



Geoscience ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (03): 648-659.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.037
• Observation Simulation and Prediction Evaluation of Superbiotic Resources • Previous Articles Next Articles
JI Yang1,2( ), BA Renji1(
), BA Renji1( ), XIAO Chengzhi3, LIU Lei1, ZHOU Xueni1,2, CAO Yating1
), XIAO Chengzhi3, LIU Lei1, ZHOU Xueni1,2, CAO Yating1
Online:2024-06-10
Published:2024-07-04
CLC Number:
JI Yang, BA Renji, XIAO Chengzhi, LIU Lei, ZHOU Xueni, CAO Yating. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Assessment of Ecological and Geological Environment Safety in the Upper Reaches of the Minjiang River from 1995 to 2020[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(03): 648-659.
| 数据名称 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|
| DEM | 地理空间数据云( |
| Landsat | 美国地质勘探局( |
| 土地利用(1995年、2001年、2009年、2020年) | 中国逐年土地覆盖数据集(annual China Land Cover Dataset, CLCD) |
| 潜在蒸散发(1995年、2001年、2009年、2020年) | 国家青藏高原科学数据中心( |
| 降雨(1995年、2001年、2009年、2020年) | 中国科学数据网( |
| 人口密度、人均GDP(1995年、2001年、2009年、2020年) | 四川统计年鉴 |
| 地层岩性与地质构造、地质灾害 | 岷江流域地质灾害详细调查成果集成报告 |
| 地下水富水性 | 四川省汶川县(茂县、黑水县、松潘县、理县)大骨病区地下水调查与供水安全示范打井工程报告 |
| 土壤类型 | 2019年四川省耕地等别数据 |
Table 1 Data information and sources
| 数据名称 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|
| DEM | 地理空间数据云( |
| Landsat | 美国地质勘探局( |
| 土地利用(1995年、2001年、2009年、2020年) | 中国逐年土地覆盖数据集(annual China Land Cover Dataset, CLCD) |
| 潜在蒸散发(1995年、2001年、2009年、2020年) | 国家青藏高原科学数据中心( |
| 降雨(1995年、2001年、2009年、2020年) | 中国科学数据网( |
| 人口密度、人均GDP(1995年、2001年、2009年、2020年) | 四川统计年鉴 |
| 地层岩性与地质构造、地质灾害 | 岷江流域地质灾害详细调查成果集成报告 |
| 地下水富水性 | 四川省汶川县(茂县、黑水县、松潘县、理县)大骨病区地下水调查与供水安全示范打井工程报告 |
| 土壤类型 | 2019年四川省耕地等别数据 |
| 指标 | 指标等级 | 指标说明 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| 高程(m) | <1500 | 1500~2000 | 2000~2500 | 2500~3000 | >3000 | 随着海拔的升高,空气变得寒冷干燥,对植物生长造成相应影响。研究区地形起伏度变化明显,区域植被垂向分布显著 | |
| 坡向(°) | 135~225 | 225~315 | 315~360 | 45~135 | 0~45 | 坡向影响山地日照时数和太阳辐射强度。研究区阳坡、半阳坡灌丛草甸发育,阴坡、半阴坡森林茂密,植被生长受坡向影响较大 | |
| 坡度(°) | >35 | 25~35 | 15~25 | 8~15 | 0~8 | 坡度决定着地表侵蚀作用的强度,影响水土流失强度、土层厚度以及土壤肥力。研究区谷坡陡峻,重力地质作用强烈 | |
| 工程地质 岩组 | 坚硬岩 | 半坚硬岩 | 软硬相间岩 | 软弱岩 | 松散土体 | 岩石物理性质影响成土母质,从而影响土壤及其生长的植物,研究区工程地质岩组分布明显,对生态环境具有一定的影响 | |
