



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (01): 130-140.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.010
宋备1( ), 苏新1(
), 苏新1( ), 吕士辉1, 倪建宇2, 廖时理2, 陶春辉2, 胡茂康1, 李世云1, 于翀涵1
), 吕士辉1, 倪建宇2, 廖时理2, 陶春辉2, 胡茂康1, 李世云1, 于翀涵1
收稿日期:2019-06-20
修回日期:2019-09-20
出版日期:2020-03-05
发布日期:2020-03-07
通讯作者:
苏新
作者简介:苏 新,女,教授,博士生导师,1957年出生,微体古生物和海洋地质专业,主要从事微体古生物、海洋地质和天然气水合物等研究。Email: xsu@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
SONG Bei1( ), SU Xin1(
), SU Xin1( ), LÜ Shihui1, NI Jianyu2, LIAO Shili2, TAO Chunhui2, HU Maokang1, LI Shiyun1, YU Chonghan1
), LÜ Shihui1, NI Jianyu2, LIAO Shili2, TAO Chunhui2, HU Maokang1, LI Shiyun1, YU Chonghan1
Received:2019-06-20
Revised:2019-09-20
Online:2020-03-05
Published:2020-03-07
Contact:
SU Xin
摘要:
龙旂热液区与断桥热液区分别是西南印度洋中脊典型的活动与非活动热液区。为研究两区内表层沉积物地球化学特征,对共59件表层沉积物进行了元素地球化学测试,对其进行物质组分、富集系数与R型聚类等分析。结果表明:两区内普遍含较高的Ca、Sr、Ba等生源元素和Fe、Mg、Si、Al等围岩元素,而构造、围岩和热液活动等因素的不同,使两区沉积物的元素地球化学特征存在差异。龙旂区沉积物出现了源于超基性围岩的组分并体现在元素聚类组合中,其沉积物中热液富集相关元素Cu、Zn、Fe和Co等。断桥区更高的生源元素含量可能指示其热液活动停止后,主要受生物沉积作用的影响,该区热液相关元素与基性围岩联系紧密,表现出Pb与W的明显富集。
中图分类号:
宋备, 苏新, 吕士辉, 倪建宇, 廖时理, 陶春辉, 胡茂康, 李世云, 于翀涵. 西南印度洋中脊活动与非活动热液区沉积物元素地球化学特征对比[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 130-140.
SONG Bei, SU Xin, LÜ Shihui, NI Jianyu, LIAO Shili, TAO Chunhui, HU Maokang, LI Shiyun, YU Chonghan. Geochemical Contrast in Sediments from Active and Inactive hydrothermal Fields on the Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(01): 130-140.
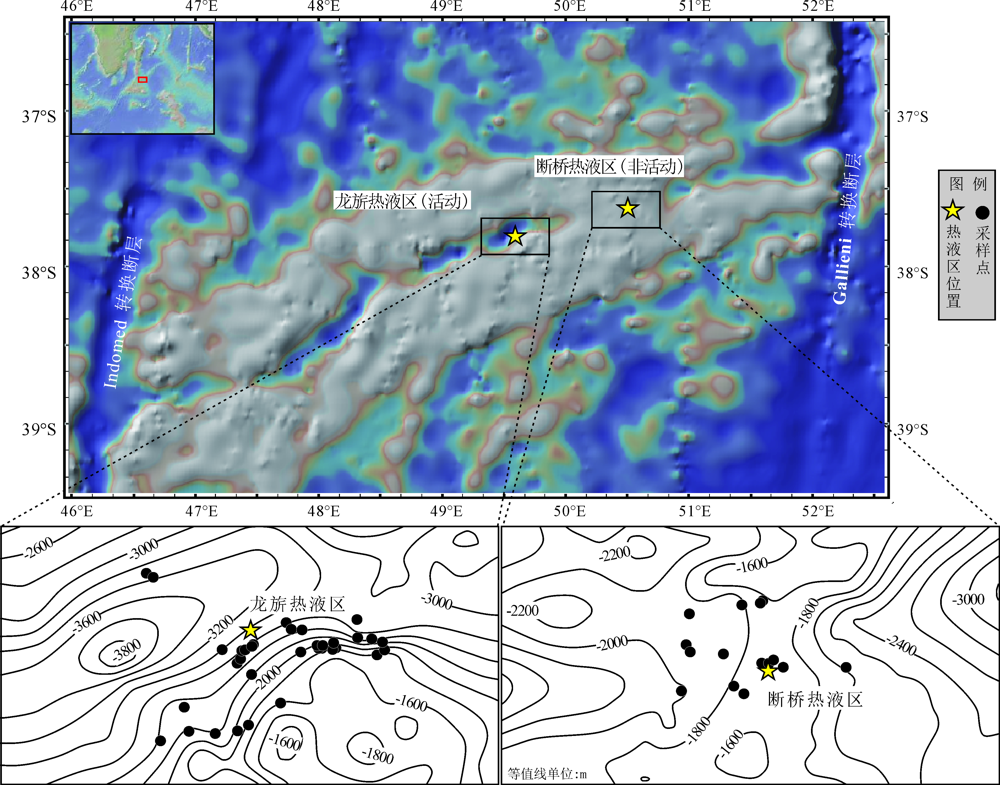
图1 研究区构造背景与样品位置分布图(热液区位置引自文献[6],构造底图来自于GeoMap App,水深与地形数据来自www.gebco.net)
Fig.1 Maps showing tectonic settings of the study area and locations of samples(location of the hydrothermal fields from reference [6], base map of geotectonic setting from GeoMap App, topographic data from www.gebco.net)
| 元素 | 龙旂热液区 | 断桥热液区 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 最大值 | 中位数 | 标准差 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 中位数 | 标准差 | ||
| SiO2 | 2.30 | 37.98 | 9.49 | 10.47 | 1.53 | 31.24 | 6.60 | 10.56 | |
| Al2O3 | 0.79 | 7.57 | 2.37 | 1.84 | 0.54 | 9.47 | 1.82 | 3.23 | |
| TFe2O3 | 0.61 | 9.03 | 2.05 | 2.57 | 0.29 | 7.84 | 1.21 | 2.78 | |
| MgO | 0.40 | 36.30 | 1.62 | 8.24 | 0.40 | 4.87 | 0.77 | 1.60 | |
| CaO | 2.01 | 50.03 | 43.24 | 13.26 | 25.42 | 53.05 | 47.61 | 9.49 | |
| Na2O | 0.41 | 2.10 | 1.46 | 0.29 | 0.92 | 2.59 | 1.40 | 0.48 | |
| K2O | 0.03 | 0.34 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.05 | |
| MnO | 0.03 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.06 | |
| TiO2 | 0.04 | 0.62 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.89 | 0.13 | 0.31 | |
| P2O5 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.03 | |
| Li | 2.57 | 12.05 | 6.35 | 2.04 | 3.33 | 11.10 | 4.58 | 1.86 | |
| Be | 0.03 | 0.44 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.51 | 0.15 | 0.12 | |
| V | 11.45 | 145.14 | 37.70 | 38.96 | 9.84 | 223.00 | 30.50 | 76.65 | |
| Cr | 0.11 | 1 814.70 | 37.70 | 477.80 | 6.02 | 153.00 | 17.50 | 47.33 | |
