



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (01): 104-116.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.009
滕田田1,2( ), 苏新1,2(
), 苏新1,2( ), 刘浩东1,2, 崔鸿鹏1,2, 陈芳3, 程思海3, 杨胜雄3, 王宏斌3, 梁金强3, 苏丕波3
), 刘浩东1,2, 崔鸿鹏1,2, 陈芳3, 程思海3, 杨胜雄3, 王宏斌3, 梁金强3, 苏丕波3
收稿日期:2019-07-30
修回日期:2019-10-20
出版日期:2020-03-05
发布日期:2020-03-07
通讯作者:
苏新
作者简介:苏 新,女,教授,博士生导师,1957年出生,微体古生物和海洋地质专业,主要从事微体古生物、海洋地质和天然气水合物调查与研究。Email: xsu@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
TENG Tiantian1,2( ), SU Xin1,2(
), SU Xin1,2( ), LIU Haodong1,2, CUI Hongpeng1,2, CHEN Fang3, CHENG Sihai3, YANG Shengxiong3, WANG Hongbin3, LIANG Jinqiang3, SU Pibo3
), LIU Haodong1,2, CUI Hongpeng1,2, CHEN Fang3, CHENG Sihai3, YANG Shengxiong3, WANG Hongbin3, LIANG Jinqiang3, SU Pibo3
Received:2019-07-30
Revised:2019-10-20
Online:2020-03-05
Published:2020-03-07
Contact:
SU Xin
摘要:
中国南海东沙一带冷泉发育,但目前国内外对深海冷泉区微生物研究甚少,特别是缺乏利用高通量测序的记录。对东沙深海冷泉区973-5站位(该站位水深约3 000 m)长约935 cm的重力岩心进行了高通量分析。结果显示:该站位微生物细胞丰度为5.3×108~34.0×108个/g,随深度变深而增加,其变化趋势与甲烷含量变化可对比,与粒度、有机碳的变化也具有相关性。测序结果显示,岩心中主要古菌类群是MBGB(39.9%)、C3(15.8%)以及ANME-1(12.0%),随着深度的变化群落组成有所改变。硫酸盐-甲烷界面(SMI,760 cm)上下出现了大量的MBGB和ANME-1类群,pH也不断增加,暗示了这一区域存在不断增强的甲烷厌氧氧化作用。岩心底部出现了一定量的ANME-1和ANME-2类群,暗示除了在SMI附近甲烷氧化和硫酸盐还原反应强烈,其下部可能还有水合物的分解与甲烷的上涌,为ANME类群生存提供了营养物质。与东沙海区其他站位相比,973-5站位的甲烷通量较高,但没有发现产甲烷菌,推测该区沉积物中高浓度的甲烷来源为周边浅部或深部断裂系统运移供给。
中图分类号:
滕田田, 苏新, 刘浩东, 崔鸿鹏, 陈芳, 程思海, 杨胜雄, 王宏斌, 梁金强, 苏丕波. 南海东沙深海冷泉区973-5重力柱沉积物古菌多样性[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 104-116.
TENG Tiantian, SU Xin, LIU Haodong, CUI Hongpeng, CHEN Fang, CHENG Sihai, YANG Shengxiong, WANG Hongbin, LIANG Jinqiang, SU Pibo. Archaeal Diversity in Sediments of Core 973-5 from Deep-sea old Seep,Dongsha Area in South China Sea[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(01): 104-116.
