



Geoscience ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (03): 660-673.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.029
• Observation Simulation and Prediction Evaluation of Superbiotic Resources • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHOU Xueni1,2,3( ), BA Renji1, XIAO Chengzhi4, CAO Yating1, JI Yang1(
), BA Renji1, XIAO Chengzhi4, CAO Yating1, JI Yang1( )
)
Online:2024-06-10
Published:2024-07-04
CLC Number:
ZHOU Xueni, BA Renji, XIAO Chengzhi, CAO Yating, JI Yang. Soil Characteristics and Spatial and Temporal Changes of Vegetations in the Lower Part of the Arid Valley Area of the Upper Reaches of Minjiang River Based on Geological Formation[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(03): 660-673.
| 地质建造单元 | 涉及的地质单元 | 主要岩性 | 地质建造环境 | 面积(km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第四纪松散堆积建造 | 第四系 | — | 河流-湖泊相 | 55.48 |
| 三叠纪复理石建造 | 波茨沟组、杂谷脑组、侏倭组 | 变质石英砂岩、板岩 | 浅海-滨海相 | 9.42 |
| 石炭纪—二叠纪碳酸盐建造 | 二叠系上统、二叠系下统、石炭系 | 深灰色灰岩 | 浅海相 | 3.17 |
| 泥盆纪泥页岩-碳酸盐岩建造 | 危关群、月里寨群 | 结晶灰岩、千枚岩 | 浅海相 | 68.92 |
| 志留纪泥砂质-碳酸盐建造 | 茂县群 | 炭质千枚岩、石英砂岩 | 浅海相 | 97.40 |
| 奥陶纪碳酸盐建造 | 奥陶系 | 结晶灰岩夹千枚岩 | 浅海相 | 1.13 |
| 寒武纪火山碎屑岩建造 | 寒武系下统 | 碳酸盐岩夹砂岩、页岩 | 俯冲-碰撞 | 0.36 |
| 震旦纪碳酸盐岩建造 | 陡山沱组、灯影组 | 砂页岩、砂岩、页岩 | 滨海相 | 4.51 |
| 元古宙中酸性岩浆岩建造 | 元古宙黑云花岗岩、元古宙石英闪长岩、元古宙斜长花岗岩 | 黑云花岗岩、石英闪长岩、斜长花岗岩 | 俯冲-碰撞 | 19.64 |
| 中元古代火山岩-熔岩建造 | 黄水河群 | 火山碎屑岩、熔岩组合 | 俯冲-碰撞 | 9.59 |
Table 1 Classification of geological formations
| 地质建造单元 | 涉及的地质单元 | 主要岩性 | 地质建造环境 | 面积(km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第四纪松散堆积建造 | 第四系 | — | 河流-湖泊相 | 55.48 |
| 三叠纪复理石建造 | 波茨沟组、杂谷脑组、侏倭组 | 变质石英砂岩、板岩 | 浅海-滨海相 | 9.42 |
| 石炭纪—二叠纪碳酸盐建造 | 二叠系上统、二叠系下统、石炭系 | 深灰色灰岩 | 浅海相 | 3.17 |
| 泥盆纪泥页岩-碳酸盐岩建造 | 危关群、月里寨群 | 结晶灰岩、千枚岩 | 浅海相 | 68.92 |
| 志留纪泥砂质-碳酸盐建造 | 茂县群 | 炭质千枚岩、石英砂岩 | 浅海相 | 97.40 |
| 奥陶纪碳酸盐建造 | 奥陶系 | 结晶灰岩夹千枚岩 | 浅海相 | 1.13 |
| 寒武纪火山碎屑岩建造 | 寒武系下统 | 碳酸盐岩夹砂岩、页岩 | 俯冲-碰撞 | 0.36 |
| 震旦纪碳酸盐岩建造 | 陡山沱组、灯影组 | 砂页岩、砂岩、页岩 | 滨海相 | 4.51 |
| 元古宙中酸性岩浆岩建造 | 元古宙黑云花岗岩、元古宙石英闪长岩、元古宙斜长花岗岩 | 黑云花岗岩、石英闪长岩、斜长花岗岩 | 俯冲-碰撞 | 19.64 |
| 中元古代火山岩-熔岩建造 | 黄水河群 | 火山碎屑岩、熔岩组合 | 俯冲-碰撞 | 9.59 |
| 数据 | 数据源 | 数据集 |
|---|---|---|
