



现代地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (03): 911-922.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2022.025
王斌1,2( ), 任涛1, 宋伊圩2, 杨可2, 王占彬2, 孙亚柯2
), 任涛1, 宋伊圩2, 杨可2, 王占彬2, 孙亚柯2
收稿日期:2021-12-06
修回日期:2022-04-20
出版日期:2022-06-10
发布日期:2022-07-19
作者简介:王 斌,男,助理工程师,1993年出生,地质学专业,主要从事固体矿产勘查研究工作。Email: wbin01@mail.cgs.gov.cn。
基金资助:
WANG Bin1,2( ), REN Tao1, SONG Yiwei2, YANG Ke2, WANG Zhanbin2, SUN Yake2
), REN Tao1, SONG Yiwei2, YANG Ke2, WANG Zhanbin2, SUN Yake2
Received:2021-12-06
Revised:2022-04-20
Online:2022-06-10
Published:2022-07-19
摘要:
西秦岭成矿带北亚带是重要的多金属成矿单元。为缩小找矿靶区,在常家山地区开展了1:2.5万水系沉积物测量工作,对采集到的1 141件样品中的Au、Ag、As、Sb、Bi、Cu、Pb、Zn、W、Mo 10种元素进行核密度估算等数理统计分析,结果显示它们的浓度高于全国水系和区域水系沉积物的平均值,表明研究区成矿潜力大。通过因子分析得到F1(Bi、Cu、Zn)、F2(Au、As、Sb)、F3(Ag、Pb)、F4(W、Mo)4个主因子。使用浓度-面积(C-A)分形模型得到各元素和因子的异常阈值,并利用克里金插值法得到相应的地球化学空间分布图;结合区域控矿因素和异常分布特征圈定出Hz1、Hz2、Hz3 3处综合异常,前缘晕、近矿晕和尾晕显示出自西北向东南分布的趋势。水系沉积物地球化学异常分析结果表明,区内构造控矿特征明显,北西方向的礼县—闾井断裂是常家山地区有利的找矿部位。
中图分类号:
王斌, 任涛, 宋伊圩, 杨可, 王占彬, 孙亚柯. 西秦岭常家山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 911-922.
WANG Bin, REN Tao, SONG Yiwei, YANG Ke, WANG Zhanbin, SUN Yake. Geochemical Characteristics and Geological Significance of Stream Sediments in Changjiashan Region, Western Qinling Orogen[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(03): 911-922.
| 元素 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | 0.088 | 0.498 | -0.401 | 0.286 |
| Ag | 0.107 | 0.114 | 0.774 | 0.106 |
| As | 0.062 | 0.747 | 0.256 | -0.033 |
