



现代地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (03): 801-813.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.043
出版日期:2025-06-10
发布日期:2025-07-03
通信作者:
*李素梅,女,研究员,1968年出生,主要从事油气地质地球化学研究工作。Email:smli@cup.edu.cn。作者简介:邓 硕,男,博士研究生,1990年出生,主要从事油气地质地球化学研究工作。Email:ds901007@163.com。
基金资助:
DENG Shuo1,2( ), LI Sumei1,2,*(
), LI Sumei1,2,*( ), LIU Jia1,2
), LIU Jia1,2
Published:2025-06-10
Online:2025-07-03
摘要:
原油中单体烃硫同位素可为判别原油成熟度和沉积环境提供关键的地球化学信息。本文采用气相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱技术(GC-MC-ICP MS)结合传统色谱质谱方法(GC-MS),对辽河西部凹陷原油中单体烃硫同位素的分布特征和影响因素进行探讨。三种成因原油的单体烃硫同位素δ34S值具有明显差异:锦州油田淡水相成熟油δ34S值(20.57‰)最高,单体烃硫同位素随着甲基化程度增加呈现先升高后降低的趋势;曙光—高升油田咸水相低熟油δ34S值(19.23‰)略低于前者,单体烃硫同位素呈现随甲基化程度增加而升高的趋势;牛心坨油田的半咸水相低熟油δ34S值(14.47‰)最低。观察到δ34S值随着成熟度增加有变重的趋势,同时Δδ34S1-mDBT-4-mDBT与成熟度参数C29甾烷ααα20S/(S+R)具有良好的负相关性,表明成熟度的控制作用,可能是影响δ34S值的最主要因素。成熟度相近原油的δ34S值与伽马蜡烷/C30藿烷具有良好的正相关性,而与C19/C23三环萜烷呈反比,表明还原性咸水环境有利于有机质的硫化作用,导致δ34S偏重。轻度生物降解作用对δ34S值影响较小,没有引起明显的同位素分馏现象。单体烃硫同位素可作为表征原油成熟度与沉积环境的有效指标,为油气资源的勘探开发提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
邓硕, 李素梅, 刘佳. 辽河西部凹陷原油单体烃硫同位素特征及其地球化学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(03): 801-813.
DENG Shuo, LI Sumei, LIU Jia. Distribution Characteristics and Geochemical Significances of the Individual Hydrocarbon Sulfur Isotopes of Crude Oils in the Liaohe Western Depression[J]. Geoscience, 2025, 39(03): 801-813.

图1 辽河西部凹陷构造位置图(a)、不同构造单元油藏平面分布示意图(b)、构造和油藏分布剖面图(c)
Fig.1 Structural location map of the Liaohe Western Depression (a), planar schematic diagram of oil reservoir distribution in different structural units (b) and structural and oil reservoir distribution profile diagram (c)
| 井号 | 油田 | 层位 | 深度 (m) | 密度 (g/cm3) | 黏度 (mPa·s) | 凝固点 (℃) | 含蜡量 (%) | 含硫量 (%) | 饱和烃 (%) | 芳烃 (%) | 非烃+沥 青质(%) | 饱 芳比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SG103 | 曙光 | 潜山 | 1786.80 | 0.82 | 3.73 | 32.00 | 14.99 | - | 72.70 | 15.70 | 11.60 | 4.63 |
| S4-8-006 | 曙光 | Es4 | 1199.50 | 0.91 | 258.07 | 16.00 | 10.52 | - | 40.60 | 23.40 | 35.90 | 1.74 |
