



现代地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (05): 1306-1320.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.014
邵威猛1( ), 牛永斌1(
), 牛永斌1( ), 程梦园1, 韩科龙2, 孙凤余1, 程怡高1, 荆楚涵1
), 程梦园1, 韩科龙2, 孙凤余1, 程怡高1, 荆楚涵1
收稿日期:2022-10-09
修回日期:2023-02-08
出版日期:2023-10-10
发布日期:2023-11-14
通讯作者:
牛永斌,男,教授,1980年出生,地质学专业,主要从事储层地质学和碳酸盐岩岩石学研究。Email:niuyongbin@hpu.edu.cn。
作者简介:邵威猛,男,硕士研究生,1998年出生,地质工程专业,主要从事储层地质学研究。Email:weimengshao@qq.com。
基金资助:
SHAO Weimeng1( ), NIU Yongbin1(
), NIU Yongbin1( ), CHENG Mengyuan1, HAN Kelong2, SUN Fengyu1, CHENG Yigao1, JING Chuhan1
), CHENG Mengyuan1, HAN Kelong2, SUN Fengyu1, CHENG Yigao1, JING Chuhan1
Received:2022-10-09
Revised:2023-02-08
Online:2023-10-10
Published:2023-11-14
摘要:
豫西北奥陶系马家沟组碳酸盐岩中多发育裂缝和溶洞。在对研究区野外露头实地观测的基础上,利用地质统计学的方法对裂缝和溶洞的发育特征进行研究,并结合区域构造演化特征对其成因机制进行详细分析。研究结果表明:(1)研究区溶洞分为小型溶洞(洞高<1 m)、中型溶洞(洞高1~5 m)、大型溶洞(洞高>5 m)三种类型,以中、小型溶洞为主。(2)依据裂缝-溶洞的发育特征及分布规律,将研究区缝洞型储集空间划分为断控型、层控型和表层岩溶型三种岩溶系统发育模式,其中断控型岩溶系统形成的缝洞发育规模最大。(3)研究区缝洞型储集空间主要形成于古生代与新生代两个时期。构造作用、岩性和水文条件是控制缝洞储集空间发育的最主要因素,其中构造作用对缝洞的空间发育和分布规律影响较大,控制缝洞的发育强度、所处部位和发育方向。岩性及水文条件对缝洞型储集空间的发育程度影响较大,岩石中方解石含量越高,地表径流越丰富,缝洞型储集空间就越发育。本研究提供了一个很好的露头类比对象,对加深理解缝洞型碳酸盐岩储层的成因机制和华北地区煤层底板水的防治具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
邵威猛, 牛永斌, 程梦园, 韩科龙, 孙凤余, 程怡高, 荆楚涵. 豫西北奥陶系马家沟组碳酸盐岩中裂缝-溶洞的发育特征及成因机制[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1306-1320.
SHAO Weimeng, NIU Yongbin, CHENG Mengyuan, HAN Kelong, SUN Fengyu, CHENG Yigao, JING Chuhan. Development Characteristics of Fracture-Cave and Their Formation Mechanism in Carbonate Rocks of Ordovician Majiagou Formation in Northwestern Henan Province[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(05): 1306-1320.