| 断裂带密度 (km2/km2) | 0.55~1.00 | 0.30~0.55 | 0.15~0.30 | 0.03~0.15 | 0~0.03 | 地球内营力形成的构造运动影响着区域生态环境。研究区构造活动强烈,对区域生态地质环境安全控制作用明显 | |
| 地下水富 水性 | 贫乏 | 弱 | 中等 | 好 | 丰富 | 水资源对区域生态环境有一定影响。研究区因地形的强烈切割,地下水径流快,径流途径短,并随深度的增加而减弱;不同类型的地下水动态差异很大 | |
| 年潜在蒸 发量(mm) | >1020 | 860~1020 | 730~860 | 600~730 | <600 | 研究区年潜在蒸发量呈现时空分布不均的特点,蒸发影响研究区植被的生长,从而影响区域生态地质环境安全 | |
| 年降雨量 (mm) | <960 | 960~1000 | 1000~1100 | 1100~1200 | >1200 | 研究区年降雨量呈现时空分布不均的特点,大气降水为土壤和水域等生态地质环境提供了必要的补给 | |
| 土壤类型 | 高山寒漠土、裸岩/雪被 | 石灰(岩) 土、粗骨土、 石质土 | 高山(亚高山)草甸土等 | 褐土、黄壤、紫色土 | 黄棕壤、暗棕壤、棕壤等 | 土壤是陆地生态系统最重要的构成部分,也是陆地生态系统的中心,不同土壤的组成、性质各异,对生态系统的影响也不同。研究区土壤呈较明显的垂向分布 | |
| 植被覆盖 度(%) | 0~10 | 10~25 | 25~50 | 50~75 | 75~100 | 植被覆盖度是区域生态系统中决定植被生产力、生物量和生态质量的关键因子,对区域生态地质环境安全提供保护作用 | |
| 土地利用 | 冰雪、 裸地等 | 农田 | 草地、湿 地等 | 灌丛 | 森林 | 土地利用类型变化影响生态系统和土地质量,对生态环境的影响至关重要 | |
| 地质灾害 (个/km2) | >1.5 | 1.0~1.5 | 0.6~1.0 | 0.2~0.6 | 0~0.2 | 研究区构造活动强烈,地质灾害频发,进而对植被、水土保持产生影响,甚至改变小范围地形地貌,影响区域生态系统。 | |
| 水源涵 养指数 | 0~15 | 15~40 | 40~55 | 55~70 | 70~100 | 水源涵养对于维护生态平衡和可持续发展具有重要的意义。研究区水源涵养能力对区域生态地质环境安全具有较强的控制作用 | |
| 土壤侵蚀 | >8000 | 5000~8000 | 2500~5000 | 500~2500 | <500 | 土壤侵蚀不仅会破坏植被,还会造成土地资源的浪费,严重制约研究区的生态地质环境安全 | |
| 人口密度 (人/km2) | >26 | 13~26 | 10~13 | 8~10 | 0~8 | 人口密度分布影响自然环境变化。研究区土地资源有限,随着人口数量的增长,人地压力增大,人地矛盾逐渐凸显,影响区域生态地质环境安全 | |
| 人均GDP (万元/人) | <0.5 | 0.5~1.0 | 1.0~2.0 | 2.0~3.0 | >3.0 | 社会经济发展是人类影响自然环境变化的重要因素。随着区域经济发展和人均GDP的提高,人们对生态环境的保护意识增强,环境保护投入加大,从而影响生态地质环境安全 | |
Table 2 Classification standards for the ecological and geological environment safety assessment indicators in upper reaches of the Minjiang river
| 指标 | 指标等级 | 指标说明 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| 高程(m) | <1500 | 1500~2000 | 2000~2500 | 2500~3000 | >3000 | 随着海拔的升高,空气变得寒冷干燥,对植物生长造成相应影响。研究区地形起伏度变化明显,区域植被垂向分布显著 | |
| 坡向(°) | 135~225 | 225~315 | 315~360 | 45~135 | 0~45 | 坡向影响山地日照时数和太阳辐射强度。研究区阳坡、半阳坡灌丛草甸发育,阴坡、半阴坡森林茂密,植被生长受坡向影响较大 | |
| 坡度(°) | >35 | 25~35 | 15~25 | 8~15 | 0~8 | 坡度决定着地表侵蚀作用的强度,影响水土流失强度、土层厚度以及土壤肥力。研究区谷坡陡峻,重力地质作用强烈 | |
| 工程地质 岩组 | 坚硬岩 | 半坚硬岩 | 软硬相间岩 | 软弱岩 | 松散土体 | 岩石物理性质影响成土母质,从而影响土壤及其生长的植物,研究区工程地质岩组分布明显,对生态环境具有一定的影响 | |
| 断裂带密度 (km2/km2) | 0.55~1.00 | 0.30~0.55 | 0.15~0.30 | 0.03~0.15 | 0~0.03 | 地球内营力形成的构造运动影响着区域生态环境。研究区构造活动强烈,对区域生态地质环境安全控制作用明显 | |
