



Geoscience ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (06): 1677-1690.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.125
• Gold-polymetallic Mineralization in Qinling Orogens • Previous Articles Next Articles
YAN Jing1( ), LIU Jingxian1, PU Wanfeng1, WEI Xueping2, LI Zhibin1
), LIU Jingxian1, PU Wanfeng1, WEI Xueping2, LI Zhibin1
Received:2021-09-11
Revised:2021-10-11
Online:2021-12-10
Published:2022-02-14
CLC Number:
YAN Jing, LIU Jingxian, PU Wanfeng, WEI Xueping, LI Zhibin. Middle-Late Triassic Tectonic Attribute in West Qinling: Evidence from Geochronology and Geochemistry of the Jiangqinaliang Intrusive Complex[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(06): 1677-1690.
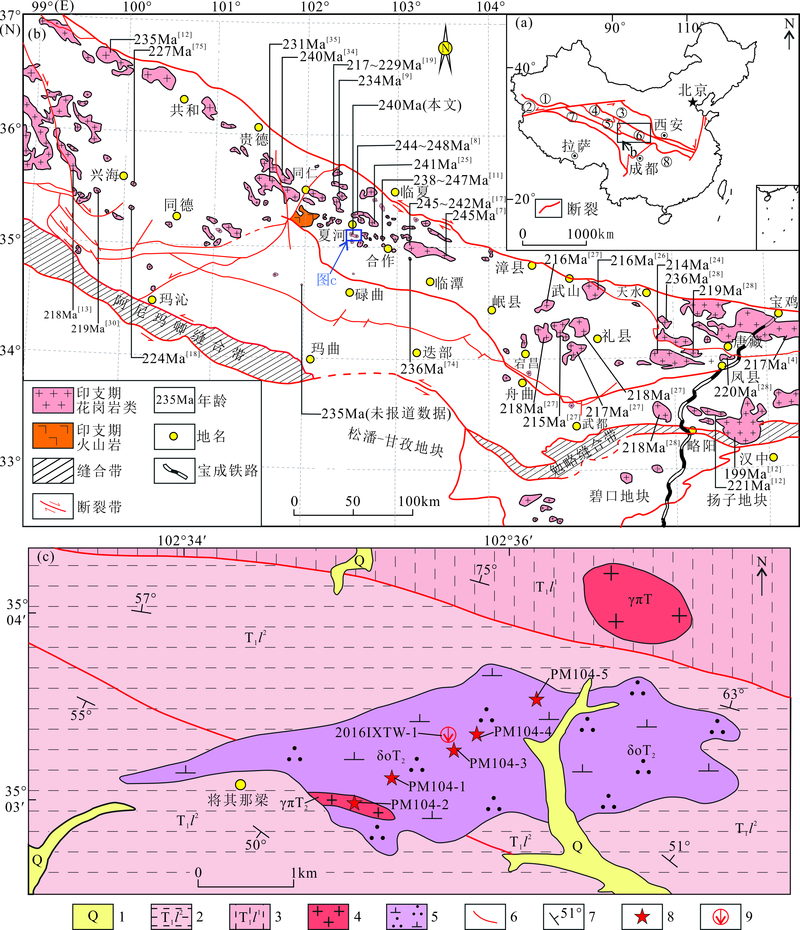
Fig.1 Tectonic framework of central orogenic belt(a), distribution map of Indosinian magmatic rocks in West Qinling(b) and simplified geological map of Jiangqinaliang intrusive complex (c)((a) modified from Lu et al.[20]; (b) modified from Feng et al.[36])
| 测试 点 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | Pb | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | ||||
| 1 | 173 | 462 | 54 | 0.37 | 0.054 22 | 0.002 04 | 0.283 36 | 0.010 84 | 0.038 05 | 0.000 52 | 389 | 81 | 253 | 9 | 241 | 3 | ||
| 2 | 227 | 513 | 61 | 0.44 | 0.049 74 | 0.001 71 | 0.260 57 | 0.009 39 | 0.038 00 | 0.000 52 | 183 | 80 | 235 | 8 | 240 | 3 | ||
| 3 | 382 | 685 | 102 | 0.56 | 0.053 26 | 0.001 84 | 0.277 92 | 0.009 29 | 0.038 07 | 0.000 50 | 339 | 78 | 249 | 7 | 241 | 3 | ||
| 5 | 165 | 413 | 47 | 0.40 | 0.054 92 | 0.003 22 | 0.282 54 | 0.015 74 | 0.037 95 | 0.000 89 | 409 | 164 | 253 | 12 | 240 | 6 | ||
| 6 | 165 | 449 | 49 | 0.37 | 0.054 46 | 0.002 74 | 0.282 46 | 0.013 93 | 0.037 96 | 0.000 59 | 391 | 113 | 253 | 11 | 240 | 4 | ||
| 7 | 212 | 510 | 61 | 0.42 | 0.050 59 | 0.002 63 | 0.262 84 | 0.013 41 | 0.038 03 | 0.000 86 | 220 | 120 | 237 | 11 | 241 | 5 | ||
| 9 | 184 | 448 | 52 | 0.41 | 0.047 94 | 0.002 55 | 0.251 81 | 0.013 09 | 0.038 08 | 0.000 68 | 95 | 122 | 228 | 11 | 241 | 4 | ||
| 11 | 304 | 528 | 78 | 0.58 | 0.050 92 | 0.002 02 | 0.265 65 | 0.010 08 | 0.038 04 | 0.000 45 | 235 | 91 | 239 | 8 | 241 | 3 | ||
| 12 | 251 | 466 | 64 | 0.54 | 0.054 25 | 0.001 85 | 0.283 41 | 0.009 68 | 0.037 94 | 0.000 50 | 389 | 78 | 253 | 8 | 240 | 3 | ||
| 13 | 320 | 565 | 82 | 0.57 | 0.051 32 | 0.001 55 | 0.267 59 | 0.008 43 | 0.037 92 | 0.000 48 | 254 | 70 | 241 | 7 | 240 | 3 | ||
| 14 | 276 | 471 | 70 | 0.59 | 0.051 26 | 0.001 87 | 0.266 40 | 0.009 98 | 0.037 96 | 0.000 51 | 254 | 90 | 240 | 8 | 240 | 3 | ||
| 15 | 174 | 478 | 50 | 0.36 | 0.049 73 | 0.001 69 | 0.259 38 | 0.008 65 | 0.037 98 | 0.000 48 | 189 | 80 | 234 | 7 | 240 | 3 | ||
| 16 | 160 | 540 | 49 | 0.30 | 0.050 39 | 0.001 69 | 0.261 93 | 0.008 27 | 0.038 04 | 0.000 45 | 213 | 44 | 236 | 7 | 241 | 3 | ||
| 19 | 293 | 497 | 78 | 0.59 | 0.050 11 | 0.002 49 | 0.260 14 | 0.012 82 | 0.037 99 | 0.000 59 | 198 | 121 | 235 | 10 | 240 | 4 | ||
| 20 | 202 | 505 | 59 | 0.40 | 0.052 91 | 0.002 49 | 0.280 49 | 0.014 22 | 0.037 98 | 0.000 86 | 324 | 107 | 251 | 11 | 240 | 5 | ||