| S3-06-03 | 曙光 | Es4 | 1307.35 | 0.88 | 120.00 | 24.00 | 15.44 | - | 51.70 | 25.20 | 23.10 | 2.05 |
| S1-32-58C | 曙光 | Es4 | 1093.05 | 0.93 | 1539.30 | 15.50 | 5.09 | - | 38.20 | 30.50 | 31.40 | 1.25 |
| D84-38-172 | 曙光 | Ng | 654.00 | 1.00 | 664977.30 | 46.00 | 1.28 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Z17-23 | 高升 | Es4中 | 1753.00 | 0.89 | 414.20 | 31.00 | 11.45 | 0.48 | 35.90 | 20.70 | 43.50 | 1.73 |
| G3-6-0151 | 高升 | Es3下 | 1641.95 | 0.93 | 2585.00 | 9.00 | - | 0.51 | 24.00 | 19.60 | 56.40 | 1.22 |
| G3-6-25 | 高升 | Es3下 | 1788.00 | 0.94 | 3524.00 | 6.00 | 5.10 | 0.53 | 27.50 | 21.10 | 51.40 | 1.30 |
| T37-29 | 牛心坨 | Es4下 | 1909.55 | 0.88 | 1178.00 | 39.00 | 13.43 | 0.40 | 37.80 | 17.20 | 45.00 | 2.20 |
| J2-8-10 | 锦州 | Es3 | 2483.90 | 0.80 | 2.47 | 9.00 | 19.57 | - | 72.60 | 15.00 | 12.40 | 4.84 |
| J150-18-119 | 锦州 | Mz | - | 0.81 | 6.10 | 25.00 | 17.89 | - | 68.70 | 14.10 | 17.20 | 4.87 |
表1 原油物理性质与族组分组成
Table 1 Physical properties and group composition for the oils from the Liaohe Western Depression
| 井号 | 油田 | 层位 | 深度 (m) | 密度 (g/cm3) | 黏度 (mPa·s) | 凝固点 (℃) | 含蜡量 (%) | 含硫量 (%) | 饱和烃 (%) | 芳烃 (%) | 非烃+沥 青质(%) | 饱 芳比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SG103 | 曙光 | 潜山 | 1786.80 | 0.82 | 3.73 | 32.00 | 14.99 | - | 72.70 | 15.70 | 11.60 | 4.63 |
| S4-8-006 | 曙光 | Es4 | 1199.50 | 0.91 | 258.07 | 16.00 | 10.52 | - | 40.60 | 23.40 | 35.90 | 1.74 |
| S3-06-03 | 曙光 | Es4 | 1307.35 | 0.88 | 120.00 | 24.00 | 15.44 | - | 51.70 | 25.20 | 23.10 | 2.05 |
| S1-32-58C | 曙光 | Es4 | 1093.05 | 0.93 | 1539.30 | 15.50 | 5.09 | - | 38.20 | 30.50 | 31.40 | 1.25 |
| D84-38-172 | 曙光 | Ng | 654.00 | 1.00 | 664977.30 | 46.00 | 1.28 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Z17-23 | 高升 | Es4中 | 1753.00 | 0.89 | 414.20 | 31.00 | 11.45 | 0.48 | 35.90 | 20.70 | 43.50 | 1.73 |
| G3-6-0151 | 高升 | Es3下 | 1641.95 | 0.93 | 2585.00 | 9.00 | - | 0.51 | 24.00 | 19.60 | 56.40 | 1.22 |
| G3-6-25 | 高升 | Es3下 | 1788.00 | 0.94 | 3524.00 | 6.00 | 5.10 | 0.53 | 27.50 | 21.10 | 51.40 | 1.30 |
