



现代地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (05): 1293-1305.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.054
李东升1( ), 高平1(
), 高平1( ), 盖海峰2, 刘若冰3, 蔡益栋1, 李刚1, 周秦2, 肖贤明1
), 盖海峰2, 刘若冰3, 蔡益栋1, 李刚1, 周秦2, 肖贤明1
收稿日期:2023-03-15
修回日期:2023-06-07
出版日期:2023-10-10
发布日期:2023-11-14
通讯作者:
高 平,男,副教授,博士生导师,1987年出生,地质资源与地质工程专业,主要从事油气地球化学方面研究。Email: gaoping1212@cugb.edu.cn。
作者简介:李东升,男,硕士,1997年出生,矿产普查与勘探专业,主要从事油气地球化学方面研究。Email: dongshengli@cugb.edu.cn。
基金资助:
LI Dongsheng1( ), GAO Ping1(
), GAO Ping1( ), GAI Haifeng2, LIU Ruobing3, CAI Yidong1, LI Gang1, ZHOU Qin2, XIAO Xianming1
), GAI Haifeng2, LIU Ruobing3, CAI Yidong1, LI Gang1, ZHOU Qin2, XIAO Xianming1
Received:2023-03-15
Revised:2023-06-07
Online:2023-10-10
Published:2023-11-14
摘要:
富有机质页岩中广泛发育的纳米孔隙是页岩气的重要储集空间。为了明确页岩有机质孔隙发育特征,以四川盆地东南部丁山地区下志留统龙马溪组页岩为研究对象,通过扫描电镜(SEM)、N2和CO2低压吸附实验,对龙马溪组页岩有机质面孔率进行统计,并对页岩中纳米孔隙结构特征进行表征。结果表明,总有机碳(TOC)含量是影响龙马溪组页岩纳米孔隙比表面积和孔容的主要因素。龙马溪组页岩有机质孔隙的比表面积和孔容均随TOC含量上升而增加,且在TOC值较高时超过无机孔隙的比表面积和孔容。孔径为2~10 nm的孔隙对龙马溪组页岩的总孔容贡献最大。焦沥青相比于其他有机质发育更多的介孔,焦沥青含量增多将导致页岩中介孔孔容显著增加,而排油效率可通过影响焦沥青含量间接导致页岩纳米孔隙发育差异,高排油效率会降低页岩介孔和总孔孔容。在龙马溪组页岩勘探开发过程中,应综合考虑TOC含量、排油效率及焦沥青含量对页岩气储集条件的影响。
中图分类号:
李东升, 高平, 盖海峰, 刘若冰, 蔡益栋, 李刚, 周秦, 肖贤明. 川东南地区龙马溪组页岩有机质纳米孔隙结构表征[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1293-1305.
LI Dongsheng, GAO Ping, GAI Haifeng, LIU Ruobing, CAI Yidong, LI Gang, ZHOU Qin, XIAO Xianming. Organic Nano-pore Textural Characteristics of the Longmaxi Formation Shale in the Southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(05): 1293-1305.

图1 四川盆地东南部丁山地区地层垂向剖面(b)及取样位置(a)(改自Gao等[39]) BT.宝塔组; LX.临湘组; WF.五峰组; GYQ.观音桥段; SNL.石牛栏组
Fig.1 Stratigraphic profile (b) and sampling location (a) in the Dingshan area, southeastern Sichuan Basin (modified from Gao et al.[39])
| 样品 | 层位 | 深度 (m) | TOC (%) | 焦沥青面 分布率(%) | 排油效率 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DY5-43 | 龙马溪组 | 3743.0 | 0.77 | 0.38 | 28.6 |
| DY5-39 | 龙马溪组 | 3749.8 | 1.24 | 0.38 | 60.3 |
| DY5-34 | 龙马溪组 | 3759.4 | 0.81 | 0.39 | 30.6 |
| DY5-23 | 龙马溪组 | 3776.8 | 0.92 | 0.42 | 35.2 |
| DY5-22 | 龙马溪组 | 3778.7 | 1.11 | 0.40 | 51.9 |
| DY5-19 | 龙马溪组 | 3784.3 | 1.49 | 0.66 | 38.0 |
| DY5-12 | 龙马溪组 | 3796.8 | 2.38 | 0.57 | 70.3 |
| DY5-09 | 龙马溪组 | 3802.4 | 2.81 | 0.64 | 71.9 |
| DY5-07 | 龙马溪组 | 3806.4 | 2.70 | 0.64 | 70.6 |
| DY5-06 | 龙马溪组 | 3808.5 | 3.69 | 0.78 | 74.1 |
| DY5-05 | 龙马溪组 | 3809.7 | 4.56 | 0.91 | 75.7 |
| DY5-02 | 五峰组 | 3814.6 | 4.39 | 1.31 | 61.7 |
表1 丁页5井页岩样品的TOC含量、焦沥青面分布率和排油效率
Table 1 TOC content, pyrobitumen surface distribution rate and oil expulsion efficiency of shale samples from Well DY 5
| 样品 | 层位 | 深度 (m) | TOC (%) | 焦沥青面 分布率(%) | 排油效率 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DY5-43 | 龙马溪组 | 3743.0 | 0.77 | 0.38 | 28.6 |
| DY5-39 | 龙马溪组 | 3749.8 | 1.24 | 0.38 | 60.3 |
| DY5-34 | 龙马溪组 | 3759.4 | 0.81 | 0.39 | 30.6 |
| DY5-23 | 龙马溪组 | 3776.8 | 0.92 | 0.42 | 35.2 |
| DY5-22 | 龙马溪组 | 3778.7 | 1.11 | 0.40 | 51.9 |
| DY5-19 | 龙马溪组 | 3784.3 | 1.49 | 0.66 | 38.0 |
| DY5-12 | 龙马溪组 | 3796.8 | 2.38 | 0.57 | 70.3 |