| 21 | 216 | 393 | 54 | 0.55 | 0.050 78 | 0.003 05 | 0.263 98 | 0.016 28 | 0.037 96 | 0.000 76 | 232 | 139 | 238 | 13 | 240 | 5 | ||
| 22 | 190 | 380 | 52 | 0.50 | 0.049 63 | 0.002 43 | 0.260 32 | 0.013 82 | 0.037 94 | 0.000 81 | 176 | 113 | 235 | 11 | 240 | 5 | ||
| 23 | 144 | 327 | 40 | 0.44 | 0.055 88 | 0.002 85 | 0.289 83 | 0.013 92 | 0.037 96 | 0.000 66 | 456 | 118 | 258 | 11 | 240 | 4 | ||
| 24 | 249 | 650 | 70 | 0.38 | 0.049 90 | 0.001 68 | 0.261 70 | 0.008 93 | 0.037 97 | 0.000 53 | 191 | 112 | 236 | 7 | 240 | 3 | ||
| 25 | 161 | 575 | 49 | 0.28 | 0.052 37 | 0.002 76 | 0.272 43 | 0.013 36 | 0.037 96 | 0.000 81 | 302 | 120 | 245 | 11 | 240 | 5 | ||
| 26 | 90 | 242 | 27 | 0.37 | 0.051 43 | 0.003 48 | 0.260 82 | 0.015 28 | 0.037 92 | 0.000 87 | 261 | 156 | 235 | 12 | 240 | 5 | ||
| 27 | 197 | 366 | 50 | 0.54 | 0.052 16 | 0.002 87 | 0.269 31 | 0.014 15 | 0.037 94 | 0.000 67 | 300 | 126 | 242 | 11 | 240 | 4 | ||
| 28 | 246 | 485 | 66 | 0.51 | 0.054 82 | 0.002 11 | 0.289 38 | 0.012 58 | 0.038 01 | 0.000 79 | 406 | 85 | 258 | 10 | 240 | 5 | ||
| 30 | 129 | 366 | 39 | 0.35 | 0.051 71 | 0.002 52 | 0.270 71 | 0.014 12 | 0.037 97 | 0.000 69 | 272 | 111 | 243 | 11 | 240 | 4 | ||
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data of quartz diorite in the Jiangqinaliang intrusive complex
| 测试 点 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | Pb | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | ||||
| 1 | 173 | 462 | 54 | 0.37 | 0.054 22 | 0.002 04 | 0.283 36 | 0.010 84 | 0.038 05 | 0.000 52 | 389 | 81 | 253 | 9 | 241 | 3 | ||
| 2 | 227 | 513 | 61 | 0.44 | 0.049 74 | 0.001 71 | 0.260 57 | 0.009 39 | 0.038 00 | 0.000 52 | 183 | 80 | 235 | 8 | 240 | 3 | ||
| 3 | 382 | 685 | 102 | 0.56 | 0.053 26 | 0.001 84 | 0.277 92 | 0.009 29 | 0.038 07 | 0.000 50 | 339 | 78 | 249 | 7 | 241 | 3 | ||
| 5 | 165 | 413 | 47 | 0.40 | 0.054 92 | 0.003 22 | 0.282 54 | 0.015 74 | 0.037 95 | 0.000 89 | 409 | 164 | 253 | 12 | 240 | 6 | ||
| 6 | 165 | 449 | 49 | 0.37 | 0.054 46 | 0.002 74 | 0.282 46 | 0.013 93 | 0.037 96 | 0.000 59 | 391 | 113 | 253 | 11 | 240 | 4 | ||
| 7 | 212 | 510 | 61 | 0.42 | 0.050 59 | 0.002 63 | 0.262 84 | 0.013 41 | 0.038 03 | 0.000 86 | 220 | 120 | 237 | 11 | 241 | 5 | ||
| 9 | 184 | 448 | 52 | 0.41 | 0.047 94 | 0.002 55 | 0.251 81 | 0.013 09 | 0.038 08 | 0.000 68 | 95 | 122 | 228 | 11 | 241 | 4 | ||
| 11 | 304 | 528 | 78 | 0.58 | 0.050 92 | 0.002 02 | 0.265 65 | 0.010 08 | 0.038 04 | 0.000 45 | 235 | 91 | 239 | 8 | 241 | 3 | ||
| 12 | 251 | 466 | 64 | 0.54 | 0.054 25 | 0.001 85 | 0.283 41 | 0.009 68 | 0.037 94 | 0.000 50 | 389 | 78 | 253 | 8 | 240 | 3 | ||
| 13 | 320 | 565 | 82 | 0.57 | 0.051 32 | 0.001 55 | 0.267 59 | 0.008 43 | 0.037 92 | 0.000 48 | 254 | 70 | 241 | 7 | 240 | 3 | ||
| 14 | 276 | 471 | 70 | 0.59 | 0.051 26 | 0.001 87 | 0.266 40 | 0.009 98 | 0.037 96 | 0.000 51 | 254 | 90 | 240 | 8 | 240 | 3 | ||
| 15 | 174 | 478 | 50 | 0.36 | 0.049 73 | 0.001 69 | 0.259 38 | 0.008 65 | 0.037 98 | 0.000 48 | 189 | 80 | 234 | 7 | 240 | 3 | ||
| 16 | 160 | 540 | 49 | 0.30 | 0.050 39 | 0.001 69 | 0.261 93 | 0.008 27 | 0.038 04 | 0.000 45 | 213 | 44 | 236 | 7 | 241 | 3 | ||