| T37-29 | 牛心坨 | Es4下 | 1909.55 | 0.88 | 1178.00 | 39.00 | 13.43 | 0.40 | 37.80 | 17.20 | 45.00 | 2.20 |
| J2-8-10 | 锦州 | Es3 | 2483.90 | 0.80 | 2.47 | 9.00 | 19.57 | - | 72.60 | 15.00 | 12.40 | 4.84 |
| J150-18-119 | 锦州 | Mz | - | 0.81 | 6.10 | 25.00 | 17.89 | - | 68.70 | 14.10 | 17.20 | 4.87 |

图2 原油饱和烃总离子流图(a)、m/z 217质量色谱图(b)
Fig.2 Total ion chromatogram (TIC) from the GC-MS of the saturated hydrocarbon fractions (a) and mass chromatograms of m/z 217 (b)
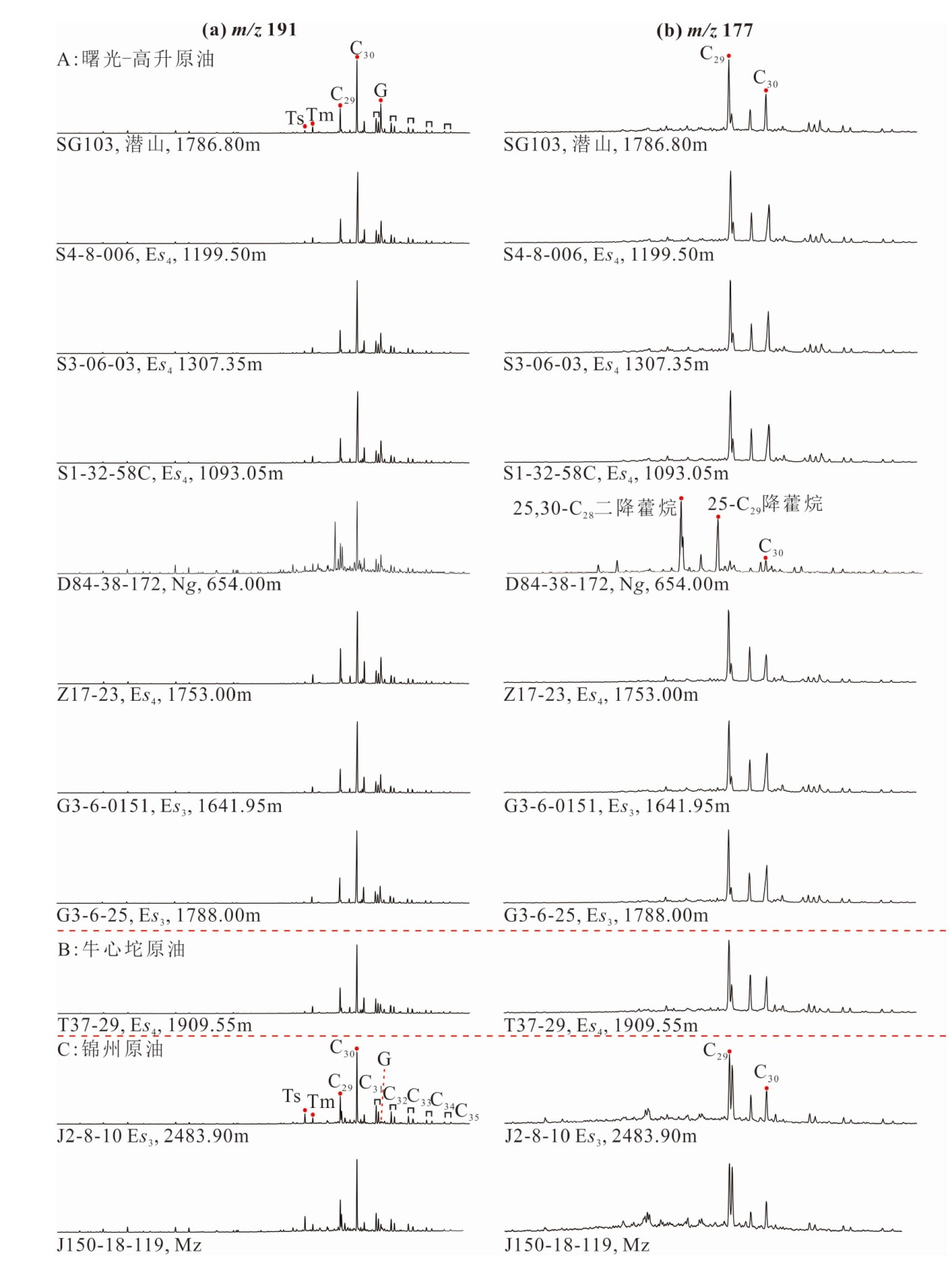
图3 原油饱和烃m/z 191(a)、m/z 177质量色谱图(b)
Fig.3 Mass chromatograms of m/z 191 (a) and m/z 177 (b) of saturated hydrocarbon fractions of the Liaohe Western Depression oils
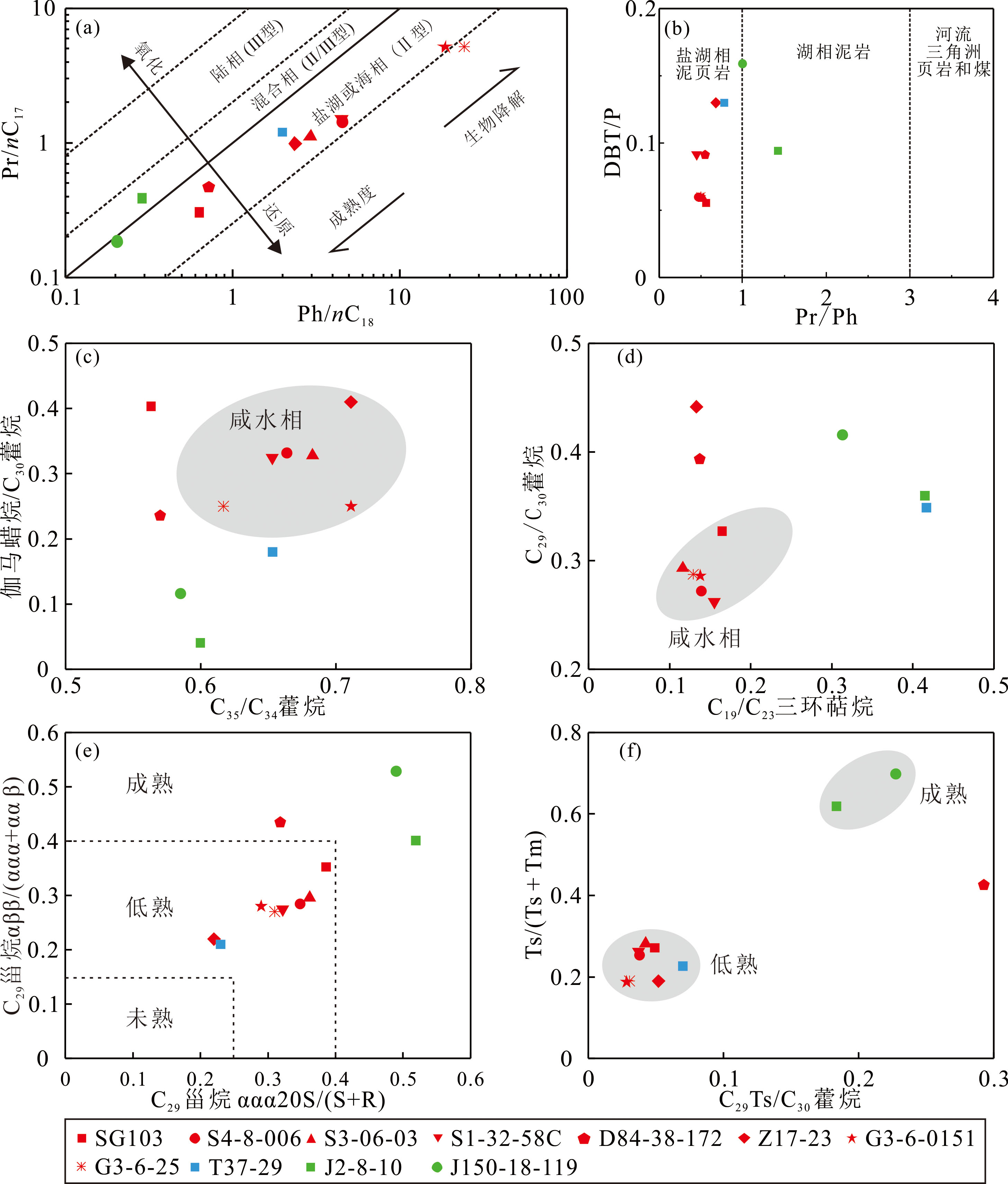
图4 辽河西部凹陷原油生物标志物参数关系图(底图(a)据Connan等[36],底图(b)据Hughes等[32])
Fig.4 Cross plots of biomarker parameters of oils from the Liaohe Western Depression oils (Base figure (a) is based on Connan et al.[36], and base figure (b) is based on Hughes et al.[32])
| 井号 | 油田 | Pr/ Ph | Pr/ nC17 | Ph/ nC18 | G/ C30H | C35/ C34H | C19/ C23TT | C29/ C30H | S/R | αββ | C29Ts/ C30H | Ts/ (Ts+Tm) | DBT/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SG103 | 曙光 | 0.56 | 0.31 | 0.63 | 0.40 | 0.56 | 0.16 | 0.33 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.27 | 0.06 |
| S4-8-006 | 曙光 | 0.47 | 1.46 | 4.48 | 0.33 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 0.27 | 0.35 | 0.28 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.06 |
| S3-06-03 | 曙光 | 0.53 | 1.12 | 2.92 | 0.33 | 0.68 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.04 | 0.28 | 0.06 |
| S1-32-58C | 曙光 | 0.45 | 1.53 | 4.52 | 0.32 | 0.65 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.09 |
| D84-38-172 | 曙光 | 0.55 | 0.47 | 0.72 | 0.24 | 0.34 | 0.14 | 0.39 | 0.32 | 0.43 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.09 |
| Z17-23 | 高升 | 0.68 | 1.00 | 2.35 | 0.41 | 0.71 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.13 |
| G3-6-0151 | 高升 | 0.50 | 5.22 | 18.77 | 0.25 | 0.71 | 0.14 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.06 |