| 干旱河谷区范围 | 山地科学数据中心 | 西南地区干旱河谷区范围[ |
| 地层岩性 | 四川省地质调查院 | 岷江流域地质灾害详细调查成果集成报告 |
| 土壤数据 | - | 2019年四川省耕地等数据 |
| 土地利用(1995年、2001年、2009年、2020年) | https://zenodo.org/ | The 30 m annual land cover datasets and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2021[ |
| 遥感数据(1995年、2001年、2009年、2020年) | 美国地质勘探局USGS( | Landsat5 TM、Landsat8 OLI |
Table 2 Data information and sources
| 数据 | 数据源 | 数据集 |
|---|---|---|
| 干旱河谷区范围 | 山地科学数据中心 | 西南地区干旱河谷区范围[ |
| 地层岩性 | 四川省地质调查院 | 岷江流域地质灾害详细调查成果集成报告 |
| 土壤数据 | - | 2019年四川省耕地等数据 |
| 土地利用(1995年、2001年、2009年、2020年) | https://zenodo.org/ | The 30 m annual land cover datasets and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2021[ |
| 遥感数据(1995年、2001年、2009年、2020年) | 美国地质勘探局USGS( | Landsat5 TM、Landsat8 OLI |
| 编码 | 一级类名称 | CLCD类型 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 耕地 | 农田 |
| 2 | 林地 | 林地 |
| 3 | 灌丛 | 灌丛 |
| 4 | 草地 | 草地 |
| 5 | 水域 | 水域、湿地 |
| 6 | 建设用地 | 不透水面 |
| 7 | 未利用土地 | 荒地、冰雪覆盖地 |
Table 3 Classification system for land-use types
| 编码 | 一级类名称 | CLCD类型 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 耕地 | 农田 |
| 2 | 林地 | 林地 |
| 3 | 灌丛 | 灌丛 |
| 4 | 草地 | 草地 |
| 5 | 水域 | 水域、湿地 |
| 6 | 建设用地 | 不透水面 |
| 7 | 未利用土地 | 荒地、冰雪覆盖地 |
| 地质建造 | N | P | Al2O3 | Na2O | K2O | CaO | MgO | TFe2O3 | Cu | Mn | Zn | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g/kg) | (μg/g) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | |
| 第四纪松散堆积建造 | 0.88 | 752.42 | 13.18 | 1.20 | 3.19 | 9.54 | 2.57 | 5.36 | 35.27 | 647.38 | 85.72 | 70.05 |
| 三叠纪复理石建造 | 1.08 | 560.00 | 12.84 | 0.97 | 3.14 | 10.85 | 2.22 | 4.48 | 42.20 | 561.33 | 74.80 | 64.90 |
| 泥盆纪泥页岩-碳酸盐岩建造 | 1.07 | 463.87 | 9.40 | 0.54 | 2.00 | 30.13 | 2.90 | 3.05 | 16.63 | 356.65 | 58.60 | 66.93 |
| 志留纪泥砂质-碳酸盐建造 | 1.05 | 683.22 | 14.00 | 1.15 | 3.69 | 7.09 | 2.86 | 5.55 | 36.91 | 603.94 | 86.42 | 86.18 |
| 中元古代火山岩-熔岩建造 | 0.42 | 492.00 | 12.57 | 1.54 | 3.51 | 7.19 | 3.63 | 4.56 | 23.83 | 710.75 | 67.40 | 64.50 |
| 元古宙中酸性岩浆岩建造 | 0.48 | 805.33 | 12.22 | 3.21 | 2.43 | 4.31 | 3.97 | 7.24 | 23.07 | 1079.00 | 82.37 | 23.60 |