| Co | 6.10 | 125.00 | 19.80 | 26.50 | 6.76 | 152.00 | 27.70 | 38.15 | |
| Ni | 21.00 | 1 575.00 | 43.70 | 348.81 | 20.80 | 90.70 | 42.30 | 17.10 | |
| Cu | 19.87 | 1 238.00 | 69.40 | 213.56 | 9.67 | 148.00 | 31.60 | 38.05 | |
| Zn | 12.79 | 210.00 | 38.20 | 46.16 | 15.80 | 100.00 | 28.65 | 29.95 | |
| Sr | 101.00 | 1 694.00 | 1 239.00 | 418.12 | 658.45 | 1 540.00 | 1 248.00 | 263.45 | |
| Y | 1.52 | 25.80 | 13.40 | 4.37 | 5.53 | 30.10 | 12.25 | 7.04 | |
| Mo | 0.16 | 4.83 | 0.35 | 0.84 | 0.17 | 0.85 | 0.32 | 0.22 | |
| Cd | 0.03 | 0.70 | 0.26 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.72 | 0.30 | 0.15 | |
| Rb | 0.32 | 10.70 | 7.05 | 2.62 | 2.36 | 7.05 | 4.27 | 1.18 | |
| Cs | 0.02 | 0.84 | 0.39 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.49 | 0.25 | 0.09 | |
| Ba | 6.41 | 735.00 | 409.00 | 170.60 | 46.70 | 381.00 | 206.50 | 92.87 | |
| W | 0.19 | 289.00 | 10.40 | 46.82 | 0.26 | 323.00 | 29.80 | 85.20 | |
| Pb | 0.72 | 7.04 | 3.89 | 1.35 | 3.64 | 44.80 | 9.23 | 8.95 | |
| Th | 0.04 | 1.30 | 0.79 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 1.11 | 0.66 | 0.19 | |
| U | 0.16 | 2.06 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.14 | 0.52 | 0.28 | 0.09 | |
| Zr | 3.29 | 52.70 | 15.00 | 10.62 | 5.44 | 72.70 | 14.75 | 22.27 | |
| LREE | 1.80 | 37.10 | 24.65 | 7.27 | 16.23 | 45.58 | 23.22 | 8.13 | |
| HREE | 0.98 | 14.09 | 7.01 | 2.45 | 3.32 | 19.05 | 6.20 | 4.89 | |
| REE | 2.78 | 48.60 | 31.15 | 8.90 | 20.20 | 55.39 | 30.63 | 11.22 | |
| LREE/HREE | 1.35 | 4.63 | 3.46 | 0.91 | 1.59 | 5.26 | 3.94 | 1.13 | |
| (La/Yb | 0.72 | 6.59 | 3.95 | 1.63 | 1.06 | 7.54 | 4.25 | 1.84 | |
| δEu* | 0.74 | 1.25 | 1.03 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 4.85 | 0.22 | 1.31 | |
| δCe* | 0.51 | 1.23 | 0.58 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.12 | 0.05 | |
| C | -0.36 | 0.03 | -0.27 | 0.06 | -0.28 | 0.18 | -0.18 | 0.11 | |
表1 研究区沉积物样品主、微量元素测试结果统计
Table 1 Statistics of the element compositions of the sediment samples from the study area
| 元素 | 龙旂热液区 | 断桥热液区 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 最大值 | 中位数 | 标准差 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 中位数 | 标准差 | ||
| SiO2 | 2.30 | 37.98 | 9.49 | 10.47 | 1.53 | 31.24 | 6.60 | 10.56 | |
| Al2O3 | 0.79 | 7.57 | 2.37 | 1.84 | 0.54 | 9.47 | 1.82 | 3.23 | |
| TFe2O3 | 0.61 | 9.03 | 2.05 | 2.57 | 0.29 | 7.84 | 1.21 | 2.78 | |
| MgO | 0.40 | 36.30 | 1.62 | 8.24 | 0.40 | 4.87 | 0.77 | 1.60 | |
| CaO | 2.01 | 50.03 | 43.24 | 13.26 | 25.42 | 53.05 | 47.61 | 9.49 | |
| Na2O | 0.41 | 2.10 | 1.46 | 0.29 | 0.92 | 2.59 | 1.40 | 0.48 | |
| K2O | 0.03 | 0.34 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.05 | |
| MnO | 0.03 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.06 | |
| TiO2 | 0.04 | 0.62 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.89 | 0.13 | 0.31 | |
| P2O5 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.03 | |
| Li | 2.57 | 12.05 | 6.35 | 2.04 | 3.33 | 11.10 | 4.58 | 1.86 | |