图5 研究区奥陶系溶洞照片 (a)穆家寨剖面的椭圆形溶洞,未充填;(b)穆家寨剖面的近圆形溶洞,钙质砾石充填;(c)黄岩剖面的巷道形溶洞,未充填;(d)甲板创剖面的长条形溶洞,未充填;(e)洞湾剖面的似方形溶洞;(f)盘古洞剖面的巷道形溶洞,未充填;(g)天堂窑剖面的拱形溶洞,未充填;(h)皇到岭剖面的溶洞,铝土质泥岩充填
Fig.5 Photos of Ordovician caves in the study area
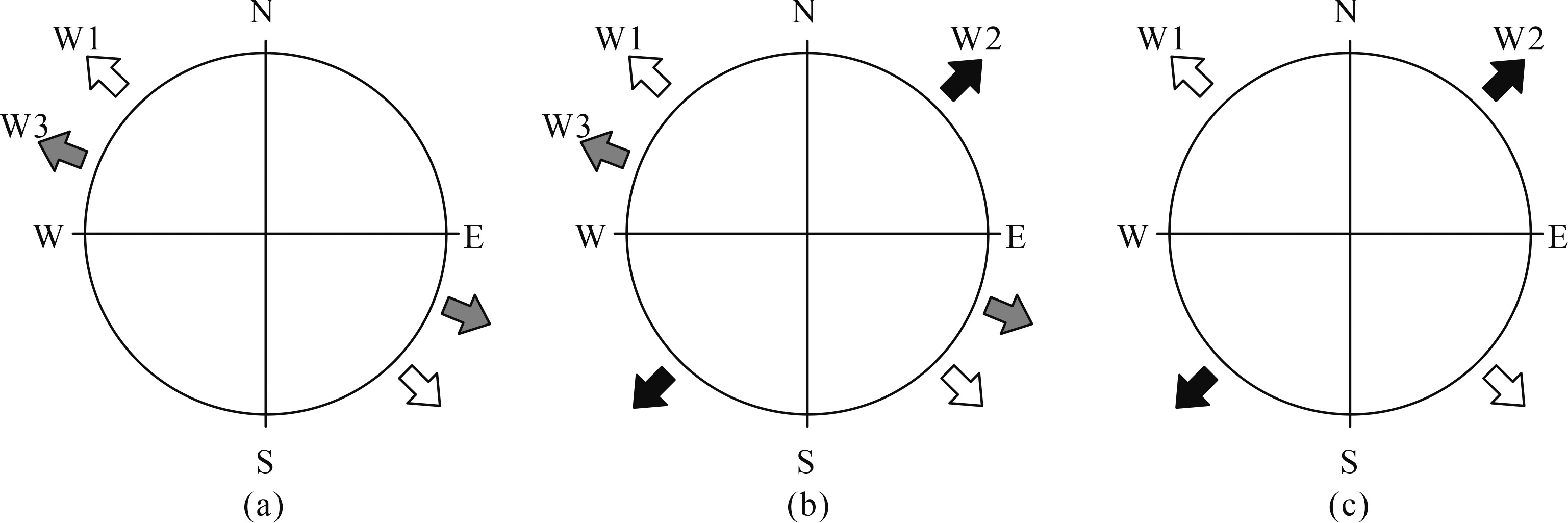
图9 研究区新生代构造应力场演化示意图(据文献[59]) (a) 穆家寨、盘古洞、甲板创新生代两期拉张应力方向;(b) 洞湾新生代三期拉张应力方向;(c) 黄岩新生代两期拉张应力方向;W1.古近纪时期;W2.中新世时期;W3.上新世以来
Fig.9 Schematic diagrams of the Cenozoic tectonic stress field evolution in the study area(after reference [59])
| [1] |
XIANG P F, JI H C, SHI Y Q, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of mesogenetic dissolution: A case study of Ordovician carbonate in the western slope of the Shulu Sag, Jizhong Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 206: 109045.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
JIN Z J, ZHU D Y, HU W X, et al. Mesogenetic dissolution of the Middle Ordovician limestone in the Tahe oilfield of Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(6): 753-763.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 杨德彬, 杨敏, 李新华, 等. 塔河油田碳酸盐岩小缝洞型储层特征及成因演化[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2021, 28(1): 41-46. |
| [4] | 牛君, 黄文辉, 蒋文龙, 等. 玉北地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩风化壳岩溶储层特征及其主控因素[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2016, 40(1): 1-13, 135. |
| [5] | 范卓颖, 林承焰, 鞠传学, 等. 塔河油田二区奥陶系优势储集体特征及控制因素[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2017, 47(1): 34-47. |
| [6] |
LIU L F, WANG P, LI Y, et al. Paleozoic Reservoir beds and their favorableness in Tazhong Areas of Tarim Basin, Northwest China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2009, 68(1/2): 1-18.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
DING W L, FAN T L, YU B S, et al. Ordovician carbonate reservoir fracture characteristics and fracture distribution forecasting in the Tazhong area of Tarim Basin, Northwest China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2012, 86/87: 62-70.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
MAO C, ZHONG J H, LI Y, et al. Ordovician carbonate rock matrix fractured-porous reservoirs in Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(6): 745-753.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 徐微, 陈冬梅, 赵文光, 等. 塔河油田奥陶系碳酸盐岩油藏溶洞发育规律[J]. 海相油气地质, 2011, 16(2): 34-41. |
| [10] |
李阳, 侯加根, 李永强. 碳酸盐岩缝洞型储集体特征及分类分级地质建模[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(4): 600-606.