Table 4 Mean values of the soil nutrient content in different geological formations
| 地质建造 | N | P | Al2O3 | Na2O | K2O | CaO | MgO | TFe2O3 | Cu | Mn | Zn | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g/kg) | (μg/g) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | (μg/g) | |
| 第四纪松散堆积建造 | 0.88 | 752.42 | 13.18 | 1.20 | 3.19 | 9.54 | 2.57 | 5.36 | 35.27 | 647.38 | 85.72 | 70.05 |
| 三叠纪复理石建造 | 1.08 | 560.00 | 12.84 | 0.97 | 3.14 | 10.85 | 2.22 | 4.48 | 42.20 | 561.33 | 74.80 | 64.90 |
| 泥盆纪泥页岩-碳酸盐岩建造 | 1.07 | 463.87 | 9.40 | 0.54 | 2.00 | 30.13 | 2.90 | 3.05 | 16.63 | 356.65 | 58.60 | 66.93 |
| 志留纪泥砂质-碳酸盐建造 | 1.05 | 683.22 | 14.00 | 1.15 | 3.69 | 7.09 | 2.86 | 5.55 | 36.91 | 603.94 | 86.42 | 86.18 |
| 中元古代火山岩-熔岩建造 | 0.42 | 492.00 | 12.57 | 1.54 | 3.51 | 7.19 | 3.63 | 4.56 | 23.83 | 710.75 | 67.40 | 64.50 |
| 元古宙中酸性岩浆岩建造 | 0.48 | 805.33 | 12.22 | 3.21 | 2.43 | 4.31 | 3.97 | 7.24 | 23.07 | 1079.00 | 82.37 | 23.60 |
| 地质建造类型 | 低覆 盖度 | 中低 覆盖度 | 中覆 盖度 | 中高 覆盖度 | 高覆 盖度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第四纪松散堆积建造 | 6.05 | 15.70 | 28.40 | 28.30 | 21.55 |
| 三叠纪复理石建造 | 0.42 | 6.88 | 23.20 | 32.10 | 37.40 |
| 泥盆纪泥页岩-碳酸盐岩建造 | 2.05 | 9.15 | 21.83 | 31.83 | 35.14 |
| 志留纪泥砂质-碳酸盐建造 | 1.19 | 15.32 | 27.41 | 30.81 | 25.27 |
| 中元古代火山岩-熔岩建造 | 6.45 | 10.05 | 19.38 | 33.38 | 30.74 |
| 元古宙中酸性岩浆岩建造 | 5.30 | 9.43 | 17.57 | 29.40 | 38.30 |
Table 5 Mean values of the proportion of area covered by vegetations in different geological formation units (%)
| 地质建造类型 | 低覆 盖度 | 中低 覆盖度 | 中覆 盖度 | 中高 覆盖度 | 高覆 盖度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第四纪松散堆积建造 | 6.05 | 15.70 | 28.40 | 28.30 | 21.55 |
| 三叠纪复理石建造 | 0.42 | 6.88 | 23.20 | 32.10 | 37.40 |
| 泥盆纪泥页岩-碳酸盐岩建造 | 2.05 | 9.15 | 21.83 | 31.83 | 35.14 |
| 志留纪泥砂质-碳酸盐建造 | 1.19 | 15.32 | 27.41 | 30.81 | 25.27 |
| 中元古代火山岩-熔岩建造 | 6.45 | 10.05 | 19.38 | 33.38 | 30.74 |
| 元古宙中酸性岩浆岩建造 | 5.30 | 9.43 | 17.57 | 29.40 | 38.30 |
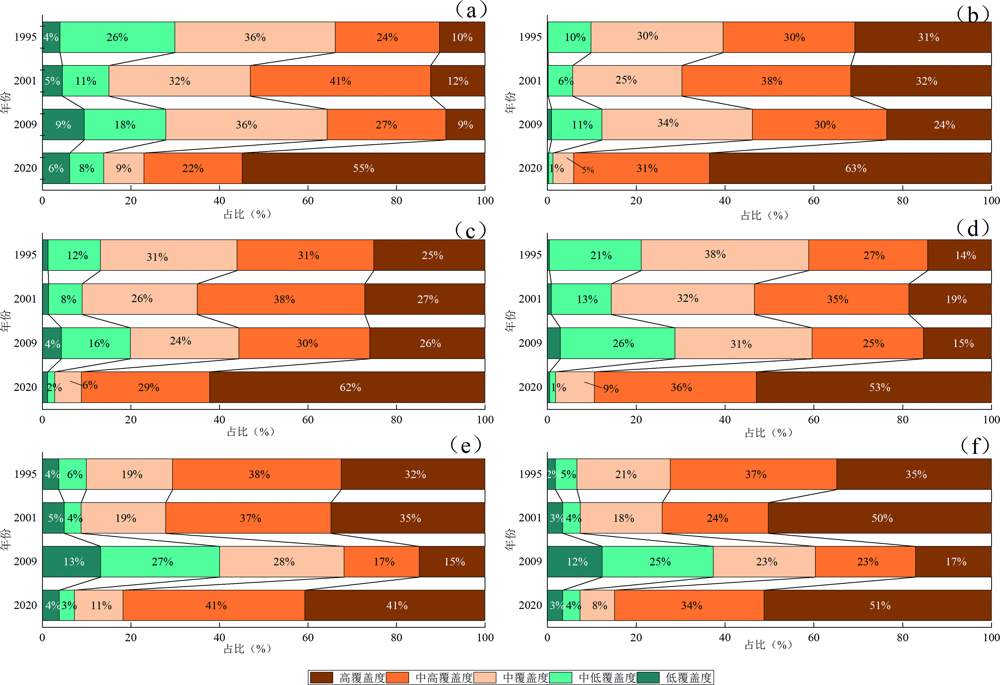
Fig.10 Percentage of area with different levels of vegetation coverage for the six types of geological formations in the study area in years of 1995, 2001, 2009 and 2020