| DY5-09 | 龙马溪组 | 3802.4 | 2.81 | 0.64 | 71.9 |
| DY5-07 | 龙马溪组 | 3806.4 | 2.70 | 0.64 | 70.6 |
| DY5-06 | 龙马溪组 | 3808.5 | 3.69 | 0.78 | 74.1 |
| DY5-05 | 龙马溪组 | 3809.7 | 4.56 | 0.91 | 75.7 |
| DY5-02 | 五峰组 | 3814.6 | 4.39 | 1.31 | 61.7 |
| 样品 | Cp/TOC(%) | |
|---|---|---|
| DY5-43 | 0.1939 | 25.1356 |
| DY5-39 | 0.1939 | 15.6788 |
| DY5-34 | 0.1991 | 24.6148 |
| DY5-23 | 0.2144 | 23.3403 |
| DY5-22 | 0.2042 | 18.4190 |
| DY5-19 | 0.3373 | 22.5782 |
| DY5-12 | 0.2912 | 12.2195 |
| DY5-09 | 0.3271 | 11.6352 |
| DY5-07 | 0.3271 | 12.1180 |
| DY5-06 | 0.3989 | 10.8216 |
| DY5-05 | 0.4657 | 10.2209 |
| DY5-02 | 0.6717 | 14.9941 |
表2 丁页5井龙马溪组页岩的焦沥青含量和Cp/TOC 比值
Table 2 Pyrobitumen content and Cp/TOC ratio of the Longmaxi Formation shale samples in Well DY 5
| 样品 | Cp/TOC(%) | |
|---|---|---|
| DY5-43 | 0.1939 | 25.1356 |
| DY5-39 | 0.1939 | 15.6788 |
| DY5-34 | 0.1991 | 24.6148 |
| DY5-23 | 0.2144 | 23.3403 |
| DY5-22 | 0.2042 | 18.4190 |
| DY5-19 | 0.3373 | 22.5782 |
| DY5-12 | 0.2912 | 12.2195 |
| DY5-09 | 0.3271 | 11.6352 |
| DY5-07 | 0.3271 | 12.1180 |
| DY5-06 | 0.3989 | 10.8216 |
| DY5-05 | 0.4657 | 10.2209 |
| DY5-02 | 0.6717 | 14.9941 |
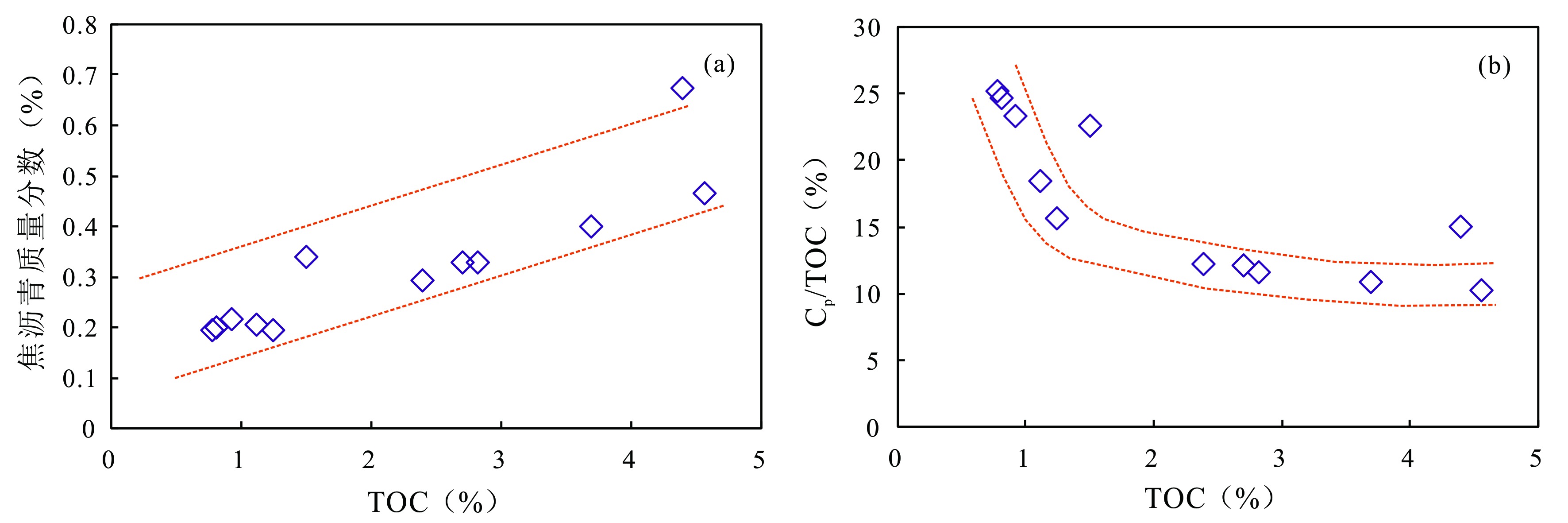
图2 丁页5井龙马溪组页岩中TOC含量与焦沥青含量(a)和Cp/TOC比值(b)的交汇图
Fig.2 Cross-plots of the TOC contents versus pyrobitumen content (a) and Cp/TOC ratio (b) of the Longmaxi Formation shale samples in Well DY5

图3 页岩中干酪根、焦沥青以及有机质孔隙在扫描电镜下的分布 (a) 扫描电镜下的干酪根与焦沥青,干酪根具有自形性,焦沥青具有它形性;(b) 干酪根部分放大后图片,可见部分孔隙,但孔径较小;(b-1) 图(b)经过图像处理后效果,白色部分表示有机质背景,黑色部分表示孔隙;(c) 焦沥青放大后图片,图中孔隙发育明显,孔径相比干酪根更大;(c-1) 图(c)经过图像处理后效果,白色部分表示有机质背景,黑色部分表示孔隙
Fig.3 Distribution of kerogen, pyrobitumen and organic matter-hosted pores in shale under SEM imaging

图4 页岩中干酪根(a)与焦沥青(b)中不同孔径面孔率分布图
Fig.4 Frequency diagrams showing the distribution of surface porosity in various-sized pores of the kerogen (a) and pyrobitumen (b) in the shale samples

图5 丁页5井龙马溪组典型页岩样品的N2氮气吸附-解吸曲线(a)和CO2等温吸附曲线(b)
Fig.5 N2 adsorption desorption curves (a) and CO2 adsorption isotherms (b) of the typical Longmaxi Formation shale samples in Well DY5
| 样品 | TOC (%) | 微孔比表面积(m2·g-1) | 非微孔比表面积(m2·g-1) | 总孔隙比表面积(m2·g-1) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机质 微孔 | 无机质 微孔 | 总微孔 | 有机质 非微孔 | 无机质 非微孔 | 总非 微孔 | 总孔 | 有机质孔 | 无机质孔 | ||||
| DY5-43 | 0.77 | 1.5601 | 10.4310 | 11.9910 | 2.9198 | 9.2389 | 12.1587 | 4.4799 | 19.6699 | 24.1497 | ||
| DY5-39 | 1.24 | 2.5011 | 11.3482 | 13.8493 | 4.6809 | 8.9460 | 13.6269 | 7.1820 | 20.2942 | 27.4762 | ||
| DY5-34 | 0.81 | 1.6351 | 11.6503 | 13.2854 | 3.0602 | 8.5125 | 11.5727 | 4.6953 | 20.1628 | 24.8581 | ||
| DY5-23 | 0.92 | 1.8573 | 10.0959 | 11.9532 | 3.4761 | 7.4745 | 10.9506 | 5.3333 | 17.5704 | 22.9038 | ||
| DY5-22 | 1.11 | 2.2412 | 9.4912 | 11.7324 | 4.1946 | 7.0429 | 11.2375 | 6.4359 | 16.5340 | 22.9699 | ||
| DY5-19 | 1.49 | 3.0207 | 10.1833 | 13.2040 | 5.6534 | 7.2446 | 12.8980 | 8.6741 | 17.4279 | 26.1020 | ||
| DY5-12 | 2.38 | 4.8181 | 10.5126 | 15.3307 | 9.0174 | 7.8447 | 16.8621 | 13.8356 | 18.3572 | 32.1928 | ||
| DY5-09 | 2.81 | 5.6835 | 11.4814 | 17.1649 | 10.6370 | 7.6172 | 18.2542 | 16.3205 | 19.0986 | 35.4191 | ||