DOI |
| [11] | 陈清华, 刘池阳, 王书香, 等. 碳酸盐岩缝洞系统研究现状与展望[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2002, 23(2): 196-202. |
| [12] |
JIA L Q, CAI C F, JIANG L, et al. Petrological and geochemical constraints on diagenesis and deep burial dissolution of the Ordovician carbonate reservoirs in the Tazhong area, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 78: 271-290.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
FU H, HAN J H, MENG W B, et al. Forming mechanism of the Ordovician Karst carbonate reservoirs on the northern slope of central Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, 2017, 4(4): 294-304.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HAN C C, LIN C Y, LU X B, et al. Petrological and geochemical constraints on fluid types and formation mechanisms of the Ordovician carbonate reservoirs in Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 178: 106-120.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
DING Z W, WANG R J, CHEN F F, et al.Origin, hydrocarbon accumulation and oil-gas enrichment of fault-karst carbonate reservoirs: A case study of Ordovician carbonate reservoirs in South Tahe area of Halahatang oilfield, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(2): 306-317.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MÉNDEZ J N, JIN Q, GONZÁLEZ M, et al. Fracture characterization and modeling of karsted carbonate reservoirs: A case study in Tahe oilfield, Tarim Basin (western China)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 112: 104104.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
李阳, 金强, 钟建华, 等. 塔河油田奥陶系岩溶分带及缝洞结构特征[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(3): 289-298.
DOI |
| [18] |
SHEN A J, ZHAO W Z, HU A P, et al. Major factors controlling the development of marine carbonate reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(5): 597-608.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
CHEN L P, ZHANG H, CAI Z X, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanisms of the unconformity-related paleokarst reservoirs in the Upper Sinian, Northwestern Tarim Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 120: 104559.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
JIU B, HUANG W H, MU N N, et al. Types and controlling factors of Ordovician paleokarst carbonate reservoirs in the southeastern Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 198: 108162.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
WANG X T, WANG J, CAO Y C, et al. Characteristics, formation mechanism and evolution model of Ordovician carbonate fault-controlled reservoirs in the Shunnan area of the Shuntuogole lower uplift, Tarim Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2022, 145: 105878.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
YAN H J, HE D B, JIA A L, et al. Characteristics and development model of Karst Reservoirs in the fourth member of Sinian Dengying Formation in central Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(4): 810-823.
DOI URL |
| [23] | 余智超, 王志章, 魏荷花, 等. 塔河油田缝洞型油藏不同成因岩溶储集体表征[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(6): 53-61. |
| [24] | 李定龙. 皖北两个奥陶系剖面岩溶岩地球化学特征对比[J]. 中国岩溶, 1999, 18(4): 319-328. |
| [25] | 李定龙. 皖北奥陶系碳酸盐岩稀土元素地球化学特征及其古岩溶意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(2): 353-365. |
| [26] | 虎维岳. 华北东部深部岩溶及煤矿岩溶水害特征[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2010, 38(2): 23-27. |
| [27] | 郑聪斌, 冀小林, 贾疏源. 陕甘宁盆地中部奥陶系风化壳古岩溶发育特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 1995, 14(3): 280-288. |
| [28] | 郑聪斌, 王飞雁, 贾疏源. 陕甘宁盆地中部奥陶系风化壳岩溶岩及岩溶相模式[J]. 中国岩溶, 1997, 16(4): 351-361. |
| [29] | 何江, 方少仙, 侯方浩, 等. 风化壳古岩溶垂向分带与储集层评价预测: 以鄂尔多斯盆地中部气田区马家沟组马五5—马五1亚段为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(5): 534-542. |
| [30] |
魏新善, 任军峰, 赵俊兴, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东部奥陶系风化壳古地貌特征嬗变及地质意义[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(9): 999-1009.