| 地下水富 水性 | 贫乏 | 弱 | 中等 | 好 | 丰富 | 水资源对区域生态环境有一定影响。研究区因地形的强烈切割,地下水径流快,径流途径短,并随深度的增加而减弱;不同类型的地下水动态差异很大 | |
| 年潜在蒸 发量(mm) | >1020 | 860~1020 | 730~860 | 600~730 | <600 | 研究区年潜在蒸发量呈现时空分布不均的特点,蒸发影响研究区植被的生长,从而影响区域生态地质环境安全 | |
| 年降雨量 (mm) | <960 | 960~1000 | 1000~1100 | 1100~1200 | >1200 | 研究区年降雨量呈现时空分布不均的特点,大气降水为土壤和水域等生态地质环境提供了必要的补给 | |
| 土壤类型 | 高山寒漠土、裸岩/雪被 | 石灰(岩) 土、粗骨土、 石质土 | 高山(亚高山)草甸土等 | 褐土、黄壤、紫色土 | 黄棕壤、暗棕壤、棕壤等 | 土壤是陆地生态系统最重要的构成部分,也是陆地生态系统的中心,不同土壤的组成、性质各异,对生态系统的影响也不同。研究区土壤呈较明显的垂向分布 | |
| 植被覆盖 度(%) | 0~10 | 10~25 | 25~50 | 50~75 | 75~100 | 植被覆盖度是区域生态系统中决定植被生产力、生物量和生态质量的关键因子,对区域生态地质环境安全提供保护作用 | |
| 土地利用 | 冰雪、 裸地等 | 农田 | 草地、湿 地等 | 灌丛 | 森林 | 土地利用类型变化影响生态系统和土地质量,对生态环境的影响至关重要 | |
| 地质灾害 (个/km2) | >1.5 | 1.0~1.5 | 0.6~1.0 | 0.2~0.6 | 0~0.2 | 研究区构造活动强烈,地质灾害频发,进而对植被、水土保持产生影响,甚至改变小范围地形地貌,影响区域生态系统。 | |
| 水源涵 养指数 | 0~15 | 15~40 | 40~55 | 55~70 | 70~100 | 水源涵养对于维护生态平衡和可持续发展具有重要的意义。研究区水源涵养能力对区域生态地质环境安全具有较强的控制作用 | |
| 土壤侵蚀 | >8000 | 5000~8000 | 2500~5000 | 500~2500 | <500 | 土壤侵蚀不仅会破坏植被,还会造成土地资源的浪费,严重制约研究区的生态地质环境安全 | |
| 人口密度 (人/km2) | >26 | 13~26 | 10~13 | 8~10 | 0~8 | 人口密度分布影响自然环境变化。研究区土地资源有限,随着人口数量的增长,人地压力增大,人地矛盾逐渐凸显,影响区域生态地质环境安全 | |
| 人均GDP (万元/人) | <0.5 | 0.5~1.0 | 1.0~2.0 | 2.0~3.0 | >3.0 | 社会经济发展是人类影响自然环境变化的重要因素。随着区域经济发展和人均GDP的提高,人们对生态环境的保护意识增强,环境保护投入加大,从而影响生态地质环境安全 | |
| 年份 | 项目 | 主成分 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | ||||||||
| 1995 | 特征值λ | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.04 | ||||||
| 贡献率(%) | 31.21 | 14.96 | 12.57 | 9.73 | 7.26 | 5.79 | |||||||
| 累计贡献率(%) | 31.21 | 46.17 | 58.74 | 68.47 | 75.73 | 81.52 | |||||||
| 2001 | 特征值λ | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.04 | ||||||
| 贡献率(%) | 30.07 | 18.51 | 11.20 | 10.02 | 7.52 | 5.17 | |||||||
| 累计贡献率(%) | 30.07 | 48.58 | 59.78 | 69.80 | 77.32 | 82.49 | |||||||
| 2009 | 特征值λ | 0.26 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.04 | ||||||
| 贡献率(%) | 33.79 | 14.46 | 11.31 | 9.80 | 8.01 | 5.88 | |||||||
| 累计贡献率(%) | 33.79 | 48.25 | 59.56 | 69.36 | 77.37 | 83.25 | |||||||
| 2020 | 特征值λ | 0.26 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.04 | ||||||
| 贡献率(%) | 34.75 | 13.96 | 11.49 | 9.21 | 7.90 | 5.47 | |||||||