| DY5-07 | 2.70 | 5.4570 | 11.8370 | 17.2940 | 10.2132 | 7.8196 | 18.0328 | 15.6702 | 19.6566 | 35.3268 | ||
| DY5-06 | 3.69 | 7.4526 | 10.5238 | 17.9765 | 13.9481 | 6.4992 | 20.4473 | 21.4007 | 17.0230 | 38.4238 | ||
| DY5-05 | 4.56 | 9.2116 | 10.6541 | 19.8658 | 17.2402 | 8.4451 | 25.6853 | 26.4519 | 19.0992 | 45.5511 | ||
| DY5-02 | 4.39 | 8.8760 | 9.9947 | 18.8708 | 16.6121 | 9.2204 | 25.8325 | 25.4881 | 19.2152 | 44.7033 | ||
表3 丁页5井龙马溪组页岩的纳米孔隙比表面积分布
Table 3 Nanopore specific surface area distribution of the Longmaxi shale samples in Well DY5
| 样品 | TOC (%) | 微孔比表面积(m2·g-1) | 非微孔比表面积(m2·g-1) | 总孔隙比表面积(m2·g-1) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机质 微孔 | 无机质 微孔 | 总微孔 | 有机质 非微孔 | 无机质 非微孔 | 总非 微孔 | 总孔 | 有机质孔 | 无机质孔 | ||||
| DY5-43 | 0.77 | 1.5601 | 10.4310 | 11.9910 | 2.9198 | 9.2389 | 12.1587 | 4.4799 | 19.6699 | 24.1497 | ||
| DY5-39 | 1.24 | 2.5011 | 11.3482 | 13.8493 | 4.6809 | 8.9460 | 13.6269 | 7.1820 | 20.2942 | 27.4762 | ||
| DY5-34 | 0.81 | 1.6351 | 11.6503 | 13.2854 | 3.0602 | 8.5125 | 11.5727 | 4.6953 | 20.1628 | 24.8581 | ||
| DY5-23 | 0.92 | 1.8573 | 10.0959 | 11.9532 | 3.4761 | 7.4745 | 10.9506 | 5.3333 | 17.5704 | 22.9038 | ||
| DY5-22 | 1.11 | 2.2412 | 9.4912 | 11.7324 | 4.1946 | 7.0429 | 11.2375 | 6.4359 | 16.5340 | 22.9699 | ||
| DY5-19 | 1.49 | 3.0207 | 10.1833 | 13.2040 | 5.6534 | 7.2446 | 12.8980 | 8.6741 | 17.4279 | 26.1020 | ||
| DY5-12 | 2.38 | 4.8181 | 10.5126 | 15.3307 | 9.0174 | 7.8447 | 16.8621 | 13.8356 | 18.3572 | 32.1928 | ||
| DY5-09 | 2.81 | 5.6835 | 11.4814 | 17.1649 | 10.6370 | 7.6172 | 18.2542 | 16.3205 | 19.0986 | 35.4191 | ||
| DY5-07 | 2.70 | 5.4570 | 11.8370 | 17.2940 | 10.2132 | 7.8196 | 18.0328 | 15.6702 | 19.6566 | 35.3268 | ||
| DY5-06 | 3.69 | 7.4526 | 10.5238 | 17.9765 | 13.9481 | 6.4992 | 20.4473 | 21.4007 | 17.0230 | 38.4238 | ||
| DY5-05 | 4.56 | 9.2116 | 10.6541 | 19.8658 | 17.2402 | 8.4451 | 25.6853 | 26.4519 | 19.0992 | 45.5511 | ||
| DY5-02 | 4.39 | 8.8760 | 9.9947 | 18.8708 | 16.6121 | 9.2204 | 25.8325 | 25.4881 | 19.2152 | 44.7033 | ||
| 样品 | TOC (%) | 微孔体积(cm3·g-1) | 介孔体积(cm3·g-1) | 宏孔体积(cm3·g-1) | 总孔体积(cm3·g-1) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机质 微孔 | 无机质 微孔 | 总微孔 | 有机质 介孔 | 无机质 介孔 | 总介孔 | 有机质 宏孔 | 无机质 宏孔 | 总宏孔 | 有机质 总孔 | 无机质 总孔 | 总孔隙 | |||||
| DY5-43 | 0.77 | 0.0004 | 0.0012 | 0.0016 | 0.0010 | 0.0043 | 0.0053 | 0 | 0.0018 | 0.0018 | 0.0014 | 0.0073 | 0.0087 | |||
| DY5-39 | 1.24 | 0.0006 | 0.0014 | 0.0020 | 0.0016 | 0.0039 | 0.0055 | 0 | 0.0012 | 0.0013 | 0.0023 | 0.0065 | 0.0088 | |||
| DY5-34 | 0.81 | 0.0004 | 0.0014 | 0.0018 | 0.0011 | 0.0043 | 0.0054 | 0 | 0.0014 | 0.0014 | 0.0015 | 0.0071 | 0.0086 | |||
| DY5-23 | 0.92 | 0.0005 | 0.0012 | 0.0017 | 0.0012 | 0.0037 | 0.0049 | 0 | 0.0013 | 0.0013 | 0.0017 | 0.0062 | 0.0079 | |||
| DY5-22 | 1.11 | 0.0005 | 0.0010 | 0.0016 | 0.0015 | 0.0034 | 0.0049 | 0 | 0.0013 | 0.0013 | 0.0020 | 0.0057 | 0.0078 | |||
| DY5-19 | 1.49 | 0.0007 | 0.0011 | 0.0018 | 0.0020 | 0.0033 | 0.0053 | 0 | 0.0011 | 0.0012 | 0.0028 | 0.0055 | 0.0083 | |||