| Be | 0.03 | 0.44 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.51 | 0.15 | 0.12 | |
| V | 11.45 | 145.14 | 37.70 | 38.96 | 9.84 | 223.00 | 30.50 | 76.65 | |
| Cr | 0.11 | 1 814.70 | 37.70 | 477.80 | 6.02 | 153.00 | 17.50 | 47.33 | |
| Co | 6.10 | 125.00 | 19.80 | 26.50 | 6.76 | 152.00 | 27.70 | 38.15 | |
| Ni | 21.00 | 1 575.00 | 43.70 | 348.81 | 20.80 | 90.70 | 42.30 | 17.10 | |
| Cu | 19.87 | 1 238.00 | 69.40 | 213.56 | 9.67 | 148.00 | 31.60 | 38.05 | |
| Zn | 12.79 | 210.00 | 38.20 | 46.16 | 15.80 | 100.00 | 28.65 | 29.95 | |
| Sr | 101.00 | 1 694.00 | 1 239.00 | 418.12 | 658.45 | 1 540.00 | 1 248.00 | 263.45 | |
| Y | 1.52 | 25.80 | 13.40 | 4.37 | 5.53 | 30.10 | 12.25 | 7.04 | |
| Mo | 0.16 | 4.83 | 0.35 | 0.84 | 0.17 | 0.85 | 0.32 | 0.22 | |
| Cd | 0.03 | 0.70 | 0.26 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.72 | 0.30 | 0.15 | |
| Rb | 0.32 | 10.70 | 7.05 | 2.62 | 2.36 | 7.05 | 4.27 | 1.18 | |
| Cs | 0.02 | 0.84 | 0.39 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.49 | 0.25 | 0.09 | |
| Ba | 6.41 | 735.00 | 409.00 | 170.60 | 46.70 | 381.00 | 206.50 | 92.87 | |
| W | 0.19 | 289.00 | 10.40 | 46.82 | 0.26 | 323.00 | 29.80 | 85.20 | |
| Pb | 0.72 | 7.04 | 3.89 | 1.35 | 3.64 | 44.80 | 9.23 | 8.95 | |
| Th | 0.04 | 1.30 | 0.79 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 1.11 | 0.66 | 0.19 | |
| U | 0.16 | 2.06 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.14 | 0.52 | 0.28 | 0.09 | |
| Zr | 3.29 | 52.70 | 15.00 | 10.62 | 5.44 | 72.70 | 14.75 | 22.27 | |
| LREE | 1.80 | 37.10 | 24.65 | 7.27 | 16.23 | 45.58 | 23.22 | 8.13 | |
| HREE | 0.98 | 14.09 | 7.01 | 2.45 | 3.32 | 19.05 | 6.20 | 4.89 | |
| REE | 2.78 | 48.60 | 31.15 | 8.90 | 20.20 | 55.39 | 30.63 | 11.22 | |
| LREE/HREE | 1.35 | 4.63 | 3.46 | 0.91 | 1.59 | 5.26 | 3.94 | 1.13 | |
| (La/Yb | 0.72 | 6.59 | 3.95 | 1.63 | 1.06 | 7.54 | 4.25 | 1.84 | |
| δEu* | 0.74 | 1.25 | 1.03 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 4.85 | 0.22 | 1.31 | |
| δCe* | 0.51 | 1.23 | 0.58 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.12 | 0.05 | |
| C | -0.36 | 0.03 | -0.27 | 0.06 | -0.28 | 0.18 | -0.18 | 0.11 | |

图3 研究区沉积物样品稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式图(球粒陨石标准化数据引自文献[48],玄武岩及橄榄岩数据引自文献[52],硫化物数据引自文献[53])
Fig.3 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of sediments samples from the study area (data of chondrite-normalization from reference [48], basalt and peridotite from reference [52], and sulfide from reference [53])

图4 研究区沉积物样品组分判别图(玄武岩数据引自文献[52]和[58],橄榄岩引自文献[52]和[59]) (a)Fe-Mg-Al判别图;(b)(Al+Ti)-Si/Al判别图
Fig.4 Discriminant results of compositions of sediment samples from the study area (data of basalt from references[52] and [58], peridotite from references [52] and [59])

图5 沉积物样品地球化学元素富集系数及各样品与已知最近热液点距离对比关系图
Fig.5 Plots of enrichment factor of geochemical elements for samples vs.distance from the proximal hydrothermal site