| G3-6-25 | 高升 | 0.50 | 5.22 | 24.29 | 0.25 | 0.62 | 0.13 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.06 |
| T37-29 | 牛心坨 | 0.78 | 1.22 | 1.98 | 0.18 | 0.65 | 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.23 | 0.13 |
| J2-8-10 | 锦州 | 1.42 | 0.39 | 0.28 | 0.04 | 0.60 | 0.41 | 0.36 | 0.52 | 0.40 | 0.18 | 0.62 | 0.09 |
| J150-18-119 | 锦州 | 1.00 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.58 | 0.31 | 0.42 | 0.49 | 0.53 | 0.23 | 0.70 | 0.16 |
表2 原油常规地球化学参数
Table 2 Basic geochemical parameters of the oils
| 井号 | 油田 | Pr/ Ph | Pr/ nC17 | Ph/ nC18 | G/ C30H | C35/ C34H | C19/ C23TT | C29/ C30H | S/R | αββ | C29Ts/ C30H | Ts/ (Ts+Tm) | DBT/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SG103 | 曙光 | 0.56 | 0.31 | 0.63 | 0.40 | 0.56 | 0.16 | 0.33 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.27 | 0.06 |
| S4-8-006 | 曙光 | 0.47 | 1.46 | 4.48 | 0.33 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 0.27 | 0.35 | 0.28 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.06 |
| S3-06-03 | 曙光 | 0.53 | 1.12 | 2.92 | 0.33 | 0.68 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.04 | 0.28 | 0.06 |
| S1-32-58C | 曙光 | 0.45 | 1.53 | 4.52 | 0.32 | 0.65 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.09 |
| D84-38-172 | 曙光 | 0.55 | 0.47 | 0.72 | 0.24 | 0.34 | 0.14 | 0.39 | 0.32 | 0.43 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.09 |
| Z17-23 | 高升 | 0.68 | 1.00 | 2.35 | 0.41 | 0.71 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.13 |
| G3-6-0151 | 高升 | 0.50 | 5.22 | 18.77 | 0.25 | 0.71 | 0.14 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.06 |
| G3-6-25 | 高升 | 0.50 | 5.22 | 24.29 | 0.25 | 0.62 | 0.13 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.06 |
| T37-29 | 牛心坨 | 0.78 | 1.22 | 1.98 | 0.18 | 0.65 | 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.23 | 0.13 |
| J2-8-10 | 锦州 | 1.42 | 0.39 | 0.28 | 0.04 | 0.60 | 0.41 | 0.36 | 0.52 | 0.40 | 0.18 | 0.62 | 0.09 |
| J150-18-119 | 锦州 | 1.00 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.58 | 0.31 | 0.42 | 0.49 | 0.53 | 0.23 | 0.70 | 0.16 |