| Sb | 0.055 | 0.750 | 0.166 | -0.037 |
| Bi | 0.792 | 0.039 | 0.039 | -0.017 |
| Cu | 0.677 | 0.192 | -0.033 | 0.269 |
| Pb | 0.114 | 0.220 | 0.706 | -0.015 |
| Zn | 0.630 | -0.023 | 0.211 | -0.105 |
| W | 0.110 | 0.064 | -0.020 | 0.738 |
| Mo | -0.072 | -0.066 | 0.076 | 0.788 |
| 特征值 | 2.146 | 1.400 | 1.189 | 1.030 |
| 方差贡献率/% | 21.460 | 13.996 | 11.889 | 10.296 |
| 累计贡献率/% | 21.460 | 35.456 | 47.345 | 57.641 |
表1 常家山地区R型因子分析旋转因子载荷矩阵
Table 1 Factor loading of R-type factor analysis with orthogonal rotation in the Changjiashan region
| 元素 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | 0.088 | 0.498 | -0.401 | 0.286 |
| Ag | 0.107 | 0.114 | 0.774 | 0.106 |
| As | 0.062 | 0.747 | 0.256 | -0.033 |
| Sb | 0.055 | 0.750 | 0.166 | -0.037 |
| Bi | 0.792 | 0.039 | 0.039 | -0.017 |
| Cu | 0.677 | 0.192 | -0.033 | 0.269 |
| Pb | 0.114 | 0.220 | 0.706 | -0.015 |
| Zn | 0.630 | -0.023 | 0.211 | -0.105 |
| W | 0.110 | 0.064 | -0.020 | 0.738 |
| Mo | -0.072 | -0.066 | 0.076 | 0.788 |
| 特征值 | 2.146 | 1.400 | 1.189 | 1.030 |
| 方差贡献率/% | 21.460 | 13.996 | 11.889 | 10.296 |
| 累计贡献率/% | 21.460 | 35.456 | 47.345 | 57.641 |
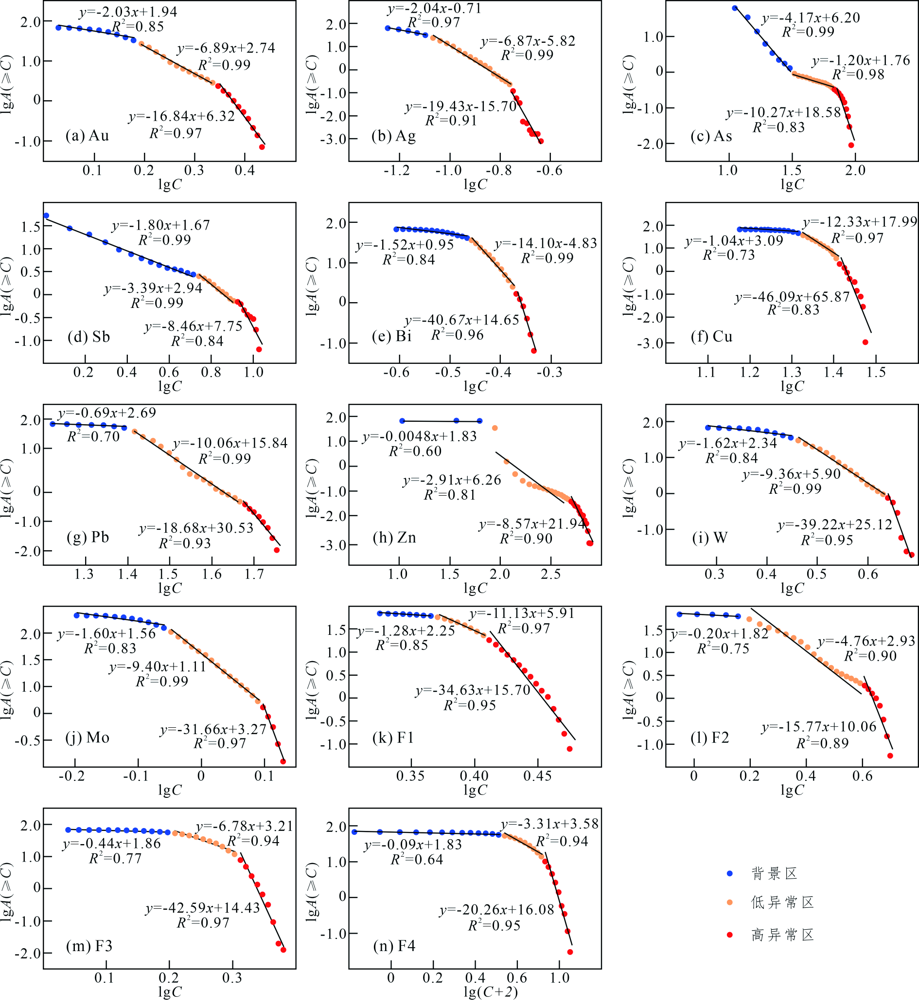
图5 常家山地区水系沉积物中不同元素和因子C-A模型双对数图
Fig.5 Double logarithm diagrams of C-A fractal model for different elements and factors of stream sediment samples from the Changjiashan region
| 元素 | 低异常值拐点 | 高异常值拐点 |
|---|---|---|
| Au | 1.56 | 2.22 |
| Ag | 0.085 | 0.172 |
| As | 30.31 | 65.78 |
