



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (04): 892-909.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.091
董博1( ), 曹代勇1,2(
), 曹代勇1,2( ), 魏迎春1,2(
), 魏迎春1,2( ), 王安民1, 李新1, 张昀1
), 王安民1, 李新1, 张昀1
出版日期:2024-08-10
发布日期:2024-10-16
通信作者:
曹代勇,男,教授,博士生导师,1955年出生,主要从事盆地构造和矿产地质研究。Email:cdy@cumtb.edu.cn。作者简介:董 博,男,博士研究生,1994年出生,主要从事煤与煤系矿产地质研究。Email:705107217@qq.com。
基金资助:
DONG Bo1( ), CAO Daiyong1,2(
), CAO Daiyong1,2( ), WEI Yingchun1,2(
), WEI Yingchun1,2( ), WANG Anmin1, LI Xin1, ZHANG Yun1
), WANG Anmin1, LI Xin1, ZHANG Yun1
Published:2024-08-10
Online:2024-10-16
摘要:
煤作为对温度、压力等地质环境条件极敏感的有机岩,地质历史演化过程中各种构造-热事件必然导致煤发生一系列物理、化学、结构和构造变化,物理模拟实验则是揭示煤变质作用机理的重要手段。本文基于煤变质热模拟实验、高温高压模拟实验方面的研究成果,着重对煤变质作用机理、演化进程及煤变质作用模拟实验的应用和发展趋势进行阐述。煤变质作用包含煤化作用和石墨化作用两个阶段,体现为多尺度、多阶段的物理化学结构演化,基本特征趋向于分子结构有序化和化学成分单一化。温度是煤变质的主导因素,而力的作用方式同样约束着煤变质作用。热模拟实验基于“时间-温度补偿原理”,采用开放、半开放和封闭等不同实验体系,模拟不同温压条件和构造-热环境下的热解过程。高温高压模拟实验基于相似性原理,在热模拟基础上加入压力变量,模拟不同温压条件和应力-应变环境,以全面模拟煤在各种构造物理化学条件下所发生的物理化学变化,探究不同温压耦合条件下煤变质作用机理、影响因素与演化途径。煤变质的热模拟及高温高压模拟实验在油气生成、煤储层评价、煤成石墨化及煤中战略性金属元素迁移等多个领域得到广泛应用,今后将朝多学科交叉融合和多场耦合模拟实验方向发展,以期更精确地模拟地层构造作用下的复杂地质条件,为深入探究煤变质作用的构造物理化学机理提供更有效的技术手段。
中图分类号:
董博, 曹代勇, 魏迎春, 王安民, 李新, 张昀. 煤变质作用的构造物理化学机理实验研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 892-909.
DONG Bo, CAO Daiyong, WEI Yingchun, WANG Anmin, LI Xin, ZHANG Yun. Advancements in Experimental Studies on the Tectonic Physical-chemical Mechanisms of Coal Metamorphism[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(04): 892-909.
| 实验组别 | 温度(℃) | 时间(min) | Ro值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 第1组 | 100 | 300000 | 0.25 |
| 第2组 | 150 | 1500 | 0.25 |
| 第3组 | 200 | 60 | 0.25 |
表1 不同加热温度和加热时间下的Ro值[42]
Table 1 Vitrinite reflectance at different heating temperatures and heating times[42]
| 实验组别 | 温度(℃) | 时间(min) | Ro值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 第1组 | 100 | 300000 | 0.25 |
| 第2组 | 150 | 1500 | 0.25 |
| 第3组 | 200 | 60 | 0.25 |
| 实验者 | 实验 年份 | 实验样品 | 实验性质 | 模拟设备 | 实验条件 | 实验成果 | 资料来源 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 温度(℃) | 压力 | |||||||||||||||
| Solomon等 | 1978 | 褐煤、 烟煤 | 热解实验 | 带加热格栅的自 动脱挥发分装置 | 300~1000 | — | 煤热解过程中氮的演化机制研究 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| Burnham等 | 1987 | 油页岩 | 热解实验 | Rock-Eval 热解仪 | 300~600 | — | 温度对生烃速率的影响及建立有机质演化动力学模型 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| Nelson等 | 1991 | 烟煤、 次烟煤 | 热解实验 | 流化床反应器 | 500~1000 | — | 温度对煤热解中燃料氮向氮氧化物前驱体转化的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| Zajusz- Zubek等 | 2003 | 焦煤 | 热解实验 | 马弗炉 | 400~1000 | — | 煤热解过程中微量元素的释放动力学机制研究 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| Behar等 | 2003 | 褐煤 | 热解实验 | Rock-Eval 热解仪 | 200~600 | — | 比较有水和无水条件下热解实验对褐煤产物组成和产率的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 侯读杰等 | 1990 | 油页岩 | 热模拟 实验 | 有机岩热解仪 | 200~550 | 模拟高压环境 | 热演化程度对轻烃分布模式的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 赵炜等 | 2002 | 褐煤、 烟煤 | 热解实验 | 石英玻璃反应器 | 600~900 | — | 温度对不同煤级煤热解生成氮化物的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 王锦平等 | 