



现代地质 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (05): 938-952.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2018.05.07
何大双1,2,3( ), 黄海平2,3(
), 黄海平2,3( ), 侯读杰2, 张鹏辉1
), 侯读杰2, 张鹏辉1
收稿日期:2017-12-20
修回日期:2018-02-20
出版日期:2018-10-10
发布日期:2018-11-04
通讯作者:
黄海平,男,教授,1962年出生,地球化学专业,从事石油地质和地球化学方面的研究工作。Email:hhp@cugb.edu.cn。
作者简介:何大双,女,博士,1989年出生,地球化学专业,从事石油地质和地球化学方面的研究工作。Email:hedashuang@igge.cn。
基金资助:
HE Dashuang1,2,3( ), HUANG Haiping2,3(
), HUANG Haiping2,3( ), HOU Dujie2, ZHANG Penghui1
), HOU Dujie2, ZHANG Penghui1
Received:2017-12-20
Revised:2018-02-20
Online:2018-10-10
Published:2018-11-04
摘要:
利用气相色谱-质谱联用仪(GC-MS)系统地分析了阿萨巴斯卡地区Mildred泥炭柱37个样品的脂类化合物,研究了它们的组成特征及可能来源。结果表明,样品中检出的正构烷烃、正烷酮、正烷醛、正烷醇、脂肪酸和脂肪酸甲酯均由高碳数化合物构成,并具明显的奇碳或偶碳优势,GC-MS质量色谱图中甾类和萜类极性化合物呈现显著的高峰。根据泥炭分子地球化学分析,Mildred泥炭柱沉积有机质主要来源于原地堆积的高等植物,苔藓类、水生植物对泥炭有机质也有一定程度的贡献,其中松柏、杜鹃花科等木本植物、莎草科草本植物以及泥炭藓类是主要的成炭植物。萜类和甾类极性化合物的分布存在明显差异,萜类化合物主要集中于剖面的上部,其形成与泥炭藓类植物存在联系;甾类化合物来源不具专属性,多与高等植物的输入有关,也可能是受微生物的改造作用而形成。
中图分类号:
何大双, 黄海平, 侯读杰, 张鹏辉. 加拿大阿萨巴斯卡地区Mildred泥炭柱脂类化合物的组成特征[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 938-952.
HE Dashuang, HUANG Haiping, HOU Dujie, ZHANG Penghui. Composition of Lipid Compounds in the Peat Deposit in Mildred Bog from the Athabasca Region, Canada[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(05): 938-952.
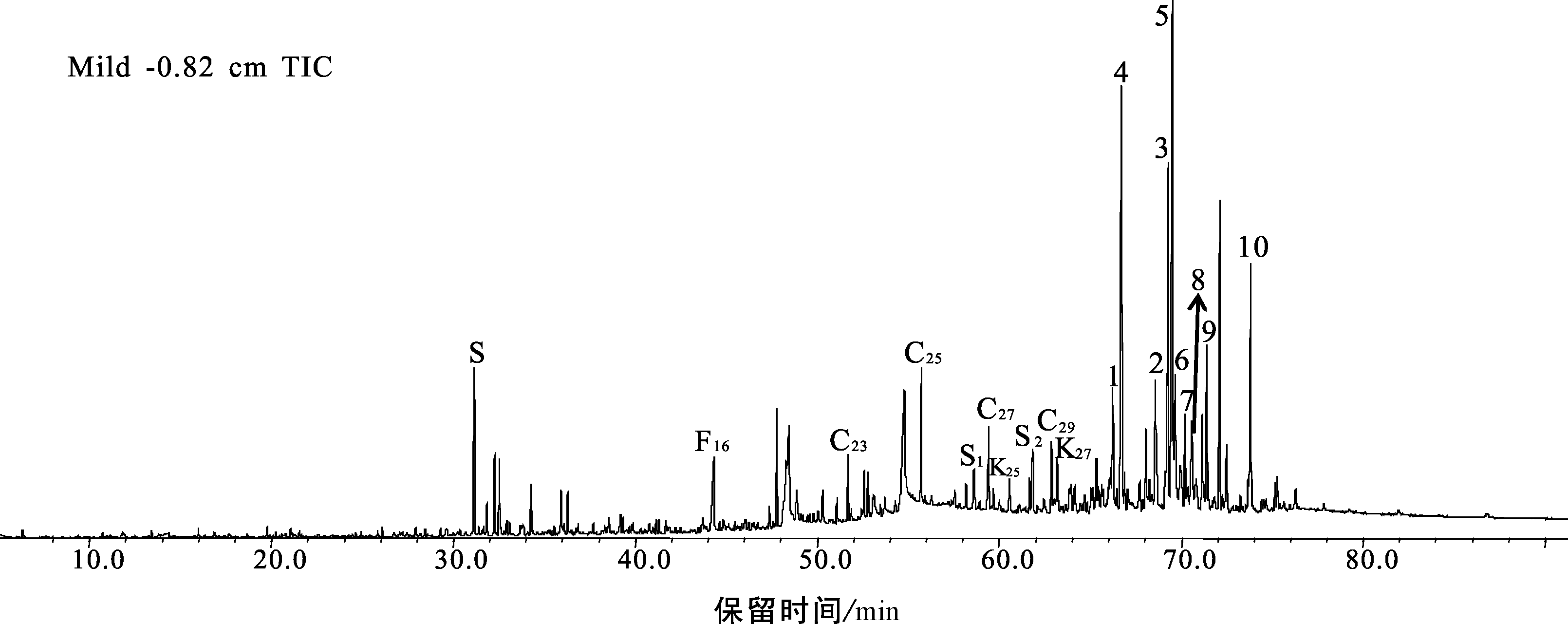
图8 Mildred泥炭样品(-0.82 cm)总离子流图(TIC)及极性化合物鉴别 S.标样D30 PD;S1.标样角鲨烷;S2.标样d4-胆甾烷;F16.C16-脂肪酸;C23.C23-正构烷烃;K25.K25-正烷酮;编号1.菜油甾醇;2.豆甾醇;3.D-弗瑞德齐墩果-14-烯-3-酮;4.α-生育酚;5.γ-谷甾醇;6.弗瑞德-3-酮;7.齐墩果烯-12-烯-3-酮;8.α-香树脂醇;9.羊毛甾醇醋酸酯;10.胆甾烷醇
Fig.8 Diagram of total ion chromatogram and the identification of polar compounds in the Mildred peatland(Sample: -0.82 cm)

图10 Mildred泥炭柱生育酚(α-、β-、γ-)和γ-内酯浓度分布、γ-内酯/生育酚比值分布
Fig.10 Distributions of α-, β-, γ-tocopherol and γ-lactone, and the γ-lactone/tocopherol ratio in the Mildred peat profile
| [1] | 王国平, 贾琳, 刘景双, 等. 国外大气沉降泥炭沼泽档案研究进展[J]. 湿地科学, 2006, 4(1): 69-74. |
| [2] | 黄咸雨, 谢树成. 泥炭沉积分子古气候研究进展[J]. 第四纪研究, 2016, 36(3): 666-673. |
| [3] |
CHAMBERS F M, DAN J C. Holocene environmental change: Contributions from the peatland archive[J]. Holocene, 2004, 14(1): 1-6.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHARMAN D J, HENDON D, PACKMAN S. Multiproxy surface wetness records from replicate cores on an ombrotrophic mire: implications for Holocene palaeoclimate records[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2015, 14(5): 451-463.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
SEREBRENNIKOVA O V, PREIS Y I, KADYCHAGOV P B, et al. Hydrocarbon composition of the organic matter of peats in the south of Western Siberia[J]. Solid Fuel Chemistry, 2010, 44(5): 324-334.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