| [1] | 周义贵. 岷江上游干旱河谷区不同土地利用/植被恢复类型土壤生态效益评价[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2014. |
| [2] | 丁明涛, 周鹏, 张永旺, 等. 岷江上游干旱河谷边界波动的定量判定及其演化特征[J]. 山地学报, 2017, 35(2): 170-178. |
| [3] | 伏耀龙. 岷江上游干旱河谷区土壤质量评价及侵蚀特征研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2012. |
| [4] | 柏松, 黄成敏, 唐亚. 岷江上游干旱河谷海拔梯度上的土壤发生特征[J]. 土壤, 2008, 40(6): 980-985. |
| [5] | 杨子松, 杨灿, 黎云祥. 岷江上游干旱河谷荒坡植物群落的稳定性分析[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2013, 29(1): 43-48. |
| [6] | 王勇军, 黄从德, 张健, 等. 岷江干旱河谷灌丛物种多样性、生物量及其关系[J]. 干旱区研究, 2010, 27(4): 567-572. |
| [7] | 王中琪, 杨斌, 陈磊, 等. 岷江上游干旱河谷震后植被恢复时空变化与地形形变的关系[J]. 科技通报, 2021, 37(11): 17-23, 48. |
| [8] | 熊亚兰, 张科利, 刘佳凤, 等. 岷江上游小流域多尺度NDVI与地形的关系研究[J]. 地球与环境, 2019, 47(4): 412-418. |
| [9] | 简中华, 徐明星, 宋明义, 等. 不同成土母质对浦江桃形李品质的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2013, 41(10): 4356-4361. |
| [10] | 孙厚云, 孙晓明, 贾凤超, 等. 河北承德锗元素生态地球化学特征及其与道地药材黄芩适生关系[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6): 1646-1667. |
| [11] | BRADY K U, KRUCKEBERG A R, BRADSHAW H D. Evolutionary ecology of plant adaptation to serpentine soils[J]. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 2005, 36: 243-266. |
| [12] | 杨志忠, 周文龙, 罗勇军, 等. 贵州镇远县耕地土壤中硒的分布特征及控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(2): 434-442. |
| [13] | CHAPELA LARA M, BUSS H L, PETT-RIDGE J C. The effects of lithology on trace element and REE behavior during tropical weathering[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 500: 88-102. |
| [14] | 刘洪, 黄瀚霄, 欧阳渊, 等. 基于地质建造的土壤地质调查及应用前景分析: 以大凉山区西昌市为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2020, 40(1): 91-105. |
| [15] | 李樋, 刘小念, 刘洪, 等. 基于地质建造的土壤营养元素空间分布特征研究: 以大凉山区为例[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2021, 28(6): 127-137. |
| [16] | 地质矿产部地质辞典办公室. 地质大辞典[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2005. |
| [17] | 欧阳渊, 张景华, 刘洪, 等. 基于地质建造的西南山区成土母质分类方案: 以大凉山区为例[J]. 中国地质调查, 2021, 8(6): 50-62. |
| [18] | 贾磊, 刘洪, 欧阳渊, 等. 基于地质建造的南方山地-丘陵区地表基质填图单元划分方案: 以珠三角新会—台山地区为例[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(4): 140-157. |