2002 | 烟煤 | 热解实验 | 马弗炉 | 400~1150 | — | 温度对煤中氯释放与析出的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 王云鹤等 | 2002 | 动力煤 | 热解实验 | 管式炉 | 600~800 | — | 热解条件对煤中重金属元素分布迁移规律的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 段钰锋等 | 2010 | 烟煤 | 热解实验 | 管式炉 | 200~800 | — | 温度对煤热解过程中汞析出-吸附特性影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 马中良等 | 2012 | 灰色泥岩 | 生排烃热 模拟实验 | 地层孔隙热 压模拟仪 | 275~500 | 模拟静岩压力、 地层流体压力 | 对比有限空间和常规高压釜模拟实验对生排烃的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 魏晓飞等 | 2012 | 高砷、锑煤 | 热解实验 | 箱式电阻炉 | 300~1200 | — | 温度、赋存状态等对煤热解过程中微量元素挥发性影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 杨建业 | 2013 | — | 流化床热 解实验 | — | 500~900 | — | 煤微量元素在不同温度下热解的迁移规律 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 实验者 | 实验 年份 | 实验样品 | 实验性质 | 模拟设备 | 实验条件 | 实验成果 | 资料来源 | |||||||||
| 温度(℃) | 压力 | |||||||||||||||
| 魏琴 | 2018 | 褐煤 | 生排烃热 模拟实验 | DK-II型地层 孔隙热压模拟仪 | 250~375 | 模拟地层压力、 静岩压力 | 煤岩热演化产物在不同温压下变化规律和地球化学特征 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 刘宁宁 | 2022 | 烟煤 | 热模拟 实验 | HXTPWR-II 型成岩成烃温 压模拟实验仪 | 200~500 | — | 温度对煤中微量元素的赋存特征和含量变化的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 陈磊等 | 2022 | 泥灰岩 | 生烃热模 拟实验 | 地层孔隙热压模 拟仪/高压釜 | 250~550 | 模拟地层压力、 静岩压力 | 不同热模拟方式对烃气碳同位素演变特征的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| Zhao等 | 2022 | 中阶烟煤镜 惰分离样品 | 热模拟 实验 | 原位FTIR 光谱/原位XRD | 30~500 30~1100 | — | 基于原位FTIR和XRD研究镜质组和惰质组热解过程中分子结构演化差异 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| Qin等 | 2022 | 低阶褐煤镜 惰分离样品 | 热模拟 实验 | 开放体系 实验装置 | 320~600 | 大气压环境 | 煤镜质组与惰质组分子结构演化差异的热模拟实验研究 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| Chen等 | 2022 | 贫煤 | 高温热模 拟实验 | NTG-SML-60W 一体化石墨化炉 | 2100~3000 | — | 添加二氧化硅矿物的高温热模拟实验对煤结构演化的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 张旭等 | 2023 | 腐殖煤 | 生烃热模 拟实验 | 高压釜 | 350~600 | 模拟地层压力、 静岩压力 | 不同阶段有机质生烃对热解煤有机孔隙发育的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| Liu等 | 2023 | 中-高阶烟煤 镜惰分离样品 | 高温热模 拟实验 | NTG-SML-60W 一体化石墨化炉 | 1800~3000 | — | 镜质组和惰质组石墨化演化特征及差异的高温热模拟实验研究 | 文献[ | ||||||||
表2 国内外煤热模拟实验成果一览
Table 2 Coal thermal simulation experiments at home and abroad
| 实验者 | 实验 年份 | 实验样品 | 实验性质 | 模拟设备 | 实验条件 | 实验成果 | 资料来源 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 温度(℃) | 压力 | |||||||||||||||
| Solomon等 | 1978 | 褐煤、 烟煤 | 热解实验 | 带加热格栅的自 动脱挥发分装置 | 300~1000 | — | 煤热解过程中氮的演化机制研究 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| Burnham等 | 1987 | 油页岩 | 热解实验 | Rock-Eval 热解仪 | 300~600 | — | 温度对生烃速率的影响及建立有机质演化动力学模型 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| Nelson等 | 1991 | 烟煤、 次烟煤 | 热解实验 | 流化床反应器 | 500~1000 | — | 温度对煤热解中燃料氮向氮氧化物前驱体转化的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| Zajusz- Zubek等 | 2003 | 焦煤 | 热解实验 | 马弗炉 | 400~1000 | — | 煤热解过程中微量元素的释放动力学机制研究 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| Behar等 | 2003 | 褐煤 | 热解实验 | Rock-Eval 热解仪 | 200~600 | — | 比较有水和无水条件下热解实验对褐煤产物组成和产率的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 侯读杰等 | 1990 | 油页岩 | 热模拟 实验 | 有机岩热解仪 | 200~550 | 模拟高压环境 | 热演化程度对轻烃分布模式的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 