| 累计贡献率(%) | 34.75 | 48.71 | 60.20 | 69.41 | 77.31 | 82.78 | |||||||
Table 3 Eigenvalue, contribution rate, and cumulative contribution rate of principal component
| 年份 | 项目 | 主成分 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | ||||||||
| 1995 | 特征值λ | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.04 | ||||||
| 贡献率(%) | 31.21 | 14.96 | 12.57 | 9.73 | 7.26 | 5.79 | |||||||
| 累计贡献率(%) | 31.21 | 46.17 | 58.74 | 68.47 | 75.73 | 81.52 | |||||||
| 2001 | 特征值λ | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.04 | ||||||
| 贡献率(%) | 30.07 | 18.51 | 11.20 | 10.02 | 7.52 | 5.17 | |||||||
| 累计贡献率(%) | 30.07 | 48.58 | 59.78 | 69.80 | 77.32 | 82.49 | |||||||
| 2009 | 特征值λ | 0.26 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.04 | ||||||
| 贡献率(%) | 33.79 | 14.46 | 11.31 | 9.80 | 8.01 | 5.88 | |||||||
| 累计贡献率(%) | 33.79 | 48.25 | 59.56 | 69.36 | 77.37 | 83.25 | |||||||
| 2020 | 特征值λ | 0.26 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.04 | ||||||
| 贡献率(%) | 34.75 | 13.96 | 11.49 | 9.21 | 7.90 | 5.47 | |||||||
| 累计贡献率(%) | 34.75 | 48.71 | 60.20 | 69.41 | 77.31 | 82.78 | |||||||
| 序号 | 指标 | AHP权重 | 1995年 | 2001年 | 2009年 | 2020年 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCA权重 | 组合权重 | PCA权重 | 组合权重 | PCA权重 | 组合权重 | PCA权重 | 组合权重 | ||||||
| 1 | 高程 | 0.0239 | 0.0942 | 0.0543 | 0.0850 | 0.0521 | 0.0858 | 0.0506 | 0.0815 | 0.0502 | |||
| 2 | 坡向 | 0.0285 | 0.0785 | 0.0541 | 0.0900 | 0.0586 | 0.0384 | 0.0369 | 0.0567 | 0.0457 | |||
| 3 | 坡度 | 0.0711 | 0.0003 | 0.0051 | 0.0027 | 0.0160 | 0.0001 | 0.0029 | 0.0002 | 0.0041 | |||
| 4 | 工程地质岩组 | 0.0797 | 0.0091 | 0.0309 | 0.0293 | 0.0559 | 0.0306 | 0.0551 | 0.0309 | 0.0565 | |||
| 5 | 断裂带密度 | 0.1059 | 0.0408 | 0.0752 | 0.0319 | 0.0673 | 0.0369 | 0.0698 | 0.0234 | 0.0566 | |||
| 6 | 地下水富水性 | 0.0298 | 0.0398 | 0.0394 | 0.0289 | 0.0340 | 0.0349 | 0.0360 | 0.0197 | 0.0276 | |||
| 7 | 年潜在蒸发量 | 0.0298 | 0.0801 | 0.0559 | 0.0554 | 0.0470 | 0.0547 | 0.0451 | 0.0273 | 0.0324 | |||
| 8 | 年降雨量 | 0.0357 | 0.0378 | 0.0420 | 0.0269 | 0.0359 | 0.0722 | 0.0567 | 0.0082 | 0.0194 | |||
| 9 | 土壤类型 | 0.0439 | 0.0980 | 0.0750 | 0.0962 | 0.0752 | 0.0996 | 0.0738 | 0.1301 | 0.0859 | |||
