| 江苏溧阳 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 4.81 | 5.49 | 0.78 | 0.47 |
| 新疆和田 | 0.12 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 0.35 | 0.07 | 8.67 | 3.70 | 0.91 | 0.48 |
| 黑龙江铁力 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 4.42 | 4.75 | 0.89 | 0.91 |
| 吉林磐石 | 0.09 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 3.53 | 1.92 | 0.44 | 1.16 |
| 新疆玛纳斯 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 5.87 | 3.51 | 2.49 | 1.70 |
表9 中国不同成因软玉稀土元素分析数据(10-6)
Table 9 Rare earth element analytical data for nephrite of different genesis of China(10-6)
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贵州罗甸 | 9.99 | 5.43 | 1.90 | 7.32 | 1.33 | 0.30 | 1.31 | 0.21 | 1.22 |
| 广西大化 | 1.31 | 1.00 | 0.29 | 1.25 | 0.28 | 0.07 | 0.33 | 0.07 | 0.38 |
| 广西巴马 | 5.93 | 2.57 | 0.87 | 3.12 | 0.73 | 0.10 | 0.61 | 0.09 | 0.58 |
| 青海格尔木 | 0.83 | 1.90 | 0.16 | 0.55 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.23 |
| 江苏溧阳 | 0.77 | 1.49 | 0.29 | 1.11 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 0.33 | 0.04 | 0.21 |
| 新疆和田 | 2.67 | 4.65 | 0.51 | 1.91 | 0.40 | 0.07 | 0.44 | 0.08 | 0.52 |
| 黑龙江铁力 | 0.69 | 1.59 | 0.19 | 0.78 | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 0.20 |
| 吉林磐石 | 0.52 | 0.49 | 0.15 | 0.76 | 0.28 | 0.06 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.36 |
| 新疆玛纳斯 | 0.54 | 2.80 | 0.19 | 0.67 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.14 |
| Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ΣREE | LREE/HREE | δCe | δEu | |
| 贵州罗甸 | 0.25 | 0.69 | 0.10 | 0.53 | 0.08 | 32.80 | 6.99 | 0.48 | 0.58 |
| 广西大化 | 0.10 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 5.67 | 4.17 | 0.60 | 0.88 |
| 广西巴马 | 0.12 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.34 | 0.05 | 15.54 | 5.77 | 0.24 | 0.48 |
| 青海格尔木 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 4.50 | 3.76 | 1.26 | 1.00 |
| 江苏溧阳 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 4.81 | 5.49 | 0.78 | 0.47 |
| 新疆和田 | 0.12 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 0.35 | 0.07 | 8.67 | 3.70 | 0.91 | 0.48 |
| 黑龙江铁力 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 4.42 | 4.75 | 0.89 | 0.91 |
| 吉林磐石 | 0.09 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 3.53 | 1.92 | 0.44 | 1.16 |
| 新疆玛纳斯 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 5.87 | 3.51 | 2.49 | 1.70 |

图8 中国不同成因软玉δCe-LREE/HREE-ΣREE空间和平面直角坐标图
Fig.8 Spatial and planar rectangular coordinate plots of δCe-LREE/HREE-ΣREE of nephrite from different genesis of China (a)δCe-LREE/HREE-ΣREE;(b)δCe-LREE/HREE;(c)δEu-ΣREE;(d)LREE/HREE-ΣREE
| [1] | 刘飞, 余晓艳. 中国软玉矿床类型及其矿物学特征[J]. 矿产与地质, 2009, 23(4):375-380. |
| [2] | 王时麒, 徐立国. 黔桂新型软玉矿床的地质特征、矿床成因及找矿方向[C]. 国家珠宝玉石质量监督检验中心,中国珠宝玉石首饰行业协会.中国国际珠宝首饰学术交流会论文集(2017). 北京: 地质出版社, 2017:7. |
| [3] | 梁国科, 吴祥珂, 黄倩心, 等. 广西巴马地区透闪石玉的发现和找矿方向探讨[J]. 南方国土资源, 2020(7):66-69. |
| [4] | 梅冥相, 李仲远. 滇黔桂地区晚古生代至三叠纪层序地层序列及沉积盆地演化[J]. 现代地质, 2004, 18(4):555-563. |
| [5] | 焦大庆, 马永生, 邓军, 等. 黔桂地区石炭纪层序地层格架及古地理演化[J]. 现代地质, 2003, 17(3):294-302. |
| [6] | LI N, BAI F, XU L L, et al. Geochemical characteristics and ore-forming mechanism of Luodian nephrite deposit, Southwest China and comparison with other nephrite deposits in Asia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2023, 160:105604. |
| [7] | BAI F, DU J M, LI J J, et al. Mineralogy,geochemistry,and petrogenesis of green nephrite from Dahua,Guangxi,Southern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 118:103362. |