赵炜等 | 2002 | 褐煤、 烟煤 | 热解实验 | 石英玻璃反应器 | 600~900 | — | 温度对不同煤级煤热解生成氮化物的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 王锦平等 | 2002 | 烟煤 | 热解实验 | 马弗炉 | 400~1150 | — | 温度对煤中氯释放与析出的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 王云鹤等 | 2002 | 动力煤 | 热解实验 | 管式炉 | 600~800 | — | 热解条件对煤中重金属元素分布迁移规律的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 段钰锋等 | 2010 | 烟煤 | 热解实验 | 管式炉 | 200~800 | — | 温度对煤热解过程中汞析出-吸附特性影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 马中良等 | 2012 | 灰色泥岩 | 生排烃热 模拟实验 | 地层孔隙热 压模拟仪 | 275~500 | 模拟静岩压力、 地层流体压力 | 对比有限空间和常规高压釜模拟实验对生排烃的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 魏晓飞等 | 2012 | 高砷、锑煤 | 热解实验 | 箱式电阻炉 | 300~1200 | — | 温度、赋存状态等对煤热解过程中微量元素挥发性影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 杨建业 | 2013 | — | 流化床热 解实验 | — | 500~900 | — | 煤微量元素在不同温度下热解的迁移规律 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 实验者 | 实验 年份 | 实验样品 | 实验性质 | 模拟设备 | 实验条件 | 实验成果 | 资料来源 | |||||||||
| 温度(℃) | 压力 | |||||||||||||||
| 魏琴 | 2018 | 褐煤 | 生排烃热 模拟实验 | DK-II型地层 孔隙热压模拟仪 | 250~375 | 模拟地层压力、 静岩压力 | 煤岩热演化产物在不同温压下变化规律和地球化学特征 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 刘宁宁 | 2022 | 烟煤 | 热模拟 实验 | HXTPWR-II 型成岩成烃温 压模拟实验仪 | 200~500 | — | 温度对煤中微量元素的赋存特征和含量变化的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 陈磊等 | 2022 | 泥灰岩 | 生烃热模 拟实验 | 地层孔隙热压模 拟仪/高压釜 | 250~550 | 模拟地层压力、 静岩压力 | 不同热模拟方式对烃气碳同位素演变特征的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| Zhao等 | 2022 | 中阶烟煤镜 惰分离样品 | 热模拟 实验 | 原位FTIR 光谱/原位XRD | 30~500 30~1100 | — | 基于原位FTIR和XRD研究镜质组和惰质组热解过程中分子结构演化差异 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| Qin等 | 2022 | 低阶褐煤镜 惰分离样品 | 热模拟 实验 | 开放体系 实验装置 | 320~600 | 大气压环境 | 煤镜质组与惰质组分子结构演化差异的热模拟实验研究 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| Chen等 | 2022 | 贫煤 | 高温热模 拟实验 | NTG-SML-60W 一体化石墨化炉 | 2100~3000 | — | 添加二氧化硅矿物的高温热模拟实验对煤结构演化的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 张旭等 | 2023 | 腐殖煤 | 生烃热模 拟实验 | 高压釜 | 350~600 | 模拟地层压力、 静岩压力 | 不同阶段有机质生烃对热解煤有机孔隙发育的影响 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| Liu等 | 2023 | 中-高阶烟煤 镜惰分离样品 | 高温热模 拟实验 | NTG-SML-60W 一体化石墨化炉 | 1800~3000 | — | 镜质组和惰质组石墨化演化特征及差异的高温热模拟实验研究 | 文献[ | ||||||||
| 实验者 | 实验 年份 | 实验 样品 | 实验 性质 | 实验条件 | 实验成果 | 资料来源 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 温度 (℃) | 围压 (MPa) | 应变量 (%) | 应变速率 (s-1) | |||||||||||||
| Bustin等 | 1986 | 无烟煤 | 高温高压变形实验 | 350~500 | 500~800 | 5~33 | 10-5 | 高温高压差异应力对Ro的影响 | 文献[76] | |||||||
| 1995 | 高级无烟煤 | 高温高压变形实验 | 400~900 | 800~1000 | 5~50 | 10-5~10-6 | 高温下共轴应力、剪应力对煤石墨化影响 | 文献[29] | ||||||||
| Ross等 | 1990 | 高级无烟煤 | 高温高压变形实验 | 300~600 | 500 | 5~33 | 10-4~10-6 | 应变能在石墨化进程中的作用 | 文献[77] | |||||||
| Mastalerz等 | 1993 | 低级烟煤、 高级无烟煤 | 静水压力共轴变形实验 | 400~800 250~600 | 200~500 | 0~50 | 10-4~10-6 | 静水压力对产气影响;共轴变形条件对Ro影响 | 文献[78] | |||||||
| Wilks等 | 1993 | 高级无烟煤 | 高温高压简单剪切变形实验 | 600~900 | 600~1000 | 0~49 | 10-5~10-6 | 高温下剪切应力在石墨化中的作用及对Ro的影响 | 文献[79] | |||||||
| Torre等 | 1997 | 褐煤 | 高压实验 | 200~350 | 50~2000 | — | — | 压力对Ro的影响 | 文献[80] | |||||||