| 10 | 植被覆盖度 | 0.1076 | 0.1693 | 0.1544 | 0.1782 | 0.1602 | 0.1505 | 0.1421 | 0.1702 | 0.1539 | |||
| 11 | 土地利用 | 0.0598 | 0.1047 | 0.0905 | 0.1097 | 0.0937 | 0.1280 | 0.0977 | 0.1537 | 0.1090 | |||
| 12 | 地质灾害 | 0.1540 | 0.0366 | 0.0859 | 0.0273 | 0.0750 | 0.0512 | 0.0992 | 0.0671 | 0.1156 | |||
| 13 | 水源涵养 | 0.0774 | 0.0913 | 0.0962 | 0.0949 | 0.0992 | 0.1196 | 0.1074 | 0.1352 | 0.1163 | |||
| 14 | 土壤侵蚀 | 0.1176 | 0.0444 | 0.0826 | 0.0375 | 0.0768 | 0.0410 | 0.0776 | 0.0384 | 0.0764 | |||
| 15 | 人口密度 | 0.0188 | 0.0458 | 0.0336 | 0.1059 | 0.0516 | 0.0207 | 0.0220 | 0.0394 | 0.0310 | |||
| 16 | 人均GDP | 0.0164 | 0.0293 | 0.0251 | 0.0001 | 0.0015 | 0.0356 | 0.0270 | 0.0178 | 0.0194 | |||
Table 4 Weights of ecological and geological environment safety assessment indicators in upper reaches of the Minjiang river
| 序号 | 指标 | AHP权重 | 1995年 | 2001年 | 2009年 | 2020年 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCA权重 | 组合权重 | PCA权重 | 组合权重 | PCA权重 | 组合权重 | PCA权重 | 组合权重 | ||||||
| 1 | 高程 | 0.0239 | 0.0942 | 0.0543 | 0.0850 | 0.0521 | 0.0858 | 0.0506 | 0.0815 | 0.0502 | |||
| 2 | 坡向 | 0.0285 | 0.0785 | 0.0541 | 0.0900 | 0.0586 | 0.0384 | 0.0369 | 0.0567 | 0.0457 | |||
| 3 | 坡度 | 0.0711 | 0.0003 | 0.0051 | 0.0027 | 0.0160 | 0.0001 | 0.0029 | 0.0002 | 0.0041 | |||
| 4 | 工程地质岩组 | 0.0797 | 0.0091 | 0.0309 | 0.0293 | 0.0559 | 0.0306 | 0.0551 | 0.0309 | 0.0565 | |||
| 5 | 断裂带密度 | 0.1059 | 0.0408 | 0.0752 | 0.0319 | 0.0673 | 0.0369 | 0.0698 | 0.0234 | 0.0566 | |||
| 6 | 地下水富水性 | 0.0298 | 0.0398 | 0.0394 | 0.0289 | 0.0340 | 0.0349 | 0.0360 | 0.0197 | 0.0276 | |||
| 7 | 年潜在蒸发量 | 0.0298 | 0.0801 | 0.0559 | 0.0554 | 0.0470 | 0.0547 | 0.0451 | 0.0273 | 0.0324 | |||
| 8 | 年降雨量 | 0.0357 | 0.0378 | 0.0420 | 0.0269 | 0.0359 | 0.0722 | 0.0567 | 0.0082 | 0.0194 | |||
| 9 | 土壤类型 | 0.0439 | 0.0980 | 0.0750 | 0.0962 | 0.0752 | 0.0996 | 0.0738 | 0.1301 | 0.0859 | |||
| 10 | 植被覆盖度 | 0.1076 | 0.1693 | 0.1544 | 0.1782 | 0.1602 | 0.1505 | 0.1421 | 0.1702 | 0.1539 | |||
| 11 | 土地利用 | 0.0598 | 0.1047 | 0.0905 | 0.1097 | 0.0937 | 0.1280 | 0.0977 | 0.1537 | 0.1090 | |||
| 12 | 地质灾害 | 0.1540 | 0.0366 | 0.0859 | 0.0273 | 0.0750 | 0.0512 | 0.0992 | 0.0671 | 0.1156 | |||