| [1] | CAI C, AMRANI A, WORDEN R H, et al. Sulfur isotopic compositions of individual organosulfur compounds and their genetic links in the Lower Paleozoic petroleum pools of the Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2016, 182: 88-108. |
| [2] | GREENWOOD P F, MOHAMMED L, GRICE K, et al. The application of compound-specific sulfur isotopes to the oil-source rock correlation of Kurdistan petroleum[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2018, 117: 22-30. |
| [3] | KE C W, LI S M, ZHANG H G, et al. Compound specific sulfur isotopes of saline lacustrine oils from the Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 195: 104361. |
| [4] | ELLIS G S, SAID-AHMAD W, LILLIS P G, et al. Effects of thermal maturation and thermochemical sulfate reduction on compound-specific sulfur isotopic compositions of organosulfur compounds in Phosphoria oils from the Bighorn Basin, USA[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2017, 103: 63-78. |
| [5] | ROSENBERG Y O, MESHOULAM A, SAID-AHMAD W, et al. Study of thermal maturation processes of sulfur-rich source rock using compound specific sulfur isotope analysis[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2017, 112: 59-74. |
| [6] | HE N, GRICE K, GREENWOOD P F. The distribution and δ34S values of organic sulfur compounds in biodegraded oils from Peace River (Alberta Basin, western Canada)[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2019, 128: 16-25. |
| [7] | AMRANI A, DEEV A, SESSIONS A L, et al. The sulfur-isotopic compositions of benzothiophenes and dibenzothiophenes as a proxy for thermochemical sulfate reduction[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2012, 84: 152-164. |
| [8] | GVIRTZMAN Z, SAID-AHMAD W, ELLIS G S, et al. Compound-specific sulfur isotope analysis of thiadiamondoids of oils from the Smackover Formation, USA[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 167: 144-161. |
| [9] | 赵雪培, 张霞, 林春明, 等. 辽河拗陷滩海东部沙河街组低渗透砂岩储层成岩作用特征[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(2): 196-204. |