| 19 | 293 | 497 | 78 | 0.59 | 0.050 11 | 0.002 49 | 0.260 14 | 0.012 82 | 0.037 99 | 0.000 59 | 198 | 121 | 235 | 10 | 240 | 4 | ||
| 20 | 202 | 505 | 59 | 0.40 | 0.052 91 | 0.002 49 | 0.280 49 | 0.014 22 | 0.037 98 | 0.000 86 | 324 | 107 | 251 | 11 | 240 | 5 | ||
| 21 | 216 | 393 | 54 | 0.55 | 0.050 78 | 0.003 05 | 0.263 98 | 0.016 28 | 0.037 96 | 0.000 76 | 232 | 139 | 238 | 13 | 240 | 5 | ||
| 22 | 190 | 380 | 52 | 0.50 | 0.049 63 | 0.002 43 | 0.260 32 | 0.013 82 | 0.037 94 | 0.000 81 | 176 | 113 | 235 | 11 | 240 | 5 | ||
| 23 | 144 | 327 | 40 | 0.44 | 0.055 88 | 0.002 85 | 0.289 83 | 0.013 92 | 0.037 96 | 0.000 66 | 456 | 118 | 258 | 11 | 240 | 4 | ||
| 24 | 249 | 650 | 70 | 0.38 | 0.049 90 | 0.001 68 | 0.261 70 | 0.008 93 | 0.037 97 | 0.000 53 | 191 | 112 | 236 | 7 | 240 | 3 | ||
| 25 | 161 | 575 | 49 | 0.28 | 0.052 37 | 0.002 76 | 0.272 43 | 0.013 36 | 0.037 96 | 0.000 81 | 302 | 120 | 245 | 11 | 240 | 5 | ||
| 26 | 90 | 242 | 27 | 0.37 | 0.051 43 | 0.003 48 | 0.260 82 | 0.015 28 | 0.037 92 | 0.000 87 | 261 | 156 | 235 | 12 | 240 | 5 | ||
| 27 | 197 | 366 | 50 | 0.54 | 0.052 16 | 0.002 87 | 0.269 31 | 0.014 15 | 0.037 94 | 0.000 67 | 300 | 126 | 242 | 11 | 240 | 4 | ||
| 28 | 246 | 485 | 66 | 0.51 | 0.054 82 | 0.002 11 | 0.289 38 | 0.012 58 | 0.038 01 | 0.000 79 | 406 | 85 | 258 | 10 | 240 | 5 | ||
| 30 | 129 | 366 | 39 | 0.35 | 0.051 71 | 0.002 52 | 0.270 71 | 0.014 12 | 0.037 97 | 0.000 69 | 272 | 111 | 243 | 11 | 240 | 4 | ||
| 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | A/CNK | Mg# | σ | A/NK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM104-1 | 59.39 | 0.53 | 18.30 | 4.09 | 3.43 | 0.05 | 3.83 | 4.46 | 3.61 | 3.09 | 0.11 | 2.40 | 103.29 | 1.05 | 67 | 2.74 | 1.97 |
| PM104-2 | 68.35 | 0.36 | 16.84 | 2.76 | 1.94 | 0.04 | 1.26 | 1.26 | 3.66 | 3.54 | 0.09 | 1.71 | 101.81 | 1.39 | 54 | 2.04 | 1.71 |
| PM104-3 | 61.28 | 0.51 | 18.11 | 4.21 | 3.43 | 0.07 | 3.32 | 4.67 | 3.30 | 3.14 | 0.10 | 1.19 | 103.33 | 1.05 | 64 | 2.27 | 2.05 |
| PM104-4 | 63.93 | 0.42 | 18.71 | 3.04 | 2.47 | 0.05 | 2.26 | 3.63 | 3.50 | 3.53 | 0.10 | 0.74 | 102.38 | 1.16 | 62 | 2.37 | 1.95 |
| PM104-5 | 59.42 | 0.40 | 23.66 | 2.84 | 2.33 | 0.04 | 2.45 | 3.34 | 3.31 | 3.35 | 0.10 | 1.01 | 102.25 | 1.56 | 65 | 2.70 | 2.61 |
| 样号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | REE | LREE | HREE |
| PM104-1 | 24.50 | 52.20 | 5.47 | 20.10 | 3.97 | 1.28 | 3.49 | 0.57 | 3.41 | 0.7 | 2.07 | 0.36 | 2.18 | 0.35 | 120.65 | 107.52 | 13.14 |
| PM104-2 | 35.30 | 85.70 | 7.32 | 25.40 | 4.39 | 1.21 | 3.76 | 0.52 | 2.74 | 0.51 | 1.48 | 0.24 | 1.41 | 0.23 | 170.17 | 159.28 | 10.89 |
| PM104-3 | 33.70 | 69.20 | 7.07 | 25.90 | 4.95 | 1.34 | 4.30 | 0.66 | 3.80 | 0.76 | 2.26 | 0.39 | 2.39 | 0.39 | 157.12 | 142.17 | 14.95 |
| PM104-4 | 43.80 | 80.90 | 8.50 | 28.90 | 4.84 | 1.34 | 4.09 | 0.56 | 2.82 | 0.53 | 1.6 | 0.27 | 1.67 | 0.27 | 180.16 | 168.36 | 11.80 |
| PM104-5 | 27.50 | 67.00 | 5.49 | 19.50 | 4.03 | 1.28 | 3.50 | 0.51 | 2.77 | 0.51 | 1.47 | 0.25 | 1.51 | 0.25 | 135.56 | 124.80 | 10.76 |
| 样号 | LREE/ HREE | δEu | δCe | (La/ Yb)N | (La/ Sm)N | (Gd/ Yb)N | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr |
| PM104-1 | 8.19 | 1.03 | 1.04 | 7.57 | 3.89 | 1.29 | 34.49 | 3.40 | 14.01 | 72.31 | 52.75 | 14.53 | 14.80 | 34.21 | 32.63 | 107.90 | 470.20 |
| PM104-2 | 14.63 | 0.89 | 1.22 | 16.87 | 5.05 | 2.15 | 35.17 | 3.90 | 6.36 | 23.94 | 7.64 | 4.47 | 4.24 | 57.36 | 39.37 | 145.50 | 305.50 |
| PM104-3 | 9.51 | 0.87 | 1.03 | 9.49 | 4.28 | 1.45 | 61.66 | 3.73 | 12.37 | 68.00 | 72.14 | 12.88 | 21.72 | 64.68 | 36.70 | 109.40 | 353.70 |
| PM104-4 | 14.27 | 0.90 | 0.95 | 17.70 | 5.70 | 1.98 | 66.74 | 4.89 | 6.66 | 45.22 | 38.62 | 8.16 | 10.29 | 52.95 | 42.33 | 152.90 | 314.80 |
| PM104-5 | 11.60 | 1.02 | 1.24 | 12.31 | 4.30 | 1.87 | 78.91 | 5.44 | 6.44 | 47.68 | 35.57 | 7.65 | 9.87 | 53.06 | 39.17 | 153.90 | 305.50 |
| 样号 | Zr | Nb | In | Cs | Ba | Hf | Ta | Tl | Pb | Bi | Th | U | Y | K | P | Ti | Sr/Y |
| PM104-1 | 99.57 | 7.63 | 0.04 | 11.79 | 1 124.00 | 8.46 | 0.98 | 0.76 | 18.35 | 23.68 | 9.46 | 2.73 | 19.32 | 12 699.00 | 239.91 | 3 117.40 | 24.30 |
| PM104-2 | 148.06 | 9.88 | 0.04 | 8.83 | 1 401.00 | 12.24 | 1.25 | 0.82 | 29.41 | 0.30 | 18.70 | 1.71 | 13.87 | 14 649.50 | 196.29 | 2 158.20 | 22.00 |
| PM104-3 | 114.51 | 9.57 | 0.05 | 8.60 | 1 362.00 | 13.13 | 1.32 | 0.70 | 31.60 | 1.00 | 12.56 | 2.95 | 20.96 | 12 740.50 | 218.10 | 2 997.50 | 16.90 |
| PM104-4 | 110.31 | 8.86 | 0.05 | 14.90 | 1 633.00 | 21.19 | 1.31 | 0.85 | 37.02 | 0.21 | 15.88 | 3.32 | 15.33 | 14 442.00 | 196.29 | 2 457.95 | 20.50 |
| PM104-5 | 117.34 | 8.64 | 0.04 | 13.47 | 1 462.00 | 19.91 | 1.22 | 0.87 | 32.83 | 0.11 | 15.48 | 1.82 | 14.15 | 13 736.50 | 218.10 | 2 338.05 | 21.60 |
Table 2 Contents of major(%), REE(10-6) and trace(10-6) elements of the Jiangqinaliang intrusive complex
| 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | A/CNK | Mg# | σ | A/NK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM104-1 | 59.39 | 0.53 | 18.30 | 4.09 | 3.43 | 0.05 | 3.83 | 4.46 | 3.61 | 3.09 | 0.11 | 2.40 | 103.29 | 1.05 | 67 | 2.74 | 1.97 |
| PM104-2 | 68.35 | 0.36 | 16.84 | 2.76 | 1.94 | 0.04 | 1.26 | 1.26 | 3.66 | 3.54 | 0.09 | 1.71 | 101.81 | 1.39 | 54 | 2.04 | 1.71 |
| PM104-3 | 61.28 | 0.51 | 18.11 | 4.21 | 3.43 | 0.07 | 3.32 | 4.67 | 3.30 | 3.14 | 0.10 | 1.19 | 103.33 | 1.05 | 64 | 2.27 | 2.05 |
| PM104-4 | 63.93 | 0.42 | 18.71 | 3.04 | 2.47 | 0.05 | 2.26 | 3.63 | 3.50 | 3.53 | 0.10 | 0.74 | 102.38 | 1.16 | 62 | 2.37 | 1.95 |
| PM104-5 | 59.42 | 0.40 | 23.66 | 2.84 | 2.33 | 0.04 | 2.45 | 3.34 | 3.31 | 3.35 | 0.10 | 1.01 | 102.25 | 1.56 | 65 | 2.70 | 2.61 |
| 样号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | REE | LREE | HREE |
| PM104-1 | 24.50 | 52.20 | 5.47 | 20.10 | 3.97 | 1.28 | 3.49 | 0.57 | 3.41 | 0.7 | 2.07 | 0.36 | 2.18 | 0.35 | 120.65 | 107.52 | 13.14 |
| PM104-2 | 35.30 | 85.70 | 7.32 | 25.40 | 4.39 | 1.21 | 3.76 | 0.52 | 2.74 | 0.51 | 1.48 | 0.24 | 1.41 | 0.23 | 170.17 | 159.28 | 10.89 |
| PM104-3 | 33.70 | 69.20 | 7.07 | 25.90 | 4.95 | 1.34 | 4.30 | 0.66 | 3.80 | 0.76 | 2.26 | 0.39 | 2.39 | 0.39 | 157.12 | 142.17 | 14.95 |
| PM104-4 | 43.80 | 80.90 | 8.50 | 28.90 | 4.84 | 1.34 | 4.09 | 0.56 | 2.82 | 0.53 | 1.6 | 0.27 | 1.67 | 0.27 | 180.16 | 168.36 | 11.80 |