| 样品编号 | 深度/cm | 样品编号 | 深度/cm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 973-5-1 | 20 | 973-5-11 | 560 |
| 973-5-2 | 70 | 973-5-12 | 610 |
| 973-5-3 | 90 | 973-5-13 | 660 |
| 973-5-4 | 145 | 973-5-14 | 715 |
| 973-5-5 | 195 | 973-5-15 | 755 |
| 973-5-6 | 245 | 973-5-16 | 795 |
| 973-5-7 | 295 | 973-5-17 | 800 |
| 973-5-8 | 395 | 973-5-18 | 805 |
| 973-5-9 | 460 | 973-5-19 | 855 |
| 973-5-10 | 510 | 973-5-20 | 915 |
表1 973-5岩心微生物样品取样编号及对应深度
Table 1 Sample number and corresponding depth of microbial samples in core 973-5
| 样品编号 | 深度/cm | 样品编号 | 深度/cm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 973-5-1 | 20 | 973-5-11 | 560 |
| 973-5-2 | 70 | 973-5-12 | 610 |
| 973-5-3 | 90 | 973-5-13 | 660 |
| 973-5-4 | 145 | 973-5-14 | 715 |
| 973-5-5 | 195 | 973-5-15 | 755 |
| 973-5-6 | 245 | 973-5-16 | 795 |
| 973-5-7 | 295 | 973-5-17 | 800 |
| 973-5-8 | 395 | 973-5-18 | 805 |
| 973-5-9 | 460 | 973-5-19 | 855 |
| 973-5-10 | 510 | 973-5-20 | 915 |
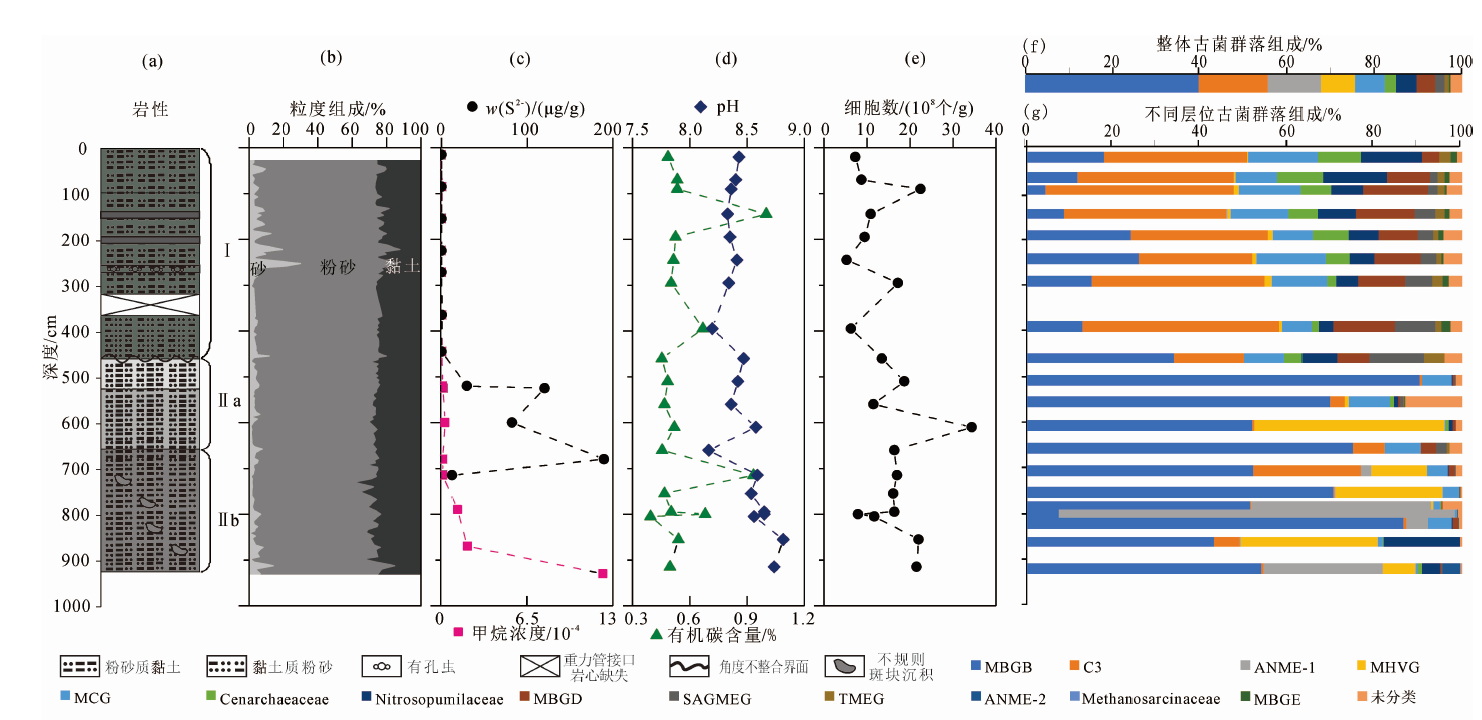
图2 973-5站位岩心岩性、地球化学参数、细胞丰度及古菌类群在不同深度的分布 (a)岩性柱及分段; (b)岩心中砂、 粉砂、黏土的百分含量; (c)岩心甲烷浓度和S2-质量分数随深度的变化; (d)岩心pH和总有机碳含量随深度的变化; (e)岩心中细胞 个数随深度的变化;(f)岩心古菌类群组成; (g)岩心中古菌类群在不同深度的分布 缩写(Abbreviations) : ANME, Anaerobic Methanotrophs; C3, C3 Group; MBGB/D/E, Marine Benthic Group B/D/E; MCG, Miscellaneous Crenarchaeotic Group; MHVG, Marine Hydrother-mal Vent Group; SAGMEG, South Africa Gold Mine Crenarchaeotic Group; TMEG, Terrestrial Miscellaneous Euryarchaeotal Group
Fig.2 Profile of lithology, geochemical paraments, cell abundance and distribution of archaeal communities of core 973-5.

图5 基于Bray-Curtis距离的各深度古菌类群非度量多尺度(NMDS)分析
Fig.5 Non-metric multi-dimensional scaling (NMDS) analysis of archaeal groups in different depths based on Bray-Curtis Similarity
| 参数 | 相关性/显著性 | 深度 | 总有机 碳含量 | 细胞 个数 | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 深度 | Pearson相关性 | 1 | |||
| 显著性(双侧) | |||||
| 有机碳 含量 | Pearson相关性 | -0.125 | 1 | ||
| 显著性(双侧) | 0.598 | ||||
| 细胞个 数 | Pearson相关性 | 0.376 | -0.132 | 1 | |
| 显著性(双侧) | 0.102 | 0.578 | |||
| pH | Pearson相关性 | 0.650** | -0.034 | 0.386 | 1 |
| 显著性(双侧) | 0.002 | 0.887 | 0.093 |
表3 973-5站位深度、总有机碳含量、微生物细胞丰度、pH间相关系数