XIE S, EVERSHED R P. Peat molecular fossils recording paleoclimatic change and organism replacement[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(20): 1749-1752.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 段毅. 甘南沼泽沉积脂类生物标志化合物的组成特征[J]. 地球化学, 2002, 31(6): 525-531. |
| [8] | 杨桂芳, 谢树成, 黄俊华, 等. 天目山泥炭类脂物记录的微生物特征和植被演替[J]. 地学前缘, 2008, 15(4): 170-177. |
| [9] |
LIU X L, LEIDER A, GILLESPIE A, et al. Identification of polar lipid precursors of the ubiquitous branched GDGT orphan lipids in a peat bog in Northern Germany[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2010, 41(7): 653-660.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
NOTT C J, XIE S, AVSEJS L A, et al. n-Alkane distributions in ombrotrophic mires as indicators of vegetation change related to climatic variation[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2000, 31(2): 231-235.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
FICKEN K J, BARBER K E, EGLINTON G. Lipid biomarker,δ13C and plant macrofossil stratigraphy of a Scottish montane peat bog over the last two millennia[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1998, 28 (3): 217-237.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
NICHOLS J E, BOOTH R K, JACKSON S T, et al. Paleohydrologic reconstruction based on n-alkane distributions in ombrotrophic peat[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2006, 37(11): 1505-1513.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
HUANG Y, BOL R, HARKNESS D D. Postglacial variations in distributions,13C and 14C contents of aliphatic hydrocarbons and bulk organic matter in three types of British acid upland soils[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1996, 24(3): 273-287.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
FICKEN K J, LI B, SWAIN D L, et al. An n-alkane proxy for the sedimentary input of submerged/floating freshwater aquatic macrophytes[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2000, 31(7): 745-749.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
MAGNAN G, BELLEN S V, DAVIES L, et al. Impact of the Little Ice Age cooling and 20th century climate change on peatland vegetation dynamics in central and northern Alberta using a multi-proxy approach and high-resolution peat chronologies[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018, 185: 230-243.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ANDERSSON R A, KUHRY P, MEYERS P, et al. Impacts of paleohydrological changes on n-alkane biomarker compositions of a Holocene peat sequence in the eastern European Russian Arctic[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2011, 42(9): 1065-1075.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