| PM104-5 | 27.50 | 67.00 | 5.49 | 19.50 | 4.03 | 1.28 | 3.50 | 0.51 | 2.77 | 0.51 | 1.47 | 0.25 | 1.51 | 0.25 | 135.56 | 124.80 | 10.76 |
| 样号 | LREE/ HREE | δEu | δCe | (La/ Yb)N | (La/ Sm)N | (Gd/ Yb)N | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr |
| PM104-1 | 8.19 | 1.03 | 1.04 | 7.57 | 3.89 | 1.29 | 34.49 | 3.40 | 14.01 | 72.31 | 52.75 | 14.53 | 14.80 | 34.21 | 32.63 | 107.90 | 470.20 |
| PM104-2 | 14.63 | 0.89 | 1.22 | 16.87 | 5.05 | 2.15 | 35.17 | 3.90 | 6.36 | 23.94 | 7.64 | 4.47 | 4.24 | 57.36 | 39.37 | 145.50 | 305.50 |
| PM104-3 | 9.51 | 0.87 | 1.03 | 9.49 | 4.28 | 1.45 | 61.66 | 3.73 | 12.37 | 68.00 | 72.14 | 12.88 | 21.72 | 64.68 | 36.70 | 109.40 | 353.70 |
| PM104-4 | 14.27 | 0.90 | 0.95 | 17.70 | 5.70 | 1.98 | 66.74 | 4.89 | 6.66 | 45.22 | 38.62 | 8.16 | 10.29 | 52.95 | 42.33 | 152.90 | 314.80 |
| PM104-5 | 11.60 | 1.02 | 1.24 | 12.31 | 4.30 | 1.87 | 78.91 | 5.44 | 6.44 | 47.68 | 35.57 | 7.65 | 9.87 | 53.06 | 39.17 | 153.90 | 305.50 |
| 样号 | Zr | Nb | In | Cs | Ba | Hf | Ta | Tl | Pb | Bi | Th | U | Y | K | P | Ti | Sr/Y |
| PM104-1 | 99.57 | 7.63 | 0.04 | 11.79 | 1 124.00 | 8.46 | 0.98 | 0.76 | 18.35 | 23.68 | 9.46 | 2.73 | 19.32 | 12 699.00 | 239.91 | 3 117.40 | 24.30 |
| PM104-2 | 148.06 | 9.88 | 0.04 | 8.83 | 1 401.00 | 12.24 | 1.25 | 0.82 | 29.41 | 0.30 | 18.70 | 1.71 | 13.87 | 14 649.50 | 196.29 | 2 158.20 | 22.00 |
| PM104-3 | 114.51 | 9.57 | 0.05 | 8.60 | 1 362.00 | 13.13 | 1.32 | 0.70 | 31.60 | 1.00 | 12.56 | 2.95 | 20.96 | 12 740.50 | 218.10 | 2 997.50 | 16.90 |
| PM104-4 | 110.31 | 8.86 | 0.05 | 14.90 | 1 633.00 | 21.19 | 1.31 | 0.85 | 37.02 | 0.21 | 15.88 | 3.32 | 15.33 | 14 442.00 | 196.29 | 2 457.95 | 20.50 |
| PM104-5 | 117.34 | 8.64 | 0.04 | 13.47 | 1 462.00 | 19.91 | 1.22 | 0.87 | 32.83 | 0.11 | 15.48 | 1.82 | 14.15 | 13 736.50 | 218.10 | 2 338.05 | 21.60 |
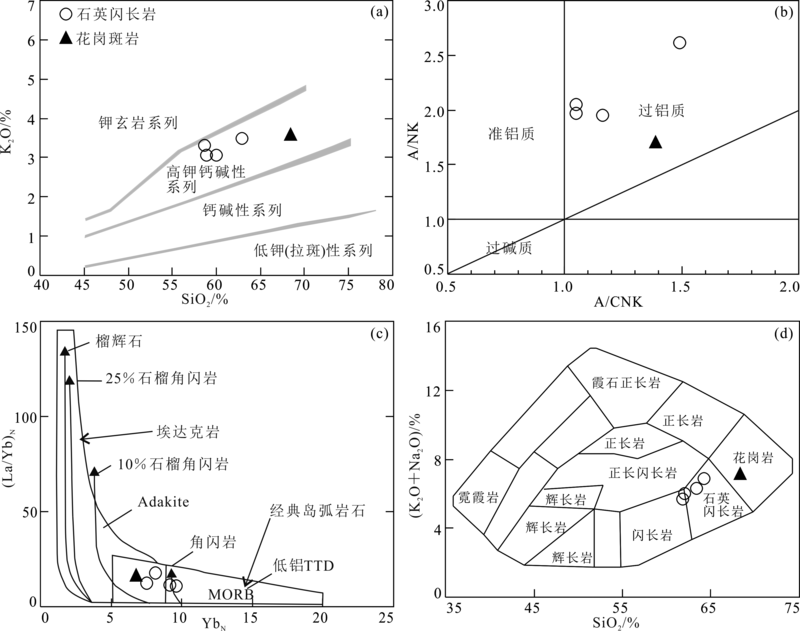
Fig.5 SiO2-K2O diagram ((a), base map after ref.[46]), A/CNK-A/NK diagram ((b), base map after ref.[47]), YbN-(La/Yb)N diagram ((c), base map after ref.[48]) and TAS diagram ((d), base map after ref.[49]) of Jiangqinaliang intrusive complex
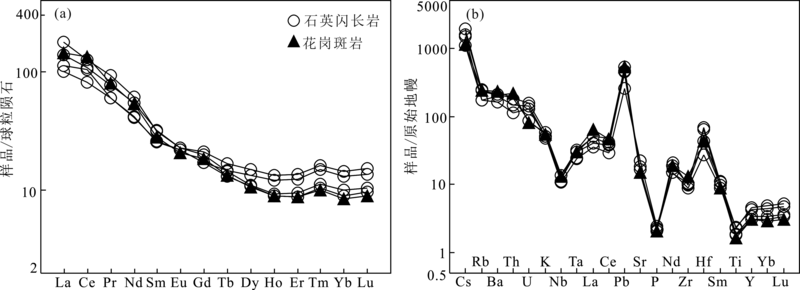
Fig.7 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spidergrams (b) for the Jiangqinaliang intrusive complex (base map after ref.[44])
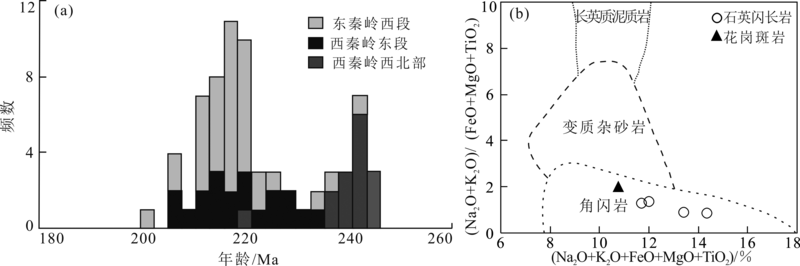
Fig.8 Distribution of ages for intrusive rock in Indosinian from West Qinling and western part of East Qinling ((a), base map after ref.[11], ages after refs.[7-35, 55-58, 65-68]) and diagram of (Na2O+K2O+FeO+MgO+TiO2)-(Na2O+K2O)/(FeO+MgO+TiO2) for the Jiangqinaliang intrusive complex ((b), base map after ref.[73])
| [1] | 王涛. 花岗岩混合成因研究及大陆动力学意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2000, 16(2):161-168. |
| [2] | 王涛, 王晓霞, 郑亚东, 等. 花岗岩构造研究及花岗岩构造动力学刍议[J]. 地质科学, 2007, 42(1):91-113. |
| [3] | 肖庆辉, 邱瑞照, 邢作云, 等. 花岗岩成因研究前沿的认识[J]. 地质论评, 2007, 53(增刊):17-27. |
| [4] |
CHAPPELL B W, BRYANT C J, WYBORN D. Peraluminous I-type granites[J]. Lithos, 2012, 153:142-153.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LUNDSTROM C C, GLAZNER A F. Silicic magmatism and the volcanic-plutonic connection[J]. Elements, 2016, 12(2) : 91-96.