| DY5-12 | 2.38 | 0.0012 | 0.0013 | 0.0025 | 0.0032 | 0.0036 | 0.0067 | 0.0001 | 0.0015 | 0.0015 | 0.0044 | 0.0064 | 0.0108 | |||
| DY5-09 | 2.81 | 0.0014 | 0.0014 | 0.0028 | 0.0037 | 0.0036 | 0.0073 | 0.0001 | 0.0013 | 0.0014 | 0.0052 | 0.0062 | 0.0114 | |||
| DY5-07 | 2.70 | 0.0013 | 0.0013 | 0.0026 | 0.0036 | 0.0040 | 0.0076 | 0.0001 | 0.0014 | 0.0015 | 0.0050 | 0.0067 | 0.0117 | |||
| DY5-06 | 3.69 | 0.0018 | 0.0011 | 0.0029 | 0.0049 | 0.0037 | 0.0085 | 0.0001 | 0.0013 | 0.0014 | 0.0068 | 0.0061 | 0.0129 | |||
| DY5-05 | 4.56 | 0.0022 | 0.0013 | 0.0036 | 0.0060 | 0.0042 | 0.0102 | 0.0001 | 0.0019 | 0.0021 | 0.0084 | 0.0074 | 0.0159 | |||
| DY5-02 | 4.39 | 0.0022 | 0.0012 | 0.0033 | 0.0058 | 0.0038 | 0.0096 | 0.0001 | 0.0009 | 0.0010 | 0.0081 | 0.0058 | 0.0139 | |||
表4 丁页5井龙马溪组页岩纳米孔隙孔容分布
Table 4 Nanopore volume distribution of the Longmaxi Formation shale samples in Well DY5
| 样品 | TOC (%) | 微孔体积(cm3·g-1) | 介孔体积(cm3·g-1) | 宏孔体积(cm3·g-1) | 总孔体积(cm3·g-1) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机质 微孔 | 无机质 微孔 | 总微孔 | 有机质 介孔 | 无机质 介孔 | 总介孔 | 有机质 宏孔 | 无机质 宏孔 | 总宏孔 | 有机质 总孔 | 无机质 总孔 | 总孔隙 | |||||
| DY5-43 | 0.77 | 0.0004 | 0.0012 | 0.0016 | 0.0010 | 0.0043 | 0.0053 | 0 | 0.0018 | 0.0018 | 0.0014 | 0.0073 | 0.0087 | |||
| DY5-39 | 1.24 | 0.0006 | 0.0014 | 0.0020 | 0.0016 | 0.0039 | 0.0055 | 0 | 0.0012 | 0.0013 | 0.0023 | 0.0065 | 0.0088 | |||
| DY5-34 | 0.81 | 0.0004 | 0.0014 | 0.0018 | 0.0011 | 0.0043 | 0.0054 | 0 | 0.0014 | 0.0014 | 0.0015 | 0.0071 | 0.0086 | |||
| DY5-23 | 0.92 | 0.0005 | 0.0012 | 0.0017 | 0.0012 | 0.0037 | 0.0049 | 0 | 0.0013 | 0.0013 | 0.0017 | 0.0062 | 0.0079 | |||
| DY5-22 | 1.11 | 0.0005 | 0.0010 | 0.0016 | 0.0015 | 0.0034 | 0.0049 | 0 | 0.0013 | 0.0013 | 0.0020 | 0.0057 | 0.0078 | |||
| DY5-19 | 1.49 | 0.0007 | 0.0011 | 0.0018 | 0.0020 | 0.0033 | 0.0053 | 0 | 0.0011 | 0.0012 | 0.0028 | 0.0055 | 0.0083 | |||
| DY5-12 | 2.38 | 0.0012 | 0.0013 | 0.0025 | 0.0032 | 0.0036 | 0.0067 | 0.0001 | 0.0015 | 0.0015 | 0.0044 | 0.0064 | 0.0108 | |||
| DY5-09 | 2.81 | 0.0014 | 0.0014 | 0.0028 | 0.0037 | 0.0036 | 0.0073 | 0.0001 | 0.0013 | 0.0014 | 0.0052 | 0.0062 | 0.0114 | |||
| DY5-07 | 2.70 | 0.0013 | 0.0013 | 0.0026 | 0.0036 | 0.0040 | 0.0076 | 0.0001 | 0.0014 | 0.0015 | 0.0050 | 0.0067 | 0.0117 | |||
| DY5-06 | 3.69 | 0.0018 | 0.0011 | 0.0029 | 0.0049 | 0.0037 | 0.0085 | 0.0001 | 0.0013 | 0.0014 | 0.0068 | 0.0061 | 0.0129 | |||
| DY5-05 | 4.56 | 0.0022 | 0.0013 | 0.0036 | 0.0060 | 0.0042 | 0.0102 | 0.0001 | 0.0019 | 0.0021 | 0.0084 | 0.0074 | 0.0159 | |||
| DY5-02 | 4.39 | 0.0022 | 0.0012 | 0.0033 | 0.0058 | 0.0038 | 0.0096 | 0.0001 | 0.0009 | 0.0010 | 0.0081 | 0.0058 | 0.0139 | |||
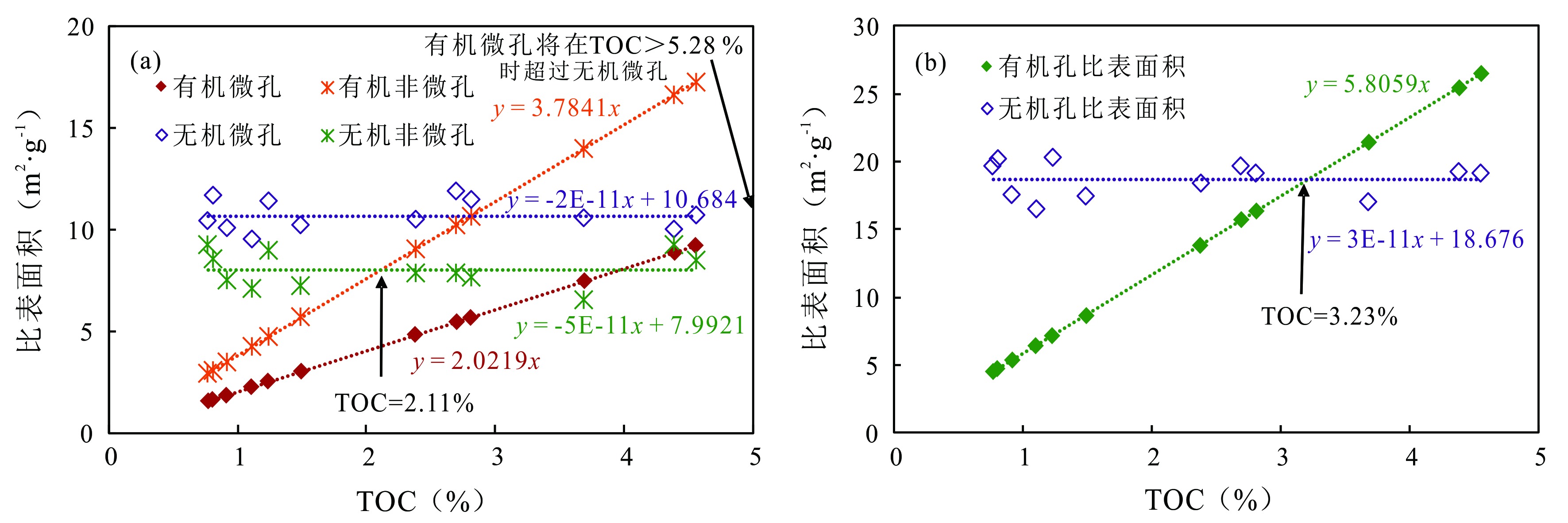
图7 丁页5井龙马溪组页岩孔隙比表面积(a)与TOC含量(b)的关系图
Fig.7 Relationship between specific pore surface area (a) and TOC (b) content of the Longmaxi Formation shale samples in Well DY5
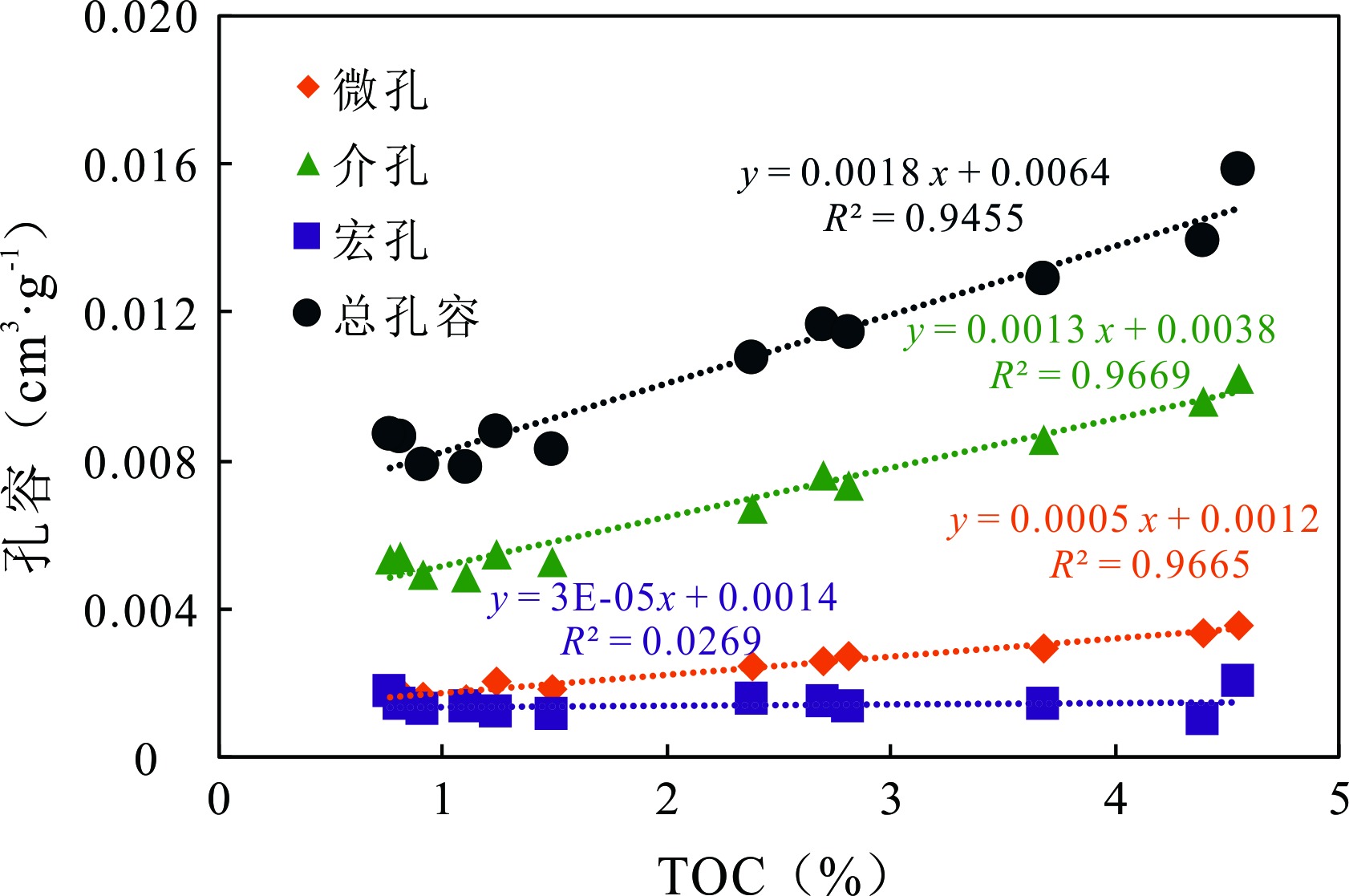
图8 丁页5井龙马溪组页岩的TOC含量和不同尺度孔容的关系
Fig.8 Relationship between TOC content and various-sized pore volume of the Longmaxi Formation shale samples in Well DY5