| 13 | 水源涵养 | 0.0774 | 0.0913 | 0.0962 | 0.0949 | 0.0992 | 0.1196 | 0.1074 | 0.1352 | 0.1163 | |||
| 14 | 土壤侵蚀 | 0.1176 | 0.0444 | 0.0826 | 0.0375 | 0.0768 | 0.0410 | 0.0776 | 0.0384 | 0.0764 | |||
| 15 | 人口密度 | 0.0188 | 0.0458 | 0.0336 | 0.1059 | 0.0516 | 0.0207 | 0.0220 | 0.0394 | 0.0310 | |||
| 16 | 人均GDP | 0.0164 | 0.0293 | 0.0251 | 0.0001 | 0.0015 | 0.0356 | 0.0270 | 0.0178 | 0.0194 | |||

Fig.4 Proportion of different ecological and geological environmental safety levels in upper reaches of the Minjiang river in 1995, 2001, 2009, and 2020

Fig.7 Proportion of areas with different degrees of ecological and geological environmental safety changes in upper reaches of the Minjiang river at different periods
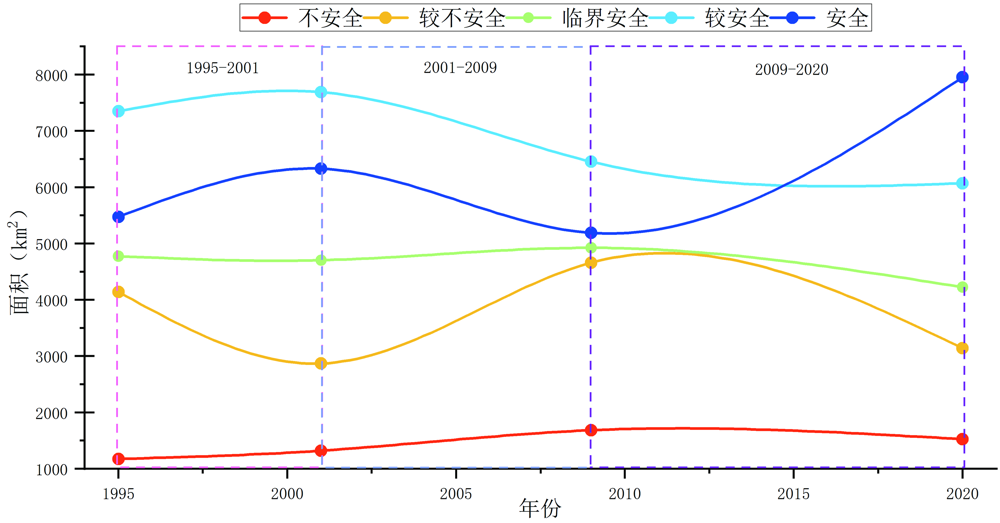
Fig.8 Curve chart of changes in ecological and geological environmental safety area at different levels in upper reaches of the Minjiang river from 1995 to 2020
| [1] | 陈国阶. 论生态安全[J]. 重庆环境科学, 2002(3): 1-3, 18. |
| [2] | 彭建兵, 兰恒星. 略论生态地质学与生态地质环境系统[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2022, 44(6): 877-893. |
| [3] | 方世南. 生态安全是国家安全体系重要基石[N]. 中国社会科学报, 2018-08-09(1). |
| [4] | 习近平在全国生态环境保护大会上强调全面推进美丽中国建设加快推进人与自然和谐共生的现代化[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 2023, 48(4): 4-7. |
| [5] | 王义娜. “三个彰显” 开创人与自然和谐共生新局面: 党的二十大报告关于生态文明建设的战略部署与安排[J]. 西藏发展论坛, 2023(2): 25-30. |
| [6] | 马娟娟. 基于PSR-ESV模型的生态安全评价研究: 以祁连山国家公园为例[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2022. |
| [7] | 汪洋. 基于PSR模型的吴起县耕地生态安全评价[J]. 农业与技术, 2022, 42(18): 102-107. |
| [8] | 向丽, 周伟, 任君, 等. 基于DPSIRM模型的高原城市湿地生态安全评价: 以湟水流域西宁段为例[J]. 生态学杂志, 2022, 41(10): 2064-2071. |
| [9] | 刘胜峰, 闫文德. 漓江流域土地生态安全时空分异及其影响因素[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2021, 41(11): 136-151. |
| [10] | 黄润秋. 生态环境地质的基本特点与技术支撑[J]. 中国地质, 2001, 28(11): 20-24. |
| [11] | 卢耀如. 长江流域国土地质-生态环境与洞庭湖综合治理的探讨[J]. 湖南地质, 1998, 17(4): 217-220, 240. |
| [12] | 卢耀如. 略论地质-生态环境与可持续发展: 黄河断流与岩溶石山保障三峡工程问题的探讨[J]. 大自然探索, 1999(1): 18-24. |
| [13] | 许向宁. 长江上游安宁河流域主要生态环境地质问题及其效应[J]. 山地学报, 2004, 22(5): 572-577. |
| [14] | 刁玉杰, 佟元清, 张森琦, 等. 青藏高原重大交通工程生态地质环境影响评价初探[J]. 公路, 2010, 55(5): 108-112. |
| [15] | 代力, 谭洪旗, 周雄. 川西锂矿带资源环境特征与生态地质环境承载力评价[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2023(4): 157-168, 173. |