| [19] | 张腾蛟, 刘洪, 欧阳渊, 等. 不同地质建造类型的生态环境功能特征: 以西昌地区为例[J]. 中国地质调查, 2021, 8(6): 35-49. |
| [20] | 王京彬, 卫晓锋, 张会琼, 等. 基于地质建造的生态地质调查方法: 以河北省承德市国家生态文明示范区综合地质调查为例[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6): 1611-1624. |
| [21] | 卫晓锋, 王京彬, 孙厚云, 等. 基于地质建造探索承德市土地利用优化路径[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2020, 47(6): 15-25. |
| [22] | 李新, 董好刚, 谢翔, 等. 地质建造与生态特征相关性分析与环境修复应用:基于大别山西段罗山地区的实践[J/OL]. 中国地质, [2024-05-15]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20230515.1545.002.html. |
| [23] | 尹东郊, 郝子文, 黄友智, 等. 1∶20万茂汶幅、灌县幅区域地质调查报告[R]. 罗江: 四川省地质局第二区域地质测量队, 1975. |
| [24] | 黄勇, 欧阳渊, 刘洪, 等. 地质建造对土壤性质的制约及其生态环境效应: 以西昌地区红壤为例[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(4): 196-212. |
| [25] | 中华人民共和国国土资源部.地质矿产实验室测试质量管理规范: DZ/T 0130—2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006. |
| [26] | 中华人民共和国国土资源部.多目标区域地球化学调查规范(1∶250000):AASHTO T 217-2014(R2018) [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版, 2015. |
| [27] | 范建容, 杨超, 包维楷, 等. 西南地区干旱河谷分布范围及分区统计分析[J]. 山地学报, 2020, 38(2): 303-313. |
| [28] | YANG J, HUANG X. The 30m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2021, 13(8): 3907-3925. |
| [29] | 田智慧, 任祖光, 魏海涛. 2000—2020年黄河流域植被时空演化驱动机制[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(2): 743-751. |
| [30] | 李苗苗, 吴炳方, 颜长珍, 等. 密云水库上游植被覆盖度的遥感估算[J]. 资源科学, 2004, 26(4): 153-159. |
| [31] | 张绪财, 金晓媚, 朱晓倩, 等. 格尔木河流域植被指数时空分布及其影响因素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(2): 461-468. |
| [32] | 中华人民共和国国土资源部.土地质量地球化学评价规范: DZ/T 0295—2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. |
| [33] | 王倩, 金晓媚, 张绪财, 等. 河北省张承地区2001—2020年植被动态变化及驱动因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(4): 881-891. |
| [34] | 卫晓锋, 樊刘洋, 孙紫坚, 等. 河北承德柴白河流域地质建造对植物群落组成的影响[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6): 1869-1880. |
| [35] | 周丽丽, 马世伟, 米彩红, 等. 冻融条件下土壤水分和速效磷垂直迁移规律[J]. 水土保持研究, 2017, 24(3): 70-74. |
| [36] | 顾涛, 郑小战, 邱啸飞, 等. 中山市神湾镇晚中生代花岗岩风化壳剖面元素地球化学特征[J]. 华南地质, 2021, 37(4): 406-417. |
| [37] | 钱信禹, 边小卫, 张亚峰, 等. 丹江源地区地质建造对土壤和植被生态空间格局的影响[J]. 现代地质, 37(4):903-913. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||