Table 3 Correlation coefficients in depth, TOC content, cell abundance and pH of core 973-5
| 参数 | 相关性/显著性 | 深度 | 总有机 碳含量 | 细胞 个数 | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 深度 | Pearson相关性 | 1 | |||
| 显著性(双侧) | |||||
| 有机碳 含量 | Pearson相关性 | -0.125 | 1 | ||
| 显著性(双侧) | 0.598 | ||||
| 细胞个 数 | Pearson相关性 | 0.376 | -0.132 | 1 | |
| 显著性(双侧) | 0.102 | 0.578 | |||
| pH | Pearson相关性 | 0.650** | -0.034 | 0.386 | 1 |
| 显著性(双侧) | 0.002 | 0.887 | 0.093 |
| 站位 | 水深/m | 细胞丰度/(106个/g) | 有机碳含量/% | 甲烷浓度/(μmol/l) | 甲烷含量/(μl/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 973-5(本文) | 2 998 | 530~3 400 | 0.4~1.0 | 311.7~76 633.6 | 2.93~721.26 |
| CL11[ | 1 607 | 21.3~104.7 | 0.8~1.2 | - | 0~1 400 |
| DSH-1[ | 3 009 | 0.5~9.6 | 0.5~0.8 | 1.59~20.34 | - |
| GMGS2-08[ | 798 | 515~2 135 | 0.5~1.5 | 0~39 300 | - |
表4 东沙973-5、CL11、DSH-1站位微生物细胞丰度(AODC法)、总有机碳含量、甲烷浓度、甲烷含量的对比
Table 4 Cell abundance (AODC method), TOC content, concentration of methane, content of methane in core 973-5, CL11, DSH-1 in Dongsha area
| 站位 | 水深/m | 细胞丰度/(106个/g) | 有机碳含量/% | 甲烷浓度/(μmol/l) | 甲烷含量/(μl/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 973-5(本文) | 2 998 | 530~3 400 | 0.4~1.0 | 311.7~76 633.6 | 2.93~721.26 |
| CL11[ | 1 607 | 21.3~104.7 | 0.8~1.2 | - | 0~1 400 |
| DSH-1[ | 3 009 | 0.5~9.6 | 0.5~0.8 | 1.59~20.34 | - |
| GMGS2-08[ | 798 | 515~2 135 | 0.5~1.5 | 0~39 300 | - |
| [1] | PARKES R J, CRAGG B, ROUSSEL E. A review of prokaryotic populations and processes in sub-seafloor sediments, including biospherei geosphere interactions[J]. Marine Geology, 2014,352:409-425. |
| [2] | KALLMEYER J, POCKALNY R, ADHIKARI R R, et al. Global distribution of microbial abundance and biomass in subseafloor sediment[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 2012,109(4):16213. |
| [3] | 苏新, 陈芳, 张勇, 等. 海洋天然气水合物勘查和识别新技术:地质微生物技术[J]. 现代地质, 2010,24(3):409-423. |
| [4] | 承磊, 郑珍珍, 王聪, 等. 产甲烷古菌研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 2016,43(5):1143-1164. |
| [5] | 李曙光, 皮呁丹, ZHANG Chuanlun. 古菌研究及其展望[J]. 中国科学技术大学学报, 2007,37(8):830-838. |
| [6] | 邬黛黛, 吴能友, 张美, 等. 东沙海域SMI与甲烷通量的关系及对水合物的指示[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2013,38(6):1309-1320. |