| [1] | BEAULIEU S E, BAKER E T, GERMAN C R, et al. An authoritative global database for active submarine hydrothermal vent fields[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2013,14(11):4892-4905. |
| [2] | BAKER E T, GERMAN C R. On the global distribution of hydrothermal vent fields[M] // GERMANCR. Mid-Ocean Ridges: Hydrothermal Interactions Between the Lithosphere and Oceans. Washington: American Geophysical Union, 2004: 245-266. |
| [3] | SINGER D A. Base and precious metal resources in seafloor massive sulfide deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014,59(6):66-72. |
| [4] | HANNINGTON M, JAMIESON J, MONECKE T, et al. The abundance of seafloor massive sulfide deposits[J]. Geology, 2011,39(12):1155-1158. |
| [5] | BEAULIEU S E, BAKER E T, GERMAN C R. Where are the undiscovered hydrothermal vents on oceanic spreading ridges?[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2015,121:202-212. |
| [6] | TAO C, LI H, JIN X, et al. Seafloor hydrothermal activity and polymetallic sulfide exploration on the southwest Indian ridge[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014,59(19):2266-2276. |
| [7] | COLLINS P C, CROOT P, CARLSSON J, et al. A primer for the environmental impact assessment of mining at seafloor massive sulfide deposits[J]. Marine Policy, 2013,42(14):198-209. |
| [8] | FITZSIMMONS J N, JOHN S G, MARSAY C M, et al. Iron persistence in a distal hydrothermal plume supported by dissolved-particulate exchange[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2017,10(3):195-201. |
| [9] | DIAS Á S, BARRIGA F J A S. Mineralogy and geochemistry of hydrothermal sediments from the serpentinite-hosted Saldanha hydrothermal field (36°34'N, 33°26'W) at MAR[J]. Marine Geology, 2006,225(1/4):157-175. |
| [10] | FEELY R A, LEWISON M, MASSOTH G J, et al. Composition and dissolution of black smoker particulates from active vents on the Juan de Fuca Ridge[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1987,92(11):11347-11363. |
| [11] | GERMAN C R, HIGGS N C, THOMSON J, et al. A geochemical study of metalliferous sediment from the TAG hydrothermal mound, 26°08'N, Mid-Atlantic Ridge[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1993,98(6):9683-9692. |
| [12] | SHEARME S, CRONAN D S, RONA P A. Geochemistry of sediments from the TAG hydrothermal field, M.A.R. at latitude 26° N[J]. Marine Geology, 1983,51(3):269-291. |
| [13] | COOGAN L A, ATTAR A, MIHALY S F, et al. Near-vent chemical processes in a hydrothermal plume: Insights from an integrated study of the Endeavour segment[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2017,18(4):1641-1660. |
| [14] | KUHN T, BURGER H, CASTRADORI D, et al. Volcanic and hydrothermal history of ridge segments near the Rodrigues Triple Junction (Central Indian Ocean) deduced from sediment geochemistry[J]. Marine Geology, 2000,169(3/4):391-409. |
| [15] | CAVE R R, GERMAN C R, THOMSON J, et al. Fluxes to sediments underlying the Rainbow hydrothermal plume at 36°14'N on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2002,66(11):1905-1923. |