| [16] | 李鹏. 地质灾害易发区生态地质环境安全时空演化研究: 以汶川地震重灾区为例[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2020. |
| [17] | HE N, ZHOU Y, WANG L, et al. Spatiotemporal evaluation and analysis of cultivated land ecological security based on the DPSIR model in Enshi autonomous prefecture, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 145: 109619. |
| [18] | 刘慧丽, 查东平, 冯明雷, 等. 基于PSFR模型的江西省东江流域生态安全评估研究[J]. 人民珠江, 2021, 42(7): 25-33. |
| [19] | 赵淑娟, 刘海英, 江涌起. 基于PSR-EES模型的绥化市土地生态安全评价及影响因素分析[J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 40(6): 46-53. |
| [20] | 廖成浩, 姚昆, 曾艳. 安宁河流域土地生态安全动态评价与预测[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2022, 34(2): 27-31, 37. |
| [21] | 吴小平, 胡建中. 岷江源地区新构造运动特征[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(3): 430-439. |
| [22] | 马俊学, 陈剑, 崔之久, 等. 基于HEC-RAS及GIS的川西叠溪古滑坡堰塞湖溃决洪水重建[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(2): 610-623. |
| [23] | 金继军, 郭长宝, 沈亚麒, 等. 四川茂县周场坪滑坡发育特征与变形监测分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(1): 103-113. |
| [24] | 李蔷, 王运生, 蒋发森. 汶川地震后岷江流域映秀至草坡段崩塌发育规律[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 2014, 25(1): 31-36. |
| [25] | 张军, 杨泽平, 梁海安, 等. 汶川县崩塌地质灾害发育规律研究[J]. 工程质量, 2017, 35(7): 38-41. |
| [26] | 常鸣, 窦向阳, 范宣梅, 等. 汶川震区暴雨泥石流激发雨型特征[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(3): 623-630. |
| [27] | 吴雨夫, 余斌, 亓星, 等. 岷江上游大白杨沟泥石流特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(1): 107-113. |
| [28] | 欧阳志云, 徐卫华, 王学志, 等. 汶川大地震对生态系统的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2008, 28(12): 5801-5809. |
| [29] | YANG J, HUANG X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019[J]. Copernicus Gmbh, 2021, 13(8): 3907-3925. |
| [30] | PENG S Z, DING Y X, LIU W Z, et al. 1 km monthly temperature and precipitation dataset for China from 1901 to 2017[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2019, 11(4): 1931-1946. |
| [31] | DING Y X, PENG S Z. Spatiotemporal change and attribution of potential evapotranspiration over China from 1901 to 2100[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2021, 145(1): 79-94. |