DOI |
| [31] | 李定龙, 杨为民, 汪才会, 等. 皖北奥陶系古岩溶宏微观特征及岩溶相模式[J]. 淮南矿业学院学报, 1998, 18(4): 1-6. |
| [32] | 李定龙, 周治安, 王桂梁. 马家沟灰岩(古)岩溶研究中的若干问题探讨[J]. 地质科技情报, 1997, 16(1): 23-28. |
| [33] | 李定龙, 周治安, 王才会, 等. 华北地区奥陶系灰岩岩溶研究的几点思考[J]. 世界地质, 1997, 16(1): 60-65, 100. |
| [34] | 贾疏源. 中国岩溶缝洞系统油气储层特征及其勘探前景[J]. 特种油气藏, 1997, 4(4): 1-5, 9. |
| [35] | 田景春, 时国, 陈辉, 等. 南华北地区奥陶系古喀斯特特征及其储层前景[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 36(6): 598-604. |
| [36] | 施和生, 王冠龙. 豫西地区岩溶作用在铝土矿成矿中的意义[J]. 中国岩溶, 1989, 8(1): 62-69. |
| [37] | 黎志豪, 许光泉, 高加林, 等. 淮南地区构造特征及其对岩溶作用的影响[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2018, 46(3): 121-126. |
| [38] | 李定龙, 杨为民, 汪才会, 等. 皖北奥陶系古岩溶分期分类及岩溶岩特征[J]. 淮南工业学院学报, 1999, 19(1): 5-12. |
| [39] |
XIONG Y, TAN X C, ZUO Z F, et al. Middle Ordovician multi-stage penecontemporaneous karstification in North China: Implications for reservoir genesis and sea level fluctuations[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 183: 103969.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
FRIESEM DAVID E, NADYA T, MINA W E, et al. Identification of fresh and burnt bat guano and pigeon droppings in Eastern Mediterranean karstic cave sites based on micromorphological and chemical characteristics[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2021, 274: 107238.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
GALÁN J, NÚÑEZ-LAHUERTA C, LÓPEZ-GARCÍA J M, et al. Did humans disturb bats? Exploring the hominin-chiropter interactions in the Sierra de Atapuerca sites (early to Middle Pleistocene, Spain)[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2019, 226: 106018.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
JORDI R, ETHEL A, MARTA A, et al. Site formation processes, human activities and palaeoenvironmental reconstructions from archaeobotanical records in cave and rock-shelter sites in NE Iberia[J]. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 2022, 299: 104612.