| [16] | HUMPHRIS S E, KLEIN F. Progress in deciphering the controls on the geochemistry of fluids in seafloor hydrothermal systems[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2018,10:315-343. |
| [17] | HANNINGTON M D, DE RONDE C D J, PETERSEN S. Sea-floor tectonics and submarine hydrothermal systems[M] // HEDENQUISTJ W.Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume. Littelton: Society of Economic Geologists, 2005: 111-141. |
| [18] |
DICK H J B, LIN J, SCHOUTEN H. An ultraslow-spreading class of ocean ridge[J]. Nature, 2003,426:405-412.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] | CANNAT M, SAUTER D, BEZOS A, et al. Spreading rate, spreading obliquity, and melt supply at the ultraslow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2008,9(4):1-26. |
| [20] | BAKER E T, CHEN Y J, MORGAN J P. The relationship between near-axis hydrothermal cooling and the spreading rate of mid-ocean ridges[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1996,142(1):137-145. |
| [21] | GERMAN C R, BAKER E T, MEVEL C, et al. Hydrothermal activity along the southwest Indian ridge[J]. Nature, 1998,395:490-493. |
| [22] | BAKER E T, EDMONDS H N, MICHAEL P J, et al. Hydrothermal venting in magma deserts: The ultraslow-spreading Gakkel and Southwest Indian Ridges[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2004,5(8):1-29. |
| [23] | SNOW J E, EDMONDS H N. Ultraslow-spreading ridges: rapid paradigm changes[J]. Oceanography, 2007,20(1):90-101. |
| [24] | 陈圆圆, 于炳松, 苏新, 等. 西南印度洋中脊钙质沉积物地球化学及矿物学特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013,32(1):107-113. |
| [25] | 黄大松, 张霄宇, 张国堙, 等. 西南印度洋中脊48.6°~51.7°E沉积物地球化学特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016,35(1):22-29. |
| [26] | VALLIER T L, KIDD R B. Volcanogenic sediments in the Indian Ocean[M] //HEIRTZLERJR. Indian Ocean Geology and Biostratigraphy.Washington: American Geophysical Union, 1977: 87-118. |
| [27] | PATTAN J N, PRATIMAJAUHAR I. Major, trace, and rare earth elements in the sediments of the Central Indian Ocean Basin: Their source and distribution[J]. Marine Geotechnology, 2001,19(2):85-106. |
| [28] | KOLLA V, HENDERSON L, BISCAYE P E. Clay mineralogy and sedimentation in the western Indian Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research, 1976,23(10):949-961. |
| [29] | 林震, 于洪军, 徐兴永, 等. 西南印度洋中脊扩张轴部(34.9°S)西翼沉积物地球化学分析及物源探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018,38(5):14-29. |
| [30] | LI Z, CHU F, JIN L, et al. Major and trace element composition of surface sediments from the Southwest Indian Ridge: evidence for the incorporation of a hydrothermal component[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2016,35(2):101-108. |
| [31] | GERMAN C R. Hydrothermal activity on the eastern SWIR (50°-70°E): Evidence from core-top geochemistry, 1887 and 1998[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2003,4(7):1-13. |