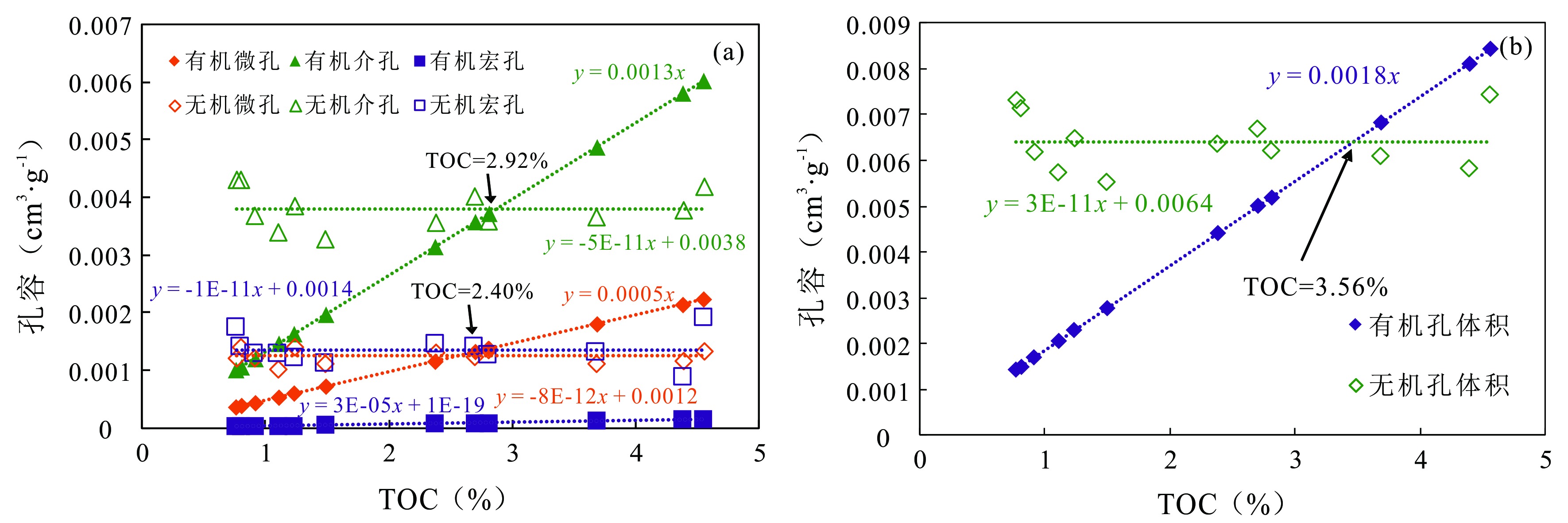
图9 丁页5井龙马溪组页岩页岩的有机质和无机质孔隙体积与TOC关系 (a) TOC对微孔、介孔及宏孔体积的影响;(b) TOC对纳米孔隙总体积的影响
Fig.9 Relationship between organic and inorganic pore volume and TOC value of the Longmaxi Formation shale samples in Well DY5
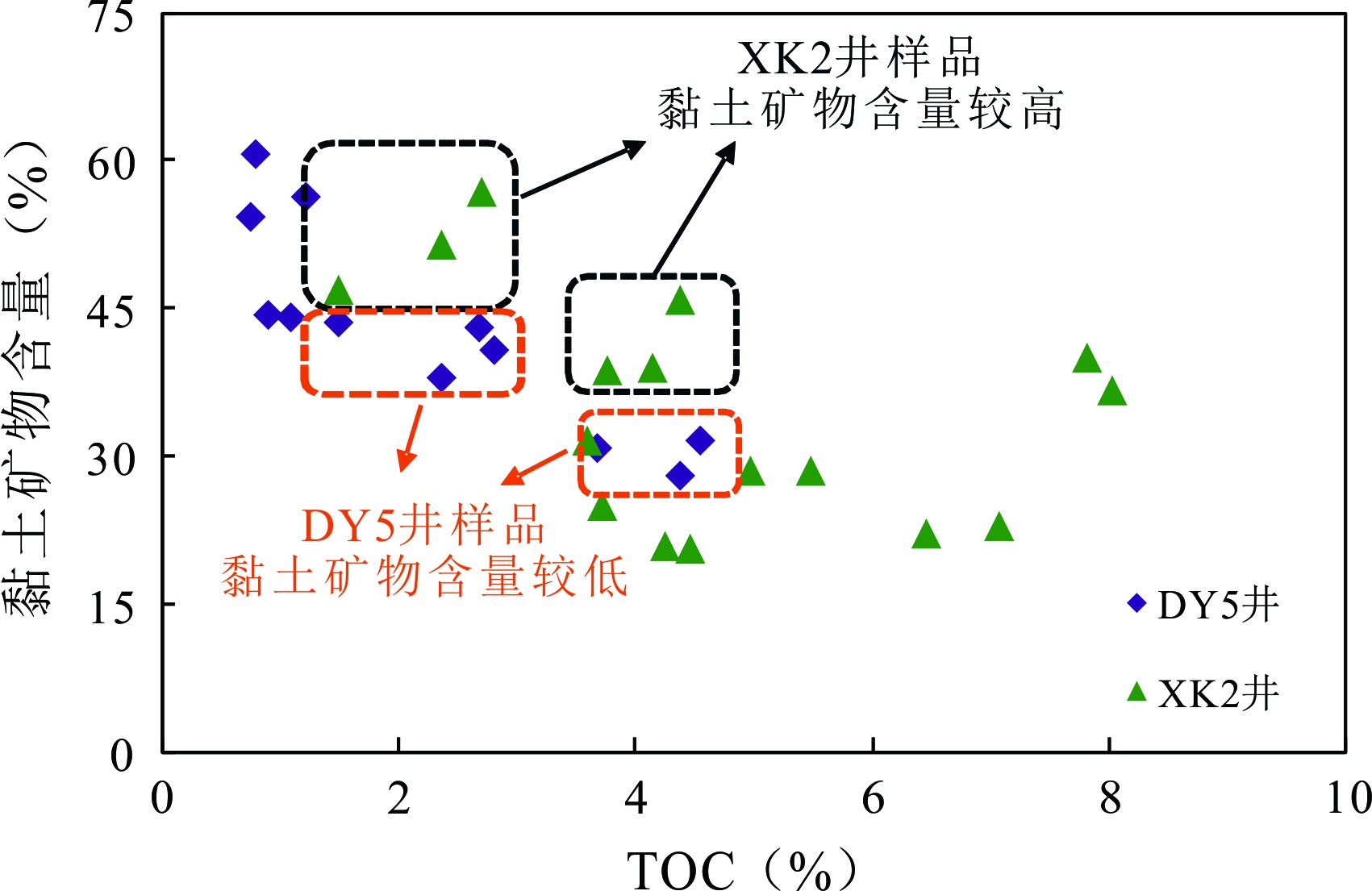
图10 龙马溪组页岩的TOC与黏土矿物含量关系(DY5井页岩数据来源于李东升等[43];XK2井页岩样品数据来源于Sun等[61])
Fig.10 Relationship between TOC and clay mineral contents of the Longmaxi Formation shale samples

图12 丁页5井龙马溪组页岩焦沥青含量对页岩纳米孔隙发育的影响 (a)焦沥青含量对页岩纳米孔隙结构的影响;(b) 经TOC归一化后页岩孔隙结构与焦沥青占有机质比例的关系
Fig.12 Effect of pyrobitumen contents on nano-pore development in the Longmaxi shale samples of Well DY5
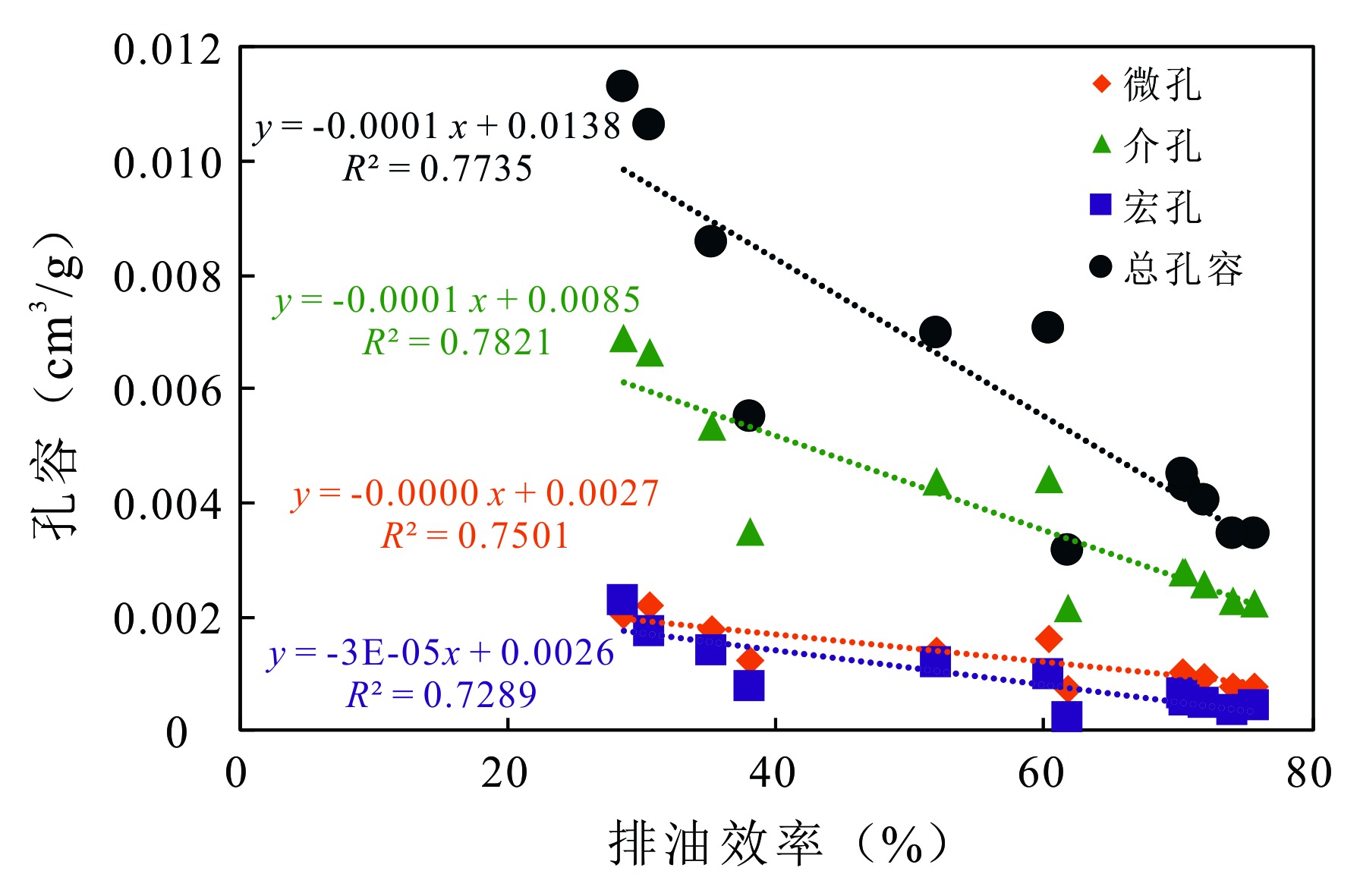
图13 丁页5井龙马溪组页岩排油效率与TOC归一化孔容的关系
Fig.13 Relationship between oil expulsion efficiency and TOC-normalized pore volume of the Longmaxi Formation shale samples in Well DY5
| [1] | 邹才能, 赵群, 王红岩, 等. 中国海相页岩气主要特征及勘探开发主体理论与技术[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(8): 1-13. |
| [2] | 刘金, 王剑, 张宝真, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组微-纳米孔隙页岩油原位赋存特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(2): 270-278. |
| [3] |
CHEN L, LIU K, JIANG S, et al. Effect of adsorbed phase density on the correction of methane excess adsorption to absolute adsorption in shale[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 420: 127678.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 陈尚斌, 朱炎铭, 王红岩, 等. 川南龙马溪组页岩气储层纳米孔隙结构特征及其成藏意义[J]. 煤炭学报, 2012, 37(3): 438-444. |
| [5] | 邹才能, 杨智, 陶士振, 等. 纳米油气与源储共生型油气聚集[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(1): 13-26. |
| [6] |
LOUCKS R G, REED R M, RUPPEL S C, et al. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6): 1071-1098.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 任梦怡, 汪泽成, 江青春, 等. 川南地区中二叠统茅口组碳酸盐岩储层孔隙特征与储层成因[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2021, 45(3): 32-43. |
| [8] | 徐祖新, 郭少斌. 中扬子地区震旦系陡山沱组页岩储层孔隙结构特征[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(1): 206-212. |
| [9] |
SLATT R M, O’BRIEN N R. Pore types in the Barnett and Woodford gas shales: Contribution to understanding gas storage and migration pathways in fine-grained rocks[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2011, 95(12): 2017-2030.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 肖贤明, 宋之光, 朱炎铭, 等. 北美页岩气研究及对我国下古生界页岩气开发的启示[J]. 煤炭学报, 2013, 38(5): 721-727. |
| [11] |
SING K S W. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984)[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1985, 57(4): 603-619.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ROSS D J K, BUSTIN R M. Characterizing the shale gas resource potential of Devonian-Mississippian strata in the Western Canada sedimentary basin: Application of an integrated formation evaluation[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2008, 92(1): 87-125.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LOUCKS R G, REED R M, RUPPEL S C, et al. Morphology, Genesis, and Distribution of Nanometer-Scale Pores in Siliceous Mudstones of the Mississippian Barnett shale[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2009, 79(12): 848-861.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