| [8] | 黄倩心, 王时麒, 梁国科, 等. 广西巴马玉的矿物学特征及其成因探讨[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2021, 40(5):977-990. |
| [9] | 李凯旋, 姜婷丽, 邢乐才, 等. 贵州罗甸玉的矿物学及矿床学初步研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2014, 34(2):223-233. |
| [10] | 杨林, 林金辉, 王雷, 等. 贵州罗甸玉岩石化学特征及成因意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2012, 32(2):12-19. |
| [11] | 钟倩, 廖宗廷, 周征宇, 等. 黔南—桂西软玉中锰质“草花”的矿物学特征、成因机理及成矿启示[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(8):1115-1126. |
| [12] | XU L G, WANG S Q. Gemological characteristics and genesis of Dahua nephrite[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2017, 35(增1):1-11. |
| [13] | 尹作为, 王文薇, 周青超. 广西大化县透闪石玉的产地特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6):114-123. |
| [14] | 张亚东, 杨瑞东, 高军波, 等. 贵州罗甸软玉矿的元素地球化学特征研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2015, 35(1):56-64. |
| [15] | 王长秋, 孙鹏, 王时麒. 大化墨玉的矿物学特征[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2014, 33(增2):1-9. |
| [16] | 王立本. 角闪石命名法——国际矿物学协会新矿物及矿物命名委员会角闪石专业委员会的报告[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2001, 20(1):84-100. |
| [17] | 蓝叶. 广西大化透闪石玉的地球化学特征及成因初探[D]. 桂林: 桂林理工大学, 2022. |
| [18] | 于海燕, 阮青锋, 廖宝丽, 等. 青海不同矿区软玉地球化学特征及Ar-Ar定年研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2018, 37(4):655-668. |
| [19] | YU H Y, WANG R C, GUO J C, et al. Study of the minerogenetic mechanism and origin of Qinghai nephrite from Golmud, Qinghai, Northwest China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2016, 59(8):1597-1609. |
| [20] | 钟华邦, 张洪石. 江苏梅岭玉的基本特征[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2002(增1):105-109. |
| [21] | 何明跃, 朱友楠, 李宏博. 江苏省溧阳梅岭玉(软玉)的宝石学研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2002(增1):99-104. |
| [22] | ZHOU Z Y, CHEN Y, LIAO Z T, et al. A petrological and mineralogical study of Liyang nephrite[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2009, 28(5):490-494. |
| [23] | 张勇, 魏华, 陆太进, 等. 新疆奥米夏和田玉矿床成因及锆石LA-ICP-MS定年研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018., 37(6):695-704. |
| [24] | 刘喜锋, 刘琰, 李自静, 等. 新疆皮山镁质矽卡岩矿床(含糖玉)成因及锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2017, 36(2):259-273. |
| [25] | LIU Y, DENG J, SHI G H, et al. Geochemistry and petrology of nephrite from Alamas, Xinjiang, NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 42(3):440-451. |
| [26] | LIU Y, ZHANG R Q, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Mineral inclusions and SHRIMP U-Pb dating of zircons from the Alamas nephrite and granodiorite: Implications for the genesis of a magnesian skarn deposit[J]. Lithos, 2015, 212:128-144. |
| [27] | LIU Y, ZHANG R Q, ABUDUWAYITI M, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages,mineral compositions and geochemistry of placer nephrite in the Yurungkash and Karakash River deposits,West Kunlun,Xinjiang,northwest China:Implication for a Magnesium Skarn[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72:699-727. |
| [28] | BAI F, LI G M, LEI J L, et al. Mineralogy, geochemistry, and petrogenesis of nephrite from Panshi, Jilin, Northeast China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 115:103171. |
| [29] |
GAO S J, BAI F, HEIDE G. Mineralogy, geochemistry and petrogenesis of nephrite from Tieli, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 107: 155-171.