| [32] | 曹凯君, 吴仲玮, 孙晓明, 等. 西南印度洋脊龙旂热液区富铝蚀变黏土矿物类型和地球化学特征研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018,37(6):607-617. |
| [33] | LIAO S, TAO C, LI H, et al. Surface sediment geochemistry and hydrothermal activity indicators in the Dragon Horn area on the Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Marine Geology, 2018,398:22-34. |
| [34] | 贾琦, 范德江, 张文强, 等. 西南印度洋中脊表层沉积物中硫化物矿物学特征与地质意义[J]. 矿物学报, 2017,37(6):725-736. |
| [35] | PAN A, YANG Q, ZHOU H, et al. Geochemical impacts of hydrothermal activity on surface deposits at the Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2018,139:1-13. |
| [36] | LIAO S, TAO C, DIAS Á A, et al. Surface sediment composition and distribution of hydrothermal derived elements at the Duanqiao-1 hydrothermal field, Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Marine Geology, 2019,416:105975. |
| [37] | DYMOND J. Geochemistry of Nazca plate surface sediments: An evaluation of hydrothermal, biogenic, detrital, and hydrogenous sources[J]. Geological Society of America Memoirs, 1981,154:133-174. |
| [38] | MARCHIG V, GUNDLACH H, MÖLLER P, et al. Some geochemical indicators for discrimination between diagenetic and hydrothermal metalliferous sediments[J]. Marine Geology, 1982,50(3):241-256. |
| [39] | KEITH M, HÄCKEL F, HAASE K M, et al. Trace element systematics of pyrite from submarine hydrothermal vents[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016,72:728-745. |
| [40] | TAO C, LIN J, GUO S, et al. First active hydrothermal vents on an ultraslow-spreading center: Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Geology, 2012,40(1):47-50. |
| [41] | ZHAO M, QIU X, LI J, et al. Three-dimensional seismic structure of the Dragon Flag oceanic core complex at the ultraslow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge (49°39'E)[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2013,14(10):4544-4563. |
| [42] | 叶俊, 石学法, 杨耀民, 等. 西南印度洋超慢速扩张脊49.6°E热液区硫化物矿物学特征及其意义[J]. 矿物学报, 2011,31(1):17-29. |
| [43] | JI F, ZHOU H, YANG Q, et al. Geochemistry of hydrothermal vent fluids and its implications for subsurface processes at the active Longqi hydrothermal field, Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2017,122:41-47. |
| [44] | 杨伟芳. 西南印度洋中脊断桥热液区成矿作用研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2017. |
| [45] | 张俊, 李余生, 林曼利, 等. 淮南张集矿水文地球化学特征及水源识别[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2014,41(6):32-37. |
| [46] | 安艳玲, 蒋浩, 吴起鑫, 等. 赤水河流域枯水期水环境质量评价研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2014,23(10):1472-1478. |
| [47] | 庄作钦. B0X PLOT——描述统计的一个简便工具[J]. 统计与预测, 2003(2):56-57. |
| [48] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publication, 1989,42(1):313-345. |
| [49] | HASKIN L A, HASKIN M A, FREY F A, et al. Relative and absolute terrestrial abundances of the rare earths[M] //AHERENS L H.Origin and Distribution of the Elements. Oxford:Pergamon Press, 1968: 889-912. |