XIONG F Y, JIANG Z X, TANG X L, et al. Characteristics and origin of the heterogeneity of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi marine shale in southeastern Chongqing, SW China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 27: 1389-1399.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ZHAO J Z, REN L, JIANG T X, et al. Ten years of gas shale fracturing in China: Review and prospect[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, 2022, 9(2): 158-175.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 李楚雄, 肖七林, 陈奇, 等. 页岩纳米级孔隙在有机质熟化过程中的演化特征及影响因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(6): 901-909. |
| [17] | 高凤琳, 王成锡, 宋岩, 等. 氩离子抛光-场发射扫描电镜分析方法在识别有机显微组分中的应用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(2): 360-367. |
| [18] | 潘妮, 赵迪斐, 魏源, 等. 渝西地区龙马溪组深层页岩矿物特征及其储层地质意义[J]. 非常规油气, 2022, 9(2): 8-14. |
| [19] |
ZHANG C, YAO Y B, DONG Y G. Heterogeneous development of micro-and meso-pores in shale kerogen: New insights from chemical structure analysis[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2022, 102: 104552.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
MILLIKEN K L, RUDNICKI M, AWWILLER D N, et al. Organic matter-hosted pore system, Marcellus Formation (Devonian), Pennsylvania[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(2): 177-200.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ZHANG W T, HU W X, BORJIGIN T, et al. Pore characteristics of different organic matter in black shale: A case study of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in the Southeast Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 111: 33-43.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
腾格尔, 卢龙飞, 俞凌杰, 等. 页岩有机质孔隙形成、保持及其连通性的控制作用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(4): 687-699.
DOI |
| [23] | 杨祥玉, 谭静强, 户瑞宁. 湘西北地区志留纪早期龙马溪组页岩储层孔隙结构特征[J]. 非常规油气, 2022, 9(5): 25-35. |
| [24] |
CHENG P, XIAO X M, TIAN H, et al. Differences in the distribution and occurrence phases of pore water in various nanopores of marine-terrestrial transitional shales in the Yangquan area of the northeast Qinshui Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2022, 137: 105510.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
CHEN L, ZUO L, JIANG Z X, et al. Mechanisms of shale gas adsorption: Evidence from thermodynamics and kinetics study of methane adsorption on shale[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 361: 559-570.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
HU G, PANG Q, JIAO K, et al. Development of organic pores in the Longmaxi Formation overmature shales: Combined effects of thermal maturity and organic matter composition[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 116: 104314.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 孙雅雄, 张坦, 丁文龙, 等. 压汞法与数字图像分析技术在致密砂岩储层微观孔隙定量分析中的应用——以鄂尔多斯盆地吴起油田X区块为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(6): 1105-1115. |