DOI URL |
| [43] | 牛永斌, 单婷婷, 董小波, 等. 豫西北奥陶系马家沟组遗迹化石及其沉积环境[J]. 沉积学报, 2015, 33(2): 211-225. |
| [44] | 牛永斌, 胡亚洲, 高文秀, 等. 豫西北奥陶系马家沟组三段遗迹组构及沉积演化规律[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(1): 15-27. |
| [45] | 牛永斌, 董小波, 朱信生, 等. 豫西北太行山奥陶系露头区裂缝发育特征及主控因素[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(4): 809-818. |
| [46] | 高玉飞, 钟建华. 塔河油田四区奥陶系储层裂缝特征及其意义[J]. 西北地质, 2013, 46(2): 186-194. |
| [47] | 高玉飞, 钟建华, 艾合买提江, 等. 塔河油田四区奥陶系裂缝特征及其成因机制研究[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(6): 1257-1267. |
| [48] | 赫俊民, 王小垚, 孙建芳, 等. 塔里木盆地塔河地区中—下奥陶统碳酸盐岩储层天然裂缝发育特征及主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(5): 1022-1030. |
| [49] | 赵向原, 胡向阳, 肖开华, 等. 川西彭州地区雷口坡组碳酸盐岩储层裂缝特征及主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(1): 30-39, 152. |
| [50] | 艾合买提江·阿不都热和曼, 钟建华, 李阳, 等. 碳酸盐岩裂缝与岩溶作用研究[J]. 地质论评, 2008, 54(4): 485-493, 578. |
| [51] | 肖阳, 刘国平, 韩春元, 等. 冀中坳陷深层碳酸盐岩储层天然裂缝发育特征与主控因素[J]. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(11): 33-42. |
| [52] | 肖玉茹, 何峰煜, 孙义梅. 古洞穴型碳酸盐岩储层特征研究: 以塔河油田奥陶系古洞穴为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2003, 24(1): 75-80, 86. |
| [53] |
商晓飞, 段太忠, 张文彪, 等. 断控岩溶主控的缝洞型碳酸盐岩内部溶蚀相带表征: 以塔河油田10区奥陶系油藏为例[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(3): 329-341.
DOI |
| [54] | 韩长城, 林承焰, 鲁新便, 等. 塔河油田奥陶系碳酸盐岩岩溶斜坡断控岩溶储层特征及形成机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(5): 644-652. |
| [55] |
闫海军, 何东博, 贾爱林, 等. 川中震旦系灯四段岩溶储集层特征与发育模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2022, 49(4): 704-715.
DOI |
| [56] | 胡文革. 塔里木盆地塔河油田潜山区古岩溶缝洞类型及其改造作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(1): 43-53. |
| [57] |
GAO Z Q, LIU Z B, GAO S L, et al. Characteristics and genetic models of Lower Ordovician carbonate reservoirs in southwest Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2016, 144: 99-112.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
王小垚, 曾联波, 魏荷花, 等. 碳酸盐岩储层缝洞储集体研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2018, 33(8): 818-832.
DOI |
| [59] | 张岳桥, 杨农, 马寅生. 太行山隆起南段新构造变形过程研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2003, 9(4): 313-329. |
| [60] | 张岳桥, 马寅生, 杨农. 太行山南缘断裂带新构造活动及其区域运动学意义[J]. 地震地质, 2003, 25(2): 169-182. |
| [61] |
YU J B, LI Z, YANG L. Fault system impact on paleokarst distribution in the Ordovician Yingshan Formation in the central Tarim Basin, northwest China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 71: 105-118.
DOI URL |
| [62] | 吴兴录. 柴达木盆地南翼山构造裂缝储层特征[J]. 特种油气藏, 2003, 10(6): 16-19, 104. |
| [63] | 周宇成, 陈清华, 孙珂, 等. 湖南地区岩溶分布特征及其发育模式[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(4): 163-173. |
| [64] | 李长海, 赵伦, 刘波, 等. 碳酸盐岩裂缝研究进展及发展趋势[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 31-48. |
| [65] | 张鹏, 侯贵廷, 潘文庆, 等. 新疆柯坪地区碳酸盐岩对构造裂缝发育的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 47(5): 831-836. |
| [66] |
ZHANG B M, LIU J J. Classification and characteristics of Karst Reservoirs in China and related theories[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2009, 36(1): 12-29.
DOI URL |
| [67] | 毛毳, 钟建华, 李阳, 等. 沉积环境对塔河油田六区奥陶系碳酸盐岩储集空间的影响[J]. 海相油气地质, 2013, 18(4): 15-22. |
| [68] |
QU H Z, LIU M Y, ZHANG Y F, et al. Paleokarstic water tables and their control on reservoirs in Ordovician Yingshan Formation, Tazhong Area, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(5): 873-883.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
ZHANG H, CAI Z X, HAO F, et al. Hydrogeomorphologic architecture of epikarst reservoirs in the Middle-Lower Ordovician, Tazhong Uplift, Tarim Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 98: 146-161.