| [50] | WRIGHT J, SCHRADER H, HOLSER W T. Paleoredox variations in ancient oceans recorded by rare earth elements in fossil apatite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987,51(3):631-644. |
| [51] | ELDERFIELD H, GREAVES M J. The rare earth elements in seawater[J]. Nature, 1982,296:214-219. |
| [52] | 韩宗珠, 张贺, 范德江, 等. 西南印度洋中脊50°E基性超基性岩石地球化学特征及其成因初探[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2012,42(9):69-76. |
| [53] | CAO Z, CAO H, TAO C, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of hydrothermal deposits from Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2012,31(2):62-69. |
| [54] | TOYODA K, MASUDA A. Sedimentary environments and chemical composition of Pacific pelagic sediments[J]. Chemical Geology, 1990,88(1):127-141. |
| [55] | 朱赖民, 高志友, 尹观, 等. 南海表层沉积物的稀土和微量元素的丰度及其空间变化[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(11):2963-2980. |
| [56] | MCMANUS J, BERELSON W M, KLINKHAMMER G P, et al. Geochemistry of barium in marine sediments: implications for its use as a paleoproxy[J]. Geochimistry et Cosmochimistry Acta, 1998,62(21/22):3453-3473. |
| [57] | PLANK T, LANGMUIR C H. The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle[J]. Chemical Geology, 1998,145(3):325-394. |
| [58] | 于淼, 苏新, 陶春辉, 等. 西南印度洋中脊49.6°E和50.5°E区玄武岩岩石学及元素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2013,27(3):497-508. |
| [59] | 陈灵. 西南印度洋中脊橄榄岩元素地球化学及其地幔动力学意义[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2016. |
| [60] | BLOEMSMA M R, ZABEL M, STUUT J B W, et al. Modeling the joint variability of grain size and chemical composition in sediments[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2012,280:135-148. |
| [61] | DYMOND J. Geochemistry of Nazca Plate surface sediments: An evaluation of hydrothermal, biogenic, detrital and hydrogeneous sources[J]. Geological Society of America Memoirs, 1981,154(12):133-173. |
| [62] | RAY D, BANERJEE R, IYER S D, et al. Glass and mineral chemistry of northern central Indian Ridge basalts: compositional diversity and petrogenetic significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009,83(6):1122-1135. |
| [63] | CRONAN D S, HODKINSON R, MOORBY S A, et al. Hydrothermal and volcaniclastic sedimentation on the Tonga-Kermadec Ridge and in its adjacent marginal basins[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1984,16(1):137-149. |
| [64] | HEATH G R, DYMOND J. Genesis and transformation of metalliferous sediments from the East Pacific Rise, Bauer Deep, and Central Basin, northwest Nazca plate[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1977,88(5):723-733. |
| [65] | DYMOND J, CORLISS J B, HEATH G R, et al. Origin of metalliferous sediments from the Pacific Ocean[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1973,84(10):3355-3372. |
| [66] | WANYINGLI M, AHMADZAHARINARI S, ISMAIL T H. Spatial geochemical distribution and sources of heavy metals in the sediment of Langat River, Western Peninsular Malaysia[J]. Environmental Forensics, 2013,14(2):133-145. |