| [28] |
TENG J, LIU B, MASTALERZ M, et al. Origin of organic matter and organic pores in the overmature Ordovician-Silurian Wufeng-Longmaxi Shale of the Sichuan Basin, China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2022, 253: 103970.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
CHEN L, JIANG Z X, LIU Q X, et al. Mechanism of shale gas occurrence: Insights from comparative study on pore structures of marine and lacustrine shales[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 104: 200-216.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
MASTALERZ M, DROBNIAK A, STANKIEWICZ A B. Origin, properties, and implications of solid bitumen in source-rock reservoirs: A review[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2018, 195: 14-36.
DOI URL |
| [31] | 腾格尔, 陶成, 胡广, 等. 排烃效率对页岩气形成与富集的影响[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(3): 325-334. |
| [32] |
GAI H, TIAN H, CHENG P, et al. Influence of retained bitumen in oil-prone shales on the chemical and carbon isotopic compositions of natural gases: Implications from pyrolysis experiments[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 101: 148-161.
DOI URL |
| [33] | 邹才能, 董大忠, 王玉满, 等. 中国页岩气特征、挑战及前景(一)[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(6): 689-701. |
| [34] | 仰云峰. 川东南志留系龙马溪组页岩沥青反射率和笔石反射率的应用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(4): 466-472. |
| [35] | 魏祥峰, 赵正宝, 王庆波, 等. 川东南綦江丁山地区上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统龙马溪组页岩气地质条件综合评价[J]. 地质论评, 2017, 63(1): 153-164. |
| [36] |
CHEN X, RONG J Y, LI Y, et al. Facies patterns and geography of the Yangtze region, South China, through the Ordovician and Silurian transition[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2004, 204(3/4): 353-372.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
GUO T L, ZHANG H R. Formation and enrichment mode of Jiaoshiba shale gas field, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(1): 31-40.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
KHAN M Z, FENG Q L, ZHANG K, et al. Biogenic silica and organic carbon fluxes provide evidence of enhanced marine productivity in the Upper Ordovician-Lower Silurian of South China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2019, 534: 109278.
DOI URL |
| [39] | GAO P, XIAO X M, HU D F, et al. Gas in place and its controlling factors of deep shale of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in the Dingshan area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science, 2022: 1-15. |
| [40] |
CHANG J Q, FAN X D, JIANG Z X, et al. Differential impact of clay minerals and organic matter on pore structure and its fractal characteristics of marine and continental shales in China[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2022, 216: 106334.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
HAO F, ZOU H Y, LU Y C. Mechanisms of shale gas storage: Implications for shale gas exploration in China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(8): 1325-1346.