BINGHAM E M, MCCLYMONT E L, VÄLIRANTA M, et al. Conservative composition of n-alkane biomarkers in Sphagnum species: implications for palaeoclimatere construction in ombrotrophic peat bogs[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2010, 41(2): 214-220.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
DUAN Y, MA L. Lipid geochemistry in a sediment core from Ruoergai Marsh deposit(Eastern Qinghai-Tibet plateau, China)[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2001, 32(12): 1429-1442.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
JANSEN B, NIEROP K G J, HAGEMAN J A, et al. The straight-chain lipid biomarker composition of plant species responsible for the dominant biomass production along two altitudinal transects in the Ecuadorian Andes[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2006, 37(11): 1514-1536.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
NICHOLS J E, HUANG Y. C23-C31 n-alkan-2-ones are biomarkers for the genus Sphagnum in freshwater peatlands[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2007, 38(11): 1972-1976.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ORTIZ J E, DÍAZ-BAUTISTA A, ALDASORO J J, et al. n-Alkan-2-ones in peat-forming plants from the Ronanzas ombrotrophic bog (Asturias, northern Spain)[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2011, 42(6): 586-592.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHENG Y, ZHOU W, LIU X, et al. n-Alkan-2-one distributions in a northeastern China peat core spanning the last 16 kyr[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2011, 42(1): 25-30.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHENG Y, ZHOU W, MEYERS P A, et al. Lipid biomarkers in the Zoigê-Hongyuan peat deposit: Indicators of Holocene climate changes in West China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2007, 38(11): 1927-1940.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
PANCOST R D, BAAS M, GEEL B V, et al. Biomarkers as proxies for plant inputs to peats: An example from a sub-boreal ombrotrophic bog[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2002, 33(7): 675-690.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
JAFFÉ R, RUSHDI A I, MEDEIROS P M, et al. Natural product biomarkers as indicators of sources and transport of sedimentary organic matter in a subtropical river[J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 64(11): 1870-1884.