| Sb | 5.19 | 8.08 |
| Bi | 0.35 | 0.43 |
| Cu | 21.1 | 26.0 |
| Pb | 26.1 | 47.6 |
| Zn | 88.9 | 479.3 |
| W | 2.90 | 4.27 |
| Mo | 0.90 | 1.23 |
| F1 | 2.35 | 2.58 |
| F2 | 1.58 | 3.91 |
| F3 | 1.62 | 2.01 |
| F4 | 1.46 | 3.39 |
表2 常家山地区水系沉积物中各元素和因子的C-A分形特征
Table 2 C-A fractal characteristics of the multi-element and factors for stream sediment samples from the Changjiashan region
| 元素 | 低异常值拐点 | 高异常值拐点 |
|---|---|---|
| Au | 1.56 | 2.22 |
| Ag | 0.085 | 0.172 |
| As | 30.31 | 65.78 |
| Sb | 5.19 | 8.08 |
| Bi | 0.35 | 0.43 |
| Cu | 21.1 | 26.0 |
| Pb | 26.1 | 47.6 |
| Zn | 88.9 | 479.3 |
| W | 2.90 | 4.27 |
| Mo | 0.90 | 1.23 |
| F1 | 2.35 | 2.58 |
| F2 | 1.58 | 3.91 |
| F3 | 1.62 | 2.01 |
| F4 | 1.46 | 3.39 |
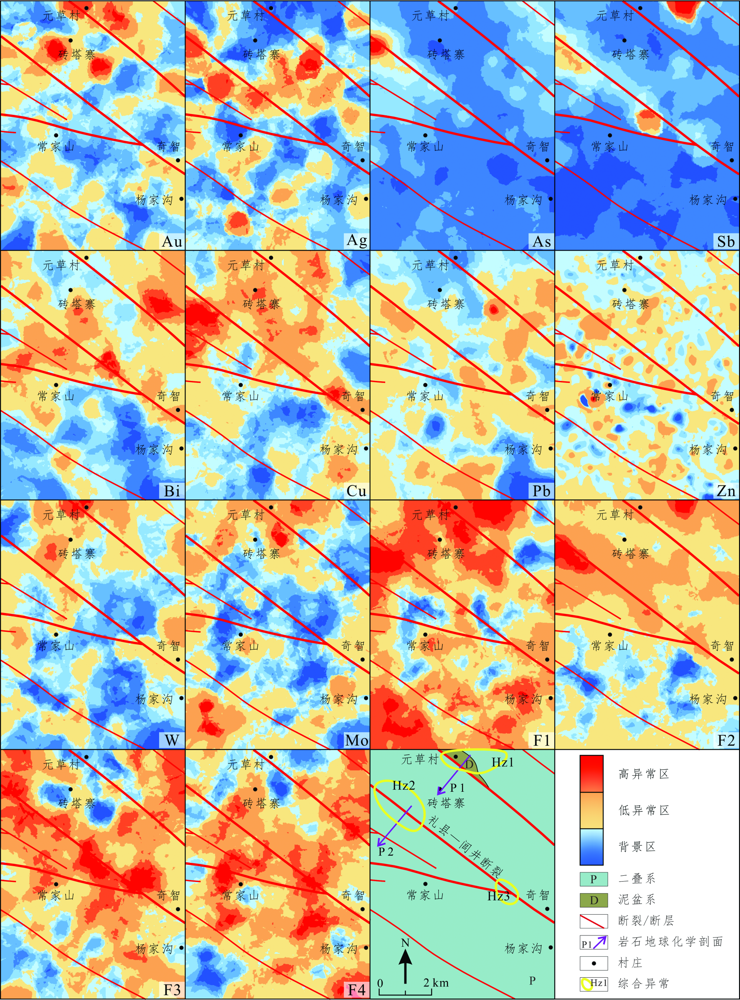
图6 常家山地区水系沉积物中不同元素和因子的地球化学空间分布和异常圈定
Fig.6 Spatial distribution maps of geochemical and anomaly delineation for different elements and factors of stream sediment samples from the Changjiashan region
| [1] |
LIU J J, DAI H Z, ZHAI D G, et al. Geological and geochemical characteristics and formation mechanisms of the Zhaishang Carlin-like type gold deposit, western Qinling Mountains, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 64: 273-298.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
XU L Y, YIN Y T, JIN S, et al. CSAMT constraints on the metallogenic mechanism of the Zhaishang gold deposit, West Qinling, China[J/OL]. Exploration Geophysics, 2021: 1-13. DOI: 10.1080/08123985.2021.1975496.