DOI URL |
| [70] | 肖玉茹, 王敦则, 沈杉平. 新疆塔里木盆地塔河油田奥陶系古洞穴型碳酸盐岩储层特征及其受控因素[J]. 现代地质, 2003, 17(1): 92-98. |
| [71] | 李宏军, 付立新, 张津宁, 等. 黄骅拗陷奥陶系岩溶储层发育特征与控制因素[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 49(3): 417-427. |
| [72] | 王健, 庞宇晗, 操应长, 等. 塔里木盆地石灰窑露头区寒武系碳酸盐岩断控岩溶储层的形成机制及指示意义[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(5): 1-12. |
| [73] | 陈华鑫, 康志宏, 康志江. 塔河油田碳酸盐岩油藏古岩溶洞穴层状结构与形成机理[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(2): 695-708. |
| [1] | 胡力文, 邹华耀, 杨伟强, 黎霆, 邓成昆, 程忠贞, 诸丹诚, 陈星岳. 川北寒武系碳酸盐岩压溶作用的影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1221-1231. |
| [2] | 陈华鑫, 康志宏, 康志江. 塔河油田碳酸盐岩油藏古岩溶洞穴层状结构与形成机理[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 695-708. |
| [3] | 白翔宇, 马郡伟, 夏清萍, 谭先锋, 李开开. 北京西山下苇甸第三统/芙蓉统界线附近碳酸盐岩地球化学特征及古环境意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 729-741. |
| [4] | 李新华, 康志宏, 刘洁, 杨德彬, 汪彦, 陈华鑫, 贺煜. 塔河油田奥陶系岩溶塌陷体结构识别及成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1830-1843. |
| [5] | 黄莫, 李明, 杨振京, 邓丽婷. 湖南益阳奥陶系五峰组—志留系周家溪群笔石[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1343-1353. |
| [6] | 雷涵, 黄文辉, 孙启隆, 车青松. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部奥陶系马五段去白云石化成因及模式[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 378-387. |
| [7] | 徐嘉宏, 康志宏, 蓝茜茜. 塔河奥陶系油藏岩溶储层类型、洞穴结构和发育模式:以塔河油田7区T615缝洞单元为例[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1181-1192. |
| [8] | 张津宁, 周建生, 付立新, 李宏军, 楼达. 黄骅坳陷奥陶系古岩溶储层锶同位素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 821-827. |
| [9] | 刘元晴, 周乐, 李伟, 王新峰, 马雪梅, 吕琳, 邓启军, 陈晨. 山东莱芜盆地碳酸盐岩热液溶蚀特征及水文地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 199-206. |
| [10] | 杨有星, 高永进, 张君峰, 周新桂, 张金虎, 白忠凯, 韩淼. 歧口和泌阳凹陷两种类型湖相碳酸盐岩沉积特点[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(04): 831-840. |
| [11] | 杜江民, 王青春, 聂万才, 罗川又, 李政, 盛军. 白云石有序度对湖相混积碳酸盐岩储集层物性的控制作用:以柴达木盆地英西地区渐新统为例[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(03): 643-652. |
| [12] | 盛军, 杨晓菁, 李纲, 徐立, 李雅楠, 王靖茹, 张彩燕, 崔海栋. 基于多尺度X-CT成像的数字岩心技术在碳酸盐岩储层微观孔隙结构研究中的应用[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(03): 653-661. |
| [13] | 张妍, 李玉嵩, 盛奇, 潘涵香, 谢玉洁. 河南省商丘地区土壤地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(02): 305-314. |
| [14] | 王媛, 林畅松, 李浩, 孙彦达, 何海全, 王清龙, 张知源, 姬牧野. 哈萨克斯坦Marsel探区下石炭统碳酸盐岩微相特征与沉积环境[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(03): 511-526. |
| [15] | 丁熊, 吴涵, 王兴志, 唐青松, 马华灵. 四川盆地三叠系颗粒碳酸盐岩储层的成因类型[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(06): 1241-1250. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||