| 周建勋等 | 1994 | 中级烟煤、 中高级无烟煤 | 变形实验 | 50~200 | 30~75 | 9 | 0.5×10-5~ 4×10-6 | 变形等对Ro等的影响 | 文献[81] | |||||||
| 姜波等 | 1998 | 中级烟煤- 高级无烟煤 | 变形实验 | 200~700 | 250~650 | 5~33 | 10-4~10-6 | 变形对Ro、微观结构和化学结构的影响 | 文献[82] | |||||||
| 金法礼等 | 1999 | 中级烟煤、 无烟煤 | 变形实验 | 200~700 | 250~650 | 5~33 | 10-5~10-6 | 不同温压条件对不同煤级煤变形行为的影响 | 文献[83] | |||||||
| 刘俊来等 | 2005 | 中级烟煤、 低级无烟煤 | 变形实验 | 200~500 | 200~500 | 10 | 5×10-6 | 不同温压条件下煤的强度变化 | 文献[84] | |||||||
| 刘高峰等 | 2011 | 褐煤-无烟煤 | 高温高压吸附实验 | 30~50 | 0~18 | — | — | 高温高压三相介质条件对煤吸附瓦斯的影响 | 文献[85] | |||||||
| 侯泉林等 | 2014 | 中-高煤 级无烟煤 | 次高温变 形实验 | 70~100 | 0~30 | — | — | 煤变形对化学结构、产生甲烷的影响 | 文献[86] | |||||||
| 于立业等 | 2015 | 无烟煤 | 变温变压 流变实验 | 300~400 | 70~90 | — | 10-4~10-7 | 温压条件和应变速率对无烟煤流变特征与机制的影响 | 文献[87] | |||||||
| 实验者 | 实验 年份 | 实验 样品 | 实验 性质 | 实验条件 | 实验成果 | 资料来源 | ||||||||||
| 温度 (℃) | 围压 (MPa) | 应变量 (%) | 应变速率 (s-1) | |||||||||||||
| 肖藏岩 | 2016 | 褐煤、气煤 | 应力-应变实验 | 50~250 | 30 | — | — | 不同温压对煤分子结构演化特征及产气情况的影响 | 文献[88] | |||||||
| 刘杰刚 | 2018 | 烟煤 | 高温高压变形实验 | 30~400 | 8~90 | 15~50 | 10-3~10-6 | 不同温压对煤的微观变形特征、演化机理和地质控制作用的影响 | 文献[89] | |||||||
| 刘和武 | 2020 | 烟煤 | 高温高压 变形实验 | 100~300 | 50~100 | 5~25 | 10-4~10-7 | 不同温压条件对构造煤脆-韧性变形机理及分子结构演化的影响 | 文献[90] | |||||||
| 刘志飞 | 2021 | 中-高阶烟煤、无烟煤镜惰分离样品 | 高温高压 模拟实验 | 600~1200 | 1000~2000 | — | — | 高温高压对不同煤岩组分在石墨化阶段结构演化的影响作用 | 文献[91] | |||||||
| Liu等 | 2023 | 高阶烟煤富惰质组分离样品 | 高温高压 模拟实验 | 600~1200 | 1000~2000 | — | — | 温压协同配合及力对惰质组单一组分石墨化进程的影响作用 | 文献[92] | |||||||
| 陈高健等 | 2024 | 中级烟煤 | 高温高压 模拟实验 | 600~1200 | 1500~2000 | — | — | 对比高温条件与高温高压条件下二氧化硅矿物对煤结构演化的影响 | 文献[93] | |||||||
表3 国内外煤高温高压模拟实验成果一览
Table 3 Domestic and foreign coal high temperature and high pressure simulation experiments
| 实验者 | 实验 年份 | 实验 样品 | 实验 性质 | 实验条件 | 实验成果 | 资料来源 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 温度 (℃) | 围压 (MPa) | 应变量 (%) | 应变速率 (s-1) | |||||||||||||
| Bustin等 | 1986 | 无烟煤 | 高温高压变形实验 | 350~500 | 500~800 | 5~33 | 10-5 | 高温高压差异应力对Ro的影响 | 文献[76] | |||||||
| 1995 | 高级无烟煤 | 高温高压变形实验 | 400~900 | 800~1000 | 5~50 | 10-5~10-6 | 高温下共轴应力、剪应力对煤石墨化影响 | 文献[29] | ||||||||
| Ross等 | 1990 | 高级无烟煤 | 高温高压变形实验 | 300~600 | 500 | 5~33 | 10-4~10-6 | 应变能在石墨化进程中的作用 | 文献[77] | |||||||
| Mastalerz等 | 1993 | 低级烟煤、 高级无烟煤 | 静水压力共轴变形实验 | 400~800 250~600 | 200~500 | 0~50 | 10-4~10-6 | 静水压力对产气影响;共轴变形条件对Ro影响 | 文献[78] | |||||||
| Wilks等 | 1993 | 高级无烟煤 | 高温高压简单剪切变形实验 | 600~900 | 600~1000 | 0~49 | 10-5~10-6 | 高温下剪切应力在石墨化中的作用及对Ro的影响 | 文献[79] | |||||||
| Torre等 | 1997 | 褐煤 | 高压实验 | 200~350 | 50~2000 | — | — | 压力对Ro的影响 | 文献[80] | |||||||
| 周建勋等 | 1994 | 中级烟煤、 中高级无烟煤 | 变形实验 | 50~200 | 30~75 | 9 | 0.5×10-5~ 4×10-6 | 变形等对Ro等的影响 | 文献[81] | |||||||
| 姜波等 | 1998 | 中级烟煤- 高级无烟煤 | 变形实验 | 200~700 | 250~650 | 5~33 | 10-4~10-6 | 变形对Ro、微观结构和化学结构的影响 | 文献[82] | |||||||
| 金法礼等 | 1999 | 中级烟煤、 无烟煤 | 变形实验 | 200~700 | 250~650 | 5~33 | 10-5~10-6 | 不同温压条件对不同煤级煤变形行为的影响 | 文献[83] | |||||||
| 刘俊来等 | 2005 | 中级烟煤、 低级无烟煤 | 变形实验 | 200~500 | 200~500 | 10 | 5×10-6 | 不同温压条件下煤的强度变化 | 文献[84] | |||||||
| 刘高峰等 | 2011 | 褐煤-无烟煤 | 高温高压吸附实验 | 30~50 | 0~18 | — | — | 高温高压三相介质条件对煤吸附瓦斯的影响 | 文献[85] | |||||||