DOI |
| [3] | 司静, 俞胜, 张淼, 等. 锁龙金矿成矿地质特征及找矿方向[J]. 甘肃地质, 2014, 23(1): 41-46. |
| [4] | 郭娜, 刘翠, 崔龙, 等. 西秦岭岷礼成矿带马坞金矿致矿火成岩组合与成矿地质背景[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(6): 1261-1276. |
| [5] |
FENG J Z, WANG D B, WANG X M, et al. Magmatic gold mi-neralization in the western Qinling Orogenic Belt: Geology and metallogenesis of the Baguamiao, Liba and Xiaogouli gold deposits[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2004, 78(2): 529-533.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ZENG Q T, MCCUAIG T C, HART C J R, et al. Structural and geochronological studies on the Liba goldfield of the west Qinling Orogen, Central China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2012, 47: 799-819.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 柯昌辉, 王晓霞, 杨阳, 等. 西秦岭地区脉岩成因与金矿关系——来自李坝金矿年代学、地球化学及Nd-Hf-S同位素的约束[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(1): 42-62. |
| [8] | 谭洪波. 甘肃金山、马泉金矿成因类型及其对比研究[J]. 西北地质, 2009, 42(4): 1-10. |
| [9] | 高永伟. 甘肃耳阳沟铅锌矿地质特征及找矿标志[J]. 甘肃地质, 2013, 22(4): 58-62. |
| [10] | 崔峤. 甘肃内生锡矿地质特征及找矿[J]. 西北地质, 1984(4): 35-43. |
| [11] | GOLDFARB R J, QIU K F, DENG J, et al. Orogenic gold deposits of China[J]. Society of Economic Geologists Special Publications, 2019, 22: 263-324. |
| [12] |
CHENG Q M. Mapping singularities with stream sediment geochemical data for prediction of undiscovered mineral deposits in Gejiu, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2007, 32: 314-324.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
YILMAZ H, SONMEZ F N, CARRANZA E J M. Discovery of Au-Ag mineralization by stream sediment and soil geochemical exploration in metamorphic terrain in western Turkey[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 158: 55-73.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
AFZAL P, MIRZAEI M, YOUSEFI M, et al. Delineation of geochemical anomalies based on stream sediment data utilizing fractal modeling and staged factor analysis[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2016, 119: 139-149.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 张七道, 肖长源, 李致伟, 等. 黔北普宜地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及成矿预测[J]. 地质与勘探, 2021, 57(5): 1040-1052. |
| [16] | 曾凯, 刘海, 黄德将, 等. 云南勐翁地区1∶5万水系沉积物测量异常特征及找矿效果分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(1): 270-280. |
| [17] | 李超, 罗先熔, 邱炜, 等. 青海省都兰县金水口地区水系沉积物地球化学异常特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(5): 1397-1410. |
| [18] | 郑卫军, 刘新会, 陈彩华. 甘肃寨上金矿床1∶5万水系沉积物测量综合评价[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2012, 20(4): 43-48. |
| [19] | 陈彩华, 孙斌, 陈翼, 等. 西秦岭中寨—十里铺地区水系沉积物测量找矿效果[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2017, 25(4): 1-9. |
| [20] | 刘伟. 西秦岭地区金矿床地球化学找矿模型[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018: 1-63. |
| [21] | 马承, 宋伊圩, 孙彪, 等. 西秦岭岷礼成矿带地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2021, 29(4): 489-499. |
| [22] |
MENG Q R, ZHANG G W. Geologic framework and tectonic evolution of the Qinling Orogen, central China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 323: 183-196.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
DONG Y P, ZHANG G W, NEUBAUER F, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling Orogen, China: Review and synthesis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41: 213-237.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
CHEN Y J, SANTOSH M. Triassic tectonics and mineral systems in the Qinling Orogen, Central China[J]. Geological Journal, 2014, 49: 338-358.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 肖力, 赵玉锁, 张文钊, 等. 西秦岭成矿带中东段金(铅锌)多金属矿成矿规律及资源潜力评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009: 4-10. |
| [26] | 陈衍景, 张静, 张复新, 等. 西秦岭地区卡林-类卡林型金矿床及其成矿时间、构造背景和模式[J]. 地质论评, 2004, 50(2): 134-148. |
| [27] |
刘家军, 刘冲昊, 王建平, 等. 西秦岭地区金矿类型及其成矿作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(5): 1-13.