DOI URL |
| [6] | 冯益民, 曹宣铎, 张二朋, 等. 西秦岭造山带的演化、构造格局和性质[J]. 西北地质, 2003, 36(1):1-10. |
| [7] | 金维浚, 张旗, 何登发, 等. 西秦岭埃达克岩的SHRIMP定年及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(3):959-966. |
| [8] | 韦萍, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 等. 西秦岭夏河花岗岩的地球化学、年代学及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(11):3981-3992. |
| [9] | 黄雄飞, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 等. 西秦岭印支期高Sr/Y花岗岩类的成因及动力学背景——以同仁地区舍哈力吉岩体为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(11):3255-3270. |
| [10] | 赵东辉, 平先权, 郑建平, 等. 西秦岭印支早期铁堂峡石英正长斑岩的地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(12):4203-4221. |
| [11] | 靳晓野, 李建威, 隋吉祥, 等. 西秦岭夏河—合作地区德乌鲁杂岩体的侵位时代、岩石成因及构造意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2013, 35(3):21-38. |
| [12] | 吴峰辉, 刘树文, 李秋根, 等. 西秦岭光头山花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学及其地质意义[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 45(5):811-818. |
| [13] | 张宏飞, 陈岳龙, 徐旺春, 等. 青海共和盆地周缘印支期花岗岩类的成因及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(12):2910-2922. |
| [14] | 张成立, 王涛, 王晓霞. 秦岭造山带早中生代花岗岩成因及其构造环境[J]. 高校地质学报, 2008, 14(3):304-316. |
| [15] |
QIN J F, LAI S C, GRAPES R, et al. Geochemical evidence for origin of magma mixing for the Triassic monzonitic granite and its enclaves at Mishuling in the Qinling orogeny (central China)[J]. Lithos, 2009, 112(3/4):259-276.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ZHU L M, ZHANG G W, CHEN Y J, et al. Zircon U-Pb ages and geochemistry of the Wenquan Mo-bearing granitioids in West Qinling, China: Constraints on the geodynamic setting for the newly discovered Wenquan Mo deposit[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011, 39(1/2) : 46-62.
DOI URL |
| [17] | 骆必继, 张宏飞, 肖尊奇. 西秦岭印支早期美武岩体的岩石成因及其构造意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(3):199-213. |
| [18] | 杨拴海, 李瑞保, 王伟峰, 等. 西秦岭西段曲如沟花岗闪长岩年代学、地球化学特征及构造意义研究[J]. 西北地质, 2015, 48(2):57-72. |
| [19] | 温志亮, 李普涛, 郭周平, 等. 西秦岭东段秦岭大堡岩体地球化学特征及地质构造意义[J]. 西北地质, 2017, 50(1):126-133. |
| [20] | 路东宇, 叶会寿, 曹晶, 等. 西秦岭江里沟复式岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学和Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(3):942-962. |
| [21] | 陈清敏, 郭岐明, 王强, 等. 西秦岭秦岭梁环斑花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄及地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(2/3):213-222. |
| [22] | 邱庆伦, 龚全胜, 卢书伟, 等. 甘肃夏河地区印支期埃达克岩的厘定及其意义[J]. 甘肃地质, 2008, 17(3):6-12. |
| [23] | 王建中, 钱壮志, 徐刚, 等. 西秦岭白马山“C”型埃达克岩成因:地球化学、Sr-Nd-Pb同位素制约[J]. 华东地质, 2016, 37(3):174-181. |
| [24] | 李佐臣, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 西秦岭糜署岭花岗岩体年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(8):2617-2634. |
| [25] | 徐学义, 李婷, 陈隽璐, 等. 西秦岭西段花岗岩浆作用与成矿[J]. 西北地质, 2012, 45(4):76-82. |
| [26] | 徐学义, 陈隽璐, 高婷, 等. 西秦岭北缘花岗质岩浆作用及构造演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(2):371-389. |
| [27] | 姜航. 西秦岭礼—岷矿集区“五朵金花”花岗质岩浆作用及其成岩大地构造背景研究[D]. 西安:西北大学, 2016. |
| [28] | 李雪峰, 李永胜, 董国臣, 等. 西秦岭东段印支期花岗质岩浆作用及构造演化:地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(6):1691-1712. |
| [29] |
GUO X, YAN Z, WANG Z, et al. Middle Triassic arc magmatism along the northeastern margin of the Tibet: U-Pb and Lu-Hf zircon characterization of the Gangcha complex in the West Qinling terrane, central China[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2012, 169(3):327-336.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 李婷, 徐学义, 陈隽璐, 等. 西秦岭造山带礼县地区中川岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其构造环境[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(6):875-883. |
| [31] | 孙小攀, 徐学义, 陈隽璐, 等. 西秦岭江里沟花岗岩体地球化学特征、年代学及地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(3):330-342. |
| [32] | 张德贤, 束正祥, 曹汇, 等. 西秦岭造山带夏河一合作地区印支期岩浆活动及成矿作用——以德乌鲁石英闪长岩和老豆石英闪长斑岩为例[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(5):1257-1273. |
| [33] | 徐多勋, 杨拴海, 李瑞保, 等. 西秦岭西段塔洞花岗闪长岩体年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2015, 37(3):22-33. |
| [34] |
LI X W, MO X X, HUANG X F, et al. U-Pb zircon geochronology, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic compositions of the EarlyIndosinian Tongren pluton in West Qinling: Petrogenesis and geodynamic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97:38-50.