| 侯泉林等 | 2014 | 中-高煤 级无烟煤 | 次高温变 形实验 | 70~100 | 0~30 | — | — | 煤变形对化学结构、产生甲烷的影响 | 文献[86] | |||||||
| 于立业等 | 2015 | 无烟煤 | 变温变压 流变实验 | 300~400 | 70~90 | — | 10-4~10-7 | 温压条件和应变速率对无烟煤流变特征与机制的影响 | 文献[87] | |||||||
| 实验者 | 实验 年份 | 实验 样品 | 实验 性质 | 实验条件 | 实验成果 | 资料来源 | ||||||||||
| 温度 (℃) | 围压 (MPa) | 应变量 (%) | 应变速率 (s-1) | |||||||||||||
| 肖藏岩 | 2016 | 褐煤、气煤 | 应力-应变实验 | 50~250 | 30 | — | — | 不同温压对煤分子结构演化特征及产气情况的影响 | 文献[88] | |||||||
| 刘杰刚 | 2018 | 烟煤 | 高温高压变形实验 | 30~400 | 8~90 | 15~50 | 10-3~10-6 | 不同温压对煤的微观变形特征、演化机理和地质控制作用的影响 | 文献[89] | |||||||
| 刘和武 | 2020 | 烟煤 | 高温高压 变形实验 | 100~300 | 50~100 | 5~25 | 10-4~10-7 | 不同温压条件对构造煤脆-韧性变形机理及分子结构演化的影响 | 文献[90] | |||||||
| 刘志飞 | 2021 | 中-高阶烟煤、无烟煤镜惰分离样品 | 高温高压 模拟实验 | 600~1200 | 1000~2000 | — | — | 高温高压对不同煤岩组分在石墨化阶段结构演化的影响作用 | 文献[91] | |||||||
| Liu等 | 2023 | 高阶烟煤富惰质组分离样品 | 高温高压 模拟实验 | 600~1200 | 1000~2000 | — | — | 温压协同配合及力对惰质组单一组分石墨化进程的影响作用 | 文献[92] | |||||||
| 陈高健等 | 2024 | 中级烟煤 | 高温高压 模拟实验 | 600~1200 | 1500~2000 | — | — | 对比高温条件与高温高压条件下二氧化硅矿物对煤结构演化的影响 | 文献[93] | |||||||

图4 实验样品应力-应变曲线和宏观变形特征[89] (a) 样品Qs2;(b) 样品Qs13;(c) 样品Qs3;(d) 样品Qs16
Fig.4 Stress-strain curves and macroscopic deformation characteristics of experimental samples[89]

图5 实验样品微观变形特征[89] (a)样品Qs5斜向交叉剪切破裂带;(b) 样品Qs3剪切裂隙带发育碎粒、糜棱化带;(c)样品Qs3顺层剪切破裂带;(d) 样品Qs22顺层牵引褶皱结构
Fig.5 Microscopic deformation characteristics of experimental samples[89]
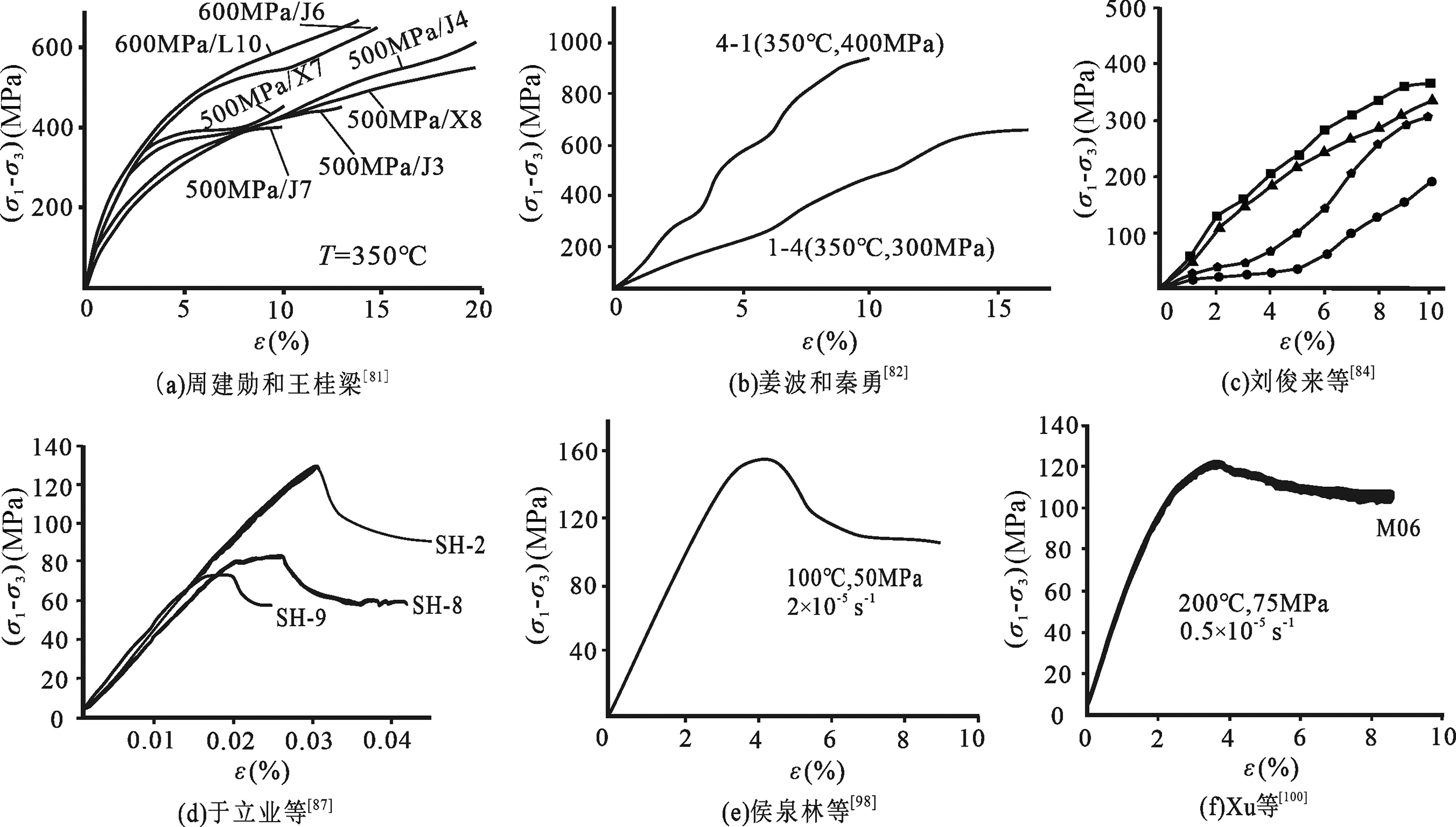
图6 固体/气体围压介质煤高温高压实验应力-应变曲线[81-82,84,87,98,100] (a)(b)(c)固体围压介质应力-应变曲线特征;(d)(e)(f) 气体围压介质应力-应变曲线特征
Fig.6 High temperature and high pressure experimental stress-strain curve of solid/gas confining medium coal[81-82,84,87,98,100]

图7 不同性质应力对煤成石墨演化起始温度影响作用(据文献[79]修改补充)
Fig.7 Effects of different stress properties on the starting temperature of coal-derived graphite evolution (modified after reference [79])
| 样品 编号 | 实验条件 | XRD参数 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 温度(℃) | 压力(GPa) | d002(nm) | La(nm) | Lc(nm) | |
| V-1 | 1200 | 1.5 | 0.3387 | 54.01 | 17.23 |
| I-1 | 1200 | 1.5 | 0.3382 | 60.79 | 17.68 |
| V-2 | 1800 | 常压 | 0.3466 | 7.49 | 3.03 |
| I-2 | 1800 | 常压 | 0.3433 | 10.76 | 3.18 |
| V-3 | 3000 | 常压 | 0.3395 | 17.60 | 11.85 |
| I-3 | 3000 | 常压 | 0.3387 | 19.4 | 17.99 |
表4 高温高压与纯高温条件下模拟结果对比[91]
Table 4 Comparison of results under high temperature with under high pressure and high temperature[91]
| 样品 编号 | 实验条件 | XRD参数 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 温度(℃) | 压力(GPa) | d002(nm) | La(nm) | Lc(nm) | |
| V-1 | 1200 | 1.5 | 0.3387 | 54.01 | 17.23 |
| I-1 | 1200 | 1.5 | 0.3382 | 60.79 | 17.68 |
| V-2 | 1800 | 常压 | 0.3466 | 7.49 | 3.03 |
| I-2 | 1800 | 常压 | 0.3433 | 10.76 | 3.18 |
| V-3 | 3000 | 常压 | 0.3395 | 17.60 | 11.85 |
| I-3 | 3000 | 常压 | 0.3387 | 19.4 | 17.99 |
| [1] | 吕古贤. 构造物理化学学科建设回顾、应用与展望[J]. 地质力学学报, 2021, 27(4): 491-496. |
| [2] | 曹代勇, 李小明, 张守仁. 构造应力对煤化作用的影响——应力降解机制与应力缩聚机制[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 2006, 36(1): 59-68. |
| [3] |
曹代勇, 刘志飞, 王安民, 等. 构造物理化学条件对煤变质作用的控制[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(1): 439-448.