| [10] | 蔡国刚, 鞠俊成. 辽河西部凹陷稠油成藏机制及深化勘探方法探讨[J]. 特种油气藏, 2010, 17(4): 35-38. |
| [11] | 李素梅, 庞雄奇, 高先志, 等. 辽河西部凹陷稠油成因机制[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 2008, (S1): 138-149. |
| [12] | 惠沙沙, 庞雄奇, 柳广弟, 等. 辽河西部凹陷沙河街组烃源岩特征及油源精细对比[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(8): 3081-3098. |
| [13] | 毛俊莉, 张金川, 丁江辉, 等. 辽河坳陷清水洼陷沙三段页岩气富集条件[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(6): 1252-1262. |
| [14] | 邓硕, 李素梅, 曹敬涛, 等. 辽河西部凹陷低熟油的高分辨质谱特征及其成因机制[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(5): 1354-1369. |
| [15] | LI S M, PANG X Q, LIU K Y, et al. Formation mechanisms of heavy oils in the Liaohe Western Depression, Bohai Gulf Basin[J]. Science in China Series D-Earth Sciences, 2008, 51(2): 156-169. |
| [16] | HUANG H, BOWLER B F J, OLDENBURG T B P, et al. The effect of biodegradation on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in reservoired oils from the Liaohe basin, NE China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2004, 35(11): 1619-1634. |
| [17] | HUANG H, BOWLER B F J, ZHANG Z, et al. Influence of biodegradation on carbazole and benzocarbazole distributions in oil columns from the Liaohe basin, NE China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2003, 34(7): 951-969. |
| [18] | SONGNIAN L, WEI H, HAIPING H. The geochemical characteristics of heavy oil and its recovery in Liaohe Basin, China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1990, 16(1): 437-449. |
| [19] | 徐二社, 黄娟, 鹿坤, 等. 致密油运聚动力研究:以渤海湾盆地东濮凹陷Wg4井沙三中致密油为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(1): 17-24. |
| [20] | 漆家福, 李晓光, 于福生, 等. 辽河西部凹陷新生代构造变形及“郯庐断裂带”的表现[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2013, 43(8): 1324-1337. |
| [21] | 单俊峰, 陈振岩, 张卓, 等. 辽河坳陷西部凹陷西斜坡古潜山的油气运移条件[J]. 现代地质, 2005, (2): 274-278. |
| [22] | 冷济高, 庞雄奇, 李晓光, 等. 辽河断陷西部凹陷油气成藏主控因素[J]. 古地理学报, 2008, (5): 473-480. |
| [23] |
王延山, 胡英杰, 黄双泉, 等. 渤海湾盆地辽河坳陷天然气地质条件、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(10): 1422-1432.