DOI |
| [30] | 唐延龄, 刘德权, 周汝洪. 新疆玛纳斯碧玉的成矿地质特征[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2002(增1):22-25. |
| [31] | 任建红. 新疆玛纳斯地区东段碧玉的矿物学及成因研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2023. |
| [32] | 李晶, 高洁, 童欣然, 等. 江苏溧阳软玉与良渚文化庄桥坟遗址出土软玉的特征对比研究[J]. 宝石和宝石学杂志, 2010, 12(3):19-25,33. |
| [1] | 刘旭, 戢兴忠, 陈强, 李源洪. 贵州普克金矿区黄铁矿和方解石地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 977-990. |
| [2] | 王启博, 张寿庭, 唐利, 李军军, 盛渊明. 豫西杨山萤石矿床成因:萤石稀土元素组成和流体包裹体热力学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1524-1537. |
| [3] | 杜贯新, 闫百泉, 孙雨, 钱程, 秦涛, 臧延庆. 松嫩平原黑土区西北部阿荣旗地下黑土稀土元素特征及环境指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 813-820. |
| [4] | 刘茂涵, 刘海燕, 张卫民, 王振, 吴通航, 王玉罡. 鄱阳湖流域赣江北支水体和沉积物中稀土元素的含量和分异特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 389-405. |
| [5] | 王艺璇, 周训, 陈梦颖, 马静茹, 海阔, 肖萌, 尚子琦, 张颖, 余鸣潇. 河北北部四处温泉的水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 494-506. |
| [6] | 吴小雷, 常晋阳, 曾南石, 徐文杰, 陶明荣, 赵刚, 韩建. 辽宁红透山铜锌矿床含矿岩系地球化学特征及找矿指示[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 362-377. |
| [7] | 远继东, 姜正龙, 代友旭, 郝连成, 张健康, 张德程, 郑立龙. 湛江湾海域表层沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 77-87. |
| [8] | 赵保具, 张艳飞, 颜开, 肖荣阁. 大兴安岭中段有色金属矿床成矿物质来源探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1380-1396. |
| [9] | 王珍珍, 李进孝, 张珂, 郭文牧, 张绍韡, 肖林. 山西西铭煤矿煤中稀土元素地球化学特征及指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 1009-1017. |
| [10] | 赵保具, 颜开, 肖荣阁. 一种稀土参数图解新方法:以内蒙古拜仁达坝-维拉斯托闪长岩成因研究为例[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 608-624. |
| [11] | 惠小朝, 蔡煜琦, 何升, 冯张生. 陕西省华阳川铀铌铅矿床碳酸岩岩石学及地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(02): 246-257. |
| [12] | 杨帆,宋云涛,张舜尧,郝志红,郭志娟,王成文,岑况. 内蒙古大石寨地区稀土元素的区域分布特征[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(4): 802-810. |
| [13] | 李景运,马生明,席明杰,陈宏强. 浙江江山—绍兴断裂带陈蔡群微量元素地球化学特征及其与成矿的关系[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(3): 493-502. |
| [14] | 童雪飞,康志宏,周磊,刘晨晓,郭瑞琴,皇甫静静. 塔里木西北缘乌什南上石炭统索格当他乌组微量稀土元素特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(2): 426-435. |
| [15] | 冯建之,张灯堂,张为民,王杏村,崔燮祥,刘宗彦,王振强. 河南小秦岭金矿稀土元素地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(6): 1151-1160. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||