DOI |
| [4] | 杨起. 煤变质作用研究[J]. 现代地质, 1992, 6(4): 437-443. |
| [5] | CAO D Y, LI X M, ZHANG S R. Influence of tectonic stress on coalification: Stress degradation mechanism and stress polycondensation mechanism[J]. Science in China (Series D): Earth Sciences, 2007, 50(1): 43-54. |
| [6] | 曹代勇, 李小明, 邓觉梅. 煤化作用与构造-热事件的耦合效应研究——盆地动力学过程的地质记录[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(4): 52-60. |
| [7] | 曹代勇, 王路, 董业绩, 等. 煤成石墨演化过程中构造应力作用机制研究[M]// 2017年中国地球科学联合学术年会论文集(十七)——专题35:沉积盆地矿产资源综合勘察专题36:盆地动力学与能源专题37:沉积岩系改造与能源矿产赋存. 北京, 中国地球物理学会, 2017: 31-32. |
| [8] | HRYCKOWIAN E, DUTCHER R R, DACHILLE F. Experimental studies of anthracite coals at high pressures and temperatures[J]. Economic Geology, 1967, 62(4): 517-539. |
| [9] | LI W, ZHU Y M, WANG G, et al. Molecular model and ReaxFF molecular dynamics simulation of coal vitrinite pyrolysis[J]. Journal of Molecular Modeling, 2015, 21(8): 188. |
| [10] | DUAN Y, WU B X, HE J X, et al. Characterization of gases and solid residues from closed system pyrolysis of peat and coals at two heating rates[J]. Fuel, 2011, 90(3): 974-979. |
| [11] | 李二庭, 马万云, 李际, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘侏罗系煤生烃热模拟实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(5): 1313-1323. |
| [12] | LE BAYON R, BREY G P, ERNST W G, et al. Experimental kinetic study of organic matter maturation: Time and pressure effects on vitrinite reflectance at 400℃[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2011, 42(4): 340-355. |
| [13] | STACH E, MACKOWSKY M-TH, TECHMULLER M, et al. Stach’s Textbook of Coal Petrology[M]. 3rd ed. Berlin: Gebruder Borntraeger, 1982. |
| [14] | 杨起. 中国煤变质作用[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 1996. |
| [15] | CAO D Y, ZHANG H, DONG Y J, et al. Nanoscale microscopic features and evolution sequence of coal-based graphite[J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2017, 17(9): 6276-6283. |
| [16] | MARQUES M, SUÁREZ-RUIZ I, FLORES D, et al. Correlation between optical, chemical and micro-structural parameters of high-rank coals and graphite[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2009, 77(3/4): 377-382. |
| [17] | 秦勇. 中国高煤级煤的显微岩石学特征及结构演化[M]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学出版社, 1994. |
| [18] | 陈家良, 邵震杰, 秦勇. 能源地质学[M]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学出版社, 2004. |
| [19] | 秦勇. 再论煤中大分子基本结构单元演化的拼叠作用[J]. 地学前缘, 1999, 6(增): 29-34. |
| [20] | 秦勇, 姜波, 王超, 等. 中国高煤级煤的电子顺磁共振特征——兼论煤中大分子基本结构单元的“拼叠作用”及其机理[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 1997, 26(2): 10-14. |
| [21] | 曹代勇, 魏迎春, 李阳, 等. 煤系石墨鉴别指标厘定及分类分级体系构建[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(6): 1833-1846. |
| [22] | 曹代勇, 魏迎春, 王安民, 等. 显微组分大分子结构演化差异性及其动力学机制——研究进展与展望[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2021, 49(1): 12-20. |
| [23] | 李焕同, 王楠, 朱志蓉, 等. 高煤级煤—隐晶质石墨的Raman光谱表征及结构演化[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2020, 48(1): 34-41. |
| [24] | 琚宜文, 林红, 李小诗, 等. 煤岩构造变形与动力变质作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(1): 158-166. |
| [25] | 王路, 董业绩, 张鹤, 等. 煤成石墨化作用的影响因素及其实验验证[J]. 矿业科学学报, 2018, 3(1): 9-19. |
| [26] | 廖清发. 淮南煤田深部煤变质作用研究[D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2010. |
| [27] | TEICHMÜLLER M, TEICHMÜLLER R. Geological Causes of Coalification[J]. Coal Science, 1966,55:133-155. |
| [28] | PEŠEK J, SÝKOROVÁ I. A review of the timing of coalification in the light of coal seam erosion, clastic dykes and coal clasts[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2006, 66(1/2):13-34. |
| [29] | BUSTIN R M, ROSS J V, ROUZAUD J N. Mechanisms of graphite formation from kerogen: Experimental evidence[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 1995, 28(1): 1-36. |
| [30] | BOSTICK N H. Microscopic measurement of the level of catage-nesis of solid organic matter in sedimentary rocks to aid exploration for petroleum and to determine former burial temperatures—a review[J]. Aspects of Diagenesis, 1979,26:17-43. |
| [31] | GONZÁLEZ D, MONTES-MORÁN M A, GARCIA A B. Graphite materials prepared from an anthracite: A structural characterization[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2003, 17(5): 1324-1329. |
| [32] | WANG A M, LI J, CAO D Y, et al. Comparison of nanopore structure evolution in vitrinite and inertinite of tectonically deformed coals: A case study in the Wutongzhuang coal mine of Hebei Province, North China[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2022, 10: 822338. |
| [33] | 曹代勇, 宁树正, 郭爱军, 等. 中国煤田构造格局与构造控煤作用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018. |
| [34] | 琚宜文, 王桂梁, 姜波. 浅层次脆性变形域中煤层韧性剪切带微观分析[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 2003, 33(7): 626-635. |
| [35] | 琚宜文, 姜波, 侯泉林, 等. 煤岩结构纳米级变形与变质变形环境的关系[J]. 科学通报, 2005, 50(17) 90-98. |
| [36] | 李小明, 曹代勇, 张守仁, 等. 不同变质类型煤的XRD结构演化特征[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2003, 31(3): 5-7. |
| [37] | LIU Y, ZHU Y M, LIU S M, et al. Molecular structure controls on micropore evolution in coal vitrinite during coalification[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2018, 199: 19-30. |