DOI |
| [24] | 陈星州, 邵建欣, 孙转, 等. 渤海湾盆地辽河坳陷稠油分布特征及主控因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(2): 317-326. |
| [25] | 周晓龙. 辽河西部凹陷雷家—高升地区原油物性特征及影响因素[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2017, 31(1): 22-5+131-2. |
| [26] | 朱芳冰. 辽河盆地西部凹陷源岩特征及低熟油分布规律研究[J]. 地球科学, 2002, (1): 25-29. |
| [27] |
AMRANI A, SESSIONS A L, ADKINS J F. Compound-specific delta34S analysis of volatile organics by coupled GC/multicollector-ICPMS[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 81(21): 9027-9034.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | PETERS K E, PETERS K E, WALTERS C C, et al. The biomarker guide[M]. Cambridge university press, 2005. |
| [29] | GRANTHAM P J. The occurence of unusual C27 and C29 sterane predominances in two types of Oman crude oil[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 9(1): 1-10. |
| [30] | VOLKMAN J K. A review of sterol markers for marine and terrigenous organic matter[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 9(2): 83-99. |
| [31] | DERENNE S, LARGEAU C, BERKALOFF C, et al. Non-hydrolysable macromolecular constituents from outer walls of Chlorella fusca and Nanochlorum eucaryotum[J]. Phytochemistry, 1992, 31(6): 1923-1929. |
| [32] | HUGHES W B, HOLBA A G, DZOU L I P. The ratios of dibenzothiophene to phenanthrene and pristane to phytane as indicators of depositional environment and lithology of petroleum source rocks[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(17): 3581-3598. |
| [33] |
SINNINGHE DAMSTé J S, KENIG F, KOOPMANS M P, et al. Evidence for gammacerane as an indicator of water column stratification[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(9): 1895-1900.
PMID |
| [34] | AZEVEDO D A, AQUINO NETO F R, SIMONEIT B R T, et al. Novel series of tricyclic aromatic terpanes characterized in Tasmanian tasmanite[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1992, 18(1): 9-16. |
| [35] | DIFAN H, JINCHAO L, DAJIANG Z. Maturation sequence of continental crude oils in hydrocarbon basins in China and its significance[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1990, 16(1): 521-529. |
| [36] | CONNAN J, CASSOU A M. Properties of gases and petroleum liquids derived from terrestrial kerogen at various maturation levels[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1980, 44(1): 1-23. |
| [37] | FEDORAK P M, WESTLAKE D W S. Microbial degradation of organic sulfur compounds in Prudhoe Bay crude oil[J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 1983, 29(3): 291-296. |
| [38] | AMRANI A. Organosulfur Compounds: Molecular and Isotopic Evolution from Biota to Oil and Gas[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2014, 42(1): 733-768. |
| [39] | 包建平, 王培荣, 朱翠山, 等. 有机硫化合物组成特征与热稳定性研究——以约旦油页岩和页岩油为例[J]. 江汉石油学院学报, 1990, 3: 1-8. |
| [40] | 杨华敏, 王萍, 陶成, 等. 天然气中硫化氢含量及硫同位素联测方法[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(1): 166-172. |
| [41] |
高文强, 夏燕青, 马素萍, 等. 烃源岩和油气中有机含硫化合物的生成、分布及应用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(11): 1615-1627.
DOI |
| [42] | 李素梅, 张宝收, 张海祖, 等. 塔中原油超高二苯并噻吩硫特征及其控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(6): 1108-1120. |
| [43] | 肖飞, 包建平, 张文艳, 等. 烷基二苯并噻吩类化合物研究进展[J]. 广东石油化工学院学报, 2012, 22(6): 16-9+22. |
| [44] | KE C, LI S, GREENWOOD P, et al. Maturity and depositional controls on compound-specific sulfur isotope values of saline lacustrine source rocks in the north Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 212: 110286. |
| [45] | RADKE M. Application of aromatic compounds as maturity indicators in source rocks and crude oils[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1988, 5(3): 224-236. |
| [46] | RADKE M, WILLSCH H. Extractable alkyldibenzothiophenes in Posidonia Shale (Toarcian) source rocks: Relationship of yields to petroleum formation and expulsion[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(23): 5223-5244. |
| [47] | 柯昌炜, 李素梅, 张洪安, 等. 东濮凹陷盐湖相烃源岩有机硫同位素分布特征及其地球化学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(2): 301-314. |
| [48] |
蔡春芳. 有机硫同位素组成应用于油气来源和演化研究进展[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(2): 159-167.