| [7] | 陈健, 申屠佳丽, 殷峻, 等. 甲烷厌氧氧化及其微生物特性研究进展[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2018,40(2):222-229. |
| [8] | 向荣, 刘芳, 陈忠, 等. 冷泉区底栖有孔虫研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2010,25(2):193-202. |
| [9] | ZHANG C L, LANOIL B. Geomicrobiology and biogeochemistry of gas hydrates and cold seeps[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004,205:187-194. |
| [10] | 罗敏, 王宏斌, 杨胜雄, 等. 南海天然气水合物研究进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2013,32(1):56-69. |
| [11] | 于兴河, 王建忠, 梁金强, 等. 南海北部陆坡天然气水合物沉积成藏特征[J]. 石油学报, 2014,35(2):253-264. |
| [12] | 苏新, 陈芳, 魏士平, 等. 南海北部冷泉区沉积物中微生物丰度与甲烷浓度变化关系的初步研究[J]. 现代地质, 2007,21(1):101-104. |
| [13] | JIANG H, DONG H, JI S, et al. Microbial diversity in the deep marine sediments from the Qiongdongnan Basin in South China Sea[J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2007,24(6):505-517. |
| [14] | JIAO L, SU X, WANG Y, et al. Microbial diversity in the hydrate-containing and-free surface sediments in the Shenhu area, South China Sea[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2015,6(4):627-633. |
| [15] | YANG Y, LEI H, SHI C. The indicative effect of structures of archaeal communities at deep-water sediment cores on natural gas hydrate: A case study from Station 973-4 in the Southwest Taiwan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015,2(6):542-547. |
| [16] | ZHANG Y, SU X, CHEN F, et al. Microbial diversity in cold seep sediments from the northern South China Sea[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2012,3(3):301-316. |
| [17] | 黄怡, 王淑红, 颜文, 等. 南海北部东沙海域天然气水合物分解事件及其与海底滑塌的关系[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018,37(4):61-69. |
| [18] | 林安均. 南海北部西沙和东沙海区浅表层沉积物孔隙水地球化学特征及对天然气水合物成矿的指示意义[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2014. |
| [19] | 曲莹. 南海北部陆坡冷泉区晚更新世以来底栖有孔虫与甲烷喷溢[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013. |
| [20] | 刘浩东. 南海北部陆坡冷泉和非冷泉沉积物古菌多样性研究[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013. |
| [21] |
BOLYEN E, RIDEOUT J R, DILLON M R, et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019,37(8):852-857.