DOI URL |
| [35] | 任文恺, 王生云, 陈礼标, 等. 青海同仁兰采地区花岗闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(4):1059-1074. |
| [36] | 冯益民, 曹宣铎, 张二朋, 等. 西秦岭造山带结构造山过程及动力学[M]. 西安: 西安地图出版社, 2003:1-263. |
| [37] | 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 等. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001:1-863. |
| [38] | 张国伟, 郭安林, 姚安平. 中国大陆构造中的西秦岭—松潘大陆构造结[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(3):23-32. |
| [39] | 李曙光, 孙卫东, 张国伟, 等. 南秦岭勉略构造带黑沟峡变质火山岩的年代学和地球化学—古生代洋盆及其闭合时代的证据[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 1996, 26(3):223-230. |
| [40] |
XU J F, PATERNO R C, LI X H, et al. MORB-type rocks from the Paleo-Tethyan Mian-Lueyang northern ophiolite in the Qinling Mountains, central China: implications for the source of the low 206Pb/ 204Pb and high 143Nd/ 144Nd mantle component in the Indian Ocean[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 198(3):323-337.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
ELENA A K, MAURICE B, JACQUES M. Discovery of Paleo-Tethys residual peridotites along the Anyemaqen-KunLun suture aone(North Tibet) Decouverte de peridotites residuelles, temoins de locean Paleo-Tethys, dans lasuture Anyemaqen-KunLun(Nord Tibet)[J]. Comptes Rendus Geosciences, 2003, 335(8):709-719.
DOI URL |
| [42] | YANG J S, SHI R D, WU C L, et al. Dur'ngoi ophiolite in East Kunlun, Northeast Tibetan plateau: evidence for paleo-Tethyan suture in Northwest China[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2009(2):303-331. |
| [43] |
ANDERSEN T. Correction of common Pb in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1/2):59-79.
DOI URL |
| [44] | LUDWIG K R. Isoplot/Ex Version 2.49. A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2003: 1-56. |
| [45] | 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16):1589-1604. |
| [46] |
PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1):63-81.
DOI URL |
| [47] | 肖庆辉, 邓晋福, 马大铨, 等. 花岗岩研究思维与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002:1-294. |
| [48] |
DEFANT M J, DRUMMOND M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347(6294):662-665.
DOI URL |
| [49] | LE MAITRE R W. Igneous Rocks, a Classification and Glossary of Terms[M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002:1-236. |
| [50] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345.
DOI URL |
| [51] | 李亮. 甘肃枣子沟金矿的地质特征及成因初步分析[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉), 2009. |
| [52] | 张宏飞, 靳兰兰, 张利, 等. 西秦岭花岗岩类地球化学和Pb-Sr-Nd同位素组成对基底性质及其构造属性的限制[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 2005, 35(10):914-926. |
| [53] | 秦江锋. 秦岭造山带晚三叠世花岗岩类成因机制及深部动力学背景[D]. 西安:西北大学, 2010. |
| [54] |
CAO X F, LÜ X B, YAO S Z, et al. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon geochronology, geochemistry and kinetics of the Wenquan ore-bearing granites from west Qinling, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011, 43(1):120-131.
DOI URL |
| [55] | 孙卫东, 李曙光, CHEN Y D, 等. 南秦岭花岗岩锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 地球化学, 2000, 29(3):209-216. |
| [56] | 弓虎军, 朱赖民, 孙博亚, 等. 南秦岭地体东江口花岗岩及其基性包体的锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(11):3029-3042. |
| [57] | 李永军, 谢其山, 栾新东, 等. 西秦岭糜署岭岩浆带成因及构造意义[J]. 新疆地质, 2004, 22(4):374-377. |
| [58] | 刘明强. 甘肃西秦岭舟曲憨班花岗岩的单颗粒锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 地质科学, 2012, 47(3):899-907. |
| [59] |
MATTAUER M, MATTE P H, MALAVIEILLE J, et al. Tectonics of the Qinling Belt: Build-up and evolution of Eastern Asia[J]. Nature, 1985, 317:496-500.
DOI URL |
| [60] | 李曙光, HART S R 郑双根, 等. 中国华北、华南陆块碰撞时代的钐-钕同位素年龄证据[J]. 中国科学:B辑, 1989, 19(3):312-319. |
| [61] |
ROWLEY D B, XUE F, TUCKER R D, et al. Ages of ultrahigh pressure metarnorphism and protolith orthogneisses from the Eastern Dabie Shan: U/Pb zircon geochronology[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 151(3/4):191-203.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
SUN W D, LI S G, CHEN Y D, et al. Timing of synorogenic granitoids in the south Qinling, central China: Constraints on the evolution of the Qinling-Dabie Orogenic Belt[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2002, 110(4):457-468.
DOI URL |
| [63] | 李曙光, 黄方, 李晖. 大别—苏鲁造山带碰撞后岩石圈拆离[J]. 科学通报, 2001, 46(17):1487-1491. |
| [64] | 高山, 张本仁, 金振民, 等. 秦岭—大别造山带下地壳拆沉作用[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 1999, 29(6):532-541. |
| [65] | 张成立, 张国伟, 晏云翔, 等. 南秦岭勉略带北光头山花岗岩体群的成因及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(3):711-720. |
| [66] | 卢欣祥, 尉向东, 肖庆辉, 等. 秦岭环斑花岗岩的年代学研究及其意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 1999, 5(4):372-377. |
| [67] | 弓虎军, 朱赖民, 孙博亚, 等. 南秦岭沙河湾、曹坪和柞水岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(2):248-264. |
| [68] | 卢欣祥, 董有, 常秋岭, 等. 秦岭印支期沙河湾奥长环斑花岗岩及其动力学意义[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 1996, 26(3):244-248. |
| [69] | 李三忠, 郑祺亮, 李玺瑶, 等. 中国东部苏鲁造山带的印支期俯冲极性及其造山过程[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(4):18-32. |
| [70] |
SISSON T W, RATAJESKI K, HANKINS W B, et al. Voluminous granitic magmas from common basaltic sources[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2005, 148(6):635-661.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
MOYEN J F. High Sr/Y and La/Yb rations: The meaning of the “adakitic signature”[J]. Lithos, 2009, 112(3/4):556-574.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
RAPP R P, WATSON E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8-32 kbar: Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4):891-931.
DOI URL |
| [73] | 辜平阳, 陈锐明, 查显锋, 等. 柴达木盆地西北缘石英闪长岩的形成时代、岩石成因及地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2018, 37(1):19-33. |
| [74] | 寇少磊, 魏立勇, 张振, 等. 西秦岭中段日多玛岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(6):1245-1259. |
| [75] | 杨瀚文, 申俊峰, 魏立勇, 等. 西秦岭西段共和盆地周缘西功卡花岗闪长岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(2):316-328. |
| [76] |
MENG Q R, WANG E Q, HU J M. Mesozoic sedimentary evolution of the northwest Sichuan Basin: Implication for continued clockwise rotation of the South China Block[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2005, 117(3/4):396-410.