| [38] | 姜波, 秦勇, 宋党育, 等. 高煤级构造煤的XRD结构及其构造地质意义[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 1998, 27(2): 6-9. |
| [39] | 李小明. 高煤级煤的变形-变质作用及其对地质环境条件的响应[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2007. |
| [40] | 李志明, 芮晓庆, 徐二社, 等. 典型Ⅱ2-Ⅲ过渡型褐煤近地质条件下生排油模拟研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(1): 249-256. |
| [41] | 赵融芳, 黄伟, 常丽萍, 等. 煤化过程的模拟研究进展[J]. 煤炭转化, 2000, 23(2): 1-6. |
| [42] | ROHRBACK B G, PETERS K E, KAPLAN I R. Geochemistry of artificially heated humic and sapropelic sediments—II:Oil and gas generation[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1984, 68(8): 961-970. |
| [43] | 侯读杰, 王培荣, 林壬子, 等. 茂名油页岩裂解气轻烃组成和热演化特征[J]. 江汉石油学院学报, 1989, 11(4): 7-11. |
| [44] | 骆艳华, 崔平, 胡润桥. 义马煤的热解及产物分布的研究[J]. 安徽工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 23(2): 160-162+168. |
| [45] | 周淑芬, 杨建丽, 刘振宇. 煤热解过程焦中硫的残留及煤中硅、铝、碳的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2010, 38(6): 652-655. |
| [46] | 李美芬, 曾凡桂, 孙蓓蕾, 等. 低煤级煤热解H2生成动力学及其与第一次煤化作用跃变的关系[J]. 物理化学学报, 2009, 25(12): 2597-2603. |
| [47] | ZHAO M, WANG A M, CAO D Y, et al. Differences in macromolecular structure evolution during the pyrolysis of vitrinite and inertinite based on in situ FTIR and XRD measurements[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(15): 5334. |
| [48] | 鞠付栋, 陈汉平, 杨海平, 等. 不同变质煤热解和气化中燃料氮的转化规律[J]. 煤炭转化, 2011, 34(3): 21-26. |
| [49] | 魏晓飞, 张国平, 李玲, 等. 黔西南高砷煤热解过程中微量元素释放规律研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2011, 31(12): 2005-2012. |
| [50] | 吴爱坪, 潘铁英, 史新梅, 等. 中低阶煤热解过程中自由基的研究[J]. 煤炭转化, 2012, 35(2): 1-5. |
| [51] | 尹浩, 刘桂建, 刘静静. 煤热解过程中含硫气体的释放特征[J]. 环境化学, 2012, 31(3): 330-334. |
| [52] | 杨会民, 王美君, 张玉龙, 等. 添加物对宁夏煤热解气相产物生成的影响[J]. 煤炭学报, 2010, 35(8): 1364-1368. |
| [53] | 张永发, 张慧荣, 田芳, 等. 无烟粉煤成型块炭化行为及热解气体生成规律[J]. 煤炭学报, 2011, 36(4): 670-675. |
| [54] | SOLOMON P R, COLKET M B. Evolution of fuel nitrogen in coal devolatilization[J]. Fuel, 1978, 57(12): 749-755. |
| [55] | BURNHAM A K, BRAUN R L, GREGG H R, et al. Comparison of methods for measuring kerogen pyrolysis rates and fitting kinetic parameters[J]. Energy & Fuels, 1987, 1(6): 452-458. |
| [56] | NELSON P F, KELLY M D, WORNAT M J. Conversion of fuel nitrogen in coal volatiles to NOx precursors under rapid heating conditions[J]. Fuel, 1991, 70(3): 403-407. |
| [ ZAJUSZ-ZUBEK E, KONIECZYŃSKI JF. Dynamics of trace elements release in a coal pyrolysis process[J]. Fuel, 2003, 82(10): 1281-1290. | |
| [58] | BEHAR F, LEWAN M D, LORANT F, et al. Comparison of artificial maturation of lignite in hydrous and nonhydrous conditions[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2003, 34(4): 575-600. |
| [59] | 赵炜, 常丽萍, 冯志华, 等. 煤热解过程中生成氮化物的研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2002, 30(5): 408-412. |
| [60] | 王锦平, 张德祥, 高晋生. 煤热解过程中氯的脱除研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2002, 27(4): 402-405. |
| [61] | 王云鹤, 李海滨, 黄海涛, 等. 重金属元素在煤热解过程中的分布迁移规律[J]. 煤炭转化, 2002, 25(3): 37-42. |
| [62] | 段钰锋, 刘玲, 王卉, 等. 煤热解过程中汞析出与汞吸附特性研究[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 2010, 41(5): 619-622,626. |
| [63] | 马中良, 郑伦举, 李志明. 烃源岩有限空间温压共控生排烃模拟实验研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(5): 955-963. |
| [64] | 杨建业. 煤热解中微量元素迁移规律的再探索[J]. 煤炭学报, 2013, 38(12): 2227-2233. |
| [65] | 魏琴. 煤温压热模拟实验中排出物及残留物的地球化学表征[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018. |
| [66] | 刘宁宁. 煤热演化模拟过程中微量元素赋存特征及迁移规律[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2022. |
| [67] | 陈磊, 郑伦举, 黄海平, 等. 碳酸盐岩烃源岩不同热模拟方式下气体碳同位素演变特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(1): 121-128,138. |
| [68] | QIN R F, WANG L, CAO D Y, et al. Thermal simulation experimental study on the difference of molecular structure evolution between vitrinite and inertinite in low-rank coal[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2022, 10: 992017. |
| [69] | CHEN G J, CAO D Y, WANG A M, et al. A high-temperature thermal simulation experiment for coal graphitization with the addition of SiO2[J]. Minerals, 2022, 12(10): 1239. |
| [70] | 张旭, 王琳霖, 蔡苏阳, 等. 有机质生烃对纳米有机孔隙形成演化的影响[J/OL]. 地球科学, 2024:1-19[2024-06-14]. |
| [71] | LIU Z F, CAO D Y, CHEN G J, et al. High-temperature graphitization characteristics of vitrinite and inertinite[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2023, 11: 1235457. |
| [72] | 谢建军, 杨学民, 吕雪松, 等. 煤热解过程中硫氮分配及迁移规律研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2004, 23(11): 1214-1218. |
| [73] | WEI X F, ZHANG G P, CAI Y B, et al. The volatilization of trace elements during oxidative pyrolysis of a coal from an endemic arsenosis area in southwest Guizhou, China[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2012, 98: 184-193. |
| [74] | 汤庆艳, 张铭杰, 余明, 等. 页岩气形成机制的生烃热模拟研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2013, 38(5): 742-747. |
| [75] | 曹代勇, 魏迎春, 秦国红, 等. 煤系战略性金属元素富集成矿的构造控制[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2023, 51(1): 66-85. |
| [76] | BUSTIN R M, ROSS J V, MOFFAT I. Vitrinite anisotropy under differential stress and high confining pressure and temperature: Preliminary observations[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 1986, 6(4): 343-351. |