PMID |
| [26] |
RIELLEY G, COLLIER R J, JONES D M, et al. The biogeochemistry of Ellesmere Lake, UK-I: source correlation of leaf wax inputs to the sedimentary lipid record[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1991, 17(6): 901-912.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 向明菊, 史继扬, 周友平, 等. 不同类型沉积物中脂肪酸的分布、演化和生烃意义[J]. 沉积学报, 1997, 28(2): 84-88. |
| [28] |
DISNAR J R, STEFANOVA M, BOURDON S, et al. Sequential fatty acid analysis of a peat core covering the last two millennia (Tritrivakely lake, Madagascar): diagenesis appraisal and consequences for palaeoenvironmental reconstruction[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2005, 36(10): 1391-1404.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 妥进才, 张明峰, 王先彬. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部东胜铀矿区沉积有机质中脂肪酸甲酯的检出及意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2006, 24(3): 432-439. |
| [30] | 瞿文川, 张平中. 太湖沉积物中长链脂肪酸甲酯化合物的检出及意义[J]. 湖泊科学, 1999, 11(3): 245-250. |
| [31] |
RONTANI J F, MARTY J C, MIQUEL J C, et al. Free radical oxidation(autoxidation) of alkenones and other microalgal lipids in seawater[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2006, 37(3): 354-368.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
OTTO A, SIMONEIT B R T. Chemosystematics and diagenesis of terpenoids in fossil conifer species and sediment from the Eocene Zeitz formation, Saxony, Germany[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(20): 3505-3527.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
HUANG X, XIE S, ZHANG C L, et al. Distribution of aliphatic des-A-triterpenoids in the Dajiuhu peat deposit, southern China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2008, 39(12): 1765-1771.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
GUIGNARD C, LEMÉE L, AMBLÈS A. Lipid constituents of peat humic acids and humin. Distinction from directly extractable bitumen components using TMAH and TEAAc thermochemolysis[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2005, 36(2): 287-297.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
DUAN Y. Pentacyclic triterpenoid ketones in peat from Gannan Marsh, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(17): 1433-1435.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
VOLKMAN J K. A review of sterol markers for marine and terrigenous organic matter[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 9(2): 83-99.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 郑红菊. 灵武煤田煤中镜质组与丝质组的甾萜类化合物对比研究[J]. 现代地质, 1994, 8(2): 187-193. |
| [38] |
YING G G, KOOKANA R S, RU Y J. Occurrence and fate of hormone steroids in the environment[J]. Environment international, 2002, 28(6): 545-551.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [2] | 杜贯新, 闫百泉, 孙雨, 钱程, 秦涛, 臧延庆. 松嫩平原黑土区西北部阿荣旗地下黑土稀土元素特征及环境指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 813-820. |
| [3] | 曹玉璐, 曾宇轲, 张元元. 基于扫描电子显微镜的重矿物物源分析方法对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 475-485. |
| [4] | 远继东, 姜正龙, 代友旭, 郝连成, 张健康, 张德程, 郑立龙. 湛江湾海域表层沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 77-87. |
| [5] | 吴龙, 柳长峰, 刘文灿, 张宏远. 青藏高原东北缘祁连山三叠系砂岩碎屑锆石U-Pb定年及其物源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1178-1193. |
| [6] | 王香莲, 黄庭, 肖河, 吴代赦, 张小龙, 程胜高, 毛绪美. 东北哈尼泥炭沉积物磁化率特征及古气候意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1323-1331. |
| [7] | 黎介, 刘宁强, 龚庆杰, 吴轩, 严桃桃. 基于微量元素岩性地球化学基因的构建与检验[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1459-1470. |
| [8] | 龚庆杰, 吴轩, 严桃桃, 刘宁强, 李晓蕾, 李睿堃, 刘梦翔. 地球化学基因的构建与检验[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 865-882. |
| [9] | 李怡佳, 阮壮, 刘帅, 常秋红, 赖玮, 杨志辉. 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘长10-长8段物源及源区构造背景研究[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 784-799. |
| [10] | 鞠鹏程, 王训练, 王振涛, 刘喜方, 仲佳爱, 张在明. 渝北温泉镇地区三叠系“绿豆岩”特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 431-449. |
| [11] | 郭若舜, 何磊, 叶思源, 赵俐红. 辽河三角洲大凌河河口湿地沉积物晚更新世以来的矿物特征及其物源、气候意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 154-165. |
| [12] | 路宗悦, 余心起, 刘满年, 张振, 魏立勇, 赵常存, 郑鑫, 寇少磊, 许安民, 王照翻. 秦昆结合部塔秀地区隆务河组碎屑锆石LA-ICP-MSU-Pb年代学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(04): 691-702. |
| [13] | 刘庆山, 魏玉帅, 张宝森, 潘婉莹. 古新世特提斯喜马拉雅南亚带石英砂岩成因及其构造意义:以藏南岗巴地区古新统基堵拉组为例[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(03): 561-573. |
| [14] | 李文博, 李晓海, 丁秋红, 陈树旺, 张健. 辽宁北部秀水盆地白垩系义县组泥岩地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(02): 284-292. |
| [15] | 徐银波, 李锋, 张家强, 孙平昌, 毕彩芹, 仝立华, 李昭. 黑龙江省老黑山盆地下白垩统穆棱组砂岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 786-795. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||