DOI URL |
| [77] | 任纪舜. 昆仑—秦岭造山系的几个问题[J]. 西北地质, 2004, 37(1):1-5. |
| [78] | 殷鸿福, 张克信. 中央造山带的演化及其特点[J]. 地球科学, 1998, 23(5):438-442. |
| [79] | 陈守建, 李荣社, 计文化, 等. 昆仑造山带二叠纪岩相古地理特征及盆山转换探讨[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(2):374-393. |
| [80] | 吴福元, 黄宝春, 叶凯, 等. 青藏高原造山带的垮塌与高原隆升[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(1):1-30. |
| [81] | 纪伟强, 吴福元, 锺孙霖, 等. 西藏南部冈底斯岩基花岗岩时代与岩石成因[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 2009, 39(7):849-871. |
| [82] | 李康宁, 刘伯崇, 狄永军. 三叠纪西秦岭西北部洋俯冲的记录:来自镁安山岩/高镁安山岩的证据[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(3):709-724. |
| [83] | 殷鸿福, 杨逢清, 黄其胜, 等. 秦岭及邻区三叠系[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1992:1-186. |
| [84] | 甘肃省地质矿产局. 甘肃省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1989:1-646. |
| [85] | 寇晓虎, 张克信, 林启祥, 等. 秦祁昆接合部二叠纪沉积建造时空分布[J]. 地球科学, 2007, 32(5):681-690. |
| [86] | 张克信, 朱云海, 林启祥, 等. 青海同仁县隆务峡地区首次发现镁铁质-超镁铁质岩带[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(6):661-667. |
| [87] | 王绘清, 朱云海, 林启祥, 等. 青海尖扎—同仁地区隆务峡蛇绿岩的形成时代及意义——来自辉长岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄的证据[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(1):86-92. |
| [88] |
PEARCE J A. Sources and settings of granitic rocks[J]. Episodes, 1996, 19(4):120-125.
DOI URL |
| [1] | LUO Haiyi, LUO Xianrong, LIU Panfeng, MA Mingliang, LU Xiansheng, JIANG Xiaoming, BAO Guangui, JIANG Yuxiong. Soil Geochemical Characteristics in the Naqu Area,Chongzuo City, Guangxi,and Their Mineral Prospecting Applications [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [2] | LI Zhipeng, YU Qiling, ZAN Lin, YU Wenduan, ZHANG Zhihuan. Geochemical Characteristics and Hydrocarbon Generation Potential of Different Lithologic Source Rocks in the Second Member of Funing Formation in Qintong Sag, Subei Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [3] | ZHANG Wei, AN Maoguo, WANG Zhipeng, YANG Qi, CHEN Huaixin, MA Xiaofeng, ZHI Chenglong, XING Qitao, PEI Changshi, WANG Na, LIU Ming. Geochemical Characteristics of Stream Sediments and Prospecting in the Middle Reach of the Nalinggele River, Qinghai Province [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(03): 690-707. |
| [4] | LIANG Dong, HUA Bei, ZHAO Dehuai, WU Hao, WAN Shengnan, TAN Chaoxin, ZHAO Xiaojian, YANG Zhipeng. Geochemical Characteristics of River Sediment and Ore Prediction in the Malashan Area of the Karakoram Region [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(03): 708-721. |
| [5] | LOU Yuanlin, CHENG Ming, TANG Yao, ZHANG Chaoming, LAN Jingzhou, YUAN Yongsheng, YANG Tao. Geochemical Characteristics,Tectonic Setting, and Mineralization of Magmatic Rocks in Gudui Area, Southern Tibet [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| [6] | CHEN Shiming, YANG Zhenxi, LEI Ziqiang, KANG Weiliang, ZHANG Jing, ZHAO Qinghu. Geochemical Characteristics and Prospecting on Stream Sediment Survey in Qianhongquan Area of Beishan in Gansu Province, China [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(06): 1513-1524. |
| [7] | LIU Tong, LIU Chuanpeng, KANG Pengyu, ZHAO Xiufang, DENG Jun, WANG Kaikai. Geochemical Characteristics and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Soils of Eastern Yinan, Shandong Province [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(04): 1173-1182. |
| [8] | LIU Yang, LI Xianqing, ZHAO Guangjie, LIU Mancang, DONG Caiyuan, LI Jin, XIAO Zhongyao. Geochemical Characteristics of Natural Gas and Hydrocarbon Charging History of the Tugeerming Area in the Eastern Kuqa Depression [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(04): 988-997. |
| [9] | ZHU Dequan, TANG Mingying, DING Zhengjiang, ZHU Haibo, WANG Weixiao, ZHANG Yu, HE Zongwei, WU Hongbin. Petrogenesis and Geodynamic Setting of Granite Porphyry Dike in Saibagou Gold Deposit,Northern Margin of Qaidam: Evidence from Geochronology and Geochemistry [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(03): 898-910. |
| [10] | WANG Bin, REN Tao, SONG Yiwei, YANG Ke, WANG Zhanbin, SUN Yake. Geochemical Characteristics and Geological Significance of Stream Sediments in Changjiashan Region, Western Qinling Orogen [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(03): 911-922. |
| [11] | LIU Yang, JIANG Bing, ZHANG Hairui, SUN Zengbing, WANG Songtao. Geochemical Characteristics of Selenium in Surface Soil of Qingzhou, Shandong [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(03): 933-940. |
| [12] | WANG Meihua. Geochemical Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Selenium-enriched Soils in Cultivated Land Around Typical Stone Coal Mines in Western Zhejiang [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(03): 941-952. |
| [13] | ZHU Biqing, CHEN Shijia, BAI Yanjun, LEI Junjie, YIN Xiangdong. Geochemical Characteristics and Source of Crude Oil in Chang 8 Member of Yanchang Formation, Ganquan Area, Ordos Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(02): 742-754. |
| [14] | HU Boxin, ZHOU Hongfei, QU Hailang, CAO Yigang, BAI Huiliang, WANG Lingtong, WANG Lixin, YANG Zhaoke, LI Yuanshen. Characteristics of Structural Superimposed Halos and Deep Prospecting Direction in the South Ore Zone of Huachanggou Gold Deposit, Shaanxi Province [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(06): 1515-1522. |
| [15] | GAO Yinhu, YIN Gang, GONG Zeqiang, GUO Mingchun. Geological Characteristics and Genesis of the Xiangtanzi Gold Deposit in Liangdang County, Gansu Province [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(06): 1523-1535. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||