| [32] | DING Y X, PENG S Z. Spatiotemporal trends and attribution of drought across China from 1901-2100[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12(2): 477. |
| [33] | PENG S Z, DING Y X, WEN Z M, et al. Spatiotemporal change and trend analysis of potential evapotranspiration over the Loess Plateau of China during 2011-2100[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2017, 233: 183-194. |
| [34] | QU L S, ZHU Q, ZHU C F et al. Monthly precipitation data set with 1 km resolution in China from 1960 to 2020[DS/OL]. V1. Science Data Bank, 2022.[2024-03-27]. |
| [35] | 钱信禹, 边小卫, 张亚峰, 等. 丹江源地区地质建造对土壤和植被生态空间格局的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(4): 903-913. |
| [36] | 金晓媚, 万力, 薛忠歧, 等. 宁夏地区水资源对植被生长的影响研究[J]. 现代地质, 2007, 21(4): 632-637. |
| [37] | 陈金月, 王石英. 岷江上游生态环境脆弱性评价[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2017, 26(3): 471-479. |
| [38] | 郭梦迪, 韩继冲, 施玥, 等. 基于DPRISM概念框架的生态环境脆弱性评价——以岷江上游为例[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2019, 41(1): 128-134. |
| [39] | 刘金山, 倪福全, 邓玉, 等. 岷江上游流域土壤侵蚀风险评估[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2019, 17(1): 105-112. |
| [40] | 邹桃红, 常雅轩, 陈鹏, 等. 基于AHP-PCA熵权组合模型的吉林省生态环境脆弱性动态评价[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2023, 31(9): 1511-1524. |
| [41] | 左伟, 王桥, 王文杰, 等. 区域生态安全评价指标与标准研究[J]. 地理学与国土研究, 2002, 18(1): 67-71. |
| [42] | 杨天翼, 赵强, 王奎峰, 等. 基于层次分析法和熵权法综合评价山东省水生态安全[J]. 济南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 35(6): 566-571, 579. |
| [43] | 徐飞, 焦玉国, 唐丽伟, 等. 泰安市山水林田湖草生态修复区生态脆弱性评价与生态修复对策研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(4): 892-902. |
| [44] | SAATY T L. Decision making-The Analytic Hierarchy and Network Processes (AHP/ANP)[J]. Journal of Systems Science and Systems Engineering, 2004, 13(1): 1-35. |
| [45] | 侯林春, 王瑛璇. 基于主成分分析的呼和浩特市土地生态安全评价[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2017, 56(9): 1796-1800. |
| [46] | 邓云涛, 张文君, 周文韬, 等. 基于AHP-PCA的熵组合权重的居民点用地适宜性评价: 以内江市为例[J]. 西南科技大学学报, 2020, 35(1): 45-50. |
| [47] | 李怀省. 对岷江林区实施天然林保护工程后的效益评价[J]. 甘肃科技, 2008, 24(1): 133-135. |
| [48] | 杨渺, 江腊海, 侯鹏, 等. “5·12” 汶川地震极重灾区灾后十年生态恢复状况评估[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2020, 29(11): 2541-2550. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||