DOI |
| [49] | AMRANI A, LEWAN M D, AIZENSHTAT Z. Stable sulfur isotope partitioning during simulated petroleum formation as determined by hydrous pyrolysis of Ghareb Limestone, Israel[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(22): 5317-5331. |
| [50] | XUE C, CHI G, LI Z, et al. Geology, geochemistry and genesis of the Cretaceous and Paleocene sandstone- and conglomerate-hosted Uragen Zn-Pb deposit, Xinjiang, China: A review[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 63: 328-342. |
| [51] | ZHANG S, ZHU G, LIANG Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the Zhaolanzhuang sour gas accumulation and thermochemical sulfate reduction in the Jixian Sag of Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2005, 36(12): 1717-1730. |
| [52] |
CANFIELD D E, HABICHT K S, THAMDRUP B. The Archean Sulfur Cycle and the Early History of Atmospheric Oxygen[J]. Science, 2000, 288: 658-661.
PMID |
| [53] | FIKE D A, GROTZINGER J P, PRATT L M, et al. Oxidation of the Ediacaran Ocean[J]. Nature, 2006, 444: 744-747. |
| [54] | SUN Y, CHEN Z, XU S, et al. Stable carbon and hydrogen isotopic fractionation of individual n-alkanes accompanying biodegradation: evidence from a group of progressively biodegraded oils[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2005, 36(2): 225-238. |
| [55] | KINNAMAN F S, VALENTINE D L, TYLER S C. Carbon and hydrogen isotope fractionation associated with the aerobic microbial oxidation of methane, ethane, propane and butane[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(2): 271-283. |
| [56] | ASIF M, GRICE K, FAZEELAT T. Assessment of petroleum biodegradation using stable hydrogen isotopes of individual saturated hydrocarbon and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon distributions in oils from the Upper Indus Basin, Pakistan[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2009, 40(3): 301-311. |
| [1] | 田臣龙, 徐凤琳, 田鹏飞. 黄淮海平原腹地公元750年以来的环境演化及地层划分[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(02): 371-383. |
| [2] | 刘备, 高先志, 李峰, 龚志愚, 罗凡, 杜小锋. 鄂西恩施地区中二叠统孤峰组黑色页岩古环境恢复与有机质富集因素[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(06): 1484-1497. |
| [3] | 邓硕, 李素梅, 曹敬涛, 黄太明, 刘佳, 张建淼, 施倩倩. 辽河西部凹陷低熟油的高分辨质谱特征及其成因机制[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(05): 1354-1369. |
| [4] | 柳坤峰, 冯昌荣, 徐磊, 祁晓鹏, 蔡振锋, 谢晋, 翟黎明, 雷浩. 新疆吾合沙鲁铜矿床含铜岩系安居安组下段砂岩粒度特征与沉积环境分析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 1134-1146. |
| [5] | 姚雅琴, 杨纪磊, 赵都菁, 齐玉民, 魏文艳, 曹洁, 杨娇娇, 李国良. 渤海湾盆地辽西凹陷古近纪微体化石组合特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 230-239. |
| [6] | 倪敏婕, 祝贺暄, 何文军, 杨森, 邹阳, 张元元. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组沉积环境与沉积模式分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1194-1207. |
| [7] | 师良, 范柏江, 王霞, 李亚婷, 黄飞飞, 戴欣洋. 鄂尔多斯盆地长9页岩烃源岩的元素组成及其古沉积环境[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1254-1263. |
| [8] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [9] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [10] | 李倩倩, 郑德顺. 豫西中元古界龙家园组二段叠层石特征及其沉积环境分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 845-857. |
| [11] | 贾冰玲, 张碧云, 汤彬, 郑德顺. 豫西寒武系辛集组含磷层沉积环境及磷酸盐富集机制[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 858-869. |
| [12] | 蒋中发, 江梦雅, 陈海龙, 刘龙松, 王学勇, 卞保力, 李娜. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷下二叠统风城组烃源岩热演化及沉积古环境评价[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1118-1130. |
| [13] | 苟富刚, 龚绪龙, 杨露梅, 张岩, 刘明遥. 长江河口百米以浅土体含盐特征及其沉积环境演化[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 462-473. |
| [14] | 陈耀飞, 侯恩刚, 高金汉, 肖红吉, 王根厚. 西藏荣玛地区上三叠统日干配错组沉积环境及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 48-57. |
| [15] | 柯昌炜, 李素梅, 张洪安, 徐田武, 张云献, 曾凡纲, 张树海, 张韩静. 东濮凹陷盐湖相烃源岩有机硫同位素分布特征及其地球化学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 301-314. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||