URL PMID |
| [22] | 史春潇. 南海北部天然气水合物潜在区微生物群落结构特征及对天然气水合物的指示意义[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2014. |
| [23] | 张必东, 邬黛黛, 吴能友. 南海北部东沙海域沉积物地球化学特征及其反映的冷泉活动[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2015,31(9):14-27. |
| [24] | 吴忆宁, 梅娟, 沈耀良. 甲烷厌氧氧化机理及其应用研究进展[J]. 生态科学, 2018,37(4):231-240. |
| [25] | AQUILINA A, KNAB N J, KNITTEL K, et al. Biomarker indicators for anaerobic oxidizers of methane in brackish-marine sediments with diffusive methane fluxes[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2010,41(4):414-426. |
| [26] | MERKEL A Y, HUBER J A, CHERNYH N A, et al. Detection of putatively thermophilic anaerobic methanotrophs in diffuse hydrothermal vent fluids[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2013,79(3):915-923. |
| [27] | SCHUBERT C J, COOLEN M J L, NERETIN L N, et al. Aerobic and anaerobic methanotrophs in the Black Sea water column[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2006,8(10):1844-1856. |
| [28] | HARRISON B K, ZHANG H, BERELSON W, et al. Variations in archaeal and bacterial diversity associated with the sulfate-methane transition zone in continental margin sediments (Santa Barbara Basin, California)[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2009,75(6):1487-1499. |
| [29] | MASON O U, CASE D H, NAEHR T H, et al. Comparison of archaeal and bacterial diversity in methane seep carbonate nodules and host sediments, Eel River Basin and Hydrate Ridge, USA[J]. Microbial Ecology, 2015,70(3):766-784. |
| [30] | SCHELLER S, YU H, CHADWICK G L, et al. Artificial electron acceptors decouple archaeal methane oxidation from sulfate reduction[J]. Science, 2016,351:703-707. |
| [31] | PACHIADAKI M G, LYKOUSIS V, STEFANOU E G, et al. Prokaryotic community structure and diversity in the sediments of an active submarine mud volcano (Kazan mud volcano, East Mediterranean Sea)[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2010,72(3):429-444. |
| [32] | AOKI M, EHARA M, SAITO Y, et al. A long-term cultivation of an anaerobic methane-oxidizing microbial community from deep-sea methane-seep sediment using a continuous-flow bioreactor[J]. PloS one, 2014,9(8):105356. |
| [33] | CUI H, SU X, CHEN F, et al. Microbial diversity of two cold seep systems in gas hydrate-bearing sediments in the South China Sea[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2019,144:230-239. |
| [34] | ROSENBERG E, DELONG E F, LORY S, et al. The Prokaryotes: Prokaryotic Communities and Ecophysiology[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2013: 123-138. |
| [35] | HE Y, LI M, PERUMAL V, et al. Genomic and enzymatic evidence for acetogenesis among multiple lineages of the archaeal phylum Bathyarchaeota widespread in marine sediments[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2016,1(3):16035. |
| [36] | JUNG M, ISLAM M A, GWAK J, et al. Nitrosarchaeum koreense gen. nov., sp. nov., an aerobic and mesophilic, ammonia-oxidizing archaeon member of the phylum thaumarchaeota isolated from agricultural soil[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2018,68(10):3084-3095. |
| [37] | 张勇, 苏新, 陈芳, 等. 南海北部陆坡神狐海域HS-373PC岩心表层沉积物古菌多样性[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2010,28(3):318-324. |
| [38] | 焦露, 苏新, 陈芳, 等. 南海北部陆坡神狐海域HS-PC500岩心微生物多样性[J]. 微生物学报, 2011,51(7):876-890. |
| [39] | TESKE A, SØRENSEN K B. Uncultured archaea in deep marine subsurface sediments: Have we caught them all?[J]. The ISMEJournal, 2008,2(1):3-18. |
| [40] |
INAGAKI F, NUNOURA T, NAKAGAWA S, et al. Biogeographical distribution and diversity of microbes in methane hydrate-bearing deep marine sediments on the Pacific ocean margin[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006,103(8):2815-2820.