DOI |
| [28] | 张斌, 刘家军. 西秦岭寨上金矿床构造控矿特征与成矿规律[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2020, 28(6): 825-836. |
| [29] | 张翔, 戴霜, 刘建宏, 等. 甘肃西秦岭金矿成矿与找矿研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017: 7-26. |
| [30] | 杜子国, 吴淦国. 西秦岭地区构造体系及金成矿构造动力学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998: 6-9. |
| [31] | 冯益民, 曹宣铎, 张二朋, 等. 西秦岭造山带的演化、构造格局和性质[J]. 西北地质, 2003, 36(1): 1-8. |
| [32] | 张国伟, 郭安林, 姚安平. 中国大陆构造中的西秦岭—松潘大陆构造结[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(3): 23-32. |
| [33] | 甘肃省地质矿产局. 中华人民共和国地质矿产部地质专报:区域地质19甘肃省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1989: 5-320. |
| [34] |
GAO S S, ZHONG Y M. Random weighting estimation of kernel density[J]. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 2010, 140: 2403-2407.
DOI URL |
| [35] | WANG S P, LI A, WEN K Y, et al. Robust kernels for kernel density estimation[J]. Economics Letters, 2020, 191: 1-5. |
| [36] | 蔡泽圆, 鲁宝亮, 熊盛青, 等. 基于自适应核密度的贝叶斯概率模型岩性识别方法研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(4): 919-927. |
| [37] |
宋鹰, 张俊霞, STEPASHKO A, 等. 基于核密度估计的碎屑颗粒年龄分析及应用:松辽盆地构造事件定年[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(4): 265-276.
DOI |
| [38] | BOTEV Z I, GROTOWSKI J F, KROESE D P, et al. Kernel density estimation via diffusion[J]. The Annals of Statistics, 2010, 38(5): 2916-2957. |
| [39] | VERMEESCH P. On the visualization of detrital age distributions[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 312: 190-194. |
| [40] | 刘建宏, 张新虎, 牛洪斌. 甘肃省区域地球化学场特征[J]. 甘肃地质, 2015, 24(4): 1-15. |
| [41] | 史长义, 梁萌, 冯斌. 中国水系沉积物39种元素系列背景值[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(2): 234-251. |
| [42] |
REIMANN C, FILZMOSER P, GARRETT R G. Factor analysis applied to regional geochemical data: problems and possibilities[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2002, 17: 185-206.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
TREIBLMAIER H, FILZMOSER P. Exploratory factor analysis revisited: How robust methods support the detection of hidden multivariate data structures in IS research[J]. Information & Management, 2010, 47: 197-207.