| [77] | ROSS J V, BUSTIN R M. The role of strain energy in creep graphitization of anthracite[J]. Nature, 1990, 343: 58-60. |
| [78] | MASTALERZ M, WILKS K R, BUSTIN R M, et al. The effect of temperature, pressure and strain on carbonization in high-volatile bituminous and anthracitic coals[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1993, 20(2): 315-325. |
| [79] | WILKS K R, MASTALERZ M, ROSS J V, et al. The effect of experimental deformation on the graphitization of Pennsylvania anthracite[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 1993, 24(1/4): 347-369. |
| [80] | DALLA TORRE M, FERREIRO MÄHLMANN R, ERNST W G. Experimental study on the pressure dependence of vitrinite maturation[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(14): 2921-2928. |
| [81] | 周建勋, 王桂梁, 邵震杰. 煤的高温高压实验变形研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 1994, 19(3): 324-332. |
| [82] | 姜波, 秦勇. 变形煤的结构演化机理及其地质意义[M]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学出版社, 1998. |
| [83] | 金法礼, 秦勇. 高温高压下煤变形的实验分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 1999, 27(1): 14-17. |
| [84] | 刘俊来, 杨光, 马瑞. 高温高压实验变形煤流动的宏观与微观力学表现[J]. 科学通报, 2005, 50(增): 56-63. |
| [85] | 刘高峰. 高温高压三相介质煤吸附瓦斯机理与吸附模型[D]. 焦作: 河南理工大学, 2011. |
| [86] | 侯泉林, 雒毅, 韩雨贞, 等. 煤的变形产气机理探讨[J]. 地质通报, 2014, 33(5): 715-722. |
| [87] | 于立业, 琚宜文, 李小诗. 基于流变实验和红外光谱检测的高煤级煤流变特征[J]. 煤炭学报, 2015, 40(2): 431-438. |
| [88] | 肖藏岩. 温压作用下低煤级煤分子结构演化及CO生成机理: 以华北北部两个煤样为例[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2016. |
| [89] | 刘杰刚. 煤高温高压变形实验及其韧性变形机理: 以宿县矿区烟煤为例[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2018. |
| [90] | 刘和武. 构造煤中应力敏感元素与矿物动力分异特征及机理研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2020. |
| [91] | 刘志飞. 基于模拟实验的煤岩显微组分石墨化差异性机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2021. |
| [92] | LIU Z F, CAO D Y, CHEN G J, et al. Experimental verification for the graphitization of inertinite[J]. Minerals, 2023, 13(7): 888. |
| [93] | 陈高健, 曹代勇, 王安民, 等. 添加二氧化硅的煤石墨化高温高压模拟实验[J]. 矿业科学学报, 2024, 9(2): 144-155. |
| [94] | CHEN B, DIAO Z J, LU H Y. Using the ReaxFF reactive force field for molecular dynamics simulations of the spontaneous combustion of lignite with the Hatcher lignite model[J]. Fuel, 2014, 116: 7-13. |
| [95] | ROSS J V, BUSTIN R M. Vitrinite anisotropy resulting from simple shear experiments at high temperature and high confining pressure[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 1997, 33(2): 153-168. |
| [96] | 周建勋. 煤的变形与光性组构的高温高压变形实验研究及煤田构造中石英的显微构造与组构[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 1991. |
| [97] | 姜波, 秦勇. 实验变形煤结构的13C-NMR特征及其构造地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 1998, 23(6): 36-39. |
| [98] | 侯泉林, 雒毅, 宋超, 等. 中煤级煤变形产气过程及其机理探讨[J]. 煤炭学报, 2014, 39(8): 1675-1682. |
| [99] | 李云波. 构造煤中应力敏感元素迁移聚集规律及动力学机制: 以淮北矿区为例[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2014. |
| [100] | XU R T, LI H J, GUO C C, et al. The mechanisms of gas generation during coal deformation: Preliminary observations[J]. Fuel, 2014, 117: 326-330. |
| [101] | 曹代勇, 王路, 刘志飞, 等. 煤系石墨成矿机理与赋存规律[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2023. |
| [102] | 高岗, 康莉, 刘敬明. 煤岩热模拟产物演化特征与煤层气形成关系[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2012, 19(6): 33-36,113. |
| [103] | 葛祝时, 左兆喜, 肖七林, 等. 海相页岩芳烃演化规律及成熟度指示意义——来自西加拿大盆地二白斑组自然演化与热模拟样品的对比研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(3): 590-600. |
| [104] | 张存杨, 张小涛, 刘岩, 等. 四川盆地二叠系大隆组页岩芳烃热演化规律及成熟度意义[J/OL]. 石油实验地质, 2024:1-13[2024-06-14]. |
| [105] | 李伍, 杨文斌, 战星羽, 等. 煤有机大分子碳结构石墨化机制[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(2): 855-868. |
| [106] |
申晓静, 岳基伟, 梁跃辉, 等. 高温高压氛围下煤体吸附瓦斯特性研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(2): 176-184.
DOI |
| [107] | 田富超, 李振榕, 李帅魁, 等. 高温高压条件下含瓦斯煤解吸——自燃演化特性实验研究[J/OL]. 煤炭科学技术, 2024:1-14[2024-06-14]. |
| [108] | 邓泽, 王红岩, 姜振学, 等. 深部煤储层孔裂隙结构对煤层气赋存的影响——以鄂尔多斯盆地东缘大宁—吉县区块为例[J/OL]. 煤炭科学技术, 2024:1-18[2024-06-14]. |
| [109] |
彭威龙, 胡国艺, 刘全有, 等. 热模拟实验研究现状及值得关注的几个问题[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(9): 1252-1263.
DOI |
| [110] | 甘笑非, 阮基富, 欧家强, 等. 高精度数值模拟技术在气藏开发中后期的应用[M]//第31届全国天然气学术年会(2019)论文集(02气藏开发). 合肥: 中国石油学会天然气专业委员会, 2019: 126-135. |
| [111] | 熊小林, 章军锋, 郑海飞, 等. 近十年来我国实验矿物岩石地球化学研究进展和展望[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2013, 32(4): 402-407. |
| [112] | 焦振华, 倪志辉, 胡浩, 等. 单轴压缩下含钻孔煤样力学行为试验与数值模拟[J/OL]. 煤炭科学技术, 2024:1-13[2024-06-14]. |
| [113] | 王敏欣, 师印光, 刘长波, 等. 机器学习模型预测煤热解产物分布研究[J/OL]. 煤炭转化, 2024:1-14[2024-06-14]. |
| [114] | 袁瑞甫, 李怀珍. 含瓦斯煤动态破坏模拟实验设备的研制与应用[J]. 煤炭学报, 2013, 38(增): 117-123. |
| [1] | 齐玉林, 张枝焕, 夏东领, 张慧敏, 黄彩霞, 郑铎, 金霄, 曹永乐, 朱雷. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部长7暗色泥岩与黑色页岩生烃动力学特征对比分析[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(04): 863-871. |
| [2] | 易传俊, 张敏, 滕梨. 热力作用对塔里木盆地海相原油中甾烷类化合物组成和分布的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(04): 853-862. |
| [3] | 陈菊林,张敏. 原油热模拟实验中重排藿烷类变化特征及其意义[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(4): 871-879. |
| [4] | 薛小花, 卢振权, 廖泽文, 刘辉. 祁连山冻土区含天然气水合物层段岩心热模拟实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(2): 413-424. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||