| [67] | SULTAN K, SHAZILI N A. Geochemical baselines of major, minor and trace elements in the tropical sediments of the Terengganu River basin, Malaysia[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research, 2010,25(4):340-354. |
| [68] | WEDEPOHL K H. The composition of the continental crust[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 1994,58(7):1217-1232. |
| [69] | BOSTROEM K, KRAEMER T, GARTNER S. Provenance and accumulation rates of opaline silica, Al, Ti, Fe, Mn, Cu, Ni and Co in Pacific pelagic sediments[J]. Chemical Geology, 1973,11(2):123-148. |
| [70] | MÜNCH U, LALOU C, HALBACH P, et al. Relict hydrothermal events along the super-slow Southwest Indian spreading ridge near 63°56'E-mineralogy, chemistry and chronology of sulfide samples[J]. Chemical Geology, 2001,177(3):341-349. |
| [71] | MÜNCH U, HALBACH P, FUJIMOTO H. Sea-floor hydrothermal mineralization from the Mt. Jourdanne, Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. JAMSTEC Journal of Deep Sea Research, 2000,16:125-132. |
| [72] | 李伟, 王建新. R型聚类分析在确定成矿岩体中的应用——以延边复兴—杜荒岭金矿化集中区为例[J]. 世界地质, 2003,22(2):147-151. |
| [1] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [2] | 张伟, 安茂国, 王志鹏, 杨启, 陈怀鑫, 马晓峰, 支成龙, 邢其涛, 裴长世, 王娜, 刘铭. 青海省那陵格勒河中游地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿远景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 690-707. |
| [3] | 梁东, 华北, 赵德怀, 吴浩, 万生楠, 谭朝欣, 赵晓健, 杨志鹏. 喀喇昆仑麦拉山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征与找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 708-721. |
| [4] | 陈世明, 杨镇熙, 雷自强, 康维良, 张晶, 赵青虎. 甘肃北山前红泉地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1513-1524. |
| [5] | 王斌, 任涛, 宋伊圩, 杨可, 王占彬, 孙亚柯. 西秦岭常家山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 911-922. |
| [6] | 朱英海, 施泽明, 王新宇, 张凯亮, 朱伯丞. 攀西大梁子铅锌矿区水系沉积物重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 923-932. |
| [7] | 白翔宇, 马郡伟, 夏清萍, 谭先锋, 李开开. 北京西山下苇甸第三统/芙蓉统界线附近碳酸盐岩地球化学特征及古环境意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 729-741. |
| [8] | 孙爽, 胡克, 李琰, 杨俊鹏. 我国沿海不同气候带山溪性河流沉积物输运特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 68-76. |
| [9] | 远继东, 姜正龙, 代友旭, 郝连成, 张健康, 张德程, 郑立龙. 湛江湾海域表层沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 77-87. |
| [10] | 王雪木, 瞿洪宝, 熊元凯, 吕琳, 胡克. 海南昌化江入海口底表沉积物粒度特征及输运趋势[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 88-95. |
| [11] | 魏定邦, 杨强, 夏建新. 深海沉积物贯入阻力影响因素及其变化规律[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1871-1879. |
| [12] | 黄清华, 席党鹏, 王辉, 张文婧, 王建伟, 曹维福, 贾卧, 王丽静. 松辽盆地北部中二叠统碳酸盐岩元素和稳定同位素地球化学特征与古环境[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1282-1295. |
| [13] | 李超, 罗先熔, 邱炜, 王宇慧, 赵欣怡, 郑超杰, 刘攀峰. 青海省都兰县金水口地区水系沉积物地球化学异常特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1397-1410. |
| [14] | 李金哲, 刘宁强, 龚庆杰, 李承柱. 广东汕头市内海湾沉积物重金属环境质量调查与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1441-1449. |
| [15] | 赵保具, 颜开, 肖荣阁. 一种稀土参数图解新方法:以内蒙古拜仁达坝-维拉斯托闪长岩成因研究为例[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 608-624. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||