URL PMID |
| [41] | 吴自军, 周怀阳, 彭晓彤. 珠江口桂山岛沉积物甲烷厌氧氧化作用研究[J]. 自然科学进展, 2007,17(7):905-912. |
| [42] | CUI H, SU X, CHEN F, et al. Vertical distribution of archaeal communities in cold seep sediments from the Jiulong methane reef area in the South China Sea[J]. Bioscience Journal, 2016,21(4):1059-1068. |
| [43] |
REED D W, FUJITA Y, DELWICHE M E, et al. Microbial communities from methane hydrate-bearing deep marine sediments[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2002,68(8):3759-3770.
URL PMID |
| [44] | 杨玉峰, 雷怀彦, 史春潇. 南海北部天然气水合物潜在区973-3岩心古菌多样性[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016,37(3):415-421. |
| [45] | 王长昆. 南海东沙晚更新世深水沉积物的磁性特征及其环境意义[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013. |
| [46] | 龚跃华, 吴时国, 张光学, 等. 南海东沙海域天然气水合物与地质构造的关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008,28(1):99-104. |
| [1] | 胡永浩, 段星星, 夏昭德, 韩宝华. 玉米根际土壤细菌群落对不同程度镉污染的响应: 以甘肃省白银市四龙镇地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 758-766. |
| [2] | 刘一林, 李灿苹, 勾丽敏, 汪洪涛, 曾宪军, 陈凤英, 郭子豪, 田鑫裕. 冷泉羽状流地震波场频谱特征与气含量关系研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 172-181. |
| [3] | 聂云峰, 于晶, 陈宏文, 万玲, 范广慧, 房强, 吴怀春. 北极斯瓦尔巴特群岛及邻区天然气水合物分解对气候、海洋环境和生物的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 1012-1024. |
| [4] | 袁建飞, 邓国仕, 徐芬, 唐业旗, 李鹏岳. 川西南喜德热田地下水水文地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(01): 200-208. |
| [5] | 李月娇,苏新,祝有海,卢振权,魏士平,崔鸿鹏,李来鹏,刘晖,张帅. 祁连山水合物分布区不同高寒生态类型冬季表层土壤中古菌群落及变化特征[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(5): 1047-1060. |
| [6] | 王淑红, 颜文, 陈忠. 海底冷泉系统中的钙同位素示踪研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(3): 589-597. |
| [7] | 黄华谷, 邸鹏飞, 陈莹莹, 冯东, 陈多福. 意大利亚平宁地区第三纪中新世“Calcari a Lucina”冷泉碳酸盐岩中结晶扇的沉积岩石学及地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(3): 545-551. |
| [8] | 栾锡武, 刘鸿, 岳保静. 海底冷泉在旁扫声纳图像上的识别[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(3): 474-480. |
| [9] | 郭依群, 李桂菊, 乔少华, 庄新国. 南中国海东沙海域水合物成藏动力学模拟[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(3): 457-462. |
| [10] | 苏新,陈芳,陆红锋,黄永样. 南海北部深海甲烷冷泉自生碳酸盐岩显微结构特征与流体活动关系初探[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(3): 376-381. |
| [11] | 陈忠,杨华平,黄奇瑜,颜文,陆钧. 南海东沙西南海域冷泉碳酸盐岩特征及其意义[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(3): 382-389. |
| [12] | 冯东, 陈多福. 黑海西北部冷泉碳酸盐岩的沉积岩石学特征及氧化还原条件的稀土元素地球化学示踪[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(3): 390-396. |
| [13] | 龚建明,张敏,陈建文,李谨,陈立英,成海燕. 天然气水合物发现区和潜在区气源成因[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(3): 415-419. |
| [14] | 苏新, 陈芳,魏士平,张勇,程思海等. 南海北部冷泉区沉积物中微生物丰度与甲烷浓度变化关系的初步研究[J]. 现代地质, 2007, 21(1): 101-104. |
| [15] | 张光学,祝有海,梁金强,吴时国,杨木壮,沙志彬. 构造控制型天然气水合物矿藏及其特征[J]. 现代地质, 2006, 20(4): 605-612. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||