DOI URL |
| [44] | 李彦伟, 罗先熔, 黄学强, 等. 因子分析在青海尕大阪矿区找矿中的应用[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2012, 27(3): 361-365. |
| [45] | 刘如英, 李同军, 童霆. 区域化探中应用因子分析方法的探讨[J]. 物探与化探, 1988, 12(3): 182-192. |
| [46] | 余金生, 李裕伟. 地质因子分析[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1985: 1-194. |
| [47] | 刘家军, 毛光剑, 吴胜华, 等. 甘肃寨上金矿床成矿特征与形成机理[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(1): 85-98. |
| [48] |
CHENG Q M, AGTERBERG F P, BALLANTYNE S B. The separation of geochemical anomalies from background by fractal methods[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1994, 51: 109-130.
DOI URL |
| [49] | 於崇文. 矿床在混沌边缘分形生长(上卷)[M]. 合肥: 安徽教育出版社, 2006: 15-88. |
| [50] | 成秋明. 非线性成矿预测理论:多重分形奇异性-广义自相似性-分形谱系模型与方法[J]. 地球科学, 2006, 31(3): 337-348. |
| [51] | 成秋明. 成矿过程奇异性与矿床多重分形分布[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2008, 27(3): 298-205. |
| [52] |
CHENG Q M, ZHAO P D. Singularity theories and methods for characterizing mineralization processes and mapping geo-anomalies for mineral deposit prediction[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2011, 2(1): 67-79.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
ZUO R G, CARRANZA E J, WANG J. Spatial analysis and visualization of exploration geochemical data[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2016, 158: 9-18.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
ZUO R G. Selection of an elemental association related to mineralization using spatial analysis[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 184: 150-157.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
AFZAL P, ALGHALANDIS Y F, MOAREFVAND P, et al. Application of power-spectrum-volume fractal method for detecting hypogene, supergene enrichment, leached and barren zones in Kahang Cu porphyry deposit, Central Iran[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 112: 131-138.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
LIU Y, ZHOU K F, CHENG Q M. A new method for geochemical anomaly separation based on the distribution patterns of singularity indices[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2017, 105: 139-147.
DOI URL |
| [57] | LIU Y, CHENG Q M, ZHOU K F. New insights into element distribution patterns in geochemistry: A perspective from fractal density[J]. Natural Resources Research, 2019, 28: 5-29. |
| [58] | 向中林, 顾雪祥, 王恩营, 等. 多重分形模式下多元素综合地球化学异常的提取[J]. 矿物学报, 2019, 39(2): 183-191. |
| [59] |
朱平平, 成秋明, 周远志, 等. 基于分形理论的板块形态重建[J]. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(4): 150-157.
DOI |
| [60] | 刘家军, 毛光剑, 吴胜华, 等. 甘肃寨上金矿床成矿特征与形成机理[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(1): 85-100. |
| [61] | 郑卫军, 刘新会, 陈彩华, 等. 甘肃岷县寨上金钨矿床中钨矿特征及找矿标志[J]. 西北地质, 2010, 43(3): 85-92. |
| [62] | 杨瀚文, 王建中, 魏立勇, 等. 甘肃寨上超大型坞、金(锑)多金属矿床成因研究[J]. 西北地质, 2021, 54(1): 125-138. |
| [63] | 徐东, 刘建宏, 赵彦庆. 甘肃西秦岭地区金矿控矿因素及找矿方向[J]. 西北地质, 2014, 47(3): 83-90. |
| [64] | 陈毓川. 中国成矿体系与区域成矿评价(下卷)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 877-907. |
| [65] |
曾庆栋, 底青云, 薛国强, 等. 成矿模式与找矿模式研究的现代科学技术[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(3): 295-308.