DOI URL |
| [42] | 刘思逸, 高平, 肖贤明, 等. 四川盆地五峰—龙马溪组黑色页岩有机岩石学特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(5): 1281-1291. |
| [43] | 李东升, 盖海峰, 程鹏, 等. 通过沥青含量定量评估过成熟页岩排油效率:以丁页 5 井龙马溪页岩为例[J/OL]. 地球化学:1-13[2023-09-01]. |
| [44] | HUNT J M. Petroleum Geochemistry and Geology[M]. New York: W H Freeman, 1996. |
| [45] |
GAO F L, SONG Y, LI Z, et al. Lithofacies and reservoir characteristics of the Lower Cretaceous continental Shahezi Shale in the Changling Fault Depression of Songliao Basin, NE China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 98: 401-421.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
赖强, 谢冰, 吴煜宇, 等. 沥青质碳酸盐岩储集层岩石物理特征及测井评价——以四川盆地安岳气田寒武系龙王庙组为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(6): 889-895.
DOI |
| [47] | 严伟, 刘帅, 冯明刚, 等. 四川盆地丁山区块页岩气储层关键参数测井评价方法[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2019, 31(3): 95-104. |
| [48] | 朱日房, 张林晔, 李政, 等. 陆相断陷盆地页岩油资源潜力评价——以东营凹陷沙三段下亚段为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(1): 129-136. |
| [49] | BARKER C. Calculated volume and pressure changes during the thermal cracking of oil to gas in reservoirs1[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1990, 74(8): 1254-1261. |
| [50] | 马卫, 李剑, 王东良, 等. 烃源岩排烃效率及其影响因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(9): 1742-1751. |
| [51] |
SUN J, XIAO X M, CHENG P, et al. The relationship between oil generation, expulsion and retention of lacustrine shales: Based on pyrolysis simulation experiments[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 196: 107625.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
CURTIS M E, CARDOTT B J, SONDERGELD C H, et al. Development of organic porosity in the Woodford Shale with increasing thermal maturity[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2012, 103: 26-31.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
BERNARD S, HORSFIELD B. Thermal maturation of gas shale systems[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2014, 42: 635-651.
DOI URL |
| [54] | 王朋飞, 姜振学, 金璨, 等. 渝东南下志留统龙马溪组页岩有机质孔隙发育特征:基于聚焦离子束氦离子显微镜(FIB-HIM)技术[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(4): 902-910. |
| [55] |
BERNARD S, HORSFIELD B, SCHULZ H M, et al. Geoche-mical evolution of organic-rich shales with increasing maturity: A STXM and TEM study of the Posidonia Shale (Lower Toarcian, northern Germany)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 31(1): 70-89.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
SUN J, XIAO X M, WEI Q, et al. Occurrence of irreducible water and its influences on gas-bearing property of gas shales from shallow Longmaxi Formation in the Xishui Area, Guizhou, Southern China[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2021, 9: 654136.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
MENG G M, LI T F, GAI H F, et al. Pore characteristics and gas preservation of the Lower Cambrian shale in a strongly deformed zone, Northern Chongqing, China[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(8): 2956.
DOI URL |
| [58] | 马勇, 钟宁宁, 程礼军, 等. 渝东南两套富有机质页岩的孔隙结构特征——来自FIB-SEM的新启示[J]. 石油实验地质, 2015, 37(1): 109-116. |
| [59] |
纪文明, 宋岩, 姜振学, 等. 四川盆地东南部龙马溪组页岩微——纳米孔隙结构特征及控制因素[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(2): 182-195.
DOI |
| [60] |
KATZ B J, ARANGO I. Organic porosity: A geochemist’s view of the current state of understanding[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2018, 123: 1-16.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
SUN J, XIAO X M, WEI Q, et al. Gas in place and its controlling factors of the shallow Longmaxi shale in the Xishui area, Guizhou, China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020, 77: 103272.
DOI URL |
| [62] | 田华, 张水昌, 柳少波, 等. 压汞法和气体吸附法研究富有机质页岩孔隙特征[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(3): 419-427. |
| [1] | 孙自明, 卞昌蓉, 刘光祥. 峨眉山地幔柱主要研究进展及四川盆地二叠纪成盆动力学机制[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1089-1099. |
| [2] | 胡力文, 邹华耀, 杨伟强, 黎霆, 邓成昆, 程忠贞, 诸丹诚, 陈星岳. 川北寒武系碳酸盐岩压溶作用的影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1221-1231. |
| [3] | 漆洋, 吕春研, 王宇慧, 唐书恒, 郗兆栋. 生物地层格架下湘西北地区五峰组—龙马溪组孔隙结构特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1292-1303. |
| [4] | 孙自明, 卞昌蓉, 张荣强, 孙炜, 武重阳, 林娟华. 四川盆地东南部震旦系灯影组四段台缘带天然气勘探前景[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 979-987. |
| [5] | 饶权, 康永尚, 黄毅, 赵群, 王红岩. 蜀南地区龙马溪组页岩气工业建产区游离气和孔隙度下限讨论[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 1054-1064. |
| [6] | 贾鹏, 黄福喜, 林世国, 宋涛, 高阳, 吕维宁, 汪少勇, 刘策, 范晶晶, 欧阳靖琳. 四川盆地及其邻区中上寒武统洗象池群沉积相与沉积模式特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 807-818. |
| [7] | 孙自明, 张荣强, 孙炜, 郝运轻, 卞昌蓉. 四川盆地东部海相下组合油气勘探领域与有利勘探方向[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 798-806. |
| [8] | 王茜, 黄永建, 张治锋, 王长红, 李祥, 刘伟. 高分辨率化学层序地层学在深水细粒沉积中的应用:以上扬子地区六塘露头五峰组—龙马溪组下段为例[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 281-292. |
| [9] | 黄宇琪, 张鹏, 张金川, 杨军伟. 湖北来凤LD-1井龙马溪组页岩孔隙结构特征分析[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 828-836. |
| [10] | 鞠鹏程, 王训练, 王振涛, 刘喜方, 仲佳爱, 张在明. 渝北温泉镇地区三叠系“绿豆岩”特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 431-449. |
| [11] | 王朋飞, 姜振学, 金璨, 吕鹏, 李鑫, 张昆, 王凯, 黄璞. 渝东南下志留统龙马溪组页岩有机质孔隙发育特征:基于聚焦离子束氦离子显微镜(FIB-HIM)技术[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(04): 902-910. |
| [12] | 王子轶, 高志前, 石文睿, 王兴志, 赵红燕. 四川盆地五峰组—龙马溪组笔石与页岩气关系探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(02): 379-388. |
| [13] | 丁熊, 吴涵, 王兴志, 唐青松, 马华灵. 四川盆地三叠系颗粒碳酸盐岩储层的成因类型[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(06): 1241-1250. |
| [14] | 谭聪, 于炳松, 阮壮, 郝士龙, 李琨, 罗忠, 刘润达. 四川盆地上三叠统须家河组高分辨率层序地层研究[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(02): 290-301. |
| [15] | 何志勇, 刘海涛, 肖伟, 杜红权. 四川盆地元坝地区下侏罗统介壳灰岩储层分布预测[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(01): 142-149. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||