DOI |
| [66] | 王伟峰, 赵天心, 宫元吉, 等. 甘肃省岷县寨上金矿床成矿规律与找矿方向研究[J]. 矿床地质, 2008, 27(增): 199-208. |
| [67] | 刘崇民. 金属矿产原生晕研究进展[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(10): 1528-1537. |
| [68] | SAIJAD T H, OMID A, HOOSHANG A H. Multivariate anomaly modeling of primary geochemical halos by U-spatial statistic algorithm development: A case study from the Sari Gunay epithermal gold deposit, Iran[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 127: 1-23. |
| [69] | ZHENG C J, LUO X R, WEN M L, et al. Axial primary halo characterization and deep orebody prediction in the Ashele cooper-zinc deposit, Xinjiang, NW China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 213: 1-16. |
| [70] | 王斌, 宋伊圩, 孙彪, 等. 甘肃寨上金矿南矿带构造叠加晕实用模型及深部找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(6): 1504-1514. |
| [71] | 路彦明, 李汉光, 陈勇敢, 等. 西秦岭寨上金矿床中石英和绢云母40Ar/39Ar定年[J]. 矿床地质, 2006, 25(5): 590-597. |
| [72] | 余超. 西秦岭寨上金矿床成矿特征与非线性成矿动力学研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015: 1-65. |
| [73] | 刘纲, 喻万强, 王晓军. 甘肃省岷县寨上大型金矿床构造控矿规律及成矿预测[J]. 矿床地质, 2008, 27(增): 15-22. |
| [74] | 刘新会, 张永文, 刘民武. 西秦岭寨上特大型金矿金的赋存状态研究[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2010, 18(5): 16-19. |
| [75] | 喻万强. 西秦岭寨上金矿床成矿作用空间结构[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015: 1-121. |
| [76] | 温志亮. 西秦岭教场坝岩体岩浆混合成因的新认识[J]. 矿物岩石, 2008, 28(3): 29-36. |
| [77] | 刘巍, 郭丽爽, 廖延福. 西秦岭中生代花岗岩锆石U-Pb-Lu-Hf同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(3): 436-448. |
| [78] |
LANG M D, CHENG Z G, ZHANG Z C, et al. Hisingerite in trachydacite from Tarim: Implications for voluminous felsic rocks in transitional large igneous province[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2020, 31(5): 875-883.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [2] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [3] | 梁东, 华北, 赵德怀, 吴浩, 万生楠, 谭朝欣, 赵晓健, 杨志鹏. 喀喇昆仑麦拉山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征与找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 708-721. |
| [4] | 娄元林, 成明, 唐侥, 张潮明, 蓝景周, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征、构造环境分析及成矿响应[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| [5] | 邓科, 王金贵, 董玉杰, 何林武, 袁仁华, 张泽国, 陈守关, 辛堂. 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世中性侵入岩的成因及对新特提斯板块北向俯冲的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 375-389. |
| [6] | 夏锦胜, 孙莉, 张鹏, 陈昌阔, 汪君珠, 司江福. 四川坪河晶质石墨矿床地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1486-1496. |
| [7] | 陈世明, 杨镇熙, 雷自强, 康维良, 张晶, 赵青虎. 甘肃北山前红泉地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1513-1524. |
| [8] | 刘同, 刘传朋, 康鹏宇, 赵秀芳, 邓俊, 王凯凯. 山东省沂南县东部土壤重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1173-1182. |
| [9] | 刘洋, 李贤庆, 赵光杰, 刘满仓, 董才源, 李谨, 肖中尧. 库车坳陷东部吐格尔明地区天然气地球化学特征及油气充注史[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 988-997. |
| [10] | 刘阳, 姜冰, 张海瑞, 孙增兵, 王松涛. 山东省青州市表层土壤硒元素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 933-940. |
| [11] | 王美华. 浙西典型石煤矿山周边耕地富硒土壤地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 941-952. |
| [12] | 朱必清, 陈世加, 白艳军, 雷俊杰, 尹相东. 鄂尔多斯盆地甘泉地区延长组长8段原油地球化学特征及来源[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 742-754. |
| [13] | 高银虎, 尹刚, 龚泽强, 郭明春. 甘肃两当湘潭子金矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1523-1535. |
| [14] | 任廷仙, 李小伟, 王可, 葛涵云, 关瑞. 西秦岭碌础坝石英闪长岩-花岗闪长岩的地球化学、矿物学研究及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1651-1676. |
| [15] | 严镜, 刘景显, 蒲万峰, 魏学平, 李智斌. 西秦岭中—晚三叠世构造属性:来自将其那梁侵入杂岩体的年代学及地球化学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1677-1690. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||